Kingdom of Numidia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the
 The Greek historians referred to these peoples as "Νομάδες" (i.e. Nomads), which by Latin interpretation became "Numidae" (but cf. also the correct use of ''Nomades''). Historian
The Greek historians referred to these peoples as "Νομάδες" (i.e. Nomads), which by Latin interpretation became "Numidae" (but cf. also the correct use of ''Nomades''). Historian  However, in 206 BC, the new king of the eastern Massylii,
However, in 206 BC, the new king of the eastern Massylii,
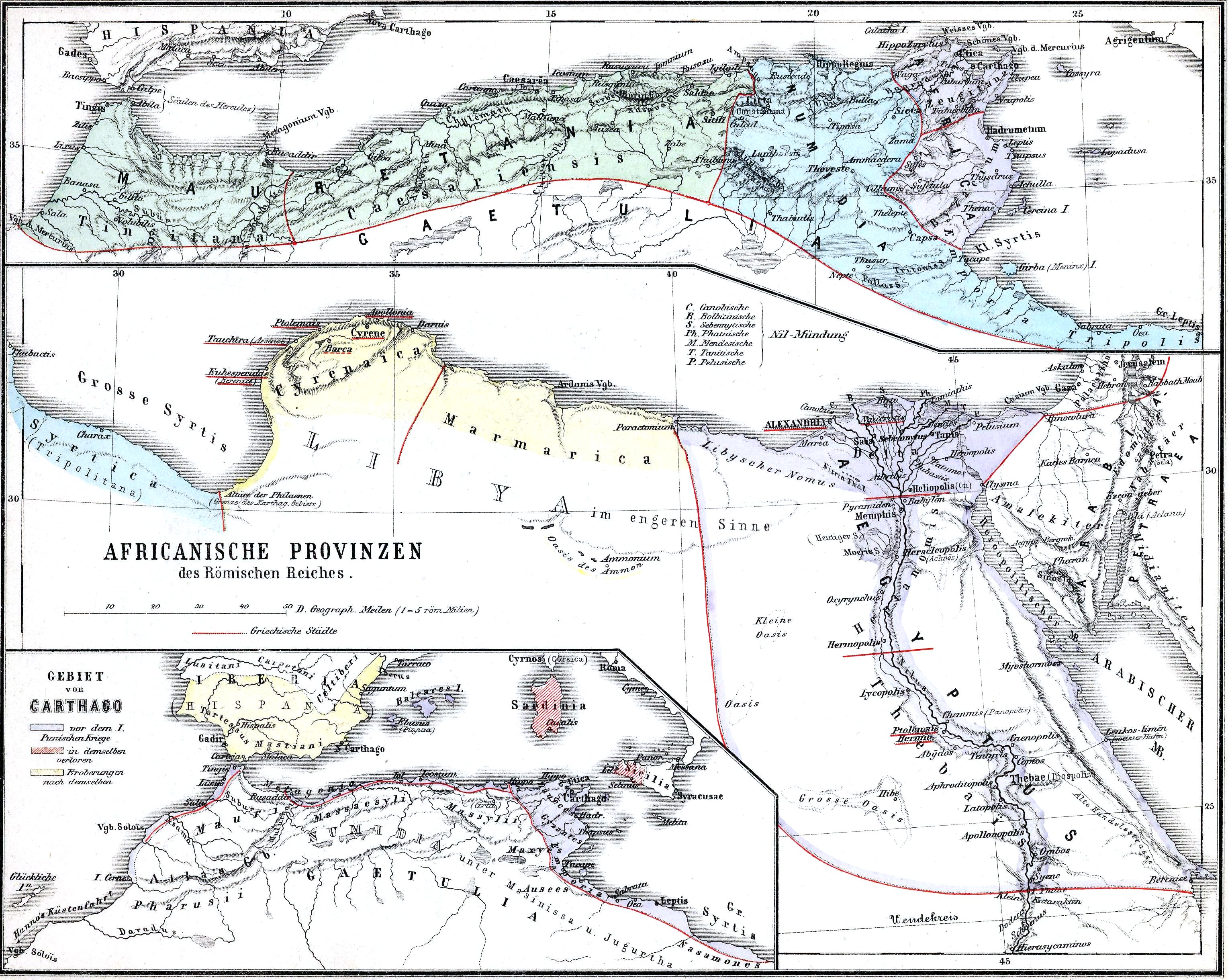 ''Eastern Numidia'' was annexed in 46 BC to create a new Roman province, ''
''Eastern Numidia'' was annexed in 46 BC to create a new Roman province, ''

 The term “Royal Numidian Architecture” was coined for the monuments that were constructed by the Numidian kings.Quinn, J. (2013). Monumental power: ‘Numidian Royal Architecture’ in context. In J. Prag & J. Quinn (Eds.), The Hellenistic West: Rethinking the Ancient Mediterranean (pp. 179-215). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139505987.008 These monuments consist of tombs, tumuli and sanctuaries. Some examples of these structures are the mausoleum of Thugga, the tomb of Beni Rhenane, a tomb at Henchur Burgu in Djerba as well as two tumulus tombs known as the Madghacen and the
The term “Royal Numidian Architecture” was coined for the monuments that were constructed by the Numidian kings.Quinn, J. (2013). Monumental power: ‘Numidian Royal Architecture’ in context. In J. Prag & J. Quinn (Eds.), The Hellenistic West: Rethinking the Ancient Mediterranean (pp. 179-215). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139505987.008 These monuments consist of tombs, tumuli and sanctuaries. Some examples of these structures are the mausoleum of Thugga, the tomb of Beni Rhenane, a tomb at Henchur Burgu in Djerba as well as two tumulus tombs known as the Madghacen and the 
Detailed map of Roman Numidia
/ref> Lambaesis was the seat of the Legio III ''Augusta'', and the most important strategic centre. It commanded the passes of the Aurès Mountains (Mons Aurasius), a mountain block that separated Numidia from the Gaetuli Berber tribes of the desert, and which was gradually occupied in its whole extent by the Romans under the Empire. Including these towns, there were altogether twenty that are known to have received at one time or another the title and status of Roman colonies; and in the 5th century, the '' Notitia Dignitatum'' enumerates no fewer than 123 sees whose bishops assembled at Carthage in 479.
