Laocoön and His Sons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The statue of ''Laocoön and His Sons'', also called the Laocoön Group ( it, Gruppo del Laocoonte), has been one of the most famous ancient sculptures ever since it was excavated in Rome in 1506 and placed on public display in the  Although mostly in excellent condition for an excavated sculpture, the group is missing several parts, and analysis suggests that it was remodelled in ancient times and has undergone a number of restorations since it was excavated. It is on display in the
Although mostly in excellent condition for an excavated sculpture, the group is missing several parts, and analysis suggests that it was remodelled in ancient times and has undergone a number of restorations since it was excavated. It is on display in the

 The story of Laocoön, a
The story of Laocoön, a
 The group was unearthed in February 1506 in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis; informed of the fact,
The group was unearthed in February 1506 in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis; informed of the fact,
 When the statue was discovered, Laocoön's right arm was missing, along with part of the hand of one child and the right arm of the other, and various sections of the snake. The older son, on the right, was detached from the other two figures. The age of the altar used as a seat by Laocoön remains uncertain. Artists and connoisseurs debated how the missing parts should be interpreted. Michelangelo suggested that the missing right arms were originally bent back over the shoulder. Others, however, believed it was more appropriate to show the right arms extended outwards in a heroic gesture.
According to
When the statue was discovered, Laocoön's right arm was missing, along with part of the hand of one child and the right arm of the other, and various sections of the snake. The older son, on the right, was detached from the other two figures. The age of the altar used as a seat by Laocoön remains uncertain. Artists and connoisseurs debated how the missing parts should be interpreted. Michelangelo suggested that the missing right arms were originally bent back over the shoulder. Others, however, believed it was more appropriate to show the right arms extended outwards in a heroic gesture.
According to  In 1906 Ludwig Pollak, archaeologist, art dealer and director of the
In 1906 Ludwig Pollak, archaeologist, art dealer and director of the
 The discovery of the ''Laocoön'' made a great impression on Italian artists and continued to influence Italian art into the
The discovery of the ''Laocoön'' made a great impression on Italian artists and continued to influence Italian art into the
 Pliny's description of ''Laocoön'' as "a work to be preferred to all that the arts of painting and sculpture have produced" has led to a tradition which debates this claim that the sculpture is the greatest of all artworks.
Pliny's description of ''Laocoön'' as "a work to be preferred to all that the arts of painting and sculpture have produced" has led to a tradition which debates this claim that the sculpture is the greatest of all artworks.
 The location where the buried statue was found in 1506 was always known to be "in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis" on the
The location where the buried statue was found in 1506 was always known to be "in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis" on the
subscription required
reprinted in ''Confronting the Classics: Traditions, Adventures and Innovations'', 2013 EBL ebooks online, Profile Books
Google Books
* Boardman, John ed., ''The Oxford History of Classical Art'', 1993, OUP, * "Chronology": Frischer, Bernard, Digital Sculpture Project: Laocoon
"An Annotated Chronology of the “Laocoon” Statue Group"
2009 * Clark, Kenneth, ''The Nude, A Study in Ideal Form'', orig. 1949, various edns, page refs from Pelican edn of 1960 * Cook, R.M., ''Greek Art'', Penguin, 1986 (reprint of 1972), * Farinella, Vincenzo, ''Vatican Museums, Classical Art'', 1985, Scala * Haskell, Francis, and Penny, Nicholas, 1981. ''Taste and the Antique: The Lure of Classical Sculpture 1500–1900'' (Yale University Press), cat. no. 52, pp. 243–47 * Herrmann, Ariel, review of ''Sperlonga und Vergil'' by
Google Books
* Rice, E. E., "Prosopographika Rhodiaka", ''The Annual of the British School at Athens'', Vol. 81, (1986), pp. 209–250, * Spivey, Nigel (2001)
''Enduring Creation: Art, Pain, and Fortitude''
"Laocoon: The Last Enigma"
translation by Bernard Frischer of Volpe, Rita and Parisi, Antonella, "Laocoonte. L'ultimo engima," in ''Archeo'' 299, January 2010, pp. 26–39 * Warden, P. Gregory, "The Domus Aurea Reconsidered", ''Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians'', Vol. 40, No. 4 (Dec., 1981), pp. 271–278, ,
University of Virginia's Digital Sculpture Project
3D models, bibliography, annotated chronology of the ''Laocoon''
''Laocoon'' photos
Laocoon and his Sons
in the ''Census'' database
FlickR group "Responses To Laocoön"
a collection of art inspired by the ''Laocoön'' group
Lessing's ''Laocoon'' etext on books.google.com
*
Laocoonte: variazioni sul mito, con una Galleria delle fonti letterarie e iconografiche su Laocoonte, a cura del Centro studi classicA, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50, luglio/settembre 2006
Nota sul ciclo di Sperlonga e sulle relazioni con il Laoocoonte Vaticano, a cura del Centro studi classicA, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50. luglio/settembre 2006
Nota sulle interpretazioni del passo di Plinio, Nat. Hist. XXXVI, 37, a cura del Centro studi classicA, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50. luglio/settembre 2006
Scheda cronologica dei restauri del Laocoonte, a cura di Marco Gazzola, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50, luglio/settembre 2006
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Laocoon And His Sons 1st-century BC sculptures 1506 archaeological discoveries Antiquities acquired by Napoleon Hellenistic sculpture Roman copies of Greek sculptures Sculptures of the Vatican Museums Tourist attractions in Rome Archaeological discoveries in Italy Hellenistic-style Roman sculptures Nude sculptures Snakes in art
Vatican Museums
The Vatican Museums ( it, Musei Vaticani; la, Musea Vaticana) are the public museums of the Vatican City. They display works from the immense collection amassed by the Catholic Church and the papacy throughout the centuries, including several of ...
