Lancaster, Lancashire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lancaster (, ) is a city and the
 A Roman fort was built by the end of the 1st century CE on the hill where
A Roman fort was built by the end of the 1st century CE on the hill where
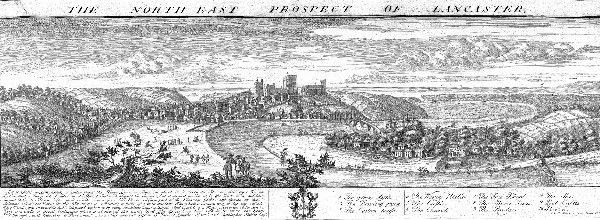 After the
After the 
 The traditional emblem of the
The traditional emblem of the  Lancaster gained a first
Lancaster gained a first
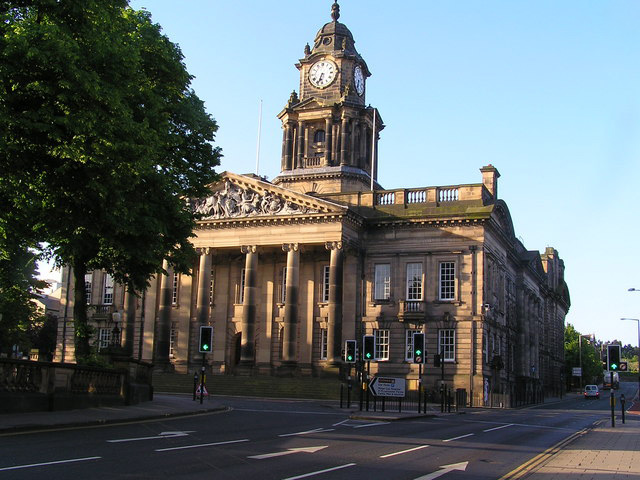 The former
The former
 The
The
 Lancaster is served by the
Lancaster is served by the

 At Bailrigg south of the city is
At Bailrigg south of the city is
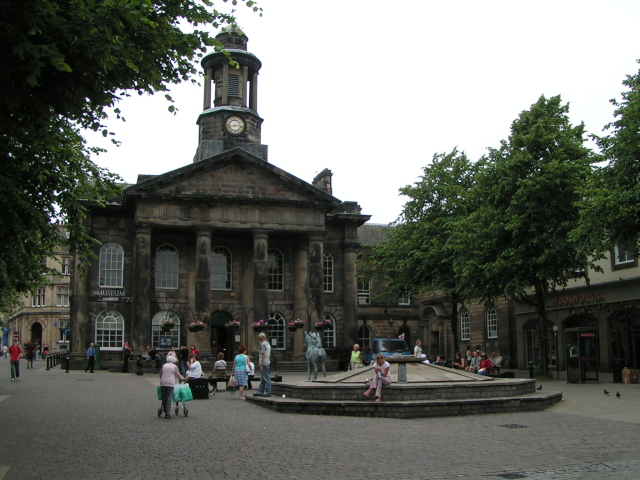
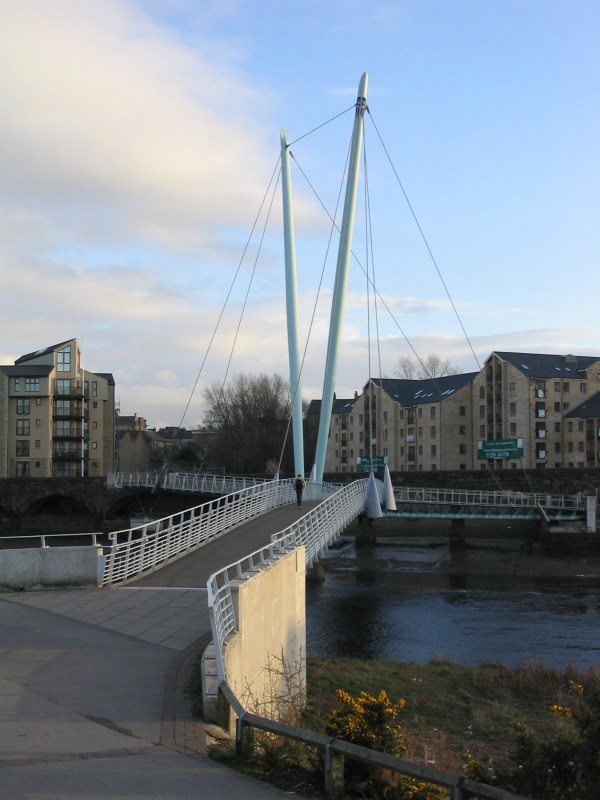
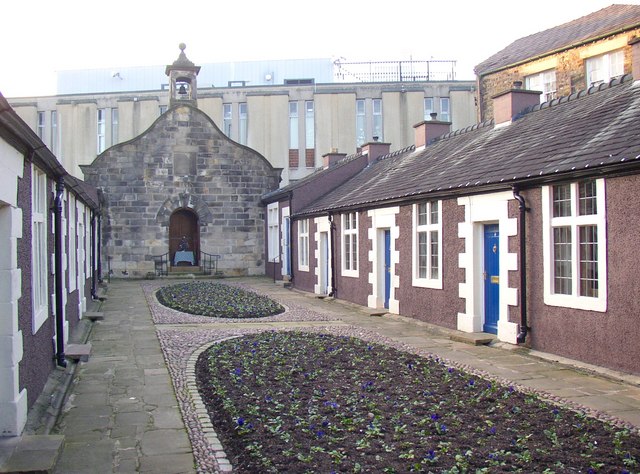


 Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of
Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of  Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months
Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months
 Lancaster's main
Lancaster's main
Lancaster City Brass
which is the oldest remaining brass band in the city celebrating its 75th anniversary in 2021 an
Batala
who recently completed 15 years of Samba Regge drumming Lancaster has been producing successful bands and musicians since the 1990s, notably the drummer Keith Baxter of 3 Colours Red and folk-metal band Skyclad, who also featured Lancaster guitarist Dave Pugh, and the thrash metal band D.A.M., who were all from Lancaster, recording two albums for the Noise International label, with Dave Pugh appearing on the second. The all-girl punk-rock band
 *
*
Lancaster City Council, Twin Towns
retrieved 21 January 2019.
Lancaster City Council
– Homepage of Lancaster City Council
Regional Europe - LancasterVisit Lancaster Website
– Tourism Website for Lancaster {{Authority control County towns in England Towns in Lancashire Roman fortifications in England Unparished areas in Lancashire Geography of the City of Lancaster
county town
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a county town is the most important town or city in a county. It is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county and the place where the county's members of Parliament are elect ...
of Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancas ...
, England, standing on the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
. Its population of 52,234 compares with one of 138,375 in the wider City of Lancaster
The City of Lancaster () is a local government district of Lancashire, England, with the status of a city and non-metropolitan district. It is named after its largest settlement, Lancaster, but covers a far larger area, which includes the to ...
local government district. The House of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 126 ...
was a branch of the English royal family. The Duchy of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is the private estate of the British sovereign as Duke of Lancaster. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income to the sovereign. The estate consists of a portfolio of lands, properti ...
still holds large estates on behalf of Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person ...
, who is also Duke of Lancaster
The Dukedom of Lancaster is an English peerage merged into the crown. It was created three times in the Middle Ages, but finally merged in the Crown when Henry V succeeded to the throne in 1413. Despite the extinction of the dukedom the title ...
. Its long history is marked by Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
, Lancaster Priory Church, Lancaster Cathedral
Lancaster Cathedral, also known as The Cathedral Church of St Peter and Saint Peter's Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It was a Roman Catholic parish church until 1924, when it was elevated to the st ...
and the Ashton Memorial
The Ashton Memorial is a folly in Williamson Park, Lancaster, Lancashire, England built between 1907 and 1909 by the millionaire industrialist Lord Ashton in memory of his second wife, Jessy, at a cost of £87,000 (equivalent to £ in ).
Des ...
. It is the seat of Lancaster University
, mottoeng = Truth lies open to all
, established =
, endowment = £13.9 million
, budget = £317.9 million
, type = Public
, city = Bailrigg, City of Lancaster
, country = England
, coor =
, campus = Bailrigg
, faculty ...
and has a campus of the University of Cumbria
The University of Cumbria is a public university in Cumbria, with its headquarters in Carlisle and other major campuses in Lancaster, Ambleside, and London. It has roots extending back to the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts, establis ...