Numidians
The Numidians were the Berber population of Numidia (Algeria and in smaller parts of Tunisia and Morocco). The Numidians were one of the earliest Berber tribes to trade with Carthaginian settlers. As Carthage grew, the relationship with the Nu ...
located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, and some parts of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii The Massylii or Maesulians were a Berber federation in eastern Numidia, which was formed by an amalgamation of smaller tribes during the 4th century BC.Nigel Bagnall, The Punic Wars, p. 270. They were ruled by a king. On their loosely defined wester ...
in the east and the Masaesyli
The Masaesyli were a Berber tribe of western Numidia (present day Algeria) and the main antagonists of the Massylii in eastern Numidia.
During the Second Punic War the Masaesyli initially supported the Roman Republic and were led by Syphax ag ...
in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa
Masinissa ( nxm, , ''MSNSN''; ''c.'' 238 BC – 148 BC), also spelled Massinissa, Massena and Massan, was an ancient Numidian king best known for leading a federation of Massylii Berber tribes during the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), ult ...
, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
and a Roman client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
.
Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River
The Moulouya River ( Berber: ''iɣẓer en Melwect'', ) is a 520 km-long river in Morocco. Its sources are located in the Ayashi mountain in the Middle Atlas. It empties into the Mediterranean Sea near Saïdia, in northeast Morocco.
Water ...
, Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
to the east, the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers.
History
Independence
 The Greek historians referred to these peoples as "Νομάδες" (i.e. Nomads), which by Latin interpretation became "Numidae" (but cf. also the correct use of ''Nomades''). Historian
The Greek historians referred to these peoples as "Νομάδες" (i.e. Nomads), which by Latin interpretation became "Numidae" (but cf. also the correct use of ''Nomades''). Historian Gabriel Camps
Gabriel Camps (May 20, 1927 – September 7, 2002) was a French archaeologist and social anthropologist, the founder of the '' Encyclopédie berbère'' and is considered a prestigious scholar on the history of the Berber people.
Biography
Gabrie ...
