Large marine ecosystem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
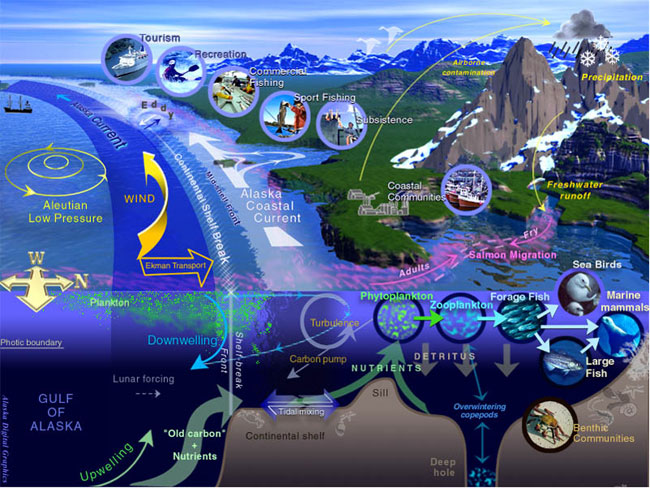 Large marine ecosystems (LMEs) are regions of the world's
Large marine ecosystems (LMEs) are regions of the world's
 The Global Environment Facility (GEF) aids in managing LMEs off the coasts of Africa and Asia by creating resource management agreements between environmental, fisheries, energy and tourism ministers of bordering countries. This means participating countries share knowledge and resources pertaining to local LMEs to promote longevity and recovery of fisheries and other industries dependent upon LMEs.Juda L, Hennessey T. 2001. Governance profiles and the management of the uses of large marine ecosystems. Ocean Development and International Law 32:41-67.
The Global Environment Facility (GEF) aids in managing LMEs off the coasts of Africa and Asia by creating resource management agreements between environmental, fisheries, energy and tourism ministers of bordering countries. This means participating countries share knowledge and resources pertaining to local LMEs to promote longevity and recovery of fisheries and other industries dependent upon LMEs.Juda L, Hennessey T. 2001. Governance profiles and the management of the uses of large marine ecosystems. Ocean Development and International Law 32:41-67.
Large Marine Ecosystems Hub
Smithsonian Ocean Portal
{{modelling ecosystems, expanded=none Marine biology Ecosystems Fisheries science Marine botany Systems ecology
 Large marine ecosystems (LMEs) are regions of the world's
Large marine ecosystems (LMEs) are regions of the world's ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s, encompassing coastal areas from river basins and estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environmen ...
to the seaward boundaries of continental shelves and the outer margins of the major ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours ...
systems. They are relatively large regions on the order of 200,000 km² or greater, characterized by distinct bathymetry
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water ...
, hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primar ...
, productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
, and trophically dependent population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
s. Productivity in LME protected areas is generally higher than in the open ocean.
The system of LMEs has been developed by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
(NOAA) to identify areas of the oceans for conservation purposes. The objective is to use the LME concept as a tool for enabling ecosystem-based management to provide a collaborative approach to management of resources within ecologically-bounded transnational areas. This will be done in an international context and consistent with customary international law as reflected in 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 ...
.
Although the LMEs cover mostly the continental margins and not the deep oceans and oceanic islands, the 66 LMEs produce about 80% of global annual marine fishery biomass. In addition, LMEs contribute $12.6 trillion in goods and services each year to the global economy. Due to their close proximity to developed coastlines, LMEs are in danger of ocean pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial, agricultural and residential waste, particles, noise, excess carbon dioxide or invasive organisms enter the ocean and cause harmful effects there. The major ...
, overexploitation, and coastal habitat alteration. NOAA has conducted studies of principal driving forces affecting changes in biomass yields for 33 of the 66 LMEs, which have been peer-reviewed and published in ten volumes.
LME-based conservation is based on recognition that the world's coastal ocean waters are degraded by unsustainable fishing practices, habitat degradation
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytopla ...
, toxic pollution, aerosol contamination, and emerging diseases, and that positive actions to mitigate these threats require coordinated actions by governments and civil society to recover depleted fish populations, restore degraded habitats and reduce coastal pollution. Five modules are considered when assessing LMEs: productivity, fish and fisheries, pollution and ecosystem health
Ecosystem health is a metaphor used to describe the condition of an ecosystem.Rapport, David (1998). "Defining ecosystem health." Pages 18-33 in Rapport, D.J. (ed.) (1998). ''Ecosystem Health.'' Blackwell Scientific. Ecosystem condition can vary ...
, socioeconomics, and governance. Periodically assessing the state of each module within a marine LME is encouraged to ensure maintained health of the ecosystem and future benefit to managing governments.
