Karamanid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Karamanids ( tr, Karamanoğulları or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman ( tr, Karamanoğulları Beyliği), was one of the
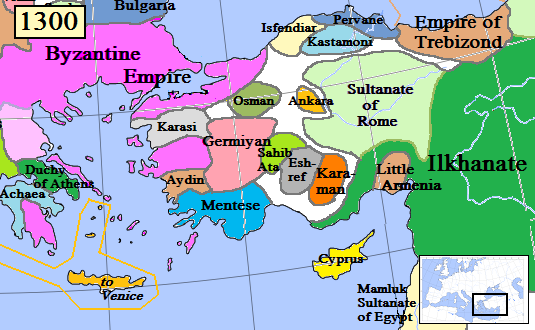 Despite these blows, the Karamanids continued to increase their power and influence, largely aided by the
Despite these blows, the Karamanids continued to increase their power and influence, largely aided by the
Anatolian beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A se ...
, centered in South-Central Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
around the present-day Karaman Province. From the middle 1300s until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia.
History
The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (roughly encompassing modern-dayAzerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
) to Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
because of the Mongol invasion in 1230.
The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe
Salur, Salyr or Salgur ( tr, Salır, tk, Salyr, fa, سالور) were an ancient Oghuz Turkic people and a sub-branch of the ''Üçok'' tribal federation. The medieval Karamanid principality in Anatolia belonged to the Karaman branch of the S ...
of Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conven ...
. According to Muhsin Yazıcıoğlu and others, they were members of the Afshar tribe
Afshar ( az, Əfşar افشار; tr, Avşar, ''Afşar''; tk, Owşar; fa, اَفشار, Āfshār) is a tribe of Oghuz Turkic origin, that split into several groups in Iran, Turkey and Afghanistan.
During the Seljuk conquests of the 11th centur ...
,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071–1330'', trans. J. Jones-Williams (New York: Taplinger, 1968), pp. 281–2. which participated in the revolt
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
led by Baba Ishak
Baba Ishak, also spelled Baba Ishāq, Babaî, or Bābā’ī, a charismatic preacher, led an uprising of the Turkoman of Anatolia against the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm well known as Babai Revolt ''c.'' 1239 until he was hanged in 1241. Balcıoğ ...
and afterwards moved to the western Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains ( Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar'') are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğird ...
, near the town of Larende
Karaman, historically known as Laranda (Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. According to ...
, where they came to serve the Seljuks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
. Nure Sofi Nûre Sûfi Bey ( tr, Nureddin Bey) was the founder of Karamanid dynasty, a Turkic dynasty which ruled part of Anatolia in the 14th and 15th centuries as a rival of the Ottoman Empire. He was the son of Hodja Sad al-Din ( tr, Hoca Sadeddin) who had ...
worked there as a woodcutter. His son, Kerîmeddin Karaman Bey
Kerîmeddin Karaman Beg ( Turkish) (Arabic: كريم ٱلدين Karīm al-Dīn Karaman Bey), sometimes Karaman Bey, was a Turkish chief founder of the dynasty Karaman-oğhlu or Karamanoğulları, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 13th ...
, gained a tenuous control over the mountainous parts of Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
in the middle of the 13th century. A persistent but spurious legend, however, claims that the Seljuq Sultan of Rum, Kayqubad I
Alā ad-Dīn Kayqubād ibn Kaykhusraw ( fa, علاء الدين كيقباد بن كيخسرو; tr, I. Alâeddin Keykûbad, 1190–1237), also known as Kayqubad I, was the Seljuq Sultan of Rûm who reigned from 1220 to 1237. He expanded th ...
, instead established a Karamanid dynasty in these lands.
Karaman Bey
Karaman, historically known as Laranda ( Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. Accordi ...
expanded his territories by capturing castles in Ermenek
Ermenek is a town and district of Karaman Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. As ancient Germanicopolis (in Isauria; has namesakes), a former bishopric, it remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
The district forms the core of the plate ...
