Koradi Thermal Power Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Koradi Thermal Power Station (KTPS) is located at Koradi near
 The water for KTPS comes from water reservoir of nearby
The water for KTPS comes from water reservoir of nearby
MAHAGENCO Koradi)
MahaGenco report giving technical details of Koradi Thermal Power Station
{{Power Plants of Maharashtra Economy of Nagpur
Science and technology in Nagpur Coal-fired power stations in Maharashtra 1974 establishments in Maharashtra Energy infrastructure completed in 1974
Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nagpur is projected to ...
, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdi ...
. The power plant is one of the four major power plants in Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: �id̪əɾbʱə is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a proposed state of central India, comprising the state's Amravati and Nagpur divisions. Amravati Division's former name is Be ...
– a power surplus region of India. The power station
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.
Many ...
began operations in 1974 and is one of the nine active power stations operated by Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Limited (Prajot), a subsidiary of Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the state governing authority for the state of Maharashtra, India. It is a democratically elected government with 288 MLAs elected to the Vidhan Sabha for a five-year term.
Maharashtra has a Maharashtra Legisl ...
owned Maharashtra State Electricity Board (MSEB). The plant operates 8 units and has a total power generation capacity of 1700 MW. A proposed 440 kilovolt high power transmission line from Koradi to Bhusawal
Bhusawal is the largest municipal council (established in 1882) in the Jalgaon district of the Indian state of Maharashtra, situated along the banks of the river Tapi. The city emerged as a major railway junction during the British Raj, and s ...
would join Nagpur with Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
. KTPS campus also contains training institute of MahaGenco for middle and senior level engineers, technicians and other staff.
Power station
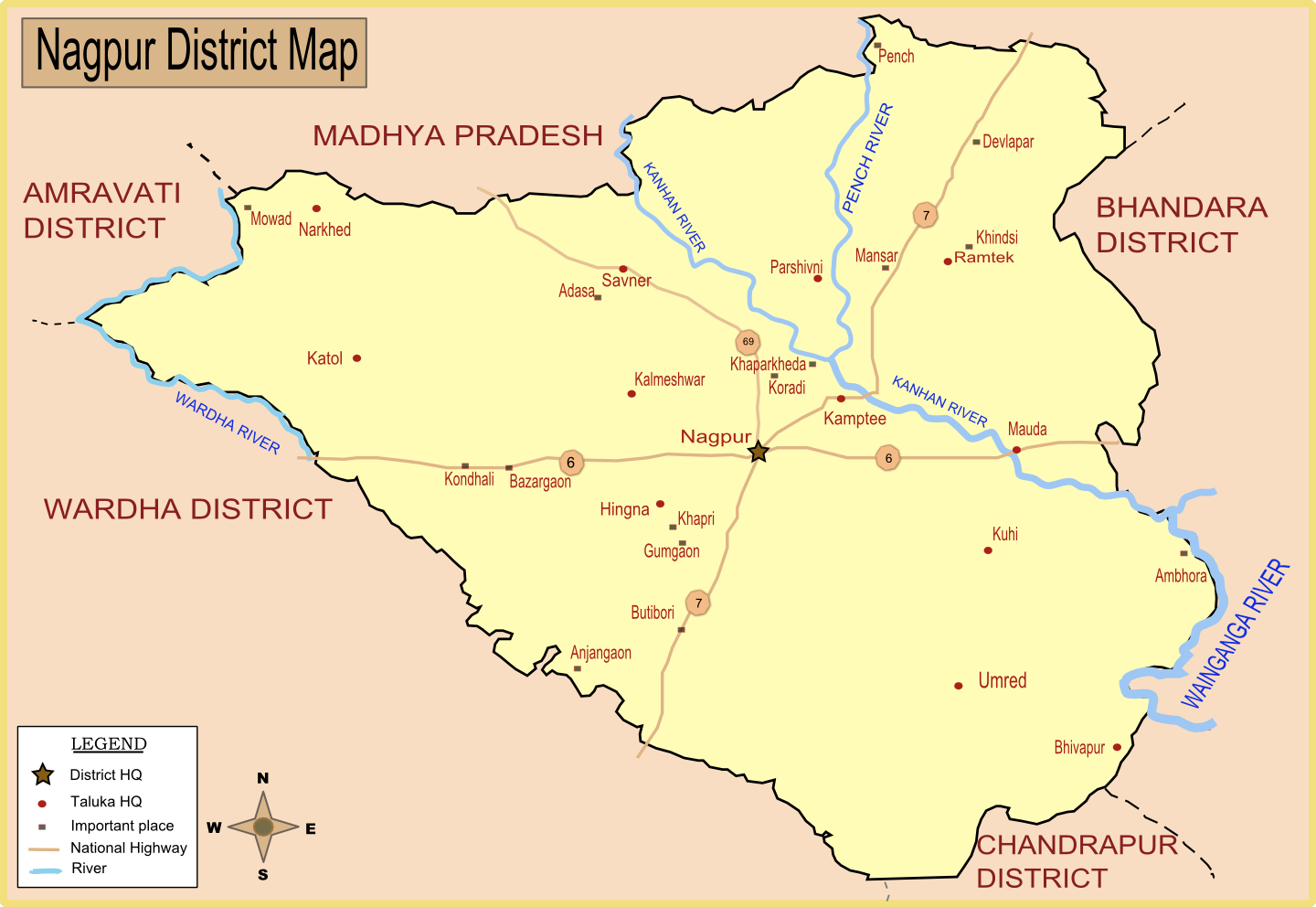
KTPS is located on the northern side of Nagpur and is spread across an area of 30,337 km2. Coal for KTPS comes from various nearby collieries of Western Coalfields Limited (WCL) located at Silewara, Pipla, Patansavangi,Kamptee
Kamptee is a suburb of Nagpur city and a municipal council in Nagpur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is part of the Nagpur metropolitan region development authority. It is the administrative center for Kamptee taluka. It i ...
