, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption =
Christogram
A Christogram ( la, Monogramma Christi) is a monogram or combination of letters that forms an abbreviation for the name of Jesus Christ, traditionally used as a religious symbol within the Christian Church.
One of the oldest Christograms is th ...
Official seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders =
, founding_location =
, type = Order of
clerics regular
Clerics regular are clerics (mostly priests) who are members of a religious order under a rule of life (regular). Clerics regular differ from canons regular in that they devote themselves more to pastoral care, in place of an obligation to the pr ...
of
pontifical right (for men)
, headquarters = Generalate:
Borgo S. Spirito 4, 00195 Roma-Prati, Italy
, coords =
, region_served = Worldwide
, num_members = 14,839 members (includes 10,721 priests) as of 2020
, leader_title = Motto
, leader_name = la, Ad Majorem Dei GloriamEnglish: ''For the Greater Glory of God''
, leader_title2 =
Superior General
A superior general or general superior is the leader or head of a religious institute in the Catholic Church and some other Christian denominations. The superior general usually holds supreme executive authority in the religious community, while t ...
, leader_name2 = Fr.
Arturo Sosa
Arturo Marcelino Sosa Abascal (born 12 November 1948) is a Venezuelan Catholic priest who serves as the 31st and present superior general of the Society of Jesus. He was elected Superior General by the Society's 36th General Congregation on ...
, SJ
, leader_title3 = Patron saints
, leader_name3 =
, leader_title4 = Ministry
, leader_name4 = Missionary, educational, literary works
, main_organ = La Civiltà Cattolica
, parent_organization =
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
, website =
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ),
is a
religious order
A religious order is a lineage of communities and organizations of people who live in some way set apart from society in accordance with their specific religious devotion, usually characterized by the principles of its founder's religious pract ...
of
clerics regular
Clerics regular are clerics (mostly priests) who are members of a religious order under a rule of life (regular). Clerics regular differ from canons regular in that they devote themselves more to pastoral care, in place of an obligation to the pr ...
of
pontifical right for men in the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
headquartered in
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. It was founded in 1540 by
Ignatius of Loyola
Ignatius of Loyola, S.J. (born Íñigo López de Oñaz y Loyola; eu, Ignazio Loiolakoa; es, Ignacio de Loyola; la, Ignatius de Loyola; – 31 July 1556), venerated as Saint Ignatius of Loyola, was a Spanish Catholic priest and theologian ...
and six companions, with the approval of
Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III ( la, Paulus III; it, Paolo III; 29 February 1468 – 10 November 1549), born Alessandro Farnese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 October 1534 to his death in November 1549.
He came to ...
. The society is engaged in
evangelization
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ.
Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are ...
and apostolic ministry in 112 nations. Jesuits work in education,
research
Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
, and cultural pursuits. Jesuits also give retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian ministries, and promote
ecumenical dialogue.
The Society of Jesus is
consecrate
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service. The word ''consecration'' literally means "association with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different grou ...
d under the
patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
of
Madonna della Strada, a title of the
Blessed Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother ...
, and it is led by a
Superior General
A superior general or general superior is the leader or head of a religious institute in the Catholic Church and some other Christian denominations. The superior general usually holds supreme executive authority in the religious community, while t ...
. The headquarters of the society, its
General Curia, is in Rome. The historic curia of Ignatius is now part of the attached to the
Church of the Gesù
, image = Church of the Gesù, Rome.jpg
, imagesize =
, caption = Giacomo della Porta's façade, precursor of Baroque
, mapframe = yes
, mapframe-caption = Click on the map for a full ...
, the Jesuit
mother church
Mother church or matrice is a term depicting the Christian Church as a mother in her functions of nourishing and protecting the believer. It may also refer to the primary church of a Christian denomination or diocese, i.e. a cathedral or a metropo ...
.
Members of the Society of Jesus are expected to accept orders to go anywhere in the world, where they might be required to live in extreme conditions. This was so because Ignatius, its leading founder, was a nobleman who had a military background. Accordingly, the opening lines of the founding document declared that the society was founded for "whoever desires to serve as a soldier of God, to strive especially for the defense and propagation of the faith, and for the progress of souls in Christian life and doctrine". Jesuits are thus sometimes referred to colloquially as "God's soldiers", "God's marines", or "the Company". The society participated in the
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
and, later, in the implementation of the
Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
.
History
Foundation

