Lancaster, England on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lancaster (, ) is a city and the county town of
 A Roman fort was built by the end of the 1st century CE on the hill where
A Roman fort was built by the end of the 1st century CE on the hill where
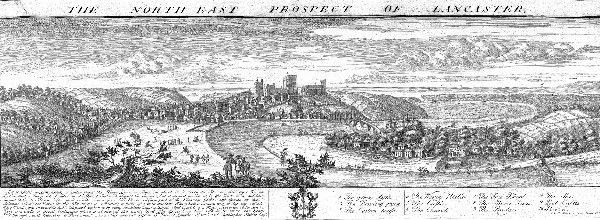 After the Norman conquest of England in 1066, Lancaster fell under the control of
After the Norman conquest of England in 1066, Lancaster fell under the control of 
 The traditional emblem of the House of Lancaster is the
The traditional emblem of the House of Lancaster is the  Lancaster gained a first charter in 1193 as a
Lancaster gained a first charter in 1193 as a
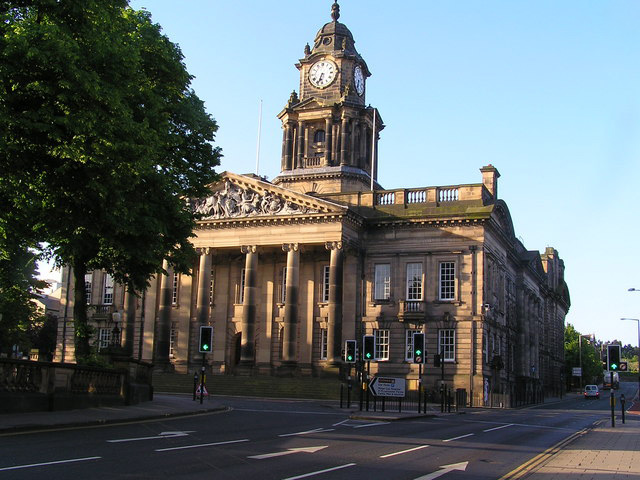 The former
The former
 The
The
 Lancaster is served by the West Coast Main Line, which runs through Lancaster railway station. The station was formerly named Lancaster Castle, to differentiate it from Lancaster Green Ayre railway station, Lancaster Green Ayre on the "Little" North Western Railway, Leeds–Morecambe line, which closed in 1966. There are through train services to and from Euston railway station, London, Glasgow Central railway station, Glasgow, Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Edinburgh, Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, Manchester Piccadilly railway station, Manchester, Leeds railway station, Leeds and Barrow-in-Furness railway station, Barrow-in-Furness, with a local service to Morecambe railway station, Morecambe.
The long-term aim of the city council is to open a railway station serving the university and south Lancaster, although this is not feasible in the short or medium term with current levels of demand. The Caton–Morecambe section of the former North Western railway is now used as a cycle path.
Lancaster is served by the West Coast Main Line, which runs through Lancaster railway station. The station was formerly named Lancaster Castle, to differentiate it from Lancaster Green Ayre railway station, Lancaster Green Ayre on the "Little" North Western Railway, Leeds–Morecambe line, which closed in 1966. There are through train services to and from Euston railway station, London, Glasgow Central railway station, Glasgow, Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Edinburgh, Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, Manchester Piccadilly railway station, Manchester, Leeds railway station, Leeds and Barrow-in-Furness railway station, Barrow-in-Furness, with a local service to Morecambe railway station, Morecambe.
The long-term aim of the city council is to open a railway station serving the university and south Lancaster, although this is not feasible in the short or medium term with current levels of demand. The Caton–Morecambe section of the former North Western railway is now used as a cycle path.
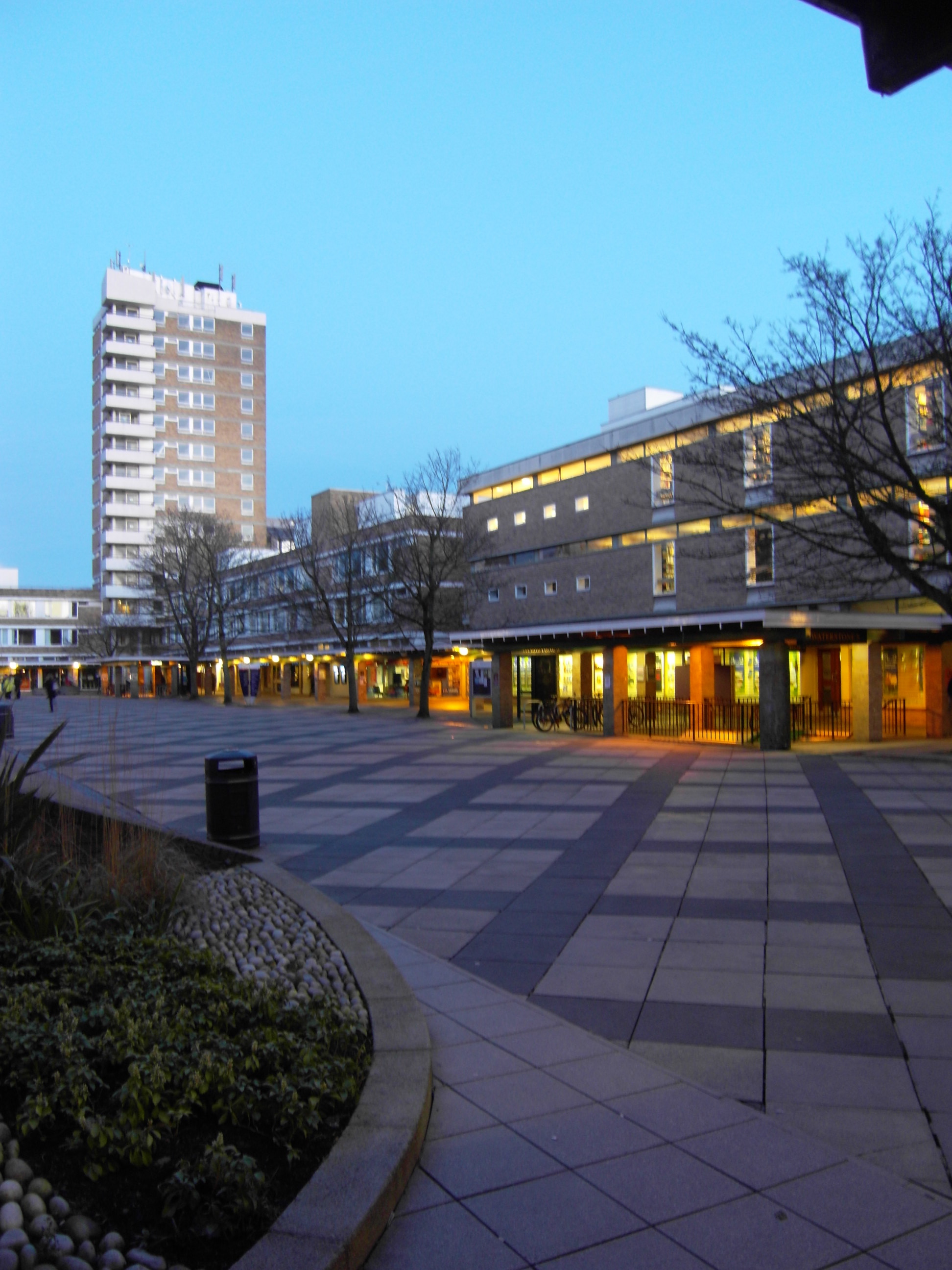

 At Bailrigg south of the city is Lancaster University, a research university founded in the 1960s with an annual income of about £319 million, 3,000 staff and 17,415 registered students. Its business school is one of two in the country to gain a six-star Research Assessment Exercise, research rating. Its physics department Research Assessment Exercise, rated #1 in the United Kingdom in 2008. InfoLab21 at the university is a Centre of Excellence for Information and Communication Technologies. LEC (Lancaster Environment Centre) has over 200 staff and shares premises with the government-funded Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, CEH. In 2017 it was rated 21st nationally for research in The Times Higher league table. For teaching, it gained the highest Gold ranking for quality in the 2017 government Teaching Excellence Framework, TEF, and in 2018 was ranked 9th for its teaching by ''The Independent'' and 9th by ''The Guardian''. ''The Times'' Higher placed it 137th worldwide for research and 58th worldwide for arts and humanities. Lancaster University was named International University of the Year by ''The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide'' in 2020. It has campuses in Malaysia, China and Ghana and plans one in Leipzig, Germany.
