Kragujevac massacre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kragujevac massacre was the mass murder of between 2,778 and 2,794 mostly
 Two resistance movements emerged following the invasion: the communist-led, multi-ethnic Partisans, and the royalist, Serbian nationalist Chetniks, although during 1941, within the occupied territory, even the Partisans consisted almost entirely of Serbs. The Partisans were led by the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, Josip Broz Tito; the Chetniks were led by
Two resistance movements emerged following the invasion: the communist-led, multi-ethnic Partisans, and the royalist, Serbian nationalist Chetniks, although during 1941, within the occupied territory, even the Partisans consisted almost entirely of Serbs. The Partisans were led by the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, Josip Broz Tito; the Chetniks were led by
 Nedić's inability to crush the Partisans and Chetniks prompted the Military Commander in Serbia to request German reinforcements from other parts of the continent. In mid-September, they transferred the 125th Infantry Regiment from Greece and the 342nd Infantry Division from France to help put down the uprising in Serbia. On 16 September, Hitler issued Directive No. 312 to ''
Nedić's inability to crush the Partisans and Chetniks prompted the Military Commander in Serbia to request German reinforcements from other parts of the continent. In mid-September, they transferred the 125th Infantry Regiment from Greece and the 342nd Infantry Division from France to help put down the uprising in Serbia. On 16 September, Hitler issued Directive No. 312 to ''
 The 6th Company's disappearance caused unease in the German ranks. A reconnaissance flight was dispatched to locate it, to no avail. The occupational authorities were unaware of the 6th Company's fate until a German officer escaped and informed them of what had transpired. He reported that the German prisoners were being humanely treated, but when Böhme became aware of the situation, he decided that retaliation was needed. He ordered the III. Battalion of the 749th Infantry Regiment to burn down Gornji Milanovac and take hostages in order to expedite the recovery of the captured German troops.
The III. Battalion started its advance on 5 October, fighting its way along the road to Gornji Milanovac and sustaining casualties in the process. Upon entering Gornji Milanovac, it gathered between 120 and 170 male hostages, among them a Chetnik commander who had been scheduled to meet his superiors the following day. ''
The 6th Company's disappearance caused unease in the German ranks. A reconnaissance flight was dispatched to locate it, to no avail. The occupational authorities were unaware of the 6th Company's fate until a German officer escaped and informed them of what had transpired. He reported that the German prisoners were being humanely treated, but when Böhme became aware of the situation, he decided that retaliation was needed. He ordered the III. Battalion of the 749th Infantry Regiment to burn down Gornji Milanovac and take hostages in order to expedite the recovery of the captured German troops.
The III. Battalion started its advance on 5 October, fighting its way along the road to Gornji Milanovac and sustaining casualties in the process. Upon entering Gornji Milanovac, it gathered between 120 and 170 male hostages, among them a Chetnik commander who had been scheduled to meet his superiors the following day. ''
 The hostages were held overnight on a public plaza in the town. In his version of events, von Bischofhausen claimed that he made objections to König, but the latter insisted that his orders, which had been issued by the commander of the 749th Infantry Regiment, were to be carried out. Shortly before the executions commenced, Ljotić obtained approval for two ''Zbor'' officials to scrutinise the hostages. Over 3,000 individuals, those identified as being "genuine nationalists" and "real patriots", were excluded from the execution lists as a result of Ljotić's intervention. Those who were not extracted from the hostage pool were accused of being communists or spreading "communist propaganda". The ''Zbor'' officials told them they were not "worth saving" because they had "infected the younger generation with their leftist ideas." The Germans considered ''Zbors involvement to be a "nuisance". According to the
The hostages were held overnight on a public plaza in the town. In his version of events, von Bischofhausen claimed that he made objections to König, but the latter insisted that his orders, which had been issued by the commander of the 749th Infantry Regiment, were to be carried out. Shortly before the executions commenced, Ljotić obtained approval for two ''Zbor'' officials to scrutinise the hostages. Over 3,000 individuals, those identified as being "genuine nationalists" and "real patriots", were excluded from the execution lists as a result of Ljotić's intervention. Those who were not extracted from the hostage pool were accused of being communists or spreading "communist propaganda". The ''Zbor'' officials told them they were not "worth saving" because they had "infected the younger generation with their leftist ideas." The Germans considered ''Zbors involvement to be a "nuisance". According to the
 On 11 November 1941, the Partisans captured a Wehrmacht officer named Renner, the area commander in
On 11 November 1941, the Partisans captured a Wehrmacht officer named Renner, the area commander in
 The massacre at Kragujevac came to symbolise the brutality of the German occupation in Yugoslav popular memory. It has drawn comparisons to the Germans'
The massacre at Kragujevac came to symbolise the brutality of the German occupation in Yugoslav popular memory. It has drawn comparisons to the Germans'
Serb
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
men and boys in Kragujevac, by German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
soldiers on 21 October 1941. It occurred in the German-occupied territory of Serbia
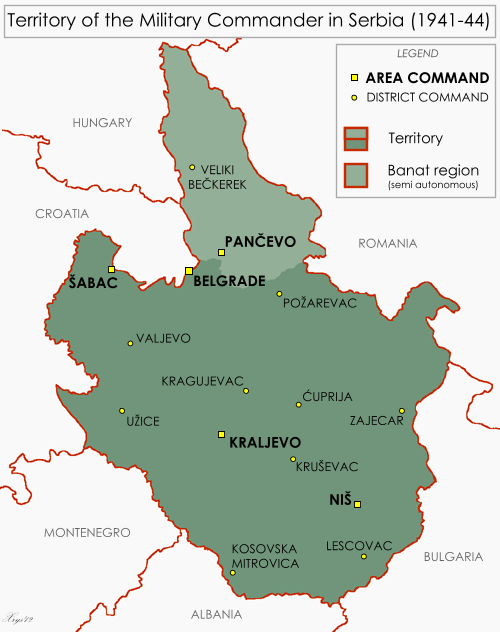
The Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia (german: Gebiet des Militärbefehlshabers in Serbien; sr, Подручје Војног заповедника у Србији, Područje vojnog zapovednika u Srbiji) was the area of the Kin ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, and came as a reprisal for insurgent attacks in the Gornji Milanovac
Gornji Milanovac ( sr-Cyrl, Гoрњи Милановац, ) is a town and municipality located in the Moravica District of central Serbia. The population of the town is 24,216, while the population of the municipality is 44,406.
The town was found ...
district that resulted in the deaths of ten German soldiers and the wounding of 26 others. The number of hostages
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seized, such as a relative, employer, law enforcement or government to act, or r ...
to be shot was calculated as a ratio of 100 hostages executed for every German soldier killed and 50 hostages executed for every German soldier wounded, a formula devised by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
with the intent of suppressing anti-Nazi resistance in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
.