. The Port of Lancaster played a big role in the city's growth, but for many years the outport
An outport is any port considered secondary to a main port (including a provincial one as opposed to a capital one), and often (especially) a small port built to support the commercial operations of a large port. The Port of Tilbury from the Port o ...
of Glasson Dock
Glasson Dock, also known as Glasson, is a village in Lancashire, England, south of Lancaster at the mouth of the River Lune. In 2011, it had a population of around 600.
History
Glasson was originally a small farming and fishing community (whi ...
has become the main shipping facility.
History
The name of the city first appeared in theDomesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
of 1086, as ''Loncastre'', where "Lon" refers to the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
and "castre" (from the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
''cæster'' and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
''castrum'' for "fort") to the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
fort that stood on the site.
Roman and Saxon eras
Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
now stands, possibly as early as the 60s CE, based on Roman coin evidence. Coin evidence also suggests that the fort was not continuously inhabited in its early years. It was rebuilt in stone about 102 CE. The fort name is known only in a shortened form; the only evidence is a Roman milestone found 4 miles outside Lancaster, with an inscription ending L MP IIII, meaning "from L – 4 miles, and that its name began with an L. The fort was perhaps named Lunium.
Roman baths were found in 1812 and can be seen near the junction of Bridge Lane and Church Street. There was presumably a bath-house with the 4th-century fort. The Roman baths incorporated a reused inscription of the Gallic Emperor Postumus
Marcus Cassianius Latinius Postumus was a Roman commander of Batavian origin, who ruled as Emperor of the splinter state of the Roman Empire known to modern historians as the Gallic Empire. The Roman army in Gaul threw off its allegiance to Ga ...
, dating from 262 to 266 CE. The 3rd-century fort was garrisoned by the ''ala Sebosiana'' and ''numerus Barcariorum Tigrisiensium''.
The ancient ''Wery Wall'' was identified in 1950 as the north wall of the 4th-century fort, which was a drastic remodelling of the 3rd-century one, while retaining the same orientation. The later fort is the only example in north-west Britain of a 4th-century type, with massive curtain-wall and projecting bastions typical of the ''Saxon Shore'' or Wales. Extension of the technique as far north as Lancaster shows that the coast between Cumberland and North Wales was not left defenceless after the west-coast attacks and the disaster in the Carausian Revolt of 296 CE, which followed from those under Albinus in 197 CE.
The fort at its largest extent covered . Evidence suggests that it stayed in use until the end of Roman occupation of Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
. Church Street and some of St Leonard's Gate probably mark the initial course of the Roman road up the valley to the fort at Over Burrow.
Little is known of Lancaster from the end of Roman rule to the early 5th century and the Norman Conquest of the late 11th century. Despite a lack of documentation for the period, it is thought that Lancaster remained inhabited. It lay on the fringes of the kingdoms of Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era=Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, y ...
and Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
and over time may have passed from one to the other. Archaeological evidence suggests there was a monastery on or near the site of today's Lancaster Priory
Lancaster Priory, formally the Priory Church of St Mary, is the Church of England parish church of the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is located near Lancaster Castle and since 1953 has been designated a Grade I listed building ...
by the 700s or 800s. The Anglo-Saxon runic
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write various Germanic languages (with some exceptions) before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised ...
"Cynibald's cross" found at the Priory in 1807 is thought to date from the late 9th century. Lancaster was probably one of several abbeys founded under Wilfrid
Wilfrid ( – 709 or 710) was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Francia, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and ...
.
Medieval
 After the
After the Norman conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqu ...
in 1066, Lancaster fell under the control of William I
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
, as stated in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
of 1086, which has the earliest known mention of Lancaster as such in any document. The founding Priory charter dated 1094 is the first known document specific to Lancaster.White, p. 57. By this time William had passed Lancaster and its surroundings to Roger de Poitou
Roger the Poitevin (Roger de Poitou) was born in Normandy in the mid-1060s and died before 1140. He was an Anglo-Norman aristocrat, possessing large holdings in both England and through his marriage in France.
He was the third son of Roger of Mo ...
. The document also suggests the monastery was refounded as a parish church some time before 1066.
Lancaster became a borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
in 1193 under King Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was ove ...
. Its first charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the re ...
, dated 12 June 1193, was from John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, Count of Mortain
The County of Mortain was a medieval county in France centered on the town of Mortain. A choice landholding, usually either kept within the family of the duke of Normandy (or the king of France) or granted to a noble in return for service and fa ...
, who later became King of England.

Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
, partly built in the 13th century and enlarged by Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
, stands on the site of a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mili ...
. During The Great Raid of 1322
The Great Raid of 1322 was a major raid carried out by Robert the Bruce, during the First Scottish War of Independence, on Northern England between 30 September and 2 November 1322, resulting in the Battle of Old Byland. Numerous raids began ...
, damage was done to the castle by Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (Scottish Gaelic: ''Raibeart an Bruis''), was King of Scots from 1306 to his death in 1329. One of the most renowned warriors of his generation, Robert eventuall ...
, though it resisted the attack and was restored and strengthened by John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399) was an English royal prince, military leader, and statesman. He was the fourth son (third to survive infancy as William of Hatfield died shortly after birth) of King Edward ...
, who added much of the Gateway Tower and a turret on the keep or Lungess Tower, which has been named "John o' Gaunt's Chair". In 1322 the Scots burnt the town. It was rebuilt but removed from its position on the hill to the slope and foot. Again in 1389, after the Battle of Otterburn, it was destroyed by the Scots. Lancaster Castle is known as the site of the Pendle witch trials
The trials of the Pendle witches in 1612 are among the most famous witch trials in English history, and some of the best recorded of the 17th century. The twelve accused lived in the area surrounding Pendle Hill in Lancashire, and were charged ...
in 1612. It was said that the court based in the castle (the Lancaster Assizes
The courts of assize, or assizes (), were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes ...
) sentenced more people to be hanged
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging ...
than any other in the country outside London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, earning Lancaster the nickname, ''"the Hanging Town"''. It also figured prominently in the suppression of Catholicism during the Reformation – at least eleven Catholic priests were executed and a memorial to them as the Lancaster Martyrs
During the English Reformation, a number of believers were executed at Lancaster in England as a consequence of their Catholic faith. They are commonly referred to as the Lancaster Martyrs and are commemorated locally by the Lancaster Martyrs Me ...
stands by the city centre.
 The traditional emblem of the
The traditional emblem of the House of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 126 ...
is the Red Rose of Lancaster
The Red Rose of Lancaster (blazoned: ''a rose gules'') was the heraldic badge adopted by the royal House of Lancaster in the 14th century. In modern times it symbolises the county of Lancashire. The exact species or cultivar which it represents i ...
, similar to that of the House of York
The House of York was a cadet branch of the English royal House of Plantagenet. Three of its members became kings of England in the late 15th century. The House of York descended in the male line from Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of Yor ...
with a white rose. The names derive from emblems of the Royal Duchies of Lancaster and York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
in the 15th century. This erupted into a civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
over rival claims to the throne during the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the throne of England, English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These w ...
.
More recently the term ''"Wars of the Roses"'' has been applied to rivalry in sports between teams from Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancas ...
and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
. It is also applied to the annual Roses Tournament between Lancaster and York universities.
charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the re ...
in 1193 as a market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
and borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
, but had to await city status until 1937. Many central buildings and ones along St George's Quay date from the 18th century, as the port became one of the UK's busiest and the fourth most important in the UK slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. Among prominent Lancaster slave-traders were Dodshon Foster
Dodshon Foster (1 September 1730 - 2 January 1793) was a merchant who profited from the slave trade. He was involved in the shipping of over 700 slaves during his career.White, p.63 His commercial success was assisted by his connection through marr ...
, Thomas Hinde and his eponymous son. However, Lancaster's role as a major port ceased as the river began to silt up. Morecambe
Morecambe ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster district in Lancashire, England. It is in Morecambe Bay on the Irish Sea.
Name
The first use of the name was by John Whitaker in his ''History of Manchester'' (1771), ...
, Glasson Dock
Glasson Dock, also known as Glasson, is a village in Lancashire, England, south of Lancaster at the mouth of the River Lune. In 2011, it had a population of around 600.
History
Glasson was originally a small farming and fishing community (whi ...
and Sunderland Point took over as outports for brief periods. Heysham Port has now eclipsed all those on the Lune.