Ignatius of Loyola
Ignatius of Loyola, S.J. (born Íñigo López de Oñaz y Loyola; eu, Ignazio Loiolakoa; es, Ignacio de Loyola; la, Ignatius de Loyola; – 31 July 1556), venerated as Saint Ignatius of Loyola, was a Spanish Catholic priest and theologian ...
, a
Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
nobleman from the
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
area of northern Spain, founded the society after discerning his spiritual vocation while recovering from a wound sustained in the
Battle of Pamplona. He composed the ''
Spiritual Exercises'' to help others follow the teachings of
Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
. In 1534, Ignatius and six other young men, including
Francis Xavier
Francis Xavier (born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta; Latin: ''Franciscus Xaverius''; Basque: ''Frantzisko Xabierkoa''; French: ''François Xavier''; Spanish: ''Francisco Javier''; Portuguese: ''Francisco Xavier''; 7 April 15063 December ...
and
Peter Faber
Peter Faber (french: Pierre Lefevre or Favre, la, Petrus Faver) (13 April 1506 – 1 August 1546) was a Jesuit priest and theologian, who was also a co-founder of the Society of Jesus, along with Ignatius of Loyola and Francis Xavier. Pope Fra ...
, gathered and professed promises of
poverty, chastity, and later obedience, including a special vow of obedience to the pope in matters of mission direction and assignment. Ignatius's plan of the order's organization was approved by
Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III ( la, Paulus III; it, Paolo III; 29 February 1468 – 10 November 1549), born Alessandro Farnese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 October 1534 to his death in November 1549.
He came to ...
in 1540 by a
bull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e., cows), bulls have long been an important symbol in many religions,
includin ...
containing the "Formula of the Institute".
On 15 August 1534, Ignatius of Loyola (born Íñigo López de Loyola), a Spaniard from the
Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
city of
Loyola, and six others mostly of
Castilian origin, all students at the
University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
, met in
Montmartre
Montmartre ( , ) is a large hill in Paris's northern 18th arrondissement. It is high and gives its name to the surrounding district, part of the Right Bank. The historic district established by the City of Paris in 1995 is bordered by Rue Ca ...
outside Paris, in a crypt beneath the church of
Saint Denis, now
Saint Pierre de Montmartre
Saint-Pierre de Montmartre () is one of the oldest surviving churches in Paris, second to the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Pres, but the lesser known of the two main churches in Montmartre, the other being the more famous 19th-century Sacré-Cœur ...
, to pronounce promises of poverty, chastity, and obedience. Ignatius' six companions were:
Francisco Xavier from
Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
(
modern Spain),
Alfonso Salmeron
Alfonso (Alphonsus) Salmerón (8 September 1515 – 13 February 1585) was a Spanish biblical scholar, a Catholic priest, and one of the first Jesuits.
Biography
He was born in Toledo, Spain on 8 September 1515. He studied literature and philoso ...
,
Diego Laínez,
Nicolás Bobadilla from
Castile (
modern Spain),
Peter Faber
Peter Faber (french: Pierre Lefevre or Favre, la, Petrus Faver) (13 April 1506 – 1 August 1546) was a Jesuit priest and theologian, who was also a co-founder of the Society of Jesus, along with Ignatius of Loyola and Francis Xavier. Pope Fra ...
from
Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
, and
Simão Rodrigues from
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
. The meeting has been commemorated in the
Martyrium of Saint Denis, Montmartre. They called themselves the , and also or "Friends in the Lord", because they felt "they were placed together by Christ." The name "company" had echoes of the military (reflecting perhaps Ignatius' background as Captain in the Spanish army) as well as of discipleship (the "companions" of Jesus). The Spanish "company" would be translated into Latin as like in , a partner or comrade. From this came "Society of Jesus" (SJ) by which they would be known more widely.
Religious orders established in the medieval era were named after particular men:
Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christianit ...
(Franciscans);
Domingo de Guzmán, later canonized as Saint Dominic (Dominicans); and
Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
(Augustinians). Ignatius of Loyola and his followers appropriated the name of Jesus for their new order, provoking resentment by other orders who considered it presumptuous. The resentment was recorded by Jesuit
José de Acosta
José de Acosta (1539 or 1540 in Medina del Campo, Spain – February 15, 1600 in Salamanca, Spain) was a sixteenth-century Spanish Jesuit missionary and naturalist in Latin America. His deductions regarding the ill effects of crossing over t ...
of a conversation with the Archbishop of Santo Domingo. In the words of one historian: "The use of the name Jesus gave great offense. Both on the Continent and in England, it was denounced as blasphemous; petitions were sent to kings and to civil and ecclesiastical tribunals to have it changed; and even
Pope Sixtus V
Pope Sixtus V ( it, Sisto V; 13 December 1521 – 27 August 1590), born Felice Piergentile, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 April 1585 to his death in August 1590. As a youth, he joined the Franciscan order ...
had signed a Brief to do away with it." But nothing came of all the opposition; there were already congregations named after the Trinity and as "God's daughters".
In 1537, the seven travelled to Italy to seek papal approval for their
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
. Pope Paul III gave them a commendation, and permitted them to be ordained priests. These initial steps led to the official founding in 1540.
They were ordained in
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
by the
bishop of Arbe
The Diocese of Arbe or Diocese of Rab or Diocese of Arba (Latin: ''Dioecesis Arbensis'') was a Roman Catholic diocese located in the town of Arbe (modern day Rab) on the Croatian island of the same name located just off the Adriatic coast of north ...
(24 June). They devoted themselves to preaching and charitable work in
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. The
Italian War of 1535-1538 renewed between
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fr ...
, Venice, the Pope, and the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, had rendered any journey to
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
impossible.
Again in 1540, they presented the project to Paul III. After months of dispute, a congregation of
cardinals
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
reported favourably upon the Constitution presented, and Paul III confirmed the order through the bull ("To the Government of the Church Militant"), on 27 September 1540. This is the founding document of the Society of Jesus as an official Catholic religious order. Ignatius was chosen as the first
Superior General
A superior general or general superior is the leader or head of a religious institute in the Catholic Church and some other Christian denominations. The superior general usually holds supreme executive authority in the religious community, while t ...
. Paul III's bull had limited the number of its members to sixty. This limitation was removed through the bull of Julius III in 1550.
In 1543, Pierre Canisius entered the Company. Ignatius sent him to Messina, where he founded the first Jesuit college in
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
.
Ignatius laid out his original vision for the new order in the "Formula of the Institute of the Society of Jesus",
[Text of the Formula of the Institute (1540)](_blank)
, Boston College
Boston College (BC) is a private Jesuit research university in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts. Founded in 1863, the university has more than 9,300 full-time undergraduates and nearly 5,000 graduate students. Although Boston College is classified ...
, Institute for Advanced Jesuit Studies, accessed 31 May 2021 which is "the fundamental charter of the order, of which all subsequent official documents were elaborations and to which they had to conform". He ensured that his formula was contained in two
papal bulls signed by Pope Paul III in 1540 and by Pope Julius III in 1550.
The formula expressed the nature, spirituality, community life, and apostolate of the new religious order. Its famous opening statement echoed Ignatius' military background:
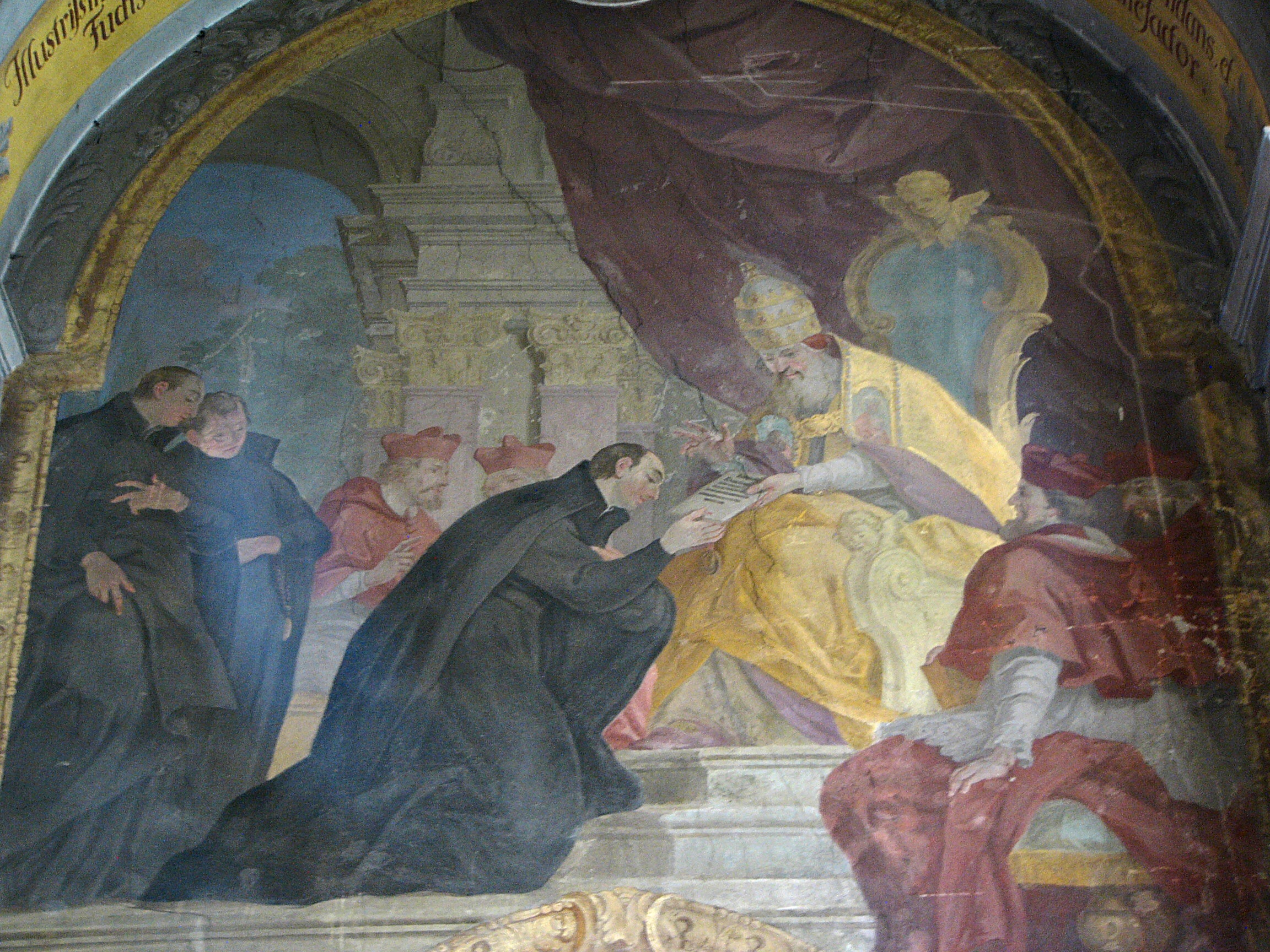

In fulfilling the mission of the "Formula of the Institute of the Society", the first Jesuits concentrated on a few key activities. First, they founded schools throughout Europe. Jesuit teachers were trained in both
classical studies
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics ...
and
theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing th ...
, and their schools reflected this. Second, they sent out missionaries across the globe to
evangelize
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ.
Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are in ...
those peoples who had not yet heard the
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
, founding missions in widely diverse regions such as modern-day
Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
, Japan,
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, and
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. One of the original seven arrived in India already in 1541. Finally, though not initially formed for the purpose, they aimed to stop
Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
from spreading and to preserve communion with
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and the
pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
. The zeal of the Jesuits overcame the movement toward Protestantism in the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
and southern
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
.
Ignatius wrote the Jesuit ''Constitutions'', adopted in 1553, which created a centralised organization and stressed acceptance of any mission to which the pope might call them. His main principle became the unofficial Jesuit motto: ("For the greater glory of God"). This phrase is designed to reflect the idea that any work that is not evil can be meritorious for the spiritual life if it is performed with this intention, even things normally considered of little importance.
The Society of Jesus is classified among institutes as a
mendicant
A mendicant (from la, mendicans, "begging") is one who practices mendicancy, relying chiefly or exclusively on alms to survive. In principle, mendicant religious orders own little property, either individually or collectively, and in many inst ...
order of
clerks regular
Clerics regular are clerics (mostly priests) who are members of a religious order under a rule of life (regular). Clerics regular differ from canons regular in that they devote themselves more to pastoral care, in place of an obligation to the pra ...
, that is, a body of priests organized for
apostolic
Apostolic may refer to:
The Apostles
An Apostle meaning one sent on a mission:
*The Twelve Apostles of Jesus, or something related to them, such as the Church of the Holy Apostles
*Apostolic succession, the doctrine connecting the Christian Churc ...
work, following a
religious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
rule, and relying on
alms
Alms (, ) are money, food, or other material goods donated to people living in poverty. Providing alms is often considered an act of virtue or charity. The act of providing alms is called almsgiving, and it is a widespread practice in a numbe ...
, or donations, for support.
The term ''Jesuit'' (of 15th-century origin, meaning "one who used too frequently or appropriated the name of Jesus") was first applied to the society in reproach (1544–1552). The term was never used by Ignatius of Loyola, but over time, members and friends of the society adopted the name with a positive meaning.
Early works

