Lake Oroville on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lake Oroville is a
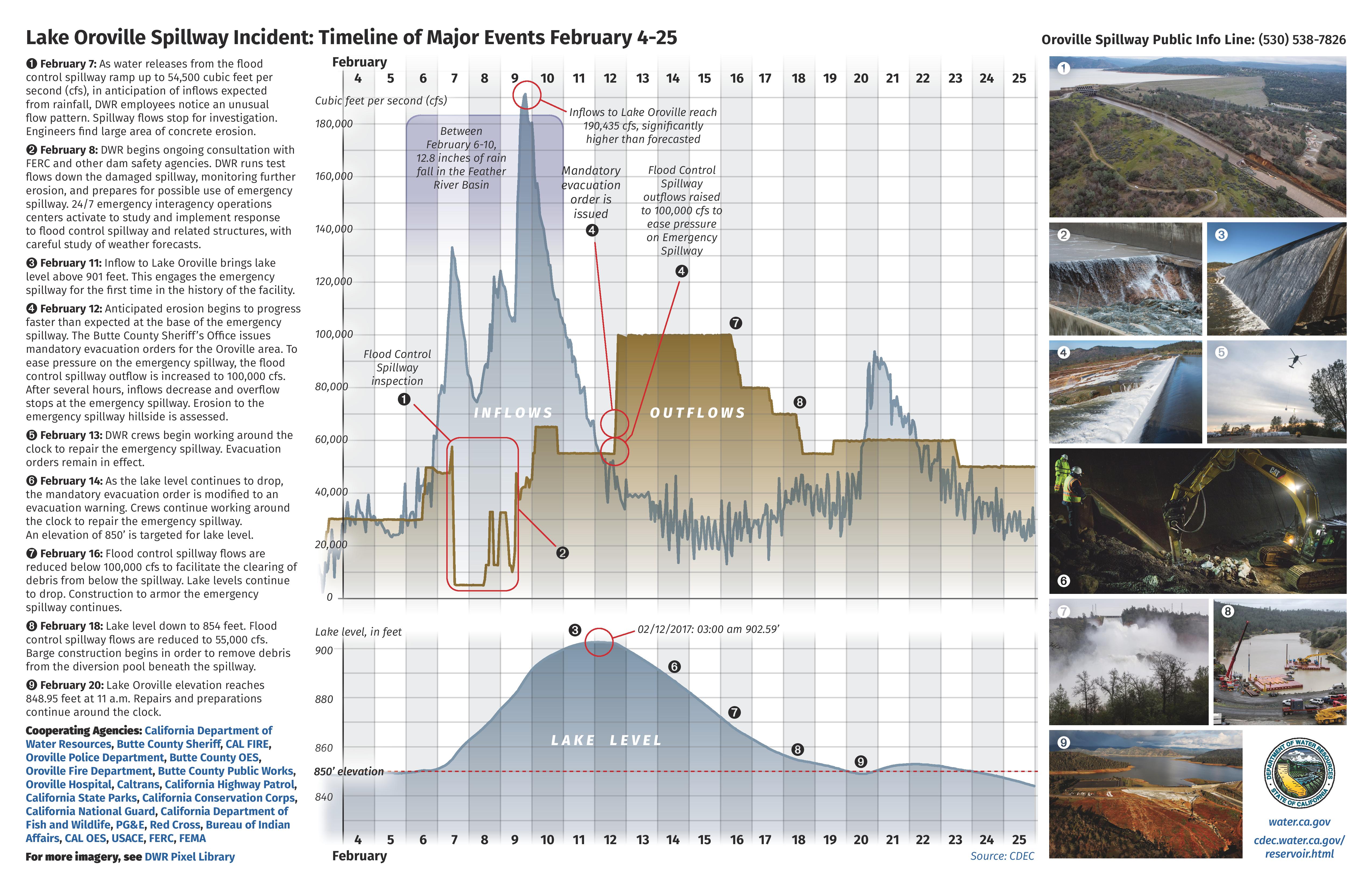
 In February 2017, extreme precipitation and high spillway releases caused significant damage to the main concrete spillway. Due to this damage, releases were cut back and lake level increased to 101% of capacity, causing the emergency spillway to overflow for the first time in the Lake's history. Below the emergency spillway, severe erosion occurred, and fear of a failure of the emergency spillway prompted an evacuation of downstream residents.