Recent history
Lancaster is mainly a service-oriented city. Products includeanimal feed
Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word ''feed'' more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input to ...
, textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
, livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
, paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distribu ...
, synthetic fibre, farm machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they ...
, HGV trailers
Trailer may refer to: a
Transportation
* Trailer (vehicle), an unpowered vehicle pulled by a powered vehicle
** Bicycle trailer, a wheeled frame for hitching to a bicycle to tow cargo or passengers
** Full-trailer
** Semi-trailer
**Horse traile ...
and mineral fibres. In recent years, a high-tech sector has emerged from Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology syste ...
and Communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
firms investing in the city.
A permanent military presence was built up with the completion of Bowerham Barracks in 1880. The Phoenix Street drill hall was completed in 1894.
In March 2004, Lancaster was granted Fairtrade City
The Fair Trade Towns campaign is the result of a grass-roots citizens movement that started in the UK in 2001 (see below). It allows citizens to get together in order to self-proclaim their town (or other local geographical area) as a region that ...
status.
Lancaster was home to the European headquarters of Reebok
Reebok International Limited () is an American fitness footwear and clothing manufacturer that is a part of Authentic Brands Group. It was established in England in 1958 as a companion company to J.W. Foster and Sons, a sporting goods company ...
. After merging with Adidas
Adidas AG (; stylized as adidas since 1949) is a German multinational corporation, founded and headquartered in Herzogenaurach, Bavaria, that designs and manufactures shoes, clothing and accessories. It is the largest sportswear manufacture ...
, Reebok moved to Bolton
Bolton (, locally ) is a large town in Greater Manchester in North West England, formerly a part of Lancashire. A former mill town, Bolton has been a production centre for textiles since Flemish weavers settled in the area in the 14th ...
and Stockport
Stockport is a town and borough in Greater Manchester, England, south-east of Manchester, south-west of Ashton-under-Lyne and north of Macclesfield. The River Goyt and Tame merge to create the River Mersey here.
Most of the town is withi ...
in 2007.
In May 2015 Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states durin ...
visited the castle for commemorations for the 750th anniversary of the creation of the Duchy of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is the private estate of the British sovereign as Duke of Lancaster. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income to the sovereign. The estate consists of a portfolio of lands, properti ...
.
Governance
 The former
The former City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and Municipal Borough
Municipal boroughs were a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1835 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in S ...
of Lancaster and the Municipal Borough of Morecambe and Heysham along with other authorities merged in 1974 to form the City of Lancaster
The City of Lancaster () is a local government district of Lancashire, England, with the status of a city and non-metropolitan district. It is named after its largest settlement, Lancaster, but covers a far larger area, which includes the to ...
district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivision ...
within the shire county of Lancashire. This was given city status in the United Kingdom
City status in the United Kingdom is granted by the monarch of the United Kingdom to a select group of communities. , there are 76 cities in the United Kingdom—55 in England, seven in Wales, eight in Scotland, and six in Northern Ireland. ...
and Lancaster City Council is the local governing body for the district. Lancaster is an unparished area
In England, an unparished area is an area that is not covered by a civil parish (the lowest level of local government, not to be confused with an ecclesiastical parish). Most urbanised districts of England are either entirely or partly unpa ...
and has no separate council. It is divided into wards such as Bulk, Castle, Ellel, John O'Gaunt (named after John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399) was an English royal prince, military leader, and statesman. He was the fourth son (third to survive infancy as William of Hatfield died shortly after birth) of King Edward ...
), Scotforth
Scotforth is a suburb in the south of the city of Lancaster in Lancashire, England. It is home to Scotforth St Paul's Church of England Primary School and St Paul's Church. The civil parish, which does not include the suburb had a populati ...
East, Scotforth West, Skerton East, Skerton West, and University and Scotforth Rural.
Political representation
Most of the city lies in theLancaster and Fleetwood
Lancaster and Fleetwood is a constituency created in 2010 represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament by Cat Smith of the Labour Party.
History
;Creation
Following their review of parliamentary representation in Lancashire, the ...
constituency for elections of Members of Parliament to the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. The current MP for Lancaster and Fleetwood
Lancaster and Fleetwood is a constituency created in 2010 represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament by Cat Smith of the Labour Party.
History
;Creation
Following their review of parliamentary representation in Lancashire, the ...
is Cat Smith
Catherine Jane Smith (born 16 June 1985) is a British politician who has served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Lancaster and Fleetwood since 2015. A member of the Labour Party, she was a member of the shadow cabinets of Jeremy Corbyn and K ...
of the Labour Party. The Skerton part of the city lies in the Morecambe and Lunesdale constituency represented by David Morris of the Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
.
Before Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the Withdrawal from the European Union, withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 Greenwich Mean Time, GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 Central Eur ...
, it was in the North West England
North West England is one of nine official regions of England and consists of the ceremonial counties of England, administrative counties of Cheshire, Cumbria, Greater Manchester, Lancashire and Merseyside. The North West had a population of ...
European Parliamentary Constituency.
In the late 1990s and early first decade of the 21st century, the city council was under the control of the Morecambe Bay Independents
The Morecambe Bay Independents (MBIs) is a local political party in Morecambe, Lancashire. The group ran Lancaster City Council from 1999 to 2003, and successfully campaigned in 2005 for the creation of Morecambe Town Council.
History
Early ...
(MBIs), who campaigned for an independent Morecambe council. In 2003, their influence waned and Labour became the largest party on the council. They formed a coalition with the Liberal Democrats and Greens. At the May 2007 local elections, Labour lost ground to the Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combin ...
s in Lancaster and the MBIs in Morecambe, resulting in no overall control, with all parties represented in a PR administration. The 2011 elections saw Labour emerge as the largest party. They reached a joint administrative arrangement with the Greens.
The 2019 Lancaster City Council election results put no party in overall control. The council is run by a coalition of Labour, Green, Eco-Socialist Independent and Liberal Democrat councillors, supported by the Independent Group, with Conservatives and MBIs in opposition. The cabinet consists of 4 Labour, 4 Green, 1 Eco-Socialist, 1 Independent Group. At 10 seats, Lancaster has one of the country's largest Green Party representations.
Geography
Lancaster is Lancashire's northernmost city, three miles () inland fromMorecambe Bay
Morecambe Bay is a large estuary in northwest England, just to the south of the Lake District National Park. It is the largest expanse of intertidal mudflats and sand in the United Kingdom, covering a total area of . In 1974, the second largest ...
on the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
(from which comes its name), and the Lancaster Canal
The Lancaster Canal is a canal in North West England, originally planned to run from Westhoughton in Lancashire to Kendal in south Cumbria ( historically in Westmorland). The section around the crossing of the River Ribble was never compl ...
. It becomes hillier from the Lune Valley eastwards, with Williamson Hill in the north-west a notable peak at .
Built-up area
Lancaster,Morecambe
Morecambe ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster district in Lancashire, England. It is in Morecambe Bay on the Irish Sea.
Name
The first use of the name was by John Whitaker in his ''History of Manchester'' (1771), ...
and Heysham have been identified by the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for ...
as forming the Lancaster/Morecambe Built-up area, with a population of 97,150 in 2011.
Green belt
There is a small portion of green belt on the northern fringe of Lancaster, covering the area into Carnforth and helping to prevent further urban expansion towards nearby Morecambe, Hest Bank, Slyne and Bolton-le-Sands.Transport
Road
 The
The M6 motorway
The M6 motorway is the longest motorway in the United Kingdom. It is located entirely within England, running for just over from the Midlands to the border with Scotland. It begins at Junction 19 of the M1 and the western end of the A14 at ...
passes to the east of Lancaster with junctions 33 and 34 to the south and north. The A6 road, one of the main historic north–south roads in England, leads south to Preston
Preston is a place name, surname and given name that may refer to:
Places
England
*Preston, Lancashire, an urban settlement
**The City of Preston, Lancashire, a borough and non-metropolitan district which contains the settlement
**County Boro ...
, Chorley
Chorley is a town and the administrative centre of the wider Borough of Chorley in Lancashire, England, north of Wigan, south west of Blackburn, north west of Bolton, south of Preston and north west of Manchester. The town's wealth came ...
and Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
and north to Carnforth
Carnforth is a market town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster in Lancashire, England, situated at the north-east end of Morecambe Bay. The parish of Carnforth had a population of 5,560 in the 2011 census, an increase from the 5,350 rec ...
