John Armstrong, Jr. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
John Armstrong Jr. (November 25, 1758April 1, 1843) was an
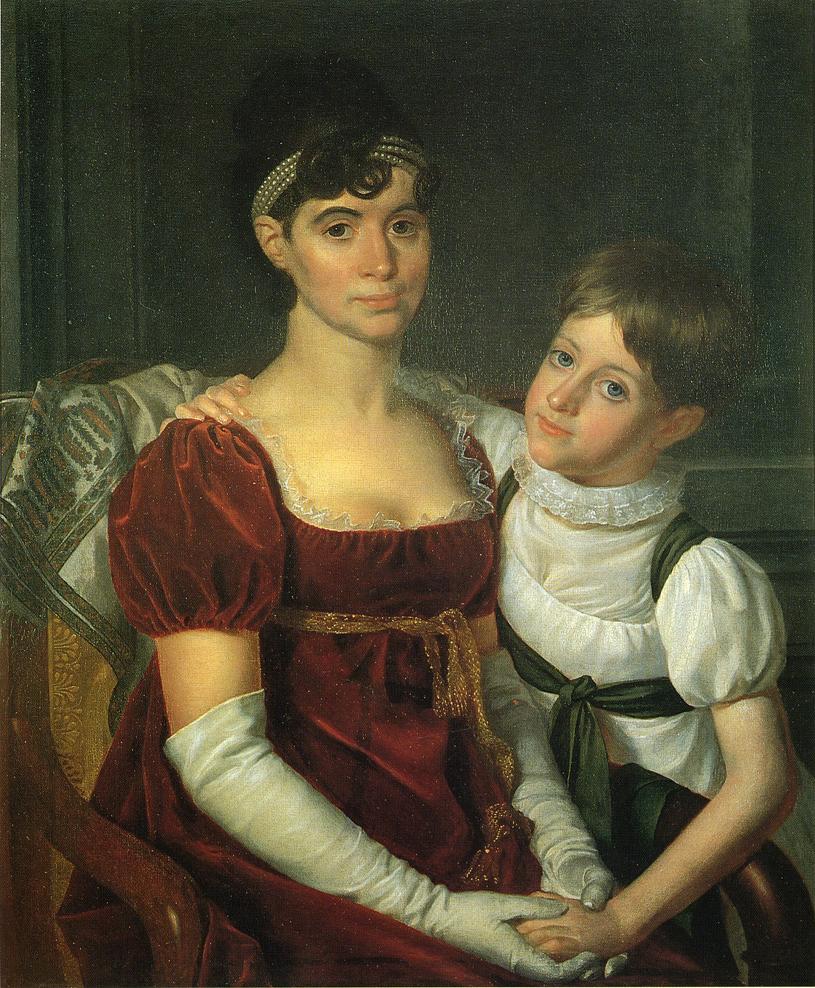
 In 1789, Armstrong married Alida Livingston (1761–1822), the youngest child of Judge Robert Livingston (1718–1775) and Margaret (
In 1789, Armstrong married Alida Livingston (1761–1822), the youngest child of Judge Robert Livingston (1718–1775) and Margaret (
Lewis, John N., "Town of Red Hook", ''History of Dutchess County'', (Frank Hasbrouck, ed.), Higginson Book Company, 1909
/ref>
American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
soldier, diplomat and statesman who was a delegate to the Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
, U.S. Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, and United States Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the President of the United States, U.S. president's United States Cabinet, Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's Presidency of George Washington, administration. A similar position, called either "Se ...
under President James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early ...
, Armstrong was United States Minister to France from 1804 to 1810.
Early life
Armstrong was born inCarlisle, Pennsylvania
Carlisle is a Borough (Pennsylvania), borough in and the county seat of Cumberland County, Pennsylvania, United States. Carlisle is located within the Cumberland Valley, a highly productive agricultural region. As of the 2020 United States census, ...