After a punitive operation was conducted in the surrounding villages, during which over 400 males were shot and four villages burned down, another 70 male Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and communists
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
who had been arrested in Kragujevac were killed. Simultaneously, males between the ages of 16 and 60, including high school students, were assembled by German troops and local collaborators, and the victims were selected from amongst them. The selected males were then marched to fields outside the city, shot with heavy machine guns, and their bodies buried in mass grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of execution, although an exact ...
s. Contemporary German military records indicate that 2,300 hostages were shot. After the war, inflated estimates ranged as high as 7,000 deaths, but German and Serbian scholars have now agreed on the figure of nearly 2,800 killed, including 144 high school students. As well as Serbs, massacre victims included Jews, Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sig ...
, Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Macedonians, Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their na ...
, and members of other nationalities.
Several senior German military officials were tried and convicted for their involvement in the reprisal shootings at the Nuremberg trials
The Nuremberg trials were held by the Allies against representatives of the defeated Nazi Germany, for plotting and carrying out invasions of other countries, and other crimes, in World War II.
Between 1939 and 1945, Nazi Germany invaded m ...
and the subsequent Nuremberg trials. The massacre had a profound effect on the course of the war in Yugoslavia. It exacerbated tensions between the two guerrilla movements, the communist-led Partisans and the royalist, Serbian nationalist
Serbian nationalism asserts that Serbs are a nation and promotes the cultural and political unity of Serbs. It is an ethnic nationalism, originally arising in the context of the general rise of nationalism in the Balkans under Ottoman rule, und ...
Chetniks, and convinced Chetnik leader Draža Mihailović that further attacks against the Germans would only result in more Serb civilian deaths. The Germans soon found mass executions of Serbs to be ineffectual and counterproductive, as they tended to drive the population into the arms of insurgents. The ratio of 100 executions for one soldier killed and 50 executions for one soldier wounded was reduced by half in February 1943, and removed altogether later in the year. The massacre is commemorated by the October in Kragujevac Memorial Park and the co-located 21 October Museum, and has been the subject of several poems and feature films. The anniversary of the massacre is commemorated annually in Serbia as the Day of Remembrance of the Serbian Victims of World War II.
Background
Encirclement and invasion of Yugoslavia
Following the 1938 betweenNazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Yugoslavia came to share its northwestern border with Germany and fell under increasing pressure as its neighbours aligned themselves with the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
. In April 1939, Italy opened a second frontier with Yugoslavia when it invaded and occupied neighbouring Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
. At the outbreak of World War II, the Yugoslav government declared its neutrality. Between September and November 1940, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
joined the Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive milit ...
, aligning themselves with the Axis, and Italy invaded Greece. Yugoslavia was by then almost completely surrounded by the Axis powers and their satellites, and its neutral stance toward the war became strained. In late February 1941, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
joined the Pact. The following day, German troops entered Bulgaria from Romania, closing the ring around Yugoslavia. Intending to secure his southern flank for the impending attack on the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, German dictator Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
began placing heavy pressure on Yugoslavia to join the Axis. On 25 March 1941, after some delay, the Yugoslav government conditionally signed the Pact. Two days later, a group of pro-Western, Serbian nationalist
Serbian nationalism asserts that Serbs are a nation and promotes the cultural and political unity of Serbs. It is an ethnic nationalism, originally arising in the context of the general rise of nationalism in the Balkans under Ottoman rule, und ...
Royal Yugoslav Air Force officers deposed the country's regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
, Prince Paul, in a bloodless coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
. They placed his teenage nephew Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a sur ...
on the throne and brought to power a "government of national unity" led by the head of the Royal Yugoslav Air Force, General Dušan Simović
Dušan Simović (; 28 October 1882 – 26 August 1962) was a Yugoslav Serb army general who served as Chief of the General Staff of the Royal Yugoslav Army and as the Prime Minister of Yugoslavia in 1940–1941.
Biography
Simović, born o ...
. The coup enraged Hitler, who immediately ordered the country's invasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity aggressively enter territory (country subdivision), territory owned by another such entity, gen ...
, which commenced on 6 April 1941.
Yugoslavia was quickly overwhelmed by the combined strength of the Axis powers and surrendered in less than two weeks. The government and royal family went into exile, and the country was occupied and dismembered by its neighbours. The German-occupied territory of Serbia
The Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia (german: Gebiet des Militärbefehlshabers in Serbien; sr, Подручје Војног заповедника у Србији, Područje vojnog zapovednika u Srbiji) was the area of the Kin ...
was limited to the pre-Balkan War
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defea ...
borders of the Kingdom of Serbia and was directly occupied by the Germans for the key rail and riverine transport routes that passed through it, as well as its valuable resources, particularly non-ferrous metals
In metallurgy, non-ferrous metals are metals or alloys that do not contain iron (allotropes of iron, ferrite, and so on) in appreciable amounts.
Generally more costly than ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals are used because of desirable proper ...
. The occupied territory covered about and had a population of 3.8 million. Hitler had briefly considered erasing all existence of a Serbian state, but this was quickly abandoned and the Germans began searching for a Serb suitable to lead a puppet government
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sover ...
in Belgrade. They initially settled on Milan Aćimović
Milan Aćimović ( sr-Cyrl, Милан Аћимовић; 31 May 1898 – 25 May 1945) was a Yugoslav politician and collaborationist with the Axis in Yugoslavia during World War II.
Early life
Milan Aćimović was born on 31 May 1898 in Pinos ...
, a staunch anti-communist who served as Yugoslavia's Minister of Internal Affairs
Minister may refer to:
* Minister (Christianity), a Christian cleric
** Minister (Catholic Church)
* Minister (government), a member of government who heads a ministry (government department)
** Minister without portfolio, a member of governme ...
in late 1939 and early 1940.
Occupation and resistance
 Two resistance movements emerged following the invasion: the communist-led, multi-ethnic Partisans, and the royalist, Serbian nationalist Chetniks, although during 1941, within the occupied territory, even the Partisans consisted almost entirely of Serbs. The Partisans were led by the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, Josip Broz Tito; the Chetniks were led by
Two resistance movements emerged following the invasion: the communist-led, multi-ethnic Partisans, and the royalist, Serbian nationalist Chetniks, although during 1941, within the occupied territory, even the Partisans consisted almost entirely of Serbs. The Partisans were led by the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, Josip Broz Tito; the Chetniks were led by Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge o ...
Draža Mihailović, an officer in the interwar Royal Yugoslav Army
The Yugoslav Army ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Jugoslovenska vojska, JV, Југословенска војска, ЈВ), commonly the Royal Yugoslav Army, was the land warfare military service branch of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia (originally Kingdom of Serbs, ...
