Kabylism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kabyle people ( kab, Izwawen or ''Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', ) are a
 Between 902 and 909 the Fatimid state had been founded by the Kutama Berbers from Lower Kabylie whose conquest of Ifriqiya resulted in the creation of the Caliphate. After the conquest of Ifriqiya the Kutama Berbers conquered the realm of the Rustamids on the way to Sijilmasa which they also then briefly conquered and where Abdullāh al-Mahdī Billa, who at the time was imprisoned, was then freed and then accepted as the Imam of the movement and installed as the Caliph, becoming the first Caliph and the founder of the ruling dynasty. The historian Heinz Halm describes the early Fatimid state as being "a hegemony of the Kutama and Sanhaja Berbers over the eastern and central Maghrib" and Prof. Dr. Loimeier states that rebellions against the Fatimids were also expressed through protest and opposition to Kutama rule.Muslim Societies in Africa: A Historical Anthropology
Between 902 and 909 the Fatimid state had been founded by the Kutama Berbers from Lower Kabylie whose conquest of Ifriqiya resulted in the creation of the Caliphate. After the conquest of Ifriqiya the Kutama Berbers conquered the realm of the Rustamids on the way to Sijilmasa which they also then briefly conquered and where Abdullāh al-Mahdī Billa, who at the time was imprisoned, was then freed and then accepted as the Imam of the movement and installed as the Caliph, becoming the first Caliph and the founder of the ruling dynasty. The historian Heinz Halm describes the early Fatimid state as being "a hegemony of the Kutama and Sanhaja Berbers over the eastern and central Maghrib" and Prof. Dr. Loimeier states that rebellions against the Fatimids were also expressed through protest and opposition to Kutama rule.Muslim Societies in Africa: A Historical Anthropology
- Roman Loimeier Indiana University Press, The weakening of the Abbasids allowed Fatimid-Kutama power to quickly expand and in 959 Ziri ibn Manad, Jawhar the Sicilian and a Kutama army conquered Fez and Sijilmasa in Morocco. In 969 under the command of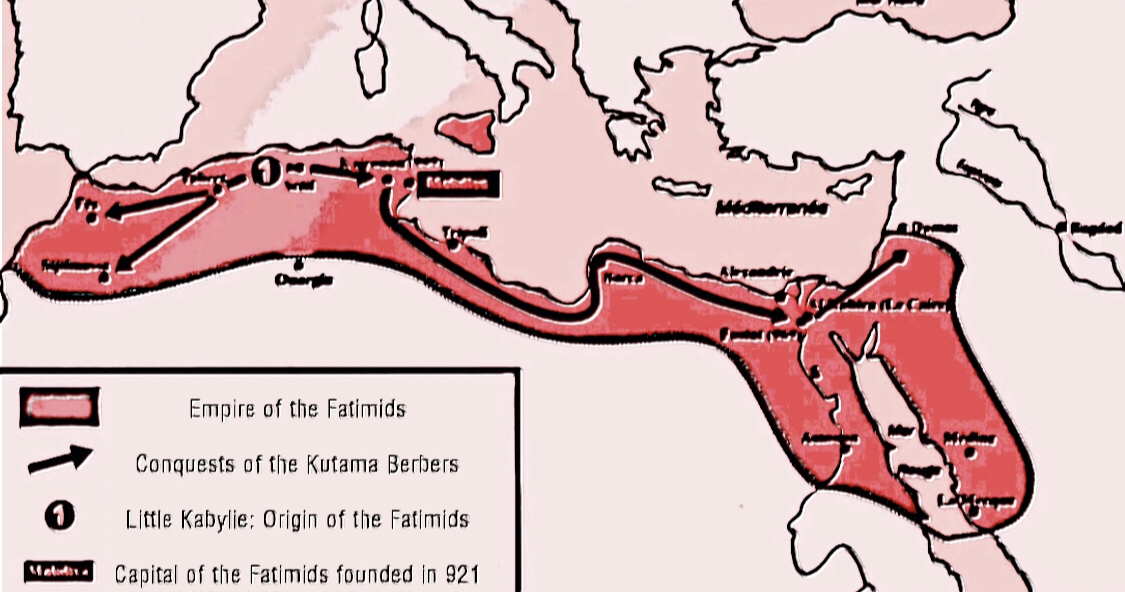
 The Kabyle were relatively independent of outside control during the period of
The Kabyle were relatively independent of outside control during the period of
Volume 4, publié par M. Th. Houtsma, Page: 600 Kabylia was the last part of northern Algeria to be colonised by the French during the years 1854-1857, despite vigorous resistance. Laidani, Amar. (2019)
The recognition of the Tamazight Languages in the Algerian Law
Studia Universitatis Babeş-Bolyai Iurisprudentia. Such leaders as Lalla Fatma n Sumer continued the resistance as late as Kabyle villages were ruled through an indirect administration based on the preservation of Kabyle traditional political institutions such as the village’s assemblies djemaas, this institution played a central role in the Kabyle’s self-governing. The djemaas would resolve disputes between the village’s inhabitants and edict the customary law rules. French officials confiscated much land from the more recalcitrant tribes and granted it to colonists, who became known as ''
Kabyle villages were ruled through an indirect administration based on the preservation of Kabyle traditional political institutions such as the village’s assemblies djemaas, this institution played a central role in the Kabyle’s self-governing. The djemaas would resolve disputes between the village’s inhabitants and edict the customary law rules. French officials confiscated much land from the more recalcitrant tribes and granted it to colonists, who became known as ''
/ref> Over time, immigrant workers also began to go to France. In the 1920s, Algerian immigrant workers in France organized the first party promoting Algerians independence. Messali Hadj, Imache Amar, Si Djilani Mohammed, and Belkacem Radjef rapidly built a strong following throughout France and Algeria in the 1930s. They developed militants who became vital to the fighting for an independent Algeria. This became widespread after World War II. Since Algeria gained independence in 1962, tensions have arisen between Kabylie and the central government on several occasions. In July 1962, the FLN (National Liberation Front) was split rather than united. Indeed, many actors who contributed to independence wanted a share of power but the
 The geography of the Kabyle region played an important role in the people's history. The difficult mountainous landscape of the Tizi Ouzou and Bejaia provinces served as a refuge, to which most of the Kabyle people retreated when under pressure or occupation. They were able to preserve their cultural heritage in such isolation from other cultural influences.