, where it remains. It is very likely the same statue that was praised in the highest terms by the main Roman writer on art, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
. The figures are near life-size and the group is a little over in height, showing the Trojan priest Laocoön and his sons Antiphantes and Thymbraeus being attacked by sea serpents.
The group has been called "the prototypical icon of human agony" in Western art, and unlike the agony often depicted in Christian art showing the Passion of Jesus
In Christianity, the Passion (from the Latin verb ''patior, passus sum''; "to suffer, bear, endure", from which also "patience, patient", etc.) is the short final period in the life of Jesus Christ.
Depending on one's views, the "Passion" m ...
and martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
s, this suffering has no redemptive power or reward. The suffering is shown through the contorted expressions of the faces (Dr. Guillaume-Benjamin Duchenne pointed out to Charles Darwin that Laocoön's bulging eyebrows are physiologically impossible), which are matched by the struggling bodies, especially that of Laocoön himself, with every part of his body straining.
Pliny attributes the work, then in the palace of Emperor Titus, to three Greek sculptors from the island of Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
: Agesander
Agesander (also ''Agesandros'', ''Hagesander'', ''Hagesandros'', or ''Hagesanderus''; grc, Ἀγήσανδρος or grc, Ἁγήσανδρος) was one, or more likely, several Greek sculptors from the island of Rhodes, working in the first cent ...
, Athenodoros and Polydorus, but does not give a date or patron. In style it is considered "one of the finest examples of the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
baroque" and certainly in the Greek tradition,Boardman, 199 but it is not known whether it is an original work or a copy of an earlier sculpture, probably in bronze, or made for a Greek or Roman commission. The view that it is an original work of the 2nd century BC now has few if any supporters, although many still see it as a copy of such a work made in the early Imperial period, probably of a bronze original. Others see it as probably an original work of the later period, continuing to use the Pergamene
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on ...
style of some two centuries earlier. In either case, it was probably commissioned for the home of a wealthy Roman, possibly of the Imperial family. Various dates have been suggested for the statue, ranging from about 200 BC to the 70s AD, though "a Julio-Claudian
, native_name_lang=Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type=Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estates=* ...
date etween 27 BC and 68 AD... is now preferred".Howard, 422
Museo Pio-Clementino
The Vatican Museums ( it, Musei Vaticani; la, Musea Vaticana) are the public museums of the Vatican City. They display works from the immense collection amassed by the Catholic Church and the papacy throughout the centuries, including several of ...
, a part of the Vatican Museums
The Vatican Museums ( it, Musei Vaticani; la, Musea Vaticana) are the public museums of the Vatican City. They display works from the immense collection amassed by the Catholic Church and the papacy throughout the centuries, including several of ...
.
Subject

Trojan
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 189 ...
priest, came from the Greek Epic Cycle
The Epic Cycle ( grc, Ἐπικὸς Κύκλος, Epikòs Kýklos) was a collection of Ancient Greek epic poems, composed in dactylic hexameter and related to the story of the Trojan War, including the '' Cypria'', the ''Aethiopis'', the so-ca ...
on the Trojan Wars, though it is not mentioned by Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
. It had been the subject of a tragedy, now lost, by Sophocles
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or c ...
and was mentioned by other Greek writers, though the events around the attack by the serpents vary considerably. The most famous account of these is now in Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
's ''Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Trojan who fled the fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of ...
'' (see the ''Aeneid'' quotation at the entry Laocoön), but this dates from between 29 and 19 BC, which is possibly later than the sculpture. However, some scholars see the group as a depiction of the scene as described by Virgil.
In Virgil, Laocoön was a priest of Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, Ποσειδῶν) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as ...
who was killed with both his sons after attempting to expose the ruse of the Trojan Horse
The Trojan Horse was a wooden horse said to have been used by the Greeks during the Trojan War to enter the city of Troy and win the war. The Trojan Horse is not mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'', with the poem ending before the war is concluded, ...
by striking it with a spear. In Sophocles, on the other hand, he was a priest of Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
, who should have been celibate but had married. The serpents killed only the two sons, leaving Laocoön himself alive to suffer. In other versions he was killed for having had sex with his wife in the temple of Poseidon, or simply making a sacrifice in the temple with his wife present. In this second group of versions, the snakes were sent by Poseidon and in the first by Poseidon and Athena, or Apollo, and the deaths were interpreted by the Trojans as proof that the horse was a sacred object. The two versions have rather different morals: Laocoön was either punished for doing wrong, or for being right.
The snakes are depicted as both biting and constricting, and are probably intended as venomous, as in Virgil. Pietro Aretino thought so, praising the group in 1537:
...the two serpents, in attacking the three figures, produce the most striking semblances of fear, suffering and death. The youth embraced in the coils is fearful; the old man struck by the fangs is in torment; the child who has received the poison, dies.In at least one Greek telling of the story the older son is able to escape, and the composition seems to allow for that possibility.
History
Ancient times
The style of the work is agreed to be that of the Hellenistic "Pergamene
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on ...
baroque" which arose in Greek Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
around 200 BC, and whose best known undoubtedly original work is the Pergamon Altar
The Pergamon Altar () was a monumental construction built during the reign of the Ancient Greek King Eumenes II in the first half of the 2nd century BC on one of the terraces of the acropolis of Pergamon in Asia Minor.
The structure was 35.64 ...
, dated c. 180–160 BC, and now in Berlin. Here the figure of Alcyoneus
In Greek mythology, Alcyoneus or Alkyoneus (; Ancient Greek: Ἀλκυονεύς ''Alkuoneus'') was a traditional opponent of the hero Heracles. He was usually considered to be one of the Gigantes ( Giants), the offspring of Gaia born from the bl ...
is shown in a pose and situation (including serpents) which is very similar to those of Laocoön, though the style is "looser and wilder in its principles" than the altar.Cook, 153
The execution of the Laocoön is extremely fine throughout, and the composition very carefully calculated, even though it appears that the group underwent adjustments in ancient times. The two sons are rather small in scale compared to their father, but this adds to the impact of the central figure. The fine white marble used is often thought to be Greek, but has not been identified by analysis.