. The two movements had widely divergent goals. Whereas the Partisans sought to turn Yugoslavia into a communist state under Tito's leadership, the Chetniks sought a return to the pre-war , whereby the Yugoslav monarchy—and, by extension, Serb political hegemony—would be restored. Communist resistance commenced in early July, shortly after the invasion of the Soviet Union, targeting both the Germans and the puppet authorities. By late August 1941, the Partisans and Chetniks were carrying out joint attacks against the Germans. The Partisans were well organised and many of their commanders had ample military experience, having fought in the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
. Within several months of the invasion, they had 8,000 fighters spread across 21 detachments in Serbia alone. Many Chetniks were either veterans of the Balkan Wars and World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
or former members of the Royal Yugoslav Army. They boasted around 20,000 fighters in the German-occupied territory of Serbia at the time of the massacre.
On 29 August, the Germans replaced Aćimović with another fervent anti-communist, the former Minister of the Army and Navy and Chief of the General Staff The Chief of the General Staff (CGS) is a post in many armed forces (militaries), the head of the military staff.
List
* Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff ( United States)
* Chief of the General Staff (Abkhazia)
* Chief of General Staff (Af ...
, General Milan Nedić
Milan Nedić ( sr-Cyrl, Милан Недић; 2 September 1878 – 4 February 1946) was a Yugoslav and Serbian army general and politician who served as the chief of the General Staff of the Royal Yugoslav Army and minister of war in the R ...
, who formed a new puppet government. In September, the Nedić government was permitted to form the Serbian Volunteer Command ( sh, Srpska dobrovoljačka komanda; SDK), an auxiliary paramilitary formation to help quell anti-German resistance. In effect, the SDK was the military arm of the fascist Yugoslav National Movement
The Yugoslav National Movement ( sh, Jugoslavenski narodni pokret / Југословенски народни покрет), also known as the United Militant Labour Organization (''Združena borbena organizacija rada'' / ''Здружена бор ...
( sh, Združena borbena organizacija rada, links=no, ''Zbor''), led by Dimitrije Ljotić
Dimitrije Ljotić ( sr-cyr, Димитрије Љотић; 12 August 1891 – 23 April 1945) was a Serbian and Yugoslav fascist politician and ideologue who established the Yugoslav National Movement (Zbor) in 1935 and collaborated with Ge ...
. It was originally intended to have a strength of 3,000–4,000 troops, but this number eventually rose to 12,000. It was headed by Kosta Mušicki, a former colonel in the Royal Yugoslav Army, whom Nedić appointed on 6 October 1941. In the early stages of the occupation, the SDK formed the bulk of Nedić's forces, which numbered around 20,000 men by late 1941.
Prelude
Anti-German uprising
 Nedić's inability to crush the Partisans and Chetniks prompted the Military Commander in Serbia to request German reinforcements from other parts of the continent. In mid-September, they transferred the 125th Infantry Regiment from Greece and the 342nd Infantry Division from France to help put down the uprising in Serbia. On 16 September, Hitler issued Directive No. 312 to ''
Nedić's inability to crush the Partisans and Chetniks prompted the Military Commander in Serbia to request German reinforcements from other parts of the continent. In mid-September, they transferred the 125th Infantry Regiment from Greece and the 342nd Infantry Division from France to help put down the uprising in Serbia. On 16 September, Hitler issued Directive No. 312 to ''Generalfeldmarschall
''Generalfeldmarschall'' (from Old High German ''marahscalc'', "marshal, stable master, groom"; en, general field marshal, field marshal general, or field marshal; ; often abbreviated to ''Feldmarschall'') was a rank in the armies of several ...
'' ( Field Marshal) Wilhelm List
Wilhelm List (14 May 1880 – 17 August 1971) was a German field marshal during World War II who was convicted of war crimes by a US Army tribunal after the war. List commanded the 14th Army in the invasion of Poland and the 12th Army in the ...
, the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
commander in Southeast Europe, ordering him to suppress all resistance in that part of the continent. That same day, the Supreme Command of the Armed Forces (''Oberkommando der Wehrmacht''; OKW) issued Hitler's order on the suppression of "Communist Armed Resistance Movements in the Occupied Areas", signed by ''Generalfeldmarschall'' Wilhelm Keitel
Wilhelm Bodewin Johann Gustav Keitel (; 22 September 188216 October 1946) was a German field marshal and war criminal who held office as chief of the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW), the high command of Nazi Germany's Armed Forces, duri ...
. This decree specified that all attacks against the Germans on the Eastern Front were to be "regarded as being of communist origin", and that 100 hostages were to be shot for every German soldier killed and 50 were to be shot for every German soldier wounded. It was intended to apply to all of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, though an identical policy had already been implemented in Serbia as early as 28 April 1941, aimed at deterring guerrilla attacks. Attacks against the Germans increased in the first half of the year and Serbia once again became a war zone. German troops fanned through the countryside burning villages, taking hostages and establishing concentration camps. The first mass executions of hostages commenced in July.
The strengthening of Germany's military presence in Serbia resulted in a new wave of mass executions and war crimes. The commanders who bore the most responsibility for these atrocities were primarily of Austrian origin and had served in the Austro-Hungarian Army
The Austro-Hungarian Army (, literally "Ground Forces of the Austro-Hungarians"; , literally "Imperial and Royal Army") was the ground force of the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy from 1867 to 1918. It was composed of three parts: the joint arm ...
during World War I. Most were ardently anti-Serb, a prejudice that the historian Stevan K. Pavlowitch links to the Nazis' wider anti- Slavic racism. On 19 September, (Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
) Franz Böhme
Franz Friedrich Böhme (15 April 1885 – 29 May 1947) was an Army officer who served in succession with the Austro-Hungarian Arny, the Austrian Army and the German Wehrmacht. He rose to the rank of general during World War II, serving as Comm ...
was appointed as Plenipotentiary Commanding General in Serbia, with direct responsibility for quelling the revolt, bringing with him the staff of XVIII Mountain Corps
XVIII. ''Armeekorps'' was formed in Salzburg, Austria, on 1 April 1938, following the Anschluss of Austria into the German Reich. During the life of the XVIII. Armeekorps, they took part in the Polish campaign, Fall Weiss, and the campaign in t ...
. He was allocated additional forces to assist him in doing so, reinforcing the three German occupation divisions already in the territory. These divisions were the 704th Infantry Division
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube (algebra), cube.
As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion ...