, the younger son of General John Armstrong and Rebecca (Lyon) Armstrong. John Armstrong Sr. was a renowned Pennsylvania soldier born in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
of Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
descent. John Jr.'s older brother was James Armstrong, who became a physician and U.S. Congressman.
After early education in Carlisle, John Jr. studied at the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University
Princeton University is a private university, private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the List of Colonial Colleges, fourth-oldest ins ...
). He broke off his studies in Princeton
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the nine ...
in 1775 to return to Pennsylvania and join the fight in the Revolutionary War.
Career
Revolutionary War
The young Armstrong initially joined a Pennsylvania militia regiment and the following year he was appointed as aide-de-camp to GeneralHugh Mercer
Hugh Mercer (16 January 1726 – 12 January 1777) was a Scottish-born American military officer and physician who participated in the Seven Years' War and Revolutionary War. Born in Pitsligo, Scotland, he studied medicine in his home country ...
of the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
. In this role, he carried the wounded and dying General Mercer from the field at the Battle of Princeton
The Battle of Princeton was a battle of the American Revolutionary War, fought near Princeton, New Jersey on January 3, 1777, and ending in a small victory for the Colonials. General Lord Cornwallis had left 1,400 British troops under the comman ...
. After the general died on January 12, 1777, Armstrong became an aide to General Horatio Gates. He stayed with Gates through the Battle of Saratoga
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion ...
then resigned due to problems with his health. In 1782 Gates asked him to return. Armstrong joined General Gates' staff as an aide with the rank of major, which he held through the rest of the war.
Newburgh letters
While in camp with Gates at Newburgh, New York, Armstrong became involved in the Newburgh Conspiracy. He is generally acknowledged as the author of the two anonymous letters directed at the officers in the camp. The first, titled "An Address to the Officers" (dated March 10, 1783), called for a meeting to discuss back pay and other grievances with the Congress and form a plan of action. AfterGeorge Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
ordered the meeting canceled and called for a milder meeting on March 15, a second address appeared that claimed that this showed that Washington supported their actions.
Washington successfully defused this protest without a mutiny. While some of Armstrong's later correspondence acknowledged his role, there was never any official action that connected him with the anonymous letters.
After the revolution
Later in 1783 Armstrong returned home to Carlisle and became an Original Member of the PennsylvaniaSociety of the Cincinnati
The Society of the Cincinnati is a fraternal, hereditary society founded in 1783 to commemorate the American Revolutionary War that saw the creation of the United States. Membership is largely restricted to descendants of military officers wh ...
. He was named the Adjutant General of Pennsylvania's militia and also served as Secretary of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
The secretary of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania (or "secretary of state") administers the Pennsylvania Department of State of the U.S. state (officially, " commonwealth") of Pennsylvania. The secretary is appointed by the governor subject to co ...
under Presidents Dickinson and Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People
* Franklin (given name)
* Franklin (surname)
* Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class
Places Australia
* Franklin, Tasmania, a township
* Division of Franklin, federal electoral d ...
. In 1784, he led a military force of four hundred militiamen into a controversy with Connecticut settlers in the Wyoming Valley of Pennsylvania. His tactics enraged the nearby states of Vermont and Connecticut, which sent their own militia into the area. Timothy Pickering was dispatched to forge a solution to the difficulty, and the settlers were able to keep title to the land they had tamed. In 1787 and 1788 Armstrong was sent as a delegate for Pennsylvania to the Congress of the Confederation
The Congress of the Confederation, or the Confederation Congress, formally referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, was the governing body of the United States of America during the Confederation period, March 1, 1781 – Mar ...
. The Congress offered to make him chief justice of the Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
. He declined this, as well as all other public offices for the next dozen years.