, Mut
Mut, also known as Maut and Mout, was a mother goddess worshipped in ancient Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush in present-day North Sudan. In Meroitic, her name was pronounced mata): 𐦨𐦴. Her name means ''mother'' in the ancient Egyptian l ...
, Ereğli, Gülnar, and Silifke
Silifke ( grc-gre, Σελεύκεια, ''Seleukeia'', la, Seleucia ad Calycadnum) is a town and district in south-central Mersin Province, Turkey, west of the city of Mersin, on the west end of Çukurova.
Silifke is near the Mediterranean co ...
. The year of the conquests is reported as 1225, during the reign of Ala al-Din Kaykubadh I (1220–1237), which seems excessively early. Karaman Bey's conquests were mainly at the expense of the Kingdom of Lesser Armenia (and perhaps at the expense of Rukn al-Din Kilij Arslan IV, 1248–1265); in any case it is certain that he fought against the Kingdom of Lesser Armenia (and probably even died in this fight) to such extent that King Hethum I (1226–1269) had to place himself voluntarily under the sovereignty of the great Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
, in order to protect his kingdom from Mamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
and Seljuks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
(1244).
The rivalry between Kilij Arslan IV
Kilij Arslan IV ( 1ca, قِلِج اَرسلان) or Rukn ad-Dīn Qilij Arslān ibn Kaykhusraw ( fa, رکن الدین قلج ارسلان بن کیخسرو) was Seljuq Sultan of Rûm after the death of his father Kaykhusraw II in 1246.
However, ...
and Izz al-Din Kaykaus II allowed the tribes in the border areas to live virtually independently. Karaman Bey helped Kaykus, but Arslan had the support of both the Mongols and Pervâne Sulayman Muin al-Din (who had the real power in the sultanate).
The Mongolian governor and general Baiju was dismissed from office in 1256 because he had failed to conquer new territories, but he continued to serve as a general and appeared, the same year, fighting the Sultan of Rum, who had not paid the tax, and he managed to defeat the sultan a second time. Rukn al-Din Kilidj Arslan IV got rid of almost all hostile begs and amir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
s except Karaman Bey, to whom he gave the town of Larende
Karaman, historically known as Laranda (Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. According to ...
(now Karaman
Karaman, historically known as Laranda ( Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. Accordin ...
, in honor of the dynasty) and Ermenek (c. 1260) in order to win him to his side. In the meantime, Bunsuz, brother of Karaman Bey, was chosen as a '' Candar'', or bodyguard, for Kilij Arslan IV
Kilij Arslan IV ( 1ca, قِلِج اَرسلان) or Rukn ad-Dīn Qilij Arslān ibn Kaykhusraw ( fa, رکن الدین قلج ارسلان بن کیخسرو) was Seljuq Sultan of Rûm after the death of his father Kaykhusraw II in 1246.
However, ...
. Their power rose as a result of the unification of Turkish clans that lived in the mountainous regions of Cilicia with the new Turkish population transferred there by Kayqubad.
Good relations between the Seljuqs and the Karamanids did not last. In 1261, on the pretext of supporting Kaykaus II, who had fled to Constantinople as a result of the intrigues of the chancellor Mu'in al-Din Suleyman, the Pervane, Karaman Bey and his two brothers, Zeynül-Hac and Bunsuz, marched toward Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
, the Seljuq capital, with 20,000 men. A combined Seljuq and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
army, led by the Pervane, defeated the Karamanid army and captured Karaman Bey's two brothers.
After Karaman Bey died in 1262, his older son, Mehmet I of Karaman, became the head of the house. He immediately negotiated alliances with other Turkmen clans to raise an army against the Seljuqs and Ilkhanids. During the 1276 revolt of Hatıroğlu Şemseddin Bey against Mongol domination in Anatolia, Karamanids also defeated several Mongol-Seljuq armies. In the Battle of Göksu in 1277 in particular, the central power of the Seljuq was dealt a severe blow. Taking advantage of the general confusion, Mehmed Bey captured Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
on 12 May and placed on the throne a pretender called Jimri, who claimed to be the son of Kaykaus. In the end, however, Mehmed was defeated by Seljuq and Mongol forces and executed with some of his brothers in 1278.