Lancaster is also home to a campus of the
At Bailrigg south of the city is Lancaster University, a research university founded in the 1960s with an annual income of about £319 million, 3,000 staff and 17,415 registered students. Its business school is one of two in the country to gain a six-star Research Assessment Exercise, research rating. Its physics department Research Assessment Exercise, rated #1 in the United Kingdom in 2008. InfoLab21 at the university is a Centre of Excellence for Information and Communication Technologies. LEC (Lancaster Environment Centre) has over 200 staff and shares premises with the government-funded Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, CEH. In 2017 it was rated 21st nationally for research in The Times Higher league table. For teaching, it gained the highest Gold ranking for quality in the 2017 government Teaching Excellence Framework, TEF, and in 2018 was ranked 9th for its teaching by ''The Independent'' and 9th by ''The Guardian''. ''The Times'' Higher placed it 137th worldwide for research and 58th worldwide for arts and humanities. Lancaster University was named International University of the Year by ''The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide'' in 2020. It has campuses in Malaysia, China and Ghana and plans one in Leipzig, Germany.
Lancaster is also home to a campus of the
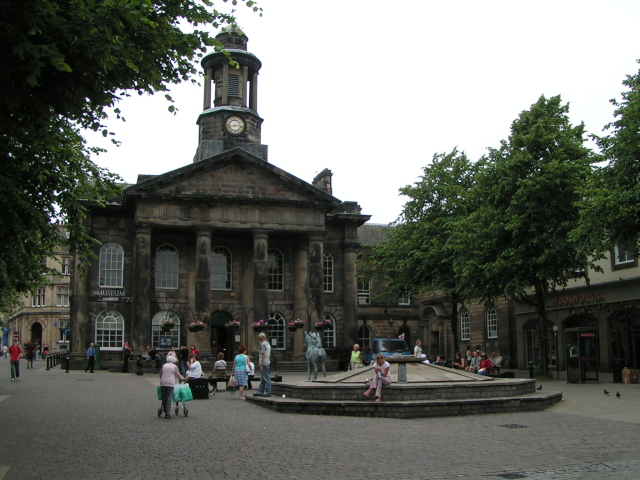


 Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of Georgian architecture.
Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of Georgian architecture.  Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Nuffield Theatre, Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Peter Scott Gallery, Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Lancaster Concert Series, Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months Williamson Park hosts outdoor performances, including a Dukes "Play in the Park", which over the past 26 years has attracted 460,000 people, as the UK's biggest outdoor walkabout theatre event.
Lancaster is known as the Northern City of Ale, with almost 30 pubs serving cask ale. The pubs include the ''White Cross'', ''Three Mariners'', ''Borough'' and ''Water Witch''. There are two cask ale breweries: Lancaster Brewery and a microbrewery run by the Borough. There is a local CAMRA (Campaign for Real Ale) branch at Lunesdale.
The Grand Theatre (Lancaster), Lancaster Grand Theatre and Duke's Playhouse, the Dukes are notable venues for live performance, as are the Yorkshire House (currently closed), Jailors Barrel, The John O' Gaunt and The Bobbin. Throughout the year events are held in and around the city, such as the Lancaster Music Festival, Lancaster Jazz Festival, and Chinese New Year celebrations in the city centre.
Every November the city hosts a daylight and art festival entitled "Light Up Lancaster", which includes a prominent fireworks display.
Lancaster still has two city-centre cinemas; Vue and the Dukes playhouse. The 1930s art deco ''Regal Cinema'' closed in 2006. The Gregson Centre is also known for small film screenings and cultural events.
Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Nuffield Theatre, Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Peter Scott Gallery, Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Lancaster Concert Series, Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months Williamson Park hosts outdoor performances, including a Dukes "Play in the Park", which over the past 26 years has attracted 460,000 people, as the UK's biggest outdoor walkabout theatre event.
Lancaster is known as the Northern City of Ale, with almost 30 pubs serving cask ale. The pubs include the ''White Cross'', ''Three Mariners'', ''Borough'' and ''Water Witch''. There are two cask ale breweries: Lancaster Brewery and a microbrewery run by the Borough. There is a local CAMRA (Campaign for Real Ale) branch at Lunesdale.
The Grand Theatre (Lancaster), Lancaster Grand Theatre and Duke's Playhouse, the Dukes are notable venues for live performance, as are the Yorkshire House (currently closed), Jailors Barrel, The John O' Gaunt and The Bobbin. Throughout the year events are held in and around the city, such as the Lancaster Music Festival, Lancaster Jazz Festival, and Chinese New Year celebrations in the city centre.
Every November the city hosts a daylight and art festival entitled "Light Up Lancaster", which includes a prominent fireworks display.
Lancaster still has two city-centre cinemas; Vue and the Dukes playhouse. The 1930s art deco ''Regal Cinema'' closed in 2006. The Gregson Centre is also known for small film screenings and cultural events.
 Lancaster's main Association football, football team, Lancaster City F.C., Lancaster City, plays in the Northern Premier League Premier Division having won promotion as champions of Division One North in 2016–2017. It plays its home matches at the Giant Axe, which can take 3,500 (513 seated) and was formed in 1911 originally as Lancaster Town F.C. Lancaster City has been seven-times Lancashire FA Challenge cup winners and in 2010-11 won the Northern Premier League President's cup for a second time. Lancaster John O' Gaunt Rowing Club is the fifth-oldest surviving rowing club in the UK, outside the universities. It competes nationally at regattas and heads races run by British Rowing. The clubhouse stands next to the weir at Skerton.
The city entertains contestants in the ''Lancaster International Youth Games'', a multi-sport 'Olympic' style event featuring competitors from Lancaster's twin towns: Rendsburg (Germany), Perpignan (France), Viana do Castelo Municipality, Viana do Castelo (Portugal), Aalborg (Denmark), Almere (Netherlands), Lublin (Poland) and Växjö (Sweden).
Lancaster Cricket Club is sited near the
Lancaster's main Association football, football team, Lancaster City F.C., Lancaster City, plays in the Northern Premier League Premier Division having won promotion as champions of Division One North in 2016–2017. It plays its home matches at the Giant Axe, which can take 3,500 (513 seated) and was formed in 1911 originally as Lancaster Town F.C. Lancaster City has been seven-times Lancashire FA Challenge cup winners and in 2010-11 won the Northern Premier League President's cup for a second time. Lancaster John O' Gaunt Rowing Club is the fifth-oldest surviving rowing club in the UK, outside the universities. It competes nationally at regattas and heads races run by British Rowing. The clubhouse stands next to the weir at Skerton.
The city entertains contestants in the ''Lancaster International Youth Games'', a multi-sport 'Olympic' style event featuring competitors from Lancaster's twin towns: Rendsburg (Germany), Perpignan (France), Viana do Castelo Municipality, Viana do Castelo (Portugal), Aalborg (Denmark), Almere (Netherlands), Lublin (Poland) and Växjö (Sweden).