, Kendal
Kendal, once Kirkby in Kendal or Kirkby Kendal, is a market town and civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England, south-east of Windermere and north of Lancaster. Historically in Westmorland, it lies within the dale of t ...
, Penrith and Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City ...
. It currently runs from Luton, Bedfordshire
Luton () is a town and unitary authority with borough status, in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 census, the Luton built-up area subdivision had a population of 211,228 and its built-up area, including the adjacent towns of Dunstable an ...
, to Carlisle, Cumbria
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City ...
. In passing through Lancaster it gives access to nearby Carnforth
Carnforth is a market town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster in Lancashire, England, situated at the north-east end of Morecambe Bay. The parish of Carnforth had a population of 5,560 in the 2011 census, an increase from the 5,350 rec ...
, Kendal
Kendal, once Kirkby in Kendal or Kirkby Kendal, is a market town and civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England, south-east of Windermere and north of Lancaster. Historically in Westmorland, it lies within the dale of t ...
and Garstang
Garstang is an ancient market town and civil parish within the Wyre borough of Lancashire, England. It is north of the city of Preston and the same distance south of Lancaster.
In 2011, the parish had a total resident population of 4,268; ...
. The Bay Gateway opened in 2016, linking Heysham and the M6 with a dual carriageway.
Lancaster's main bus operator is Stagecoach Cumbria & North Lancashire, with a network of services from Lancaster bus station throughout the Lancaster District and frequent services to more distant places such as Kendal
Kendal, once Kirkby in Kendal or Kirkby Kendal, is a market town and civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England, south-east of Windermere and north of Lancaster. Historically in Westmorland, it lies within the dale of t ...
, Keswick, Kirkby Lonsdale
Kirkby Lonsdale () is a town and civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England, on the River Lune. Historically in Westmorland, it lies south-east of Kendal on the A65. The parish recorded a population of 1,771 in the 2001 ...
, Preston
Preston is a place name, surname and given name that may refer to:
Places
England
*Preston, Lancashire, an urban settlement
**The City of Preston, Lancashire, a borough and non-metropolitan district which contains the settlement
**County Boro ...
and Blackpool
Blackpool is a seaside resort in Lancashire, England. Located on the northwest coast of England, it is the main settlement within the borough also called Blackpool. The town is by the Irish Sea, between the Ribble and Wyre rivers, and is ...
. There are frequent buses to Lancaster University
, mottoeng = Truth lies open to all
, established =
, endowment = £13.9 million
, budget = £317.9 million
, type = Public
, city = Bailrigg, City of Lancaster
, country = England
, coor =
, campus = Bailrigg
, faculty ...
, with the No. 1 and No. 1A services running every 10–15 minutes using double-deckers, with less frequent services 4, 41 and 42.
Other routes are covered by Kirkby Lonsdale Coach Hire, including the 582 to Kirkby Lonsdale
Kirkby Lonsdale () is a town and civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England, on the River Lune. Historically in Westmorland, it lies south-east of Kendal on the A65. The parish recorded a population of 1,771 in the 2001 ...
, Settle and Skipton
Skipton (also known as Skipton-in-Craven) is a market town and civil parish in the Craven district of North Yorkshire, England. Historically in the East Division of Staincliffe Wapentake in the West Riding of Yorkshire, it is on the Riv ...
and the 89 to Knott End-on-Sea.
Rail
 Lancaster is served by the
Lancaster is served by the West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest ...
, which runs through Lancaster railway station Lancaster may refer to:
Lands and titles
*The County Palatine of Lancaster, a synonym for Lancashire
*Duchy of Lancaster, one of only two British royal duchies
* Duke of Lancaster
* Earl of Lancaster
*House of Lancaster, a British royal dynasty ...
. The station was formerly named Lancaster Castle, to differentiate it from Lancaster Green Ayre on the Leeds–Morecambe line
The Leeds–Morecambe line, also known as the Bentham line, is a railway line running between Leeds, Skipton, Lancaster and Morecambe in northern England. The service is operated by Northern. The route covered by the service was historically ...
, which closed in 1966. There are through train services to and from London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popu ...
, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
, Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
, Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by popul ...
and Barrow-in-Furness
Barrow-in-Furness is a port town in Cumbria, England. Historically in Lancashire, it was incorporated as a municipal borough in 1867 and merged with Dalton-in-Furness Urban District in 1974 to form the Borough of Barrow-in-Furness. In 2023 t ...
, with a local service to Morecambe
Morecambe ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster district in Lancashire, England. It is in Morecambe Bay on the Irish Sea.
Name
The first use of the name was by John Whitaker in his ''History of Manchester'' (1771), ...
.
The long-term aim of the city council is to open a railway station serving the university and south Lancaster, although this is not feasible in the short or medium term with current levels of demand. The Caton–Morecambe section of the former North Western railway is now used as a cycle path.
Water and air
Historically, the Port of Lancaster gained importance in the 18th century. In 1750 theLancaster Port Commission
Lancaster Port Commission is the Statutory Harbour Authority for the Port of Lancaster. It is now based at Glasson Dock. It was set up by act of parliament to facilitate the role that the port could play in international trade, particularly the A ...
was established to develop the port. However, in more recent years, shipping visits Glasson Dock
Glasson Dock, also known as Glasson, is a village in Lancashire, England, south of Lancaster at the mouth of the River Lune. In 2011, it had a population of around 600.
History
Glasson was originally a small farming and fishing community (whi ...
, where the Port commission is now based.
The Lancaster Canal
The Lancaster Canal is a canal in North West England, originally planned to run from Westhoughton in Lancashire to Kendal in south Cumbria ( historically in Westmorland). The section around the crossing of the River Ribble was never compl ...
and River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
pass through the city.
The nearest airports are Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
and Blackpool
Blackpool is a seaside resort in Lancashire, England. Located on the northwest coast of England, it is the main settlement within the borough also called Blackpool. The town is by the Irish Sea, between the Ribble and Wyre rivers, and is ...
.
Cycling
In 2005, Lancaster was one of six English towns chosen to be cycling demonstration towns to promote cycling as a means of transport.Education
 At Bailrigg south of the city is
At Bailrigg south of the city is Lancaster University
, mottoeng = Truth lies open to all
, established =
, endowment = £13.9 million
, budget = £317.9 million
, type = Public
, city = Bailrigg, City of Lancaster
, country = England
, coor =
, campus = Bailrigg
, faculty ...
, a research university founded in the 1960s with an annual income of about £319 million, 3,000 staff and 17,415 registered students. Its business school is one of two in the country to gain a six-star research rating. Its physics department rated #1 in the United Kingdom in 2008. InfoLab21 at the university is a Centre of Excellence for Information and Communication Technologies. LEC (Lancaster Environment Centre) has over 200 staff and shares premises with the government-funded CEH. In 2017 it was rated 21st nationally for research in The Times Higher league table. For teaching, it gained the highest Gold ranking for quality in the 2017 government TEF, and in 2018 was ranked 9th for its teaching by ''The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publish ...
'' and 9th by ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers '' The Observer'' and '' The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the ...
''. ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ( ...
'' Higher placed it 137th worldwide for research and 58th worldwide for arts and humanities. Lancaster University was named International University of the Year by ''The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide'' in 2020. It has campuses in Malaysia, China and Ghana and plans one in Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, Germany.
Lancaster is also home to a campus of the University of Cumbria
The University of Cumbria is a public university in Cumbria, with its headquarters in Carlisle and other major campuses in Lancaster, Ambleside, and London. It has roots extending back to the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts, establis ...
– more centrally located on the site of the former St Martin's College
St Martin's College was a British higher education college with campuses in Lancaster, Ambleside and Carlisle, as well as sites in Whitehaven, Barrow and London. It provided undergraduate and postgraduate courses in the arts, humanities, b ...
– which was inaugurated in 2007. It provides undergraduate and postgraduate courses in the arts, social sciences, business, teacher training, health care and nursing.
Jamea Al Kauthar Islamic College, in the former Royal Albert Hospital
The Royal Albert Hospital was a hospital in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It opened in 1870 as an institution for the care and education of children with learning problems. By 1909 there were 662 children in residence. Following new legi ...
building on Ashton Road, is an independent girls' school, providing education in a Muslim tradition.