, however, disputes this claim, favoring instead an African origin for the term.
The name appears first in Polybius (second century BC) to indicate the peoples and territory west of Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
including the entire north of Algeria as far as the river Mulucha ( Muluya), about west of Oran.
The Numidians were composed of two great tribal groups: the Massylii The Massylii or Maesulians were a Berber federation in eastern Numidia, which was formed by an amalgamation of smaller tribes during the 4th century BC.Nigel Bagnall, The Punic Wars, p. 270. They were ruled by a king. On their loosely defined wester ...
in eastern Numidia, and the Masaesyli
The Masaesyli were a Berber tribe of western Numidia (present day Algeria) and the main antagonists of the Massylii in eastern Numidia.
During the Second Punic War the Masaesyli initially supported the Roman Republic and were led by Syphax ag ...
in the west. During the first part of the Second Punic War, the eastern Massylii, under their king Gala
Gala may refer to:
Music
* ''Gala'' (album), a 1990 album by the English alternative rock band Lush
*'' Gala – The Collection'', a 2016 album by Sarah Brightman
*GALA Choruses, an association of LGBT choral groups
*''Gala'', a 1986 album by T ...
, were allied with Carthage, while the western Masaesyli, under king Syphax, were allied with Rome. The Kingdom of Masaesyli under Syphax extended from the Moulouya river to Oued Rhumel.
 However, in 206 BC, the new king of the eastern Massylii,
However, in 206 BC, the new king of the eastern Massylii, Masinissa
Masinissa ( nxm, , ''MSNSN''; ''c.'' 238 BC – 148 BC), also spelled Massinissa, Massena and Massan, was an ancient Numidian king best known for leading a federation of Massylii Berber tribes during the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), ult ...
, allied himself with Rome, and Syphax of the Masaesyli switched his allegiance to the Carthaginian side. At the end of the war, the victorious Romans gave all of Numidia to Masinissa of the Massylii. At the time of his death in 148 BC, Masinissa's territory extended from the Moulouya to the boundary of the Carthaginian territory, and also southeast as far as Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
to the gulf of Sirte, so that Numidia entirely surrounded Carthage (Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
, ''Punica'', 106) except towards the sea. Furthermore, after the capture of Syphax the king in modern day Morocco with his capital based in Tingis, Bokkar, had become a vassal of Massinissa. Massinissa had also penetrated as far south beyond the Atlas to the Gaetuli and Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ber, ⴼⵣⵣⴰⵏ, Fezzan; ar, فزان, Fizzān; la, Phazania) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ...
was part of his domain.
In 179 B.C. Masinissa had received a golden crown from the inhabitants of Delos as he had offered them a shipload of grain. A statue of Masinissa was set up in Delos in honour of him as well as an inscription dedicated to him in Delos by a native from Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
. His sons too had statues of them erected on the island of Delos and the King of Bithynia, Nicomedes, had also dedicated a statue to Masinissa.
After the death of the long-lived Masinissa around 148 BC, he was succeeded by his son Micipsa
Micipsa (Numidian: MKWSN; , ; died BC) was the eldest legitimate son of Masinissa, the King of Numidia, a Berber kingdom in North Africa. Micipsa became the King of Numidia in 148 BC.
Early life
In 151 BC, Masinissa sent Micipsa and his brother ...
. When Micipsa died in 118 BC, he was succeeded jointly by his two sons Hiempsal I
Hiempsal I (died c. 117 BC), son of Micipsa and grandson of Masinissa, was a king of Numidia in the late 2nd century BC.
Micipsa, on his deathbed, left his two sons, Adherbal and Hiempsal, together with his cousin, Jugurtha, joint heirs of hi ...
and Adherbal and Masinissa's illegitimate grandson, Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen ( Libyco-Berber ''Yugurten'' or '' Yugarten'', c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Jugurtha and his two adoptive brothers, Hiempsal and A ...
, who was very popular among the Numidians. Hiempsal and Jugurtha quarrelled immediately after the death of Micipsa. Jugurtha had Hiempsal killed, which led to open war with Adherbal.