Lancaster Cricket Club is sited near the
Lancaster City Brass
which is the oldest remaining brass band in the city celebrating its 75th anniversary in 2021 an
Batala
who recently completed 15 years of Samba Regge drumming Lancaster has been producing successful bands and musicians since the 1990s, notably the drummer Keith Baxter (drummer), Keith Baxter of 3 Colours Red and folk-metal band Skyclad, who also featured Lancaster guitarist Dave Pugh, and the thrash metal band D.A.M., who were all from Lancaster, recording two albums for the Noise International label, with Dave Pugh appearing on the second. The all-girl punk-rock band Angelica (band), Angelica used the Lancaster Musicians' Co-operative, the main rehearsal and recording studio in the area. The city has also produced many other musicians, including singer and songwriter John Waite, who first became known as lead singer of The Babys and had a solo #1 hit in the US, "Missing You (John Waite song), Missing You". As part of the band Bad English, John Waite also had a #1 hit in the Billboard top hundred in the 1970s called "When I See You Smile". Additionally, Paul James, better known as The Rev, former guitarist of English punk band Towers of London (band), Towers of London who is now in the band Day 21 and plays guitar live on tour for The Prodigy; Chris Acland, drummer of the early 1990s shoegaze band Lush (band), Lush; Tom English, drummer of North East indie band Maxïmo Park and Steve Kemp (musician), Steve Kemp, drummer of the indie band Hard-Fi. Lancaster continues to produce bands and musicians such as singer-songwriter Jay Diggins, and acts like The Lovely Eggs, receiving considerable national radio play and press coverage in recent years. More recently, Lancaster locals Massive Wagons signed to Nottingham-based independent label Earache Records. The city is also the founding home of the dance-music sound systems Rhythm Method and ACME Bass Company. Pioneers in the field of the free party, these two systems and others forged strong representations of the genre in the North West of England in the 1990s. Since 2006, Lancaster Library has hosted regular music events under the ''Get it Loud in Libraries'' initiative. Musicians such as The Wombats, The Thrills, Kate Nash, Adele and Bat for Lashes have taken part. Get It Loud in Libraries has gained national exposure, featuring on The One Show on BBC1 and having gigs reviewed in ''Observer Music Monthly'', ''NME'' and ''Art Rocker''. Notable popular music venues include Duke's Playhouse, The Dukes, Grand Theatre (Lancaster), The Grand Theatre, The Gregson Centre, The Bobbin, The Pub and The Yorkshire House, which since 2006 has hosted such acts as John Renbourn, Polly Paulusma, Marissa Nadler, Baby Dee, Diane Cluck, Alasdair Roberts (musician), Alasdair Roberts, Jesca Hoop, Lach (musician), Lach, Jack Lewis (musician), Jack Lewis, Tiny Ruins and 2008 Mercury Prize nominees Rachel Unthank and the Winterset. Other venues include the Dalton Rooms, the Park Hotel and The Hall, China Street. These host Lancaster's diverse music culture, such as the Lancaster Speakeasy or Stylus. The Lancaster Jazz and Lancaster Music Festivals are respectively held every September and October, at venues throughout the city. In 2013 the headline jazz act was The Neil Cowley Trio, performing at The Dukes, whilst one of the Lancaster Music Festival headline acts was Jay Diggins at the Dalton Rooms.
 *
*
Lancaster City Council, Twin Towns
retrieved 21 January 2019.
Lancaster City Council
– Homepage of Lancaster City Council
Regional Europe - LancasterVisit Lancaster Website
– Tourism Website for Lancaster {{Authority control Lancaster, Lancashire, County towns in England Towns in Lancashire Roman fortifications in England Unparished areas in Lancashire Geography of the City of Lancaster
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
, England, standing on the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
. Its population of 52,234 compares with one of 138,375 in the wider City of Lancaster
The City of Lancaster () is a local government district of Lancashire, England, with the status of a city and non-metropolitan district. It is named after its largest settlement, Lancaster, but covers a far larger area, which includes the to ...
local government district. The House of Lancaster was a branch of the English royal family. The Duchy of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is the private estate of the British sovereign as Duke of Lancaster. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income to the sovereign. The estate consists of a portfolio of lands, properti ...
still holds large estates on behalf of Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person t ...
, who is also Duke of Lancaster
The Dukedom of Lancaster is an English peerage merged into the crown. It was created three times in the Middle Ages, but finally merged in the Crown when Henry V succeeded to the throne in 1413. Despite the extinction of the dukedom the title ...
. Its long history is marked by Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
, Lancaster Priory Church, Lancaster Cathedral and the Ashton Memorial
The Ashton Memorial is a folly in Williamson Park, Lancaster, Lancashire, England built between 1907 and 1909 by the millionaire industrialist Lord Ashton in memory of his second wife, Jessy, at a cost of £87,000 (equivalent to £ in ).
Desc ...
. It is the seat of Lancaster University and has a campus of the University of Cumbria
The University of Cumbria is a public university in Cumbria, with its headquarters in Carlisle and other major campuses in Lancaster, Ambleside, and London. It has roots extending back to the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts, establis ...
. The Port of Lancaster
The Port of Lancaster was located at the lowest crossing point on the River Lune and constitutes the central element of maritime Lancaster in north-west England. It dates back to Roman times, but is now based at Glasson Dock.
History Early origin ...
played a big role in the city's growth, but for many years the outport
An outport is any port considered secondary to a main port (including a provincial one as opposed to a capital one), and often (especially) a small port built to support the commercial operations of a large port. The Port of Tilbury from the Port ...
of Glasson Dock
Glasson Dock, also known as Glasson, is a village in Lancashire, England, south of Lancaster at the mouth of the River Lune. In 2011, it had a population of around 600.
History
Glasson was originally a small farming and fishing community (whi ...
has become the main shipping facility.
History
The name of the city first appeared in theDomesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
of 1086, as ''Loncastre'', where "Lon" refers to the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
and "castre" (from the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
''cæster'' and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''castrum'' for "fort") to the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
fort that stood on the site.
Roman and Saxon eras
Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
now stands, possibly as early as the 60s CE, based on Roman coin evidence. Coin evidence also suggests that the fort was not continuously inhabited in its early years. It was rebuilt in stone about 102 CE. The fort name is known only in a shortened form; the only evidence is a Roman milestone found 4 miles outside Lancaster, with an inscription ending L MP IIII, meaning "from L – 4 miles, and that its name began with an L. The fort was perhaps named Lunium.
Roman baths were found in 1812 and can be seen near the junction of Bridge Lane and Church Street. There was presumably a bath-house with the 4th-century fort. The Roman baths incorporated a reused inscription of the Gallic Emperor Postumus
Marcus Cassianius Latinius Postumus was a Roman commander of Batavian origin, who ruled as Emperor of the splinter state of the Roman Empire known to modern historians as the Gallic Empire. The Roman army in Gaul threw off its allegiance to Ga ...
, dating from 262 to 266 CE. The 3rd-century fort was garrisoned by the ''ala Sebosiana'' and ''numerus Barcariorum Tigrisiensium''.
The ancient ''Wery Wall'' was identified in 1950 as the north wall of the 4th-century fort, which was a drastic remodelling of the 3rd-century one, while retaining the same orientation. The later fort is the only example in north-west Britain of a 4th-century type, with massive curtain-wall and projecting bastions typical of the ''Saxon Shore'' or Wales. Extension of the technique as far north as Lancaster shows that the coast between Cumberland and North Wales was not left defenceless after the west-coast attacks and the disaster in the Carausian Revolt of 296 CE, which followed from those under Albinus in 197 CE.
The fort at its largest extent covered . Evidence suggests that it stayed in use until the end of Roman occupation of Britain. Church Street and some of St Leonard's Gate probably mark the initial course of the Roman road up the valley to the fort at Over Burrow.
Little is known of Lancaster from the end of Roman rule to the early 5th century and the Norman Conquest of the late 11th century. Despite a lack of documentation for the period, it is thought that Lancaster remained inhabited. It lay on the fringes of the kingdoms of Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879) Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era= Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ...
and Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
and over time may have passed from one to the other. Archaeological evidence suggests there was a monastery on or near the site of today's Lancaster Priory
Lancaster Priory, formally the Priory Church of St Mary, is the Church of England parish church of the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is located near Lancaster Castle and since 1953 has been designated a Grade I listed building. ...
by the 700s or 800s. The Anglo-Saxon runic
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write various Germanic languages (with some exceptions) before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised ...
"Cynibald's cross" found at the Priory in 1807 is thought to date from the late 9th century. Lancaster was probably one of several abbeys founded under Wilfrid
Wilfrid ( – 709 or 710) was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Francia, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and ...
.
Medieval
 After the Norman conquest of England in 1066, Lancaster fell under the control of
After the Norman conquest of England in 1066, Lancaster fell under the control of William I
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
, as stated in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
of 1086, which has the earliest known mention of Lancaster as such in any document. The founding Priory charter dated 1094 is the first known document specific to Lancaster.White, p. 57. By this time William had passed Lancaster and its surroundings to Roger de Poitou
Roger the Poitevin (Roger de Poitou) was born in Normandy in the mid-1060s and died before 1140. He was an Anglo-Norman aristocrat, possessing large holdings in both England and through his marriage in France.
He was the third son of Roger of Mo ...
. The document also suggests the monastery was refounded as a parish church some time before 1066.
Lancaster became a borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
in 1193 under King Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was ...
. Its first charter, dated 12 June 1193, was from John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, Count of Mortain
The County of Mortain was a medieval county in France centered on the town of Mortain. A choice landholding, usually either kept within the family of the duke of Normandy (or the king of France) or granted to a noble in return for service and fa ...