The area supported local dynasties (Numidia, Fatimids in the Kutama periods, Zirids, Hammadids, and Hafsids of Bejaïa) or Algerian modern nationalism, and the war of independence. The region was repeatedly occupied by various conquerors. Romans and Byzantines controlled the main road and valley during the period of antiquity and avoided the mountains (Mont ferratus). During the spread of Islam, Arabs controlled plains but not all the countryside (they were called ''el aadua'': enemy by the Kabyle).
The
The geography of the Kabyle region played an important role in the people's history. The difficult mountainous landscape of the Tizi Ouzou and Bejaia provinces served as a refuge, to which most of the Kabyle people retreated when under pressure or occupation. They were able to preserve their cultural heritage in such isolation from other cultural influences.
The area supported local dynasties (Numidia, Fatimids in the Kutama periods, Zirids, Hammadids, and Hafsids of Bejaïa) or Algerian modern nationalism, and the war of independence. The region was repeatedly occupied by various conquerors. Romans and Byzantines controlled the main road and valley during the period of antiquity and avoided the mountains (Mont ferratus). During the spread of Islam, Arabs controlled plains but not all the countryside (they were called ''el aadua'': enemy by the Kabyle).
The 
 Algerian provinces with significant Kabyle-speaking populations include Tizi Ouzou,
Algerian provinces with significant Kabyle-speaking populations include Tizi Ouzou,
 The Kabyle have been fierce activists in promoting the cause of Berber (''Amazigh'') identity. The movement has three groups: those Kabyle who identify as part of a larger Berber nation (
The Kabyle have been fierce activists in promoting the cause of Berber (''Amazigh'') identity. The movement has three groups: those Kabyle who identify as part of a larger Berber nation (
James Minahan, ''Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations: D-K''
Good Publishing Group, 2002, p.863. Quote: "Outside North Africa, the largest Kabyle community, numbering around 1 million, is in France." Some notable French people are of full or partial Kabyle descent.
 *
*
Provisional Government of Kabylie (ANAVAD)
Kabyle Movement of Autonomy
Kabyle centric news site
Social web site
Kabyle centric news site
Ethnologue.com about Kabyle language
Cultural site
Analysis
{{authority control Ethnic groups in Algeria Indigenous peoples of North Africa Berber peoples and tribes
Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–19 ...
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
indigenous to Kabylia
Kabylia ('' Kabyle: Tamurt n Leqbayel'' or ''Iqbayliyen'', meaning "Land of Kabyles", '','' meaning "Land of the Tribes") is a cultural, natural and historical region in northern Algeria and the homeland of the Kabyle people. It is part of ...
in the north of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, spread across the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. It separates the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range. It stretches around through ...
, east of Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
. They represent the largest Berber-speaking population of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and the second largest in North Africa.
Many of the Kabyles have emigrated from Algeria, influenced by factors such as the Algerian Civil War
The Algerian Civil War ( ar, rtl=yes, الْحَرْبُ الْأَهْلِيَّةُ الجَزَائِرِيَّةُ, al-Ḥarb al-ʾAhlīyah al-Jazāʾirīyah) was a civil war in Algeria fought between the Algerian government and various I ...
, cultural repression by the central Algerian government, and overall industrial decline. Their diaspora has resulted in Kabyle people living in numerous countries. Large populations of Kabyle people settled in France and, to a lesser extent, Canada (mainly Québec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
) and United States.
The Kabyle people speak Kabyle, a Berber language. Since the Berber Spring of 1980, they have been at the forefront of the fight for the official recognition of Berber languages in Algeria.
History
Fatimid Caliphate
- Roman Loimeier Indiana University Press, The weakening of the Abbasids allowed Fatimid-Kutama power to quickly expand and in 959 Ziri ibn Manad, Jawhar the Sicilian and a Kutama army conquered Fez and Sijilmasa in Morocco. In 969 under the command of
Jawhar
Jawhar is a city and a municipal council in Palghar district of Maharashtra state in Konkan division of India. Jawhar was a capital city of the erstwhile Koli princely state of Jawhar.
Situated in the ranges of the Western Ghats, Jawhar i ...
