Kodava language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kodava (, natively: ''Koḍava takkï'', , meaning 'speech of Kodavas', Angloid name: Codava, Coorgi) is a Dravidian language spoken in Kodagu district (Coorg) in Southern
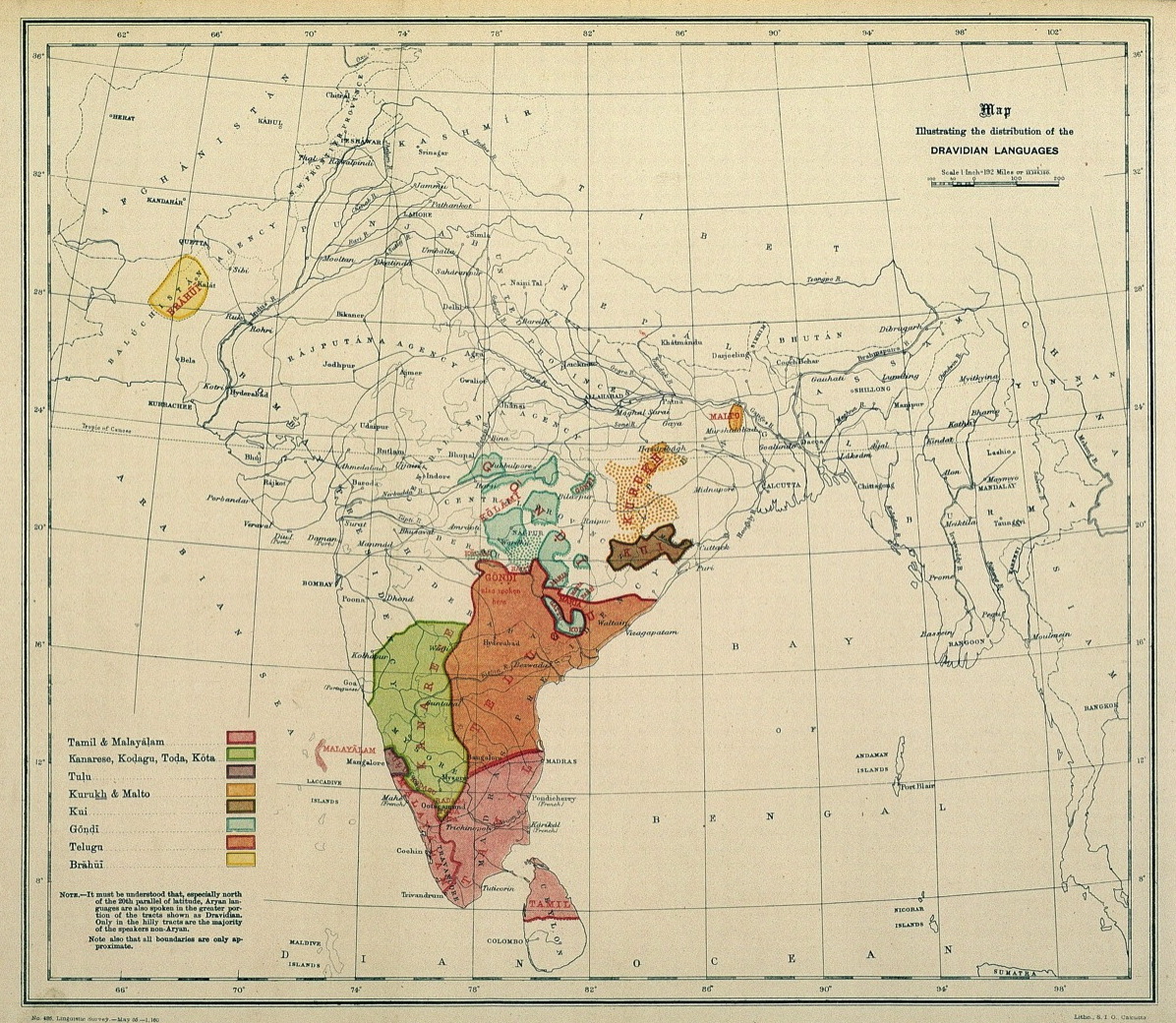 In Kannada, the region was called Kodagu and the people Kodaga. Natively, the people were called Kodava and the land was called Kodavu in the folksongs. Comparative Dravidian studies show that the Kodava language belongs to the South Dravidian language group.
