Languages of the Roman Empire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Latin was the language of the Romans from the earliest known period. Writing under the first Roman emperor
Latin was the language of the Romans from the earliest known period. Writing under the first Roman emperor  The birth certificates and wills of Roman citizens had to be written in Latin until the time of Alexander Severus (reigned 222–235). Illiterate Roman subjects would have someone such as a government scribe ''( scriba)'' read or write their official documents for them. Laws and edicts were posted in writing as well as read out. Public art and religious ceremonies were ways to communicate imperial ideology regardless of language spoken or ability to read. An early form of story ballet ''(pantomimus)'' was brought to Rome by Greek performers and became popular throughout the multilingual Empire in part because it relied on gesture rather than verbal expression.
Latin was the official language of the
The birth certificates and wills of Roman citizens had to be written in Latin until the time of Alexander Severus (reigned 222–235). Illiterate Roman subjects would have someone such as a government scribe ''( scriba)'' read or write their official documents for them. Laws and edicts were posted in writing as well as read out. Public art and religious ceremonies were ways to communicate imperial ideology regardless of language spoken or ability to read. An early form of story ballet ''(pantomimus)'' was brought to Rome by Greek performers and became popular throughout the multilingual Empire in part because it relied on gesture rather than verbal expression.
Latin was the official language of the

 The dominance of Latin and Greek among the literate elite may obscure the continuity of spoken languages, since all cultures within the Roman Empire were predominantly oral. In areas where Syriac, Coptic, and Aramaic were spoken, they coexisted with Greek.
The dominance of Latin and Greek among the literate elite may obscure the continuity of spoken languages, since all cultures within the Roman Empire were predominantly oral. In areas where Syriac, Coptic, and Aramaic were spoken, they coexisted with Greek.
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
was the official language of the Roman Empire, but other languages were regionally important, such as Greek. Latin was the original language of the Romans and remained the language of imperial administration, legislation, and the military throughout the classical period. In the West, it became the lingua franca and came to be used for even local administration of the cities including the law courts. After all freeborn male inhabitants of the Empire were universally enfranchised in 212 AD, a great number of Roman citizens
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
would have lacked Latin, though they were expected to acquire at least a token knowledge, and Latin remained a marker of " Romanness".
After the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in late 4th century BCE, Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
had become a shared language around the eastern Mediterranean and diplomatic communications in the East, even beyond the borders of the Empire. The international use of Greek was one condition that enabled the spread of Christianity, as indicated for example by the choice of Greek as the language of the New Testament in the Bible and its use for the ecumenical councils of the Christian Roman Empire rather than Latin. With the dissolution of the Empire in the West, Greek became the more dominant language of the Roman Empire in the East, modernly referred to as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
.
As the communication in ancient society was predominantly oral, it can be difficult to determine the extent to which regional or local languages continued to be spoken or used for other purposes under Roman rule. Some evidence exists in inscriptions, or in references in Greek and Roman texts to other languages and the need for interpreters. For Punic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of t ...
, Coptic, and Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
or Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
, a significant amount of epigraphy or literature survives. The Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
were widespread throughout much of western Europe, and while the orality of Celtic education left scant written records, Celtic epigraphy is limited in quantity but not rare. The Germanic languages of the Empire have left next to no inscriptions or texts, with the exception of Gothic. Multilingualism contributed to the "cultural triangulation" by means of which an individual who was neither Greek nor Roman might construct an identity through the processes of Romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
and Hellenization
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the H ...
.
After the decentralization of political power in late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, Latin developed locally in the Western provinces into branches that became the Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
, including Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, French, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Catalan, Occitan and Romanian. By the early 21st century, the first or second language of more than a billion people derived from Latin. Latin itself remained an international medium of expression for diplomacy and for intellectual developments identified with Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
up to the 17th century, and for law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
to the present.
Latin
 Latin was the language of the Romans from the earliest known period. Writing under the first Roman emperor
Latin was the language of the Romans from the earliest known period. Writing under the first Roman emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: th ...
emphasizes that Latin was a source of Roman unity and tradition
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or ...
. In Virgil's epic ''Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Trojan who fled the fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of th ...
'' about the founding of Rome
The tale of the founding of Rome is recounted in traditional stories handed down by the ancient Romans themselves as the earliest history of their city in terms of legend and myth. The most familiar of these myths, and perhaps the most famous o ...
, the supreme deity Jupiter dictates that the refugee Trojans who have come to settle in Italy will use the language of the native Latini
The Latins (Latin: ''Latini''), sometimes known as the Latians, were an Italic tribe which included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome (see Roman people). From about 1000 BC, the Latins inhabited the small region known to the Romans a ...
as a means of unification: "they will keep the speech ''(sermo)'' and ''mores
Mores (, sometimes ; , plural form of singular , meaning "manner, custom, usage, or habit") are social norms that are widely observed within a particular society or culture. Mores determine what is considered morally acceptable or unacceptable ...
'' of their fathers ... and I will make them all Latins with one mode of expression" ''(uno ore,'' literally "with one mouth"). The Julio-Claudian
, native_name_lang=Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type=Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estates=* ...
emperors, who claimed descent from the Virgilian hero Aeneas, encouraged high standards of correct Latin ''(Latinitas)'', a linguistic movement identified in modern terms as Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later period ...
, and favored Latin for conducting official business.
Latin became the language of conquered areas because local people started speaking it, and not because the population was displaced by Latin-speakers. Latin was not imposed officially on peoples brought under Roman rule. Saint Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
observed that Romans preferred for Latin to be adopted ''per pacem societatis'', through a social pact
The Social Pact (french: Pacte social, nl, Sociaal Pact), was an unofficial political agreement concluded between corporate, labour, and civil service representatives in Belgium which laid the basis for a political compromise after World War II. ...
. This language policy contrasts with that of Alexander, who aimed to impose Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
throughout his empire as the official language. Latin was not a requirement for Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
, and there was no state-supported schooling that privileged it as the medium for education: fluency was desirable for its "high cultural, political, legal, social and economic value".
Latin was needed for Imperial service and advancement, and was the language used for the internal functioning of government. Edicts and official communications of the emperor were in Latin, including rulings on local laws that might be in another language.
The Romans placed a high value on the written word, as indicated by their obsession with documentation and public inscriptions. The Imperial bureaucracy was so dependent on writing that the Babylonian Talmud (bT Shabbat 11a) declared "if all seas were ink, all reeds were pen, all skies parchment, and all men scribes, they would be unable to set down the full scope of the Roman government's concerns." Estimates of the average literacy rate in the Empire range from 5 to 30 percent or higher, depending in part on the definition of "literacy". The lack of state intervention in access to education was a barrier to literacy, since formal education was available only to children from families who could pay for it.
 The birth certificates and wills of Roman citizens had to be written in Latin until the time of Alexander Severus (reigned 222–235). Illiterate Roman subjects would have someone such as a government scribe ''( scriba)'' read or write their official documents for them. Laws and edicts were posted in writing as well as read out. Public art and religious ceremonies were ways to communicate imperial ideology regardless of language spoken or ability to read. An early form of story ballet ''(pantomimus)'' was brought to Rome by Greek performers and became popular throughout the multilingual Empire in part because it relied on gesture rather than verbal expression.
Latin was the official language of the
The birth certificates and wills of Roman citizens had to be written in Latin until the time of Alexander Severus (reigned 222–235). Illiterate Roman subjects would have someone such as a government scribe ''( scriba)'' read or write their official documents for them. Laws and edicts were posted in writing as well as read out. Public art and religious ceremonies were ways to communicate imperial ideology regardless of language spoken or ability to read. An early form of story ballet ''(pantomimus)'' was brought to Rome by Greek performers and became popular throughout the multilingual Empire in part because it relied on gesture rather than verbal expression.