Armstrong resumed public life after the resignation of John Laurance as U.S. Senator from New York. As a Jeffersonian Republican he was elected in November 1800 to a term ending in March 1801. He took his seat on November 6, and was re-elected on January 27 for a full term (1801–07), but resigned on February 5, 1802. DeWitt Clinton
DeWitt Clinton (March 2, 1769February 11, 1828) was an American politician and naturalist. He served as a United States senator, as the mayor of New York City, and as the seventh governor of New York. In this last capacity, he was largely res ...
was elected to fill the vacancy, but resigned in 1803, and Armstrong was appointed temporarily to his old seat.
In February 1804, Armstrong was elected again to the U.S. Senate to fill the vacancy caused by the resignation of Theodorus Bailey, thus moving from the Class 3 to the Class 1 seat on February 25, but served only four months before President Jefferson appointed him U.S. Minister to France
The United States ambassador to France is the official representative of the president of the United States to the president of France. The United States has maintained diplomatic relations with France since the American Revolution. Relations we ...
.
To Paris Armstrong brought as his private secretary the United-Irish exile, David Bailie Warden. After serving as Consul, Warden was to author the first major work of reference for the diplomatic corps; a "pioneering" contribution to "the emergence of doctrinal views and a specialist literature on international law".
Armstrong served as Minister in Paris until September 1810. In 1806 he had also briefly also represented the United States at the court of Spain.
When the War of 1812 broke out, Armstrong was called to military service. He was commissioned as a Brigadier General, and placed in charge of the defenses for the port of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. Then in 1813 President Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
named him Secretary of War.
Henry Adams
Henry Brooks Adams (February 16, 1838 – March 27, 1918) was an American historian and a member of the Adams political family, descended from two U.S. Presidents.
As a young Harvard graduate, he served as secretary to his father, Charles Fra ...
wrote of him:
''In spite of Armstrong's services, abilities, and experience, something in his character always created distrust. He had every advantage of education, social and political connection, ability and self-confidence; he was only fifty-four years old, which was also the age of Monroe; but he suffered from the reputation of indolence and'' Armstrong made a number of valuable changes to the armed forces but was so convinced that the British would 'not' attack Washington D.C. that he did nothing to defend the city even when it became clear it was the objective of the invasion force. After the American defeat at the Battle of Bladensburg and the subsequent burning of Washington, Madison, usually a forgiving man, forced him to resign in September 1814.intrigue Intrigue may refer to: TV and film * ''Intrigue'' (1920 film), a 1920 German silent drama film * ''Intrigue'' (1942 film), a Spanish film * ''Intrigue'' (1947 film), 1947 film directed by Edwin L. Marin * ''The Intrigue'', 1916 silent film dra .... So strong was the prejudice against him that he obtained only eighteen votes against fifteen in the Senate on his confirmation; and while the two senators from Virginia did not vote at all, the two from Kentucky voted in the negative. Under such circumstances, nothing but military success of the first order could secure a fair field for Monroe's rival.
Later life
Armstrong returned to his farm and resumed a quiet life. He published a number of histories, biographies, and some works on agriculture. He died atLa Bergerie
Rokeby, also known as La Bergerie, is a historic estate and federally recognized historic district located at Barrytown in Dutchess County, New York, United States. It includes seven contributing buildings and one contributing structure.
History
T ...
(later renamed Rokeby), the farm estate he built in Red Hook, New York
Red Hook is a town in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The population was 9,953 at the time of the 2020 census, down from 11,319 in 2010. The name is supposedly derived from the red foliage on trees on a small strip of land on the Hu ...
in 1843 and is buried in the cemetery in Rhinebeck. Following the death of Paine Wingate
Paine Wingate (May 14, 1739March 7, 1838) was an American preacher, farmer, and statesman from Stratham, New Hampshire. He served New Hampshire in the Continental Congress and both the United States Senate and House of Representatives.
Early ...
in 1838, he became the last surviving delegate to the Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
, and the only one to be photographed.