, Inder, Walni, Gondegaon and Saoner
Saoner is a city and tehsil headquarters in north part of Nagpur district in state of Maharashtra, India. The town is governed by Savner municipal council. It is from Nagpur city. Saoner is located on the bank of Kolar River. It is historically ...
. These are at an average distance of away. The plant approximately requires 16,000 to 17,000 tonnes of coal per day.
 The water for KTPS comes from water reservoir of nearby
The water for KTPS comes from water reservoir of nearby Totaladoh
Totaladoh is a census town
In India and some other countries, a census town is designated as a town that satisfies certain characteristics.
India
In India, a census town is one which is not statutorily notified and administered as a town, but ...
hydroelectric power station. Also, Nagpur Municipal Corporation (NMC) provides treated water from its sewage treatment plant. According to MSEB, the average unit cost of power generation at KTPS is 6.28 paise
Paisa (also transliterated as ''pice'', ''pesa'', ''poysha'', ''poisha'' and ''baisa'') is a monetary unit in several countries. The word is also a generalised idiom for money and wealth. In India, Nepal, and Pakistan, the ''Paisa'' currently equa ...
/kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bill ...
at 70 percent load factor while it is 13.52 paise/kWh at 25 percent load factor. The average cost for transmitting this power to Mumbai is 1.26 paise/kWh.
Since its commissioning, KTPS saw expansion in stages. First unit of 115 MW began in 1974. Later, three more units each of 115 MW, were added between 1975 and 1976 while 200 MW unit was added in 1978. The Project Managers for construction of 200/210 MW units were Sri P.S. Khirwadkar followed by Sri C.N.Swamy. Two more units, of 210 MW each, between 1982 and 1983. Major developments were undertaken by Ashok R Agrawal who developed the Power Plant. MSEB has finalized further expansion by increasing the capacity of 3 units to 660 MW thereby taking the total capacity of KTPS to 1560 MW. The work is expected to finish by 2014. Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) is expected to get equity participation by supplying important equipments in the expansion plan.
In order to reduce air pollution the plant's units are equipped with electrostatic precipitator
An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a filterless device that removes fine particles, like dust and smoke, from a flowing gas using the force of an induced electrostatic charge minimally impeding the flow of gases through the unit.
In con ...
s.
Capacity
Thermal Power Research Center
The Central Power Research Institute (CPRI) ofGovernment of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
, which serves as regulating body for testing of instruments and uploading of licenses in India, is going to set up a ''Thermal Research Centre (TRC)'' at Koradi. However, the KTPS expansion plans have created a problems in land acquisition for TRC.
Disruptions
On 27 February 2005, a major fire broke out at KTPS and had to be shut down causing blackouts in most districts ofMarathawada
Marathwada () is a proposed state and geographical region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It was formed during the Nizam's rule and was part of the then Hyderabad State. The region coincides with the Aurangabad division of Maharashtra ...
. In May 2007, the power plant was shut down due a strike by workers.
References
Mahagenco has sought permission from Maharashtra Electricity Regulatory Commission (MERC) to close down unit 5 and 6 of Koradi (200 MW and 210 MW). Genco wants to shut 1,040MW generation Ashish Roy , TNN , 4 July 2014External links
MAHAGENCO Koradi)
MahaGenco report giving technical details of Koradi Thermal Power Station
{{Power Plants of Maharashtra Economy of Nagpur
Science and technology in Nagpur Coal-fired power stations in Maharashtra 1974 establishments in Maharashtra Energy infrastructure completed in 1974