Latin was the official language of the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
until the mid-6th century, and remained the most common language for military use even in the Eastern empire until the 630s. By contrast, only two bishops are known to have spoken Latin at the ecumenical councils held during the reign of Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after the death of his ...
(d. 450 AD).
Greek

Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
had become the common language of the eastern Mediterranean and into Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
after the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. Lucian even imagines that Greek is the universal language of the dead in the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
. In late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, a Greek-speaking majority lived in the Greek peninsula
Greece is a country of the Balkans, in Southeastern Europe, bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cretan and the Libyan Seas, an ...
and islands
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
, major cities of the East, and most of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
. Greek continued as the language of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, and developed into a distinctive medieval Greek that gave rise to modern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the ...
.
The emperor Claudius tried to limit the use of Greek, and on occasion revoked the citizenship of those who lacked Latin. Even in addressing the Roman Senate, however, he drew on his own bilingualism in communicating with Greek-speaking ambassadors. Suetonius quotes him as referring to "our two languages," and the employment of two imperial secretaries, one for Greek and one Latin, dates to his reign.
The everyday interpenetration of the two languages is indicated by bilingual inscriptions, which sometimes even switch back and forth between Greek and Latin. The epitaph of a Greek-speaking soldier, for instance, might be written primarily in Greek, with his rank and unit in the Roman army expressed in Latin.
In the Eastern empire, laws and official documents were regularly translated into Greek from Latin. Both languages were in active use by government officials and the Church during the 5th century. From the 6th century, Greek culture was studied in the West almost exclusively through Latin translation. Latin loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
s appear liberally in Greek texts on technical topics from late antiquity and the Byzantine period.
Language reform movements
Atticism was a trend of theSecond Sophistic
The Second Sophistic is a literary-historical term referring to the Greek writers who flourished from the reign of Nero until c. 230 AD and who were catalogued and celebrated by Philostratus in his ''Lives of the Sophists''. However, some recent ...
. Intellectuals such as Aelius Aristides
Publius Aelius Aristides Theodorus ( grc-gre, Πόπλιος Αἴλιος Ἀριστείδης Θεόδωρος; 117–181 AD) was a Greek orator and author considered to be a prime example as a member of the Second Sophistic, a group of celebr ...
sought to restore the standards of classical Greek characteristic of the Attic dialect
Attic Greek is the Greek dialect of the ancient region of Attica, including the ''polis'' of Athens. Often called classical Greek, it was the prestige dialect of the Greek world for centuries and remains the standard form of the language that is ...
, represented by Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; el, Δημοσθένης, translit=Dēmosthénēs; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual pr ...
, and other authors from the Classical period. Prose stylists who aspired to Atticism tried to avoid the vulgarisms of koine—an impractical goal, but this linguistic purism also reflected the 2nd-century flourishing of grammarians and lexicographer
Lexicography is the study of lexicons, and is divided into two separate academic disciplines. It is the art of compiling dictionaries.
* Practical lexicography is the art or craft of compiling, writing and editing dictionaries.
* Theoretica ...
s. Expertise in language and literature contributed to preserving Hellenic culture in the Roman Imperial world.
Among other reforms, the emperor Diocletian (reigned 284–305) sought to renew the authority of Latin, and the Greek expression ἡ κρατοῦσα διάλεκτος ''(hē kratousa dialektos)'' attests to the continuing status of Latin as "the language of power." The scholar Libanius
Libanius ( grc-gre, Λιβάνιος, Libanios; ) was a teacher of rhetoric of the Sophist school in the Eastern Roman Empire. His prolific writings make him one of the best documented teachers of higher education in the ancient world and a criti ...
(4th century) regarded Latin as causing a decline in the quality of Greek rhetoric. In the early 6th century, the emperor Justinian engaged in a quixotic effort to reassert the status of Latin as the language of law, even though in his time Latin no longer held any currency as a living language in the East.
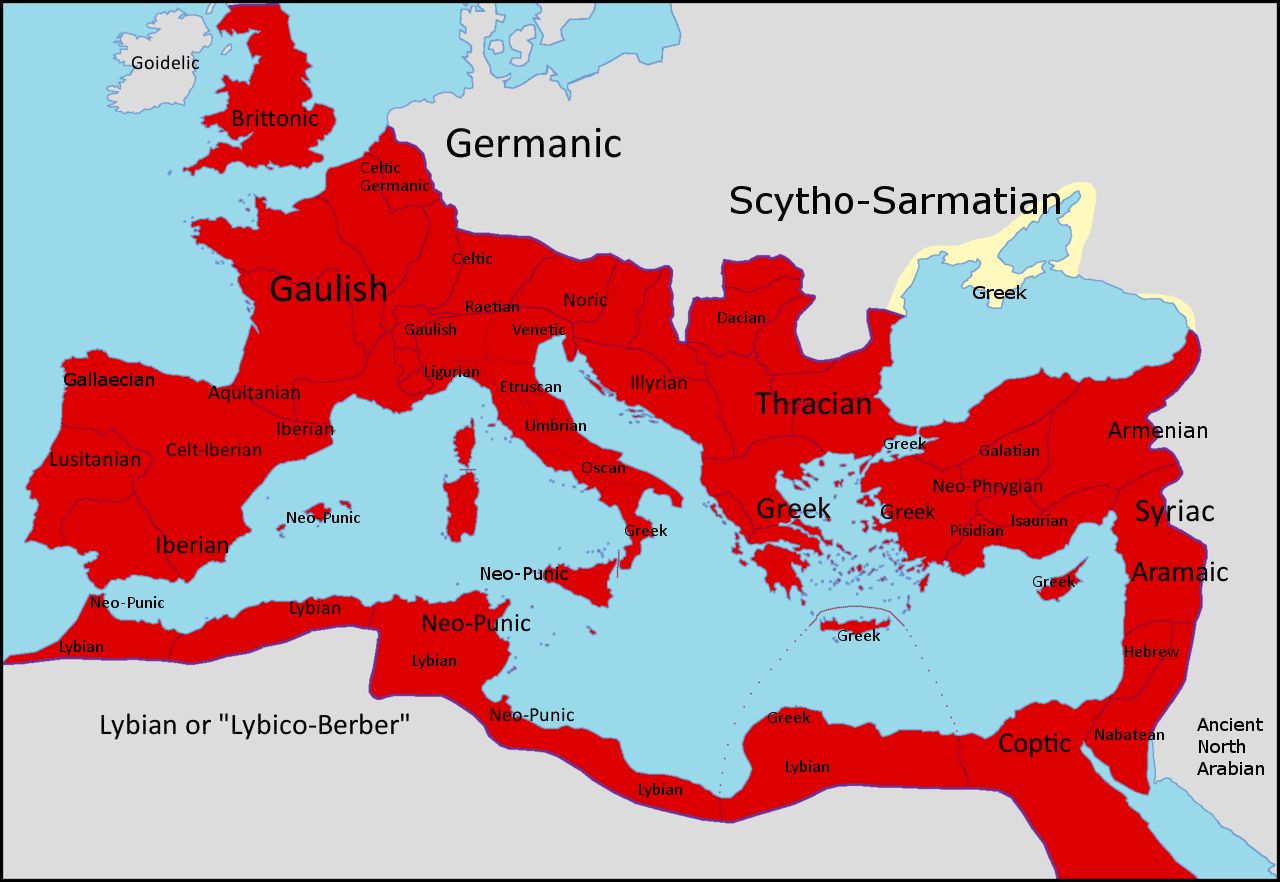
Regional languages

Aramaic and Syriac
Aramaic was the primary language of Syria and Mesopotamia, with several dialects. Syriac was in use aroundAntioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
, one of the three largest cities of the Empire, and particularly by Christians. Syriac literature is known from the latter 2nd century, spreading from the Christian community in Edessa. Early Syriac literature was produced in a largely Greek intellectual milieu until the 4th century, but was distinctive for its use of rich symbolism and emphasis on verse forms, and influenced Greek writers such as Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Chris ...