In Kannada, the region was called Kodagu and the people Kodaga. Natively, the people were called Kodava and the land was called Kodavu in the folksongs. Comparative Dravidian studies show that the Kodava language belongs to the South Dravidian language group.
Kodava Literature
Kodava Samaj
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kodava Language Agglutinative languages Dravidian languages Languages of Karnataka Endangered languages of India
Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
.
It is an endangered language. The term Kodava has two related usages. Firstly, it is the name of the Kodava language and culture followed by a number of communities from Kodagu
Kodagu district () (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative List of districts of Karnataka, district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State at which point it was merged ...
. Secondly, within the Kodava-speaking communities and region (Kodagu
Kodagu district () (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative List of districts of Karnataka, district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State at which point it was merged ...
), it is a demonym for the dominant Kodava people
The Kodavas (Codavas or Kodagas) also called Coorgs are an endogamous Dravidian peoples, Dravidian ethnolinguistic group from the region of Kodagu district, Kodagu in the southern Indian state of Karnataka, who natively speak the Kodava langu ...
. Hence, the Kodava language is not only the primary language
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers ...
of the Kodavas but also of many other castes and tribes in Kodagu. The language has two dialects: Mendele (spoken in Northern and Central Kodagu, i.e. outside Kodagu's Kiggat naadu) and Kiggat (spoken in Kiggat naadu, in Southern Kodagu).
Historically, it has been associated to Old Canarese or Hale Kannada However, it has been re-analysed as a language by early 20th century academics. Now it is considered as an intermediate language between Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
, Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
, Tamil, and Tulu in comparative linguistics.
It is traditionally written using the thirke script which is an abugida
An abugida (; from Geʽez: , )sometimes also called alphasyllabary, neosyllabary, or pseudo-alphabetis a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as units; each unit ...
. The 2011 Census of India reports 96,918 persons who returned Kodava as their mother tongue and 16,939 who returned Coorgi/Kodagu, for a total of 113,857 persons coming under the parent group which is again identified as Coorgi/Kodagu (another name for Kodava) as the mother tongue.
History
 In Kannada, the region was called Kodagu and the people Kodaga. Natively, the people were called Kodava and the land was called Kodavu in the folksongs. Comparative Dravidian studies show that the Kodava language belongs to the South Dravidian language group.
In Kannada, the region was called Kodagu and the people Kodaga. Natively, the people were called Kodava and the land was called Kodavu in the folksongs. Comparative Dravidian studies show that the Kodava language belongs to the South Dravidian language group.
Grammar
The grammar of Kodagu has been systematically studied and documented since at least around 1867 when Captain R.A. Cole published the seminal work ''An Elementary Grammar of the Coorg Language''.Phonology
Vowels
Dravidian vowel systems contain five vowel qualities i.e. those usually corresponding to ''a, e, i, o'' and ''u.,'' with a short and long variants for each. However, Kodava has two more: the mid and high (close) back unrounded vowels, with corresponding long variants.Consonants
Kodava and Kannada share a lack of palatalization of word-initial ''*k-'', which is a feature found in the Tamil-Malayalam branch.Writing system
The Kodava (Kodagu) language was popularly written in the Kannada script. Dr. IM Muthanna, developed a script to Kodava Thakk in 1971, and as of 2022, Karnataka Kodava Sahitya Academy, a government body for the development of Kodava Language, accepted the script developed by Dr IM Muthanna as the official script of Kodava Language. It is also widely used acrossKodagu
Kodagu district () (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative List of districts of Karnataka, district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State at which point it was merged ...
, Although around 7 scripts were developed over a period from 1889 to 2008, Only Dr. IM Muthanna's script is considered as the most acceptable script for Kodava Language.