Pliny
In Pliny's survey of Greek and Roman stone sculpture in his encyclopedic '' Natural History'' (XXXVI, 37), he says:....in the case of several works of very great excellence, the number of artists that have been engaged upon them has proved a considerable obstacle to the fame of each, no individual being able to engross the whole of the credit, and it being impossible to award it in due proportion to the names of the several artists combined. Such is the case with the Laocoön, for example, in the palace of the Emperor Titus, a work that may be looked upon as preferable to any other production of the art of painting or of ronzestatuary. It is sculptured from a single block, both the main figure as well as the children, and the serpents with their marvellous folds. This group was made in concert by three most eminent artists, Agesander, Polydorus, and Athenodorus, natives of Rhodes.It is generally accepted that this is the same work as is now in the Vatican. It is now very often thought that the three Rhodians were copyists, perhaps of a
bronze sculpture
Bronze is the most popular metal for Casting (metalworking), cast metal sculptures; a cast bronze sculpture is often called simply "a bronze". It can be used for statues, singly or in groups, reliefs, and small statuettes and figurines, as w ...
from Pergamon, created around 200 BC.Stewart, Andrew W. (1996), "Hagesander, Athanodorus and Polydorus", in Hornblower, Simon, Oxford Classical Dictionary, Oxford: Oxford University Press. It is noteworthy that Pliny does not address this issue explicitly, in a way that suggests "he regards it as an original". Pliny states that it was located in the palace of the emperor Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
, and it is possible that it remained in the same place until 1506 (see "Findspot" section below). He also asserts that it was carved from a single piece of marble, though the Vatican work comprises at least seven interlocking pieces. The phrase translated above as "in concert" (''de consilii sententia'') is regarded by some as referring to their commission rather than the artists' method of working, giving in Nigel Spivey's translation: " he artistsat the behest of council designed a group...", which Spivey takes to mean that the commission was by Titus, possibly even advised by Pliny among other ''savants''.
The same three artists' names, though in a different order (Athenodoros, Agesander
Agesander (also ''Agesandros'', ''Hagesander'', ''Hagesandros'', or ''Hagesanderus''; grc, Ἀγήσανδρος or grc, Ἁγήσανδρος) was one, or more likely, several Greek sculptors from the island of Rhodes, working in the first cent ...
, and Polydorus), with the names of their fathers, are inscribed on one of the sculptures at Tiberius's villa at Sperlonga (though they may predate his ownership), but it seems likely that not all the three masters were the same individuals. Though broadly similar in style, many aspects of the execution of the two groups are drastically different, with the Laocoon group of much higher quality and finish.
Some scholars used to think that honorific inscriptions found at Lindos
Lindos (; grc-gre, Λίνδος) is an archaeological site, a fishing village and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it ...
in Rhodes dated Agesander and Athenodoros, recorded as priests, to a period after 42 BC, making the years 42 to 20 BC the most likely date for the Laocoön group's creation. However the Sperlonga inscription, which also gives the fathers of the artists, makes it clear that at least Agesander is a different individual from the priest of the same name recorded at Lindos, though very possibly related. The names may have recurred across generations, a Rhodian habit, within the context of a family workshop (which might well have included the adoption
Adoption is a process whereby a person assumes the parenting of another, usually a child, from that person's biological or legal parent or parents. Legal adoptions permanently transfer all rights and responsibilities, along with filiation, fro ...
of promising young sculptors). Altogether eight "signatures" (or labels) of an Athenodoros are found on sculptures or bases for them, five of these from Italy. Some, including that from Sperlonga, record his father as Agesander. The whole question remains the subject of academic debate.
Renaissance
 The group was unearthed in February 1506 in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis; informed of the fact,
The group was unearthed in February 1506 in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis; informed of the fact, Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or t ...
, an enthusiastic classicist, sent for his court artists. Michelangelo was called to the site of the unearthing of the statue immediately after its discovery, along with the Florentine architect Giuliano da Sangallo
Giuliano da Sangallo (c. 1445 – 1516) was an Italian sculptor, architect and military engineer active during the Italian Renaissance. He is known primarily for being the favored architect of Lorenzo de' Medici, his patron. In this role, Giu ...
and his eleven-year-old son Francesco da Sangallo
Francesco da Sangallo (1494–1576) was an Italian Renaissance sculptor, the son of the architect and sculptor Giuliano da Sangallo.
Sangallo was born in Florence. His father took him at the age of ten to Rome where, in 1506, he was present a ...
, later a sculptor, who wrote an account over sixty years later:
The first time I was in Rome when I was very young, the pope was told about the discovery of some very beautiful statues in a vineyard near Santa Maria Maggiore. The pope ordered one of his officers to run and tell Giuliano da Sangallo to go and see them. So he set off immediately. Since Michelangelo Buonarroti was always to be found at our house, my father having summoned him and having assigned him the commission of the pope’s tomb, my father wanted him to come along, too. I joined up with my father and off we went. I climbed down to where the statues were when immediately my father said, "That is the Laocoön, which Pliny mentions". Then they dug the hole wider so that they could pull the statue out. As soon as it was visible everyone started to draw (or "started to have lunch"), all the while discoursing on ancient things, chatting as well about the ones in Florence.Julius acquired the group on March 23, giving De Fredis a job as a scribe as well as the customs revenues from one of the gates of Rome. By August the group was placed for public viewing in a niche in the wall of the brand new Belvedere Garden at the Vatican, now part of the Vatican Museums, which regard this as the start of their history. As yet it had no base, which was not added until 1511, and from various prints and drawings from the time the older son appears to have been completely detached from the rest of the group. In July 1798 the statue was taken to France in the wake of the French conquest of Italy, though the replacement parts were left in Rome. It was on display when the new Musée Central des Arts, later the Musée Napoléon, opened at the
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
in November 1800. A competition was announced for new parts to complete the composition, but there were no entries. Some plaster sections by François Girardon
François Girardon (10 March 1628 – 1 September 1715) was a French sculptor of the Louis XIV style or French Baroque, best known for his statues and busts of Louis XIV and for his statuary in the gardens of the Palace of Versailles.