Personal life
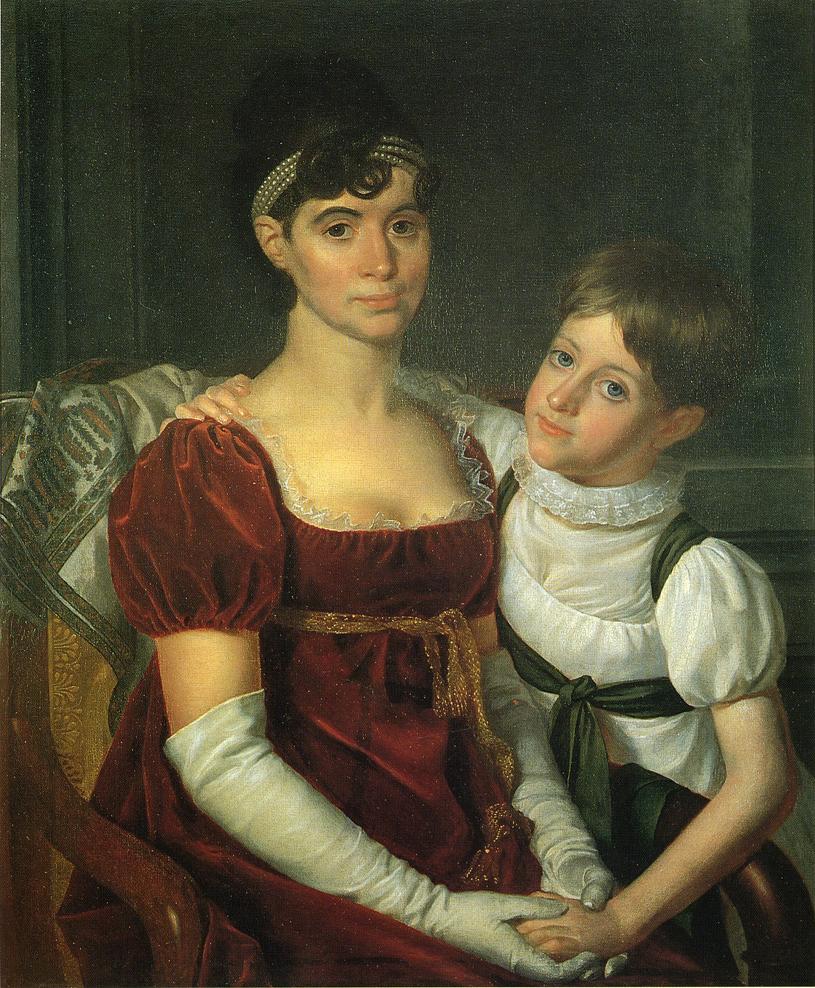
 In 1789, Armstrong married Alida Livingston (1761–1822), the youngest child of Judge Robert Livingston (1718–1775) and Margaret (
In 1789, Armstrong married Alida Livingston (1761–1822), the youngest child of Judge Robert Livingston (1718–1775) and Margaret (née
A birth name is the name of a person given upon birth. The term may be applied to the surname, the given name, or the entire name. Where births are required to be officially registered, the entire name entered onto a birth certificate or birth re ...
Beekman) Livingston. Alida was also the sister of Chancellor Robert R. Livingston and Edward Livingston
Edward Livingston (May 28, 1764May 23, 1836) was an American jurist and statesman. He was an influential figure in the drafting of the Louisiana Civil Code of 1825, a civil code based largely on the Napoleonic Code. Livingston represented both ...
. Together they had seven children:
* Maj Horatio Gates Armstrong
Horatio Gates Armstrong (June 1, 1790 – April 6, 1858) was an American soldier who fought in the War of 1812.
Early life and career
Armstrong was born on June 1, 1790, and was named after General Horatio Gates, whom his father had been aide ...
(1790–1858), soldier in the War of 1812.
* Henry Beekman Armstrong (1791–1854), also a soldier in the War of 1812.