Phase 1 of emergency spillway repairs was completed in 2017. The main spillway was successfully reconstructed by November 1, 2018.
In February 2017, extreme precipitation and high spillway releases caused significant damage to the main concrete spillway. Due to this damage, releases were cut back and lake level increased to 101% of capacity, causing the emergency spillway to overflow for the first time in the Lake's history. Below the emergency spillway, severe erosion occurred, and fear of a failure of the emergency spillway prompted an evacuation of downstream residents.
Phase 1 of emergency spillway repairs was completed in 2017. The main spillway was successfully reconstructed by November 1, 2018.
 Lake Oroville has a Mediterranean type climate with hot, dry summers and cool wet winters. A semi-permanent, high pressure area of the mid-Pacific Ocean dominates and controls the weather in northern California. During the summer this high-pressure cell pushes storm tracks into the north causing this hot dry summer. In winter, it moves south allowing storms to cross northern California bringing wetter and cooler winters.
The annual average high temperature is and annual average low is with average temperature of . The coldest months are winter – December to January with average high and low . The warmest months are in the summer – June, July, and August with average high . The average annual rainfall precipitation is ; January is the wettest month at and July the driest at .
In 2015, Northern California experienced a drastic drought reducing the lake level to 39% capacity in January 2016.
The year 2017 has made up for the five-year drought by having above-average precipitation. The excess of water created a new danger – see 2017 Oroville Dam crisis.
In 2021, another drought affected California which resulted in the lake level falling to 35% of its capacity in July. In August, the Hyatt hydroelectric plant was turned off for the first time when levels fell near the minimum necessary to generate power ( above sea level). The loss of power could cause an increased number of rolling blackouts during the summer heat wave. Operations resumed in January 2022 following significant rainfall in December.
Lake Oroville has a Mediterranean type climate with hot, dry summers and cool wet winters. A semi-permanent, high pressure area of the mid-Pacific Ocean dominates and controls the weather in northern California. During the summer this high-pressure cell pushes storm tracks into the north causing this hot dry summer. In winter, it moves south allowing storms to cross northern California bringing wetter and cooler winters.
The annual average high temperature is and annual average low is with average temperature of . The coldest months are winter – December to January with average high and low . The warmest months are in the summer – June, July, and August with average high . The average annual rainfall precipitation is ; January is the wettest month at and July the driest at .
In 2015, Northern California experienced a drastic drought reducing the lake level to 39% capacity in January 2016.
The year 2017 has made up for the five-year drought by having above-average precipitation. The excess of water created a new danger – see 2017 Oroville Dam crisis.
In 2021, another drought affected California which resulted in the lake level falling to 35% of its capacity in July. In August, the Hyatt hydroelectric plant was turned off for the first time when levels fell near the minimum necessary to generate power ( above sea level). The loss of power could cause an increased number of rolling blackouts during the summer heat wave. Operations resumed in January 2022 following significant rainfall in December.
Current Conditions, Oroville Reservoir, California Department of Water Resources
{{State Water Project {{Sierra Nevada {{Authority control 1968 establishments in California California State Recreation Areas California State Water Project Feather Headwaters Feather River Oroville, California Oroville Oroville Oroville Seaplane bases in the United States
reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contr ...
formed by the Oroville Dam impounding the Feather River, located in Butte County, northern California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
. The lake is situated northeast of the city of Oroville, within the Lake Oroville State Recreation Area
Lake Oroville State Recreation Area (LOSRA) is a state park unit of California, United States, surrounding Lake Oroville, a reservoir on the Feather River. It is located in Butte County, California, Butte County outside Oroville, California. Th ...
, in the western foothills of the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primar ...