 Despite these blows, the Karamanids continued to increase their power and influence, largely aided by the
Despite these blows, the Karamanids continued to increase their power and influence, largely aided by the Mamluks
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, especially during the reign of Baybars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
. Karamanids captured Konya on two more occasions in the beginning of the 14th century, but were driven out the first time by emir Chupan, the Ilkhanid
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
governor of Anatolia, and the second time by Chupan's son and successor Timurtash. An expansion of Karamanoğlu power occurred after the fall of the Ilkhanids. A second expansion coincided with Karamanoğlu Alâeddin Ali Bey's marriage to Nefise Hatun, the daughter of the Ottoman sultan Murat I, the first important contact between the two dynasties.
As Ottoman power expanded into the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, Aleaddin Ali Bey captured the city of Beyşehir
Beyşehir () is a large town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. The town is located on the southeastern shore of Lake Beyşehir and is marked to the west and the southwest by the steep lines and forests of the Tauru ...
, which had been an Ottoman city. However, it did not take much time for the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
to react and march on Konya, the Karamanoğlu capital city. A treaty between the two kingdoms was formed, and peace existed until the reign of Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted ...
.
Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kü ...
gave control of the Karamanid lands to Mehmet Bey, the oldest son of Aleaddin Ali Bey. After Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted ...
died in 1403, the Ottoman Empire went into a political crisis as the Ottoman family fell prey to internecine strife. It was an opportunity not only for Karamanids but also for all of the Anatolian ''beyliks''. Mehmet Bey assembled an army to march on Bursa
( grc-gre, Προῦσα, Proûsa, Latin: Prusa, ota, بورسه, Arabic:بورصة) is a city in northwestern Turkey and the administrative center of Bursa Province. The fourth-most populous city in Turkey and second-most populous in the ...
. He captured the city and damaged it; this would not be the last Karamanid invasion of Ottoman lands. However, Mehmet Bey was captured by Bayezid Pasha and sent to prison. He apologized for what he had done and was forgiven by the Ottoman ruler.
Ramazanoğlu Ali Bey captured Tarsus while Mehmet Bey was in prison. Mustafa Bey, son of Mehmet Bey, retook the city during a conflict between the Emirs of Sham and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
. After that, the Egyptian sultan Sayf ad-Din Inal sent an army to retake Tarsus from the Karamanids. The Egyptian Mamluks damaged Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
after defeating the Karamanids, and Mehmet Bey retreated from Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
. Ramazanoğlu Ali Bey pursued and captured him; according to an agreement between the two leaders, Mehmet Bey was exiled to Egypt for the rest of his life.
During the Crusade of Varna against the Ottomans in 1443–44, Karamanid İbrahim Bey marched on Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki ...
and Kütahya
Kütahya () (historically, Cotyaeum or Kotyaion, Greek: Κοτύαιον) is a city in western Turkey which lies on the Porsuk river, at 969 metres above sea level. It is inhabited by some 578,640 people (2022 estimate). The region of Kütahya ha ...
, destroying both cities. In the meantime, the Ottoman sultan Murad II
Murad II ( ota, مراد ثانى, Murād-ı sānī, tr, II. Murad, 16 June 1404 – 3 February 1451) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1421 to 1444 and again from 1446 to 1451.
Murad II's reign was a period of important economic deve ...
was returning from Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a hi ...
with a victory against the Hungarian Crusaders. Like all other Islamic emirates in Anatolia, the Karamanids were accused of treason. Hence, İbrahim Bey accepted all Ottoman terms. The Karamanid state was eventually terminated by the Ottomans in 1487, as the power of their Mameluke allies was declining. To never again gather and threaten the integrity of the Empire, they killed a large part of the population and displaced the entire population to the last man. Some were resettled in various parts of Anatolia. Large groups were accommodated in northern Iran on the territory of present-day Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
. The main part was brought to the newly conquered territories in north-eastern Bulgaria – the Ludogorie region, another group – to what is now northern Greece and southern Bulgaria— present-day Kardzhali
Kardzhali ( bg, Кърджали , ''Kărdžali''; tr, Kırcaali; gr, Κάρτζαλι, ''Kártzali''), sometimes spelt Kardžali or Kurdzhali, is a town in the Eastern Rhodopes in Bulgaria, centre of Kardzhali Municipality and Kardzhali Pro ...
region and Macedonia. Ottomans founded Karaman Eyalet from former territories of Karamanids.