* John Armstrong (1794–1852), who moved to New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
and took up life as a gentleman farmer at La Bergerie
Rokeby, also known as La Bergerie, is a historic estate and federally recognized historic district located at Barrytown in Dutchess County, New York, United States. It includes seven contributing buildings and one contributing structure.
History
T ...
, a farm purchased from her family in Dutchess County
Dutchess County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 295,911. The county seat is the city of Poughkeepsie. The county was created in 1683, one of New York's first twelve counties, and later organ ...
* Robert Livingston Armstrong (1797–1834)
* Margaret Rebecca Armstrong (1800–1872), who married William Backhouse Astor Sr.
William Backhouse Astor Sr. (September 19, 1792 – November 24, 1875) was an American business magnate who inherited most of his father John Jacob Astor's fortune. He worked as a partner in his father's successful export business. His massive in ...
(1792–1875) of the prominent Astor family.
* James Kosciuszko Armstrong (1801–1868)
* William Armstrong (1814–1902), who married Lucy A. Hickernell (1816–1894).
Armstrong died in Red Hook, New York
Red Hook is a town in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The population was 9,953 at the time of the 2020 census, down from 11,319 in 2010. The name is supposedly derived from the red foliage on trees on a small strip of land on the Hu ...
on April 1, 1843. He was buried at the Rhinebeck Cemetery in Rhinebeck, New York
Rhinebeck is a village (New York), village in the Rhinebeck (town), New York, town of Rhinebeck in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The population was 2,657 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Poughkeepsie, New York, Poughkeepsie– ...
.
Residences
Almont
Armstrong's initial farm in Dutchess County, called "Altmont" (also known as "The Meadows"), was originally part of the Schuyler patent. In 1795, he purchased a part of the farm from the Van Benthuysen family, and converted an existing barn into a two-story Federal style dwelling with twelve rooms. Around 1800, Armstrong sold "Almont" to Andrew and Anna Verplanck Deveaux. Deveaux died in 1812; in 1816 his widow sold "Deveaux Park" to John Stevens. The mansion burned down around 1879. In 1908, lumber rights to the white oak and chestnut forests were sold for timber for the New York market./ref>
La Bergerie
After the death of Margaret Beekman Livingston, widow of Judge Robert Livingston, much of the Clermont land was distributed among the heirs. John R. Livingston received the land that would become the "Messena" estate. His sister Alida Livingston Armstrong inherited the property just to the south. There the Armstrong's created "La Bergerie", in English "the sheepfold" – an estate where they raised Merino sheep. The Merino sheep were a gift from the French EmperorNapoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
on Armstrong's departure after being Minister. The Astors purchased it for a summer home and renamed it Rokeby. Margaret Chanler Aldrich
Margaret Livingston Chanler Aldrich (1870–1963) was an American philanthropist, poet, nurse, and woman's suffrage advocate. She served as a nurse with the American Red Cross during the Spanish–American War and Philippine–American War, tra ...
, great-granddaughter of Margaret Armstrong Astor, married Richard Aldrich. Rokeby remains in the Aldrich family.
See also
*Rokeby (Barrytown, New York)
Rokeby, also known as La Bergerie, is a historic estate and federally recognized historic district located at Barrytown in Dutchess County, New York, United States. It includes seven contributing buildings and one contributing structure.
History
...
References
Further reading
* Skeen, Carl E. ''John Armstrong Jr., 1758–1843: A Biography.'' Syracuse Univ Press, 1982. .External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Armstrong, John Jr. 1758 births 1843 deaths People from Carlisle, Pennsylvania People of colonial Pennsylvania Livingston family American people of Scotch-Irish descent Madison administration cabinet members United States Secretaries of War Continental Congressmen from Pennsylvania Democratic-Republican Party United States senators from New York (state) Ambassadors of the United States to France 18th-century American politicians 19th-century American politicians 19th-century American diplomats United States Army generals Continental Army officers from Pennsylvania United States Army personnel of the War of 1812