Further education
* Lancaster and Morecambe CollegeSecondary schools
*Lancaster Royal Grammar School
Lancaster Royal Grammar School (LRGS) is a selective grammar school (day and boarding) for boys aged 11–18 in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. Old students belong to The Old Lancastrians. The school's sixth form opened to girls in 2019. LRGS i ...
and Lancaster Girls' Grammar School are selective-entry grammar schools. In 2016 both were rated by the ''Sunday Times
''The Sunday Times'' is a British newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of News UK, w ...
''in the top 50 UK schools based on student achievement.
* Ripley St Thomas Church of England Academy
*Our Lady's Catholic College
Our Lady's Catholic College (OLCC) is a mixed sex secondary school for pupils aged 11–18. It is located in Skerton, just off the A6 road, north of the River Lune, Lancaster in the North West of England. Formerly Our Lady's Catholic High Sch ...
*Central Lancaster High School
Central Lancaster High School (CLHS) is a coeducational secondary school and sixth form located in Lancaster, England. Located on Crag Road on the Ridge area in east Lancaster. In recent years, the school has been performing well below average ...
* Skerton Community High School (now closed)
Primary schools
* Lancaster Steiner School *Scotforth St Pauls CofE Primary School *Moorside Primary School *St Bernadette's Catholic Primary School *Bowerham Primary School *The Cathedral Catholic Primary School *Dallas Road Community Primary School *Willow Lane (formerly Marsh) Community Primary School *Castle View (formerly Ridge) Community Primary School *Lancaster Christ Church CofE Primary School *St Joseph's Catholic Primary School *Skerton St Lukes CofE Primary School *Lancaster Ryelands Primary School Special Educational Needs (SEN) Schools *The Loyne *Morecambe Road SchoolCulture


 Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of
Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of Georgian architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover— George I, George II, Ge ...
. Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
, the Priory Church of St. Mary and the Edwardian Ashton Memorial
The Ashton Memorial is a folly in Williamson Park, Lancaster, Lancashire, England built between 1907 and 1909 by the millionaire industrialist Lord Ashton in memory of his second wife, Jessy, at a cost of £87,000 (equivalent to £ in ).
Des ...
are among the sites of historical importance. Its many museums include Lancaster City Museum
Lancaster City Museum is a museum in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is housed in the former Lancaster Town Hall building in Market Square.
History
The Old Town Hall building in which the museum is housed is recorded in the National Heritag ...
, Maritime Museum
A maritime museum (sometimes nautical museum) is a museum specializing in the display of objects relating to ships and travel on large bodies of water. A subcategory of maritime museums are naval museums, which focus on navies and the milita ...
, the Cottage Museum, and Judges' Lodgings Museum.
Lancaster Friends Meeting House dating from 1708, is the longest continual Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
meeting site in the world, with an original building built in 1677. George Fox
George Fox (July 1624 – 13 January 1691) was an English Dissenter, who was a founder of the Religious Society of Friends, commonly known as the Quakers or Friends. The son of a Leicestershire weaver, he lived in times of social upheaval and ...
, founder of Quakerism, was near the site several times in the 1660s and spent two years imprisoned in Lancaster Castle. The meeting house holds regular Quaker meetings and a wide range of cultural activities including adult learning, meditation, art classes, music and political meetings. The Lancaster Grand Theatre is another historic cultural venue, under its many names. It has played a major part in social and cultural life since it was built in 1782.
 Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months
Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months Williamson Park
Williamson Park in Lancaster, England, was constructed by millionaire James Williamson, 1st Baron Ashton, and his father, also called James Williamson. Its focal point is the Ashton Memorial. The park now covers an area of 53.6 acres (217,000 ...
hosts outdoor performances, including a Dukes "Play in the Park", which over the past 26 years has attracted 460,000 people, as the UK's biggest outdoor walkabout theatre event.
Lancaster is known as the Northern City of Ale, with almost 30 pubs serving cask ale. The pubs include the ''White Cross'', ''Three Mariners'', ''Borough'' and ''Water Witch''. There are two cask ale breweries: Lancaster Brewery and a microbrewery run by the Borough. There is a local CAMRA (Campaign for Real Ale
The Campaign for Real Ale (CAMRA) is an independent voluntary consumer organisation headquartered in St Albans, England, which promotes real ale, cider and perry and traditional British pubs and clubs. With just under 155,000 members, it is ...
) branch at Lunesdale.
The Lancaster Grand Theatre and the Dukes are notable venues for live performance, as are the Yorkshire House (currently closed), Jailors Barrel, The John O' Gaunt and The Bobbin. Throughout the year events are held in and around the city, such as the Lancaster Music Festival, Lancaster Jazz Festival, and Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year is the festival that celebrates the beginning of a new year on the traditional lunisolar and solar Chinese calendar. In Chinese and other East Asian cultures, the festival is commonly referred to as the Spring Festival () a ...
celebrations in the city centre.
Every November the city hosts a daylight and art festival entitled "Light Up Lancaster", which includes a prominent fireworks display.
Lancaster still has two city-centre cinemas; Vue and the Dukes playhouse. The 1930s art deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
''Regal Cinema'' closed in 2006. The Gregson Centre is also known for small film screenings and cultural events.
Art and literature
John Henderson (c.1770-1853) painted many views of the town. One of these together with a poetical illustration (which relates to the treacherous sands of Morecambe Bay) byLetitia Elizabeth Landon
Letitia Elizabeth Landon (14 August 1802 – 15 October 1838) was an English poet and novelist, better known by her initials L.E.L.
The writings of Landon are transitional between Romanticism and the Victorian Age. Her first major breakthrough ...
was published in Fisher's Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1833
Sport
 Lancaster's main
Lancaster's main football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
team, Lancaster City
Lancaster City Football Club is an English semi-professional non-League football club based in the northern city of Lancaster, Lancashire. They currently compete in and play at Giant Axe. They are full members of the Lancashire County Footba ...
, plays in the Northern Premier League Premier Division
The Northern Premier League is an English football league that was founded in 1968. It has four divisions: the Premier Division (which stands at level 7 of the English football league system), Division One East, Division One West and Division ...
having won promotion as champions of Division One North in 2016–2017. It plays its home matches at the Giant Axe, which can take 3,500 (513 seated) and was formed in 1911 originally as Lancaster Town F.C. Lancaster City has been seven-times Lancashire FA Challenge cup winners and in 2010-11 won the Northern Premier League President's cup for a second time. Lancaster John O' Gaunt Rowing Club
Lancaster John O'Gaunt Rowing Club (JOG) is an English rowing club based at Lancaster on the River Lune. Its origins date back to 1842 making it the fifth oldest surviving rowing club in the United Kingdom outside the universities.
History
Lan ...
is the fifth-oldest surviving rowing club in the UK, outside the universities. It competes nationally at regattas and heads races run by British Rowing
British Rowing, formerly the Amateur Rowing Association (ARA), is the national governing body for the sport of rowing (both indoor and on-water rowing). It is responsible for the training and selection of individual rowers and crews representi ...
. The clubhouse stands next to the weir at Skerton.
The city entertains contestants in the ''Lancaster International Youth Games'', a multi-sport 'Olympic' style event featuring competitors from Lancaster's twin towns: Rendsburg
Rendsburg ( da, Rendsborg, also ''Rensborg'', nds, Rendsborg, also ''Rensborg'') is a town on the River Eider and the Kiel Canal in the central part of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) of Rendsburg-Eck ...
(Germany), Perpignan
Perpignan (, , ; ca, Perpinyà ; es, Perpiñán ; it, Perpignano ) is the prefecture of the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France, in the heart of the plain of Roussillon, at the foot of the Pyrenees a few kilometres from the ...
(France), Viana do Castelo (Portugal), Aalborg
Aalborg (, , ) is Denmark's List of cities in Denmark by population, fourth largest town (behind Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense) with a population of 119,862 (1 July 2022) in the town proper and an Urban area, urban population of 143,598 (1 July ...
(Denmark), Almere
Almere () is a planned city and municipality in the province of Flevoland, Netherlands, located about 20 km to the east of Amsterdam (as the crow flies) across the IJmeer.
Bordering Lelystad and Zeewolde, the municipality of Almere compr ...
(Netherlands), Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
(Poland) and Växjö
Växjö ( ) is a city and the seat of Växjö Municipality, Kronoberg County, Sweden. It had 70,489 inhabitants (2019) out of a municipal population of 95,995 (2021). It is the administrative, cultural, and industrial centre of Kronoberg County ...
(Sweden).