. Known as the second-largest reservoir in California, Lake Oroville is treated as a keystone facility within the California State Water Project by storing water, providing flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
, recreation, freshwater releases assist in controlling the salinity intrusion into the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta and protecting fish and wildlife.
The lake is a popular nationally renowned bass
Bass or Basses may refer to:
Fish
* Bass (fish), various saltwater and freshwater species
Music
* Bass (sound), describing low-frequency sound or one of several instruments in the bass range:
** Bass (instrument), including:
** Acoustic bass gui ...
fishing location, while coho salmon
The coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch;'' Karuk: achvuun) is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family (biology), family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientif ...
are stocked from the Feather River Fish Hatchery. This hatchery is a main component of Lake Oroville.
History
The local indigenous tribe were the Konkow Maidu (translation is 'man') who originally settled the lake region and Feather River for many years. Today many of the small towns including Oroville were originally occupied by the Maidu people. In 2002, aSonoma State
Sonoma State University (SSU, Sonoma State, or Sonoma) is a public university in Rohnert Park in Sonoma County, California, US. It is one of the smallest members of the California State University (CSU) system. Sonoma State offers 92 Bachelor's ...
study took archaeological inventory of the of Lake Oroville to learn 250 sites are from the prehistoric era relating to the Native American life along the Feather River and an additional 478 sites dating to the Gold Rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New ...
. These sites included open-air residential sites, caves and rockshelters, limited lithic scatters, rock art, quarries and workshops, bedrock milling sites and cemetery areas. Natives' lives were disrupted by gold discovery in 1848 and the miners infiltrated their lands. In April 1848, only three months after gold was discovered at Sutter's Mill, John Bidwell found gold on the Feather River at a spot known today as the town of Bidwell Bar. Bidwell began to work the claim using local Konkow Maidu workers, due to the rapid spreading news of the California strikes under a year California's non-native population climbed from 20,000 to 100,000 and by 1850, Butte County alone supported 3,052 miners.
Construction on the dam began in 1957 to relocate what is now Highway 70 and the then Western Pacific (now Union Pacific) Railroad. A few years later the partially completed dam checked flooding on the Feather River in December 1964. This saved the Sacramento Valley from flooding.
Prior to impoundment by the Oroville Dam, the current main basin of Lake Oroville was the location of the confluence of the North Fork Feather River
The North Fork Feather River is a watercourse of the northern Sierra Nevada in the U.S. state of California. It flows generally southwards from its headwaters near Lassen Peak to Lake Oroville, a reservoir formed by Oroville Dam in the foothill ...
with the Feather River () and the now-inundated towns of Bidwell () and Land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various isla ...
(). Completed in 1968, Oroville Dam is an earthen dam and is the tallest dam located in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, measuring over high and across. The dam was the largest earth-fill dam in the world until succeeded by Aswan High Dam
The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1960s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan Lo ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
. It was built by the California Department of Water Resources as part of the California State Water Project. The dam houses the Edward Hyatt Powerplant, an underground hydro-electric plant that was completed in 1967. Six generators are used to provide a maximum generating capacity of 819 MW.
