Kursk Oblast on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kursk Oblast ( rus, Курская область, r=Kurskaya oblast, p=ˈkurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of
 Kursk Oblast is one of Russia's major producers of iron ore. The area of the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly has one of the richest iron-ore deposits in the world. Rare earths and base metals also occur in commercial quantities in several locations. Refractory loam,
Kursk Oblast is one of Russia's major producers of iron ore. The area of the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly has one of the richest iron-ore deposits in the world. Rare earths and base metals also occur in commercial quantities in several locations. Refractory loam,
 Population: 1,127,081 ( 2010 Census);
;2012
*Births: 13 318 (11.9 per 1000)
*Deaths: 18 529 (16.6 per 1000)
;
2009 - 1.53 , 2010 - 1.55 , 2011 - 1.61 , 2012 - 1.70 , 2013 - 1.67 , 2014 - 1.70 , 2015 - 1.72 , 2016 - 1.64(e)
;
*
Population: 1,127,081 ( 2010 Census);
;2012
*Births: 13 318 (11.9 per 1000)
*Deaths: 18 529 (16.6 per 1000)
;
2009 - 1.53 , 2010 - 1.55 , 2011 - 1.61 , 2012 - 1.70 , 2013 - 1.67 , 2014 - 1.70 , 2015 - 1.72 , 2016 - 1.64(e)
;
*Unknown Eastern Ukraine
The Ukrainian Week (14 March 2012) The annual growth rate of the oblast's population is negative; death rate exceeds overall birth rates and immigration. ;Religion According to a 2012 survey 68.7% of the population of Kursk Oblast adheres to the
 The largest universities of Kursk Oblast is Kursk State University,
The largest universities of Kursk Oblast is Kursk State University,
 Slavic tribes of the Severians inhabited the area. From 830 the Kursk was part of the Rus' Khaganate and
Slavic tribes of the Severians inhabited the area. From 830 the Kursk was part of the Rus' Khaganate and
 The center-right pro-government United Russia Party and the left Communist Party of the Russian Federation are Kursk Oblast's major political parties. Traditionally, the Communist Party is the strongest in the Oblast's rural area.
The center-right pro-government United Russia Party and the left Communist Party of the Russian Federation are Kursk Oblast's major political parties. Traditionally, the Communist Party is the strongest in the Oblast's rural area.
Official website of Kursk OblastOfficial website of Kursk Oblast
Kursk Region History and General Information
* {{Use mdy dates, date=November 2015 States and territories established in 1934
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
(an oblast). Its administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
is the city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
of Kursk. As of the 2010 Census, Kursk Oblast has a population of 1,127,081.
Geography
The oblast, with an average elevation of , occupies the southern slopes of the middle-Russian plateau. The surface is hilly and intersected by ravines. The central part of Kursk oblast is more elevated than the Seym Valley to the west. The Timsko-Shchigrinsky ridge contains the highest point in the oblast at above the sea level. The low relief, gentle slopes, and mild winters make the area suitable for farming, and much of the forest has been cleared. Chernozem soils cover around 70% of the oblast's territory;podsol
In soil science, podzols are the typical soils of coniferous or boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on heathland, which is often a construct of ...
soils cover 26%.
;Borders:
''Internal'': Bryansk Oblast (NW) (border length: ), Oryol Oblast (N, ), Lipetsk Oblast (NE, ), Voronezh Oblast (E, ), Belgorod Oblast (S, ).
''International'': Sumy Oblast of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
(W, ).
Rivers
Kursk Oblast contributes to two major drainage areas: the Dnieper River and the Don River (78% and 22% respectively). There are 902 rivers and streams in the oblast, with a total length of approximately . Major rivers include theSeym
The Seim (also transcribed as Seym and Sejm, in ; ) is a west-flowing river in Russia and Ukraine. Its length is (250 km within Ukraine) and its basin area about . It is the largest tributary of the Desna.
Places on the river are: Kursk, Kur ...
and the Psyol.
Lakes
The inland waters of Kursk oblast consist of 145 artificial lakes and about 550 small ponds.Natural resources
mineral sands
Heavy mineral sands are a class of ore deposit which is an important source of zirconium, titanium, thorium, tungsten, rare-earth elements, the industrial minerals diamond, sapphire, garnet, and occasionally precious metals or gemstones.
Heavy m ...
, and chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
are quarried and processed in the region. The oblast's reserves of artesian-well water are proving useful for medical purposes.
