Lake-effect snow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer
 Some key elements are required to form lake-effect precipitation and which determine its characteristics: instability, fetch, wind shear, upstream moisture, upwind lakes, synoptic (large)-scale forcing, orography/topography, and snow or ice cover.
Some key elements are required to form lake-effect precipitation and which determine its characteristics: instability, fetch, wind shear, upstream moisture, upwind lakes, synoptic (large)-scale forcing, orography/topography, and snow or ice cover.
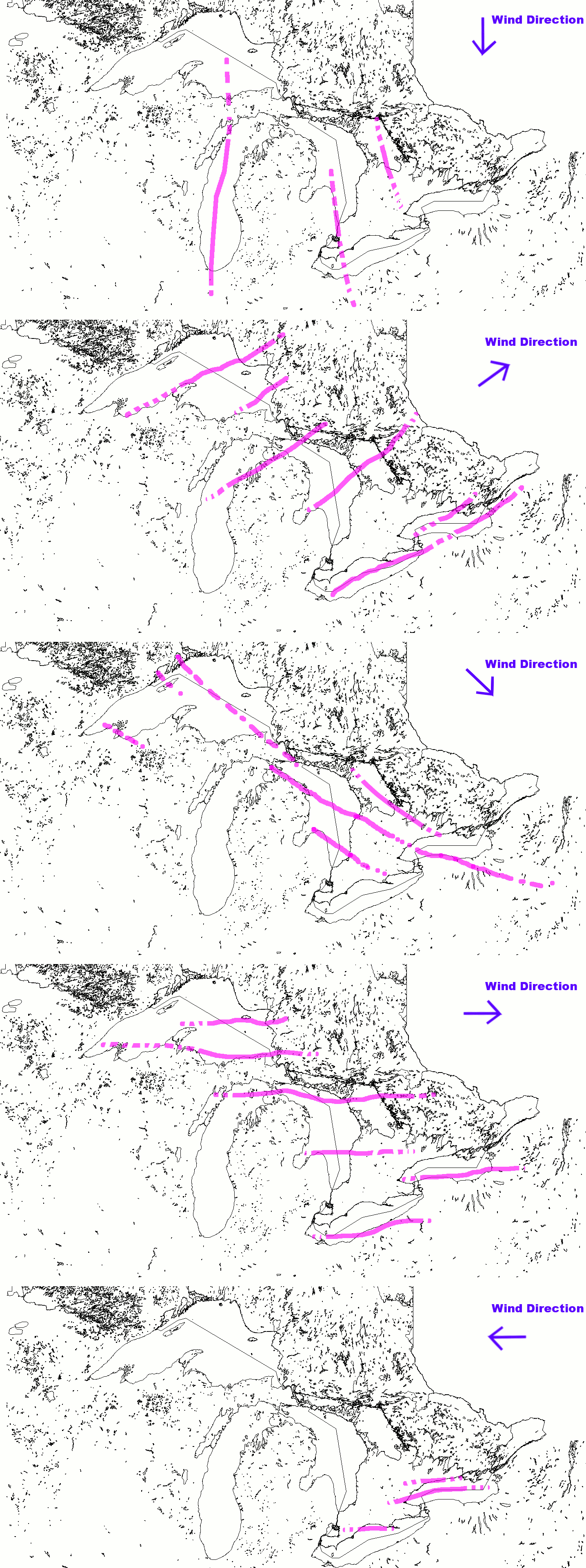

 Cold winds in the winter typically prevail from the northwest in the Great Lakes region, producing the most dramatic lake-effect snowfalls on the southern and eastern shores of the
Cold winds in the winter typically prevail from the northwest in the Great Lakes region, producing the most dramatic lake-effect snowfalls on the southern and eastern shores of the
File:Buffalo2001-20.jpg,
File:Caspian-lake-effect.gif, IRIMO radar animation of lake effect snow in southern coast of Caspian Sea in the north of Iran
File:Caspiansatelliteimage.jpg, Lake-effect clouds over
File:Snow-chart.png, Chart showing the sea-effect snow event of January 1987 in the UK: A continuous stream of showers deposited over of snow over SE coastal regions.
