Kipunada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kipunada (
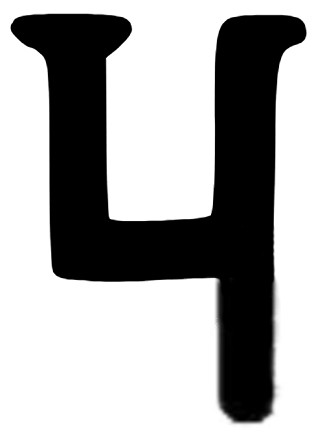

 ''Ki-pu-ṇa-dha''), also Kipanadha, was probably the last ruler of the
''Ki-pu-ṇa-dha''), also Kipanadha, was probably the last ruler of the


 ), presumably connected to the
), presumably connected to the
File:Samudra Gandhara coin, Punjabi mint Circa CE 350-375.jpg, Local coin minted in the 

 ''Sa-mu-dra'', under the king's left arm), presumably
''Sa-mu-dra'', under the king's left arm), presumably 

 ''Ki-ra-da'' under the king's left arm), who ruled circa 350 CE.
''Ki-ra-da'' under the king's left arm), who ruled circa 350 CE.
Coins of late Kushan emperors
Kushan emperors 4th-century Indian monarchs {{Asia-royal-stub
Brahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' o ...
: 
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
around 335-350 CE. He is known for his gold coinage. He succeeded Shaka I. Kipunada was probably only a local ruler in the area of Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and ...
, in western Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
, and he may have been a subject of Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by se ...
Emperor Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
.
Gupta and Kidarite successors
The coins of Kipunada in Central and Western Punjab were followed by peculiar coins minted locally in Punjab, with the name "Samudra" on them (Gupta script
The Gupta script (sometimes referred to as Gupta Brahmi script or Late Brahmi script)Sharma, Ram. '' 'Brahmi Script' ''. Delhi: BR Publishing Corp, 2002 was used for writing Sanskrit and is associated with the Gupta Empire of the Indian subcon ...
:
 ), presumably connected to the
), presumably connected to the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
ruler Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
. Soon after this, coinage was issued in Punjab by Kidarite Hun rulers known as Kirada
Kirada (Brahmi: ''Ki-ra-da'', ruled 335-345 CE), is considered by modern scholarship as the first known ruler of the Kidarite Huns in the area of Gandhara in northwestern India, possibly at the same time as another Kidarite ruler named Yosada.
...
, Peroz Feroz or Firuz is a Persian name meaning 'victorious', derived from the middle Persian name Peroz or Piruz. Related names are Phiroze, Feroze, and Parviz.
It may refer to:
People (historical)
* Peroz I (), Sasanian king of Iran
* Peroz II (), Sa ...
and then the famous Kidara
Kidara I (Late Brahmi script: ''Ki-da-ra'') fl. 350-390 CE) was the first major ruler of the Kidarite Kingdom, which replaced the Indo-Sasanians in northwestern India, in the areas of Kushanshahr, Gandhara, Kashmir and Punjab.
Reign
Kidara hims ...
, who occupied the territory formerly held by the Kushans."In the Punjab the stylistic progression of the gold series from Kushan to Kidarite is clear: imitation staters were issued first in the name of Samudragupta, then by Kirada, 'Peroz' and finally Kidara" in
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
area with the name "Samudra" (
 ''Sa-mu-dra'', under the king's left arm), presumably
''Sa-mu-dra'', under the king's left arm), presumably Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', (c. 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of the dynasty. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Li ...
, immediately followed those of Kipunada.
File:HUNNIC TRIBES, Kidarites Kirada Circa 340-345.jpg, The next coins were those of Kidarite
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Eur ...
Hun kings, starting with Kirada
Kirada (Brahmi: ''Ki-ra-da'', ruled 335-345 CE), is considered by modern scholarship as the first known ruler of the Kidarite Huns in the area of Gandhara in northwestern India, possibly at the same time as another Kidarite ruler named Yosada.
...
(
Notes
External links
Coins of late Kushan emperors
Kushan emperors 4th-century Indian monarchs {{Asia-royal-stub