The Jesuits were founded just before the
Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
(1545–1563) and ensuing
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
that would introduce reforms within the Catholic Church, and so counter the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
throughout Catholic Europe.
Ignatius and the early Jesuits did recognize, though, that the hierarchical church was in dire need of reform. Some of their greatest struggles were against corruption,
venality, and spiritual lassitude within the Catholic Church. Ignatius insisted on a high level of academic preparation for the clergy in contrast to the relatively poor education of much of the clergy of his time. The Jesuit vow against "ambitioning prelacies" can be seen as an effort to counteract another problem evidenced in the preceding century.
Ignatius and the Jesuits who followed him believed that the reform of the church had to begin with the conversion of an individual's heart. One of the main tools the Jesuits have used to bring about this conversion is the Ignatian retreat, called the
Spiritual Exercises. During a four-week period of silence, individuals undergo a series of directed
meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
s on the purpose of life and contemplations on the life of Christ. They meet regularly with a
spiritual director
Spiritual direction is the practice of being with people as they attempt to deepen their relationship with the divine, or to learn and grow in their personal spirituality. The person seeking direction shares stories of their encounters of the di ...
who guides their choice of exercises and helps them to develop a more discerning love for Christ.
The retreat follows a "Purgative-Illuminative-Unitive" pattern in the tradition of the spirituality of
John Cassian
John Cassian, also known as John the Ascetic and John Cassian the Roman ( la, Ioannes Eremita Cassianus, ''Ioannus Cassianus'', or ''Ioannes Massiliensis''; – ), was a Christian monk and theologian celebrated in both the Western and Eastern ...
and the
Desert Fathers
The Desert Fathers or Desert Monks were early Christian hermits and ascetics, who lived primarily in the Scetes desert of the Roman province of Egypt, beginning around the third century AD. The is a collection of the wisdom of some of the ea ...
. Ignatius' innovation was to make this style of contemplative
mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in ...
available to all people in active life. Further, he used it as a means of rebuilding the spiritual life of the church. The Exercises became both the basis for the training of Jesuits and one of the essential ministries of the order: giving the exercises to others in what became known as "retreats".
The Jesuits' contributions to the late
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
were significant in their roles both as a missionary order and as the first religious order to operate colleges and universities as a principal and distinct ministry. By the time of Ignatius' death in 1556, the Jesuits were already operating a network of 74 colleges on three continents. A precursor to
liberal education
A liberal education is a system or course of education suitable for the cultivation of a free (Latin: ''liber'') human being. It is based on the medieval concept of the liberal arts or, more commonly now, the liberalism of the Age of Enlightenment ...
, the Jesuit plan of studies incorporated the Classical teachings of
Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was a revival in the study of classical antiquity, at first in Italy and then spreading across Western Europe in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. During the period, the term ''humanist'' ( it, umanista) referred to teache ...
into the
Scholastic structure of Catholic thought.
In addition to the teachings of
faith
Faith, derived from Latin ''fides'' and Old French ''feid'', is confidence or trust in a person, thing, or In the context of religion, one can define faith as "belief in God or in the doctrines or teachings of religion".
Religious people ofte ...
, the Jesuit (1599) would standardize the study of
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, classical literature, poetry, and philosophy as well as non-European languages, sciences, and the arts. Furthermore, Jesuit schools encouraged the study of
vernacular literature
Vernacular literature is literature written in the vernacular—the speech of the "common people".
In the European tradition, this effectively means literature not written in Latin nor Koine Greek. In this context, vernacular literature appeared ...
and
rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate par ...
, and thereby became important centres for the training of lawyers and public officials.
The Jesuit schools played an important part in winning back to Catholicism a number of European countries which had for a time been predominantly Protestant, notably
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. Today, Jesuit colleges and universities are located in over one hundred nations around the world. Under the notion that God can be encountered through created things and especially art, they encouraged the use of ceremony and decoration in Catholic ritual and devotion. Perhaps as a result of this appreciation for art, coupled with their spiritual practice of "finding God in all things", many early Jesuits distinguished themselves in the visual and
performing arts
The performing arts are arts such as music, dance, and drama which are performed for an audience. They are different from the visual arts, which are the use of paint, canvas or various materials to create physical or static art objects. Perfo ...
as well as in music. The theater was a form of expression especially prominent in Jesuit schools.
Jesuit priests often acted as
confessors to kings during the
early modern period. They were an important force in the Counter-Reformation and in the Catholic missions, in part because their relatively loose structure (without the requirements of living and celebration of the
Liturgy of Hours in common) allowed them to be flexible and meet diverse needs arising at the time.
Expansion of the order

After much training and experience in theology, Jesuits went across the globe in search of converts to Christianity. Despite their dedication, they had little success in Asia, except in the
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. For instance, early missions in Japan resulted in the government granting the Jesuits the feudal fiefdom of
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
in 1580. This was removed in 1587 due to fears over their growing influence. Jesuits did, however, have much success in Latin America. Their ascendancy in societies in the Americas accelerated during the seventeenth century, wherein Jesuits created new missions in Peru, Colombia, and Bolivia; as early as 1603, there were 345 Jesuit priests in Mexico alone.

Francis Xavier
Francis Xavier (born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta; Latin: ''Franciscus Xaverius''; Basque: ''Frantzisko Xabierkoa''; French: ''François Xavier''; Spanish: ''Francisco Javier''; Portuguese: ''Francisco Xavier''; 7 April 15063 December ...
, one of the original companions of
Loyola, arrived in
Goa (
Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a s ...
) in 1541 to carry out evangelical service in the Indies. In a 1545 letter to John III of Portugal, he requested an
Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
to be installed in Goa to combat heresies like crypto-Judaism and crypto-Islam. Under
Portuguese royal patronage
The ''Padroado'' (, "patronage") was an arrangement between the Holy See and the Kingdom of Portugal and later the Portuguese Republic, through a series of concordats by which the Holy See delegated the administration of the local churches and gra ...
, Jesuits thrived in Goa and until 1759 successfully expanded their activities to education and healthcare. In 1594 they founded the first Roman-style academic institution in the East, St. Paul Jesuit College (Macau), St. Paul Jesuit College in Macau, China. Founded by Alessandro Valignano, it had a great influence on the learning of Eastern languages (Chinese and Japanese) and culture by missionary Jesuits, becoming home to the first western sinologists such as Matteo Ricci. Jesuit efforts in Goa were interrupted by the Suppression of the Society of Jesus, expulsion of the Jesuits from Portuguese territories in 1759 by the powerful Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, 1st Marquis of Pombal, Marquis of Pombal, Secretary of State in Portugal.
The Portuguese Jesuit António de Andrade founded a mission in Western Tibet in 1624. Two Jesuit missionaries, Johann Grueber and Albert Dorville, reached Lhasa (prefecture-level city), Lhasa, in Tibet, in 1661. The Italian Jesuit Ippolito Desideri established a new Jesuit mission in Lhasa and Central Tibet (1716–21) and gained an exceptional mastery of Tibetan language and culture, writing a long and very detailed account of the country and its religion as well as treatises in Tibetan that attempted to refute key Buddhist ideas and establish the truth of Catholic Christianity.
Jesuit Mission (Christian), missions in America became controversial in Europe, especially in Spain and Portugal where they were seen as interfering with the proper colonial enterprises of the royal governments. The Jesuits were often the only force standing between the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans and slavery. Together throughout South America but especially in present-day Brazil and
Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
, they formed Christian Native American city-states, called "Jesuit reduction, reductions". These were societies set up according to an idealized theocracy, theocratic model. The efforts of Jesuits like Antonio Ruiz de Montoya to protect the natives from enslavement by Spanish and Portuguese colonizers would contribute to the call for the society's suppression. Jesuit priests such as Manuel da Nóbrega and José de Anchieta founded several towns in Brazil in the 16th century, including São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, and were very influential in the pacification, religious conversion, and education of indigenous nations. They also built schools, organized people into villages, and created a writing system for the local languages of Brazil.
José de Anchieta and Manuel da Nóbrega were the first Jesuits that Ignacio de Loyola sent to America.