Hydrology
Lake Oroville and Oroville Dam are part of the Oroville–Thermalito Complex, a water infrastructure complex including the Hyatt Powerplant, Thermalito Diversion Dam and Powerplant, the Feather River Fish Hatchery, Thermalito Power Canal, Thermalito Forebay, Thermalito Pumping-Generating Plant, Thermalito Afterbay, and the Lake Oroville Visitors Center. The lake is fed by the North Fork, Middle Fork, West Branch and South Forks of the Feather River watershed. This watershed drains an area of . The North Fork and Middle Fork Feather Rivers comprise of this area which includes portions of the foothill and mountain regions of the northern Sierra Nevada and southern Cascade Range. Storing over , it is the second-largest reservoir in California, after Shasta Lake. About one-third of the water released from the reservoir goes to uses between the Oroville and Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta. Lake Oroville plays an important role in flood management, water quality, and the health of fisheries affecting areas downstream like the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta. During the warm season, the primary source of streamflow is melting snow, occurring April 1 – July 31, and Lake Oroville receives about 40 percent of the annual total inflow. The lake's storage and releases are a key part of the hydropower and water-supply facilities of the Oroville Complex, the reason it's a pillar and major source of flexibility of the SWP. The downstream flow limits set by the USACE for Lake Oroville are north of Honcut Creek, above the mouth of the Yuba River, and south of the Bear River. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) licenses hydroelectric facilities such as the Edward Hyatt Power Plant at Oroville Dam. California's Department of Water Resources and stakeholders recently participated in a six-year renewal process for a 50-year hydroelectric license for the Oroville Facilities. This agreement commits the state to: restore salmon and steelhead habitat, improved river recreation and community benefits, and a fish passage study to determine and launch a project to enhance passage in the Feather and surrounding river basins. Due to federal flood control requirements, by mid-October each year, the lake's storage must be reduced to a specified level within the range of a maximum flood control pool of and a minimum of . Each day the allowable level within the range is recalculated using an index reflecting the watershed wetness and the anticipation of heavy runoff from incoming storms. As a wet season like 1997-98 occurred progresses the allowable storage trends to coincide with the maximum flood control pool. The reservoir operators must balance the conflicting objectives of controlling the current flood event and preparing for a possible future one.Spillway emergency
 In February 2017, extreme precipitation and high spillway releases caused significant damage to the main concrete spillway. Due to this damage, releases were cut back and lake level increased to 101% of capacity, causing the emergency spillway to overflow for the first time in the Lake's history. Below the emergency spillway, severe erosion occurred, and fear of a failure of the emergency spillway prompted an evacuation of downstream residents.
Phase 1 of emergency spillway repairs was completed in 2017. The main spillway was successfully reconstructed by November 1, 2018.
In February 2017, extreme precipitation and high spillway releases caused significant damage to the main concrete spillway. Due to this damage, releases were cut back and lake level increased to 101% of capacity, causing the emergency spillway to overflow for the first time in the Lake's history. Below the emergency spillway, severe erosion occurred, and fear of a failure of the emergency spillway prompted an evacuation of downstream residents.
Phase 1 of emergency spillway repairs was completed in 2017. The main spillway was successfully reconstructed by November 1, 2018.

Recreation
The lake offers multiple recreational activities for the public to participate in. The Lake Oroville Visitor Center has a museum, exhibits, videos and a store. People like to look through the two high-powered telescopes on the 47-foot tall tower to see the lake, Sierra Nevada, valley, foothills, and the Sutter Buttes mountain range.Fishing
Fishing is described as outstanding at Lake Oroville State Recreation Area. People can fish for largemouth, smallmouth, and spotted bass, Chinook, catfish, mackinaw, sturgeon, white crappie and brown trout. The largest mackinaw caught was and a white crappie. It is permitted all year long but a California sport fishing license is required. TheCalifornia Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment
The Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, commonly referred to as OEHHA (pronounced oh-EEE-ha), is a specialized department within the cabinet-level California Environmental Protection Agency ( CalEPA) with responsibility for evaluatin ...
(OEHHA) has developed a safe eating advisory for Lake Oroville based on levels of mercury or PCBs found in fish caught from this water body.
Boating
Boating occurs year round, including waterskiing,wakeboarding
Wakeboarding is a water sport in which the rider, standing on a wakeboard (a board with foot bindings), is towed behind a motorboat across its wake and especially up off the crest in order to perform aerial maneuvers. A hallmark of wakeboardin ...
, houseboat
A houseboat is a boat that has been designed or modified to be used primarily as a home. Most houseboats are not motorized as they are usually moored or kept stationary at a fixed point, and often tethered to land to provide utilities. Ho ...
s, PWC
PricewaterhouseCoopers is an international professional services brand of firms, operating as partnerships under the PwC brand. It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is considered one of the Big Four accounti ...
, and trolling. There are five multi-lane boat launch ramps. These are located at Bidwell Canyon, Loafer Creek, Spillway, Lime Saddle, Enterprise, Nelson Bar, Vinton Gulch, Foreman Creek, and Dark Canyon. Boat supplies and rentals are available on the south end of the Lake at Bidwell Marina or the north end at Lake Oroville Marina.