, 714th Infantry Division and 717th Infantry Division. Böhme boasted a profound hatred of Serbs and encouraged his predominantly Austrian-born troops to exact "vengeance" against them. His primary grievances were the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir presumptive to the Austro-Hungarian throne, and his wife, Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, were assassinated on 28 June 1914 by Bosnian Serb student Gavrilo Princip. They were shot at close range whil ...
and subsequent Austro-Hungarian military defeats at the hands of the Royal Serbian Army
The Army of the Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Војска Краљевине Србије, Vojska Kraljevine Srbije), known in English as the Royal Serbian Army, was the army of the Kingdom of Serbia that existed between 1882 and 1918, succeed ...
, which he thought could only be rectified by the reprisal shooting of Serbian civilians. "Your objective," Böhme declared, "is to be achieved in a land where, in 1914, streams of German blood flowed because of the treachery of the Serbs, men and women. You are the avengers of those dead."
Clashes at Gornji Milanovac
Surrender of the 6th Company
By late September 1941, the town ofGornji Milanovac
Gornji Milanovac ( sr-Cyrl, Гoрњи Милановац, ) is a town and municipality located in the Moravica District of central Serbia. The population of the town is 24,216, while the population of the municipality is 44,406.
The town was found ...
had effectively been cut off from the rest of German-occupied Serbia by the frequent disruption of road and rail transport leading to and from it. On 29 September, elements of the Takovo
Takovo ( sr-cyr, Таково) is a village in the municipality of Gornji Milanovac, Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the village has a population of 458 people.Popis stanovništva, domaćinstava i Stanova 2002. Knjiga 1: Nacionalna ili etni� ...
Chetnik and Čačak
Čačak ( sr-Cyrl, Чачак, ) is a city and the administrative center of the Moravica District in central Serbia. It is located in the West Morava Valley within the geographical region of Šumadija. , the city proper has 73,331 inhabitants, wh ...
Partisan detachments attacked Gornji Milanovac, which was defended by the 6th Company of the 920th (Local Defence) Battalion. The 6th Company's garrison was based out of a local school. The guerrillas did not expect to capture the garrison, but undertook the attack in order to generate new recruits from the surrounding area. The local Chetnik commander, Zvonimir Vučković, became aware of the Partisan plans and decided to join in the attack to avoid the significant loss of prestige that would result from allowing the Partisans to attack alone. The insurgents launched a morning attack against the school. Although they were successful in overrunning the sentry posts, the Germans' heavy machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) ar ...
s soon stopped the assault. In 90 minutes of fighting, ten Germans were killed and 26 wounded. The two insurgent groups judged that continuing the assault would be too costly and Vučković suggested negotiating with the Germans.
Knowing the Germans would be far more likely to carry out negotiations with royalists than with communists, the Partisans allowed the Chetniks to conduct the negotiating in order to lure the garrison out of the town. A Chetnik envoy delivered an ultimatum to the garrison, demanding that it surrender to the guerrillas. The ultimatum was rejected. Thirty minutes later, a second Chetnik envoy appeared, guaranteeing the 6th Company unmolested passage to Čačak on the condition that it left Gornji Milanovac the same day. He further requested that the town and its inhabitants be spared from any possible reprisals. The commander of the 6th Company agreed and evacuated the garrison. Around outside Gornji Milanovac, the 6th Company was surrounded by the guerrillas and forced to surrender.
III. Battalion's punitive expedition
 The 6th Company's disappearance caused unease in the German ranks. A reconnaissance flight was dispatched to locate it, to no avail. The occupational authorities were unaware of the 6th Company's fate until a German officer escaped and informed them of what had transpired. He reported that the German prisoners were being humanely treated, but when Böhme became aware of the situation, he decided that retaliation was needed. He ordered the III. Battalion of the 749th Infantry Regiment to burn down Gornji Milanovac and take hostages in order to expedite the recovery of the captured German troops.
The III. Battalion started its advance on 5 October, fighting its way along the road to Gornji Milanovac and sustaining casualties in the process. Upon entering Gornji Milanovac, it gathered between 120 and 170 male hostages, among them a Chetnik commander who had been scheduled to meet his superiors the following day. ''
The 6th Company's disappearance caused unease in the German ranks. A reconnaissance flight was dispatched to locate it, to no avail. The occupational authorities were unaware of the 6th Company's fate until a German officer escaped and informed them of what had transpired. He reported that the German prisoners were being humanely treated, but when Böhme became aware of the situation, he decided that retaliation was needed. He ordered the III. Battalion of the 749th Infantry Regiment to burn down Gornji Milanovac and take hostages in order to expedite the recovery of the captured German troops.
The III. Battalion started its advance on 5 October, fighting its way along the road to Gornji Milanovac and sustaining casualties in the process. Upon entering Gornji Milanovac, it gathered between 120 and 170 male hostages, among them a Chetnik commander who had been scheduled to meet his superiors the following day. ''Hauptmann
is a German word usually translated as captain when it is used as an officer's rank in the German, Austrian, and Swiss armies. While in contemporary German means 'main', it also has and originally had the meaning of 'head', i.e. ' literally ...
'' ( Captain) Fiedler, the III. Battalion's commanding officer, hoped to use this man to contact the Chetnik command and organize a prisoner exchange
A prisoner exchange or prisoner swap is a deal between opposing sides in a conflict to release prisoners: prisoners of war, spies, hostages, etc. Sometimes, dead bodies are involved in an exchange.
Geneva Conventions
Under the Geneva Conven ...
. Fearing that such an action would jeopardize the recovery of the German prisoners, Fiedler decided not to raze Gornji Milanovac.
Around this time, Fiedler received an SOS signal from nearby Rudnik, where another German unit was involved in heavy fighting with the guerrillas. Fiedler decided to redirect the III. Battalion to Rudnik to relieve the unit. Assuming he would have to pass through Gornji Milanovac on his way back, he decided to postpone the taking of hostages in Gornji Milanovac and the razing of the town until his return from Rudnik. Contrary to Fiedler's expectations, the battalion was ordered back to Kragujevac immediately after relieving the unit at Rudnik, and was thus unable to raze Gornji Milanovac. Böhme was furious, and on 15 October, he sent the III. Battalion back to Gornji Milanovac to carry out his original orders. The battalion returned to Gornji Milanovac the same day, but now only forty people could be found to be taken as hostages. The town was then razed. This time, no attempt to exchange the hostages was made.
Kraljevo massacre
On 15–16 October, ten German soldiers were killed and 14 wounded during a joint Partisan-Chetnik attack onKraljevo
Kraljevo ( sr-cyr, Краљево, ) is a List of cities in Serbia, city and the administrative center of the Raška District in central Serbia. It is situated on the confluence of West Morava and Ibar River, Ibar, in the geographical region of � ...
, a city about south of Belgrade and southeast of Gornji Milanovac. On 15 October, troops of the 717th Infantry Division shot 300 civilians from Kraljevo in reprisal. These reprisal killings continued over the following days, and by 17 or 20 October, German troops had rounded up and shot 1,736 men and 19 "communist" women from the city and its outskirts, despite attempts by local collaborationists to mitigate the punishment. These executions were personally supervised by the commander of the 717th Infantry Division, (Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
) Paul Hoffman.