Biograph ...
, over 150 years old, were used instead. After Napoleon's final defeat at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Sevent ...
in 1815 most (but certainly not all) of the artworks plundered by the French were returned, and the Laocoön reached Rome in January 1816.
Restorations
Vasari
Giorgio Vasari (, also , ; 30 July 1511 – 27 June 1574) was an Italian Renaissance Master, who worked as a painter, architect, engineer, writer, and historian, who is best known for his work ''The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculpt ...
, in about 1510 Bramante
Donato Bramante ( , , ; 1444 – 11 April 1514), born as Donato di Pascuccio d'Antonio and also known as Bramante Lazzari, was an Italian architect and painter. He introduced Renaissance architecture to Milan and the High Renaissance st ...
, the Pope's architect, held an informal contest among sculptors to make replacement right arms, which was judged by Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual ...
, and won by Jacopo Sansovino
Jacopo d'Antonio Sansovino (2 July 1486 – 27 November 1570) was an Italian Renaissance sculptor and architect, best known for his works around the Piazza San Marco in Venice. These are crucial works in the history of Venetian Renaissance arc ...
. The winner, in the outstretched position, was used in copies but not attached to the original group, which remained as it was until 1532, when Giovanni Antonio Montorsoli, a pupil of Michelangelo, added his even more straight version of Laocoön's outstretched arm, which remained in place until modern times. In 1725–1727 Agostino Cornacchini
Agostino Cornacchini (August 27, 1686 – 1754) was an Italian sculptor and painter of the Rococo period, active mainly in Rome.
He was born in Pescia and died in Rome. In 1712, Cornacchini established himself in the household of his uncle, Card ...
added a section to the younger son's arm, and after 1816 Antonio Canova
Antonio Canova (; 1 November 1757 – 13 October 1822) was an Italian Neoclassical sculptor, famous for his marble sculptures. Often regarded as the greatest of the Neoclassical artists,. his sculpture was inspired by the Baroque and the cla ...
tidied up the group after their return from Paris, without being convinced by the correctness of the additions but wishing to avoid a controversy.
Museo Barracco
Museo Barracco di Scultura Antica (Italian, ''Barracco Museum of Antique Sculpture'') is a museum in Rome, Italy, featuring a collection of works acquired by the collector Giovanni Barracco, who donated his collection to the City of Rome in 1902. ...
, discovered a fragment of a marble arm in a builder's yard in Rome, close to where the group was found. Noting a stylistic similarity to the Laocoön group he presented it to the Vatican Museums: it remained in their storerooms for half a century. In 1957 the museum decided that this armbent, as Michelangelo had suggestedhad originally belonged to this Laocoön, and replaced it. According to Paolo Liverani: "Remarkably, despite the lack of a critical section, the join between the torso and the arm was guaranteed by a drill hole on one piece which aligned perfectly with a corresponding hole on the other."
In the 1980s the statue was dismantled and reassembled, again with the Pollak arm incorporated. The restored portions of the children's arms and hands were removed. In the course of disassembly, it was possible to observe breaks, cuttings, metal tenons, and dowel holes which suggested that in antiquity, a more compact, three-dimensional pyramidal grouping of the three figures had been used or at least contemplated. According to Seymour Howard, both the Vatican group and the Sperlonga sculptures "show a similar taste for open and flexible pictorial organization that called for pyrotechnic piercing and lent itself to changes at the site, and in new situations".
The more open, planographic composition along a plane, used in the restoration of the Laocoön group, has been interpreted as "apparently the result of serial reworkings by Roman Imperial as well as Renaissance and modern craftsmen". A different reconstruction was proposed by Seymour Howard, to give "a more cohesive, baroque-looking and diagonally-set pyramidal composition", by turning the older son as much as 90°, with his back to the side of the altar, and looking towards the frontal viewer rather than at his father.Howard, 422 and 417 quoted in turn. See also "Chronology" at 1959 The findings Seymour Howard documented do not change his belief about the organization of the original. But dating the reworked coil ends by measuring the depth of the surface crust and comparing the metal dowels in the original and reworked portions allows one to determine the provenance of the parts and the sequence of the repairs. Other suggestions have been made.
Influence
 The discovery of the ''Laocoön'' made a great impression on Italian artists and continued to influence Italian art into the
The discovery of the ''Laocoön'' made a great impression on Italian artists and continued to influence Italian art into the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
period. Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was ins ...
is known to have been particularly impressed by the massive scale of the work and its sensuous Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
aesthetic, particularly its depiction of the male figures. The influence of the ''Laocoön'', as well as the Belvedere Torso
__NOTOC__
The Belvedere Torso is a tall fragmentary marble statue of a male nude, known to be in Rome from the 1430s, and signed prominently on the front of the base by "Apollonios, son of Nestor, Athenian", who is unmentioned in ancient literat ...
, is evidenced in many of Michelangelo's later sculptures, such as the '' Rebellious Slave'' and the ''Dying Slave
The ''Dying Slave'' is a sculpture by the Italian Renaissance artist Michelangelo. Created between 1513 and 1516, it was to serve with another figure, the '' Rebellious Slave'', at the tomb of Pope Julius II. It is a marble figure 2.15 metres (7' ...