File:Lakeeffect.png, NetWeather radar image showing "lake-effect" snow over Kent and northeast England
National Weather Service Official Lake Effect Page
Ćöbased in Buffalo, NY
Lake effect forecasting
Video of a snowsquall timelapse while driving on Highway 407 ETR in Greater Toronto
, Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory
A BBC forecast of lake effect snow in the UK in 1991
{{Severe weather terminology (United States) navbox Climatology Snow or ice weather phenomena Upper Peninsula of Michigan fr:Bourrasque de neige#Bourrasques en aval de plans d'eau
lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor
(99.9839 ┬░C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg┬ĘK)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg┬ĘK)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
from the lake and rises up through the colder air above. The vapor then freezes and is deposited on the leeward (downwind) shores.
The same effect also occurs over bodies of saline water, when it is termed ocean-effect or bay-effect snow. The effect is enhanced when the moving air mass is uplifted by the orographic influence of higher elevations on the downwind shores. This uplifting can produce narrow but very intense bands of precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
, which deposit at a rate of many inches of snow each hour, often resulting in a large amount of total snowfall.
The areas affected by lake-effect snow are called snowbelts. These include areas east of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
in North America, the west coasts of northern Japan, the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: ą┐ąŠą╗čāąŠčüčéčĆąŠą▓ ąÜą░ą╝čćą░čéą║ą░, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and w ...
in Russia, and areas near the Great Salt Lake, Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
, Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53┬░N to 66┬░N latitude and from ...
, Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
, and North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
.
Lake-effect blizzards are the blizzard-like conditions resulting from lake-effect snow. Under certain conditions, strong winds can accompany lake-effect snows creating blizzard-like conditions; however, the duration of the event is often slightly less than that required for a blizzard warning in both the US and Canada.
If the air temperature is low enough to keep the precipitation frozen, it falls as lake-effect snow. If not, then it falls as lake-effect rain. For lake-effect rain or snow to form, the air moving across the lake must be significantly cooler than the surface air (which is likely to be near the temperature of the water surface). Specifically, the air temperature at an altitude where the air pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars ...
is (roughly vertically) should be lower than the temperature of the air at the surface. Lake-effect occurring when the air at is much colder than the water surface can produce thundersnow, snow showers accompanied by lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average ...
and thunder (caused by larger amounts of energy available from the increased instability).
Formation
Instability
A temperature difference of (or as past researchers have estimated: between 15 and 25 ┬░C) between the lake temperature and the height in the atmosphere (about at which barometric pressure measures ) provides for absolute instability and allows vigorous heat and moisture transportation vertically. Atmospheric lapse rate and convective depth are directly affected by both the mesoscale lake environment and the synoptic environment; a deeper convective depth with increasingly steep lapse rates and a suitable moisture level allow for thicker, taller lake-effect precipitation clouds and naturally a much greater precipitation rate.Fetch
The distance that an air mass travels over a body of water is called fetch. Because most lakes are irregular in shape, different angular degrees of travel yield different distances; typically, a fetch of at least is required to produce lake-effect precipitation. Generally, the larger the fetch, the more precipitation produced. Larger fetches provide the boundary layer with more time to become saturated with water vapor and for heat energy to move from the water to the air. As the air mass reaches the other side of the lake, the engine of rising and cooling water vapor pans itself out in the form of condensation and falls as snow, usually within of the lake, but sometimes up to about .