Timeline
Round-up
Kragujevac is anindustrial city
An industrial city or industrial town is a town or city in which the municipal economy, at least historically, is centered around industry, with important factories or other production facilities in the town. It has been part of most countries' i ...
in Central Serbia, about south of Belgrade, and east of Gornji Milanovac. It had a population of more than 40,000 in 1941, and was the headquarters of a German military district. The city was also home to Yugoslavia's largest armaments factory, which had between 7,000 and 8,000 workers before the invasion.
A report was written by the military district commander in Kragujevac, Otto von Bischofhausen, immediately after the massacre. This report was addressed to Böhme, and was later tendered in evidence at the Subsequent Nuremberg trials. According to von Bischofhausen, in the late evening of 18 October, all male Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
in Kragujevac, along with some communists, were arrested according to lists, totalling 70 persons. As this constituted far too few hostages to meet the quota of 2,300, it was proposed to collect the balance by arrests on the streets, squares and houses of Kragujevac, in an operation to be conducted by the III. Battalion of the 749th Infantry Regiment and the I. Battalion of the 724th Infantry Regiment, part of the 704th Infantry Division. In response to this proposal, von Bischofhausen claimed that he suggested to the garrison commander, Major Paul König, that instead of using the population of Kragujevac, the required hostages be gathered from surrounding villages which were known to be "completely strewn with communists". According to von Bischofhausen's account, this suggestion was initially accepted by König, and on 19 October, the III. Battalion "mopped up" the villages of Mečkovac and Maršić and the I. Battalion conducted a similar operation in the villages of Grošnica and Milatovac. A total of 422 men were shot in these four villages, without any German losses.
On the evening of 19 October, von Bischofhausen again met with König and was told that the original proposal was to be implemented the following day in order to collect the 2,300 hostages. The following evening, the male Jews and communists, who had been held without food since their arrest, were shot by German troops at the barracks and courtyard where they were being held. Simultaneously, males between the ages of 16 and 60 were arrested within Kragujevac itself. They were detained in the barracks of a former motorised battalion at Stanovija Field. Over 7,000 hostages were assembled. German troops and ethnic German
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
units from the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
were involved in the round-up, as was the 5th Regiment of the SDK, under the command of Marisav Petrović. According to von Bischofhausen, König permitted several classes of males to be excluded from the round-up, including those with a special pass issued by von Bischofhausen's district headquarters, members of a vital profession or trade, and those who were members of Ljotić's movement. When too few adult males could be located, high school students were also rounded up. Also seized were priests and monks from the city's churches. Each hostage was registered and his belongings noted meticulously.
Executions
 The hostages were held overnight on a public plaza in the town. In his version of events, von Bischofhausen claimed that he made objections to König, but the latter insisted that his orders, which had been issued by the commander of the 749th Infantry Regiment, were to be carried out. Shortly before the executions commenced, Ljotić obtained approval for two ''Zbor'' officials to scrutinise the hostages. Over 3,000 individuals, those identified as being "genuine nationalists" and "real patriots", were excluded from the execution lists as a result of Ljotić's intervention. Those who were not extracted from the hostage pool were accused of being communists or spreading "communist propaganda". The ''Zbor'' officials told them they were not "worth saving" because they had "infected the younger generation with their leftist ideas." The Germans considered ''Zbors involvement to be a "nuisance". According to the
The hostages were held overnight on a public plaza in the town. In his version of events, von Bischofhausen claimed that he made objections to König, but the latter insisted that his orders, which had been issued by the commander of the 749th Infantry Regiment, were to be carried out. Shortly before the executions commenced, Ljotić obtained approval for two ''Zbor'' officials to scrutinise the hostages. Over 3,000 individuals, those identified as being "genuine nationalists" and "real patriots", were excluded from the execution lists as a result of Ljotić's intervention. Those who were not extracted from the hostage pool were accused of being communists or spreading "communist propaganda". The ''Zbor'' officials told them they were not "worth saving" because they had "infected the younger generation with their leftist ideas." The Germans considered ''Zbors involvement to be a "nuisance". According to the social scientist
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of socie ...
Jovan Byford, it was never intended or likely to reduce the overall number of hostages killed in reprisal, and served only to ensure the exclusion of those that were deemed by ''Zbor'' to be worth saving.
On the morning of 21 October, the assembled men and boys were marched to a field outside the town. Over a period of seven hours, they were lined up in groups of 50 to 120 and shot with heavy machine guns. "Go ahead and shoot", said an elderly teacher, "I am conducting my class". He was shot together with his students. As they faced the firing squad
Execution by firing squad, in the past sometimes called fusillading (from the French ''fusil'', rifle), is a method of capital punishment, particularly common in the military and in times of war. Some reasons for its use are that firearms are ...
, many hostages sang the patriotic song ''Hey, Slavs
"Hey, Slavs" is a patriotic song dedicated to the Slavs which was used as the national anthem of various countries during the 20th century.
Its lyrics were first written in 1834 under the title "Hey, Slovaks" ("Hej, Slováci") by Samo Tomáši ...
'', which became Yugoslavia's national anthem
A national anthem is a patriotic musical composition symbolizing and evoking eulogies of the history and traditions of a country or nation. The majority of national anthems are marches or hymns in style. American, Central Asian, and Europea ...
after the war. One German soldier was shot for refusing to participate in the killings. A German report stated: "The executions in Kragujevac occurred although there had been no attacks on members of the Wehrmacht in this city, for the reason that not enough hostages could be found elsewhere." Even some German informant
An informant (also called an informer or, as a slang term, a “snitch”) is a person who provides privileged information about a person or organization to an agency. The term is usually used within the law-enforcement world, where informant ...
s were inadvertently killed. "Clearly", the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
historian Mark Levene writes, "Germans in uniform were not ''that'' particular about who they shot in reprisal, especially in the Balkans, where the populace were deemed subhuman."
Victims of the mass executions included Serbs, Jews, Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sig ...
, Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Macedonians, Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their na ...
and members of other nationalities. Following the massacre, the Wehrmacht held a military parade through the city centre. On 31 October, Böhme sent a report to the acting Wehrmacht commander in Southeast Europe, ''General der Pioniere
''General der Pioniere'' (en: ''General of the engineers'') was a General of the branch rank of the German Army in Nazi Germany. Until the end of World War II in 1945, this particular general officer rank was on three-star level ( OF-8), equi ...
'' (Lieutenant General) Walter Kuntze __NOTOC__
Walter Kuntze (23 February 1883 – 1 April 1960) was a German general and war criminal during World War II who commanded the 12th Army. He was the commanding officer responsible for the execution of men and teenage boys in the Kragu ...