War with Rome
By 112 BC, Jugurtha resumed his war with Adherbal. He incurred the wrath of Rome in the process by killing some Roman businessmen who were aiding Adherbal. After a brief war with Rome, Jugurtha surrendered and received a highly favourable peace treaty, which raised suspicions of bribery once more. The local Roman commander was summoned to Rome to face corruption charges brought by his political rival Gaius Memmius. Jugurtha was also forced to come to Rome to testify against the Roman commander, where Jugurtha was completely discredited once his violent and ruthless past became widely known, and after he had been suspected of murdering a Numidian rival. War broke out between Numidia and theRoman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
and several legions were dispatched to North Africa under the command of the Consul Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus (c. 155 BC – 91 BC) was an ancient Roman statesman and general, he was a leader of the Optimates, the conservative faction of the Roman Senate. He was a bitter political opponent of Gaius Marius. He was consul ...
. The war dragged out into a long and seemingly endless campaign as the Romans tried to defeat Jugurtha decisively. Frustrated at the apparent lack of action, Metellus' lieutenant Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
returned to Rome to seek election as Consul. Marius was elected, and then returned to Numidia to take control of the war. He sent his Quaestor Sulla to neighbouring Mauretania in order to eliminate their support for Jugurtha. With the help of Bocchus I
Bocchus, often referred to as Bocchus I for clarity, was king of Mauretania from - 80 BCE. He was father-in-law to the Numidian king Jugurtha, with whom he initially allied against the Romans in the Jugurthine War, a lengthy and indecisive conf ...
of Mauretania, Sulla captured Jugurtha and brought the war to a conclusive end. Jugurtha was brought to Rome in chains and was placed in the Tullianum
The Mamertine Prison ( it, Carcere Mamertino), in antiquity the Tullianum, was a prison (''carcer'') with a dungeon ('' oubliette'') located in the Comitium in ancient Rome. It is said to have been built in the 7th century BC and was situated o ...
.
Jugurtha was executed by the Romans in 104 BC, after being paraded through the streets in Gaius Marius' Triumph.
Divided kingdom
After the death of Jugurtha, the far west of Numidia was added to the lands ofBocchus I
Bocchus, often referred to as Bocchus I for clarity, was king of Mauretania from - 80 BCE. He was father-in-law to the Numidian king Jugurtha, with whom he initially allied against the Romans in the Jugurthine War, a lengthy and indecisive conf ...
, king of Mauretania. A rump kingdom continued to be governed by native princes. It appears that on the death of King Gauda in 88 BC, the kingdom was divided into a larger eastern kingdom and a smaller western kingdom (roughly the Petite Kabylie). The kings of the east minted coins, while no known coins of the western kings survive. The western kings may have been vassals of the eastern..
The civil war between Caesar and Pompey brought an end to independent Numidia in 46 BC. The western kingdom between the Sava (Oued Soummam
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), Maghrebi Arabic, North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemerality, ephemeral) S ...
) and Ampsaga ( Oued-el-Kebir) rivers passed to Bocchus II
Bocchus II was a king of Mauretania in the 1st century BC. He was the son of Mastanesosus, who died in 49 BC, upon which Bocchus inherited the throne.
Biography
He was surely the son of Mastanesosus, king of Mauretania. His father was identifie ...
, while the eastern kingdom became a Roman province. The remainder of the western kingdom plus the city of Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria.
Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city ...
, which may have belonged to either kingdom, became briefly an autonomous principality under Publius Sittius Publius Sittius (died 44 BC) was a Roman equites and mercenary commander. As a mercenary he was employed by king Bocchus II of East-Mauretania. Sittius fought for Bocchus against king Juba I of Numidia, capturing Juba's capital of Cirta and defeati ...
. Between 44 and 40 BC, the old western kingdom was once again under a Numidian king, Arabio
Arabio (or Arabion) was the last independent Numidian king, ruling the western region between 44 and 40 BC. According to Appian, he was a son of Masinissa II and probable grandson of Gauda, who had divided Numidia between his sons in 88&nbs ...
, who killed Sittius and took his place. He involved himself in Rome's civil wars and was himself killed.
Roman provinces
Africa Nova
Numidia was a Roman province on the North African coast, comprising roughly the territory of north-east Algeria.
History
The people of the area were first identified as Numidians by Polybius around the 2nd century BC, although they were often ...