Wind shear
Directional shear is one of the most important factors governing the development of squalls; environments with weak directional shear typically produce more intense squalls than those with higher shear levels. If directional shear between the surface and the height in the atmosphere at which the barometric pressure measures is greater than 60┬░, nothing more than flurries can be expected. If the directional shear between the body of water and the vertical height at which the pressure measures is between 30┬░ and 60┬░, weak lake-effect bands are possible. In environments where the shear is less than 30┬░, strong, well organized bands can be expected. Speed shear is less critical but should be relatively uniform. The wind-speed difference between the surface and vertical height at which the pressure reads should be no greater than so as to prevent the upper portions of the band from shearing off. However, assuming the surface to winds are uniform, a faster overall velocity works to transport moisture more quickly from the water, and the band then travels much farther inland.Upstream moisture
A lower upstream relative humidity lake effect makes condensation, clouds, and precipitation more difficult to form. The opposite is true if the upstream moisture has a high relative humidity, allowing lake-effect condensation, cloud, and precipitation to form more readily and in a greater quantity.Upwind lakes
Any large body of water upwind impacts lake-effect precipitation to the lee of a downwind lake by adding moisture or pre-existing lake-effect bands, which can reintensify over the downwind lake. Upwind lakes do not always lead to an increase of precipitation downwind.Synoptic forcing
Vorticity advection aloft and large upscale ascent help increase mixing and the convective depth, while cold air advection lowers the temperature and increases instability.Orography and topography
Typically, lake-effect precipitation increases with elevation to the lee of the lake as topographic forcing squeezes out precipitation and dries out the squall much faster.Snow and ice cover
As a lake gradually freezes over, its ability to produce lake-effect precipitation decreases for two reasons. Firstly, the open ice-free liquid surface area of the lake shrinks. This reduces fetch distances. Secondly, the water temperature nears freezing, reducing overall latent heat energy available to produce squalls. To end the production of lake-effect precipitation, a complete freeze is often not necessary. Even when precipitation is not produced, cold air passing over warmer water may produce cloud cover. Fast-moving mid-latitude cyclones, known asAlberta clipper
An Alberta clipper, also known as an Alberta low, Alberta cyclone, Alberta lee cyclone, Canadian clipper, or simply clipper, is a fast-moving low-pressure system that originates in or near the Canadian province of Alberta just east of the Rocky ...
s, often cross the Great Lakes. After the passage of a cold front, winds tend to switch to the northwest, and a frequent pattern is for a long-lasting low-pressure area to form over the Canadian Maritimes
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% o ...
, which may pull cold northwestern air across the Great Lakes for a week or more, commonly identified with the negative phase of the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO). Since the prevailing winter winds tend to be colder than the water for much of the winter, the southeastern shores of the lakes are almost constantly overcast, leading to the use of the term "the Great Gray Funk" as a synonym for winter. These areas allegedly contain populations that suffer from high rates of seasonal affective disorder, a type of psychological depression thought to be caused by lack of light.
Great Lakes region
United States

Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. This lake effect results in much greater snowfall amounts on the southern and eastern shores compared to the northern and western shores of the Great Lakes.
The most affected areas include the Upper Peninsula of Michigan; Central New York; Western New York; Northwestern Pennsylvania; Northeastern Ohio; southwestern Ontario and central Ontario; Northeastern Illinois (along the shoreline of Lake Michigan); northwestern and north central Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
(mostly between Gary and Elkhart); northern Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
(near Lake Superior); and West Michigan. Tug Hill in New York's North Country region has the second-most snow amounts of any nonmountainous location within the continental U.S., trailing only the Upper Peninsula, which can average over of snow per year.
Lake-effect snows on the Tug Hill plateau (east of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The CanadaŌĆōUnited States border sp ...
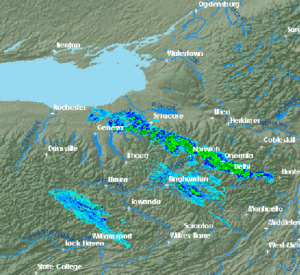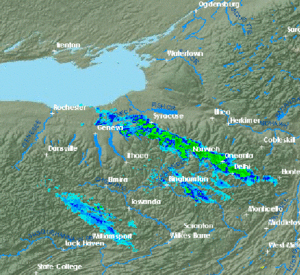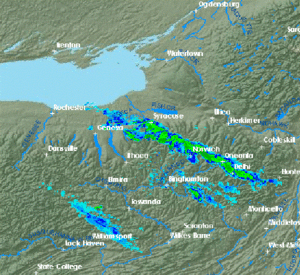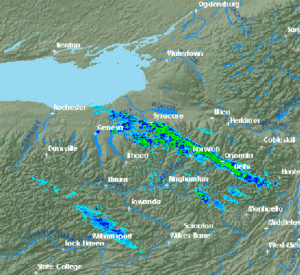
) can frequently set daily records for snowfall in the United States. Tug Hill receives, typically, over of snow each winter. In February 2007, a prolonged lake-effect snow event left of snow on the Tug Hill Plateau. Syracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, United States. It is the fifth-most populous city in the state of New York following New York City, Buffalo, Yonkers, and Rochester.
At the 2020 census, the city' ...
, directly south of the Tug Hill Plateau, receives significant lake-effect snow from Lake Ontario, and averages of snow per year, which is enough snowfall to be considered one of the "snowiest" large cities in America.