Lancaster Cricket Club is sited near the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
. It has two senior teams that participate in the Palace Shield. Rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
is a popular sport in the area, with the local clubs being Vale of Lune RUFC and Lancaster CATS.
Lancaster is home to the Golf Centre, Lansil Golf Club, Forest Hills and Lancaster Golf Club. It also has a Lancaster Amateur Swimming and Waterpolo Club that competes in the north-west. It trains at Salt Ayre and at Lancaster University Sports Centre. Lancaster is home to a senior UK team. Water polo
Water polo is a competitive team sport played in water between two teams of seven players each. The game consists of four quarters in which the teams attempt to score goals by throwing the ball into the opposing team's goal. The team with th ...
is also popular in the area.
The local athletics track near the Salt Ayre Sports Centre is home to both Lancaster and Morecambe AC. It regularly fields athletes across disciplines including track and field, cross country, road and fell running. It competes in several local and national leagues including the Young Athletics League, the Northern Athletics League and the local Mid Lancs League (Cross-Country in Winter, and Track and Field in Summer).
Music
The city's semi-professional Haffner Orchestra has a reputation for classical music. It performs in the Ashton Hall in the city centre and at Lancaster University. During parades and festivals it is common to see two other long standing musical groups performLancaster City Brass
which is the oldest remaining brass band in the city celebrating its 75th anniversary in 2021 an
Batala
who recently completed 15 years of Samba Regge drumming Lancaster has been producing successful bands and musicians since the 1990s, notably the drummer Keith Baxter of 3 Colours Red and folk-metal band Skyclad, who also featured Lancaster guitarist Dave Pugh, and the thrash metal band D.A.M., who were all from Lancaster, recording two albums for the Noise International label, with Dave Pugh appearing on the second. The all-girl punk-rock band
Angelica
''Angelica'' is a genus of about 60 species of tall biennial and perennial herbs in the family Apiaceae, native to temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere, reaching as far north as Iceland, Lapland, and Greenland. They gr ...
used the Lancaster Musicians' Co-operative, the main rehearsal and recording studio in the area.
The city has also produced many other musicians, including singer and songwriter John Waite, who first became known as lead singer of The Babys
The Babys are a British rock group best known for their songs " Isn't It Time" and "Every Time I Think of You". Both songs were composed by Jack Conrad and Ray Kennedy, and each reached No. 13 on the U.S. ''Billboard'' Hot 100 and No. 8 on th ...
and had a solo #1 hit in the US, " Missing You". As part of the band Bad English
Bad English was an American/British glam metal supergroup formed in 1987. It reunited Journey keyboardist Jonathan Cain with singer John Waite and bassist Ricky Phillips, his former bandmates in the Babys, along with Journey guitarist Neal ...
, John Waite also had a #1 hit in the Billboard top hundred in the 1970s called "When I See You Smile
"When I See You Smile" is a song written by Diane Warren and performed by American-British glam metal band Bad English. It was released in September 1989 as the second single taken from their self-titled debut album released in 1989. The power ...
". Additionally, Paul James, better known as The Rev, former guitarist of English punk band Towers of London who is now in the band Day 21
Day 21 were a short-lived English punk rock group, led by Jimmy Pursey.
On 21 January 2008, Pursey announced that, due to ongoing confusion to fans, he would no longer be associated with the name Sham 69, and that his new band
Band or BAND ...
and plays guitar live on tour for The Prodigy
The Prodigy are an English electronic dance music band formed in Braintree, Essex, in 1990 by producer, keyboard player and songwriter Liam Howlett. The original line-up also featured dancer and singer Keith Flint and dancer and occasional ...
; Chris Acland
Christopher John Dyke Acland (7 September 1966 – 17 October 1996) was an English drummer and songwriter. He was the drummer of the London-based alternative rock band Lush.
Early life
Acland was born at the Royal Lancaster Infirmary in Lanca ...
, drummer of the early 1990s shoegaze band Lush; Tom English, drummer of North East indie band Maxïmo Park and Steve Kemp, drummer of the indie band Hard-Fi
Hard-Fi are an English indie rock band, formed in 2003 in Staines-upon-Thames, Surrey. The band's most recent lineup before going on hiatus consisted of Richard Archer (lead vocals and guitar), Kai Stephens ( bass guitar and backing vocals) and ...
.
Lancaster continues to produce bands and musicians such as singer-songwriter Jay Diggins
Jay Diggins (born 17 September 1974) is an English singer-songwriter. He is best known for his work with John ParishLakin, Nick"If you fall from grace..." '' Lancaster Guardian'', Lancaster, 14 June 2013. and for turning down an opportunity to ...
, and acts like The Lovely Eggs
The Lovely Eggs are a two-piece lo-fi psychedelic punk rock band from Lancaster, England. They consist of married couple Holly Ross and David Blackwell. Ross was formerly the lead singer and guitarist in the all-female band Angelica.
Career ...
, receiving considerable national radio play and press coverage in recent years. More recently, Lancaster locals Massive Wagons
Massive Wagons are a British jazz combo/rock band from Lancaster founded in 2009.
The band are currently signed to Nottingham-based independent record label Earache Records (having inked their deal in October 2017) and in 2018 released their ...
signed to Nottingham-based independent label Earache Records. The city is also the founding home of the dance-music sound systems Rhythm Method and ACME Bass Company. Pioneers in the field of the free party, these two systems and others forged strong representations of the genre in the North West of England in the 1990s.
Since 2006, Lancaster Library has hosted regular music events under the ''Get it Loud in Libraries'' initiative. Musicians such as The Wombats
The Wombats are an English indie rock band formed in Liverpool in 2003, consisting of Matthew Murphy (lead vocals, guitar, keyboards), Tord Øverland Knudsen (bass, backing vocals, keyboards), and Dan Haggis (drums, backing vocals, keyboards) ...
, The Thrills
The Thrills are an Irish rock band, formed in 2001 in Dublin, Ireland. The band was founded by lead vocalist Conor Deasy and guitarist Daniel Ryan, guitarist and bass player Padraic McMahon, pianist Kevin Horan and drummer Ben Carrigan. Their bre ...
, Kate Nash
Kate Marie Nash (born 6 July 1987) is an English singer-songwriter and actress.
Nash launched her music career in 2005. Her 2007 single " Foundations" became a hit and brought her to public attention in the UK. Her debut album, '' Made of Bricks ...
, Adele
Adele Laurie Blue Adkins (, ; born 5 May 1988), professionally known by the mononym Adele, is an English singer and songwriter. After graduating in arts from the BRIT School in 2006, Adele signed a rec ...
and Bat for Lashes
Natasha Khan (born 25 October 1979), known professionally as Bat for Lashes, is an English singer, songwriter, producer, and multi-instrumentalist. She has released five studio albums: '' Fur and Gold'' (2006), ''Two Suns'' (2009), '' The Hau ...
have taken part. Get It Loud in Libraries has gained national exposure, featuring on The One Show on BBC1 and having gigs reviewed in ''Observer Music Monthly'', '' NME'' and ''Art Rocker''.
Notable popular music venues include The Dukes, The Grand Theatre, The Gregson Centre, The Bobbin, The Pub and The Yorkshire House, which since 2006 has hosted such acts as John Renbourn
John Renbourn (8 August 1944 – 26 March 2015) was an English guitarist and songwriter. He was best known for his collaboration with guitarist Bert Jansch as well as his work with the folk group Pentangle, although he maintained a solo care ...
, Polly Paulusma
Polly Paulusma (born 10 November 1976) is an English singer-songwriter.
Career
Her first album, ''Scissors in my Pocket'', was largely recorded and produced by herself at her home. A second album, ''Cosmic Rosy Spine Kites'' (a virtual anagra ...
, Marissa Nadler, Baby Dee, Diane Cluck, Alasdair Roberts, Jesca Hoop, Lach, Jack Lewis, Tiny Ruins
Tiny Ruins are a musical ensemble from Auckland, New Zealand.
History
Tiny Ruins began as an alias for singer-songwriter Hollie Fullbrook, who recorded as a solo artist prior to 2009.Simon Grig/ref> drummer Gary Hunt
Gary Hunt (born 11 J ...
and 2008 Mercury Prize
The Mercury Prize, formerly called the Mercury Music Prize, is an annual music prize awarded for the best album released in the United Kingdom by a British or Irish act. It was created by Jon Webster and Robert Chandler in association with the ...
nominees Rachel Unthank and the Winterset
Rachel () was a Biblical figure, the favorite of Jacob's two wives, and the mother of Joseph and Benjamin, two of the twelve progenitors of the tribes of Israel. Rachel's father was Laban. Her older sister was Leah, Jacob's first wife. Her aun ...