Jesuit scholars working in foreign missions were very dedicated in studying the local languages and strove to produce Latinized grammars and dictionary, dictionaries. This included: Japanese (see , also known as , "Vocabulary of the Japanese Language", a Japanese–Portuguese dictionary written 1603); Vietnamese language, Vietnamese (Portuguese missionaries created the Vietnamese alphabet,
[Jacques, Roland (2004).]
Bồ Đào Nha và công trình sáng chế chữ quốc ngữ: Phải chăng cần viết lại lịch sử?
" Translated by Nguyễn Đăng Trúc. In ''Các nhà truyền giáo Bồ Đào Nha và thời kỳ đầu của Giáo hội Công giáo Việt Nam (Quyển 1)'' – ''Les missionnaires portugais et les débuts de l'Eglise catholique au Viêt-nam (Tome 1)'' (in Vietnamese & French). Reichstett, France: Định Hướng Tùng Thư. . which was later formalized by Avignon missionary Alexandre de Rhodes with his 1651 Dictionarium Annamiticum Lusitanum et Latinum, trilingual dictionary); Tupi language, Tupi (the main language of Brazil); and the pioneering study of Sanskrit in the West by Jean François Pons in the 1740s.
Jesuit missionaries were active among indigenous peoples in New France in North America, many of them compiling dictionaries or glossaries of the First Nations in Canada, First Nations and Native American languages they had learned. For instance, before his death in 1708, Jacques Gravier, vicar general of the Illinois Mission (Christian), Mission in the Mississippi River valley, compiled a Kaskaskia Illinois–French dictionary, considered the most extensive among works of the missionaries. Extensive documentation was left in the form of ''The Jesuit Relations'', published annually from 1632 until 1673.
Britain
Whereas Jesuits were active in the 16th century, due to the prosecution of Catholics in the Elizabethan times, an 'English' province was only established in 1623. Whereas the first pressing issue of early Jesuits, in what today is the UK, was to establish places for training priests, the Society's activities today are much broader than that. After an English College was opened in Rome (1579), a Jesuit seminary was opened at Valladolid (1589), then one in Seville (1592), which culminated in a place of study in Louvain (1614). This was the earliest foundation of what would later be called Heythrop College. Campion Hall founded in 1896, has been a presence within Oxford University since then. In terms of other longer-established manifestations of the Jesuits commitment to working in Britain, four Jesuit churches remain today in London alone, with four further places of workship in England, and two in Scotland.
For a recent assessment of the Jesuits in Britain's work, see Melanie McDonagh's article.
China


The Jesuits first entered China through the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese settlement on Colonial Macau, Macau, where they settled on Ilha Verde, Green Island and founded St. Paul's College, Macau, St. Paul's College.
The Jesuit China missions of the 16th and 17th centuries introduced Western science and astronomy, then undergoing Scientific Revolution, its own revolution, to China. The Scientific Revolution, scientific revolution brought by the Jesuits coincided with a time when scientific innovation had declined in China:
For over a century, Jesuits like Michele Ruggieri, Matteo Ricci, Diego de Pantoja, Philippe Couplet, Michal Boym, and François Noël (missionary), François Noël refined translations and disseminated history of Chinese science, Chinese knowledge, Chinese culture, culture, history of China, history, and Chinese philosophy, philosophy to Europe. Their
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
works popularized the name "Confucius" and had considerable influence on the Deists and other Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers, some of whom were intrigued by the Jesuits' attempts to reconcile Confucianism, Confucian morality with Catholic Church, Catholicism.
Upon the arrival of the Franciscan Order, Franciscans and other monastic orders, Jesuit accommodation of Chinese culture and rituals led to the long-running Chinese Rites controversy. Despite the personal testimony of the Kangxi Emperor and many Jesuit converts that Chinese veneration of ancestors and Confucianism, Confucius was a nonreligious token of respect, 's papal decree ruled that such behavior constituted impermissible forms of idolatry and superstition in 1704; his papal legate, legate Charles-Thomas Maillard De Tournon, Tournon and the Charles Maigrot, Bishop of Fujian, tasked with presenting this finding to the Kangxi Emperor, displayed such extreme ignorance that the emperor mandated the expulsion of Christian missionaries unable to abide by the terms of Ricci's Chinese catechism.
[.] Tournon's Latae sententiae, summary and automatic excommunication for any violators of Clement's decree—upheld by the 1715 papal bull, bull —led to the swift collapse of all the missions in China;
the last Jesuits were finally expelled after 1721.
Canada