A small amount of lake-effect snow from the Finger Lakes falls in upstate New York, as well. If the wind blows almost the entire length of either Cayuga Lake or Seneca Lake, Ithaca
Ithaca most commonly refers to:
*Homer's Ithaca, an island featured in Homer's ''Odyssey''
*Ithaca (island), an island in Greece, possibly Homer's Ithaca
*Ithaca, New York, a city, and home of Cornell University and Ithaca College
Ithaca, Ithaka ...
or Watkins Glen, respectively, can have a small lake-effect snowstorm.
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also ha ...
produces a similar effect for a zone stretching from the eastern suburbs of Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
through Erie to Buffalo. Remnants of lake-effect snows from Lake Erie have been observed to reach as far south as Garrett County, Maryland, and as far east as Geneva, New York. Because it is not as deep as the other lakes, Erie warms rapidly in the spring and summer, and is frequently the only Great Lake to freeze over in winter. Once frozen, the resulting ice cover alleviates lake-effect snow downwind of the lake. Based on stable isotope evidence from lake sediment coupled with historical records of increasing lake-effect snow, global warming has been predicted to result in a further increase in lake-effect snow.
A very large snowbelt in the United States exists on the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, near the cities of Houghton, Marquette, and Munising. These areas typically receive of snow each season. For comparison, on the western shore, Duluth, Minnesota
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior, Wisconsin, Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: Downtown Dul ...
receives per season. Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
and Lake Huron rarely freeze because of their size and depth; hence, lake-effect snow can fall continually in the Upper Peninsula and Canadian snowbelts during the winter. Main areas of the Upper Peninsula snow belt include the Keweenaw Peninsula and Baraga, Marquette and Alger Counties, where Lake Superior contributes to lake-effect snow, making them a prominent part of the Midwestern snow belt. Records of of snow or more have been set in many communities in this area. The Keweenaw Peninsula averages more snowfall than almost anywhere in the United StatesŌĆömore than anywhere east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
and most of all nonmountainous regions of the continental United States. Because of the howling storms across Lake Superior, which cause dramatic amounts of precipitation, the lake-effect snow is said to make the Keweenaw Peninsula the snowiest place east of the Rockies. Only one official weather station exists in this region. Located in Hancock, Michigan
Hancock is a city in Houghton County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is across the Keweenaw Waterway from the city of Houghton on the Keweenaw Peninsula. The population was 4,634 at the 2010 census. The Weather Channel has consistently ra ...
; this station averages well over per year. Farther north in the peninsula, lake-effect snow can occur with any wind direction. The road commission in Keweenaw County, Michigan, collects unofficial data in a community called Delaware, and it strictly follows the guidelines set forth by the National Weather Service. This station averages over per season. Even farther north, a ski resort called Mount Bohemia
Mount Bohemia is the 5th highest point in the Keweenaw Peninsula and the 52nd highest prominent peak in Michigan with an elevation of .
Mount Bohemia is host to a ski resort bearing the same name located at the northernmost portion of the Keweenaw ...
receives an unofficial annual average of . Herman, Michigan, averages of snow every year. Lake-effect snow can cause blinding whiteouts in just minutes, and some storms can last days.
Western Michigan, western Northern Lower Michigan, and Northern Indiana can get heavy lake-effect snows as winds pass over Lake Michigan and deposit snows over Muskegon, Traverse City, Grand Rapids, Kalamazoo
Kalamazoo ( ) is a city in the southwest region of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Kalamazoo County. At the 2010 census, Kalamazoo had a population of 74,262. Kalamazoo is the major city of the Kalamazoo-Portage Metropo ...
, New Carlisle, South Bend, and Elkhart, but these snows abate significantly before Lansing
Lansing () is the capital of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is mostly in Ingham County, although portions of the city extend west into Eaton County and north into Clinton County. The 2020 census placed the city's population at 112,644, maki ...
or Fort Wayne, Indiana. When winds become northerly or aligned between 330 and 390┬░, a single band of lake-effect snow may form, which extends down the length of Lake Michigan. This long fetch often produces a very intense, yet localized, area of heavy snowfall, affecting cities such as Laporte and Gary.
Lake-effect snow is uncommon in Detroit, Toledo, Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee i ...
, and Chicago, because the region's dominant winds are from the northwest, making them upwind from their respective Great Lakes, although they, too, can see lake-effect snow during easterly or northeasterly winds. More frequently, the north side of a low-pressure system picks up more moisture over the lake as it travels east, creating a phenomenon called lake-enhanced precipitation.
Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from Sou ...
, after of snow fell from December 24, 2001, to December 28, 2001
File:Fultonles.jpg, Fulton, New York, after a snowburst dropped of snow over most of Oswego County January 28ŌĆō31, 2004
File:Snow-removal-cleveland-4.jpg, The Veteran's Day storm of November 9ŌĆō14, 1996, may be the most severe early-season lake-effect snow storm the Great Lakes has witnessed in the past 50 years. At the height of the storm, over 160,000 customers were without power in Greater Cleveland alone, as the storm produced isolated snowfall tallies approaching .
Ontario, Canada
Because Southwestern Ontario is surrounded by water on three sides, many parts of Southwestern and Central Ontario get a large part of their winter snow from lake-effect snow. This region is notorious for the whiteouts that can suddenly reduce highway visibility on North AmericaŌĆÖs busiest highway (Ontario Highway 401
King's Highway 401, commonly referred to as Highway 401 and also known by its official name as the MacdonaldŌĆōCartier Freeway or colloquially referred to as the four-oh-one,
is a controlled-access 400-series highway in the Canadian provi ...
) from clear to zero. The region most commonly affected spans from Port Stanley in the west, the Bruce Peninsula in the north, Niagara-on-the-Lake to the east, and Fort Erie
Fort Erie is a town on the Niagara River in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. It is directly across the river from Buffalo, New York, and is the site of Old Fort Erie which played a prominent role in the War of 1812.
Fort Erie is one of Ni ...
to the south. The heaviest accumulations usually happen in the Bruce Peninsula, which is between Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. So long as the Great Lakes are not frozen over, the only time the Bruce Peninsula does not get lake-effect snow is when the wind is directly from the south.
Toronto and Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
are usually spared lake-effect squalls because they are not on the leeward side of Lake Ontario during the dominant northwest winds. Some central and northern portions of the Greater Toronto Area, though, can be affected a few times each year by lake-effect snow from Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. T ...
. Downtown Toronto and Hamilton get most of their lake-effect snow when the wind comes from the southeast or east, over Lake Ontario. Such easterly winds are usually associated with a winter cyclone passing just to the south of the Great Lakes.
When the wind is from the north, the snowbelt runs north-south from Grand Bend to Sarnia
Sarnia is a city in Lambton County, Ontario, Canada. It had a 2021 population of 72,047, and is the largest city on Lake Huron. Sarnia is located on the eastern bank of the junction between the Upper and Lower Great Lakes where Lake Huron f ...
and London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. Areas such as Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November 39 AD ŌĆō 30 April 65 AD), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba (modern-day C├│rdoba), in Hispania Baetica. He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imperial ...
and Kincardine have experienced some of the heaviest snowsqualls from Lake Huron in this region. When the wind is slightly more westerly, the snowbelt runs from Tobermory, Owen Sound, and Grand Bend to as far south and east as Arthur, Orangeville and Caledon. This snowbelt often reaches Kitchener and can affect the Halton and Peel regions of the Greater Toronto Area. These northwesterly winds usually also bring snow southeast of Georgian Bay, which can reach beyond Lake Scugog
Lake Scugog is an artificially flooded lake in Scugog, Regional Municipality of Durham and the unitary city of Kawartha Lakes in central Ontario, Canada. It lies between the communities of Port Perry and Lindsay. The lake has been raised and l ...
. A westerly wind sends lake-effect streamers east from Owen Sound to Gravenhurst, Barrie
Barrie is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada, about north of Toronto. The city is within Simcoe County and located along the shores of Kempenfelt Bay, the western arm of Lake Simcoe. Although physically in Simcoe County, Barrie is politicall ...
, and Orillia
Orillia is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is in Simcoe County between Lake Couchiching and Lake Simcoe. Although it is geographically located within Simcoe County, the city is a List of municipalities in Ontario#Single-tier municipalities, single ...
