Kadosh Hakadashim on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
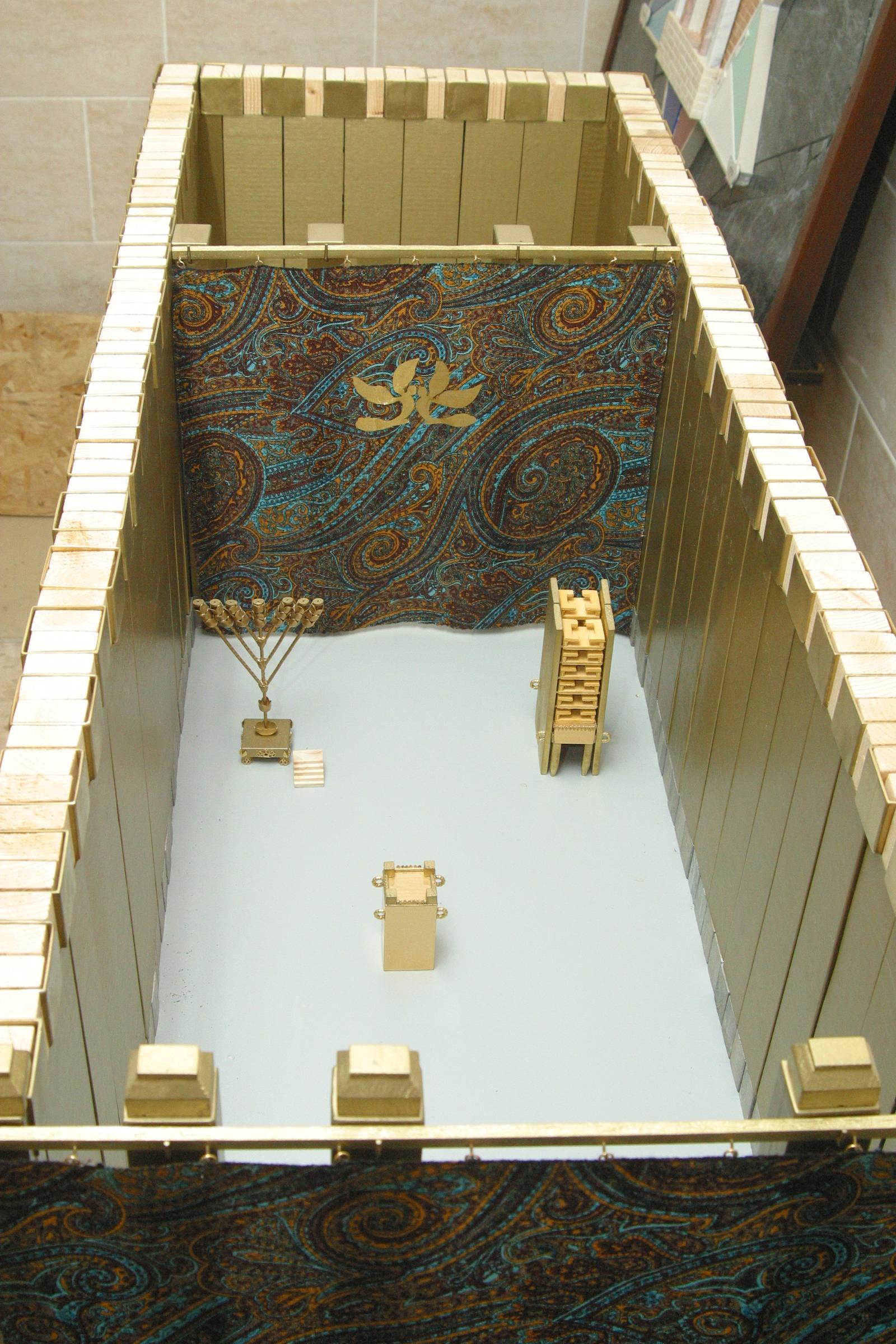 The Holy of Holies (
The Holy of Holies (
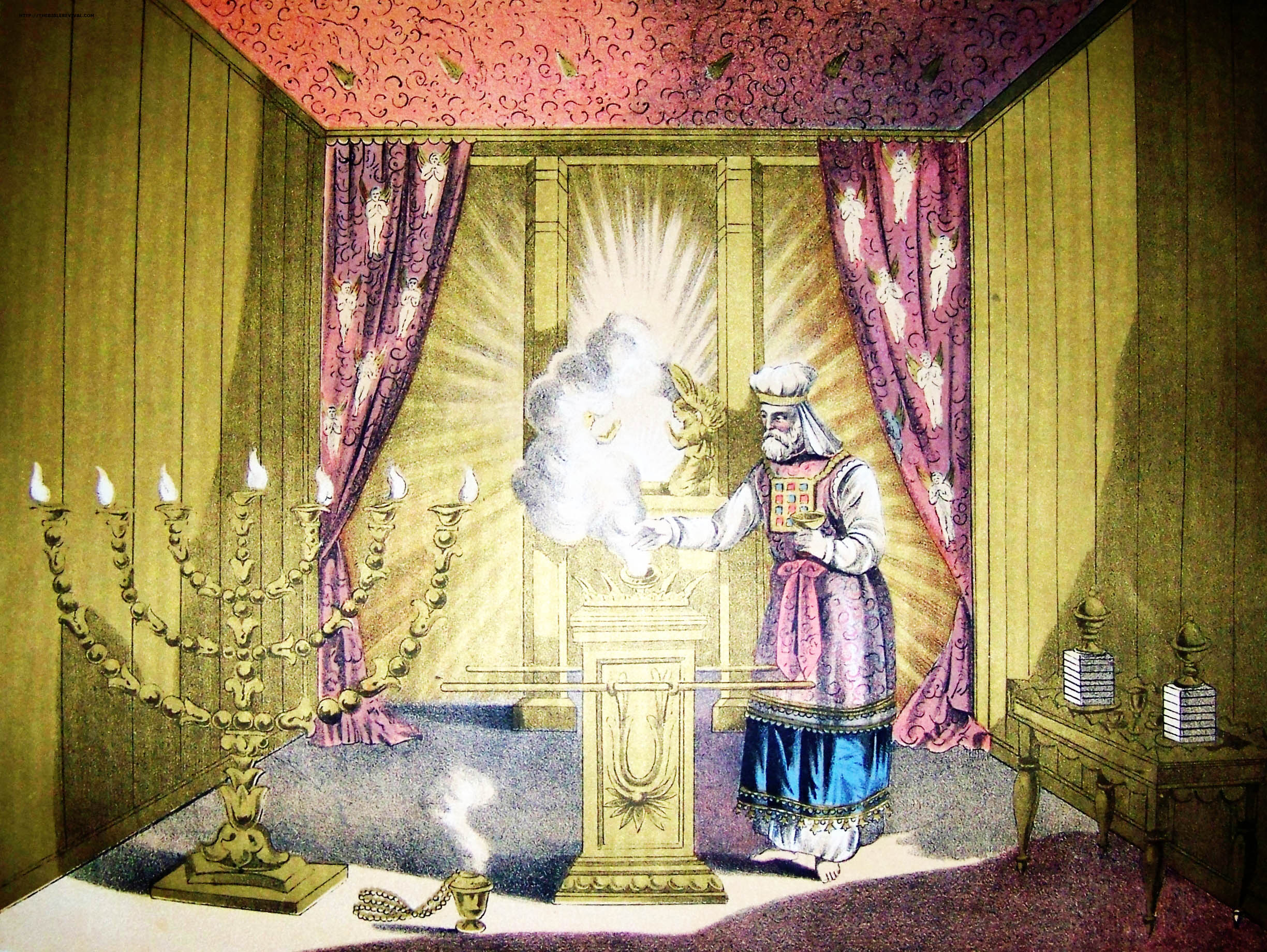 The construction "Holy of Holies" is a translation of the Hebrew (
The construction "Holy of Holies" is a translation of the Hebrew (
 According to the
According to the
 The Holy of Holies (
The Holy of Holies (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
: ''Qōḏeš haqQŏḏāšīm'' or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also הַדְּבִיר ''haDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Tabernacle According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
, where '' Tabernacle According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
's presence appeared. According to Hebrew tradition, the area was defined by four pillars that held up the veil of the covering, under which the Ark of the Covenant was held above the floor. According to the Hebrew scripture, the Ark contained the Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (Biblical Hebrew עשרת הדברים \ עֲשֶׂרֶת הַדְּבָרִים, ''aséret ha-dvarím'', lit. The Decalogue, The Ten Words, cf. Mishnaic Hebrew עשרת הדיברות \ עֲשֶׂרֶת הַדִּבְ ...
, which were given by God to Moses on Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai ( he , הר סיני ''Har Sinai''; Aramaic: ܛܘܪܐ ܕܣܝܢܝ ''Ṭūrāʾ Dsyny''), traditionally known as Jabal Musa ( ar, جَبَل مُوسَىٰ, translation: Mount Moses), is a mountain on the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. It is ...
. The Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
was said to have been built by King Solomon for keeping the Ark.