, the Fatimid Kutama troops conquered Egypt from the Ikhsidids, the Kutama Berber general Ja'far ibn Fallah Ja'far ibn Fallah () or ibn Falah was a general in the service of the Fatimid Caliphate. He led the first Fatimid attempt to conquer Bilad al-Sham, Syria in 970–971, but his attack on Byzantine-held Antioch was repulsed, and he lost his life in Ju ...
was instrumental in this success: he led the troops that crossed the river Nile and according to al-Maqrizi, captured the boats used to do this from a fleet sent by Ikhshidid loyalists from Lower Egypt. The Kutama general Ja’far then invaded Palestine and conquered Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
, the capital, he then conquered Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
and made himself the master of the city and then he moved north and conquered Tripoli. It was around this time period that the Fatimid Caliphate reached its territorial peak of 4,100,000 km2.

Zirid Dynasty
The Zirid Dynasty was a family of Sanhadja Berbers with origins in the Kabyle mountains. During their reign they established their rule over the entireMaghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
and also established rule in parts of Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
. They also had suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is ca ...
over the Emirate of Sicily through the Kalbite emirs and later assassinated the ruler and took over the island. When the Emirate of Sicily was split into separate taifa
The ''taifas'' (singular ''taifa'', from ar, طائفة ''ṭā'ifa'', plural طوائف ''ṭawā'if'', a party, band or faction) were the independent Muslim principalities and kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula (modern Portugal and Spain), re ...
s, Ayyub Ibn Tamim entered Sicily and united all of the taifas under his rule until he left the island.
Hammadid Dynasty
TheHammadids
The Hammadid dynasty () was a branch of the Sanhaja Berber dynasty that ruled an area roughly corresponding to north-eastern modern Algeria between 1008 and 1152. The state reached its peak under Nasir ibn Alnas during which it was briefly the ...
came to power after declaring their independence from the Zirids. They managed to conquer land in all of the Maghreb region, capturing and possessing significant territories such as: Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
, Béjaïa
Béjaïa (; ; ar, بجاية, Latn, ar, Bijāya, ; kab, Bgayet, Vgayet), formerly Bougie and Bugia, is a Mediterranean port city and commune on the Gulf of Béjaïa in Algeria; it is the capital of Béjaïa Province, Kabylia. Béjaïa is ...
, Tripoli, Sfax
Sfax (; ar, صفاقس, Ṣafāqis ) is a city in Tunisia, located southeast of Tunis. The city, founded in AD849 on the ruins of Berber Taparura, is the capital of the Sfax Governorate (about 955,421 inhabitants in 2014), and a Mediterrane ...
, Susa, Fez, Ouargla and Sijilmasa
Sijilmasa ( ar, سجلماسة; ; also transliterated Sijilmassa, Sidjilmasa, Sidjilmassa and Sigilmassa) was a medieval Moroccan city and trade entrepôt at the northern edge of the Sahara in Morocco. The ruins of the town extend for five miles a ...
. South of Tunisia, they also possessed a number of oases
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical im ...
that were the termini of trans-Saharan trade
Trans-Saharan trade requires travel across the Sahara between sub-Saharan Africa and North Africa. While existing from prehistoric times, the peak of trade extended from the 8th century until the early 17th century.
The Sahara once had a very d ...
routes.
Kingdom of Ait Abbas and Kingdom of Kuku
These two Kabyle Kingdoms managed to maintain their independence and participated in notable battles alongside theRegency of Algiers
The Regency of Algiers ( ar, دولة الجزائر, translit=Dawlat al-Jaza'ir) was a state in North Africa lasting from 1516 to 1830, until it was conquered by the French. Situated between the regency of Tunis in the east, the Sultanate o ...
, such as the campaign of Tlemcen
The Campaign of Tlemcen or Tlemcen campaign was a military operation led by the Saadians of Mohammed ash-Sheikh against Tlemcen in 1557, then under the domination of the Regency of Algiers, a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. Mohammed ash-Shei ...
and the conquest of Fez. In the early 16th century Sultan Abdelaziz of the Beni Abbes managed to defeat the Ottomans several times, notably in the First Battle of Kalaa of the Beni Abbes.
 The Kabyle were relatively independent of outside control during the period of
The Kabyle were relatively independent of outside control during the period of Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
rule in North Africa. They lived primarily in three different kingdoms: the Kingdom of Kuku
The Kingdom of Kuku (''Kingdom of Koukou'') was a Kabyle Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, ...
, the Kingdom of Ait Abbas, and the principality of Aït Jubar.''E. J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913-1936''Volume 4, publié par M. Th. Houtsma, Page: 600 Kabylia was the last part of northern Algeria to be colonised by the French during the years 1854-1857, despite vigorous resistance. Laidani, Amar. (2019)
The recognition of the Tamazight Languages in the Algerian Law
Studia Universitatis Babeş-Bolyai Iurisprudentia. Such leaders as Lalla Fatma n Sumer continued the resistance as late as
Mokrani Mokrani is a surname, and may refer to;
Mokrani derives from المقراني ( El Mokrani), a town in Algeria.
* Cheikh Mokrani (1815–1871) - Leader of the Mokrani Revolt
The Mokrani Revolt ( ar, مقاومة الشيخ المقراني, lit ...
's rebellion in 1871.
 Kabyle villages were ruled through an indirect administration based on the preservation of Kabyle traditional political institutions such as the village’s assemblies djemaas, this institution played a central role in the Kabyle’s self-governing. The djemaas would resolve disputes between the village’s inhabitants and edict the customary law rules. French officials confiscated much land from the more recalcitrant tribes and granted it to colonists, who became known as ''
Kabyle villages were ruled through an indirect administration based on the preservation of Kabyle traditional political institutions such as the village’s assemblies djemaas, this institution played a central role in the Kabyle’s self-governing. The djemaas would resolve disputes between the village’s inhabitants and edict the customary law rules. French officials confiscated much land from the more recalcitrant tribes and granted it to colonists, who became known as ''pieds-noirs
The ''Pieds-Noirs'' (; ; ''Pied-Noir''), are the people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French rule from 1830 to 1962; the vast majority of whom departed for mainland France as soon as Alger ...