During the French colonisation of New France in the 17th century, Jesuits played an active role in North America. When Samuel de Champlain established the foundations of the French colony at Québec, he was aware of native tribes who possessed their own languages, customs, and traditions. These natives that inhabited modern day Ontario, Québec, and the areas around Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay were the Montagnais, the Algonquins, and the Wyandot people, Huron. Champlain believed that these had souls to be saved, so in 1614 he initially obtained the Recollects, a reform branch of the Franciscans in France, to convert the native inhabitants. In 1624 the French Recollects realized the magnitude of their task and sent a delegate to France to invite the Society of Jesus to help with this mission. The invitation was accepted, and Jesuits Jean de Brébeuf, Ennemond Masse, and Charles Lalemant arrived in Quebec in 1625. Lalemant is considered to have been the first author of one of the The Jesuit Relations, ''Jesuit Relations of New France'', which chronicled their evangelization during the 17th century.
The Jesuits became involved in the Jesuit Missions amongst the Huron, Huron mission in 1626 and lived among the Huron peoples. Brébeuf learned the native language and created the first Huron language dictionary. Outside conflict forced the Jesuits to leave New France in 1629 when Quebec was Surrender of Quebec, surrendered to the Kingdom of England, English. But in 1632 Quebec was returned to the French under the Treaty of Saint Germain-en-Laye and the Jesuits returned to Huron territory, modern Huronia (region), Huronia.
In 1639, Jesuit Jerome Lalemant decided that the missionaries among the Hurons needed a local residence and established Sainte-Marie among the Hurons, Sainte-Marie, which expanded into a living replica of European society. It became the Jesuit headquarters and an important part of Canadian history. Throughout most of the 1640s the Jesuits had great success, establishing five chapels in Huronia and baptising over one thousand Huron natives. However, as the Jesuits began to expand westward they encountered more Iroquois natives, rivals of the Hurons. The Iroquois grew jealous of the Hurons' wealth and fur trade system, and began to attack Huron villages in 1648. They killed missionaries and burned villages, and the Hurons scattered. Both Jean de Brébeuf and Gabriel Lalemant were tortured and killed in the Iroquois raids; they have been canonized as martyrs in the Catholic Church. With the knowledge of the invading Iroquois, the Jesuit Paul Ragueneau burned down Sainte-Marie instead of allowing the Iroquois the satisfaction of destroying it. By late June 1649, the French and some Christian Hurons built Sainte-Marie II on Christian Island (Isle de Saint-Joseph). However, facing starvation, lack of supplies, and constant threats of Iroquois attack, the small Sainte-Marie II was abandoned in June 1650; the remaining Hurons and Jesuits departed for Quebec and Ottawa. After a series of epidemics, beginning in 1634, some Huron began to mistrust the Jesuits and accused them of being sorcerers casting spells from their books. As a result of the Iroquois raids and outbreak of disease, many missionaries, traders, and soldiers died. Today, the Huron tribe, also known as the Wyandot people, Wyandot, have a First Nations reserve in Quebec, Canada, and three major settlements in the United States.
After the collapse of the Huron nation, the Jesuits were to undertake the task of converting the Iroquois, something they had attempted in 1642 with little success. In 1653 the Iroquois nation had a fallout with the Dutch. They then signed a peace treaty with the French and a mission was established. The Iroquois took the treaty lightly and soon turned on the French again. In 1658, the Jesuits were having very little success and were under constant threat of being tortured or killed, but continued their effort until 1687 when they abandoned their permanent posts in the Iroquois homeland.
By 1700, Jesuits turned to maintaining Quebec, Montreal, and Ottawa without establishing new posts. During the Seven Years' War, Quebec was Conquest of New France (1758–1760), captured by the British in 1759 and New France came under British control. The British barred the immigration of more Jesuits to New France, and by 1763, there were only 21 Jesuits stationed in New France. By 1773 only 11 Jesuits remained. During the same year the British crown laid claim to New France and declared that the Society of Jesus in New France was dissolved.
The dissolution of the Order left in place substantial estates and investments, amounting to an income of approximately £5,000 a year, and the Council for the Affairs of the Province of Quebec, later succeeded by the Legislative Assembly of Quebec, assumed the task of allocating the funds to suitable recipients, chiefly schools.
The Jesuit mission in Quebec was re-established in 1842. There were a number of Jesuit colleges founded in the decades following; one of these colleges evolved into present-day Université Laval, Laval University.
United States
In the United States, the order is best known for its Jesuit missions in North America, missions to the Native Americans in the early 17th century, its Association of Jesuit Colleges and Universities, network of colleges and universities, and (in Europe before 1773) its politically conservative role in the Catholic Counter Reformation.
The Society of Jesus, in the United States, is organized into geographic provinces, each of which being headed by a provincial superior. Today, there are four Jesuit provinces operating in the United States: the USA Eastern United States, East, USA Central United States, Central and Southern United States, Southern, USA Midwestern United States, Midwest, and USA Western United States, West Provinces. At their height, there were ten provinces. Though there had been mergers in the past, a major reorganization of the provinces began in early 21st century, with the aim of consolidating into four provinces by 2020.
Ecuador
The Church of la Compañía de Jesús, Quito, Church of the Society of Jesus ( es, La Iglesia de la Compañía de Jesús, links=no), known colloquially as , is a Jesuit church in Quito, Ecuador. It is among the best-known churches in Quito because of its large central nave, which is profusely decorated with gold leaf, Gilding, gilded plaster and wood carvings. Inspired by two Rome, Roman Jesuit churches – the Church of the Gesu, Chiesa del Gesù (1580) and the Sant'Ignazio, Chiesa di Sant'Ignazio di Loyola (1650) – is one of the most significant works of Spanish Baroque architecture in South America and Quito's most ornate church.
Over the 160 years of its construction, the architects of incorporated elements of four architectural styles, although the Baroque is the most prominent. Mudéjar (Moorish) influence is seen in the geometrical figures on the pillars; the Churrigueresque characterizes much of the ornate decoration, especially in the interior walls; finally the Neoclassical style adorns the Chapel of Saint Mariana de Jesús (in early years a winery).
Mexico
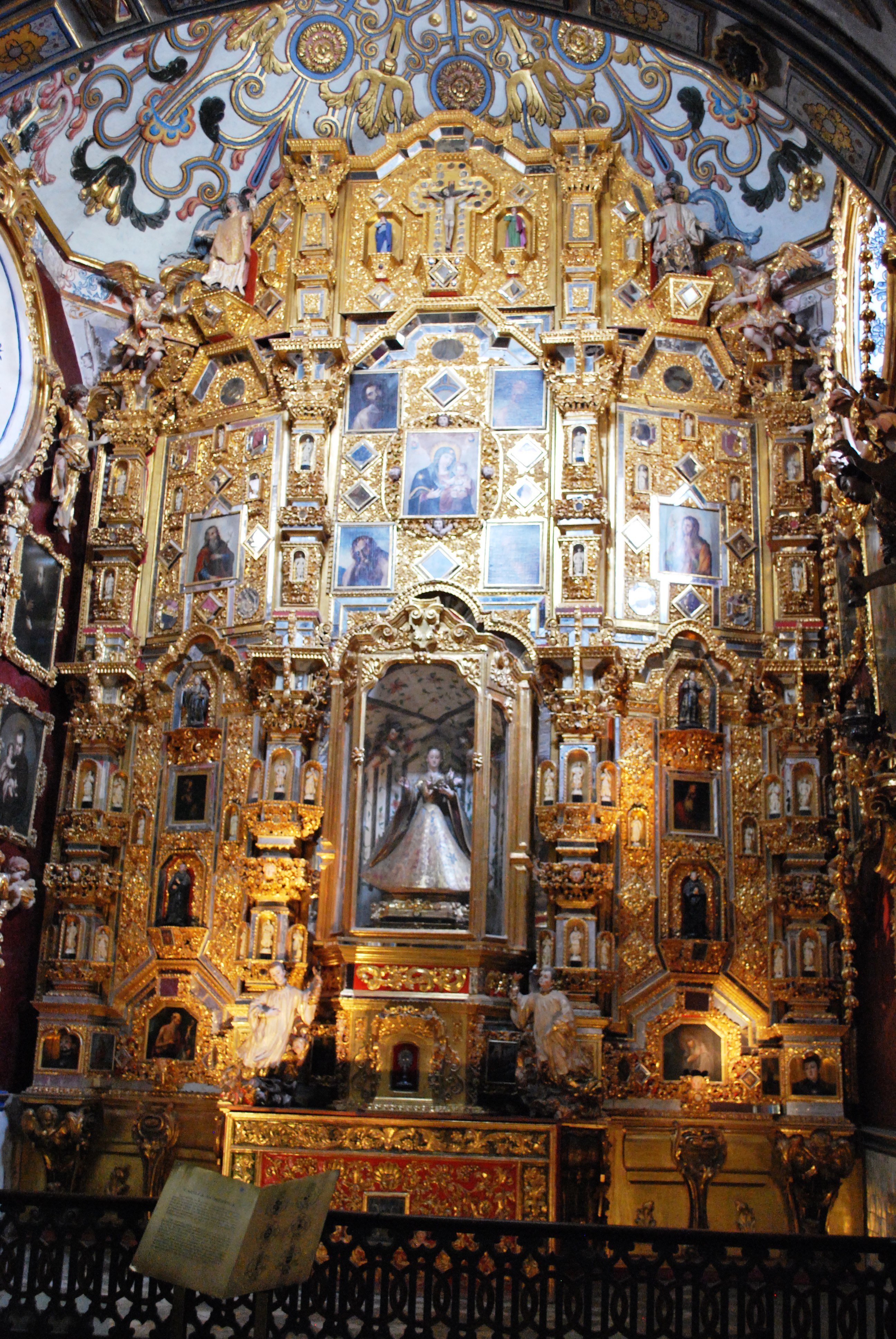
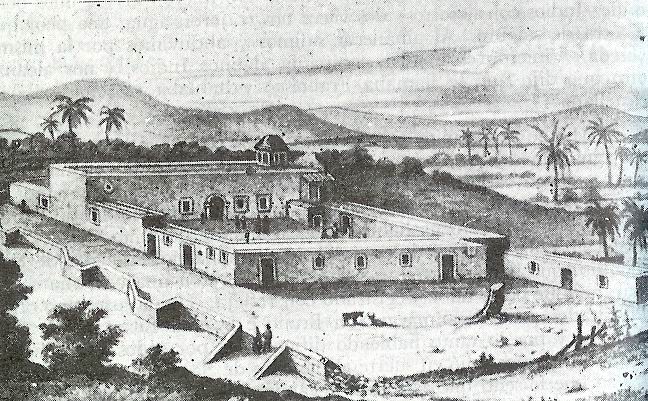