. Other venues include the Dalton Rooms, the Park Hotel and The Hall, China Street. These host Lancaster's diverse music culture, such as the Lancaster Speakeasy or Stylus.
The Lancaster Jazz and Lancaster Music Festivals are respectively held every September and October, at venues throughout the city. In 2013 the headline jazz act was The Neil Cowley Trio, performing at The Dukes, whilst one of the Lancaster Music Festival headline acts was Jay Diggins
Jay Diggins (born 17 September 1974) is an English singer-songwriter. He is best known for his work with John ParishLakin, Nick"If you fall from grace..." '' Lancaster Guardian'', Lancaster, 14 June 2013. and for turning down an opportunity to ...
at the Dalton Rooms.
Media
Heart North Lancashire & Cumbria
Heart North Lancashire & Cumbria (formerly The Bay) was a local radio station owned and operated by Global Radio as part of the Heart network. It broadcast to north Lancashire and south Cumbria from studios in Lancaster.
History The Bay
The ...
(formerly "The Bay") has been a commercial radio station for north Lancashire and south Cumbria. Its studios are based at St George's Quay in the city and it broadcasts on three frequencies: 96.9 FM (Lancaster), 102.3 FM (Windermere) and 103.2 FM (Kendal). It is now part of the Manchester-based Heart North West
Heart North West is a regional radio station owned and operated by Global as part of the Heart network. It broadcasts to North West England from studios in the Spinningfields area of Manchester city centre.
Overview
Century Radio (1998–2009) ...
.
Beyond Radio is a voluntary, non-profit community radio station for Lancaster and Morecambe and broadcasts on 103.5FM and online. Operated by Proper Community Media (Lancaster) Ltd, the station and broadcasts 24 hours a day from The Old Bowling Pavilion in Palatine Avenue Park, Bowerham. It took over from Diversity FM, a community radio station run by Lancaster and District YMCA, which had closed in April 2012.
Lancaster University has its own student radio station, Bailrigg FM
Bailrigg FM (formerly known as University Radio Bailrigg (URB) and Radio Bailrigg) is a student radio station at Lancaster University. It operates in a music format predominantly featuring pop, but also broadcasts news, drama, comedy, and enterta ...
, broadcasting on 87.7 FM, and an online student-run television station called LA1:TV (formerly LUTube.tv) and a student-run newspaper named SCAN
Scan may refer to:
Acronyms
* Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry (SCAN), a psychiatric diagnostic tool developed by WHO
* Shared Check Authorization Network (SCAN), a database of bad check writers and collection agency for ba ...
.
The city is home to the film production company A1 Pictures, which founded the independent film brand Capture.
Commercially available newspapers include the tabloids ''The Lancaster Guardian'' and ''The Visitor'' (mainly targeted at residents of Morecambe). Both are based on the White Lund Industrial Estate in Morecambe. ''Virtual Lancaster'', founded in 1999, is a non-commercial volunteer-led resource website also featuring local news, events and visitor information.
Places of interest
 *
*Ashton Memorial
The Ashton Memorial is a folly in Williamson Park, Lancaster, Lancashire, England built between 1907 and 1909 by the millionaire industrialist Lord Ashton in memory of his second wife, Jessy, at a cost of £87,000 (equivalent to £ in ).
Des ...
*Duke's Playhouse
The Dukes is a theatre in Lancaster, England. It is the county's only producing theatre venue, and is an Arts Council England National Portfolio Organisation. As well as producing two theatre productions each year, it also hosts a varied prog ...
* Lancaster Grand Theatre
* Greaves Park
* The Judges Lodgings
*Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
*Lancaster Cathedral
Lancaster Cathedral, also known as The Cathedral Church of St Peter and Saint Peter's Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It was a Roman Catholic parish church until 1924, when it was elevated to the st ...
*Lancaster City Museum
Lancaster City Museum is a museum in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is housed in the former Lancaster Town Hall building in Market Square.
History
The Old Town Hall building in which the museum is housed is recorded in the National Heritag ...
*Lancaster Priory
Lancaster Priory, formally the Priory Church of St Mary, is the Church of England parish church of the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is located near Lancaster Castle and since 1953 has been designated a Grade I listed building ...
*Lancaster Royal Grammar School
Lancaster Royal Grammar School (LRGS) is a selective grammar school (day and boarding) for boys aged 11–18 in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. Old students belong to The Old Lancastrians. The school's sixth form opened to girls in 2019. LRGS i ...
* Lancaster Town Hall
*Lune Millennium Bridge
The Lune Millennium Bridge is a cable-stayed footbridge which spans the River Lune in Lancaster, England.
It was designed by Whitby Bird and Partners, and built at a cost of £1.8m to commemorate the millennium of 2000. The bridge forms a "Y" ...
* Quayside Maritime Museum
* Queen Victoria Memorial
* Ruskin Library at Lancaster University
, mottoeng = Truth lies open to all
, established =
, endowment = £13.9 million
, budget = £317.9 million
, type = Public
, city = Bailrigg, City of Lancaster
, country = England
, coor =
, campus = Bailrigg
, faculty ...
* The Gregson Centre
* Storey Gallery
* Westfield War Memorial Village
*Williamson Park
Williamson Park in Lancaster, England, was constructed by millionaire James Williamson, 1st Baron Ashton, and his father, also called James Williamson. Its focal point is the Ashton Memorial. The park now covers an area of 53.6 acres (217,000 ...
Notable people
Arts and entertainment
* Joe Abercrombie (born 1974) – fantasy writer and film editor, was born in Lancaster and attended LRGS. * Cherith Baldry (born 1947) – children's and fantasy writer, was born in Lancaster. *Laurence Binyon
Robert Laurence Binyon, CH (10 August 1869 – 10 March 1943) was an English poet, dramatist and art scholar. Born in Lancaster, England, his parents were Frederick Binyon, a clergyman, and Mary Dockray. He studied at St Paul's School, London ...
(1869–1943) – poet and dramatist, was born in Lancaster.
*Hubert Henry Norsworthy
Hubert Henry Norsworthy (1885 - 18 August 1961) was an organist and composer based in England.
Life
He was born in Haverigg, Millom in Cumberland in 1885, the son of John Henry Norsworthy and Annie Dawson.
During the First World War he served ...
(1885–1961) – organist and composer, died in Lancaster.
* Mabel Pakenham-Walsh (1937–2013) – artist, was born in Lancaster.
* Jon Richardson (born 1982) – comedian, grew up in Lancaster and attended LRGS.
* Thomas Thompson (1880–1951) – writer and broadcaster
* John Waite (born 1952) – rock musician, was born in Lancaster.
*Dustin Demri-Burns
Dustin Demri-Burns (born 11 July 1978) is a British actor, comedian and writer. He is best known for his work in ''Cardinal Burns''.
He appeared in films as the roles of Danny Sinclair in the 2013 film '' Alan Partridge: Alpha Papa'' (2013), Vik ...
(born 1978) – actor, writer and comedian
* Keith Wilkinson – television news reporter, was born in Lancaster
Business
*Henry Cort
Henry Cort (c. 1740 – 23 May 1800) was an English ironware producer although formerly a Navy pay agent. During the Industrial Revolution in England, Cort began refining iron from pig iron to wrought iron (or bar iron) using innovative producti ...
(c. 1741–1800) – English ironmaster and inventor, was probably born in Lancaster.
* James Crosby (born 1956) – chief executive of HBOS
HBOS plc was a banking and insurance company in the United Kingdom, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Lloyds Banking Group, having been taken over in January 2009. It was the holding company for Bank of Scotland plc, which operated the Ba ...
until 2006, attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School.
* Thomas Edmondson (1792–1851) – businessman and inventor of the Edmondson railway ticket, was born in Lancaster.
*Robert Gillow
Robert Gillow (1704–1772) was an English furniture manufacturer, who founded Gillow & Co.
Early life
Robert Gillow was born on 2 August 1704 in Singleton, Lancashire to a prominent English recusant Roman Catholic family. He served an apprenti ...
(1704–1772) was the founder of Gillows of Lancaster, an English furniture manufacturer.