'' During this period, the French carried out many arrests and deported resisters, mainly to New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
in the South Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. Due to French colonization, many Kabyle emigrated to other areas inside and outside Algeria.Bélaïd Abane, ''L'Algérie en guerre: Abane Ramdane et les fusils de la rébellion'', p. 74/ref> Over time, immigrant workers also began to go to France. In the 1920s, Algerian immigrant workers in France organized the first party promoting Algerians independence. Messali Hadj, Imache Amar, Si Djilani Mohammed, and Belkacem Radjef rapidly built a strong following throughout France and Algeria in the 1930s. They developed militants who became vital to the fighting for an independent Algeria. This became widespread after World War II. Since Algeria gained independence in 1962, tensions have arisen between Kabylie and the central government on several occasions. In July 1962, the FLN (National Liberation Front) was split rather than united. Indeed, many actors who contributed to independence wanted a share of power but the
ALN
Aluminium nitride ( Al N) is a solid nitride of aluminium. It has a high thermal conductivity of up to 321 W/(m·K) and is an electrical insulator. Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potenti ...
(National Liberation Army) directed by Houari Boumédiène
Houari Boumédiène ( ar, ; ALA-LC: ''Hawwārī Būmadyan''; born Mohammed Ben Brahim Boukherouba; 23 August 1932 – 27 December 1978) was an Algerian politician and army colonel who served as Chairman of the Revolutionary Council of Al ...
, joined by Ahmed Ben Bella, had the upper hand because of their military forces.
In 1963 the FFS party of Hocine Aït Ahmed
Hocine Aït Ahmed ( ar, حسين آيت أحمد; 20 August 1926 – 23 December 2015) was an Algerian politician. He was founder and leader until 2009 of the historical political opposition in Algeria.
Life
Aït Ahmed was born at Aï ...
contested the authority of the FLN, which had promoted itself as the only party in the nation. Aït Ahmed and others considered the central government led by Ben Bella authoritarian, and on September 3, 1963, the FFS (Socialist Forces front) was created by Hocine Aït Ahmed
Hocine Aït Ahmed ( ar, حسين آيت أحمد; 20 August 1926 – 23 December 2015) was an Algerian politician. He was founder and leader until 2009 of the historical political opposition in Algeria.
Life
Aït Ahmed was born at Aï ...
. This party grouped opponents of the regime then in place, and a few days after its proclamation, Ben Bella sent the army into Kabylie to repress the insurrection. Colonel Mohand Oulhadj also took part in the FFS and in the Maquis ( fr) because he considered that the ''mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term t ...
'' were not treated as they should be. In the beginning, the FFS wanted to negotiate with the government but since no agreement was reached, the maquis took up arms and swore not to give them up as long as democratic principles and justice were a part of the system. But after Mohand Oulhadj's defection, Aït Ahmed could barely sustain the movement and after the FLN congress on April 16, 1964, which reinforced the government's legitimacy, he was arrested in October 1964. As a consequence, the insurrection was a failure in 1965 because it was hugely repressed by the forces of the ALN, under Houari Boumédiène. In 1965 Aït Ahmed was sentenced to death, but later pardoned by Ben Bella. Approximately 400 deaths were counted amongst the maquis.
In 1980, protesters mounted several months of demonstrations in Kabylie demanding the recognition of Berber as an official language; this period has been called the Berber Spring. In 1994–1995, the Kabyle conducted a school boycott, termed the "strike of the school bag". In June and July 1998, they protested, in events that turned violent, after the assassination of singer Matoub Lounès and passage of a law requiring use of the Arabic language in all fields.
In the months following April 2001 (called the Black Spring), major riots among the Kabyle took place following the killing of Masinissa Guermah, a young Kabyle, by gendarmes. At the same time, organized activism produced the ''Arouch
The Arouch Movement or Berber Arouch Citizens' Movement ( Kabyle: Leɛṛac; French: ''Mouvement citoyen des Aarchs'') is an organization in Algeria representing the Kabyle people, a Berber group of the province of Kabylie. Their name, ''Arouch'', ...
'', and neo-traditional local councils. The protests gradually decreased after the Kabyle won some concessions from President Abdelaziz Bouteflika
Abdelaziz Bouteflika (; ar, عبد العزيز بوتفليقة, ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz Būtaflīqa ; 2 March 1937 – 17 September 2021) was an Algerian politician and diplomat who served as President of Algeria from 1999 to his resignation in 2019 ...
.
On 6 January 2016, Tamazight was officially recognized in Algeria's constitution as a language equal to Arabic.
Geography
 The geography of the Kabyle region played an important role in the people's history. The difficult mountainous landscape of the Tizi Ouzou and Bejaia provinces served as a refuge, to which most of the Kabyle people retreated when under pressure or occupation. They were able to preserve their cultural heritage in such isolation from other cultural influences.