Visitors can rent kayaks, canoes, sailboats, paddleboats and more at the Forebay Aquatic Center located at the North Forebay.
Camping
Another major activity is camping by using the campground, floating campsites, boat-in camps, or equestrian campsites.Feather River fish hatchery
A key component of Lake Oroville is the hatchery that manages thriving populations ofChinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus '' Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ...
and steelhead trout for the Feather River ecosystem. It has an interesting history of how it came to be.
In the past there have been many attempts to artificially spawn salmon, shad, and trout in the Feather River and its drainages. Before the Oroville Dam was constructed, a majority of the fish hatcheries were located on the eastern side of the mountain range (about 100 miles northeast of the hatchery's current location). The first hatchery was constructed in 1916, the Yuba River Shad Hatchery was built on the Feather River to stop the over fishing of shad in the lower Sacramento River. This effort failed, leading to the hatchery closure, because the Shad's first run did not produce enough eggs and the river had a light run. The main goal of Domingo Springs, built in 1916, was to supply fish to the lakes and streams in Lassen National Park and the surrounding area. In 1937 floods damaged the hatchery and eventually was abandoned. The next phase, built near Clio in Plumas County, was a 60 trout hatchery building and employee cabins that operated for 30 years. In 1953 the work was outdated so the operation was abandoned, creating a 14-year gap in hatchery work. The Department of Water Resources built the Oroville Dam in 1961 that altered the river flow so DWR built the present hatchery with the Department of Fish and Wildlife. The dam blocked salmon and steelhead access to upstream spawning areas, so to further mitigate fisheries impacts, a barrier and ladder system was built that allows adult salmon and steelhead to be captured at the Feather River Fish Hatchery.
Today the hatchery is managed by the California Department of Fish and Wildlife raising spring and fall-run Chinook salmon and steelhead along the Feather River, directly below Lake Oroville. The hatchery is divided into two sections. The first section located on the east side of Table Mountain Boulevard includes: fish barrier dam, observation platform and underwater viewing. The second section located on the west side of Table Mountain Boulevard includes: spawning room, hatchery and rearing ponds. Salmon spawning operations can be observed mid-September until mid-November, but fish are present in the rearing ponds all year.
Annually on the 4th Saturday of September the Oroville Salmon Festival occurs at the hatchery and downtown Oroville. It is known as the only California salmon festival where personnel work Chinook salmon to harvest and fertilize eggs.
Climate
 Lake Oroville has a Mediterranean type climate with hot, dry summers and cool wet winters. A semi-permanent, high pressure area of the mid-Pacific Ocean dominates and controls the weather in northern California. During the summer this high-pressure cell pushes storm tracks into the north causing this hot dry summer. In winter, it moves south allowing storms to cross northern California bringing wetter and cooler winters.
The annual average high temperature is and annual average low is with average temperature of . The coldest months are winter – December to January with average high and low . The warmest months are in the summer – June, July, and August with average high . The average annual rainfall precipitation is ; January is the wettest month at and July the driest at .
In 2015, Northern California experienced a drastic drought reducing the lake level to 39% capacity in January 2016.
The year 2017 has made up for the five-year drought by having above-average precipitation. The excess of water created a new danger – see 2017 Oroville Dam crisis.
In 2021, another drought affected California which resulted in the lake level falling to 35% of its capacity in July. In August, the Hyatt hydroelectric plant was turned off for the first time when levels fell near the minimum necessary to generate power ( above sea level). The loss of power could cause an increased number of rolling blackouts during the summer heat wave. Operations resumed in January 2022 following significant rainfall in December.
Lake Oroville has a Mediterranean type climate with hot, dry summers and cool wet winters. A semi-permanent, high pressure area of the mid-Pacific Ocean dominates and controls the weather in northern California. During the summer this high-pressure cell pushes storm tracks into the north causing this hot dry summer. In winter, it moves south allowing storms to cross northern California bringing wetter and cooler winters.