, and may even reach as far south and east as York Region in the Greater Toronto Area. When the wind is from the southwest, lake-effect streamers from Lake Huron and Georgian Bay run from Noelville to Sudbury Sudbury may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sudbury Reef, Queensland
Canada
* Greater Sudbury, Ontario (official name; the city continues to be known simply as Sudbury for most purposes)
** Sudbury (electoral district), one of the city's federal el ...
, Gravenhurst, and Algonquin Provincial Park. Winds from this same direction coming over Lake Ontario cause squalls to come ashore from Cobourg through the Belleville area to Kingston and the Thousand Islands, with Prince Edward County being the area most vulnerable to extreme snowfall amounts. Some snow bands can occasionally reach Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Qu├®bec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
and Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
, while snow originating from Lake Erie, Lake Ontario, and even Lake Michigan can impact southern Ontario. Easterly winds primarily affect the Niagara Peninsula. Local lake-effect snowsqualls can occasionally occur downwind of Lake Simcoe when the lake is unfrozen, usually in early winter or late fall.
Lake Superior has its own independent snowbelts, affecting Wawa, Sault Ste. Marie, Marathon, the Keweenaw Peninsula in Upper Michigan, and Pukaskwa National Park. Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its populati ...
is usually not affected by lake-effect snow, unless it is associated with a winter storm.
Elsewhere in the United States
The southern and southeastern sides of the Great Salt Lake receive significant lake-effect snow. Since the Great Salt Lake never freezes, the lake effect can influence the weather along theWasatch Front
The Wasatch Front is a metropolitan region in the north-central part of the U.S. state of Utah. It consists of a chain of contiguous cities and towns stretched along the Wasatch Range from approximately Provo in the south to Logan in the nort ...
year-round. The lake effect largely contributes to the annual snowfall amounts recorded south and east of the lake, and in average snowfall reaching in the Wasatch Range. The snow, which is often very light and dry because of the semiarid climate, is referred to as the "Greatest Snow on Earth" in the mountains. Lake-effect snow contributes to roughly six to eight snowfalls per year in Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
, with about 10% of the city's precipitation being contributed by the phenomenon.
Similar snowfall can occur near large inland bays, where it is known as bay-effect snow. Bay-effect snows fall downwind of Delaware Bay, Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
, and Massachusetts Bay when the basic criteria are met, and on rarer occasions along Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18 ...
.
The Finger Lakes of New York are long enough for lake-effect precipitation.
The Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
twin cities of Sherman and Denison are known, in rare instances, to have experienced lake-effect snow from nearby Lake Texoma due to the lake's size (it is the third-largest lake in Texas or along its borders).
On one occasion in December 2016, lake-effect snow fell in central Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
from a lake band off Ross Barnett Reservoir
The Ross Barnett Reservoir, often called the Rez, is a reservoir of the Pearl River between Madison and Rankin counties in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The lake serves as the state's largest drinking water resource, and is managed by the Pe ...
.
Oklahoma City even had a band of lake-effect snow off of Lake Hefner in February 2018.
Owasso/Collinsville, Oklahoma outside of Tulsa, had lake effect snow off Lake Oolagah during a winter storm in February 2021.
The Truckee Meadows and other parts of northern Nevada, which are normally in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primar ...
, when conditions are right, can have severe snowfall as a result of lake effect from Lake Tahoe. Recent severe examples of this phenomenon have occurred as recently as 2004, dumping several feet of snow in the normally dry region.
The West Coast occasionally experiences ocean-effect showers, usually in the form of rain at lower elevations south of about the mouth of the Columbia River. These occur whenever an Arctic air mass from western Canada is drawn westward out over the Pacific Ocean, typically by way of the Fraser Valley, returning shoreward around a center of low pressure. Cold air flowing southwest from the Fraser Valley can also pick up moisture over the Strait of Georgia and Strait of Juan de Fuca, then rise over the northeastern slopes of the Olympic Mountains
The Olympic Mountains are a mountain range on the Olympic Peninsula of the Pacific Northwest of the United States. The mountains, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges, are not especially high ŌĆō Mount Olympus is the highest at ; however, the easte ...
, producing heavy, localized snow between Port Angeles
Port Angeles ( ) is a city and county seat of Clallam County, Washington, United States. With a population of 19,960 as of the 2020 census, it is the largest city in the county. The population was estimated at 20,134 in 2021.
The city's har ...
and Sequim
Sequim ( ) is a city in Clallam County, Washington, United States. It is located along the Dungeness River near the base of the Olympic Mountains. The 2010 census counted a population of 6,606.
Sequim lies within the rain shadow of the Olympic M ...
, as well as areas in Kitsap County, Washington, Kitsap County and the Puget Sound region.