Climate
The oblast's location at the center of the European part of Russia gives the region a medium continentalclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
: warm summers and relatively mild winters. In July the average daytime high temperature is . In January the average high is . The average number of frost-free days ranges from 150 in the north to 160 in the south. The growing season in Kursk Oblast varies, from 180 days in the north to 195 days in the southwest. The average annual precipitation for the oblast is , but it ranges from in the northwest to about or less in the southeastern corner. Rainfall peaks during June and July. The snow depth in Kursk Oblast differs considerably, from in the north of the oblast, to in the south. Annual sunshine is 1775 hours.
Flora and fauna
Kursk Oblast forms a part of the Eastern European forest-steppe. One-quarter of Kursk oblast was once heavily wooded. Hardwood timbers included oak,ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non-gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
, and elm. Now forests cover only 10% of the oblast. Animals native to the area are numerous. Pike, bleak
Bleak may refer to:
Fish
* Species of the genus '' Alburnus''
* ''Alburnoides bipunctatus'', also known as the schneider
Music
* "Bleak", a song by Opeth from ''Blackwater Park
''Blackwater Park'' is the fifth studio album by Swedish progressi ...
, and perch abound in local rivers. Otter and badger, as well as wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
, red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of ...
, and roe deer
The roe deer (''Capreolus capreolus''), also known as the roe, western roe deer, or European roe, is a species of deer. The male of the species is sometimes referred to as a roebuck. The roe is a small deer, reddish and grey-brown, and well-adapt ...
remain numerous in many parts of the area.
Administrative divisions
Demographics
 Population: 1,127,081 ( 2010 Census);
;2012
*Births: 13 318 (11.9 per 1000)
*Deaths: 18 529 (16.6 per 1000)
;
2009 - 1.53 , 2010 - 1.55 , 2011 - 1.61 , 2012 - 1.70 , 2013 - 1.67 , 2014 - 1.70 , 2015 - 1.72 , 2016 - 1.64(e)
;
*
Population: 1,127,081 ( 2010 Census);
;2012
*Births: 13 318 (11.9 per 1000)
*Deaths: 18 529 (16.6 per 1000)
;
2009 - 1.53 , 2010 - 1.55 , 2011 - 1.61 , 2012 - 1.70 , 2013 - 1.67 , 2014 - 1.70 , 2015 - 1.72 , 2016 - 1.64(e)
;
*Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
- 96.5%
*Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
- 1.3%
*Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
- 0.5%
*Others - 1.7%
*52,722 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
According to the 1897 census
The first general census of the population of the Russian Empire in 1897 ( pre-reform Russian: ) was the first and only nation-wide census performed in the Russian Empire (the Grand Duchy of Finland was excluded). It recorded demographic data as ...
, there were 77.3% Russians and 22.3% Ukrainians in the Kursk Governorate. The 1932 forced end to Ukrainization in southern Russia (Soviet Republic) led to a massive decline of reported Ukrainians in these regions in the 1937 Soviet Census compared to the 1926 First All-Union Census of the Soviet Union.The Ukrainian Week (14 March 2012) The annual growth rate of the oblast's population is negative; death rate exceeds overall birth rates and immigration. ;Religion According to a 2012 survey 68.7% of the population of Kursk Oblast adheres to the
Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
. In addition, 24% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious
"Spiritual but not religious" (SBNR), also known as "spiritual but not affiliated" (SBNA), is a popular phrase and initialism used to self-identify a life stance of spirituality that does not regard organized religion as the sole or most valuable ...
", 4% is atheist, and 3.3% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question.
Education
 The largest universities of Kursk Oblast is Kursk State University,
The largest universities of Kursk Oblast is Kursk State University, Kursk State Technical University
SouthWest State University (former SWSU) (russian: Юго-Западный государственный университет, ''Yugo-Zapadnyj gosudarstvennyj universitet''), for a time the КurskSTU (russian: КурскГТУ), ''kurskij poli ...
, Kursk State Medical University
Kursk State Medical University is a Russian medical university located in Kursk, western Russia, established in 1935. In 1994 it was granted university status.
History
The decision to create a medical institute was taken in 1935, and the first ...
and Kursk State Agricultural Academy
Kursk ( rus, Курск, p=ˈkursk) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur River (Kursk Oblast), Kur, Tuskar River, Tuskar, and Seym River, Sey ...
which are located in the city of Kursk. There are also 19 other higher education facilities in Kursk Oblast.