'', created for the tomb of Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or t ...
. Several of the ''ignudi
The Sistine Chapel ceiling ( it, Soffitto della Cappella Sistina), painted in fresco by Michelangelo between 1508 and 1512, is a cornerstone work of High Renaissance art. The Sistine Chapel is the large papal chapel built within the Vatica ...
'' and the figure of Haman
Haman ( ; also known as Haman the Agagite or Haman the evil) is the main antagonist in the Book of Esther, who according to the Hebrew Bible was an official in the court of the Persian empire under King Ahasuerus, commonly identified as Xerxes I ...
in the Sistine Chapel ceiling
The Sistine Chapel ceiling ( it, Soffitto della Cappella Sistina), painted in fresco by Michelangelo between 1508 and 1512, is a cornerstone work of High Renaissance art. The Sistine Chapel is the large papal chapel built within the Vatican ...
draw on the figures. Raphael used the face of Laocoön for his Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
in his ''Parnassus
Mount Parnassus (; el, Παρνασσός, ''Parnassós'') is a mountain range of central Greece that is and historically has been especially valuable to the Greek nation and the earlier Greek city-states for many reasons. In peace, it offers ...
'' in the Raphael Rooms
The four Raphael Rooms ( it, Stanze di Raffaello) form a suite of reception rooms in the Apostolic Palace, now part of the Vatican Museums, in Vatican City. They are famous for their frescoes, painted by Raphael and his workshop. Together wit ...
, expressing blindness rather than pain.
The Florentine sculptor Baccio Bandinelli
Baccio Bandinelli (also called Bartolommeo Brandini; 12 November 1493 – shortly before 7 February 1560), was an Italian Renaissance sculptor, draughtsman, and painter.
Biography
Bandinelli was the son of a prominent Florentine goldsmith, ...
was commissioned to make a copy by the Medici Pope Leo X
Pope Leo X ( it, Leone X; born Giovanni di Lorenzo de' Medici, 11 December 14751 December 1521) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 March 1513 to his death in December 1521.
Born into the prominent political an ...
. Bandinelli's version, which was often copied and distributed in small bronzes, is in the Uffizi
The Uffizi Gallery (; it, Galleria degli Uffizi, italic=no, ) is a prominent art museum located adjacent to the Piazza della Signoria in the Historic Centre of Florence in the region of Tuscany, Italy. One of the most important Italian museums ...
Gallery, Florence, the Pope having decided it was too good to send to François I of France as originally intended. A bronze casting, made for François I at Fontainebleau
Fontainebleau (; ) is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southeast of the centre of Paris. Fontainebleau is a sub-prefecture of the Seine-et-Marne department, and it is the seat of the ''arrondissemen ...
from a mold taken from the original under the supervision of Primaticcio
Francesco Primaticcio (April 30, 1504 – 1570) was an Italian Mannerist painter, architect and sculptor who spent most of his career in France.
Biography
Born in Bologna, he trained under Giulio Romano in Mantua and became a pupil of ...
, is at the Musée du Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
. There are many copies of the statue, including a well-known one in the Grand Palace
The Grand Palace ( th, พระบรมมหาราชวัง, Royal Institute of Thailand. (2011). ''How to read and how to write.'' (20th Edition). Bangkok: Royal Institute of Thailand. .) is a complex of buildings at the heart of Ba ...
of the Knights of St. John
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headqu ...
in Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. Many still show the arm in the outstretched position, but the copy in Rhodes has been corrected.
The group was rapidly depicted in prints
In molecular biology, the PRINTS database is a collection of so-called "fingerprints": it provides both a detailed annotation resource for protein families, and a diagnostic tool for newly determined sequences. A fingerprint is a group of conserved ...
as well as small models, and became known all over Europe. Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Vecellio (; 27 August 1576), known in English as Titian ( ), was an Italians, Italian (Republic of Venice, Venetian) painter of the Renaissance, considered the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school (art), ...
appears to have had access to a good cast or reproduction from about 1520, and echoes of the figures begin to appear in his works, two of them in the '' Averoldi Altarpiece'' of 1520–1522. A woodcut
Woodcut is a relief printing technique in printmaking. An artist carves an image into the surface of a block of wood—typically with gouges—leaving the printing parts level with the surface while removing the non-printing parts. Areas tha ...
, probably after a drawing by Titian, parodied the sculpture by portraying three apes instead of humans. It has often been interpreted as a satire on the clumsiness of Bandinelli's copy, or as a commentary on debates of the time around the similarities between human and ape anatomy. It has also been suggested that this woodcut was one of a number of Renaissance images that were made to reflect contemporary doubts as to the authenticity of the ''Laocoön Group'', the 'aping' of the statue referring to the incorrect pose of the Trojan priest who was depicted in ancient art in the traditional sacrificial pose, with his leg raised to subdue the bull. Over 15 drawings of the group made by Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
in Rome have survived, and the influence of the figures can be seen in many of his major works, including his ''Descent from the Cross
The Descent from the Cross ( el, Ἀποκαθήλωσις, ''Apokathelosis''), or Deposition of Christ, is the scene, as depicted in art, from the Gospels' accounts of Joseph of Arimathea and Nicodemus taking Christ down from the cross after hi ...
'' in Antwerp Cathedral
The Cathedral of Our Lady ( nl, Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal) is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Antwerp, Belgium. Today's see of the Diocese of Antwerp started in 1352 and, although the first stage of construction was ended in 1521, has never be ...
.
The original was seized and taken to Paris by Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
after his conquest of Italy in 1799, and installed in a place of honour in the Musée Napoléon at the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
. Following the fall of Napoleon, it was returned by the Allies to the Vatican in 1816.