The annual average high temperature is and annual average low is with average temperature of . The coldest months are winter – December to January with average high and low . The warmest months are in the summer – June, July, and August with average high . The average annual rainfall precipitation is ; January is the wettest month at and July the driest at .
In 2015, Northern California experienced a drastic drought reducing the lake level to 39% capacity in January 2016.
The year 2017 has made up for the five-year drought by having above-average precipitation. The excess of water created a new danger – see 2017 Oroville Dam crisis.
In 2021, another drought affected California which resulted in the lake level falling to 35% of its capacity in July. In August, the Hyatt hydroelectric plant was turned off for the first time when levels fell near the minimum necessary to generate power ( above sea level). The loss of power could cause an increased number of rolling blackouts during the summer heat wave. Operations resumed in January 2022 following significant rainfall in December.
Wildlife
Species of fish
The species raised at the Feather River Fish Hatchery includeChinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus '' Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ...
(''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') and steelhead trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).
Chinook salmon are supported by California streams. They display a wide array of life history patterns allowing them to live in the diverse, variable riverine and ocean environments. As anadromous
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousa ...
fish, they migrate upstream as adults to spawn in freshwater streams, and as juveniles migrate downstream to the ocean, where they grow into mature adults. There are seventeen distinct runs of Chinook salmon recognized in California, classified into six major groups or evolutionarily significant units. Currently, these are a Species of Concern under the Federal Endangered Species Act.
The hatchery spawn, rear and release the Fall and Spring Run Chinook salmon of local origin. The trout, being an anadromous form of rainbow trout, spawn for multiple years in rivers and creeks, transition into the ocean but return to the rivers to start the lifecycle again.
Downriver facilities
The Hyatt Generating–Pumping Plant source water for the Feather River is released from two discharge tunnels at up to during peak demand and "little or no release the remainder of the day". The power plant also routinely draws up to of Feather River water for "pumpback" into Lake Oroville. NOTE: Pumpback returns Feather River water back to Lake Oroville during off-peak periods when California Edison Company external power is inexpensive, allowing subsequent hydroelectric generation (6-7% of Hyatt total) during peak (higher price) periods. Hyatt releases are stored in the {{Convert, 4.40, mi, km, abbr=on serpentine river channel (Thermalito Diversion Pool) which extends from the river's source to the Thermalito Diversion Dam.{{Cite map, date=2022-05-30 , title=Oroville Dam , url=http://www.wikimapia.org/#lat=39.5338357&lon=-121.5181017&z=16&l=0&m=b&search=Oroville%20Dam , website= wikimapia.org , access-date=2022-05-30 NOTE: The Wikimapia path line from thespillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure th ...
's confluence with the Feather River/Thermalito Diversion Pool to the Thermalito Diversion Dam defines 12 line segments of the river channel.
See also
* California State Water Project * Feather Headwaters * Feather River *Lake Oroville State Recreation Area
Lake Oroville State Recreation Area (LOSRA) is a state park unit of California, United States, surrounding Lake Oroville, a reservoir on the Feather River. It is located in Butte County, California, Butte County outside Oroville, California. Th ...
* List of dams and reservoirs in California
Following is a list of dams and reservoirs in California in a sortable table. There are over 1,400 named dams and 1,300 named reservoirs in the state of California.
Dams in service
:''Please add to this list from the below sources.''
Former ...
* List of lakes in California
* List of largest reservoirs in the United States
This is a list of largest reservoirs in the United States, including all artificial lakes with a capacity greater than or equal to . Figures given are for maximum storage capacity (flood pool) of reservoirs, not regular storage volume (conservat ...
* List of largest reservoirs of California
References
{{Reflist, 2External links
{{CommonsCurrent Conditions, Oroville Reservoir, California Department of Water Resources
{{State Water Project {{Sierra Nevada {{Authority control 1968 establishments in California California State Recreation Areas California State Water Project Feather Headwaters Feather River Oroville, California Oroville Oroville Oroville Seaplane bases in the United States