While snow of any type is very rare in Florida, the phenomenon of gulf-effect snow has been observed along the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico a few times in history. More recently, "ocean-effect" snow occurred on January 24, 2003, when wind off the Atlantic, combined with air temperatures in the 30 ┬░F range, brought snow flurries briefly to the Atlantic Coast of northern Florida seen in the air as far south as Cape Canaveral.
Elsewhere in Canada
Lake Winnipeg, Lake Manitoba and Lake Winnipegosis in Manitoba historically have seen lake-effect snow as early as late October, and it is common throughout early to mid-November. Towards the end of November, the lakes sufficiently cool and begin to freeze, ending the lake-effect snow. A brief period of lake-effect snow is also common near Great Bear Lake and Great Slave Lake in the Northwest Territories during early winter (usually early to mid-October); the lake-effect season for both lakes is very short, though. The lakes are frozen roughly eight months of the year, and as a result, have very little time to warm during the summer. Other small lakes such as Lake Athabasca in northern Saskatchewan and Lake Nipigon in northwestern Ontario produce early-season lake-effect snows. Smallwood Reservoir, a man-made lake located in Labrador, has on occasion generated lake-effect snow. The Canadian Maritimes, specifically Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island, are often affected by such snow squalls when an Arctic winter airmass moves over unfrozen waters. In PEI, sea-effect snow is often generated when a cold north wind blows over the unfrozen Gulf of St. Lawrence, dumping heavy snow on the north shore. In Nova Scotia, a cold north-west wind can produce sea-effect snow over the Cape Breton Highlands from the Gulf of St. Lawrence, and the Annapolis Valley from the Bay of Fundy; in the latter case, the sea-effect snow season can continue all winter as the Bay of Fundy remains open owing to its extreme tidal currents. The east coast of southern Vancouver Island, British Columbia, experiences occasional episodes of sea-effect snow during winter due to cold easterly outflow winds from the British Columbia interior, typically through the Fraser Valley, crossing the always open waters of the Strait of Georgia.Eurasia
Lake-effect or sea-effect snow occurs in other countries, near large lakes or large sea areas. In Eurasia, it occurs in the regions of theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
in Georgia, Romania, Bulgaria and northern Turkey, the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
in Iran, the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
in Italy, the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
, the Irish Sea, the Aegean Sea, the Balearic Islands, and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53┬░N to 66┬░N latitude and from ...
, as well as areas surrounding the Sea of Japan.
Because the southern Black Sea is relatively warm (around 13 ┬░C or 55 ┬░F at the beginning of winter, typically 10 to 6 ┬░C or 50 to 43 ┬░F by the end), sufficiently cold air aloft can create significant snowfalls in a relatively short period of time. Due to its location on a peninsula between the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara, Istanbul is very prone to lake-effect snow and this weather phenomenon occurs almost every winter. This type of precipitation is generated by the warmer Black Sea temperature and colder air temperature, over the Istanbul area. In February 2005, a lake-effect snowfall left of snow, and in March 1987, a three-week-long lake-effect snowfall accompanied with strong winds (lake-effect blizzard) left of snow in Istanbul. The snowfall in the eastern regions of the Black Sea is amplified by the orographic effect of the nearby Caucasus Mountains, often resulting in snowfall of several meters, especially at higher elevations.
In the Adriatic regions of Italy and in the eastern Apennine Mountains, the sea-effect snow phenomenon with air masses coming from Northern or Eastern Europe (and Russia) can be incredibly heavy and can last for days. In the hills and mountains, it can result in snowfalls of several meters, as it happened in February 2012. These huge amounts of snow can also fall in short periods of time.
In Northern Europe, cold, dry air masses from Russia can blow over the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53┬░N to 66┬░N latitude and from ...
and cause heavy snow squalls on areas of the southern and eastern coasts of Sweden, as well as on the Danish island of Bornholm, the east coast of Jutland and the northern coast of Poland. For the northern parts of the Baltic Sea, this happens mainly in the early winter, since it freezes later. Southeast Norway can also experience heavy sea snow events with east-north-easterly winds. Especially, coastal areas from Kragero to Kristiansand have had incredible snow depths in the past with intense persistent snowbands from Norwegian Sea (the coastal city of Arendal recorded in a single week in late February 2007). Although Fennoscandia is lined with an abundance of lakes, this type of snowfall is rare in these, due to the shallow freshwater freezing early in the cold interiors. One notable exception happened in the middle of May 2008, as Leksand on the since-long unfrozen lake of Siljan (lake), Siljan got on the ground.