The Jesuits in New Spain distinguished themselves in several ways. They had high standards for acceptance to the order and many years of training. They attracted the patronage of elite families whose sons they educated in rigorous newly founded Jesuit ("colleges"), including San Pedro y San Pablo College (Museum of Light), Colegio de San Pedro y San Pablo, San Ildefonso College, Colegio de San Ildefonso, and the Museo Nacional del Virreinato, Colegio de San Francisco Javier, Tepozotlan. Those same elite families hoped that a son with a vocation to the priesthood would be accepted as a Jesuit. Jesuits were also zealous in evangelization of the indigenous, particularly on the northern frontiers.
To support their and members of the Society of Jesus, the Jesuits acquired landed estates that were run with the best-practices for generating income in that era. A number of these haciendas were donated by wealthy
elites. The donation of a hacienda to the Jesuits was the spark igniting a conflict between 17th-century bishop of Puebla Juan de Palafox y Mendoza, Don Juan de Palafox and the Jesuit colegio in that city. Since the Jesuits resisted paying the tithe on their estates, this donation effectively took revenue out of the church hierarchy's pockets by removing it from the tithe rolls.
Many of Jesuit haciendas were huge, with Palafox asserting that just two colleges owned 300,000 head of sheep, whose wool was transformed locally in Puebla to cloth; six sugar plantations worth a million pesos and generating an income of 100,000 pesos. The immense Jesuit hacienda of Santa Lucía produced , the fermented juice of the agave cactus whose main consumers were the lower classes and indigenous peoples in Spanish cities. Although most haciendas had a free work force of permanent or seasonal labourers, the Jesuit haciendas in Mexico had a significant number of black slaves.
The Jesuits operated their properties as an integrated unit with the larger Jesuit order; thus revenues from haciendas funded their . Jesuits did significantly expand missions to the indigenous in the northern frontier area and a number were martyred, but the crown supported those missions. Mendicant orders that had real estate were less economically integrated, so that some individual houses were wealthy while others struggled economically. The Franciscans, who were founded as an order embracing poverty, did not accumulate real estate, unlike the Augustinians and Dominicans in Mexico.
The Jesuits engaged in conflict with the episcopal hierarchy over the question of payment of tithes, the ten percent tax on agriculture levied on landed estates for support of the church hierarchy from bishops and cathedral chapters to parish priests. Since the Jesuits were the largest religious order holding real estate, surpassing the Dominicans and Augustinians who had accumulated significant property, this was no small matter. They argued that they were exempt, due to special pontifical privileges. In the mid-17th century, bishop of Puebla, Don Juan de Palafox took on the Jesuits over this matter and was so soundly defeated that he was recalled to Spain, where he became the bishop of the minor diocese of Osma.
As elsewhere in the Spanish empire, the Jesuits were expelled from Mexico in 1767. Their haciendas were sold off and their colegios and Spanish missions in Baja California, missions in Baja California were taken over by other orders. Exiled Mexican-born Jesuit Francisco Javier Clavijero wrote an important history of Mexico while in Italy, a basis for creole patriotism. Andrés Cavo also wrote an important text on Mexican history that Carlos María de Bustamante published in the early nineteenth-century. An earlier Jesuit who wrote about the history of Mexico was Diego Luis de Motezuma (1619–99), a descendant of the Aztec monarchs of Tenochtitlan. Motezuma's was completed in 1696. He "aimed to show that Mexican emperors were a legitimate dynasty in the 17th-century in the European sense".
The Jesuits were allowed to return to Mexico in 1840 when General Antonio López de Santa Anna was once more president of Mexico. Their re-introduction to Mexico was "to assist in the education of the poorer classes and much of their property was restored to them".
Northern Spanish America

The Jesuits arrived in the Viceroyalty of Peru by 1571; it was a key area of the Spanish empire, with not only dense indigenous populations but also huge deposits of silver at Potosí. A major figure in the first wave of Jesuits was
José de Acosta
José de Acosta (1539 or 1540 in Medina del Campo, Spain – February 15, 1600 in Salamanca, Spain) was a sixteenth-century Spanish Jesuit missionary and naturalist in Latin America. His deductions regarding the ill effects of crossing over t ...
(1540–1600), whose book (1590) introduced Europeans to Spain's American empire via fluid prose and keen observation and explanation, based on 15 years in Peru and some time in New Spain (Mexico). Viceroy of Peru Francisco de Toledo, Don Francisco de Toledo urged the Jesuits to evangelize the indigenous peoples of Peru, wanting to put them in charge of parishes, but Acosta adhered to the Jesuit position that they were not subject to the jurisdiction of bishops and to catechize in indigenous parishes would bring them into conflict with the bishops. For that reason, the Jesuits in Peru focused on education of elite men rather than the indigenous populations.

To minister to newly arrived African slaves, Alonso de Sandoval (1576–1651) worked at the port of Cartagena de Indias. Sandoval wrote about this ministry in (1627), describing how he and his assistant Peter Claver, Pedro Claver, later canonized, met slave transport ships in the harbour, went below decks where 300–600 slaves were chained, and gave physical aid with water, while introducing the Africans to Christianity. In his treatise, he did not condemn slavery or the ill-treatment of slaves, but sought to instruct fellow Jesuits to this ministry and describe how he catechized the slaves.
Rafael Ferrer (Jesuit), Rafael Ferrer was the first Jesuit of Quito to explore and found missions in the upper Amazon River, Amazon regions of South America from 1602 to 1610, which belonged to the Audiencia Real, Audiencia (high court) of Quito that was a part of the Viceroyalty of Peru until it was transferred to the newly created Viceroyalty of New Granada in 1717. In 1602, Ferrer began to explore the Aguarico, Napo, and Marañon rivers (Sucumbios region, in what is today Ecuador and Peru), and between 1604 and 1605 set up missions among the Cofane natives. He was martyred by an apostate native in 1610.
In 1639, the Audiencia of Quito organized an expedition to renew its exploration of the Amazon river and the Quito Jesuit (Jesuita Quiteño) Cristóbal de Acuña was a part of this expedition. The expedition disembarked from the Napo river 16 February 1639 and arrived in what is today Pará Brazil on the banks of the Amazon river on 12 December 1639. In 1641, Acuña published in Madrid a memoir of his expedition to the Amazon river entitled , which for academics became a fundamental reference on the Amazon region.
In 1637, the Jesuits Gaspar Cugia and Lucas de la Cueva from Quito began establishing the Mainas missions in territories on the banks of the Marañón River, around the Pongo de Manseriche region, close to the Spanish settlement of Borja, Peru, Borja. Between 1637 and 1652 there were 14 missions established along the Marañón River and its southern tributaries, the Huallaga River, Huallaga and the Ucayali River, Ucayali rivers. Jesuit Lucas de la Cueva and Raimundo de Santacruz opened up two new routes of communication with Quito, through the Pastaza River, Pastaza and Napo River, Napo rivers.
Between 1637 and 1715, Samuel Fritz founded 38 missions along the length of the Amazon river, between the Napo and Negro rivers, that were called the Omagua Missions. These missions were continually attacked by the Brazilian Bandeirantes beginning in the year 1705. In 1768, the only Omagua mission that was left was San Joaquin de Omaguas, since it had been moved to a new location on the Napo river away from the Bandeirantes.
In the immense territory of Maynas, the Jesuits of Quito made contact with a number of indigenous tribes which spoke 40 different languages, and founded a total of 173 Jesuit missions encompassing 150,000 inhabitants. Because of the constant epidemics (smallpox and measles) and warfare with other tribes and the Bandeirantes, the total number of Jesuit Missions were reduced to 40 by 1744. The Jesuit missions offered the indigenous people Christianity, iron tools, and a small degree of protection from the slavers and the colonists. In exchange, the indigenous had to submit to Jesuit discipline and adopt, at least superficially, a life style foreign to their experience. The population of the missions was only sustained by frequent expeditions into the jungle by Jesuits, soldiers, and Christian Indians to capture indigenous people and force them to return or to settle in the missions. At the time when the Jesuits were expelled from Spanish America in 1767, the Jesuits of Quito registered 36 missions run by 25 Jesuits of Quito in the Audiencia of Quito – 6 in the Napo and Aguarico Missions and 19 in the Pastaza and Iquitos Missions, with the population at 20,000 inhabitants.
Paraguay
The Guaraní people of eastern Paraguay and neighboring Brazil and Argentina were in crisis in the early 17th century. Recurrent epidemics of European diseases had reduced their population by up 50 percent and the forced labor of the encomiendas by the Spanish and mestizo colonists had made virtual slaves of many. Franciscan missionaries began establishing missions called reductions in the 1580s.
The first Jesuits arrived in Asunción in 1588 and founded their first mission (or reduction) of San Ignacio, Paraguay, San Ignacio Guazú in 1609. The objectives of the Jesuits were to make Christians of the Guaraní, impose European values and customs (which were regarded as essential to a Christian life), and isolate and protect the Guaraní from European colonists and slavers. "
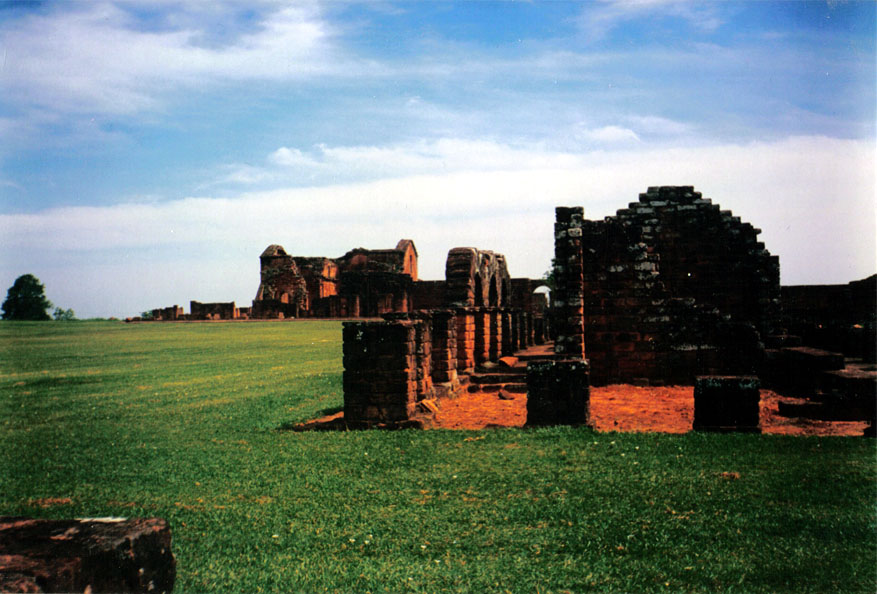