History
 Slavic tribes of the Severians inhabited the area. From 830 the Kursk was part of the Rus' Khaganate and
Slavic tribes of the Severians inhabited the area. From 830 the Kursk was part of the Rus' Khaganate and Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas o ...
states. Although territory of Kursk Oblast had been populated since the end of the last ice age, information about the cities was scant until 1596 when the Kursk stronghold was built. Later it was part of Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
under the Jagiellonian dynasty. It was lost in the Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars to the Muscovite Rus'. A real growth of the area around Kursk began soon after that, with a large migration from Central Russia after famine in the beginning of the 17th century. Between 1708 and 1719, Kursk was a part of the newly created Kiev Governorate. From 1719 to 1727 it was a part of Belgorod province of Kiev Governorate. Later Kursk uyezd was a part of Belgorod Governorate. On 23 May 1779, Kursk Governorate was established. The latter subdivision existed until 1928, when the territory of Kursk Governorate became a part of Central Black Earth Oblast
Central Black Earth Oblast (russian: Центрально-Чернозёмная область, ''Tsentralno-Chernozyomnaya oblast'') was an '' oblast'' (a first-level administrative and municipal unit) of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialis ...
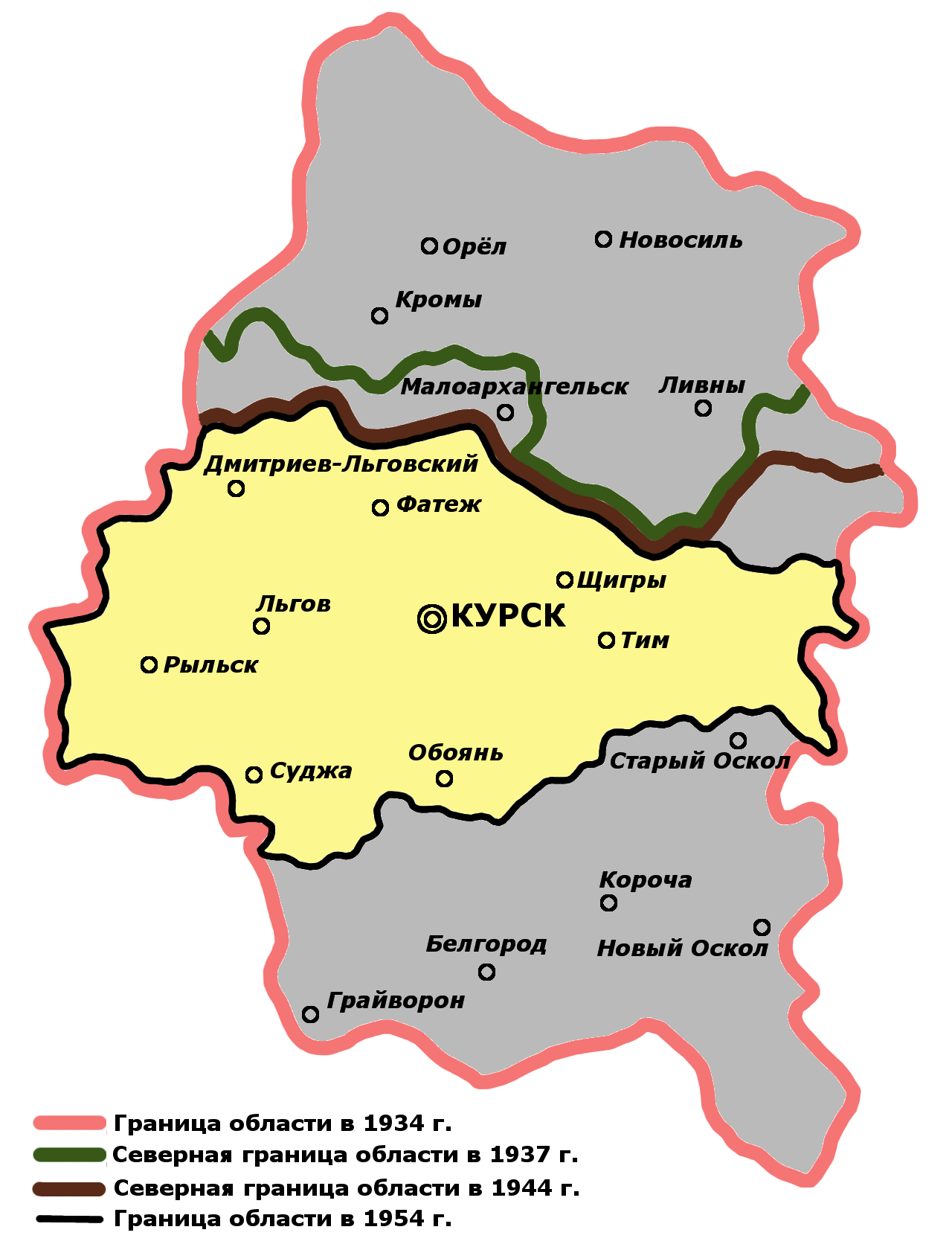
. As Central Chernozem Oblast was very large its administration was very difficult, on 13 June 1934 it was divided into two oblasts: Kursk Oblast and Voronezh Oblast. In the period between 1934 and 1954, oblasts' borders were frequently adjusted. However, the area and borders of the oblast have remained stable from 1954.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the territory of Kursk Oblast was occupied by the German troops from fall of 1941 until summer of 1943. The Battle of Kursk, which was one of the major battles of World War II, took place in the region between 5 July 1943 and 23 August 1943.