, who later became King of England.

Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
, partly built in the 13th century and enlarged by Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
, stands on the site of a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
garrison. During The Great Raid of 1322
The Great Raid of 1322 was a major raid carried out by Robert the Bruce, during the First Scottish War of Independence, on Northern England between 30 September and 2 November 1322, resulting in the Battle of Old Byland. Numerous raids began ...
, damage was done to the castle by Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (Scottish Gaelic: ''Raibeart an Bruis''), was King of Scots from 1306 to his death in 1329. One of the most renowned warriors of his generation, Robert eventual ...
, though it resisted the attack and was restored and strengthened by John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399) was an English royal prince, military leader, and statesman. He was the fourth son (third to survive infancy as William of Hatfield died shortly after birth) of King Edward ...
, who added much of the Gateway Tower and a turret on the keep or Lungess Tower, which has been named "John o' Gaunt's Chair". In 1322 the Scots burnt the town. It was rebuilt but removed from its position on the hill to the slope and foot. Again in 1389, after the Battle of Otterburn
The Battle of Otterburn took place according to Scottish sources on 5 August 1388, or 19 August according to English sources, as part of the continuing border skirmishes between the Scots and English.
The best remaining record of the bat ...
, it was destroyed by the Scots. Lancaster Castle is known as the site of the Pendle witch trials
The trials of the Pendle witches in 1612 are among the most famous witch trials in English history, and some of the best recorded of the 17th century. The twelve accused lived in the area surrounding Pendle Hill in Lancashire, and were charged ...
in 1612. It was said that the court based in the castle (the Lancaster Assizes) sentenced more people to be hanged
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging i ...
than any other in the country outside London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, earning Lancaster the nickname, ''"the Hanging Town"''. It also figured prominently in the suppression of Catholicism during the Reformation – at least eleven Catholic priests were executed and a memorial to them as the Lancaster Martyrs
During the English Reformation, a number of believers were executed at Lancaster in England as a consequence of their Catholic faith. They are commonly referred to as the Lancaster Martyrs and are commemorated locally by the Lancaster Martyrs M ...
stands by the city centre.
 The traditional emblem of the House of Lancaster is the
The traditional emblem of the House of Lancaster is the Red Rose of Lancaster
The Red Rose of Lancaster (blazoned: ''a rose gules'') was the heraldic badge adopted by the royal House of Lancaster in the 14th century. In modern times it symbolises the county of Lancashire. The exact species or cultivar which it represents i ...
, similar to that of the House of York with a white rose. The names derive from emblems of the Royal Duchies of Lancaster and York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
in the 15th century. This erupted into a civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
over rival claims to the throne during the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
.
More recently the term ''"Wars of the Roses"'' has been applied to rivalry in sports between teams from Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
. It is also applied to the annual Roses Tournament
The Roses Tournament is an annual sports competition between Lancaster University and the University of York in England, often described as the largest inter-university sports tournament in Europe. It is organised by their respective Students' ...
between Lancaster and York universities.
market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
and borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
, but had to await city status until 1937. Many central buildings and ones along St George's Quay date from the 18th century, as the port became one of the UK's busiest and the fourth most important in the UK slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. Among prominent Lancaster slave-traders were Dodshon Foster, Thomas Hinde
Doctor Thomas Hinde (July 10, 1737 – September 28, 1828) was Northern Kentucky's first physician, a member of the British Royal Navy, an American Revolutionary, personal physician to Patrick Henry, and treated General Wolfe when he died in ...
and his eponymous son. However, Lancaster's role as a major port ceased as the river began to silt up. Morecambe, Glasson Dock
Glasson Dock, also known as Glasson, is a village in Lancashire, England, south of Lancaster at the mouth of the River Lune. In 2011, it had a population of around 600.
History
Glasson was originally a small farming and fishing community (whi ...
and Sunderland Point took over as outports for brief periods. Heysham Port
Heysham Port is the port of Heysham, Lancashire, England. It is served by Heysham Port railway station.
History
In 1891, the Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844. The Midland was ...
has now eclipsed all those on the Lune.
Recent history
Lancaster is mainly a service-oriented city. Products include animal feed, textiles,chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
, livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animal ...
, paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distrib ...
, synthetic fibre
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants (like cotton) ...
, farm machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they ...
, HGV trailers
Trailer may refer to: a
Transportation
* Trailer (vehicle), an unpowered vehicle pulled by a powered vehicle
** Bicycle trailer, a wheeled frame for hitching to a bicycle to tow cargo or passengers
** Full-trailer
** Semi-trailer
**Horse trail ...
and mineral fibres. In recent years, a high-tech sector has emerged from Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of Data (computing), data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information te ...
and Communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
firms investing in the city.
A permanent military presence was built up with the completion of Bowerham Barracks
Bowerham Barracks was a military installation in Lancaster.
History
The barracks were built in the Fortress Gothic Revival Style between 1876 and 1880 on the former Bowerham Estate as the depot for the two battalions of the 4th (King's Own) R ...
in 1880. The Phoenix Street drill hall was completed in 1894.
In March 2004, Lancaster was granted Fairtrade City
The Fair Trade Towns campaign is the result of a grass-roots citizens movement that started in the UK in 2001 (see below). It allows citizens to get together in order to self-proclaim their town (or other local geographical area) as a region that ...
status.
Lancaster was home to the European headquarters of Reebok
Reebok International Limited () is an American fitness footwear and clothing manufacturer that is a part of Authentic Brands Group. It was established in England in 1958 as a companion company to J.W. Foster and Sons, a sporting goods company ...
. After merging with Adidas, Reebok moved to Bolton
Bolton (, locally ) is a large town in Greater Manchester in North West England, formerly a part of Lancashire. A former mill town, Bolton has been a production centre for textiles since Flemish weavers settled in the area in the 14th ...
and Stockport in 2007.
In May 2015 Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
visited the castle for commemorations for the 750th anniversary of the creation of the Duchy of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is the private estate of the British sovereign as Duke of Lancaster. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income to the sovereign. The estate consists of a portfolio of lands, properti ...
.
Governance
 The former
The former City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and Municipal Borough
Municipal boroughs were a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1835 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in S ...
of Lancaster and the Municipal Borough of Morecambe and Heysham
Morecambe and Heysham was a municipal borough in Lancashire, England. It was formed in 1928 by the merging of Morecambe Municipal Borough and Heysham Urban District, and abolished in 1974 when it was absorbed into the City of Lancaster
The ...
along with other authorities merged in 1974 to form the City of Lancaster
The City of Lancaster () is a local government district of Lancashire, England, with the status of a city and non-metropolitan district. It is named after its largest settlement, Lancaster, but covers a far larger area, which includes the to ...
district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
within the shire county
A non-metropolitan county, or colloquially, shire county, is a county-level entity in England that is not a metropolitan county. The counties typically have populations of 300,000 to 1.8 million. The term ''shire county'' is, however, an unoffi ...
of Lancashire. This was given city status in the United Kingdom
City status in the United Kingdom is granted by the monarch of the United Kingdom to a select group of communities. , there are 76 cities in the United Kingdom—55 in England, seven in Wales, eight in Scotland, and six in Northern Ireland. ...
and Lancaster City Council is the local governing body for the district. Lancaster is an unparished area
In England, an unparished area is an area that is not covered by a civil parish (the lowest level of local government, not to be confused with an ecclesiastical parish). Most urbanised districts of England are either entirely or partly unpa ...
and has no separate council. It is divided into wards such as Bulk, Castle, Ellel, John O'Gaunt (named after John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399) was an English royal prince, military leader, and statesman. He was the fourth son (third to survive infancy as William of Hatfield died shortly after birth) of King Edward ...
), Scotforth East, Scotforth West, Skerton East, Skerton West, and University and Scotforth Rural.
Political representation
Most of the city lies in the Lancaster and Fleetwood constituency for elections of Members of Parliament to theHouse of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. The current MP for Lancaster and Fleetwood is Cat Smith
Catherine Jane Smith (born 16 June 1985) is a British politician who has served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Lancaster and Fleetwood since 2015. A member of the Labour Party, she was a member of the shadow cabinets of Jeremy Corbyn and Ke ...
of the Labour Party. The Skerton part of the city lies in the Morecambe and Lunesdale constituency represented by David Morris of the Conservative Party.
Before Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC ...
, it was in the North West England European Parliamentary Constituency.