In addition to recurrent epidemics, the Guaraní were threatened by the slave-raiding Bandeirantes from Brazil, who captured natives and sold them as slaves to work in sugar plantations or as concubines and household servants. Having depleted native populations near São Paulo, they discovered the richly populated Jesuit missions. Initially, the missions had few defenses against the slavers and thousands of Guaraní were captured and enslaved. Beginning in 1631, the Jesuits moved their missions from the Guayrá province (present day Brazil and Paraguay), about southwest to the three borders region of Paraguay, Argentina, and Brazil. About 10,000 of 30,000 Guaraní in the missions chose to accompany the Jesuits. In 1641 and 1642, armed by the Jesuits, Guaraní armies defeated the Bandeirantes and ended the worst of the slave trade in their region. From this point on the Jesuit missions enjoyed growth and prosperity, punctuated by epidemics. At the peak of their importance in 1732, the Jesuits presided over 141,000 Guaraní (including a sprinkling of other peoples) who lived in about 30 missions.
The opinions of historians differ with regard to the Jesuit missions. The missions are much-romanticized with the Guaraní portrayed as innocent children of nature and the Jesuits as their wise and benevolent guides to an earthly utopia. "Proponents...highlight that the Jesuits protected the Indians from exploitation and preserved the Guaraní language and other aspects of indigenous culture." "By means of religion," wrote the 18th century philosopher d'Alembert, "the Jesuits established a monarchical authority in Paraguay, founded solely on their powers of persuasion and on their lenient methods of government. Masters of the country, they rendered happy the people under their sway." Voltaire called the Jesuit missions "a triumph of humanity".
To the contrary the detractors say that 'the Jesuits took away the Indians' freedom, forced them to radically change their lifestyle, physically abused them, and subjected them to disease." Moreover, the missions were inefficient and their economic success "depended on subsidies from the Jesuit order, special protection and privileges from the Crown, and the lack of competition" The Jesuits are portrayed as "exploiters" who "sought to create a kingdom independent of the Spanish and Portuguese Crowns."
The Revolt of the Comuneros (Paraguay), Comunero Revolt (1721 to 1735) was a serious protest by Spanish and mestizo Paraguayans against the Jesuit missions. The residents of Paraguay violently protested the pro-Jesuit government of Paraguay, Jesuit control of Guaraní labor, and what they regarded as unfair competition for the market for products such as yerba mate. Although the revolt ultimately failed and the missions remained intact, the Jesuits were expelled from institutions they had created in Asunción.
In 1756, the Guaraní protested the relocation of seven missions, fighting (and losing) a brief war with both the Spanish and Portuguese. The Jesuits were accused of inciting the Guaraní to rebel. In 1767, Charles III of Spain (1759–88) expelled the Jesuits from the Americas. The expulsion was part of an effort in the Bourbon Reforms to assert more Spanish control over its American colonies.
[ Edited by Michael Meyer and William Beezley.] In total, 78 Jesuits departed from the missions leaving behind 89,000 Guaraní in 30 missions.
Colonial Brazil


Tomé de Sousa, first Governorate General of Brazil, Governor General of Brazil, brought the first group of Jesuits to the colony. The Jesuits were officially supported by the King, who instructed Tomé de Sousa to give them all the support needed to Christianize the indigenous peoples.
The first Jesuits, guided by Manuel da Nóbrega, Juan de Azpilcueta Navarro, Leonardo Nunes, and later José de Anchieta, established the first Jesuit missions in Salvador and in São Paulo dos Campos de Piratininga, the settlement that gave rise to the city of São Paulo. Nóbrega and Anchieta were instrumental in the defeat of the French colonists of France Antarctique by managing to pacify the Tamoio natives, who had previously fought the Portuguese. The Jesuits took part in the foundation of the city of Rio de Janeiro in 1565.
The success of the Jesuits in converting the indigenous peoples is linked to their efforts to understand the native cultures, especially their languages. The first grammar of the Tupian languages, Tupi language was compiled by José de Anchieta and printed in Coimbra in 1595. The Jesuits often gathered the aborigines in communities (the Jesuit Reductions) where the natives worked for the community and were evangelised.
The Jesuits had frequent disputes with other colonists who wanted to enslave the natives. The action of the Jesuits saved many natives from being enslaved by Europeans, but also disturbed their ancestral way of life and inadvertently helped spread infectious diseases against which the aborigines had no natural defenses. Slave labor and trade were essential for the economy of Brazil and other American colonies, and the Jesuits usually did not object to the enslavement of African peoples, but rather critiqued the conditions of slavery. In cases where individual Jesuit priests criticised the institution of African slavery, they were censored and sent back to Europe.
Suppression and restoration
The Suppression of the Jesuits in Portugal, France, the Two Sicilies, Duchy of Parma, Parma, and the Spanish Empire by 1767 was deeply troubling to Pope Clement XIII, the society's defender. On 21 July 1773 his successor, Pope Clement XIV, issued the papal brief , decreeing:
The suppression was carried out on political grounds in all countries except Prussia for a time, and Russia, where Catherine the Great had forbidden its promulgation. Because millions of Catholics (including many Jesuits) lived in First Partition of Poland, the Polish provinces recently part-annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia, the Society was able to maintain its continuity and carry on its work all through the stormy period of suppression. Subsequently, Pope Pius VI granted formal permission for the continuation of the society in Russia and Poland, with Stanislaus Czerniewicz, Stanisław Czerniewicz elected superior of the province in 1782. He was followed by Gabriel Lenkiewicz, Franciszek Kareu and Gabriel Gruber until 1805, all elected locally as Temporary Vicars General. Pope Pius VII had resolved during his captivity in France to restore the Jesuits universally, and on his return to Rome he did so without much delay. On 7 August 1814, with the bull , he reversed the suppression of the society, and therewith another Polish Jesuit, Tadeusz Brzozowski, who had been elected as Superior in Russia in 1805, acquired universal jurisdiction. On his death in 1820 the Jesuits were expelled from Russia by tsar Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I.
The period following the Restoration of the Jesuits in 1814 was marked by tremendous growth, as evidenced by the large number of Jesuit colleges and universities established during the 19th century. During this time in the United States, 22 of the society's 28 universities were founded or taken over by the Jesuits. It has been suggested that the experience of suppression had served to heighten orthodoxy among the Jesuits. While this claim is debatable, Jesuits were generally supportive of papal authority within the church, and some members became associated with the Ultramontanist movement and the declaration of Papal Infallibility in 1870.
[Hasler, A. B., (1981) ''How the Pope Became Infallible: Pius IX and the Politics of Persuasion'' (Doubleday; Garden City, NY), p. 58]
In Switzerland, the Swiss Federal Constitution, constitution was modified and Jesuits were banished in 1848, following the defeat of the Sonderbund Catholic defence alliance. The ban was lifted on 20 May 1973, when 54.9 per cent of voters accepted a referendum modifying the Constitution.
Early 20th century
In the Constitution of Norway from 1814, a relic from the earlier anti-Catholic laws of Denmark–Norway, Paragraph 2, known as the Jesuit clause, originally read: "The Evangelical-Lutheran religion remains the public religion of the State. Those inhabitants, who confess thereto, are bound to raise their children to the same. Jesuits and monastic orders are not permitted. Jews are still prohibited from entry to the Realm." Jews were first allowed into the realm in 1851 after the famous Norwegian poet Henrik Wergeland had campaigned for it. Monastic orders were permitted in 1897, but the ban on Jesuits was only lifted in 1956.
Republican Spain in the 1930s passed laws banning the Jesuits on grounds that they were obedient to a power different from the state. Pope Pius XI wrote about this: "It was an expression of a soul deeply hostile to God and the Catholic religion, to have disbanded the Religious Orders that had taken a vow of obedience to an authority different from the legitimate authority of the State. In this way it was sought to do away with the Society of Jesus – which can well glory in being one of the soundest auxiliaries of the ''Chair of Saint Peter'' – with the hope, perhaps, of then being able with less difficulty to overthrow in the near future, the Christian faith and morale in the heart of the Spanish nation, which gave to the Church of God the grand and glorious figure of Ignatius Loyola."
Post-Vatican II
The 20th century witnessed both growth and decline of the order. Following a trend within the Catholic priesthood at large, Jesuit numbers peaked in the 1950s and have declined steadily since. Meanwhile, the number of Jesuit institutions has grown considerably, due in large part to a post–Vatican II focus on the establishment of Jesuit secondary schools in inner-city areas and an increase in voluntary lay groups inspired in part by the Spiritual Exercises of Ignatius of Loyola, ''Spiritual Exercises''. Among the notable Jesuits of the 20th century, John Courtney Murray was called one of the "architects of the
Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
" and drafted what eventually became the council's endorsement of religious freedom, .
In Latin America, the Jesuits had significant influence in the development of liberation theology, a movement that was controversial in the Catholic community after the negative assessment of it by Pope John Paul II in 1984.
Under Superior General Pedro Arrupe, social justice and the preferential option for the poor emerged as dominant themes of the work of the Jesuits. When Arrupe was paralyzed by a stroke in 1981, Pope John Paul II, not entirely pleased with the progressive turn of the Jesuits, took the unusual step of appointing the venerable and aged Paolo Dezza for an interim to oversee "the authentic renewal of the Church", instead of the progressive American priest Vincent O'Keefe whom Arrupe had preferred. In 1983 John Paul gave leave for the Jesuits to appoint a Peter Hans Kolvenbach, successor to Arrupe.
On 16 November 1989, six Jesuit priests (Ignacio Ellacuría, Segundo Montes, Ignacio Martín-Baró, Joaquin López y López, Juan Ramon Moreno, and Amado López), Elba Ramos their housekeeper, and Celia Marisela Ramos her daughter, were murdered by the El Salvador, Salvadoran military on the campus of the University of Central America in San Salvador, El Salvador, because they had been labeled as subversives by the government. The assassinations galvanized the society's peace and justice movements, including annual protests at the Western Hemisphere Institute for Security Cooperation at Fort Benning, Georgia, Fort Benning, Georgia, United States, where several of the assassins had been trained under US government sponsorship.
On 21 February 2001, the Jesuit priest Avery Dulles, an internationally known author, lecturer, and theologian, was created a cardinal of the Catholic Church by Pope John Paul II. The son of former Secretary of State John Foster Dulles, Avery Dulles was long known for his carefully reasoned argumentation and fidelity to the teaching office of the church. An author of 22 books and over 700 theological articles, Dulles died on 12 December 2008 at Fordham University, where he had taught for twenty years as the Laurence J. McGinley Professor of Religion and Society. He was, at his passing, one of ten Jesuit cardinals in the Catholic Church.
In 2002,
Boston College
Boston College (BC) is a private Jesuit research university in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts. Founded in 1863, the university has more than 9,300 full-time undergraduates and nearly 5,000 graduate students. Although Boston College is classified ...
president and Jesuit priest William P. Leahy initiated the Church in the 21st Century program as a means of moving the church "from crisis to renewal". The initiative has provided the society with a platform for examining issues brought about by the worldwide Catholic sex abuse cases, including the priesthood, celibacy, Human sexuality, sexuality, women's roles, and the role of the laity.