The area supported local dynasties (Numidia, Fatimids in the Kutama periods, Zirids, Hammadids, and Hafsids of Bejaïa) or Algerian modern nationalism, and the war of independence. The region was repeatedly occupied by various conquerors. Romans and Byzantines controlled the main road and valley during the period of antiquity and avoided the mountains (Mont ferratus). During the spread of Islam, Arabs controlled plains but not all the countryside (they were called ''el aadua'': enemy by the Kabyle).
The
The geography of the Kabyle region played an important role in the people's history. The difficult mountainous landscape of the Tizi Ouzou and Bejaia provinces served as a refuge, to which most of the Kabyle people retreated when under pressure or occupation. They were able to preserve their cultural heritage in such isolation from other cultural influences.
The area supported local dynasties (Numidia, Fatimids in the Kutama periods, Zirids, Hammadids, and Hafsids of Bejaïa) or Algerian modern nationalism, and the war of independence. The region was repeatedly occupied by various conquerors. Romans and Byzantines controlled the main road and valley during the period of antiquity and avoided the mountains (Mont ferratus). During the spread of Islam, Arabs controlled plains but not all the countryside (they were called ''el aadua'': enemy by the Kabyle).
The Regency of Algiers
The Regency of Algiers ( ar, دولة الجزائر, translit=Dawlat al-Jaza'ir) was a state in North Africa lasting from 1516 to 1830, until it was conquered by the French. Situated between the regency of Tunis in the east, the Sultanate o ...
, under Ottoman influence, tried to have indirect influence over the people ( makhzen tribes of Amraoua, and marabout).
The French gradually and totally conquered the region and set up a direct administration. Béjaïa
Béjaïa (; ; ar, بجاية, Latn, ar, Bijāya, ; kab, Bgayet, Vgayet), formerly Bougie and Bugia, is a Mediterranean port city and commune on the Gulf of Béjaïa in Algeria; it is the capital of Béjaïa Province, Kabylia. Béjaïa is ...
and Bouira, where they are a majority, as well as Boumerdes, Setif, Bordj Bou Arreridj, and Jijel
Jijel ( ar, جيجل), the classical Igilgili, is the capital of Jijel Province in north-eastern Algeria. It is flanked by the Mediterranean Sea in the region of Corniche Jijelienne and had a population of 131,513 in 2008.
Jijel is the administr ...
. Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
also has a significant Kabyle population, where they make up more than half of the capital's population.
The Kabyle region is referred to as ''Al Qabayel'' ("tribes") by the Arabic-speaking population and as ''Kabylie'' in French. Its indigenous inhabitants call it ''Tamurt Idurar'' ("Land of Mountains") or ''Tamurt n Iqbayliyen''/''Tamurt n Iqbayliyen'' ("Land of the Kabyle"). It is part of the Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. It separates the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range. It stretches around through ...
and is located at the edge of the Mediterranean.
Culture and society
Language
The Kabyleethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
speak Kabyle, a Berber language
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight,, ber, label=Tuareg Tifinagh, ⵜⵎⵣⵗⵜ, ) are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by Berber commun ...
of the Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic s ...
family. As second and third languages, many people speak Algerian Arabic and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
.
During the first centuries of their history, Kabyles used the Tifinagh writing system. Since the beginning of the 19th century, and under French influence, Kabyle intellectuals began to use the Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern ...
. It is the basis for the modern Berber Latin alphabet.
After the independence of Algeria
Independence Day ( ar, عيد استقلال, french: Jour de l'Indépendance), observed annually on 5 July, is a National Holiday in Algeria commemorating colonial Algerian independence from France on 5 July 1962.
Algerian War (1954–196 ...
, some Kabyle activists tried to revive the Old Tifinagh alphabet. This new version of Tifinagh has been called Neo-Tifinagh
Tifinagh ( Tuareg Berber language: or , ) is a script used to write the Berber languages. Tifinagh is descended from the ancient Libyco-Berber alphabet. The traditional Tifinagh, sometimes called Tuareg Tifinagh, is still favored by the Tuar ...
, but its use remains limited to logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name it represents as in a wo ...
s. Kabyle literature has continued to be written in the Latin script.
Religion
The Kabyle people are mainlyMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, with a small Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
minority. Many '' Zawaya'' exist all over the region; the Rahmaniyya
The Raḥmâniyya (Arabic: الرحمانية) is an Algerian Sufi order (tariqa or brotherhood) founded by Kabyle religious scholar Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥman al-Azhari Bu Qabrayn in the 1770s. It was initially a branch of the Khalwat ...
is the most prolific.
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
s of Kabyle background generally live in France. Recently, the Protestant community has had significant growth, particularly among Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
denominations.
Economy
The traditional economy of the area is based onarboriculture
Arboriculture () is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants. The science of arboriculture studies how these plants grow and respond to cultural practices and to their environmen ...
(orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of ...
s and olive trees) and on the craft industry (tapestry
Tapestry is a form of textile art, traditionally woven by hand on a loom. Tapestry is weft-faced weaving, in which all the warp threads are hidden in the completed work, unlike most woven textiles, where both the warp and the weft threads ma ...
or pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
). Mountain and hill farming is gradually giving way to local industry (textile and agro-alimentary). In the middle of the 20th century, with the influence and funding by the Kabyle diaspora, many industries were developed in this region. It has become the second most important industrial region in the country after Algiers.