In the late 1990s and early first decade of the 21st century, the city council was under the control of the Morecambe Bay Independents
The Morecambe Bay Independents (MBIs) is a local political party in Morecambe, Lancashire. The group ran Lancaster City Council from 1999 to 2003, and successfully campaigned in 2005 for the creation of Morecambe Town Council.
History
Earl ...
(MBIs), who campaigned for an independent Morecambe council. In 2003, their influence waned and Labour became the largest party on the council. They formed a coalition with the Liberal Democrats and Greens. At the May 2007 local elections, Labour lost ground to the Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combi ...
s in Lancaster and the MBIs in Morecambe, resulting in no overall control, with all parties represented in a PR administration. The 2011 elections saw Labour emerge as the largest party. They reached a joint administrative arrangement with the Greens.
The 2019 Lancaster City Council election
Elections to Lancaster City Council were held on 2 May 2019 at the same time as other 2019 United Kingdom local elections. Local elections are held every four years with all councillors up for election in multi-member electoral wards.
Co ...
results put no party in overall control. The council is run by a coalition of Labour, Green, Eco-Socialist Independent and Liberal Democrat councillors, supported by the Independent Group, with Conservatives and MBIs in opposition. The cabinet consists of 4 Labour, 4 Green, 1 Eco-Socialist, 1 Independent Group. At 10 seats, Lancaster has one of the country's largest Green Party representations.
Geography
Lancaster is Lancashire's northernmost city, three miles () inland fromMorecambe Bay
Morecambe Bay is a large estuary in northwest England, just to the south of the Lake District National Park. It is the largest expanse of intertidal mudflats and sand in the United Kingdom, covering a total area of . In 1974, the second larges ...
on the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
(from which comes its name), and the Lancaster Canal
The Lancaster Canal is a canal in North West England, originally planned to run from Westhoughton in Lancashire to Kendal in south Cumbria ( historically in Westmorland). The section around the crossing of the River Ribble was never complete ...
. It becomes hillier from the Lune Valley eastwards, with Williamson Hill in the north-west a notable peak at .
Built-up area
Lancaster, Morecambe andHeysham
Heysham ( ) is a coastal town in Lancashire, England, overlooking Morecambe Bay. It is a ferry port, with services to the Isle of Man and Ireland, and the site of two nuclear power stations.
Demography
Administratively, Heysham is part of th ...
have been identified by the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for t ...
as forming the Lancaster/Morecambe Built-up area, with a population of 97,150 in 2011.
Green belt
There is a small portion of green belt on the northern fringe of Lancaster, covering the area into Carnforth and helping to prevent further urban expansion towards nearby Morecambe, Hest Bank, Slyne and Bolton-le-Sands.Transport
Road
 The
The M6 motorway
The M6 motorway is the longest motorway in the United Kingdom. It is located entirely within England, running for just over from the Midlands to the border with Scotland. It begins at Junction 19 of the M1 and the western end of the A14 at ...
passes to the east of Lancaster with junctions 33 and 34 to the south and north. The A6 road This is a list of roads designated A6.
* A006 road (Argentina), a road connecting Las Cuevas with the Christ the Redeemer monument in the border between Argentina and Chile
* ''A6 highway (Australia)'' may refer to :
** A6 (Sydney), a road connec ...
, one of the main historic north–south roads in England, leads south to Preston, Chorley and Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
and north to Carnforth
Carnforth is a market town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster in Lancashire, England, situated at the north-east end of Morecambe Bay. The parish of Carnforth had a population of 5,560 in the 2011 census, an increase from the 5,350 reco ...
, Kendal, Penrith and Carlisle. It currently runs from Luton, Bedfordshire, to Carlisle, Cumbria
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City ...
. In passing through Lancaster it gives access to nearby Carnforth
Carnforth is a market town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster in Lancashire, England, situated at the north-east end of Morecambe Bay. The parish of Carnforth had a population of 5,560 in the 2011 census, an increase from the 5,350 reco ...
, Kendal and Garstang. The Heysham to M6 Link Road, Bay Gateway opened in 2016, linking Heysham and the M6 with a dual carriageway.
Lancaster's main bus operator is Stagecoach Cumbria & North Lancashire, with a network of services from Lancaster bus station throughout the Lancaster District and frequent services to more distant places such as Kendal, Keswick, Cumbria, Keswick, Kirkby Lonsdale, Preston and Blackpool. There are frequent buses to Lancaster University, with the No. 1 and No. 1A services running every 10–15 minutes using double-deckers, with less frequent services 4, 41 and 42.
Other routes are covered by Kirkby Lonsdale Coach Hire, including the 582 to Kirkby Lonsdale, Settle and Skipton and the 89 to Knott End-on-Sea.
Rail
 Lancaster is served by the West Coast Main Line, which runs through Lancaster railway station. The station was formerly named Lancaster Castle, to differentiate it from Lancaster Green Ayre railway station, Lancaster Green Ayre on the "Little" North Western Railway, Leeds–Morecambe line, which closed in 1966. There are through train services to and from Euston railway station, London, Glasgow Central railway station, Glasgow, Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Edinburgh, Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, Manchester Piccadilly railway station, Manchester, Leeds railway station, Leeds and Barrow-in-Furness railway station, Barrow-in-Furness, with a local service to Morecambe railway station, Morecambe.
The long-term aim of the city council is to open a railway station serving the university and south Lancaster, although this is not feasible in the short or medium term with current levels of demand. The Caton–Morecambe section of the former North Western railway is now used as a cycle path.
Lancaster is served by the West Coast Main Line, which runs through Lancaster railway station. The station was formerly named Lancaster Castle, to differentiate it from Lancaster Green Ayre railway station, Lancaster Green Ayre on the "Little" North Western Railway, Leeds–Morecambe line, which closed in 1966. There are through train services to and from Euston railway station, London, Glasgow Central railway station, Glasgow, Edinburgh Waverley railway station, Edinburgh, Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham, Manchester Piccadilly railway station, Manchester, Leeds railway station, Leeds and Barrow-in-Furness railway station, Barrow-in-Furness, with a local service to Morecambe railway station, Morecambe.
The long-term aim of the city council is to open a railway station serving the university and south Lancaster, although this is not feasible in the short or medium term with current levels of demand. The Caton–Morecambe section of the former North Western railway is now used as a cycle path.
Water and air
Historically, thePort of Lancaster
The Port of Lancaster was located at the lowest crossing point on the River Lune and constitutes the central element of maritime Lancaster in north-west England. It dates back to Roman times, but is now based at Glasson Dock.
History Early origin ...
gained importance in the 18th century. In 1750 the Lancaster Port Commission was established to develop the port. However, in more recent years, shipping visits Glasson Dock
Glasson Dock, also known as Glasson, is a village in Lancashire, England, south of Lancaster at the mouth of the River Lune. In 2011, it had a population of around 600.
History
Glasson was originally a small farming and fishing community (whi ...
, where the Port commission is now based.
The Lancaster Canal
The Lancaster Canal is a canal in North West England, originally planned to run from Westhoughton in Lancashire to Kendal in south Cumbria ( historically in Westmorland). The section around the crossing of the River Ribble was never complete ...
and River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
pass through the city.
The nearest airports are Manchester Airport, Manchester, Liverpool John Lennon Airport, Liverpool and Blackpool Airport, Blackpool.
Cycling
In 2005, Lancaster was one of six English towns chosen to be Cycling town, cycling demonstration towns to promote cycling as a means of transport.Education
 At Bailrigg south of the city is Lancaster University, a research university founded in the 1960s with an annual income of about £319 million, 3,000 staff and 17,415 registered students. Its business school is one of two in the country to gain a six-star Research Assessment Exercise, research rating. Its physics department Research Assessment Exercise, rated #1 in the United Kingdom in 2008. InfoLab21 at the university is a Centre of Excellence for Information and Communication Technologies. LEC (Lancaster Environment Centre) has over 200 staff and shares premises with the government-funded Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, CEH. In 2017 it was rated 21st nationally for research in The Times Higher league table. For teaching, it gained the highest Gold ranking for quality in the 2017 government Teaching Excellence Framework, TEF, and in 2018 was ranked 9th for its teaching by ''The Independent'' and 9th by ''The Guardian''. ''The Times'' Higher placed it 137th worldwide for research and 58th worldwide for arts and humanities. Lancaster University was named International University of the Year by ''The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide'' in 2020. It has campuses in Malaysia, China and Ghana and plans one in Leipzig, Germany.