''Laocoön'' as an ideal of art
 Pliny's description of ''Laocoön'' as "a work to be preferred to all that the arts of painting and sculpture have produced" has led to a tradition which debates this claim that the sculpture is the greatest of all artworks.
Pliny's description of ''Laocoön'' as "a work to be preferred to all that the arts of painting and sculpture have produced" has led to a tradition which debates this claim that the sculpture is the greatest of all artworks. Johann Joachim Winkelmann
Johann Joachim Winckelmann (; ; 9 December 17178 June 1768) was a German art historian and archaeologist. He was a pioneering Hellenist who first articulated the differences between Greek, Greco-Roman and Roman art. "The prophet and founding ...
(1717–1768) wrote about the paradox of admiring beauty while seeing a scene of death and failure. The most influential contribution to the debate, Gotthold Ephraim Lessing
Gotthold Ephraim Lessing (, ; 22 January 1729 – 15 February 1781) was a philosopher, dramatist, publicist and art critic, and a representative of the Enlightenment era. His plays and theoretical writings substantially influenced the develop ...
's essay ''Laocoon: An Essay on the Limits of Painting and Poetry'', examines the differences between visual and literary art by comparing the sculpture with Virgil's verse. He argues that the artists could not realistically depict the physical suffering of the victims, as this would be too painful. Instead, they had to express suffering while retaining beauty.
Johann Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as treat ...
said the following in his essay, ''Upon the Laocoon'' "A true work of art, like a work of nature, never ceases to open boundlessly before the mind. We examine,we are impressed with it,it produces its effect; but it can never be all comprehended, still less can its essence, its value, be expressed in words.
The most unusual intervention in the debate, William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the Romantic poetry, poetry and visual art of t ...
's annotated print ''Laocoön'', surrounds the image with graffiti-like commentary in several languages, written in multiple directions. Blake presents the sculpture as a mediocre copy of a lost Israelite original, describing it as "Jehovah & his two Sons Satan & Adam as they were copied from the Cherubim Of Solomons Temple by three Rhodians & applied to Natural Fact or History of Ilium". This reflects Blake's theory that the imitation of ancient Greek and Roman art was destructive to the creative imagination, and that Classical sculpture represented a banal naturalism in contrast to Judeo-Christian spiritual art.
The central figure of ''Laocoön'' served as loose inspiration for the Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
in Horatio Greenough
Horatio Greenough (September 6, 1805 – December 18, 1852) was an American sculptor best known for his United States government commissions '' The Rescue'' (1837–50), ''George Washington'' (1840), and ''The Discovery of America'' (1840–4 ...
's '' The Rescue'' (1837–1850) which stood before the east facade of the United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called The Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the seat of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, which is formally known as the United States Congress. It is located on Capitol Hill ...
for over 100 years.
Near the end of Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
' 1843 novella, ''A Christmas Carol
''A Christmas Carol. In Prose. Being a Ghost Story of Christmas'', commonly known as ''A Christmas Carol'', is a novella by Charles Dickens, first published in London by Chapman & Hall in 1843 and illustrated by John Leech. ''A Christmas ...
'', Ebenezer Scrooge self-describes "making a perfect Laocoön of himself with his stockings" in his hurry to dress on Christmas morning.
John Ruskin
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and pol ...
disliked the sculpture and compared its "disgusting convulsions" unfavourably with work by Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was ins ...
, whose fresco of ''The Brazen Serpent,'' on a corner pendentive of the Sistine Chapel
The Sistine Chapel (; la, Sacellum Sixtinum; it, Cappella Sistina ) is a chapel in the Apostolic Palace, the official residence of the pope in Vatican City. Originally known as the ''Cappella Magna'' ('Great Chapel'), the chapel takes its nam ...
, also involves figures struggling with snakesthe fiery serpents of the Book of Numbers
The book of Numbers (from Greek Ἀριθμοί, ''Arithmoi''; he, בְּמִדְבַּר, ''Bəmīḏbar'', "In the desert f) is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible, and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah. The book has a long and ...
. He invited contrast between the "meagre lines and contemptible tortures of the Laocoon" and the "awfulness and quietness" of Michelangelo, saying "the slaughter of the Dardan priest" was "entirely wanting" in sublimity
In aesthetics, the sublime (from the Latin '' sublīmis'') is the quality of greatness, whether physical, moral, intellectual, metaphysical, aesthetic, spiritual, or artistic. The term especially refers to a greatness beyond all possibility ...
. Furthermore, he attacked the composition on naturalistic grounds, contrasting the carefully studied human anatomy of the restored figures with the unconvincing portrayal of the snakes:
In 1910 the critic Irving Babbit used the title ''The New Laokoon: An Essay on the Confusion of the Arts'' for an essay on contemporary culture at the beginning of the 20th century. In 1940 Clement Greenberg
Clement Greenberg () (January 16, 1909 – May 7, 1994), occasionally writing under the pseudonym K. Hardesh, was an American essayist known mainly as an art critic closely associated with American modern art of the mid-20th century and a formali ...
adapted the concept for his own essay entitled ''Towards a Newer Laocoön'' in which he argued that abstract art now provided an ideal for artists to measure their work against. A 2007 exhibition at the Henry Moore Institute
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
in turn copied this title while exhibiting work by modern artists influenced by the sculpture.