, reporting that 2,300 hostages had been shot in Kragujevac.
Aftermath
Response
The Partisan commander and later historianMilovan Djilas
Milovan Djilas (; , ; 12 June 1911 – 30 April 1995) was a Yugoslav communist politician, theorist and author. He was a key figure in the Partisan movement during World War II, as well as in the post-war government. A self-identified democrat ...
recalled in his memoirs how the Kragujevac massacre gripped all of Serbia in "deathly horror". Throughout the war, local collaborators pressured the Germans to implement stringent vetting procedures to ensure that "innocent civilians" were not executed, though only when the hostages were ethnic Serbs. The scale of the massacres in Kragujevac and Kraljevo resulted in no quarter being given to German POWs by the guerrillas. "The enemy changed his attitude toward German prisoners," one senior Wehrmacht officer reported. "They are now usually being maltreated and shot." By the time Böhme was relieved as Plenipotentiary Commanding General in December 1941, between 20,000 and 30,000 civilians had been killed in German reprisal shootings. The ratio of 100 executions for each soldier killed and 50 executions for each soldier wounded was reduced by half in February 1943, and removed altogether later in the year. Henceforth, each individual execution had to be approved by Special Envoy Hermann Neubacher. The massacres in Kragujevac and Kraljevo caused German military commanders in Serbia to question the efficacy of such killings, as they pushed thousands of Serbs into the hands of anti-German guerrillas. In Kraljevo, the entire Serbian workforce of an airplane factory producing armaments for the Germans was shot. This helped convince the OKW that arbitrary shootings of Serbs not only incurred a significant political cost but were also counterproductive.
The killings at Kragujevac and Kraljevo exacerbated tensions between the Partisans and Chetniks. They also convinced Mihailović that active resistance was futile for as long as the Germans held an unassailable military advantage in the Balkans, and that killing German troops would only result in the unnecessary deaths of tens of thousands of Serbs. He therefore decided to scale back Chetnik guerrilla attacks and wait for an Allied landing in the Balkans. The killings occurred only a few days before Captain Bill Hudson, a Special Operations Executive
The Special Operations Executive (SOE) was a secret British World War II organisation. It was officially formed on 22 July 1940 under Minister of Economic Warfare Hugh Dalton, from the amalgamation of three existing secret organisations. Its pu ...
officer, met with Mihailović at his Ravna Gora headquarters. Hudson witnessed the aftermath of the massacre and noted the psychological toll it exacted. "Morning and night was the most desolating atmosphere," he recounted, "because the women were out in the fields, and every sunrise and sunset you would hear the wails. This had a very strong effect on Mihailović." "The tragedy gave to Nedić convincing proof that the Serbs would be biologically exterminated if they were not submissive," Djilas wrote, "and to the Chetniks proof that the Partisans were prematurely provoking the Germans". Mihailović's decision to refrain from attacking the Germans led to a rift with Tito and the Partisans. The Chetniks' non-resistance made it easier for the Germans to confront the Partisans, who for much of the remainder of the war could not defeat them in open combat.
Legal proceedings and casualty estimates
 On 11 November 1941, the Partisans captured a Wehrmacht officer named Renner, the area commander in
On 11 November 1941, the Partisans captured a Wehrmacht officer named Renner, the area commander in Leskovac
Leskovac (Serbian Cyrillic: Лесковац, ) is a city and the administrative center of the Jablanica District in southern Serbia. According to the 2022 census, City of Leskovac has a 124,889 inhabitants.
Etymology
Leskovac was historicall ...
, who was taking part in an anti-Partisan sweep around Lebane
Lebane ( sr-cyr, Лебане) is a town and municipality located in Jablanica District of southern Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 10,062 inhabitants, while the municipality has 20,000 inhabitants.
Geography
The ...
. Mistaking him for König, who by some accounts had given Renner a cigarette case engraved with his name, the Partisans executed Renner as a war criminal. For almost fifty years, it was widely believed that König, and not Renner, had been killed by the Partisans. In 1952, a plaque was erected at the place where König was purported to have been killed, and a song was written about the incident. In the 1980s, it was conclusively proven that the German officer executed by the Partisans in November 1941 was not König. A new plaque was thus dedicated in 1990.
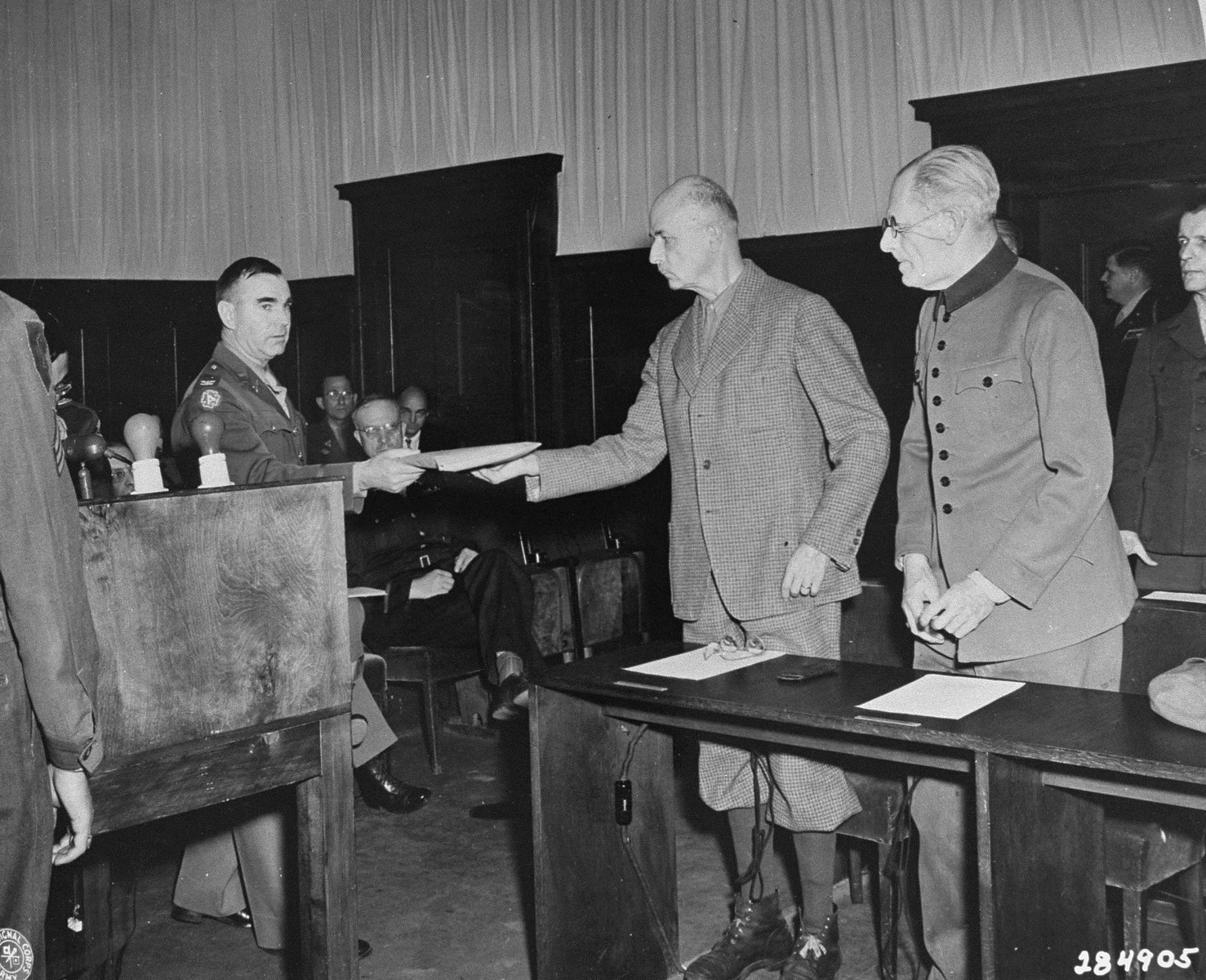
List and Böhme were both captured at the end of the war. On 10 May 1947, they were charged with war crimes and crimes against humanity as part of the Hostages Trial
The Hostages Trial (or, officially, ''The United States of America v. Wilhelm List, et al.'') was held from
8 July 1947 until 19 February 1948 and was the seventh of the twelve trials for war crimes that United States authorities held in their oc ...