Lancaster is also home to a campus of the
At Bailrigg south of the city is Lancaster University, a research university founded in the 1960s with an annual income of about £319 million, 3,000 staff and 17,415 registered students. Its business school is one of two in the country to gain a six-star Research Assessment Exercise, research rating. Its physics department Research Assessment Exercise, rated #1 in the United Kingdom in 2008. InfoLab21 at the university is a Centre of Excellence for Information and Communication Technologies. LEC (Lancaster Environment Centre) has over 200 staff and shares premises with the government-funded Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, CEH. In 2017 it was rated 21st nationally for research in The Times Higher league table. For teaching, it gained the highest Gold ranking for quality in the 2017 government Teaching Excellence Framework, TEF, and in 2018 was ranked 9th for its teaching by ''The Independent'' and 9th by ''The Guardian''. ''The Times'' Higher placed it 137th worldwide for research and 58th worldwide for arts and humanities. Lancaster University was named International University of the Year by ''The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide'' in 2020. It has campuses in Malaysia, China and Ghana and plans one in Leipzig, Germany.
Lancaster is also home to a campus of the University of Cumbria
The University of Cumbria is a public university in Cumbria, with its headquarters in Carlisle and other major campuses in Lancaster, Ambleside, and London. It has roots extending back to the Society for the Encouragement of Fine Arts, establis ...
– more centrally located on the site of the former St Martin's College – which was inaugurated in 2007. It provides undergraduate and postgraduate courses in the arts, social sciences, business, teacher training, health care and nursing.
Jamea Al Kauthar Islamic College, in the former Royal Albert Hospital building on Ashton Road, is an independent girls' school, providing education in a Muslim tradition.
Further education
*Lancaster and Morecambe CollegeSecondary schools
*Lancaster Royal Grammar School and Lancaster Girls' Grammar School are selective-entry grammar schools. In 2016 both were rated by the ''Sunday Times''in the top 50 UK schools based on student achievement. *Ripley St Thomas Church of England Academy *Our Lady's Catholic College *Central Lancaster High School *Skerton Community High School (now closed)Primary schools
*Lancaster Steiner School *Scotforth St Pauls CofE Primary School *Moorside Primary School *St Bernadette's Catholic Primary School *Bowerham Primary School *The Cathedral Catholic Primary School *Dallas Road Community Primary School *Willow Lane (formerly Marsh) Community Primary School *Castle View (formerly Ridge) Community Primary School *Lancaster Christ Church CofE Primary School *St Joseph's Catholic Primary School *Skerton St Lukes CofE Primary School *Lancaster Ryelands Primary School Special Educational Needs (SEN) Schools *The Loyne *Morecambe Road SchoolCulture


 Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of Georgian architecture.
Lancaster has a range of historic buildings and venues, having retained many fine examples of Georgian architecture. Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
, the Lancaster Priory, Priory Church of St. Mary and the Edwardian Ashton Memorial
The Ashton Memorial is a folly in Williamson Park, Lancaster, Lancashire, England built between 1907 and 1909 by the millionaire industrialist Lord Ashton in memory of his second wife, Jessy, at a cost of £87,000 (equivalent to £ in ).
Desc ...
are among the sites of historical importance. Its many museums include Lancaster City Museum, Custom House, Lancaster, Maritime Museum, the Cottage Museum, and Judges Lodgings, Lancaster, Judges' Lodgings Museum.
Lancaster Friends Meeting House dating from 1708, is the longest continual Quaker meeting site in the world, with an original building built in 1677. George Fox, founder of Quakers, Quakerism, was near the site several times in the 1660s and spent two years imprisoned in Lancaster Castle. The meeting house holds regular Quaker meetings and a wide range of cultural activities including adult learning, meditation, art classes, music and political meetings. The Lancaster Grand Theatre is another historic cultural venue, under its many names. It has played a major part in social and cultural life since it was built in 1782.
 Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Nuffield Theatre, Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Peter Scott Gallery, Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Lancaster Concert Series, Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months Williamson Park hosts outdoor performances, including a Dukes "Play in the Park", which over the past 26 years has attracted 460,000 people, as the UK's biggest outdoor walkabout theatre event.
Lancaster is known as the Northern City of Ale, with almost 30 pubs serving cask ale. The pubs include the ''White Cross'', ''Three Mariners'', ''Borough'' and ''Water Witch''. There are two cask ale breweries: Lancaster Brewery and a microbrewery run by the Borough. There is a local CAMRA (Campaign for Real Ale) branch at Lunesdale.
The Grand Theatre (Lancaster), Lancaster Grand Theatre and Duke's Playhouse, the Dukes are notable venues for live performance, as are the Yorkshire House (currently closed), Jailors Barrel, The John O' Gaunt and The Bobbin. Throughout the year events are held in and around the city, such as the Lancaster Music Festival, Lancaster Jazz Festival, and Chinese New Year celebrations in the city centre.
Every November the city hosts a daylight and art festival entitled "Light Up Lancaster", which includes a prominent fireworks display.
Lancaster still has two city-centre cinemas; Vue and the Dukes playhouse. The 1930s art deco ''Regal Cinema'' closed in 2006. The Gregson Centre is also known for small film screenings and cultural events.
Lancaster is known nationally for its Arts scene. There are 600 business and organisations in the region involved directly or indirectly in arts and culture.
In 2009 several major arts bodies based in the district formed a consortium called Lancaster Arts Partners (LAP) to champion strategic development of arts activities in Lancaster District. Notable partners include Ludus Dance, More Music, the Dukes among others. LAP curates and promotes "Lancaster First Fridays", a monthly multi-disciplinary mini-festival under its brand "Lancaster Arts City".
Lancaster University has a public arts organisation, part of LAP, known as Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University. Its programmes include Lancaster's Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Nuffield Theatre, Nuffield Theatre, one of the largest professional studio theatres in Europe, the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Peter Scott Gallery, Peter Scott Gallery, with the most significant collection of Royal Lancastrian ceramics in Britain, and the Lancaster Arts at Lancaster University#Lancaster Concert Series, Lancaster International Concerts Series, drawing nationally and internationally renowned classical and world-music artists.
The gallery in the Storey Creative Industries Centre is now programmed and run by Lancaster City Council. In 2013 the previous incumbent organisation "The Storey Gallery" moved out of the building and reformed as "Storey G2". The Storey Creative Industries Centre is also home to Lancaster's Litfest, which runs an annual literature festival. In the summer months Williamson Park hosts outdoor performances, including a Dukes "Play in the Park", which over the past 26 years has attracted 460,000 people, as the UK's biggest outdoor walkabout theatre event.
Lancaster is known as the Northern City of Ale, with almost 30 pubs serving cask ale. The pubs include the ''White Cross'', ''Three Mariners'', ''Borough'' and ''Water Witch''. There are two cask ale breweries: Lancaster Brewery and a microbrewery run by the Borough. There is a local CAMRA (Campaign for Real Ale) branch at Lunesdale.
The Grand Theatre (Lancaster), Lancaster Grand Theatre and Duke's Playhouse, the Dukes are notable venues for live performance, as are the Yorkshire House (currently closed), Jailors Barrel, The John O' Gaunt and The Bobbin. Throughout the year events are held in and around the city, such as the Lancaster Music Festival, Lancaster Jazz Festival, and Chinese New Year celebrations in the city centre.
Every November the city hosts a daylight and art festival entitled "Light Up Lancaster", which includes a prominent fireworks display.
Lancaster still has two city-centre cinemas; Vue and the Dukes playhouse. The 1930s art deco ''Regal Cinema'' closed in 2006. The Gregson Centre is also known for small film screenings and cultural events.
Art and literature
John Henderson (c.1770-1853) painted many views of the town. One of these together with a poetical illustration (which relates to the treacherous sands of Morecambe Bay) by Letitia Elizabeth Landon was published in Fisher's Drawing Room Scrap Book, 1833Sport
 Lancaster's main Association football, football team, Lancaster City F.C., Lancaster City, plays in the Northern Premier League Premier Division having won promotion as champions of Division One North in 2016–2017. It plays its home matches at the Giant Axe, which can take 3,500 (513 seated) and was formed in 1911 originally as Lancaster Town F.C. Lancaster City has been seven-times Lancashire FA Challenge cup winners and in 2010-11 won the Northern Premier League President's cup for a second time. Lancaster John O' Gaunt Rowing Club is the fifth-oldest surviving rowing club in the UK, outside the universities. It competes nationally at regattas and heads races run by British Rowing. The clubhouse stands next to the weir at Skerton.