The Sea of Japan creates snowfall in the mountainous western Japanese prefectures of Niigata Prefecture, Niigata and Nagano Prefecture, Nagano, parts of which are known collectively as Snow country (Japan), snow country (''Yukiguni''). In addition to the Sea of Japan, other parts of Japan, as well as Korea and Shandong Peninsula, experience these same conditions.
Because the Aegean Sea (Greece), is warm in the winter, when cold air masses from Siberia advance in the area, they pick up much moisture, resulting in heavy snowfalls in eastern Central Greece, eastern Thessaly, eastern Peloponnese, south-eastern Chalkidiki, the Cyclades, and Crete (more commonly in the mountainous areas). In 2008, a severe snowstorm blanketed Athens, dropping of snow and causing huge traffic jams.
Moving of polar or Siberian high-pressure centers along Caspian Sea regarding to relatively warmer water of this sea can make heavy snowfalls in the northern coast of Iran. Several blizzards have been reported in this region during the last decades. In February 2014, heavy snowfall reached on the coastline in Gilan Province, Gilan and Mazandaran Province, Mazandaran provinces of Iran. The heaviest snowfall was reported in Abkenar, Gilan, Abkenar village near Anzali Lagoon.
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
on January 7, 2008
File:Lake effect pic.jpg, Lake effect snow in Athens on February 16, 2021
File:Lake effect pic 1.jpg, Lake effect snow in Athens on February 16, 2021
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, easterly winds bringing cold continental air across theNorth Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
can lead to a similar phenomenon. Locally, it is also known as "lake-effect snow" despite the snow coming in from the sea rather than a lake. Similarly during a north-westerly wind, snow showers can form coming in from the Liverpool Bay, coming down the Cheshire Plain, Cheshire gap, causing snowfall in the West Midlands (region), West MidlandsŌĆöthis formation resulted in the white Christmas of 2004 in the area, and most recently the heavy snowfall of 8 December 2017 and 30 January 2019. A similar phenomenon can affect the city of Inverness in the Scottish Highlands, where cold north-east winds cause heavy snow to form in the Moray Firth; this was the case with the White Hogmanay of 2009, which caused the street party to be cancelled. Northerly and north-westerly winds can cause the effect to occur over the Irish Sea and Bristol Channel feeding snow into South West England and eastern Ireland. Western Scotland and northern Ireland can also see snow showers from a north or north-westerly wind over the Atlantic.
Since the North Sea is relatively warm (around at the beginning of winter, typically by the end), sufficiently cold air aloft can create significant snowfalls in a relatively short period of time. The best-known example occurred in January 1987 South-East England snowfall, January 1987, when record-breaking cold air (associated with an upper low) moved across the North Sea towards the UK. The end result was over 2 ft of snow for coastal areas, leading to communities being cut off for over a week. The latest of these events to affect Britain's east coast occurred on November 30, 2017; February 28, 2018; and March 17, 2018; in connection with the 2018 Great Britain and Ireland cold wave. The second event of winter 2017/18 was particularly severe, with up to falling in total over the 27thŌĆō28th.
Similarly, northerly winds blowing across the relatively warm waters of the English Channel during cold spells can bring significant snowfall to the French region of Normandy, where snow drifts exceeding 10 ft (3 m) were measured in March 2013.
See also
* Horizontal convective rolls * OWLeS, Ontario winter lake-effect systems * Planetary boundary layer * Sea smoke Warnings about lake-effect snow: :United States: ::* Lake effect snow advisory ::* Lake effect snow watch ::* Lake effect snow warning ::* Severe weather terminology (United States) :Canada: ::* Snowsquall warning ::* Severe weather terminology (Canada)References
External links
National Weather Service Official Lake Effect Page
Ćöbased in Buffalo, NY
Lake effect forecasting
Video of a snowsquall timelapse while driving on Highway 407 ETR in Greater Toronto
, Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory
A BBC forecast of lake effect snow in the UK in 1991
{{Severe weather terminology (United States) navbox Climatology Snow or ice weather phenomena Upper Peninsula of Michigan fr:Bourrasque de neige#Bourrasques en aval de plans d'eau