Flag
According toAbraham Cresques
Abraham Cresques (, 1325–1387), whose real name was Cresques (son of) Abraham, was a 14th-century Jewish cartographer from Palma, Majorca (then part of the Crown of Aragon). In collaboration with his son, Jehuda Cresques, Cresques is credit ...
' ''Catalan Atlas
The Catalan Atlas ( ca, Atles català, ) is a medieval world map, or mappamundi, created in 1375 that has been described as the most important map of the Middle Ages in the Catalan language, and as "the zenith of medieval map-work".
It was p ...
'' (compiled in 1375), the flag of ''Karamanoğlu'' consisted of a blue six-edged star. In the medieval times
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, this star was a popular Islamic symbol (especially among the Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named a ...
Madhhab
A ( ar, مذهب ', , "way to act". pl. مَذَاهِب , ) is a school of thought within '' fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence).
The major Sunni Mathhab are Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i and Hanbali.
They emerged in the ninth and tenth centurie ...
) known as the Seal of Solomon
The Seal of Solomon or Ring of Solomon ( he, חותם שלמה, '; ar, خاتم سليمان, ') is the legendary signet ring attributed to the Israelite king Solomon in medieval mystical traditions, from which it developed in parallel within ...
due to the belief that the Jewish king, King Solomon
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the ti ...
was a prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
, and was used by several of the Anatolian beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A se ...
(such as the Isfendiyarids). As such the seal was also used by Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in their mosque decorations, coins and even in the personal flags of individual Pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignita ...
(e.g. that of Hayreddin Barbarossa
Hayreddin Barbarossa ( ar, خير الدين بربروس, Khayr al-Din Barbarus, original name: Khiḍr; tr, Barbaros Hayrettin Paşa), also known as Hızır Hayrettin Pasha, and simply Hızır Reis (c. 1466/1478 – 4 July 1546), was an O ...
http://www.fahnenversand.de/fotw/misc/tr~barb.jpg ). It adorned the tombs of several early Islamic figures in Medina until the destruction of al-Baqi cemetery. Al-Buni and Ibn Arabi
Ibn ʿArabī ( ar, ابن عربي, ; full name: , ; 1165–1240), nicknamed al-Qushayrī (, ) and Sulṭān al-ʿĀrifīn (, , ' Sultan of the Knowers'), was an Arab Andalusian Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher, extremely influen ...
consider the seal to represent the Greatest Name
Greatest may refer to:
* ''Greatest!'', a 1959 album by Johnny Cash
* ''Bee Gees Greatest'', a 1979 album by Bee Gees
* ''Greatest'' (The Go-Go's album), 1990
* ''Greatest'' (Duran Duran album), 1998
* Greatest (song), a song by Eminem
* "Greate ...
, and its use remains common in contemporary Muslim esoteric circles.
Power of the Karamanid state in Anatolia
According to Mesâlik-ül-Ebsâr, written by Şehâbeddin Ömer, the Karamanid army had 25,000 riders and 25,000saracens
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia ...
. They could also rely on some Turkmen tribes and their warriors.
Their economic activities depended mostly on control of strategic commercial areas such as Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
, Karaman
Karaman, historically known as Laranda ( Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. Accordin ...
and the ports of Lamos, Silifke
Silifke ( grc-gre, Σελεύκεια, ''Seleukeia'', la, Seleucia ad Calycadnum) is a town and district in south-central Mersin Province, Turkey, west of the city of Mersin, on the west end of Çukurova.
Silifke is near the Mediterranean co ...