The city entertains contestants in the ''Lancaster International Youth Games'', a multi-sport 'Olympic' style event featuring competitors from Lancaster's twin towns: Rendsburg (Germany), Perpignan (France), Viana do Castelo Municipality, Viana do Castelo (Portugal), Aalborg (Denmark), Almere (Netherlands), Lublin (Poland) and Växjö (Sweden).
Lancaster Cricket Club is sited near the
Lancaster's main Association football, football team, Lancaster City F.C., Lancaster City, plays in the Northern Premier League Premier Division having won promotion as champions of Division One North in 2016–2017. It plays its home matches at the Giant Axe, which can take 3,500 (513 seated) and was formed in 1911 originally as Lancaster Town F.C. Lancaster City has been seven-times Lancashire FA Challenge cup winners and in 2010-11 won the Northern Premier League President's cup for a second time. Lancaster John O' Gaunt Rowing Club is the fifth-oldest surviving rowing club in the UK, outside the universities. It competes nationally at regattas and heads races run by British Rowing. The clubhouse stands next to the weir at Skerton.
The city entertains contestants in the ''Lancaster International Youth Games'', a multi-sport 'Olympic' style event featuring competitors from Lancaster's twin towns: Rendsburg (Germany), Perpignan (France), Viana do Castelo Municipality, Viana do Castelo (Portugal), Aalborg (Denmark), Almere (Netherlands), Lublin (Poland) and Växjö (Sweden).
Lancaster Cricket Club is sited near the River Lune
The River Lune (archaically sometimes Loyne) is a river in length in Cumbria and Lancashire, England.
Etymology
Several elucidations for the origin of the name ''Lune'' exist. Firstly, it may be that the name is Brittonic in genesis and der ...
. It has two senior teams that participate in the Palace Shield. Rugby union is a popular sport in the area, with the local clubs being Vale of Lune RUFC and Lancaster CATS.
Lancaster is home to the Golf Centre, Lansil Golf Club, Forest Hills and Lancaster Golf Club. It also has a Lancaster Amateur Swimming and Waterpolo Club that competes in the north-west. It trains at Salt Ayre and at Lancaster University Sports Centre. Lancaster is home to a senior UK team. Water polo is also popular in the area.
The local athletics track near the Salt Ayre Sports Centre is home to both Lancaster and Morecambe AC. It regularly fields athletes across disciplines including track and field, cross country, road and fell running. It competes in several local and national leagues including the Young Athletics League, the Northern Athletics League and the local Mid Lancs League (Cross-Country in Winter, and Track and Field in Summer).
Music
The city's semi-professional Haffner Orchestra has a reputation for classical music. It performs in the Ashton Hall in the city centre and at Lancaster University. During parades and festivals it is common to see two other long standing musical groups performLancaster City Brass
which is the oldest remaining brass band in the city celebrating its 75th anniversary in 2021 an
Batala
who recently completed 15 years of Samba Regge drumming Lancaster has been producing successful bands and musicians since the 1990s, notably the drummer Keith Baxter (drummer), Keith Baxter of 3 Colours Red and folk-metal band Skyclad, who also featured Lancaster guitarist Dave Pugh, and the thrash metal band D.A.M., who were all from Lancaster, recording two albums for the Noise International label, with Dave Pugh appearing on the second. The all-girl punk-rock band Angelica (band), Angelica used the Lancaster Musicians' Co-operative, the main rehearsal and recording studio in the area. The city has also produced many other musicians, including singer and songwriter John Waite, who first became known as lead singer of The Babys and had a solo #1 hit in the US, "Missing You (John Waite song), Missing You". As part of the band Bad English, John Waite also had a #1 hit in the Billboard top hundred in the 1970s called "When I See You Smile". Additionally, Paul James, better known as The Rev, former guitarist of English punk band Towers of London (band), Towers of London who is now in the band Day 21 and plays guitar live on tour for The Prodigy; Chris Acland, drummer of the early 1990s shoegaze band Lush (band), Lush; Tom English, drummer of North East indie band Maxïmo Park and Steve Kemp (musician), Steve Kemp, drummer of the indie band Hard-Fi. Lancaster continues to produce bands and musicians such as singer-songwriter Jay Diggins, and acts like The Lovely Eggs, receiving considerable national radio play and press coverage in recent years. More recently, Lancaster locals Massive Wagons signed to Nottingham-based independent label Earache Records. The city is also the founding home of the dance-music sound systems Rhythm Method and ACME Bass Company. Pioneers in the field of the free party, these two systems and others forged strong representations of the genre in the North West of England in the 1990s. Since 2006, Lancaster Library has hosted regular music events under the ''Get it Loud in Libraries'' initiative. Musicians such as The Wombats, The Thrills, Kate Nash, Adele and Bat for Lashes have taken part. Get It Loud in Libraries has gained national exposure, featuring on The One Show on BBC1 and having gigs reviewed in ''Observer Music Monthly'', ''NME'' and ''Art Rocker''. Notable popular music venues include Duke's Playhouse, The Dukes, Grand Theatre (Lancaster), The Grand Theatre, The Gregson Centre, The Bobbin, The Pub and The Yorkshire House, which since 2006 has hosted such acts as John Renbourn, Polly Paulusma, Marissa Nadler, Baby Dee, Diane Cluck, Alasdair Roberts (musician), Alasdair Roberts, Jesca Hoop, Lach (musician), Lach, Jack Lewis (musician), Jack Lewis, Tiny Ruins and 2008 Mercury Prize nominees Rachel Unthank and the Winterset. Other venues include the Dalton Rooms, the Park Hotel and The Hall, China Street. These host Lancaster's diverse music culture, such as the Lancaster Speakeasy or Stylus. The Lancaster Jazz and Lancaster Music Festivals are respectively held every September and October, at venues throughout the city. In 2013 the headline jazz act was The Neil Cowley Trio, performing at The Dukes, whilst one of the Lancaster Music Festival headline acts was Jay Diggins at the Dalton Rooms.
Media
Heart North Lancashire & Cumbria (formerly "The Bay") has been a commercial radio station for north Lancashire and south Cumbria. Its studios are based at St George's Quay in the city and it broadcasts on three frequencies: 96.9 FM (Lancaster), 102.3 FM (Windermere) and 103.2 FM (Kendal). It is now part of the Manchester-based Heart North West. Beyond Radio is a voluntary, non-profit community radio station for Lancaster and Morecambe and broadcasts on 103.5FM and online. Operated by Proper Community Media (Lancaster) Ltd, the station and broadcasts 24 hours a day from The Old Bowling Pavilion in Palatine Avenue Park, Bowerham Barracks, Bowerham. It took over from Diversity FM, a community radio station run by Lancaster and District YMCA, which had closed in April 2012. Lancaster University has its own student radio station, Bailrigg FM, broadcasting on 87.7 FM, and an online student-run television station called LA1:TV (formerly LUTube.tv) and a student-run newspaper named SCAN (newspaper), SCAN. The city is home to the film production company A1 Pictures, which founded the independent film brand Capture. Commercially available newspapers include the tabloids ''The Lancaster Guardian'' and ''The Visitor'' (mainly targeted at residents of Morecambe). Both are based on the White Lund Industrial Estate in Morecambe. ''Virtual Lancaster'', founded in 1999, is a non-commercial volunteer-led resource website also featuring local news, events and visitor information.Places of interest
 *
*Ashton Memorial
The Ashton Memorial is a folly in Williamson Park, Lancaster, Lancashire, England built between 1907 and 1909 by the millionaire industrialist Lord Ashton in memory of his second wife, Jessy, at a cost of £87,000 (equivalent to £ in ).
Desc ...
*Duke's Playhouse
*Grand Theatre (Lancaster), Lancaster Grand Theatre
*Greaves Park Hotel, Lancaster, Greaves Park
*Judges Lodgings, Lancaster, The Judges Lodgings
*Lancaster Castle
Lancaster Castle is a medieval castle and former prison in Lancaster in the English county of Lancashire. Its early history is unclear, but it may have been founded in the 11th century on the site of a Roman fort overlooking a crossing of ...