, Basil
Basil (, ; ''Ocimum basilicum'' , also called great basil, is a culinary herb of the family Lamiaceae (mints). It is a tender plant, and is used in cuisines worldwide. In Western cuisine, the generic term "basil" refers to the variety also k ...
and Theodoret. Among the earliest Syriac literature was the '' Diatessaron'' of Tatian, and translations of sections from the Bible.
The prolific Syrian scholar Bardesanes knew Greek and sent his son for schooling in Athens, but chose to write in his ethnic language. In addition to Syriac homilies
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ex ...
and treatise
A treatise is a formal and systematic written discourse on some subject, generally longer and treating it in greater depth than an essay, and more concerned with investigating or exposing the principles of the subject and its conclusions." Tre ...
s, Bardesanes wrote 150 hymns "of enormous influence and doubtful doctrine". Other Syriac literature of the time included Christian treatises, dialogues, and apocryphal Acts. Some Syriac literature had Gnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
elements, and also played a role in the dissemination of Manicheanism. From the 5th century onward, it included Monophysite and Nestorian
Nestorianism is a term used in Christian theology and Church history to refer to several mutually related but doctrinarily distinct sets of teachings. The first meaning of the term is related to the original teachings of Christian theologian ...
writings.
Works by the Syriac writer Ephraim were translated into Greek. The satirist and rhetorician Lucian came from Samosata
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.province of Syria; although he wrote in Greek, he calls himself a Syrian, and a reference to himself as a " barbarian" suggests that he spoke Syriac.
Soldiers from
 "Coptic" is the modern term for the form of ancient Egyptian that had developed in late antiquity. Written Coptic as a literary language seems to have resulted from a conscious effort among Egypt's educated class to revive their cultural heritage.
In the 4th century, Coptic script—based on the Greek alphabet with additional characters from Egyptian demotic to reflect Egyptian phonology—is found in documents in several dialects, including Old Bohairic, Fayumic, Achmimic, and
"Coptic" is the modern term for the form of ancient Egyptian that had developed in late antiquity. Written Coptic as a literary language seems to have resulted from a conscious effort among Egypt's educated class to revive their cultural heritage.
In the 4th century, Coptic script—based on the Greek alphabet with additional characters from Egyptian demotic to reflect Egyptian phonology—is found in documents in several dialects, including Old Bohairic, Fayumic, Achmimic, and
 Celtiberian is documented as a written language only after contact with the Romans in the 2nd century BC. Of 103 Celtiberian inscriptions, thirty in Iberian script are hospitality tokens ''(tesserae hospitales)'', twenty of which are in the shape of animals. The social custom of pledging mutual support among families or communities was compatible with '' hospitium'' in Roman culture, and the Celtiberians continued to produce the tokens, though switching to Latin, into the 2nd century of the Imperial era. Under Augustus, the territory of the Celtiberians became part of the
Celtiberian is documented as a written language only after contact with the Romans in the 2nd century BC. Of 103 Celtiberian inscriptions, thirty in Iberian script are hospitality tokens ''(tesserae hospitales)'', twenty of which are in the shape of animals. The social custom of pledging mutual support among families or communities was compatible with '' hospitium'' in Roman culture, and the Celtiberians continued to produce the tokens, though switching to Latin, into the 2nd century of the Imperial era. Under Augustus, the territory of the Celtiberians became part of the
 Bilingualism in a Germanic language and Latin was especially important in the military for officers in command of units recruited from Germanic-speaking areas. Tacitus observes that Arminius, the Cheruscan officer who later led a disastrously successful rebellion against the Romans, was bilingual. The emperor Julian employed a bilingual Germanic
Bilingualism in a Germanic language and Latin was especially important in the military for officers in command of units recruited from Germanic-speaking areas. Tacitus observes that Arminius, the Cheruscan officer who later led a disastrously successful rebellion against the Romans, was bilingual. The emperor Julian employed a bilingual Germanic
 In the Western Empire, Latin gradually replaced the Celtic languages, which were related to it by a shared Indo-European origin. Commonalities in syntax and vocabulary facilitated the adoption of Latin. Mediterranean Gaul ( southern France) had become trilingual (Greek, Latin, Gaulish) by the mid-1st century BC. The importance of Latin in gaining access to the ruling power structure caused the rapid extinction of inscriptions in scripts that had been used to represent local languages on the
In the Western Empire, Latin gradually replaced the Celtic languages, which were related to it by a shared Indo-European origin. Commonalities in syntax and vocabulary facilitated the adoption of Latin. Mediterranean Gaul ( southern France) had become trilingual (Greek, Latin, Gaulish) by the mid-1st century BC. The importance of Latin in gaining access to the ruling power structure caused the rapid extinction of inscriptions in scripts that had been used to represent local languages on the
 In the provinces of Africa westwards of
In the provinces of Africa westwards of
Reconciling archaeological and linguistic evidence for Berber prehistory
suggests that although Berber had split off from Afroasiatic several thousand years ago, Proto-Berber itself can only be reconstructed to a period as late as 200 CE, with modern-day Berber languages displaying low internal diversity. The presence of
 In Egypt, Coptic predominated, but Greek had been in use since the conquest of Alexander, and Latin and Greek were the administrative languages during the Roman Imperial period.
In Egypt, Coptic predominated, but Greek had been in use since the conquest of Alexander, and Latin and Greek were the administrative languages during the Roman Imperial period.
 Outside the military, Latin never became the language of everyday life in the East. An exception was the
Outside the military, Latin never became the language of everyday life in the East. An exception was the
 Inscriptions in Greek and Latin set up by Jews attest to Jewish bi- or multilingualism, and their distribution in the Empire reflects the Jewish diaspora. These may have the Hebrew tag ''
Inscriptions in Greek and Latin set up by Jews attest to Jewish bi- or multilingualism, and their distribution in the Empire reflects the Jewish diaspora. These may have the Hebrew tag ''
 The international use of Greek was one factor enabling the spread of Christianity, as indicated for example by the use of Greek for the
The international use of Greek was one factor enabling the spread of Christianity, as indicated for example by the use of Greek for the
 The Greek Magical Papyri ''(PGM)'' reflect Greco-Egyptian syncretism, incorporating not only Egyptian and Hellenistic religion, but Near Eastern elements, including Jewish magic and dashes of Christian magic. Egyptian and Greek deities, the God of the Jews and Judaic angels, and
The Greek Magical Papyri ''(PGM)'' reflect Greco-Egyptian syncretism, incorporating not only Egyptian and Hellenistic religion, but Near Eastern elements, including Jewish magic and dashes of Christian magic. Egyptian and Greek deities, the God of the Jews and Judaic angels, and

 After the decentralization of political power in late antiquity, Latin developed locally into branches that became the
After the decentralization of political power in late antiquity, Latin developed locally into branches that became the
here
.
Palmyra
Palmyra (; Palmyrene: () ''Tadmor''; ar, تَدْمُر ''Tadmur'') is an ancient city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early secon ...
even used their dialect of Aramaic for inscriptions, in a striking exception to the rule that Latin was the language of the military.
Coptic
 "Coptic" is the modern term for the form of ancient Egyptian that had developed in late antiquity. Written Coptic as a literary language seems to have resulted from a conscious effort among Egypt's educated class to revive their cultural heritage.