Politics
 The Kabyle have been fierce activists in promoting the cause of Berber (''Amazigh'') identity. The movement has three groups: those Kabyle who identify as part of a larger Berber nation (
The Kabyle have been fierce activists in promoting the cause of Berber (''Amazigh'') identity. The movement has three groups: those Kabyle who identify as part of a larger Berber nation (Berberists
Berberism or Amazighism is a Berbers, Berber political-cultural movement of ethnic, geographic, or cultural nationalism, started mainly in Kabylie, Kabylia (Algeria) and in Morocco, later spreading to the rest of the Berber communities in the M ...
); those who identify as part of the Algerian nation (known as "Algerianists", some view Algeria as an essentially Berber nation); and those who consider the Kabyle to be a distinct nation separate from (but akin to) other Berber peoples (known as Kabylists).
* Two political parties dominate in Kabylie and have their principal support base there: the Socialist Forces Front
, Berber: Tirni Iɣallen Inemlayen (RƔN)
, logo = Socialist Forces Front.png
, leader1_title = First National Secretary
, leader1_name = Youcef Aouchiche
, leader2_title =
, leader2_name =
, foundation =
...
(FFS), led by Ali Laskri who replaced Hocine Aït Ahmed
Hocine Aït Ahmed ( ar, حسين آيت أحمد; 20 August 1926 – 23 December 2015) was an Algerian politician. He was founder and leader until 2009 of the historical political opposition in Algeria.
Life
Aït Ahmed was born at Aï ...
, and the Rally for Culture and Democracy
The Rally for Culture and Democracy ( ber, Agraw i Yidles d Tugdut; ar, التجمع من أجل الثقافة والديمقراطية; french: Rassemblement pour la Culture et la Démocratie, RCD) is a political party in Algeria. It promotes ...
(RCD), led by Mohcine Belabbès who replaced Saïd Sadi
Saïd Sadi ( Kabyle: Saεid Seεdi) (born 26 August 1947) is an Algerian politician who was President of the Rally for Culture and Democracy (RCD) until 2012. He is founder of the first Algerian human rights league.
Born at Aghribs, now in Tiz ...
. Both parties are secularist, Berberist
Berberism or Amazighism is a Berber political-cultural movement of ethnic, geographic, or cultural nationalism, started mainly in Kabylia (Algeria) and in Morocco, later spreading to the rest of the Berber communities in the Maghreb region of ...
and Algerianist.
* The Arouch emerged during the Black Spring of 2001 as a revival of the village assembly, a traditional Kabyle form of democratic organization. The Arouch share roughly the same political views as the FFS and the RCD.
* The MAK (Movement for the Autonomy of Kabylie) also emerged during the Black Spring, It claimed the right for a regional autonomy of Kabylie. On 21 April 2010, MAK proclaimed a Provisional Government of Kabylie in exile (ANAVAD). Ferhat Mehenni was elected president by the National Council of the MAK. In 2013, MAK officially became an independentist movement and changed its name to The Mouvement for the Self-determination of Kabylie.
Diaspora
For historical and economic reasons, many Kabyles have emigrated to France, both for work and to escape political persecution. They now number around 1 million people.Good Publishing Group, 2002, p.863. Quote: "Outside North Africa, the largest Kabyle community, numbering around 1 million, is in France."
Notable people
Sport
 *
* Mohamed Allek
Mohamed Allek ar, محمد علاك ; (17 August 1974 – 8 March 2016) was a Paralympian Track and field, athlete from Algeria, competing mainly in category T37 (classification), T37 sprint events. He was born in Agouni Gueghrane ...
* Karim Benzema
Karim Mostafa Benzema (born 19 December 1987) is a French professional footballer who plays as a striker for and captains La Liga club Real Madrid. A creative and prolific forward, Benzema is regarded as one of the best strikers of all time. ...
* Soraya Haddad
Soraya Haddad (born 30 September 1984) is an Algerian judoka. She won abronze medal in the 52 kg weight class at the 2008 Summer Olympics. She has been the African champion five times: 2004, 2005, 2008, 2011 and 2012, and also a bronze me ...
* Kheira Hamraoui
Kheira Hamraoui (born 13 January 1990) is a French professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for Division 1 Féminine club Paris Saint-Germain and the France national team.
Club career Youth career
Hamraoui began her football career ...
* Mohand Cherif Hannachi
* Rabah Madjer
* Kylian Mbappé
Kylian Mbappé Lottin (born 20 December 1998) is a French professional footballer who plays as a forward for club Paris Saint-Germain and the France national team. Considered one of the best players in the world, he is renowned for his dri ...
* Mahieddine Meftah
* Moussa Saïb
* Samir Aït Saïd
* Hocine Soltani
Hocine Soltani (December 1972 – March 2002) was an Algerian boxer, who won two Olympic medals. In 1992, the southpaw placed third in the featherweight division (54–57 kg), and at the 1996 Summer Olympics he won the gold medal in the l ...