of the subsequent Nuremberg trials. One of the crimes specifically listed in Count 1 of the indictment was the massacre of 2,300 hostages in Kragujevac. Böhme committed suicide before his arraignment. List was found guilty on Count 1, as well as on another count. He was sentenced to life imprisonment in 1948, but was released due to ill health in December 1952. Despite this, he lived until June 1971. Keitel was found guilty of war crimes and crimes against humanity at the Nuremberg Trials
The Nuremberg trials were held by the Allies against representatives of the defeated Nazi Germany, for plotting and carrying out invasions of other countries, and other crimes, in World War II.
Between 1939 and 1945, Nazi Germany invaded m ...
, and subsequently hanged. Hoffmann, whom the local population dubbed the "butcher of Kraljevo and Kragujevac", was promoted to command the more capable 352nd Infantry Division
The 352nd Infantry Division (''352. Infanterie-Division'') was an infantry division of the German Army during World War II. Deployed on the Western Front, the division defended Omaha Beach on D-Day, 6 June 1944.
History Formation and stre ...
in November 1941. He ended the war as the commander of a prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. ...
, having been demoted for refusing to shoot deserters in the Ukraine. The 717th Infantry Division was reorganised as the 117th Jäger Division later in the war and its troops took part in the massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
of hundreds of Greek civilians at Kalavryta
Kalavryta ( el, Καλάβρυτα) is a town and a municipality in the mountainous east-central part of the regional unit of Achaea, Greece. The town is located on the right bank of the river Vouraikos, south of Aigio, southeast of Patras and ...
in December 1943.
At least 31 mass graves were discovered in Kragujevac and its surroundings after the war. In 1969, the historian Jozo Tomasevich
Josip "Jozo" Tomasevich (March 16, 1908 – October 15, 1994; hr, Josip Jozo Tomašević) was an American economist and military historian. He was professor emeritus at San Francisco State University.
Education and career
Tomašević was born ...
wrote that, despite German official sources stating 2,300 hostages had been shot, both the Partisans and Chetniks had agreed that the number of victims was about 7,000. He further stated that careful investigation by the scholar Jovan Marjanović in 1967 had put the figure at about 5,000. In 1975, Tomasevich noted that some estimates of the number of those killed were as high as 7,000, but that the foremost authority on German terror in Serbia, Venceslav Glišić, placed the figure at about 3,000. In 2007, Pavlowitch wrote that inflated figures of 6,000–7,000 victims were advanced and widely believed for many years, but that German and Serbian scholars had recently agreed on the figure of 2,778. In the same year, the curator of the 21st October Museum at Kragujevac, Staniša Brkić, published a book listing the names and personal data of 2,794 victims. Of the total killed, 144 were high school students, and five of the victims were 12 years old. The last living survivor of the massacre, Dragoljub Jovanović, died in October 2018 at the age of 94. He survived despite sustaining eleven bullet wounds and had to have one of his legs amputated. After the war, he was appointed the inaugural director of the 21st October Museum.
Legacy
Commemoration
 The massacre at Kragujevac came to symbolise the brutality of the German occupation in Yugoslav popular memory. It has drawn comparisons to the Germans'
The massacre at Kragujevac came to symbolise the brutality of the German occupation in Yugoslav popular memory. It has drawn comparisons to the Germans' destruction
Destruction may refer to:
Concepts
* Destruktion, a term from the philosophy of Martin Heidegger
* Destructive narcissism, a pathological form of narcissism
* Self-destructive behaviour, a widely used phrase that ''conceptualises'' certain kin ...
of the Czechoslovak village of Lidice
Lidice (, german: Liditz) is a municipality and village in Kladno District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 600 inhabitants.
Lidice is built near the site of the previous village of the same name, which was co ...
in June 1942 and the massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
of the inhabitants of Oradour-sur-Glane, France in June 1944.