* Lancaster Cathedral
*Lancaster City Museum
*Lancaster Priory
Lancaster Priory, formally the Priory Church of St Mary, is the Church of England parish church of the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, England. It is located near Lancaster Castle and since 1953 has been designated a Grade I listed building. ...
*Lancaster Royal Grammar School
*Lancaster Town Hall
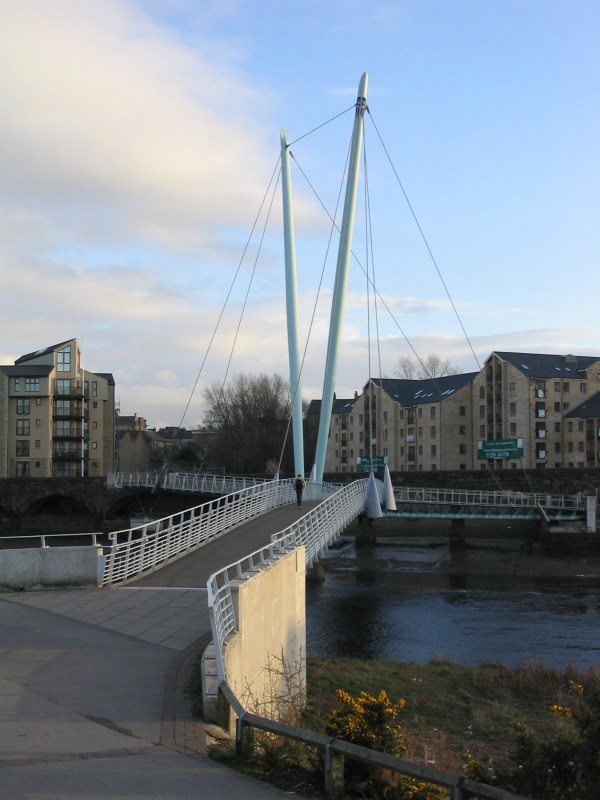
*Lune Millennium Bridge
*Maritime Museum (Lancaster), Quayside Maritime Museum
*Queen Victoria Memorial, Lancaster, Queen Victoria Memorial
*Ruskin Library at Lancaster University
*The Gregson Centre
*The Storey (Institute), Storey Gallery
*Westfield War Memorial Village
*Williamson Park, Lancaster, Williamson Park
Notable people
Arts and entertainment
*Joe Abercrombie (born 1974) – fantasy writer and film editor, was born in Lancaster and attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School, LRGS. *Cherith Baldry (born 1947) – children's and fantasy writer, was born in Lancaster. *Laurence Binyon (1869–1943) – poet and dramatist, was born in Lancaster. *Hubert Henry Norsworthy (1885–1961) – organist and composer, died in Lancaster. *Mabel Pakenham-Walsh (1937–2013) – artist, was born in Lancaster. *Jon Richardson (born 1982) – comedian, grew up in Lancaster and attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School, LRGS. *Thomas Thompson (writer), Thomas Thompson (1880–1951) – writer and broadcaster *John Waite (born 1952) – rock musician, was born in Lancaster. *Dustin Demri-Burns (born 1978) – actor, writer and comedian *Keith Wilkinson (reporter), Keith Wilkinson – television news reporter, was born in LancasterBusiness
*Henry Cort (c. 1741–1800) – English ironmaster and inventor, was probably born in Lancaster. *James Crosby (British businessman), James Crosby (born 1956) – chief executive of HBOS until 2006, attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School. *Thomas Edmondson (1792–1851) – businessman and inventor of the Edmondson railway ticket, was born in Lancaster. *Robert Gillow (1704–1772) was the founder of Gillows of Lancaster, an English furniture manufacturer. *Ronald Halstead, Sir Ronald Halstead (1927–2021) – chair and Chief Executive of the Beecham Group in 1984–1985 and Deputy Chair of British Steel (1967–1999), British Steel in 1986–1994 was born in Lancaster and attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School. *James Williamson, 1st Baron Ashton, James Williamson (1842–1930) – businessman and politician who created Williamson Park and Ashton memorial, was born in Lancaster and attended Lancaster Royal Grammar School.Crime
*Lauren Jeska (born 1974) – a transgender athlete, was convicted of the attempted murder of an official, Ralph Knibbs. *Edward Stringer, (1819–1863) – convict and prospector, discovered the Walhalla, Victoria goldfield in Australia. *Buck Ruxton (1899–1936) – marital murderer, resided and practised medicine at 2 Dalton Square.Politics and journalism
*Henry D. Gilpin (1801–1860) – Attorney General of the United States, was born in Lancaster. *Erik de Mauny (1920–1997) – foreign correspondent, died in Lancaster. *Sir Lancelot Sanderson (1863–1944) – Conservative MP and judge, died in Lancaster.Science and humanities
*J. L. Austin (1911–1960) – philosopher and developer of the theory of speech acts, was born in Lancaster. *John Ambrose Fleming (1849–1945) – electrical engineer and physicist, was born in Lancaster. *Edward Frankland (1825–1899) – chemist who originated the concept of valence, was born near Lancaster and educated at LRGS. *Jaroslav Krejčí (sociologist), Jaroslav Krejčí (1916–2014) – Czech-British sociologist, was a professor at the University of Lancaster and died in Lancaster. *Geoffrey Leech (1936–2014) – linguistics researcher, was a professor at the University of Lancaster and died in Lancaster. *Richard Owen (1804–1892) – biologist who coined the term "dinosaur", lived in Brock Street. *William Turner (anatomist), William Turner (1832–1916) – anatomist and academic, was born in Lancaster. *Paul Wellings (born 1953) – ecologist, served as a professor and Vice-Chancellor of Lancaster University. *Emily Williamson (1855–1936), English philanthropist and co-founder of the RSPB, was born in Lancaster. *Gavin Wood (born 1980) – co-founded and headed Ethereum.Sport
*Michael Allen (cricketer), Michael Allen (1933–1995) – international cricketer, died in Lancaster. *Arthur Bate (1908–1993) – professional football (soccer), footballer, died in Lancaster. *James Beattie (footballer), James Beattie (born 1978) – professional footballer, was born in Lancaster. *Harold Douthwaite (1900–1972) – first-class cricketer, was born and died in Lancaster. *Scott Durant (born 1988) – Olympic gold medal-winning rower, was a pupil at Lancaster Royal Grammar School *Trevor Glover (born 1951) – first-class cricketer and rugby union player, was born in Lancaster. *William Gregson (cricketer), William Gregson (1877–1963) – first-class cricketer, died in Lancaster. *Sarah Illingworth (born 1963) – international cricketer (New Zealand), was born in Lancaster. *Edward Jackson (cricketer, born 1849), Edward Jackson (1849–1926) – first-class cricketer, was born in Lancaster. *John Jackson (cricketer, born 1841), John Jackson (1841–1906) – first-class cricketer, was born in Lancaster. *Scott McTominay (born 1996) – professional footballer currently with Manchester United F.C., Manchester United, was born in Lancaster. *John Pinch (rugby), John Pinch (1870–1946) – international rugby union player, was born and died in Lancaster. *Jason Queally (born 1970) – Olympic gold medal-winning cyclist, was a pupil at Lancaster Royal Grammar School. *Matt Rogerson (born 1993) – professional Rugby Union player currently with London Irish, was born in Lancaster *Fred Shinton (1883–1923) – professional footballer, died in Lancaster. *Alan Warriner-Little (born 1962) – champion darts player, was born in Lancaster.Twinned cities
Lancaster is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with:retrieved 21 January 2019.
See also
*St John the Evangelist's Church, Lancaster *St Thomas' Church, Lancaster *Christ Church, Lancaster *Duke of Lancaster
The Dukedom of Lancaster is an English peerage merged into the crown. It was created three times in the Middle Ages, but finally merged in the Crown when Henry V succeeded to the throne in 1413. Despite the extinction of the dukedom the title ...
*Duchy of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is the private estate of the British sovereign as Duke of Lancaster. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income to the sovereign. The estate consists of a portfolio of lands, properti ...
*Lancaster power stations
*Lancaster Bomber
References
Bibliography
* *External links
Lancaster City Council
– Homepage of Lancaster City Council
– Tourism Website for Lancaster {{Authority control Lancaster, Lancashire, County towns in England Towns in Lancashire Roman fortifications in England Unparished areas in Lancashire Geography of the City of Lancaster