In the 4th century, Coptic script—based on the Greek alphabet with additional characters from Egyptian demotic to reflect Egyptian phonology—is found in documents in several dialects, including Old Bohairic, Fayumic, Achmimic, and
"Coptic" is the modern term for the form of ancient Egyptian that had developed in late antiquity. Written Coptic as a literary language seems to have resulted from a conscious effort among Egypt's educated class to revive their cultural heritage.
In the 4th century, Coptic script—based on the Greek alphabet with additional characters from Egyptian demotic to reflect Egyptian phonology—is found in documents in several dialects, including Old Bohairic, Fayumic, Achmimic, and Sahidic
Coptic (Bohairic Coptic: , ) is a language family of closely related dialects, representing the most recent developments of the Egyptian language, and historically spoken by the Copts, starting from the third-century AD in Roman Egypt. Coptic ...
. At this time Coptic emerged as a fully literary language, including major translations of Greek scriptures, liturgical texts, and patristic works. From the 4th to 7th centuries, original works—including homilies, saints' lives, monastic rules, letters, and exhortation
Advice (also called exhortation) is a form of relating personal or institutional opinions, belief systems, values, recommendations or guidance about certain situations relayed in some context to another person, group or party. Advice is often off ...
s—were composed in Coptic, primarily in the Sahidic dialect. As a writing system, Coptic was used for everyday purposes such as inventories and real estate transactions, as well as for poetry. By the 640s, when Egypt came under Arab rule, Coptic-speaking Christians constituted the majority of the population. At the end of the 7th century, legal texts might still be written in Coptic: in one example, a bilingual Greek-Arabic protocol with a reference to Mohammed precedes a document entirely in Coptic that invokes the Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God th ...
.
Punic
Punic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of t ...
, the Semitic language of the Carthaginians, continued to be used in North Africa during the Imperial period. Before the Roman conquest in 146 BC, nearly all Punic inscriptions had been votive to the deities Tanit
Tanit ( Punic: 𐤕𐤍𐤕 ''Tīnīt'') was a Punic goddess. She was the chief deity of Carthage alongside her consort Baal-Hamon.
Tanit is also called Tinnit. The name appears to have originated in Carthage (modern day Tunisia), though it doe ...
and Ba'al
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied t ...
or funerary commemorations, but during the Roman era a broader range of content is found in Neo-Punic
The Punic language, also called Phoenicio-Punic or Carthaginian, is an extinct variety of the Phoenician language, a Canaanite language of the Northwest Semitic branch of the Semitic languages. An offshoot of the Phoenician language of coastal We ...
, often appearing with parallel texts in Latin or Greek. A striking occurrence of Neo-Punic is found at the otherwise thoroughly Roman temple of Roma and Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, built 14–19 AD at Leptis Magna. One of the latest Neo-Punic inscriptions on a monument dates to the reign of Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(81–96 AD). No inscription in Punic script on stone can be dated later than the 2nd or 3rd century. Latin script was used to write Punic in the 4th and 5th centuries.
Punic was spoken at the highest level of society: the emperor Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
(reigned 193–211) was born in Leptis Magna and spoke Punic as well as Latin and Greek, while his sister supposedly had little command of Latin at all. Augustine, who was from North Africa, several times mentions Punic; he observed that it was related to Hebrew and Syriac, and his knowledge of Punic helped him figure out transliterated Semitic words from the Bible.
Celtic
Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
at the beginning of the Imperial period include Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switze ...
, spoken in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
(''Gallia,'' present-day France, Belgium, Switzerland and northwestern Italy); Celtiberian and Gallaecian, in parts of Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
(Spain and Portugal); Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
in Britannia (Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
), and Galatian, a branch of Celtic brought to Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
by the Gallic invasions of the 3rd century BC. The place name Galatia, a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
, derives from the Greek word for "Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They s ...
" or "Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
", ''Galatai''. Loanwords from Gaulish are recorded in Latin as early as the time of Ennius (ca. 239–169 BC), due to the presence of Celtic settlements on the Italian peninsula. By late antiquity, some Gaulish words had become so Latinized that their origin was no longer recognized as such.
 Celtiberian is documented as a written language only after contact with the Romans in the 2nd century BC. Of 103 Celtiberian inscriptions, thirty in Iberian script are hospitality tokens ''(tesserae hospitales)'', twenty of which are in the shape of animals. The social custom of pledging mutual support among families or communities was compatible with '' hospitium'' in Roman culture, and the Celtiberians continued to produce the tokens, though switching to Latin, into the 2nd century of the Imperial era. Under Augustus, the territory of the Celtiberians became part of the
Celtiberian is documented as a written language only after contact with the Romans in the 2nd century BC. Of 103 Celtiberian inscriptions, thirty in Iberian script are hospitality tokens ''(tesserae hospitales)'', twenty of which are in the shape of animals. The social custom of pledging mutual support among families or communities was compatible with '' hospitium'' in Roman culture, and the Celtiberians continued to produce the tokens, though switching to Latin, into the 2nd century of the Imperial era. Under Augustus, the territory of the Celtiberians became part of the Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia was the ...
province. Written Celtiberian ceases early in the reign of Augustus, if not before.
Several references to Gaulish in late antiquity may indicate that it continued to be spoken. Irenaeus
Irenaeus (; grc-gre, Εἰρηναῖος ''Eirēnaios''; c. 130 – c. 202 AD) was a Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the dev ...
, bishop of Lugdunum (present-day Lyon) from 177 AD, complains that he has to communicate with his parishioners in their "barbarous tongue", probably Gaulish. The jurist Ulpian (170–228) mentions the need to recognize Gaulish verbal contracts. Lampridius says that a druidess made a prophecy in Gaulish to Alexander Severus (208–235). Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
(331–420), who had first-hand knowledge, observes that the Gallic Treveri
The Trēverī ( Gaulish: *''Trēueroi'') were a Celtic tribe of the Belgae group who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle from around 150 BCE, if not earlier, until their displacement by the Franks. Their domain lay within the southern fri ...
speak a language "more or less the same" as that of the Galatians. The collection of pharmacological recipes by Marcellus of Bordeaux (late 4th- or early 5th-century) contains several Gaulish words, mainly plant names, and seems to indicate that the language remained in use for at least some purposes such as traditional medicine and magic. Sulpicius Severus
Sulpicius Severus (; c. 363 – c. 425) was a Christian writer and native of Aquitania in modern-day France. He is known for his chronicle of sacred history, as well as his biography of Saint Martin of Tours.
Life
Almost all that we know of Sev ...
(363–425), also from Gallia Aquitania, takes note of Gaulish-Latin bilingualism, with Gaulish as the first language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
. Other mentions of people who speak "in the Gallic manner" ''(gallice)'' or similar may refer to speaking Latin with a regional Gaulish accent.
Much of historical linguistics
Historical linguistics, also termed diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time. Principal concerns of historical linguistics include:
# to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages
# ...
scholarship postulates that Gaulish was indeed still spoken as late as the mid to late 6th century in France. Despite considerable Romanization of the local material culture, the Gaulish language is held to have survived and had coexisted with spoken Latin during the centuries of Roman rule of Gaul.
Germanic
Next to nothing is recorded of theGermanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, E ...
spoken in the Empire, with the exception of Gothic. A phrase of Gothic is quoted in an elegiac couplet
The elegiac couplet is a poetic form used by Greek lyric poets for a variety of themes usually of smaller scale than the epic. Roman poets, particularly Catullus, Propertius, Tibullus, and Ovid, adopted the same form in Latin many years late ...
from the '' Latin Anthology'', and more substantially parts of the Gospels were translated into Gothic and preserved by the 6th-century Codex Argenteus
The Codex Argenteus (Latin for "Silver Book/Codex") is a 6th-century illuminated manuscript, originally containing part of the 4th-century translation of the Christian Bible into the Gothic language. Traditionally ascribed to the Arian bi ...