Modules of Ecosystem Condition
Productivity
The productivity of a marine ecosystem can be measured in several ways. Measurements pertaining to zooplankton biodiversity and species composition, zooplankton biomass, water-column structure, photosynthetically active radiation, transparency, chlorophyll-a, nitrate, and primary production are used to assess changes in LME productivity and potential fisheries yield. Sensors attached to the bottom of ships or deployed on floats can measure these metrics and be used to quantitatively describe changes in productivity alongside physical changes in the water column such as temperature and salinity. This data can be used in conjunction with satellite measurements of chlorophyll and sea surface temperatures to validate measurements and observe trends on greater spatial and temporal scales.Fish and Fisheries
Bottom-trawl surveys and pelagic-species acoustic surveys are used to assess changes in fish biodiversity and abundance in LMEs. Fish populations can be surveyed for stock identification, length, stomach content, age-growth relationships, fecundity, coastal pollution and associated pathological conditions, as well as multispecies trophic relationships. Fish trawls can also collect sediment and inform us about ocean-bottom conditions such as anoxia.Pollution and Ecosystem Health
Pollution and eutrophication can have significant impacts on ecosystem health and result in changing biomass yields. LMEs are emplaced in an effort to maintain healthy and sustainable conditions in spite of environmental change and global warming. A health ecosystem should maintain a relatively constant metabolic activity level, internal structure and organization, making it resistant to change over time. Health is assessed on both a population and species level. Observations are made pertaining to bioaccumulation of contaminants, frequency of harmful algal blooms and diseases, water column contents and water quality, reproductive capacity and more. Eutrophication and nutrient overloading can be measured as a function of nitrogen and phosphate in a given location.Socioeconomic
By integrating socioeconomic metrics with ecosystem management solutions, scientific findings can be utilized to benefit both the environment and economy of local regions. Management efforts must be practical and cost-effective. The Department of Natural Resource Economics at the University of Rhode Island has created a method for measuring and understanding the human dimensions of LMEs and for taking into consideration both socioeconomic and environmental costs and benefits of managing Large Marine Ecosystems. This is especially important in island nations and small states which depend heavily on fisheries production for income.Governance
 The Global Environment Facility (GEF) aids in managing LMEs off the coasts of Africa and Asia by creating resource management agreements between environmental, fisheries, energy and tourism ministers of bordering countries. This means participating countries share knowledge and resources pertaining to local LMEs to promote longevity and recovery of fisheries and other industries dependent upon LMEs.Juda L, Hennessey T. 2001. Governance profiles and the management of the uses of large marine ecosystems. Ocean Development and International Law 32:41-67.
The Global Environment Facility (GEF) aids in managing LMEs off the coasts of Africa and Asia by creating resource management agreements between environmental, fisheries, energy and tourism ministers of bordering countries. This means participating countries share knowledge and resources pertaining to local LMEs to promote longevity and recovery of fisheries and other industries dependent upon LMEs.Juda L, Hennessey T. 2001. Governance profiles and the management of the uses of large marine ecosystems. Ocean Development and International Law 32:41-67.
LMEs around the Globe
* East Bering Sea *Gulf of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska (Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east ...
* California Current
The California Current is a cold water Pacific Ocean current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur. It is considered an Eastern bound ...
* Gulf of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja C ...
* Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
* Southeast U.S. Continental Shelf
* Northeast U.S. Continental Shelf
* Scotian Shelf
The Scotian Shelf is a geological formation, part of the Continental shelf, located southwest of Nova Scotia, Canada. It covers an area of , is long and ranges in width from . It has an average depth of . The Scotian Shelf contains the ecological ...
* Newfoundland-Labrador Shelf
* Insular Pacific-Hawaiian
* Pacific Central-American Coastal
* Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
* Humboldt Current
* Patagonian Shelf
* South Brazil Shelf
* East Brazil Shelf
* North Brazil Shelf
* West Greenland Shelf
* East Greenland Shelf
* Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
* Norwegian Shelf
* North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
* Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
* Celtic-Biscay Shelf
* Iberian Coastal
* Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
* Canary Current
The Canary Current is a wind-driven surface current that is part of the North Atlantic Gyre. This eastern boundary current branches south from the North Atlantic Current and flows southwest about as far as Senegal where it turns west and later j ...
* Guinea Current
* Benguela Current
* Agulhas Current
The Agulhas Current () is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the east coast of Africa from 27°S to 40°S. It is narrow, swift and strong. It is suggested that it is the largest western boundary curren ...
* Somali Coastal Current
Somali may refer to:
Horn of Africa
* Somalis, an inhabitant or ethnicity associated with Greater Somali Region
** Proto-Somali, the ancestors of modern Somalis
** Somali culture
** Somali cuisine
** Somali language, a Cushitic language
** Somal ...
* Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
* Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
* Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line betwee ...
* Gulf of Thailand
* South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phi ...
* Sulu-Celebes Sea
* Indonesian Sea
* North Australian Shelf
* Northeast Australian Shelf/Great Barrier Reef
* East-Central Australian Shelf
* Southeast Australian Shelf
* Southwest Australian Shelf
* West-Central Australian Shelf
* Northwest Australian Shelf
* New Zealand Shelf
* East China Sea
* Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea. It is one of four seas named after common colour ter ...
* Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black or or the is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
* Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, i ...
* Oyashio Current
, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean an ...
* Sea of Okhotsk
* West Bering Sea
* Chukchi Sea
* Beaufort Sea
* East Siberian Sea
* Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, t ...
* Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. ...
* Iceland Shelf
* Faroe Plateau Faroe may refer to:
* Faroe Islands, an archipelago in the North Atlantic and a part of the Kingdom of Denmark
**Faroese people
** Faroese language
* Danish ship ''Færøe''
* Fårö, an island off Gotland, Sweden
* Farø, an island south of Zeala ...
* Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
* Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
* Hudson Bay
* Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
See also
*Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
* Marine ecosystem
Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the sur ...
* Marine life
Large Marine Ecosystems Hub
References
External links
Smithsonian Ocean Portal
{{modelling ecosystems, expanded=none Marine biology Ecosystems Fisheries science Marine botany Systems ecology