''. ''Western Numidia'' was also annexed as part of the province ''Africa Nova'' after the death of its last king, Arabio
Arabio (or Arabion) was the last independent Numidian king, ruling the western region between 44 and 40 BC. According to Appian, he was a son of Masinissa II and probable grandson of Gauda, who had divided Numidia between his sons in 88&nbs ...
, in 40 BC, and subsequently the province (except of ''Western Numidia'') was united with province '' Africa Vetus'' by Emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
in 25 BC, to create the new province ''Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
''. During the brief period (30–25 BC) Juba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
(son of Juba I
Juba I of Numidia ( lat, IVBA, xpu, ywbʿy; –46BC) was a king of Numidia (reigned 60–46 BC). He was the son and successor to Hiempsal II.
Biography
In 81 BC Hiempsal had been driven from his throne; soon afterwards, Pompey was sent to Af ...
) ruled as a client king of Numidia on the territory of former province ''Africa Nova''.
In AD 40, the western portion of Africa Proconsularis, including its legionary garrison, was placed under an imperial ''legatus'', and in effect became a separate province of Numidia, though the ''legatus'' of Numidia remained nominally subordinate to the proconsul of Africa until AD 203. In 193 AD, under Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
, Numidia was separated from Africa Proconsularis, and governed by an imperial procurator
Procurator (with procuracy or procuratorate referring to the office itself) may refer to:
* Procurator, one engaged in procuration, the action of taking care of, hence management, stewardship, agency
* ''Procurator'' (Ancient Rome), the title o ...
.
In the reorganization of the empire by Diocletian, Numidia was divided in two provinces: the north became Numidia Cirtensis
Numidia was a Roman province on the North African coast, comprising roughly the territory of north-east Algeria.
History
The people of the area were first identified as Numidians by Polybius around the 2nd century BC, although they were often ...
, with capital at Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria.
Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city ...
, while the south, which included the Aurès Mountains and was threatened by raids, became Numidia Militiana, "Military Numidia", with capital at the legionary base of Lambaesis
Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa (''Lambèse'' in colonial French), is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, southeast of Batna and west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also a Lat ...
.
Subsequently Emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
reunited the two provinces in a single one, administered from Cirta, which was now renamed ''Constantina'' (modern Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
) in his honour. Its governor was raised to the rank of ''consularis ''Consularis'' is a Latin adjective indicating something pertaining to the position or rank of consul. In Ancient Rome it was also used as a noun (plural ''consulares'') to designate those senators who had held the office of consul or attained co ...
'' in 320, and the province remained one of the six provinces of the Diocese of Africa
The Diocese of Africa ( la, Dioecesis Africae) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of North Africa, except Mauretania Tingitana. Its seat was at Carthage, and it was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of It ...
until the invasion of the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
in 428, which began its slow decay, accompanied by desertification. It was restored to Roman rule after the Vandalic War
The Vandalic War was a conflict fought in North Africa between the forces of the Byzantine Empire and the Vandalic Kingdom of Carthage in 533–534. It was the first of Justinian I's wars of reconquest of the Western Roman Empire.
The Vandal ...
, when it became part of the new Praetorian prefecture of Africa.
Architecture

 The term “Royal Numidian Architecture” was coined for the monuments that were constructed by the Numidian kings.Quinn, J. (2013). Monumental power: ‘Numidian Royal Architecture’ in context. In J. Prag & J. Quinn (Eds.), The Hellenistic West: Rethinking the Ancient Mediterranean (pp. 179-215). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139505987.008 These monuments consist of tombs, tumuli and sanctuaries. Some examples of these structures are the mausoleum of Thugga, the tomb of Beni Rhenane, a tomb at Henchur Burgu in Djerba as well as two tumulus tombs known as the Madghacen and the
The term “Royal Numidian Architecture” was coined for the monuments that were constructed by the Numidian kings.Quinn, J. (2013). Monumental power: ‘Numidian Royal Architecture’ in context. In J. Prag & J. Quinn (Eds.), The Hellenistic West: Rethinking the Ancient Mediterranean (pp. 179-215). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139505987.008 These monuments consist of tombs, tumuli and sanctuaries. Some examples of these structures are the mausoleum of Thugga, the tomb of Beni Rhenane, a tomb at Henchur Burgu in Djerba as well as two tumulus tombs known as the Madghacen and the Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania
The Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania is a funerary monument located on the road between Cherchell and Algiers, in Tipaza Province, Algeria. The mausoleum is the tomb where the Numidian Berber King Juba II (son of Juba I of Numidia) and the Queen Cleop ...
