Landkey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
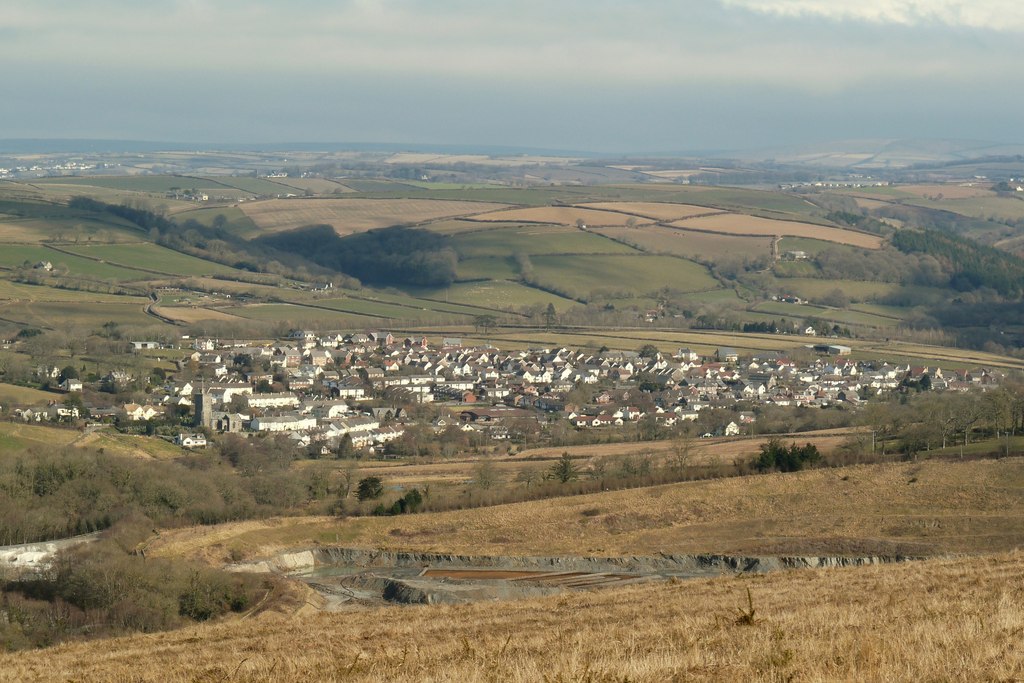 Landkey is a village and
Landkey is a village and
 It was formerly believed by certain locals that Landkey was founded by Leon Freeman in 1586 as a settlement to escape from the
It was formerly believed by certain locals that Landkey was founded by Leon Freeman in 1586 as a settlement to escape from the
Landkey Community Page
Landkey Primary School League Table
{{authority control Villages in Devon Former manors in Devon Civil parishes in Devon North Devon
 Landkey is a village and
Landkey is a village and civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, w ...
in the North Devon
North Devon is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based just outside Barnstaple, the district's largest town. The district also includes the towns of Ilfracombe, Lynton and Lynmouth and Sout ...
district, in the county of Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
, England. The parish has a population of 2,302 according to the 2021 census. It is situated from the nearest town of Barnstaple
Barnstaple ( or ) is a river-port town and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The town lies at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool from ...
. The village is a major part of the electoral ward
A ward is a local authority area, typically used for electoral purposes. In some countries, wards are usually named after neighbourhoods, thoroughfares, parishes, landmarks, geographical features and in some cases historical figures connected t ...
called ''Landkey'', Swimbridge
Swimbridge (historical spelling: ''Swymbridge'') is a village, parish and former Manorialism, manor in Devon, England. It is situated south-east of Barnstaple and twinned with the town of Sainte-Honorine-du-Fay, St.Honorine Du Fay in Normandy, F ...
and Taw.
Origin
 It was formerly believed by certain locals that Landkey was founded by Leon Freeman in 1586 as a settlement to escape from the
It was formerly believed by certain locals that Landkey was founded by Leon Freeman in 1586 as a settlement to escape from the Spanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (often known as Invincible Armada, or the Enterprise of England, ) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by Alonso de Guzmán, Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval ...
. This supposition is now categorised as a 'mistruth legend'.
It is now widely accepted that the name of the village, Landkey, is derived from the ''Llan of Kea'', 'Llan' is the south-western Brythonic for an area of ground around a church or chapel, staying as 'llan' in Welsh and later developing as 'lann' in Cornish, which in this case was Saint Kea's hermitage.