. While Latin gained some Germanic loanwords, most linguistic influence ran the other way.
military tribune
A military tribune (Latin ''tribunus militum'', "tribune of the soldiers") was an officer of the Roman army who ranked below the legate and above the centurion. Young men of Equestrian rank often served as military tribune as a stepping stone ...
as a spy. The officers and secretaries who kept the records preserved in the Vindolanda tablets
The Vindolanda tablets were, at the time of their discovery, the oldest surviving handwritten documents in Britain (they have since been antedated by the Bloomberg tablets). They are a rich source of information about life on the northern fro ...
were Batavian, but their Latin contains no hint; the common soldiers of their units, however, may have retained their Germanic speech. Less commonly, Latin-speaking officers learned a Germanic language through their service and acted as interpreters. Acquiring Germanic might be regarded as a dubious achievement inducing anxieties of "barbarism": in 5th-century Gaul, Sidonius Apollinaris
Gaius Sollius Modestus Apollinaris Sidonius, better known as Sidonius Apollinaris (5 November of an unknown year, 430 – 481/490 AD), was a poet, diplomat, and bishop. Sidonius is "the single most important surviving author from 5th-century Gaul ...
thinks it funny that his learned friend Syagrius
Syagrius (430 – 486 or 487 or 493–4) was a Roman general and the last ruler of a Roman rump state in northern Gaul, now called the Kingdom of Soissons. Gregory of Tours referred to him as King of the Romans. Syagrius's defeat by king Clovis ...
has become fluent in Germanic.
Multilingualism
Trilingualism was perhaps not uncommon among educated people who came from regions where a language other than Latin or Greek was spoken. The Latin novelistApuleius
Apuleius (; also called Lucius Apuleius Madaurensis; c. 124 – after 170) was a Numidian Latin-language prose writer, Platonist philosopher and rhetorician. He lived in the Roman province of Numidia, in the Berber city of Madauros, modern- ...
also wrote in Greek, and had learned Punic from his mother. The Babatha Archive is a suggestive example of practical multilingualism. These papyri, named for a Jewish woman in the province of Arabia and dating from 93 to 132 AD, mostly employ Aramaic, the local language, written in Greek characters with Semitic and Latin influences; a petition to the Roman governor
A Roman governor was an official either elected or appointed to be the chief administrator of Roman law throughout one or more of the many Roman province, provinces constituting the Roman Empire.
The generic term in Roman legal language was ''Re ...
, however, was written in Greek.
One striking example of multilingualism as well as multiculturalism in the Empire is a 2nd-century epitaph for a woman named Regina, discovered in 1878 near the Roman fort at South Shields, northeast England. The inscription is written in Latin and Palmyrene Aramaic, the language of Regina's husband, Barates, who has been identified with a standardbearer ''(vexillarius
left, A reenactor, equipped as a ''vexillifer'', with a ''vexillum'' standard
Vexillarius is a term referring to one of several distinct types of Roman soldier.
A vexillarius or vexillifer was one of the ''signiferi'' in a Roman legion. His dut ...
)'' of that name from Palmyra, Syria. He was most likely in the military stationed along Hadrian's Wall. The Latin, however, is constructed grammatically in the manner of Greek honorific inscriptions typical of Palmyra, suggesting that Barates was bilingual in Aramaic and Greek, and added Latin as a third language. The Latin portion is larger and longer, and provides most of the information. The Palmyrene is carved in a fluid cursive script, and conveys only the name of Regina and an expression of grief. Since few people in Britain could have read Palmyrene, its use may be Barates' personal statement of his identity and emotions. A fourth linguistic element is the name ''Regina'', which can be either Latin or Celtic. Such names seem often to have been chosen for their deliberate duality. Regina herself is identified as from the British Catuvellauni
The Catuvellauni (Common Brittonic: *''Catu-wellaunī'', "war-chiefs") were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.
The fortunes of the Catuvellauni and their ...
, a people whose '' civitas'' capital was Verulamium
Verulamium was a town in Roman Britain. It was sited southwest of the modern city of St Albans in Hertfordshire, England. A large portion of the Roman city remains unexcavated, being now park and agricultural land, though much has been built upon ...
, but the Gallo-Brittonic spelling ''Catuallauna'' ( feminine) is used in the Latin inscription.
Geographical distribution
Italian peninsula and Sicily
In Italy, the written use of Latin had replaced Oscan—like Latin, an Italic language—and Etruscan by the end of the 1st century AD. Oscan graffiti are preserved by theeruption of Vesuvius
Of the many eruptions of Mount Vesuvius, a major stratovolcano in southern Italy, the best-known is its eruption in 79 AD, which was one of the deadliest in European history. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD is one of the best-known in h ...
in AD 79 at Pompeii and Herculaneum, which was in the Oscan region, and a couple may date before or after an earlier regional earthquake in AD 62. In the mid-1st century, the emperor Claudius, who had keen antiquarian interests, knew Etruscan and wrote a multi-volume history of the Etruscans, but the work has not survived.
Multilingualism had been characteristic of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
for centuries, resulting from occupations by the Carthaginians, Greeks, and Romans. While the slave trade during the Republican period brought speakers of Greek and other languages from the East to the island, Greek was the language of higher-status persons such as government officials and businessmen during the Imperial era. Immigration to Sicily in the early Empire originated more often in places where Latin was spoken than in Greek-speaking areas. African speakers of Latin were a significant presence in Sicily. Christian inscriptions are far more likely to be in Greek. In late antiquity, Greek-Latin bilingualism was common enough that it would have been acquired through everyday personal interaction. The Jewish communities of Syracuse seem to have been bilingual in Greek and Hebrew. There is some Sicilian evidence of Syriac.
Western provinces
 In the Western Empire, Latin gradually replaced the Celtic languages, which were related to it by a shared Indo-European origin. Commonalities in syntax and vocabulary facilitated the adoption of Latin. Mediterranean Gaul ( southern France) had become trilingual (Greek, Latin, Gaulish) by the mid-1st century BC. The importance of Latin in gaining access to the ruling power structure caused the rapid extinction of inscriptions in scripts that had been used to represent local languages on the
In the Western Empire, Latin gradually replaced the Celtic languages, which were related to it by a shared Indo-European origin. Commonalities in syntax and vocabulary facilitated the adoption of Latin. Mediterranean Gaul ( southern France) had become trilingual (Greek, Latin, Gaulish) by the mid-1st century BC. The importance of Latin in gaining access to the ruling power structure caused the rapid extinction of inscriptions in scripts that had been used to represent local languages on the Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
''(Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
)'' and in Gaul. Among other aspects of a distinctive Gallo-Roman culture was the creation of Gallo-Latin text. In Latin commemorative inscriptions, individuals with Celtic names rarely identify themselves as "Celtic" or "Gallic"; they are much more likely to name the people of their '' civitas'' (such as Aedui
The Aedui or Haedui (Gaulish: *''Aiduoi'', 'the Ardent'; grc, Aἴδουοι) were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the modern Burgundy region during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
The Aedui had an ambiguous relationship with the Roman Republic a ...
, Remi, Pictones
The Pictones were a Gallic tribe dwelling south of the Loire river, in the modern departments of Vendée, Deux-Sèvres and Vienne, during the Iron Age and Roman period.
Name
They are mentioned as ''Pictonibus'' and ''Pictones'' by Julius Caes ...
