Large Indian civet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The large Indian civet (''Viverra zibetha'') is a
 The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its
The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its
 The large Indian civet is solitary and nocturnal. It spends most of the time on the ground. Its diet includes fish, birds, lizards, frogs, insects, scorpions and other
The large Indian civet is solitary and nocturnal. It spends most of the time on the ground. Its diet includes fish, birds, lizards, frogs, insects, scorpions and other
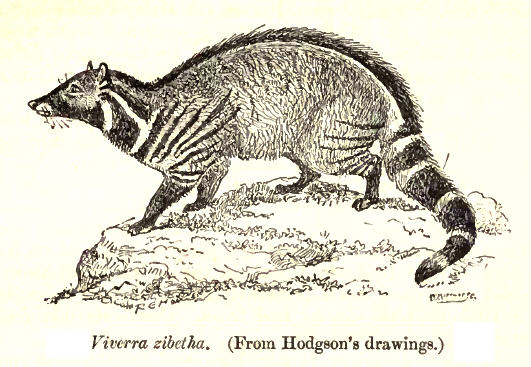 ''Viverra zibetha'' was the scientific name for the large Indian civet introduced by
''Viverra zibetha'' was the scientific name for the large Indian civet introduced by
viverrid
Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids () comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, ...
native to South and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
. It is listed as Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. T ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
. The global population is considered decreasing mainly because of trapping-driven declines in heavily hunted and fragmented areas, notably in China, and the heavy trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
as wild meat.
Characteristics
 The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its
The large Indian civet is grey or tawny and has a black spinal stripe running from behind the shoulders to the root of the tail. The front of the muzzle has a whitish patch emphasized by blackish behind on each side. The chin and fore throat are blackish. The sides and lower surface of the neck are banded with black stripes and white spaces in between. The tail has a variable number of complete black and white rings. Its claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
s are retractable. The soles of the feet are hairy.
As indicated by its common name, this is a relatively large civet, almost certainly the largest of the ''Viverra
''Viverra'' is a mammalian genus that was first nominated and described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 as comprising several species including the large Indian civet (''V. zibetha''). The genus was subordinated to the viverrid family by John Edward G ...
'' species and exceeded in size among the Viverridae family only by African civet
The African civet (''Civettictis civetta'') is a large viverrid native to sub-Saharan Africa, where it is considered common and widely distributed in woodlands and secondary forests. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 200 ...
s and binturong
The binturong (''Arctictis binturong'') (, ), also known as the bearcat, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. It is uncommon in much of its range, and has been assessed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because of a declining pop ...
s. Its head-and-body length ranges from with a long tail. The hind foot measures . Its weight ranges from . Some sources claim the species can weigh up to (though possibly attained in captivity).
Distribution and habitat
The large Indian civet ranges fromNepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
, northeast India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
to Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, the Malay peninsula and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
to Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, Laos, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and China.
In Nepal, large Indian civet was recorded up to in the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
, which constitutes the highest altitudinal record in this country.
In China, the wild large Indian civet population declined drastically by 94–99% since the 1950s following deforestation, due to hunting for the fur trade, use of its musk glands as medicine and for the perfume
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Th ...
industry. By the 1990s, it was largely confined to the north of Guangdong Province in southern China, but has not been recorded in Hainan Island
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly ...
during surveys between 1998 and 2008.
Ecology and behaviour
 The large Indian civet is solitary and nocturnal. It spends most of the time on the ground. Its diet includes fish, birds, lizards, frogs, insects, scorpions and other
The large Indian civet is solitary and nocturnal. It spends most of the time on the ground. Its diet includes fish, birds, lizards, frogs, insects, scorpions and other arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s, crabs, as well as poultry and rubbish.
Little is known about its breeding behaviour. It is thought that it breeds throughout the year and has two litters per year, with two to four young per litter.
Radio-tracked large Indian civets in Thailand had home ranges of .
Conservation
''Viverra zibetha'' is totally protected in Malaysia under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and listed on Category II of the China Wildlife Protection Law. China listed it as ‘Endangered’ under criteria A2acd, and it is a class II protected State species (due to trapping for food and scent glands). It is protected in Thailand, Vietnam and Myanmar. It is found in several protected areas throughout its range. The population of India is listed on CITES Appendix III. InHong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
, it is a protected species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and invas ...
under the Wild Animals Protection Ordinance Cap 170, though it has not been recorded in a natural state in Hong Kong since the 1970s, and is considered extirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
.
Taxonomy
 ''Viverra zibetha'' was the scientific name for the large Indian civet introduced by
''Viverra zibetha'' was the scientific name for the large Indian civet introduced by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalise ...
in 1758.
Several naturalists proposed species and subspecies in the 19th and 20th centuries, of which the following were recognised as valid subspecies by 2005:
* ''V. z. zibetha'' is the nominate subspecies and thought to occur from Nepal eastwards to Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
.
*''Viverra ashtoni'' described by Robert Swinhoe in 1864 was a skin of an individual that was shot near the upper Min River in China's Fujian Province
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
; occurs in China.
*''V. z. picta'' described by Robert Charles Wroughton in 1915 was based on two skins from the vicinity of Hkamti by the upper Chindwin River in Myanmar; occurs from Assam and northern Myanmar to Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
.
*''V. z. pruinosa'' also described by Wroughton in 1915 was a skin of an adult male large Indian civet from Myanmar's Tanintharyi Region
Tanintharyi Region ( my, တနင်္သာရီတိုင်းဒေသကြီး, ; Mon: or ; ms, Tanah Sari; formerly Tenasserim Division and subsequently Tanintharyi Division, th, ตะนาวศรี, RTGS: ''Tanao Si'', ; ...
; occurs from southern Myanmar to Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, ...
.
*''V. z. hainana'' described by Ying-Xiang Wang and Xu in 1983 from Hainan Island.
The validity of ''Viverra tainguensis'' described in 1997 by Sokolov, Rozhnov and Pham Chong from Tây Nguyên
Central Highlands ( vi, Cao nguyên Trung phần), Western Highlands ( vi, Tây Nguyên) or Midland Highlands ( vi, Cao nguyên Trung bộ) is one of the regions of Vietnam. It contains the provinces of Đắk Lắk, Đắk Nông, Gia Lai, K ...
in Gia Lai Province in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
has been seriously questioned, and it is now generally considered a synonym of ''V. zibetha''.
Local names
*In Uttar Pradesh (Ballia ) it is called 'Khatwas'.. *In Bengali it is called ''Bham'' or ''Gondho Gokul''. *In Assamese it is called ''Haga Gendera''. *InMalay language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Rejang script, Rencong: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spo ...
it is called ''Musang kasturi'' (musang = civet, kasturi = musk), due to its musky smell.
*In Thai, it is called ''chamot phaeng hang plong'' (ชะมดแผงหางปล้อง; ; lit. "circular tailed/maned genet")
*In Lao, it is called ''ngen phaeng hang kan'' (ເຫງັນແຜງຫາງກ່ານ; ; lit. "stripe-tailed/maned civet")
*In Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
it is called 'Veruku' (വെരുക്)
References
External links
{{Taxonbar, from=Q757265 Mammals of Southeast Asia Mammals of Nepal Mammals of India Mammals of Bangladesh Fauna of Hong Kong Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Carnivorans of Malaysia Mammals of Singapore