, Anamur, and Manavgat.
Karamanid architecture
66mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s, 8 hammams, 2 caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes covering ...
s and 3 medreses built by the Karamanids survived to the present day. Notable examples of Karamanid architecture include:
* Hasbey Medrese (1241)
* Şerafettin Mosque (13th century)
* İnce Minare (Dar-ül Hadis) Medrese (1258–1279)
* Hatuniye Medrese (Karaman)
* Mevlana Mosque and Tomb in Konya
* Mader-i Mevlana (Aktekke) mosque in Karaman
* Ibrahim Bey Mosque (Imaret) in Karaman
List of rulers
# Nûreddin Sûfi Bey (Capital City: Ereğli) (1250–1256) #Kerîmeddin Karaman Bey
Kerîmeddin Karaman Beg ( Turkish) (Arabic: كريم ٱلدين Karīm al-Dīn Karaman Bey), sometimes Karaman Bey, was a Turkish chief founder of the dynasty Karaman-oğhlu or Karamanoğulları, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 13th ...
(Capital City: Ermenek
Ermenek is a town and district of Karaman Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. As ancient Germanicopolis (in Isauria; has namesakes), a former bishopric, it remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
The district forms the core of the plate ...
) (1256?-1261)
# Şemseddin I. Mehmed Bey (1261–1277), notable for making Turkish the official language
# Güneri Bey (1277–1300)
# Bedreddin Mahmut Bey (1300–1308)
# Yahşı Han Bey (1308–1312) (Capital City: Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
)
# Bedreddin I. İbrahim Bey (1312–1333, 1348–1349)
# Alâeddin Halil Mirza Bey (1333–1348)
# Fahreddin Ahmed Bey (1349–1350)
# Şemseddin Bey (1350–1351)
# Hacı Sûfi Burhâneddin Musa Bey (Capital City: Mut
Mut, also known as Maut and Mout, was a mother goddess worshipped in ancient Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush in present-day North Sudan. In Meroitic, her name was pronounced mata): 𐦨𐦴. Her name means ''mother'' in the ancient Egyptian l ...
) (1351–1356)
# Seyfeddin Süleyman Bey (1357–1361)
# Damad I. Alâeddin Ali Bey (1361–1398)
# Sultanzâde II. Mehmed Bey (1398–1399, 1402–1420, 1421–1423)
# Damad Bengi Ali Bey (1423–1424)
# Damad II. İbrahim Bey (1424–1464)
# Sultanzâde İshak Bey (1464)
# Sultanzâde Pîr Ahmed Bey (1464–1469)
# Kasım Bey (1469–1483)
# Turgutoğlu Mahmud Bey (1483–1487)
See also
*Karamanlides
The Karamanlides ( el, Καραμανλήδες; tr, Karamanlılar), also known as Karamanli Greeks or simply Karamanlis, are a traditionally Turkish-speaking Greek Orthodox people native to the Karaman and Cappadocia regions of Anatolia.
Th ...
* Karaman
Karaman, historically known as Laranda ( Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. Accordin ...
* Karaman Province
* Anatolian Turkish Beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A seco ...
* List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties.
Asia
Middle East Arabian Peninsula
* Banu Wajih (926–965)
* Sharif of Mecca (967–1925)
* Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253)
* Sulaymanids (1063–1174)
* Mahdids (1159–1174)
*Kathiri (Hadhramau ...
* Caramania In the 18th and 19th centuries, Karamania (or Caramania) was an exonym used by Europeans for the southern (Mediterranean) coast of Anatolia, then part of the Ottoman Empire (current Turkey). It can also refer to the general south central Anatolian r ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * *Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Karamanids Anatolian beyliks 1487 disestablishments States and territories established in 1250 States and territories established in 1277 History of Adana Province History of Aksaray Province History of Antalya Province History of Karaman Province History of Kayseri Province History of Kırşehir Province History of Konya Province History of Mersin Province History of Nevşehir Province History of Niğde Province History of Osmaniye Province History of Konya Former empires in Asia