) or their voting tribe ''(tribus)'' as Roman citizens. Several major writers of Latin came from the Iberian peninsula in the Imperial period, including Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
, Lucan, Quintilian, Martial, and Prudentius
Aurelius Prudentius Clemens () was a Roman Christian poet, born in the Roman province of Tarraconensis (now Northern Spain) in 348.H. J. Rose, ''A Handbook of Classical Literature'' (1967) p. 508 He probably died in the Iberian Peninsula some ti ...
. However despite acquisition of Latin, Gaulish is held by some to have held on quite a long time, lasting at least until the middle of the 6th century CE, despite considerable Romanization in the local material culture.
Most of the 136 Greek inscriptions from Mediterranean Gaul (the Narbonensis), including those from originally Greek colonies, are post- Augustan. Their content indicates that Greek was used increasingly for specialized purposes: "education, medicine, acting, agnostic activities, art, magic, religion, including Christianity". Inscriptions from Marseilles (ancient Massilia), founded as a Greek Phocaea
Phocaea or Phokaia (Ancient Greek: Φώκαια, ''Phókaia''; modern-day Foça in Turkey) was an ancient Ionian Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia. Greek colonists from Phocaea founded the colony of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, in ...
n colony around 600 BC, show the continued use of Greek, especially in education and medicine, into the 2nd and 3rd centuries of the Imperial era. In the 4th century, the Latin poet and scholar Ausonius
Decimius Magnus Ausonius (; – c. 395) was a Roman poet and teacher of rhetoric from Burdigala in Aquitaine, modern Bordeaux, France. For a time he was tutor to the future emperor Gratian, who afterwards bestowed the consulship on him ...
, from Gallia Aquitania (present-day Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefect ...
), characterizes his physician father as speaking Attic Greek with more eloquence than Latin.
Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
, not an Indo-European language, survived in the region of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
. The people of southwestern Gaul and northeastern Hispania (roughly present-day Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Janu ...
and Navarre) were regarded by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
as ethnically distinct from the Celts, and the Aquitanian language they spoke was Vasconic like Basque, judging from place names. The Aquitani adopted Latin under Roman rule.
Gaulish survived in Gaul into the late 6th century, and played a decisive role in the formation of Gallo-Romance languages. Latin did not become as deeply entrenched in the province of Britannia, and may have dwindled rapidly after the Roman withdrawal around 410 AD, although pockets of Latin-speaking Britons survived in western Britain until about 700 AD. The evidence of Latin loanwords into Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
suggests that the Latin of Roman Britain was academic, in contrast to the everyday conversational Latin ("Vulgar" Latin) on the continent.
African provinces
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
(a region colonised by Greeks since the 7th century BC), the people of Carthage and other Phoenician colonies
Colonies in antiquity were post-Iron Age city-states founded from a mother-city (its "metropolis"), not from a territory-at-large. Bonds between a colony and its metropolis remained often close, and took specific forms during the period of classic ...
spoke and wrote Punic, with Latin common in urban centers. Other Roman Africans spoke Afroasiatic languages
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
(Libyan
Demographics of Libya is the demography of Libya, specifically covering population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, and religious affiliations, as well as other aspects of the Libyan population. The ...
, Numidian
Numidia (Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisi ...
), debatably early versions of Berber.
Punic was used for legends on coins during the time of Tiberius (1st century AD), and Punic inscriptions appear on public buildings into the 2nd century, some bilingual with Latin. Inscriptions might also be trilingual: one pertaining to Imperial cult
An imperial cult is a form of state religion in which an emperor or a dynasty of emperors (or rulers of another title) are worshipped as demigods or deities. "Cult" here is used to mean "worship", not in the modern pejorative sense. The cult may ...
presents "the official Latin, the local Punic, and the Greek of passing traders and an educated or cosmopolitan elite".
Inscriptions in Libyan use a script similar to ''tifinagh
Tifinagh ( Tuareg Berber language: or , ) is a script used to write the Berber languages. Tifinagh is descended from the ancient Libyco-Berber alphabet. The traditional Tifinagh, sometimes called Tuareg Tifinagh, is still favored by the Tuar ...
'', usually written vertically from the bottom up. The 23 characters are "of a rather rigid geometric form". Bilingual examples are found with either Punic or Latin, and indicate that some people who could write these languages could also at least transliterate their names into the Libyan script. Although Libyan inscriptions are concentrated southeast of Hippo
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant ...
, near the present-day Algerian-Tunisia border, their distribution overall suggests that knowledge of the language was not confined to isolated communities.
Notable writers of Latin from Africa during the Imperial period include the novelist Apuleius
Apuleius (; also called Lucius Apuleius Madaurensis; c. 124 – after 170) was a Numidian Latin-language prose writer, Platonist philosopher and rhetorician. He lived in the Roman province of Numidia, in the Berber city of Madauros, modern- ...
, and the Church Fathers Tertullian
Tertullian (; la, Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus; 155 AD – 220 AD) was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of L ...
and Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North A ...
. Latin-speaking communities remained in North Africa, particularly around Carthage, during the period of the Vandal Kingdom (435–534), but died out by the late 7th century, with the Arab conquest.
Roger Blench (2018)Blench, Roger. 2018Reconciling archaeological and linguistic evidence for Berber prehistory
suggests that although Berber had split off from Afroasiatic several thousand years ago, Proto-Berber itself can only be reconstructed to a period as late as 200 CE, with modern-day Berber languages displaying low internal diversity. The presence of
Punic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of t ...
borrowings in Proto-Berber points to the diversification of modern Berber language varieties subsequent to the fall of Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
in 146 B.C.; only Guanche Guanche may refer to:
*Guanches, the indigenous people of the Canary Islands
*Guanche language, an extinct Berber language, spoken by the Guanches until the 16th or 17th century
*''Conus guanche
''Conus guanche'' is a species of sea snail, a ma ...
and Zenaga lack Punic loanwords. Additionally, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
loanwords in Proto-Berber point to the breakup of Proto-Berber between 0-200 A.D. During the time of the Roman Empire, Roman innovations such as the ox-plough, camel, and orchard management were adopted by Berber communities along the ''limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a ...
'', or borders of the Roman Empire, resulting in a new trading culture involving the use of a lingua franca which became Proto-Berber.
Egypt
 In Egypt, Coptic predominated, but Greek had been in use since the conquest of Alexander, and Latin and Greek were the administrative languages during the Roman Imperial period.
In Egypt, Coptic predominated, but Greek had been in use since the conquest of Alexander, and Latin and Greek were the administrative languages during the Roman Imperial period. Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, founded in 331 BC under Greek rule and one of the three largest cities of the Roman Empire, was a leading city in Greek intellectual life during the Hellenistic and Imperial periods. Famed for the Library of Alexandria, it was also a center for the dissemination of Christianity, which spread first among Greek speakers in Egypt.
Around 700 AD, Greek was replaced for administrative use by Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, the language of the conquerors. Coptic began to decline, and from this point, was preserved mainly for liturgical purposes.
Eastern empire
Although Greek was in common use around the Mediterranean and into Asia Minor even beyond Imperial borders, linguistic distribution in the eastern part of the Empire was complex. Now-extinct language
An extinct language is a language that no longer has any speakers, especially if the language has no living descendants. In contrast, a dead language is one that is no longer the native language of any community, even if it is still in use, l ...
s in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
included Galatian (the form of Celtic introduced by invading Gauls in the 3rd century BC), Phrygian, Pisidian, and Cappadocian, attested by Imperial-era inscriptions. Christian sources also mention the survival of Galatian, Cappadocian, Mysian, and Isaurian in Asia Minor. Like Greek and Latin, these are categorized as Indo-European. Phrygian is not named as a language in a literary text until the 6th century, but is preserved in about a hundred funerary inscriptions in Greek script, most accompanied by Greek text as well and dating from the 3rd century. A Cappadocian accent in speaking Greek seems to be mentioned in a few sources.