* Sir Ronald Halstead (1927–2021) – chair and Chief Executive of the Beecham Group
The Beecham Group plc was a British pharmaceutical company. It was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. Beecham, after having merged with American pharmaceutical company SmithKline Beckman to become SmithKline Beecham, merged with Glaxo We ...
in 1984–1985 and Deputy Chair of British Steel in 1986–1994 was born in Lancaster and attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School.
* James Williamson (1842–1930) – businessman and politician who created Williamson Park and Ashton memorial, was born in Lancaster and attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School.
Crime
* Lauren Jeska (born 1974) – a transgender athlete, was convicted of the attempted murder of an official, Ralph Knibbs. *Edward Stringer, (1819–1863) – convict and prospector, discovered theWalhalla, Victoria
Walhalla is a town in Victoria, Australia, founded as a gold-mining community in late 1862, and at its peak, home to around 4,000 residents. As of 2016, the town has a population of 20 permanent residents, though it has a large proportion of ...
goldfield in Australia.
*Buck Ruxton
Buck Ruxton (born Bukhtyar Chompa Rustomji Ratanji Hakim; 21 March 1899 – 12 May 1936) was an Indian-born physician convicted and subsequently hanged for the September 1935 murders of his common-law wife, Isabella Ruxton (née Kerr), and the f ...
(1899–1936) – marital murderer, resided and practised medicine at 2 Dalton Square.
Politics and journalism
*Henry D. Gilpin
Henry Dilworth Gilpin (April 14, 1801 – January 29, 1860) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the 14th Attorney General of the United States under President Martin Van Buren from 1840 to 1841. He served as the 2nd Solicitor of ...
(1801–1860) – Attorney General of the United States
The United States attorney general (AG) is the head of the United States Department of Justice, and is the chief law enforcement officer of the federal government of the United States. The attorney general serves as the principal advisor to the ...
, was born in Lancaster.
* Erik de Mauny (1920–1997) – foreign correspondent, died in Lancaster.
*Sir Lancelot Sanderson (1863–1944) – Conservative MP and judge, died in Lancaster.
Science and humanities
*J. L. Austin
John Langshaw Austin (26 March 1911 – 8 February 1960) was a British philosopher of language and leading proponent of ordinary language philosophy, perhaps best known for developing the theory of speech acts.
Austin pointed out that we u ...
(1911–1960) – philosopher and developer of the theory of speech acts
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
, was born in Lancaster.
*John Ambrose Fleming
Sir John Ambrose Fleming FRS (29 November 1849 – 18 April 1945) was an English electrical engineer and physicist who invented the first thermionic valve or vacuum tube, designed the radio transmitter with which the first transatlantic r ...
(1849–1945) – electrical engineer and physicist, was born in Lancaster.
*Edward Frankland
Sir Edward Frankland, (18 January 18259 August 1899) was an English chemist. He was one of the originators of organometallic chemistry and introduced the concept of combining power or valence. An expert in water quality and analysis, he was ...
(1825–1899) – chemist who originated the concept of valence, was born near Lancaster and educated at LRGS.
* Jaroslav Krejčí (1916–2014) – Czech-British sociologist, was a professor at the University of Lancaster
, mottoeng = Truth lies open to all
, established =
, endowment = £13.9 million
, budget = £317.9 million
, type = Public
, city = Bailrigg, City of Lancaster
, country = England
, coor =
, campus = Bailrigg
, faculty = ...
and died in Lancaster.
*Geoffrey Leech
Geoffrey Neil Leech FBA (16 January 1936 – 19 August 2014) was a specialist in English language and linguistics. He was the author, co-author, or editor of over 30 books and over 120 published papers. His main academic interests were English ...
(1936–2014) – linguistics researcher, was a professor at the University of Lancaster and died in Lancaster.
*Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Ow ...
(1804–1892) – biologist who coined the term "dinosaur", lived in Brock Street.
* William Turner (1832–1916) – anatomist and academic, was born in Lancaster.
*Paul Wellings
Professor Paul William Wellings CBE DL FRSN FRSA FAICD is an Australian/British ecologist and long serving university leader. He is notable for his past service as Vice-Chancellor of University of Wollongong (2012-21), Vice-Chancellor of Lancas ...
(born 1953) – ecologist, served as a professor and Vice-Chancellor of Lancaster University.
*Emily Williamson
Emily Williamson (''née'' Bateson; 17 April 1855 – 12 January 1936), was an English philanthropist. She was co-founder of the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) with Eliza Phillips in 1891. The society started as the Plumage L ...
(1855–1936), English philanthropist and co-founder of the RSPB, was born in Lancaster.
* Gavin Wood (born 1980) – co-founded and headed Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether (Abbreviation: ETH; sign: Ξ) is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. Among cryptocurrencies, ether is second only to bitcoin in market capita ...
.
Sport
* Michael Allen (1933–1995) – international cricketer, died in Lancaster. * Arthur Bate (1908–1993) – professionalfootballer
A football player or footballer is a sportsperson who plays one of the different types of football. The main types of football are association football, American football, Canadian football, Australian rules football, Gaelic football, rugb ...
, died in Lancaster.
* James Beattie (born 1978) – professional footballer, was born in Lancaster.
* Harold Douthwaite (1900–1972) – first-class cricketer, was born and died in Lancaster.
* Scott Durant (born 1988) – Olympic gold medal-winning rower, was a pupil at Lancaster Royal Grammar School
* Trevor Glover (born 1951) – first-class cricketer and rugby union player, was born in Lancaster.
* William Gregson (1877–1963) – first-class cricketer, died in Lancaster.
* Sarah Illingworth (born 1963) – international cricketer (New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
), was born in Lancaster.
* Edward Jackson (1849–1926) – first-class cricketer, was born in Lancaster.
* John Jackson (1841–1906) – first-class cricketer, was born in Lancaster.
*Scott McTominay
Scott Francis McTominay (born 8 December 1996) is a professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for club Manchester United and the Scotland national team.
McTominay is a graduate of the Manchester United youth academy and made his senio ...
(born 1996) – professional footballer currently with Manchester United
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
, was born in Lancaster.
* John Pinch (1870–1946) – international rugby union player, was born and died in Lancaster.
* Jason Queally (born 1970) – Olympic gold medal-winning cyclist, was a pupil at Lancaster Royal Grammar School.
*Matt Rogerson
Matt Rogerson (born 29 June 1993) is an English professional rugby union player. He currently captains London Irish in Premiership Rugby, the top flight of English rugby.
Professional career
Matt Rogerson signed his first professional contract ...
(born 1993) – professional Rugby Union player currently with London Irish
London Irish RFC is a professional rugby union club which competes in the Premiership, the top division of English rugby union. The club has also competed in the Anglo-Welsh Cup, the European Champions Cup and European Challenge Cup. Whil ...
, was born in Lancaster
*Fred Shinton
Frederick Shinton (7 March 1883 – 11 April 1923) was an English footballer who played at centre forward or inside right. He scored 103 goals from 163 appearances in the Football League.
Biography
Shinton was born in Wednesbury. He turned pr ...
(1883–1923) – professional footballer, died in Lancaster.
*Alan Warriner-Little
Alan Warriner-Little (born Warriner; 24 March 1962) is an English former professional darts player. Nicknamed The Iceman, he is a former World Grand Prix champion and a former runner-up at the World Professional Darts Championship.
Darts car ...
(born 1962) – champion darts player, was born in Lancaster.
Twinned cities
Lancaster is twinned with:retrieved 21 January 2019.
See also
*St John the Evangelist's Church, Lancaster
St John the Evangelist's Church is a redundant Anglican church in North Road, Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* listed building, and is under the care of the ...
* St Thomas' Church, Lancaster
* Christ Church, Lancaster
*Duke of Lancaster
The Dukedom of Lancaster is an English peerage merged into the crown. It was created three times in the Middle Ages, but finally merged in the Crown when Henry V succeeded to the throne in 1413. Despite the extinction of the dukedom the title ...
*Duchy of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is the private estate of the British sovereign as Duke of Lancaster. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income to the sovereign. The estate consists of a portfolio of lands, properti ...
* Lancaster power stations
*Lancaster Bomber
The Avro Lancaster is a British World War II, Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the S ...
References
Bibliography
* *External links
Lancaster City Council
– Homepage of Lancaster City Council
– Tourism Website for Lancaster {{Authority control County towns in England Towns in Lancashire Roman fortifications in England Unparished areas in Lancashire Geography of the City of Lancaster