. There are also altars that were built at Simitthus and Kbor Klib. All of these monuments were built within the area ruled by Massinissa and his descendants.

Major cities
Numidia became highly romanized and was studded with numerous towns. The chief towns of Roman Numidia were: in the north,Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria.
Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city ...
or modern Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
, the capital, with its port Russicada
Russicada presentday Skikda, was the Mediterranean port city serving Cirta, the capital of the Kingdom of Numidia in Ancient Algeria.
It overlooked the straits between Sicily (Europe) and Numidia (Africa), a place of significant relevance in ...
(Modern Skikda
Skikda ( ar, سكيكدة; formerly Philippeville from 1838 to 1962 and Rusicade in ancient times) is a city in northeastern Algeria and a port on the Mediterranean. It is the capital of Skikda Province and Skikda District.
History
The Phoeni ...
); and Hippo Regius (near Bône
Annaba ( ar, عنّابة, "Place of the Jujubes"; ber, Aânavaen), formerly known as Bon, Bona and Bône, is a seaport city in the northeastern corner of Algeria, close to the border with Tunisia. Annaba is near the small Seybouse River ...
), well known as the see of St. Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North A ...
. To the south in the interior military roads led to Theveste
Theveste was a Roman colony situated in the present Tébessa, Algeria.
History
In 146 BC, the Romans conquered the region, where existed an old city called " Tbessa". Theveste was founded by the Romans in 75 AD near an old Berber village locate ...
(Tebessa) and Lambaesis
Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa (''Lambèse'' in colonial French), is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, southeast of Batna and west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also a Lat ...
(Lambessa) with extensive Roman remains, connected by military roads with Cirta and Hippo, respectively./ref> Lambaesis was the seat of the Legio III ''Augusta'', and the most important strategic centre. It commanded the passes of the Aurès Mountains (Mons Aurasius), a mountain block that separated Numidia from the Gaetuli Berber tribes of the desert, and which was gradually occupied in its whole extent by the Romans under the Empire. Including these towns, there were altogether twenty that are known to have received at one time or another the title and status of Roman colonies; and in the 5th century, the '' Notitia Dignitatum'' enumerates no fewer than 123 sees whose bishops assembled at Carthage in 479.
Episcopal sees
See Numidia (Roman province)#Episcopal sees.See also
* List of Kings of Numidia *Numidians
The Numidians were the Berber population of Numidia (Algeria and in smaller parts of Tunisia and Morocco). The Numidians were one of the earliest Berber tribes to trade with Carthaginian settlers. As Carthage grew, the relationship with the Nu ...
* Numidian cavalry
Numidian cavalry was a type of light cavalry developed by the Numidians. After they were used by Hannibal during the Second Punic War, they were described by the Roman historian Livy as "by far the best horsemen in Africa."
History
Numidian cava ...
* Roman Libya
The area of North Africa which has been known as Libya since 1911 was under Roman domination between 146 BC and 672 AD (even if in the meantime it was taken by the Vandals in 430 AD, and then recaptured by the Byzantines). The Latin name ''Libya'' ...
* Africa (Roman province)
* Shawiya language
Shawiya, or Shawiya Berber, also spelt Chaouïa (native form: ''Tacawit'' ), is a Zenati Berber language spoken in Algeria by the Shawiya people. The language's primary speech area is the Awras Mountains in Eastern Algeria and the surrounding ...
References
Further reading
* * * * {{Authority control Countries in ancient Africa States and territories established in the 3rd century BC 3rd-century BC establishments 202 BC 200s BC establishments 1st-century BC disestablishments in the Roman Empire 1st-century BC disestablishments Berber dynasties Roman client kingdoms Provinces of the Byzantine Empire Ancient Greek geography of North Africa Former kingdoms