 Outside the military, Latin never became the language of everyday life in the East. An exception was the
Outside the military, Latin never became the language of everyday life in the East. An exception was the Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Character ...
of Berytus (present-day Beirut), where a Latin education could be obtained, and which became famous for its school of Roman law.
Danubian provinces and Balkans
TheDanubian provinces
The Danubian provinces of the Roman Empire were the provinces of the Lower Danube, within a geographical area encompassing the middle and lower Danube basins, the Eastern Alps, the Dinarides, and the Balkans. They include Noricum, Dacia ( Trajan ...
lay within a geographical area encompassing the middle and lower Danube basin
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
s, the Eastern Alps
Eastern Alps is the name given to the eastern half of the Alps, usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley up to the Splügen Pass at the Alpine divide and down the Liro River to Lake Como in t ...
, the Dinarides
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herz ...
, and the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. Provinces in this general region include Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, ...
, Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
, Dalmatia, Moesia, Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, Scythia, and Pannonia.
The relative influence of Latin versus Greek and vice versa in this area and in the Balkans in general, is sometimes demarcated by the Jireček Line.
Greek had been in use in the southern part of the Balkans since the late 4th century BC, as a result of the Macedonian conquests of Philip and Alexander. The ancient Macedonian language, perhaps a Greek dialect, may have been spoken in some parts of what is now Macedonia and northern Greece; to the north of this area, Paeonian
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones).
The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, a ...
would have been used, and to the south Epirot, both scantily attested.
Illyrian was spoken in the northwest, and to the northeast Thracian and Dacian. These three languages, all Indo-European, are thought to be candidates for the ancestor of Albanian. From his exile in Tomis on the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
(present-day Constanța, Romania), the Augustan poet Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
learned Getic (Dacian) and Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
, and noted that Greek was spoken with a markedly Getic accent. Inscriptions from Tomis in the Imperial period are generally Greek, with Thracian personal names and religious references.
Jewish diaspora
 Inscriptions in Greek and Latin set up by Jews attest to Jewish bi- or multilingualism, and their distribution in the Empire reflects the Jewish diaspora. These may have the Hebrew tag ''
Inscriptions in Greek and Latin set up by Jews attest to Jewish bi- or multilingualism, and their distribution in the Empire reflects the Jewish diaspora. These may have the Hebrew tag ''shalom
''Shalom'' ( he, שָׁלוֹם ''šālōm''; also spelled as ''sholom'', ''sholem'', ''sholoim'', ''shulem'') is a Hebrew word meaning ''peace'', ''harmony'', ''wholeness'', ''completeness'', ''prosperity'', ''welfare'' and ''tranquility'' and ...
'' at the end. Evidence for Jews in Egypt is preserved by papyri until the Jewish revolt of 116–117. In the first half of the 5th century, Greek coexisted with Hebrew and Jewish Aramaic in the Jewish communities of Palaestina Prima
Palaestina Prima or Palaestina I was a Byzantine province that existed from the late 4th century until the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 630s, in the region of Palestine. It was temporarily lost to the Sassanid Empire (Persian Empire) in ...
and Secunda, and is found in mosaic inscriptions even in synagogues.
Like the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond ...
, the Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Philo Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt. Philo's de ...
and the historian '' Philo Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt. Philo's de ...
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
—included gentiles among their intended audience. The Sibylline Oracles and the Wisdom of Solomon are other examples of Jewish literature in Greek from this general period.
No surviving Greek texts written after the year 100 CE can be securely identified as having a Jewish author. After this time, Jewish writings in Greek became irrelevant to Christians, who were thus unlikely to preserve them. The manuscription tradition of medieval Jewish culture has preserved only writings in Hebrew and Aramaic.
Christian communities
The '' Epistle to Diognetus'' states that language was not a determining factor in Christian identity; Christians might speak any language. By late antiquity, at least someChristian literature
Christian literature is the literary aspect of Christian media, and it constitutes a huge body of extremely varied writing.
Scripture
While falling within the strict definition of literature, the Bible is not generally considered literature. Ho ...
had been created for virtually every language in regular use throughout the Empire.
 The international use of Greek was one factor enabling the spread of Christianity, as indicated for example by the use of Greek for the
The international use of Greek was one factor enabling the spread of Christianity, as indicated for example by the use of Greek for the Epistles of Paul
The Pauline epistles, also known as Epistles of Paul or Letters of Paul, are the thirteen books of the New Testament attributed to Paul the Apostle, although the authorship of some is in dispute. Among these epistles are some of the earliest extan ...
. Constantine, the first emperor to actively support Christianity, presumably knew some Greek, but Latin was spoken in his court, and he used an interpreter to address Greek-speaking bishops at the Council of Nicaea. In the Christian Latin West, Greek became associated with " paganism" and regarded as a foreign language (''lingua peregrina)''. Saint Augustine confessed that he loathed Greek and found it hard to learn. By late antiquity, however, it was possible to speak Greek as a primary language while not conceiving of oneself as a "Hellene" in matters of religion and culture. In the first half of the 5th century, Greek was the standard language in which bishops communicated, and the ''Acta Conciliorum'' ("Acts of the Church Councils") were recorded originally in Greek and then translated into Latin, Syriac, or Coptic. During this period, Latin played only a subordinate role in the ecumenical councils, as did representatives from the Western empire. Although traditionally Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
is regarded as having been established as a Christian language by this time, it does not appear in the ''Acta''. There are hints that Coptic might be spoken at the councils, but no secure record. On-the-spot translation into Greek was available for the participant who used his own language, including some who are referred to as "Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
", " Saracens" or " Ishmaelites". Christian content has been found in a few Arabic inscriptions from the 6th century.
Ritual language
The form of private or personalized ritual characterized as "magic" might be conducted in a hodgepodge of languages. Magic, and even some therapies for illnesses, almost always involved incantation or the reciting of spells ''( carmina)'', often accompanied by the ritualized creation of inscribed tablets ''(lamellae)'' or amulets. These are known from both archaeological artifacts and written texts such as the Greek Magical Papyri, a collection of spells dating variously from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. Although Augustus attempted to suppress magic by burning some 2,000 esoteric books early in his reign, magical practices were disseminated widely throughout the Greco-Roman world, and attest to an awareness of multilingualism among the peoples of the Empire. Spells were not translated, because their efficacy was thought to reside in their precise wording; a language such as Gaulish thus may have persisted for private ritual purposes when it no longer had everyday currency. The Greek Magical Papyri ''(PGM)'' reflect Greco-Egyptian syncretism, incorporating not only Egyptian and Hellenistic religion, but Near Eastern elements, including Jewish magic and dashes of Christian magic. Egyptian and Greek deities, the God of the Jews and Judaic angels, and
The Greek Magical Papyri ''(PGM)'' reflect Greco-Egyptian syncretism, incorporating not only Egyptian and Hellenistic religion, but Near Eastern elements, including Jewish magic and dashes of Christian magic. Egyptian and Greek deities, the God of the Jews and Judaic angels, and Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
are named. The ''PGM'' are written primarily in Greek with substantial passages in Demotic Egyptian
Demotic (from grc, δημοτικός ''dēmotikós'', 'popular') is the ancient Egyptian script derived from northern forms of hieratic used in the Nile Delta, and the stage of the Egyptian language written in this script, following Late Egypt ...
and inserted strings of syllables that are "pronounceable, though unintelligible". These '' voces magicae'' ("magic words") occur throughout magic texts and inscriptions, and often suggest corrupt Coptic or Egyptian, Hebrew, Aramaic or other Semitic languages, and Celtic. Hebrew and Greek appear in Demotic magical texts; Coptic magic incorporates Hebrew; Egyptian pops up in Latin spells. While many ''voces magicae'' may be deliberate neologism
A neologism Greek νέο- ''néo''(="new") and λόγος /''lógos'' meaning "speech, utterance"] is a relatively recent or isolated term, word, or phrase that may be in the process of entering common use, but that has not been fully accepted int ...
s or obscurantism, scholars have theorized that the more recognizable passages may be the products of garbled or misunderstood transmission, either in copying a source text or transcribing oral material.