Ancient Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
traditions viewed the Holy of Holies as the spiritual junction of Heaven and Earth, the " axis mundi".
As a part of the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem, the Holy of Holies was situated somewhere on Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
; its precise location in the Mount being a matter of dispute, with some classical Jewish sources identifying its location with the Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure.
Over tim ...
, which sits under the Dome of the Rock. Other Jewish scholars argue that contemporary reports would place the Temple to the north or to the east of the current Dome of the Rock.
The Christian Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
associated the Holy of Holies with the Well of Souls
The Well of Souls ( ar, بئر الأرواح, Biʾr al-Arwaḥ; sometimes translated Pit of Souls, Cave of Spirits, or Well of Spirits), is a partly natural, partly man-made cave located inside the Foundation Stone ("Noble Rock" in Islam) under ...
, a small cave that lies underneath the Foundation Stone in the Dome of the Rock.
Hebrew terminology and translation
 The construction "Holy of Holies" is a translation of the Hebrew (
The construction "Holy of Holies" is a translation of the Hebrew (Tiberian Hebrew
Tiberian Hebrew is the canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) committed to writing by Masoretic scholars living in the Jewish community of Tiberias in ancient Galilee under the Abbasid Caliphate. They wrote in the form of Tiberian ...
: ''Qṓḏeš haQŏḏāšîm''), which is intended to express a superlative. Examples of similar constructions are "servant of servants" (Gen 9:25), "Sabbath of sabbaths" (Ex 31:15), "God of gods" (Deut 10:17), " Vanity of vanities" (Eccl 1:2), " Song of songs" (Song of Songs 1:1), "king of kings" (Ezra 7:12), etc. The Bible distinguishes the proper noun "Holy of Holies" from the superlative adjective by the definite article, viz. ''Qṓḏeš HaQŏḏāšîm'' is the room and ''qṓḏeš qāḏāšîm'' is used otherwise. This adds an additional level of superlativity; the only matching examples of the prior set are "God of gods" and "Song of songs."
In the Authorized King James Version, "Holy of Holies" is always translated as "Most Holy Place". This is in keeping with the intention of the Hebrew idiom to express the utmost degree of holiness. Thus, the name "Most Holy Place" was used to refer to the "Holy of Holies" in many English documents.
A related term is the ''debir A Biblical word, dvir () may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Names
* Debir King of Eglon, a Canaanite king of Eglon, slain by Joshua (). Aided by miracles, Joshua's army routed the Canaanite military, forcing Debir and the other kings to seek refuge in a cave ...
'' () transliterated in the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond ...
(the Greek translation as ''dabir'' (), which either means the back (i.e. western) part of the Sanctuary, or derives from the verb stem D-B-R, "to speak", justifying the translation in the Latin Vulgate as ''oraculum'', from which the traditional English translation "oracle" (KJV, 1611) derives.
Ancient Israel
Tabernacle
 According to the
According to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' God In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
may dwell among the Israelites, '' God In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
gave Moses instructions for erecting a sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a sa ...
. The directions provide for:
# A wooden ark, gilded inside and outside, for the Tablets of the Covenant, with a pure gold cover as the "mercy seat
According to the Hebrew Bible, the ''kaporet'' ( ''kapōreṯ'') or mercy seat was the gold lid placed on the Ark of the Covenant, with two cherubim beaten out of the ends to cover and create the space into which Yahweh was said to appear. This ...
" for the Divine Presence
Divine presence, presence of God, Inner God, or simply presence is a concept in religion, spirituality, and theology that deals with the ability of God to be " present" with human beings.
According to some types of monotheism God is omnipresen ...
;
# A gilt table for the " Table of Showbread", on which loaves of bread were arranged;
# A golden menorah, lampstand of 7 oil lamps for a light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
never to be extinguished;
# The dwelling, including the curtains for the roof, the walls made of boards resting on silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
feet and held together by wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
en bolts, the multi-colored curtain
A curtain is a piece of cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fa ...
veiling the Holy of Holies (of blue, purple, crimson, white and gold), the table and candlestick
A candlestick is a device used to hold a candle in place. Candlesticks have a cup or a spike ("pricket") or both to keep the candle in place. Candlesticks are less frequently called "candleholders".
Before the proliferation of electricity, candl ...
, and the outer curtain;
# A sacrificial altar
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly ex ...
made of bronzed boards for its '' korban''/sacrifice;
# The outer court formed by pillars
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
resting on bronze pedestal
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In ...
s and connected by hooks and crossbars of silver, with embroidered curtains;
# Recipe and preparation of the oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
for the Lampstand.