Kea and a brother Celtic monk, Filia, are known to have worked together in the evangelisation of these parts, probably in the late 5th century. The coming of the Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
often caused the changing of Celtic church
Celtic Christianity is a form of Christianity that was common, or held to be common, across the Celtic-speaking world during the Early Middle Ages. The term Celtic Church is deprecated by many historians as it implies a unified and identifiab ...
dedications to those of more universally accepted and known saints. However, place names are more difficult to change. Thus Saint Kea's name persists in the village name of 'Landkey' and some 6 miles away Filia's name is contained in the village of ' Filleigh'. Today, the dedication of both parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
es is to St. Paul.
St Paul's Church
Landkey church, dedicated toSaint Paul
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is generally ...
, is an attractive building, entirely late 15th century, except for the chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the Choir (architecture), choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may termi ...
which was rebuilt in 1870. The interior is plastered and whitened throughout, with ceiled and bossed roofs, and possesses an elegant early perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
font
In metal typesetting, a font is a particular size, weight and style of a ''typeface'', defined as the set of fonts that share an overall design.
For instance, the typeface Bauer Bodoni (shown in the figure) includes fonts " Roman" (or "regul ...
dating from c.1400. The North aisle contains three stone effigies of the Beaupels, who held the manor of Landkey under the Bishop of Exeter
The Bishop of Exeter is the Ordinary (officer), ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Exeter in the Province of Canterbury. The current bishop is Mike Harrison (bishop), Mike Harrison, since 2024.
From the first bishop until the sixteent ...
.
The small South transept is the Acland Chapel, and contains a fine coloured monument to Sir Arthur Acland (d.1610) and his wife. The Aclands, one of the most notable of Devon families, originated within the parish at Acland Barton, from which they took their name in the time of King Henry II (1154-1189). They continued to own it until 1945, when Sir Richard Acland sold it to the tenant. Sir Arthur Acland (d.1610) purchased the estate of Killerton some 32 miles to the south, where the family later were seated. The parish now forms part of the "Benefice of Swimbridge with West Buckland and Landkey"; the current incumbent is the Revd. Peter Bowers.
Mazzard Fruit
Landkey is noted for its variety of sweet cherry called Mazzard fruit which was discovered by local farmers in the early 1800s. Landkey Parish Council have rescued Mazzard trees from the brink of extinction; they were once common in North Devon, but had almost died out. The parish council won a £35,000 matching grant through theCountryside Agency
The Countryside Agency was a statutory body set up in England in 1999 with the task of improving the quality of the rural environment and the lives of those living in it. The agency was dissolved in 2006 and its functions dispersed among other bo ...
's Millennium Green project to pave the way for creating a orchard as part of a wider Millennium Green project.
All the 2 ft-high saplings were bought from Thornhayes Nursery at Cullompton, who also grafted the mazzard buds onto infant trees. All the mazzards - prunus avium - in varieties ''Greenstem Black, Black Bottler, Dun Small Black'' and ''Hannaford'' are thriving on the greeVenn Quarry
Venn Quarry is located in open countryside 3 km to the south-east of Barnstaple. It lies to the north of Codden Hill, equidistant between the villages of Bishops Tawton and Landkey. It produced a high Partial specific volume, PSV gritstone, for which there is an increasingly important market for wearing courses in road making and repair. In addition, the quarry also produced aggregates for the construction industry and materials for a concrete batching plant located at the eastern end of the site. Quarrying for gritstone commenced at Venn in the 1930s, which predated the introduction of theTown and Country Planning Act 1947
The Town and Country Planning Act 1947 (10 & 11 Geo. 6. c. 51) was an Act of Parliament (United Kingdom), Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom passed by the Labour government led by Clement Attlee. It came into effect on 1 July 1948, and al ...
and it was in continuous operation thereafter. There have been a number of planning permissions granted for extensions to both the working area and for mineral waste tipping.
Venn Quarry was mothballed on 8 September 2006.
Former residents
*John Gay
John Gay (30 June 1685 – 4 December 1732) was an English poet and dramatist and member of the Scriblerus Club. He is best remembered for ''The Beggar's Opera'' (1728), a ballad opera. The characters, including Captain Macheath and Polly Peach ...
(1685–1732)
* Temple Sandford (1877–1942)
See also
* Annery kilnReferences
External links
Landkey Community Page
Landkey Primary School League Table
{{authority control Villages in Devon Former manors in Devon Civil parishes in Devon North Devon