The Coorgi is an alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
developed by the linguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
Gregg M. Cox that is used by a number of individuals within Kodagu district of India to write the endangered Dravidian language of Kodava, also known sometimes as ''Coorgi''.
The script uses a combination of 26 consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
letters, eight vowel
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness a ...
letters and a diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...
marker. Each letter represents a single sound and there are no capital letter
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing system ...
s. A computer-based font has been created.
The script was developed out of the request by a group of Kodava individuals to have a distinct script for Kodava Takk, to distinguish the language. Kodava Takk is generally written in the Kannada script, but can also be found written in the Malayalam script, especially along the borders with Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
. The new script is intended as a unified writing system for all Kodava Takk speakers.
Recently an old Kodava script from the 14th century was discovered, it is now called the Thirke script.
Various other scripts were made by Kodava writers like Iychettira M Muthanna, Koravanda Appayya, Appaneravanda Kiran Subbaiah.
Comparisons
Linguistically, Kodava/Kodagu language belongs to the South Dravidian subfamily of the Dravidian family. Further within the South Dravidian subfamily, it belongs to the subgroup Tamil-Malayalam-Kodagu-Kota-Toda. It is closely related to and influenced byKannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
, Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
, Tamil and Tulu. A majority of the words are common between Kodava and Beary bashe
Byari or Beary (ಬ್ಯಾರಿ) is a geographically isolated dialect of Malayalam spoken by the Byaris who are part of the Muslim community in Tulu Nadu region of Coastal Karnataka and Northern Kerala ( Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, and Kasar ...
, a dialect which is a mixture of Tulu and Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
spoken by the Beary Muslims and Kodava Thiyyar communities. Kodava is also closely related to the Kasaragod and Kannur dialects of Malayalam, which are in turn related to Beary.
Literature
Family histories, rituals and other records were scripted on palm leaves called Pattole (patt=palm, ole=leaf) by astrologers in the ancient times. When Kodava was written, it was usually with Kannada script, sometimes with minor modifications. The folk songs of the Kodavas, called the Palame (also known as the Balo Patt or Dudi Patt), were orally transmitted across several generations. The language had no significant writtenliterature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
until the twentieth century. Appachcha Kavi, a playwright, and Nadikerianda Chinnappa, a folk compiler, are the two important poets and writers of the Kodava language. Other important writers in the language were B D Ganapathy and I M Muthanna. In 2005, after requests from the Kodagu community, German linguist Gerard Cox created a script unique to Kodava called the Coorgi-Cox script. It uses straight lines for 5 vowels, and has circles for diphthongs.
The Pattole Palame, a collection of Kodava folksongs and traditions compiled in the early 1900s by Nadikerianda Chinnappa, was first published in 1924. The most important Kodava literature, it is said to be one of the earliest, if not the earliest, collection of folklore of a community in an Indian language. Nearly two-thirds of the book consists of folksongs that were handed down orally through generations, sung even today during marriage and death ceremonies and during festivals relating to the seasons and in honour of local deities and heroes. Traditionally known as Balo Pat, these songs are sung by four men who beat dudis (drums) as they sing. Kodava folk dances are performed to the beat of many of these songs. The Pattole Palame was written using the Kannada script originally; it has been translated into English by Boverianda Nanjamma and Chinnappa, grandchildren of Nadikerianda Chinnappa, and has been published by Rupa & Co., New Delhi.
Cinema
The Kodava Cinema industry is very small. A few movies portraying the native culture and traditions of the Kodavas have been produced in this language. The first Kodava film 'Nada Mann Nada Kool' was directed by S.R.Rajan and produced in the year 1972.Kodava words
Words for family members
Recent developments
Since 2021, the Mangalore University teaches an MA degree in the Kodava language.References
Bibliography
* *Further reading
*External links
Kodava Literature
Kodava Samaj
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kodava Language Agglutinative languages Dravidian languages Languages of Karnataka Endangered languages of India