According to the Bible, the Holy of Holies was covered by a veil
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the head or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has been prominent ...
, and no one was allowed to enter except the High Priest, and even he would only enter once a year on Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
, to offer the blood of sacrifice and incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also b ...
. The Bible reports that in the wilderness, on the day that the tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
was first raised up, the cloud of the Lord covered the tabernacle (). There are other times that this was recorded, and instructions were given that the Lord would appear in the cloud upon the mercy seat (''kapporet''), and at that time the priests should not enter into the tabernacle (Leviticus 16:2). According to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Ark of the Covenant with representation of Cherubim. Upon completion of the dedication of the Tabernacle, the Voice of God spoke to Moses "from between the Cherubim" ().
 When the Temple was rebuilt after the Babylonian captivity, the Ark was no longer present in the Holy of Holies; instead, a portion of the floor was raised slightly to indicate the place where it had stood. In Jewish tradition, two curtains separated the Holy of Holies from the lesser Holy place during the period of the Second Temple. These curtains were woven with motifs directly from the loom, rather than embroidered, and each curtain had the thickness of a handbreadth (ca. 9 cm.).
When the Temple was rebuilt after the Babylonian captivity, the Ark was no longer present in the Holy of Holies; instead, a portion of the floor was raised slightly to indicate the place where it had stood. In Jewish tradition, two curtains separated the Holy of Holies from the lesser Holy place during the period of the Second Temple. These curtains were woven with motifs directly from the loom, rather than embroidered, and each curtain had the thickness of a handbreadth (ca. 9 cm.).
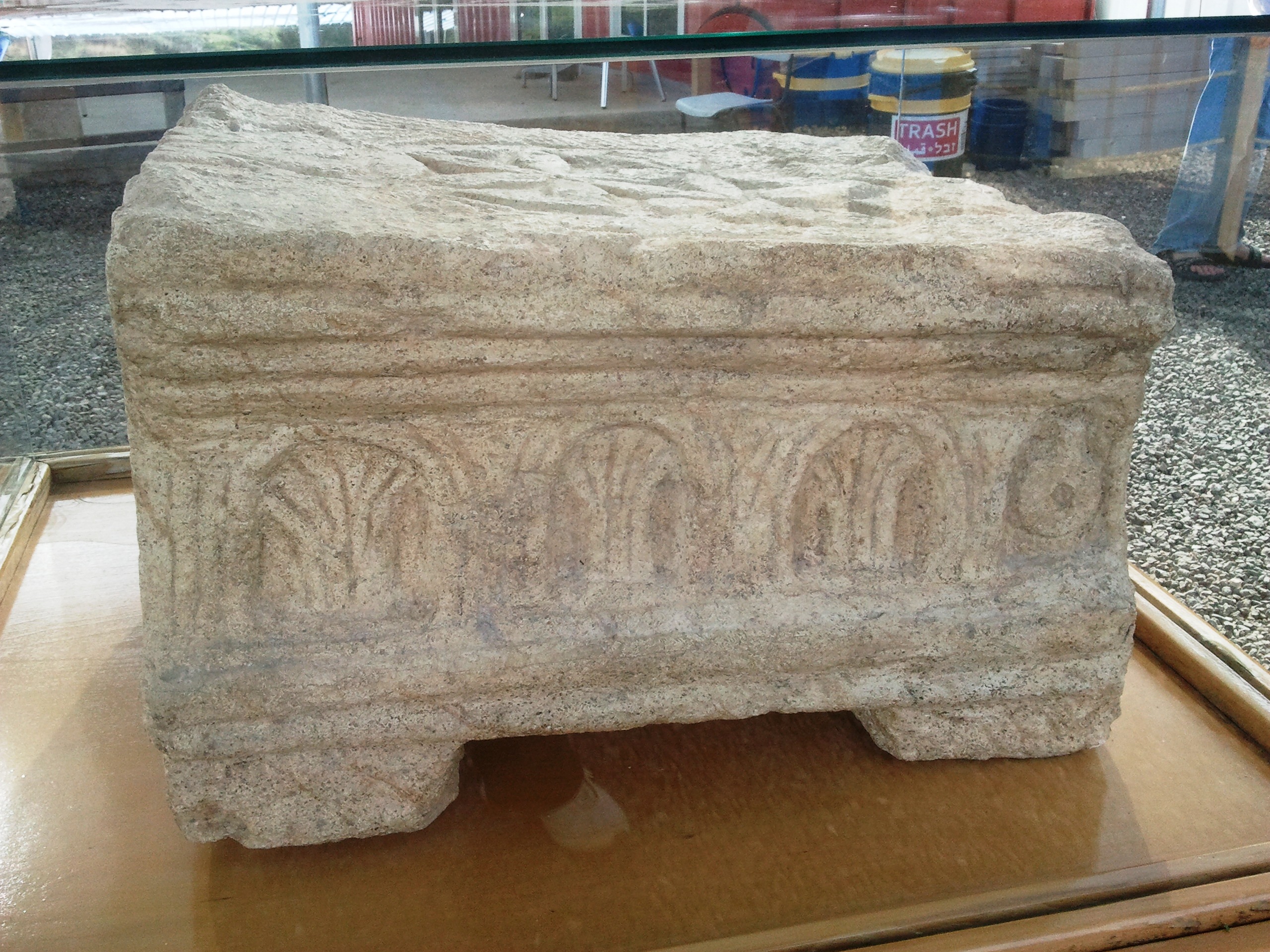
 Traditional Judaism regards the Holy of Holies as the place where the presence of
Traditional Judaism regards the Holy of Holies as the place where the presence of
 The exact location of the Holy of Holies is a contentious issue, as elements of questioning the exact placement of the Temple are often associated with Temple denial. There are three main theories as to where exactly the Temple stood on the Mount: where the Dome of the Rock is now located; to the north of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Asher Kaufman); or to the east of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Joseph Patrich of the
The exact location of the Holy of Holies is a contentious issue, as elements of questioning the exact placement of the Temple are often associated with Temple denial. There are three main theories as to where exactly the Temple stood on the Mount: where the Dome of the Rock is now located; to the north of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Asher Kaufman); or to the east of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Joseph Patrich of the