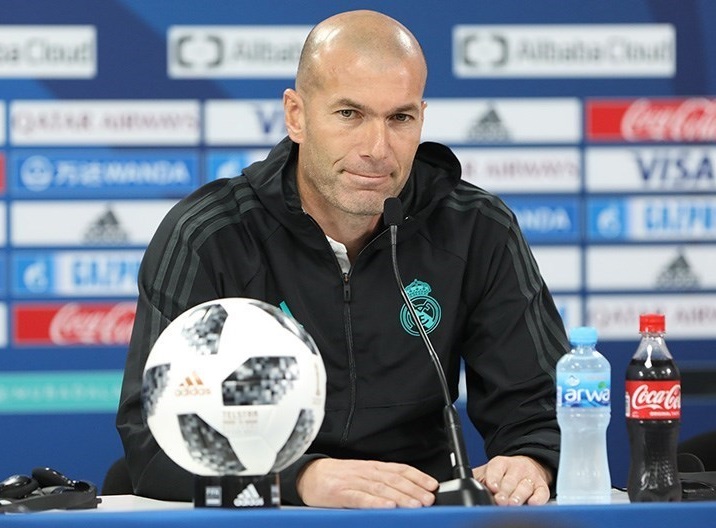
* Zinedine Zidane
Zinedine Yazid Zidane (; born 23 June 1972), popularly known as Zizou, is a French professional football manager and former player who played as an attacking midfielder. He most recently coached Spanish club Real Madrid and is one of the mos ...
Business
* Alexandre Djouhri *Issad Rebrab
Issad Rebrab ( ar, يسعد ربراب; born 1944), is an Algerian billionaire businessman, CEO of the Cevital industrial group, the largest private company in Algeria, active in steel, food, agribusiness and electronics. In 2019, he was sentenced ...
Cinema
* Isabelle Adjani * M'hamed Arezki * Ramzy Bedia * Yamina Benguigui *Yasmine Bleeth
Yasmine Amanda Bleeth (born June 14, 1968) is an American actress and model. Her television roles include Caroline Holden on ''Baywatch'', Ryan Fenelli on ''Ryan's Hope'', and LeeAnn Demerest on ''One Life to Live''.
Early life and career
Bleeth ...
*Dany Boon
Dany Boon (; born Daniel Farid Hamidou on 26 June 1966) is a French actor, film director, screenwriter and producer.
Starting out as a comedian during the 1990s, he found success in 2008 as an actor and director in the film comedy ''Welcome to ...
* Habiba Djahnine
*Fellag
Mohamed Fellag (born 31 March 1950 in Azeffoun, Tizi Ouzou) is an Algerian comedian, writer, humorist, and actor. In 1958, at the height of the Algerian war of independence, his father took him and his younger brother, for their safety, to stay ...
*Jalil Lespert
Jalil Lespert (born 11 May 1976) is a French actor, screenwriter and director.
Life and career
Born to an ethnic French (Pied-Noir) father, actor Jean Lespert, and an Algerian mother, who is an attorney and a jurist, Lespert first studied law, ...
* Samy Naceri
* Marie-José Nat
* Daniel Prévost
* Rouiched
*Erika Sawajiri
is a Japanese former actress, singer, and model. After starting out as a junior model, Sawajiri transitioned to acting in 2002 and has starred in ''Break Through!'', '' Shinobi: Heart Under Blade'', and '' 1 Litre of Tears'', for all of which sh ...
* Jacques Villeret
* Malik Zidi
Music
* Abderrahmane Abdelli * Assia * Slimane Azem * Chimène Badi *Alain Bashung
Alain Bashung (, born Alain Claude Baschung; 1 December 1947 – 14 March 2009) was a French singer, songwriter and actor. Credited with reviving the French chanson in "a time of French musical turmoil", he is often regarded in his home country a ...
* Chérifa
* Malika Domrane
* Idir
* Mohamed Iguerbouchène
* Marina Kaye
*Souad Massi
Souad Massi (سعاد ماسي; born August 23, 1972), is an Algerian Berber singer, songwriter and guitarist. She began her career performing in the Kabyle political rock band Atakor, before leaving the country following a series of death thre ...
* Matoub Lounes
* Lounis Aït Menguellet
*Kamel Messaoudi
Kamel Messaoudi ( ar, كمال مسعودي), (30 January 1961; Bouzaréah, Algeria – 10 December 1998; Algiers) was an Algerian Chaabi music performer, highly regarded as one of the greatest musicians in Algeria history.
Biography
He was ...
* Emma Saïd Ben Mohamed
* Marcel Mouloudji
*El Hadj M'Hamed El Anka
El Hadj M'Hamed El Anka ( ar, الحاج محمد العنقة}), (May 20, 1907 in Algiers – November 23, 1978 in Algiers) also known as Hadj Muhammed Al Anka, El-Hadj M'Hamed El Anka (and various other combinations), was considered a Grand Mast ...
* Rilès
* Sinik
*DJ Snake
William Sami Étienne Grigahcine (born 13 June 1986), known by his stage name DJ Snake, is an Algerian French music producer and DJ, first achieving international recognition in 2013 by releasing an instrumentation-oriented single called " Turn D ...
*Soolking
Abderraouf Derradji ( ar, عبد الرؤوف درّاجي; born 10 December 1989), known professionally as Soolking, is an Algerian singer and rapper. He started his career under the pseudonym MC Sool until 2013 before adopting his new stage na ...
*Rachid Taha
Rachid Taha ( ar, رشيد طه, Latn, ar, Rashīd Ṭāhā, ; 18 September 1958 – 12 September 2018) was an Algerian singer and activist based in France described as "sonically adventurous". His music was influenced by many different styles ...
*Takfarinas
Hacène Zermani (born 1958 in Algiers, Algeria), known by the stage name Takfarinas, is an Algerian Kabyle Yal musician. Takfarinas took his surname from the ancient warrior of North Africa Tacfarinas who fought against the presence of the Roma ...
Paint
*M'hamed Issiakhem
M'hamed Issiakhem (17 June 1928 – 1 December 1985) is one of the founders of the modern Algerian painting.