The territory of Kursk Oblast was the region in which the 4th leader of the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
, Nikita Khrushchev, was born.
Politics
During theSoviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
period, the high authority in the oblast was shared between three persons: The first secretary of the Kursk CPSU Committee (who in reality had the biggest authority), the chairman of the oblast Soviet (legislative power), and the Chairman of the oblast Executive Committee (executive power). In 1991, CPSU lost power, and the head of the Oblast administration, and eventually the governor was appointed/elected alongside elected regional parliament.
The Charter of Kursk Oblast is the fundamental law of the region. The Kursk Oblast Duma
The Kursk Oblast Duma (russian: Курская областная дума, Kurskaya oblastnaya duma) is the regional parliament of Kursk Oblast, a federal subject of Russia. A total of 45 deputies are elected for five-year terms.
Elections 202 ...
is the province's standing legislative (representative) body. The Legislative Assembly exercises its authority by passing laws, resolutions, and other legal acts and by supervising the implementation and observance of the laws and other legal acts passed by it. The highest executive body is the Oblast Government, which includes territorial executive bodies such as district administrations, committees, and commissions that facilitate development and run the day to day matters of the province. The Oblast administration supports the activities of the Governor who is the highest official and acts as guarantor of the observance of the oblast Charter in accordance with the Constitution of Russia.
 The center-right pro-government United Russia Party and the left Communist Party of the Russian Federation are Kursk Oblast's major political parties. Traditionally, the Communist Party is the strongest in the Oblast's rural area.
The center-right pro-government United Russia Party and the left Communist Party of the Russian Federation are Kursk Oblast's major political parties. Traditionally, the Communist Party is the strongest in the Oblast's rural area.
Economy
Industry
The oblast's industrial production dropped rapidly during the 1990s, as an industrial crisis was stimulated by the nationwide economic crisis which followed the collapse of theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. However, by the end of the decade output was increasing. Moreover, the manufacturing sector, despite a sagging economy in the late 20th century, continues to account for about 40% of the oblast's GDP. The engineering, electric-power, metal-working, chemicals, and food processing are the dominant industries.
Agriculture
Most of the main farming areas are used for natural pastures or cultivation, which involves mainly wheat,sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet ('' Beta vulgaris''). Together ...
, and fodder crops. The main categories of productive holdings are wheat farms, dairy farms, poultry farms, and beef cattle. Agricultural lands cover , or 77% of the oblast's territory.
Transportation
The transportation industry of Kursk Oblast, with easy access to national and international markets, is the basis for the oblast's development. The most important modes of transport throughout the oblast are by railway and road. Total length of railway network is . Two major rail links pass through Kursk Oblast: Moscow–Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.
and Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
– Voronezh. Region roads serve all towns and rural settlements through road network. In addition, there is an airport in the oblast which was opened to international flights in July 1997.
Railroads
Railroads are one of the most important component parts of the transportation system in the oblast. There is a total of sixty-five railway stations in the oblast. The operational length of the railways is , of which are access roads. The length of the electrified lines is . The density of the railroads in Kursk Oblast is one of the highest in Russia. The largest railway junctions are Kursk, Lgov, andKastornoye
Kastornoye (russian: Кастóрное) is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) and the administrative center of Kastorensky District of Kursk Oblast, Russia. Population: Telephone code: +7 47157; postal code: 306700.
It was firs ...
. Oblast's railroads are a part of the Moscow and South Eastern Railway systems.
Tourism
Kursk Oblast's natural attraction is the Central Black Earth Nature Reserve, which offers great opportunity for hiking. Oblast's forests and others undeveloped areas are ideal for hunting, fishing, and camping. Traditional art and architecture are preserved in the town-museum of Rylsk and others historical towns of Kursk Oblast.See also
* List of Chairmen of the Kursk Oblast DumaReferences
Notes
Sources
* *External links
Official website of Kursk Oblast
Kursk Region History and General Information
* {{Use mdy dates, date=November 2015 States and territories established in 1934