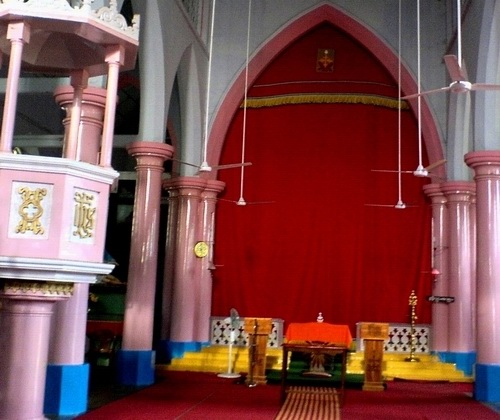 The Saint Thomas Christians (also known as Nasrani or Syrian Christians) from Kerala, South India still follow much Jewish Christian tradition.Ross, Israel J. (1979). "Ritual and Music in South India: Syrian Christian Liturgical Music in Kerala". ''Asian Music''. 11 (1): 80–98. In Nasrani tradition the Holy of Holies is kept veiled for much of the time. The red veil covers the inner altar or the main altar. It is unveiled only during the central part of the main Nasrani ritual. The main ritual of the Saint Thomas Christians is the Qurbana.
The Saint Thomas Christians (also known as Nasrani or Syrian Christians) from Kerala, South India still follow much Jewish Christian tradition.Ross, Israel J. (1979). "Ritual and Music in South India: Syrian Christian Liturgical Music in Kerala". ''Asian Music''. 11 (1): 80–98. In Nasrani tradition the Holy of Holies is kept veiled for much of the time. The red veil covers the inner altar or the main altar. It is unveiled only during the central part of the main Nasrani ritual. The main ritual of the Saint Thomas Christians is the Qurbana.
'' Ark of the Covenant with representation of Cherubim. Upon completion of the dedication of the Tabernacle, the Voice of God spoke to Moses "from between the Cherubim" ().
Solomon's Temple
The Holy of Holies was the inner sanctuary within theTabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
and Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
when Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by th ...
and the Second Temple were standing. A brocade curtain (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
: ''parochet''), made with cherubim motifs woven directly into the fabric from the loom, divided the Holy of Holies from the lesser Holy place. The Holy of Holies was located in the westernmost end of the Temple building, being a perfect cube: 20 cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding ...
s by 20 cubits by 20 cubits. The inside was in total darkness and contained the Ark of the Covenant, gilded inside and out, in which was placed the Tablets of the Covenant. According to both Jewish and Christian tradition, Aaron's rod
Aaron's rod refers to any of the walking sticks carried by Moses's brother, Aaron, in the Torah. The Bible tells how, along with Moses's rod, Aaron's rod was endowed with miraculous power during the Plagues of Egypt that preceded the Exodus. T ...
and a pot of manna
Manna ( he, מָן, mān, ; ar, اَلْمَنُّ; sometimes or archaically spelled mana) is, according to the Bible, an edible substance which God provided for the Israelites during their travels in the desert during the 40-year period follow ...
were also in the ark. The Ark was covered with a lid made of pure gold, known as the "mercy seat
According to the Hebrew Bible, the ''kaporet'' ( ''kapōreṯ'') or mercy seat was the gold lid placed on the Ark of the Covenant, with two cherubim beaten out of the ends to cover and create the space into which Yahweh was said to appear. This ...