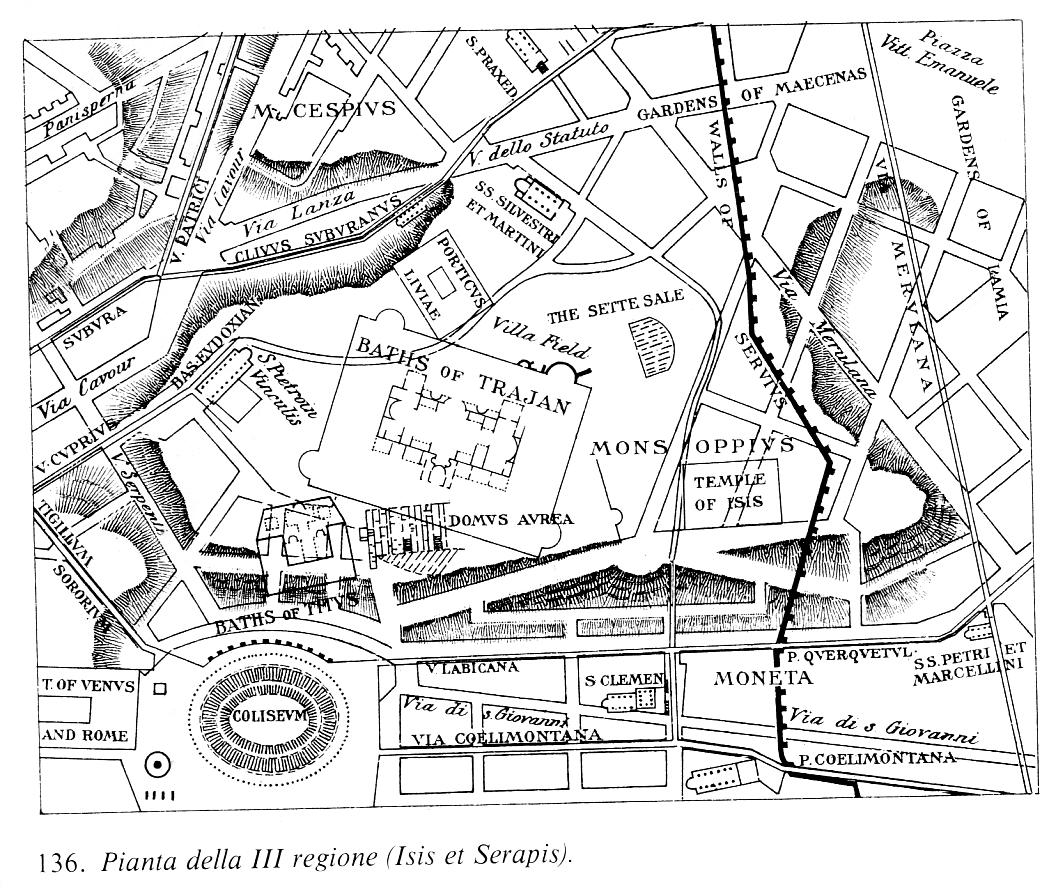
Findspot
 The location where the buried statue was found in 1506 was always known to be "in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis" on the
The location where the buried statue was found in 1506 was always known to be "in the vineyard of Felice De Fredis" on the Oppian Hill
The Oppian Hill (Latin, ''Oppius Mons''; it, Colle Oppio) is the southern spur of the Esquiline Hill, one of the Seven hills of Rome, Italy. It is separated from the Cispius on the north by the valley of the Suburra, and from the Caelian H ...
(the southern spur of the Esquiline Hill
The Esquiline Hill (; la, Collis Esquilinus; it, Esquilino ) is one of the Seven Hills of Rome. Its southernmost cusp is the ''Oppius'' (Oppian Hill).
Etymology
The origin of the name ''Esquiline'' is still under much debate. One view is ...
), as noted in the document recording the sale of the group to the Pope. But over time, knowledge of the site's precise location was lost, beyond "vague" statements such as Sangallo's "near Santa Maria Maggiore" (see above) or it being "near the site of the Domus Aurea" (the palace of the Emperor Nero); in modern terms near the Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world ...
. An inscribed plaque of 1529 in the church of Santa Maria in Aracoeli
The Basilica of St. Mary of the Altar of Heaven ( la, Basilica Sanctae Mariae de Ara coeli in Capitolio, it, Basilica di Santa Maria in Ara coeli al Campidoglio) is a titular basilica in Rome, located on the highest summit of the Campidoglio. ...
records the burial of De Fredis and his son there, covering his finding of the group but giving no occupation. Research published in 2010 has recovered two documents in the municipal archives (badly indexed, and so missed by earlier researchers), which have established a much more precise location for the find: slightly to the east of the southern end of the Sette Sale, the ruined cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by ...
for the successive imperial baths at the base of the hill by the Colosseum.Volpe and Parisi
The first document records De Fredis' purchase of a vineyard of about 1.5 hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100- metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre i ...
s from a convent for 135 ducat
The ducat () coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages from the 13th to 19th centuries. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained ...
s on 14 November 1504, exactly 14 months before the finding of the statue. The second document, from 1527, makes it clear that there is now a house on the property, and clarifies the location; by then De Fredis was dead and his widow rented out the house. The house appears on a map of 1748, and still survives as a substantial building of three storeys, in the courtyard of a convent. The area remained mainly agricultural until the 19th century, but is now entirely built up. It is speculated that De Fredis began building the house soon after his purchase, and as the group was reported to have been found some four metres below ground, at a depth unlikely to be reached by normal vineyard-digging operations, it seems likely that it was discovered when digging the foundations for the house, or possibly a well for it.
The findspot was inside and very close to the Servian Wall
The Servian Wall ( la, Murus Servii Tullii; it, Mura Serviane) was an ancient Roman defensive barrier constructed around the city of Rome in the early 4th century BC. The wall was built of volcanic tuff and was up to in height in places, wide ...
, which was still maintained in the 1st century AD (possibly converted to an aqueduct), though no longer the city boundary, as building had spread well beyond it. The spot was within the Gardens of Maecenas
The Gardens of Maecenas, or ''Horti Maecenatis'', constituted the luxurious ancient Roman estate of Gaius Maecenas, an Augustan-era imperial advisor and patron of the arts. The property was among the first in Italy to emulate the style of Persia ...