Biography
M'hamed Issiakhem born on 17 June 1928 in Taboudoucht, a small village near Azeffoun, around 43 kilometers from Tizi O ...
* Hamid Tibouchi
Politics
*Abane Ramdane
Abane Ramdane (June 10, 1920 – December 26, 1957) was an Algerian political activist and revolutionary. He played a key role in the organization of the independence struggle during the Algerian war. His influence was so great that he was known ...
* Ferhat Abbas
*Belaïd Abrika Belaïd Abrika ( ar, بلعيد عبريكا, born December 10, 1969 in Tizi Ouzou) is a professor of economics at the Mouloud Mammeri University of Tizi-Ouzou. He has become one of the best-known modern Kabyles through his role as a leader and spok ...
*Hocine Aït Ahmed
Hocine Aït Ahmed ( ar, حسين آيت أحمد; 20 August 1926 – 23 December 2015) was an Algerian politician. He was founder and leader until 2009 of the historical political opposition in Algeria.
Life
Aït Ahmed was born at Aï ...
*Lucius Alfenus Senecio Lucius Alfenus Senecio was a Roman figure of the late 2nd and early 3rd centuries.
Career
Born in Curculum, Africa (Roman province) ( Djemila, Algeria), Lucius Alfenus Senecio was a Numidian ( Romanised Berber). He served as ''procurator Augusti'' ...
* Nasir ibn Alnas
* Fadela Amara
* Belkacem Lounes
* Mohand Arav Bessaoud
* Lalla Fatma n Sumer
*Firmus
According to the ''Historia Augusta'', Firmus (died 273) was a usurper during the reign of Aurelian. The contradictory accounts of his life and the man himself are considered to be a complete fabrication, perhaps based on the later Firmus.
His ...
*Amirouche Aït Hamouda
Amirouche Aït Hamouda ( ar, عميروش آيت حمودة), commonly called Colonel Amirouche, was a leader in the Algerian War, organizing the irregular military of the Wilaya III. He is considered a national hero in Algeria.
He was killed d ...
*Krim Belkacem
Krim Belkacem ( ar, عبد الكريم بلقاسم or ) (September 14, 1922, Aït Yahia Moussa, Tizi Ouzou Province – October 18, 1970) was the historic leader of the National Liberation Front during the Algerian War. As vice-president of ...
* Ferhat Mehenni
*Saïd Mohammedi
Colonel Saïd Mohammedi ( ar, السعيد محمدي; 27 December 1912 – 6 December 1994), or Si Nacer, was an Algerian nationalist and politician.
Early life and collaborationism
Born in the Berber Kabyle region of Tizi Ouzou, Saïd ...
* Sheikh Mokrani
* Belkacem Radjef
*Saïd Sadi
Saïd Sadi ( Kabyle: Saεid Seεdi) (born 26 August 1947) is an Algerian politician who was President of the Rally for Culture and Democracy (RCD) until 2012. He is founder of the first Algerian human rights league.
Born at Aghribs, now in Tiz ...
* Buluggin ibn Ziri
Natural Science
* Mustapha Ishak-Boushaki *Noureddine Melikechi
Noureddine Melikechi, D.Phil (born in 1958) is an Algerian atomic, molecular, and optical physicist, educator and inventor. He is the author of more than 125 peer-reviewed publications, three book chapters and 15 patents. Melikechi is a membe ...
* Rachid Ouyed
Literature
* Si Amar * Mohammed Arkoun * Taos Amrouche *Salem Chaker
Salem Chaker (born 1950 in Nevers) is an Algerian linguist. A specialist in Berber linguistics (syntax, diachrony, sociolinguistics), he is recognized as the "dean" of modern Berber studies.
Biography
Salem Chaker was born in 1950 in Nevers, ...
*Tahar Djaout
Tahar Djaout (11 January 1954 – 2 June 1993) was an Algerian journalist, poet, and fiction writer. He was assassinated in 1993 by the Armed Islamic Group.
Early life
He was born in 1954 in Oulkhou, a village in the Kabylie region. After unive ...
* Nabile Farès
*Mouloud Feraoun
Mouloud Feraoun (8 March 1913 – 15 March 1962) was an Algerian writer and martyr of the Algerian revolution born in Tizi Hibel, Kabylie. Some of his books, written in French, have been translated into several languages including English and Ge ...
*Mouloud Mammeri
Mouloud Mammeri () was an Algerian writer, anthropologist and linguist.
Biography
He was born on December 28, 1917, in Ait Yenni, in Tizi Ouzou Province, French Algeria. He attended a primary school in his native village, then emigrated to ...
* Si Mohand
* Mohand Tazerout
* Tassadit Yacine
* Salem Zenia
See also
*List of Kabyle people
A list of Kabyle people
Musicians
* Amour Abdenour, Algerian singer (active since 1969)
* Abderrahmane Abdelli, singer
* Myriam Abel, singer
* Kenza Farah, French singer
* Lounis Ait Menguellet, singer
* Idir, singer
* Lounes Matoub, Be ...
Notes and references
External links
Provisional Government of Kabylie (ANAVAD)
Kabyle Movement of Autonomy
Kabyle centric news site
Social web site
Kabyle centric news site
Ethnologue.com about Kabyle language
Cultural site
Analysis
{{authority control Ethnic groups in Algeria Indigenous peoples of North Africa Berber peoples and tribes