",() which was covered by the beaten gold cherubim wings, creating the space for the Divine Presence
Divine presence, presence of God, Inner God, or simply presence is a concept in religion, spirituality, and theology that deals with the ability of God to be " present" with human beings.
According to some types of monotheism God is omnipresen ...
().
Second Temple
 When the Temple was rebuilt after the Babylonian captivity, the Ark was no longer present in the Holy of Holies; instead, a portion of the floor was raised slightly to indicate the place where it had stood. In Jewish tradition, two curtains separated the Holy of Holies from the lesser Holy place during the period of the Second Temple. These curtains were woven with motifs directly from the loom, rather than embroidered, and each curtain had the thickness of a handbreadth (ca. 9 cm.).
When the Temple was rebuilt after the Babylonian captivity, the Ark was no longer present in the Holy of Holies; instead, a portion of the floor was raised slightly to indicate the place where it had stood. In Jewish tradition, two curtains separated the Holy of Holies from the lesser Holy place during the period of the Second Temple. These curtains were woven with motifs directly from the loom, rather than embroidered, and each curtain had the thickness of a handbreadth (ca. 9 cm.). Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
records that Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
profaned the Temple by insisting on entering the Holy of Holies in 63 BCE. When Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
captured the city during the First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
, Roman soldiers took down the curtain and used it to wrap therein golden vessels retrieved from the Temple.
Day of Atonement
The Holy of Holies was entered once a year by the High Priest on theDay of Atonement
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day's o ...
, to sprinkle the blood of sacrificial animals (a bull offered as atonement for the Priest and his household, and a goat offered as atonement for the people) and offer incense upon the Ark of the Covenant and the mercy seat
According to the Hebrew Bible, the ''kaporet'' ( ''kapōreṯ'') or mercy seat was the gold lid placed on the Ark of the Covenant, with two cherubim beaten out of the ends to cover and create the space into which Yahweh was said to appear. This ...
that sat on top of the ark in the First Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by th ...
(the Second Temple had no ark and the blood was sprinkled where the Ark would have been and the incense was put on the Brazen Altar of incense). The animal was sacrificed and the blood was carried into the most holy place. The gold was also found in the Most Holy Place.

In ancient Judaism
TheMagdala stone
The Magdala stone is a carved stone block unearthed by archaeologists in a Galilean synagogue in Israel, dating to before the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem in the year 70.
It is notable for detailed carvings depicting the Se ...
is thought to be a representation of the Holy of Holies carved before the destruction of the Temple in the year 70.
In Rabbinical Judaism
TraditionalJudaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
regards the location where the inner sanctuary was originally located, on the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
(Mount Moriah Moriah is a mountain identified in the Book of Genesis; believed in Judaism, Christianity and Islam to be associated with the sacrifice of Abraham's son.
It may also be the Temple Mount.
Moriah may also refer to:
Places
In Australia:
*Moriah Colle ...
), as retaining some or all of its original sanctity for use in a future Third Temple
The "Third Temple" ( he, , , ) refers to a hypothetical rebuilt Temple in Jerusalem. It would succeed Solomon's Temple and the Second Temple, the former having been destroyed during the Babylonian siege of Jerusalem in and the latter havin ...
. The exact location of the Holy of Holies is a subject of dispute.
 Traditional Judaism regards the Holy of Holies as the place where the presence of
Traditional Judaism regards the Holy of Holies as the place where the presence of God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
dwells. The Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
gives detailed descriptions of Temple architecture and layout. According to the Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cent ...
Tractate Yoma, the ''Kodesh Hakodashim'' (Holy of Holies) is located in the center of the esplanade from a North-South perspective, but significantly to the West from an East–West perspective, with all the major courtyards and functional areas lying to its east.
The Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
supplies additional details, and describes the ritual performed by the High Priest. During the ritual, the High Priest would pronounce the Tetragrammaton
The Tetragrammaton (; ), or Tetragram, is the four-letter Hebrew theonym (transliterated as YHWH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four letters, written and read from right to left (in Hebrew), are ''yodh'', '' he'', '' waw'', and ...
, the only point according to traditional Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
that it was pronounced out loud. According to Jewish tradition, the people prostrated themselves fully on the ground when it was said. According to the Talmud, the High Priest's face upon exit from the Holy of Holies was radiant.