, founded by Gaius Maecenas
Gaius Cilnius Maecenas ( – 8 BC) was a friend and political advisor to Octavian (who later reigned as emperor Augustus). He was also an important patron for the new generation of Augustan poets, including both Horace and Virgil. During the rei ...
the ally of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
and patron of the arts. He bequeathed the gardens to Augustus in 8 BC, and Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
lived there after he returned to Rome as heir to Augustus in 2 AD. Pliny said the ''Laocoön'' was in his time at the palace of Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
(''qui est in Titi imperatoris domo''), then heir to his father Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Emp ...
, but the location of Titus's residence remains unknown; the imperial estate of the Gardens of Maecenas may be a plausible candidate. If the ''Laocoön'' group was already in the location of the later findspot by the time Pliny saw it, it might have arrived there under Maecenas or any of the emperors. The extent of the grounds of Nero's Domus Aurea is now unclear, but they do not appear to have extended so far north or east, though the newly rediscovered findspot-location is not very far beyond them.
Warden, 275, approximate map of the grounds is fig. 3
Notes
References
* Barkan, Leonard, ''Unearthing the Past: Archaeology and Aesthetics in the Making of Renaissance Culture'', 1999, Yale University Press, * Beard, Mary,Times Literary Supplement
''The Times Literary Supplement'' (''TLS'') is a weekly literary review published in London by News UK, a subsidiary of News Corp.
History
The ''TLS'' first appeared in 1902 as a supplement to '' The Times'' but became a separate publication ...
, "Arms and the Man: The restoration and reinvention of classical sculpture", 2 February 2001subscription required
reprinted in ''Confronting the Classics: Traditions, Adventures and Innovations'', 2013 EBL ebooks online, Profile Books
Google Books
* Boardman, John ed., ''The Oxford History of Classical Art'', 1993, OUP, * "Chronology": Frischer, Bernard, Digital Sculpture Project: Laocoon
"An Annotated Chronology of the “Laocoon” Statue Group"
2009 * Clark, Kenneth, ''The Nude, A Study in Ideal Form'', orig. 1949, various edns, page refs from Pelican edn of 1960 * Cook, R.M., ''Greek Art'', Penguin, 1986 (reprint of 1972), * Farinella, Vincenzo, ''Vatican Museums, Classical Art'', 1985, Scala * Haskell, Francis, and Penny, Nicholas, 1981. ''Taste and the Antique: The Lure of Classical Sculpture 1500–1900'' (Yale University Press), cat. no. 52, pp. 243–47 * Herrmann, Ariel, review of ''Sperlonga und Vergil'' by
Roland Hampe
Roland Hampe (2 December 1908 - 23 January 1981) was a German classical archaeologist. From 1959-1975 he was a professor at Heidelberg University.Hölscher, Tonio.Hampe, Roland" '' Brill's New Pauly Supplements'' I - Volume 6 : History of classic ...
, '' The Art Bulletin'', Vol. 56, No. 2, Medieval Issue (Jun., 1974), pp. 275–277,
* Howard, Seymour, "Laocoon Rerestored", ''American Journal of Archaeology'', Vol. 93, No. 3 (Jul., 1989), pp. 417–422,
* Isager, Jacob, ''Pliny on Art and Society: The Elder Pliny's Chapters On The History Of Art'', 2013, Routledge, Google Books
* Rice, E. E., "Prosopographika Rhodiaka", ''The Annual of the British School at Athens'', Vol. 81, (1986), pp. 209–250, * Spivey, Nigel (2001)
''Enduring Creation: Art, Pain, and Fortitude''
University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public land-grant research university system in the U.S. state of California. The system is composed of the campuses at Berkeley, Davis, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, University of Califor ...
Press,
* Smith, R.R.R., ''Hellenistic Sculpture, a handbook'', Thames & Hudson, 1991,
* Stewart, A., "To Entertain an Emperor: Sperlonga, Laokoon and Tiberius at the Dinner-Table", ''The Journal of Roman Studies'', Vol. 67, (1977), pp. 76–90,
* "Volpe and Parisi": Digital Sculpture Project: Laocoon"Laocoon: The Last Enigma"
translation by Bernard Frischer of Volpe, Rita and Parisi, Antonella, "Laocoonte. L'ultimo engima," in ''Archeo'' 299, January 2010, pp. 26–39 * Warden, P. Gregory, "The Domus Aurea Reconsidered", ''Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians'', Vol. 40, No. 4 (Dec., 1981), pp. 271–278, ,
External links
University of Virginia's Digital Sculpture Project
3D models, bibliography, annotated chronology of the ''Laocoon''
''Laocoon'' photos
Laocoon and his Sons
in the ''Census'' database
FlickR group "Responses To Laocoön"
a collection of art inspired by the ''Laocoön'' group
Lessing's ''Laocoon'' etext on books.google.com
*
Laocoonte: variazioni sul mito, con una Galleria delle fonti letterarie e iconografiche su Laocoonte, a cura del Centro studi classicA, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50, luglio/settembre 2006
Nota sul ciclo di Sperlonga e sulle relazioni con il Laoocoonte Vaticano, a cura del Centro studi classicA, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50. luglio/settembre 2006
Nota sulle interpretazioni del passo di Plinio, Nat. Hist. XXXVI, 37, a cura del Centro studi classicA, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50. luglio/settembre 2006
Scheda cronologica dei restauri del Laocoonte, a cura di Marco Gazzola, "La Rivista di Engramma" n. 50, luglio/settembre 2006
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Laocoon And His Sons 1st-century BC sculptures 1506 archaeological discoveries Antiquities acquired by Napoleon Hellenistic sculpture Roman copies of Greek sculptures Sculptures of the Vatican Museums Tourist attractions in Rome Archaeological discoveries in Italy Hellenistic-style Roman sculptures Nude sculptures Snakes in art