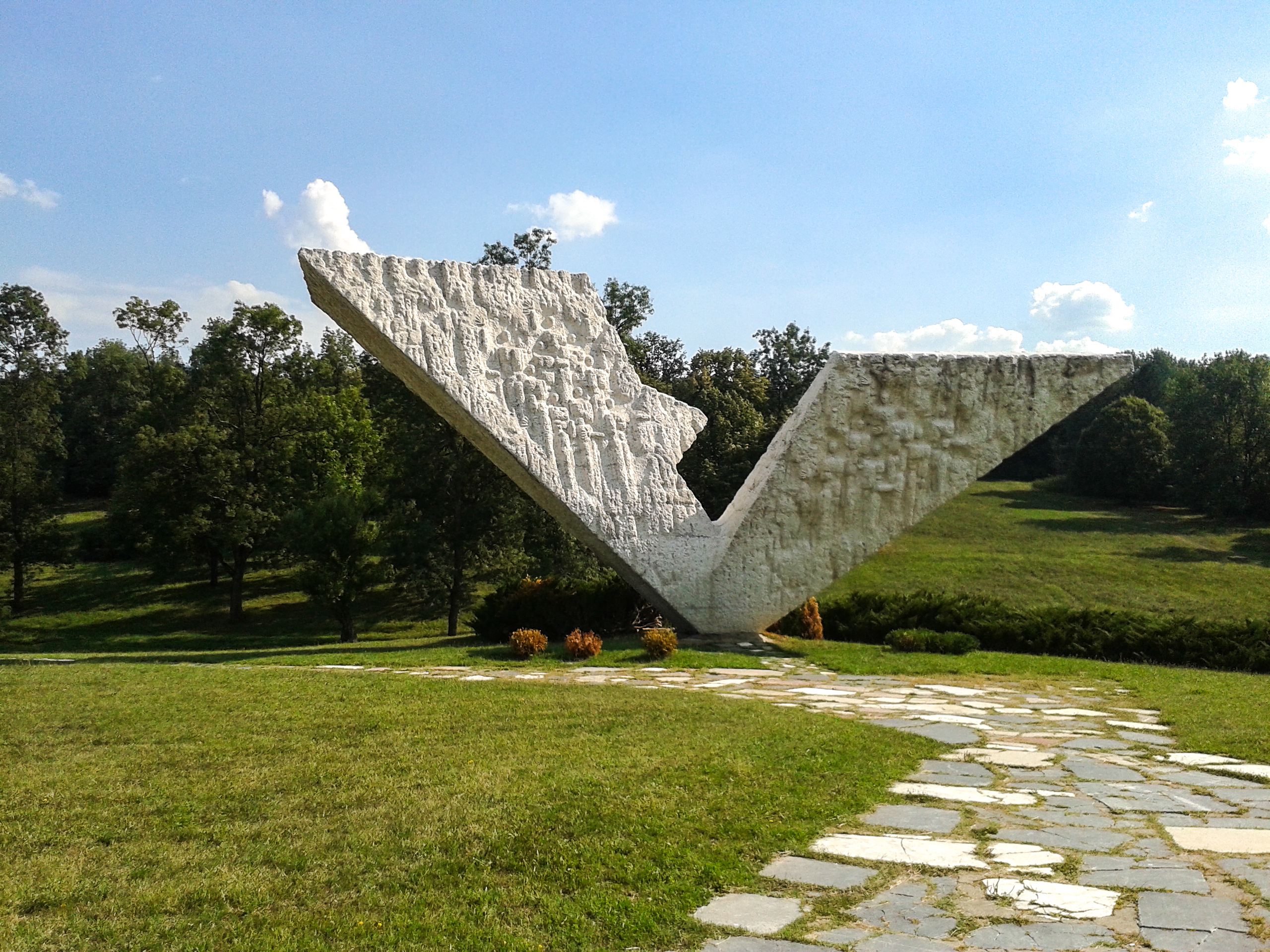
To commemorate the victims of the massacre, the whole of Šumarice was designated as a memorial park in 1953. It is now known as the October in Kragujevac Memorial Park, and covers encompassing the area that contains the mass graves. The 21st October Museum was founded within the park on 15 February 1976. Šumarice is the site of a televised annual commemoration known as the Great School Lesson ( sr, Veliki školski čas, italics=yes, links=no) that attracts thousands of attendees every year. The park contains several monuments, including the Interrupted Flight monument to the murdered high school students and their teachers, and the monuments Pain and Defiance, One Hundred for One, and Resistance and Freedom. The site sustained damage during the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) carried out an aerial bombing campaign against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War. The air strikes lasted from 24 March 1999 to 10 June 1999. The bombings continued until an a ...
in 1999.
In 2012, the National Assembly of Serbia
The National Assembly ( sr-cyr, Народна скупштина, Narodna skupština, ) is the unicameral legislature of Serbia. The assembly is composed of 250 deputies who are proportionally elected to four-year terms by secret ballot. The a ...
passed a law declaring 21 October the Day of Remembrance of the Serbian Victims of World War II. Germany's Federal Cabinet has never officially apologized for any of the mass executions committed in Serbia by the Wehrmacht during World War II, including the Kragujevac massacre. On 21 October 2021, Vice President of the Bundestag
The president of the Bundestag (german: Präsident des Deutschen Bundestages or ) presides over the sessions of the Bundestag, the federal parliament of Germany, with functions similar to that of a speaker (politics), speaker in other countries. ...
Claudia Roth became the first senior German government official to attend the annual commemoration at Šumarice. "My intention in attending was to underline that we will not let the crimes of the Nazis and the Wehrmacht be forgotten," Roth remarked, "and that, building on that remembrance, we want to foster good and friendly relations with our Serbian friends and partners."
Depictions in art
The Serbian poet and writerDesanka Maksimović
Desanka Maksimović ( sr-Cyrl, Десанка Максимовић; 16 May 1898 – 11 February 1993) was a Serbian poet, writer and translator. Her first works were published in the literary journal ''Misao'' in 1920, while she was studying at th ...
wrote a poem about the massacre titled ''Krvava bajka'' ("A Bloody Fairy Tale"). The poem was later included in the Yugoslav secondary school curriculum and schoolchildren were required to memorise it. It ranks among the most famous Serbian-language poems. Recitations of it form the centerpiece of the annual commemoration ceremonies at Šumarice. In 1965, the Belgian poet Karel Jonckheere wrote the poem ''Kinderen met krekelstem'' ("Children with Cricket Voices"), also about the massacre. ''The Blue Butterfly'', a book of poetry by Richard Berengarten
Richard Berengarten (born 4 June 1943) is an English poet. Having lived in Italy, Greece, the US and the former Yugoslavia, his perspectives as a poet combine English, French, Mediterranean, Jewish, Slavic, American and Oriental influences. His ...
, is based on the poet's experiences while visiting Kragujevac in 1985, when a blue butterfly landed on his hand at the entrance to the memorial museum.
The massacre has been the subject of two feature films: ''Prozvan je i '' ('' is Called Out''; 1962) and ''Krvava bajka'' (''A Bloody Fairy Tale''; 1969), named after the eponymous poem.
See also
*List of massacres in Yugoslavia
This is a list of massacres in Yugoslavia during the 20th century.
Inter-war period (1919–41)
* Šahovići massacre
* Rugova Massacre
World War II
1946–1991
* Foibe massacres
Croatian War
The Zagreb rocket attacks is one of the many ...
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{coord, 44, 0, 40, N, 20, 54, 40, E, display=title, region:RS_type:city_source:GNS-enwiki 1941 in Serbia Antiziganism in Europe Collective punishment Kragujevac Mass murder in 1941 Massacres in 1941 Massacres in Serbia Massacres in Yugoslavia Massacres of men Massacres of Serbs Nazi war crimes in Serbia October 1941 events The Holocaust Serbia under German occupation Violence against men in Europe World War II massacres War crimes of the Wehrmacht