While under normal circumstances, access to the Holy of Holies was restricted to the High Priest and only on Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
, the Talmud suggests that repair crews were allowed inside as needed but were lowered from the upper portion of the room via enclosures so that they only saw the area they were to work on.
Synagogue architecture
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
regards the Torah ark
A Torah ark (also known as the ''Heikhal'', or the ''Aron Kodesh'') refers to an ornamental chamber in the synagogue that houses the Torah scrolls.
History
The ark, also known as the ''ark of law'', or in Hebrew the ''Aron Kodesh'' or ''aron ha- ...
, a place in a synagogue where the Torah scrolls
A ( he, סֵפֶר תּוֹרָה; "Book of Torah"; plural: ) or Torah scroll is a handwritten copy of the Torah, meaning the five books of Moses (the first books of the Hebrew Bible). The Torah scroll is mainly used in the ritual of Tor ...
are kept, as a miniature Holy of Holies.
Modern location
 The exact location of the Holy of Holies is a contentious issue, as elements of questioning the exact placement of the Temple are often associated with Temple denial. There are three main theories as to where exactly the Temple stood on the Mount: where the Dome of the Rock is now located; to the north of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Asher Kaufman); or to the east of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Joseph Patrich of the
The exact location of the Holy of Holies is a contentious issue, as elements of questioning the exact placement of the Temple are often associated with Temple denial. There are three main theories as to where exactly the Temple stood on the Mount: where the Dome of the Rock is now located; to the north of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Asher Kaufman); or to the east of the Dome of the Rock (Professor Joseph Patrich of the Hebrew University
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; he, הַאוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה הַעִבְרִית בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם) is a public research university based in Jerusalem, Israel. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Dr. Chaim Weiz ...
).See article in the ''World Jewish Digest'', April 2007
The location of the Holy of Holies is, naturally, connected to the location of the Jewish Temple. The location of the Temple, however, had become uncertain already less than 150 years after the Second Temple's destruction, as detailed in the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
. Chapter 54 of the Tractate Berakhot states that the Holy of Holies was directly aligned with the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
, which would have placed the Holy of Holies slightly to the north of the Dome of the Rock, as Kaufman postulated. Chapter 54 of the Tractate Yoma and chapter 26 of the Tractate Sanhedrin, on the other hand, assert that the Holy of Holies stood directly on the Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure.
Over tim ...
.
The Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
associated the Holy of Holies with the Well of Souls
The Well of Souls ( ar, بئر الأرواح, Biʾr al-Arwaḥ; sometimes translated Pit of Souls, Cave of Spirits, or Well of Spirits), is a partly natural, partly man-made cave located inside the Foundation Stone ("Noble Rock" in Islam) under ...
, which is located under the Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure.
Over tim ...
of the Dome of the Rock. Most Orthodox Jews today completely avoid climbing up to Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
, to prevent them from accidentally stepping on any holy areas. A few Orthodox Jewish authorities, following the opinion of the medieval scholar Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Tora ...
, permit Jews to visit parts of the Temple Mount known not to be anywhere near any of the sanctified areas. Orthodox Jewish visitors to the Temple Mount, who come especially from those groups associated with the Temple Institute
The Temple Institute, known in Hebrew as Machon HaMikdash ( he, מכון המקדש), is an organization in Israel focusing on the endeavor of establishing the Third Temple. Its long-term aims are to build the third Jewish temple on the Temple M ...
and its efforts to rebuild a Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
, seek to conform to the minimal requirements for coming near the Temple, such as immersing in a mikvah ("collection of water"; a ritual of purification), not coming during or following menstruation or immediately following a seminal emission, not showing their back towards its presumed location, etc.
To avoid religious conflict, Jewish visitors caught praying or bringing ritual objects are usually expelled from the area by police.