Inscriptions for the practice of magic in Gaul show the characteristic use of Greek for spells in the Imperial period. A 2nd-century curse tablet
A curse tablet ( la, tabella defixionis, defixio; el, κατάδεσμος, katadesmos) is a small tablet with a curse written on it from the Greco-Roman world. Its name originated from the Greek and Latin words for "pierce" and "bind". The tabl ...
from Autun ( Augustodunum) lists the names of those to be cursed in Latin, two magic words in Greek, and a series of ''voces magicae''. A ''defixio
A curse tablet ( la, tabella defixionis, defixio; el, κατάδεσμος, katadesmos) is a small tablet with a curse written on it from the Greco-Roman world. Its name originated from the Greek and Latin words for "pierce" and "bind". The table ...
'' (binding spell) from Amélie-les-Bains seems composed in Celtic with bits of Latin. A ''lamella'' from Roman Britain has been interpreted as Hebrew written in Greek characters.
Christians in late antiquity might insert Hebrew into Greek exorcisms. Saint Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
reports an odd story about a Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
-Latin bilingual man of the '' Candidati'' Imperial bodyguard who, in a state of demonic possession, began speaking perfect Aramaic, a language he did not know.
Legal language
Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Ju ...
was written in Latin, and the "letter of the law" was tied strictly to the words in which it was expressed. Any language, however, could be binding in more general verbal contracts and procedures grounded in the ''ius gentium
The ''ius gentium'' or ''jus gentium'' (Latin for "law of nations") is a concept of international law within the ancient Roman legal system and Western law traditions based on or influenced by it. The ''ius gentium'' is not a body of statute law n ...
'' or international law. The ''ius gentium'' was not a written legal code, but was thought to exist among all peoples as a matter of natural law
Natural law ( la, ius naturale, ''lex naturalis'') is a system of law based on a close observation of human nature, and based on values intrinsic to human nature that can be deduced and applied independently of positive law (the express enacte ...
. Roman jurists show a concern for local languages such as Punic, Gaulish, and Aramaic in assuring the correct understanding and application of laws and oaths.
While the birth certificates and wills of Roman citizens had to be written in Latin until the 220s, in the legal opinion of Ulpian (ca. 215), '' fideicommissa'' (bequest
A bequest is property given by will. Historically, the term ''bequest'' was used for personal property given by will and ''deviser'' for real property. Today, the two words are used interchangeably.
The word ''bequeath'' is a verb form for the act ...
s in trust) were not limited to Latin or even Greek, but could also be created in "Punic, Gaulish or any other" language. Originally, a testator
A testator () is a person who has written and executed a last will and testament that is in effect at the time of their death. It is any "person who makes a will."Gordon Brown, ''Administration of Wills, Trusts, and Estates'', 3d ed. (2003), p. 556 ...
's ''fideicommissum'' placed the heir under a moral rather than legal obligation, and Ulpian asserted that "any kind of speech contains the obligation of its words, provided that each party understands the other's language himself or through accurate interpreters". The jurist Gaius distinguished between verbal contracts that derived their validity from formulaic utterance in Latin, and obligations expressing a mutual understanding of the ''ius gentium'' regardless of whether the parties were Roman or not.
Linguistic legacy

 After the decentralization of political power in late antiquity, Latin developed locally into branches that became the
After the decentralization of political power in late antiquity, Latin developed locally into branches that became the Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
, including Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, French, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Romanian, Catalan, Sardinian, Aromanian, African Romance
African Romance or African Latin is an extinct Romance language that was spoken in the Roman province of Africa by the Roman Africans during the later Roman and early Byzantine Empires, and several centuries after the annexation of the region by ...
, Mozarabic
Mozarabic, also called Andalusi Romance, refers to the medieval Romance varieties spoken in the Iberian Peninsula in territories controlled by the Islamic Emirate of Córdoba and its successors. They were the common tongue for the majority of ...
, Dalmatian, and Venetian, among others. As an international language of learning and literature, Latin itself continued as an active medium of expression for diplomacy and for intellectual developments identified with Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
up to the 17th century, and for law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
to the present.
Greek continued as the language of the Byzantine Empire, but never replaced certain languages with which it had long coexisted, such as Coptic in Egypt, and Aramaic in Syria and Mesopotamia.Adams, "''Romanitas'' and the Latin Language," p. 199; Treadgold, ''A History of the Byzantine State and Society,'' pp. 5, 7.
References
Bibliography
Books
Monographs
* Adams, J.N. ''Bilingualism and the Latin Language.'' Cambridge University Press, 2003. * Anderson, Graham ''The Second Sophistic: A Cultural Phenomenon in the Roman Empire.'' Routledge, 1993. * Ando, Clifford. ''Imperial Ideology and Provincial Loyalty in the Roman Empire''. University of California Press, 2000. *Clackson, James; Horrocks, Geoffrey. ''The Blackwell History of the Latin Language.'' Blackwell, 2007, 2011. * Goodman, Martin Welsh. ''Mission and Conversion: Proselytizing in the Religious History of the Roman Empire''. Oxford University Press, 1994. * Herman, József. ''Vulgar Latin''. Translated by Roger Wright, based on the original 1975 publication in French. Pennsylvania State University Press, 2000. * Millar, Fergus. ''A Greek Roman Empire: Power and Belief under Theodosius II (408–450)''. University of California Press, 2006. * Mullen, Alex. ''Southern Gaul and the Mediterranean: Multilingualism and Multiple Identities in the Iron Age and Roman Periods.'' Cambridge University Press, 2013. * Treadgold, Warren. ''A History of the Byzantine State and Society''. Stanford University Press, 1997.By multiple contributors
* ''Apologetics in the Roman Empire: Pagans, Jews, and Christians''. Edited by Mark Edwards, Martin Goodman, and Simon Price, with Christopher Rowland. Oxford University Press, 1999. * ''A Companion to the Latin Language.'' Edited by James Clackson. Blackwell, 2011. * ''Multilingualism in the Graeco-Roman Worlds.'' Edited by Alex Mullen. Cambridge University Press, 2012. * ''The Oxford Handbook of the Literatures of the Roman Empire''. Edited by Daniel L. Selden and Phiroze Vasunia. Oxford University Press (most of the chapters are available onlinhere
.
Articles
* Adams, J.N. "''Romanitas'' and the Latin Language." ''Classical Quarterly'' 53.1 (2003) 184–205. * MacMullen, Ramsey. "Provincial Languages in the Roman Empire." ''American Journal of Philology'' 87.1 (1966) 1–17. * Millar, Fergus. "Local Cultures in the Roman Empire: Libyan, Punic and Latin in Roman Africa." ''Journal of Roman Studies'' 58 (1968) 126–134. * Moatti, Claudia. "Translation, Migration, and Communication in the Roman Empire: Three Aspects of Movement in History." ''Classical Antiquity'' 25.1 (2006) 109–140. * Rance, Philip. "The ''De Militari Scientia'' or Müller Fragment as a Philological Resource. Latin in the East Roman Army and Two New Loanwords in Greek: ''palmarium'' and ''*recala''." ''Glotta'' 86 (2010) 63–92. {{JSTOR, 41219881 Roman Empire Languages of Europe Multilingualism Diaspora languages Ancient languages Language policy by country Cultural assimilation