In apocryphal literature
According to the ancient apocryphal ''Lives of the Prophets'', after the death of Zechariah ben Jehoiada, the priests of the Temple could no more, as before, see the apparitions of the angels of the Lord, nor could make divinations with the Ephod, nor give responses from the ''Debir''.Christianity
New Testament
The Greek New Testament retains the pre-Christian Septuagint phrase "Holy of the Holies" ''hágion ''(Singular number, sg Neuter gender, n)'' tōn hagíōn'' () without the definite article as "Holies of Holies" ''hágia ''(Plural number, pl neuter gender, n)'' hagíōn'' () in Hebrews 9:3. In the Vulgate of Jerome, Saint Jerome, these are rendered as ''sanctum sanctorum'' and ''sancta sanctorum'', respectively. The Greek language was the common language upon Hellenization of much of the Middle East after the death of Alexander the Great, and the division of his empire among four generals. The Jews of the Diaspora spoke it; the Vulgate was a faithful translation for Christian Rome.Christian traditions
Certain branches of Christianity, including the Eastern Orthodox Church, and the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church continue to have a tradition of a Holy of Holies that they regard as a Most sacred sites, most sacred site. The ciborium (architecture), ciborium, a permanent canopy over the altar in some churches, once surrounded by curtains at points in the liturgy, symbolizes the Holy of Holies. Some Christian churches, particularly the Catholic Church, consider the Church tabernacle, or its location (often at the rear of the sanctuary), as the symbolic equivalent of the Holy of Holies, due to the storage of consecrated Sacramental bread, hosts in that vessel.Eastern Orthodox Church
The Greek phrase refers to the Tabernacle or Temple. The name in Greek language, Greek for the sanctuary of a church is (''Hieron Vema'', see Bema#Christianity), in Russian language, Russian it is called Святой Алтарь (''Svyatoy Altar'' – literally: "Holy Altar"), and in Romanian it is called ''Sfântul Altar''.Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
A cognate term in Ge'ez language, Ge'ez is found in the Ethiopian Orthodox Church, Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church: ''Qidduse Qiddusan'', referring to the innermost sanctuary of an Orthodox Christian church, where the Tabot is kept and only clergy may enter. This is also called the "Bete Mekdes”. Every Ethiopian Orthodox church has one, and it is covered with a Curtain. There are often three entry points, symbolising the Holy Trinity. In the middle, there is always an altar where the church's Tabot is kept. There can be as many altars as the number of Tabots."Malabar Nasrani tradition
Roman Catholic Church
The Latin Vulgate Bible translates ''Qṓḏeš HaqQŏḏāšîm'' as Sanctum sanctorum (Ex 26:34). Reproducing in Latin the Hebrew construction, the expression is used as a superlative of the neuter adjective ''sanctum'', to mean "a thing most holy". It is used by Roman Catholics to refer to holy objects beyond the Holy of Holies, and is specifically often used as an alternative name for a Church tabernacle, tabernacle, due to the object being a storage chamber for Sacramental bread, consecrated host and thus where the presence of God is most represented. The Vulgate also refers to the Holy of Holies with the plural form ''Sancta sanctorum'' (2 Chr 5:7), arguably a synecdoche referring to the holy objects hosted there. This form is also used more broadly in Catholic tradition with reference to sanctuaries other than theTemple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
. A notable example is for the Sancta Sanctorum, Chiesa di San Lorenzo in Palatio ad Sancta Sanctorum, a chapel in the complex of St John Lateran in Rome.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Salt Lake Temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) contains a Holy of Holies wherein the church's President of the Church (LDS Church), president—acting as the Presiding High Priest—enters to fulfill the relationship between the High Priest of Israel and God in accordance with the LDS Church's interpretation of the Book of Exodus () and Latter-day Saint religious texts.Seventh-Day Adventist Church
Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-Day Adventism (SDA) believes that the Holy of Holies on Earth was a copy of the true tabernacle in heaven, and this view can also be seen in other Christian denomination, Christian denominations. Because in Epistle to the Hebrews, Hebrews, God commands Moses to make sure that all things according to the pattern shewed to thee in Mount Sinai, the Mount Sinai (Heb 8:2,5). After the "Great Disappointment", preacher O. R. L. Crosier, Hiram Edson, and F. B. Hahn published new insights into Christ's sanctuary ministry that Jesus began to minister in the heavenly sanctuary after His Ascension of Jesus, ascension (Heb 9:24). Seventh-day Adventist Church, Seventh-Day Adventism (SDA) believes that just as the High Priest of Israel, high priest completed the special ministry onYom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
and blessed the Israelites. Christ will come and bless his people after cleaning the Holy of Holies in heaven (Heb 9:23).
See also
* Church tabernacle, the box in which the Eucharist is kept in some Christian denominations *Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure.
Over tim ...
, the rock at the centre of the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem
* Honden, the most sacred building at a Shinto shrine
* Holy of Holies (LDS Church), a small room located in the Salt Lake Temple
* Most Holy Place, in various religions
* Sanctum sanctorum, a Latin translation of the biblical term ''Holy of Holies''
* Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by th ...
, in ancient Jerusalem
* Warren's Gate, an ancient entrance into the Temple platform in Jerusalem
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Holy Of Holies Tabernacle and Temples in Jerusalem Yom Kippur Eastern Christian liturgy Jewish sacrificial law Hebrew Bible words and phrases Superlatives in religion Ark of the Covenant