In April 2005, Thomas J. Reese, editor of the American Jesuit weekly magazine '' America (Jesuit magazine), America'', resigned at the request of the society. The move was widely published in the media as the result of pressure from the Vatican, following years of criticism by the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith on articles touching subjects such as AIDS, HIV/AIDS, religious pluralism, Catholic Church and homosexuality, homosexuality, and the right of life for the unborn. Following his resignation, Reese spent a year-long sabbatical at Santa Clara University before being named a fellow at the Woodstock Theological Center in Washington, D.C., and later Senior Analyst for the ''National Catholic Reporter''. President Barack Obama appointed him to the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom in 2014 and again in 2016.
On 2 February 2006, Peter Hans Kolvenbach informed members of the Society of Jesus that, with the consent of Pope Benedict XVI, he intended to step down as Superior General in 2008, the year he would turn 80.
On 22 April 2006, Feast of Our Lady, Mother of the Society of Jesus, Pope Benedict XVI greeted thousands of Jesuits on Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage to Rome, and took the opportunity to thank God "for having granted to your Company the gift of men of extraordinary sanctity and of exceptional apostolic zeal such as St Ignatius of Loyola, St Francis Xavier, and Beatification, Bl
Peter Faber
Peter Faber (french: Pierre Lefevre or Favre, la, Petrus Faver) (13 April 1506 – 1 August 1546) was a Jesuit priest and theologian, who was also a co-founder of the Society of Jesus, along with Ignatius of Loyola and Francis Xavier. Pope Fra ...
". He said "St Ignatius of Loyola was above all a man of God, who gave the first place of his life to God, to his greater glory and his greater service. He was a man of profound prayer, which found its center and its culmination in the daily Eucharistic Celebration."
In May 2006, Benedict XVI also wrote a letter to Superior General Peter Hans Kolvenbach on the occasion of the 50th anniversary of Pope Pius XII's encyclical , on devotion to the Sacred Heart, because the Jesuits have always been "extremely active in the promotion of this essential devotion".
In his 3 November 2006 visit to the Pontifical Gregorian University, Benedict XVI cited the university as "one of the greatest services that the Society of Jesus carries out for the universal Church".
The 35th General Congregation of the Society of Jesus convened on 5 January 2008 and elected Adolfo Nicolás as the new Superior General on 19 January 2008. In a letter to the Fathers of the Congregation, Benedict XVI wrote:

In 2013, Jesuit Cardinal Jorge Bergoglio became Pope Francis. Before he became pope, he was appointed bishop when he was in "virtual estrangement from the Jesuits" since he was seen as "an enemy of liberation theology" and viewed by others as "still far too orthodox". He was criticised for colluding with the National Reorganization Process, Argentine junta, while biographers characterised him as working to save the lives of other Jesuits.
As a Jesuit pope, he has been stressing discernment over following rules, changing the culture of the clergy to steer away from clericalism and to move toward an ethic of service, i.e to have the "smell of sheep," staying close to the people. After his papal election, the Superior General of the Jesuits Adolfo Nicolás praised Pope Francis as a "brother among brothers".
On 2 October 2016, General Congregation 36 convened in Rome, convoked by Superior General Adolfo Nicolás, who had announced his intention to resign at age 80. On 14 October, the 36th General Congregation of the Society of Jesus elected
Arturo Sosa
Arturo Marcelino Sosa Abascal (born 12 November 1948) is a Venezuelan Catholic priest who serves as the 31st and present superior general of the Society of Jesus. He was elected Superior General by the Society's 36th General Congregation on ...
, a Venezuelan, as its thirty-first Superior General.
The General Congregation of Jesuits who elected Arturo Sosa in 2016 asked him to bring to completion the process of discerning Jesuit priorities for the time ahead. Sosa devised a plan that enlisted all Jesuits and their lay collaborators in the process of discernment over a 16-month period. Then in February 2019 he presented the results of the discernment, a list of four priorities for Jesuit ministries for the next ten years.
Pope Francis gave his approval to these priorities, saying that they were in harmony with the church's present priorities and with the programmatic letter of his pontificate, .
Ignatian spirituality
The spirituality practiced by the Jesuits, called Ignatian spirituality, ultimately based on the Catholic faith and the gospels, is drawn from the ''Constitutions'', ''The Letters'', and ''Autobiography'', and most specially from Ignatius' ''
Spiritual Exercises'', whose purpose is "to conquer oneself and to regulate one's life in such a way that no decision is made under the influence of any inordinate attachment". The ''Exercises'' culminate in a Christian contemplation#Acquired contemplation, contemplation whereby one develops a facility to "find God in all things".
Formation
The formation (training) of Jesuits seeks to prepare men spiritually, academically, and practically for the ministries they will be called to offer the church and world. Ignatius was strongly influenced by the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
, and he wanted Jesuits to be able to offer whatever ministries were most needed at any given moment and, especially, to be ready to respond to missions (assignments) from the pope. Formation for priesthood normally takes between eight and fourteen years, depending on the man's background and previous education, and final vows are taken several years after that, making Jesuit formation among the longest of any of the religious orders.
Governance of the society
The society is headed by a
Superior General
A superior general or general superior is the leader or head of a religious institute in the Catholic Church and some other Christian denominations. The superior general usually holds supreme executive authority in the religious community, while t ...
with the formal title ''Praepositus Generalis'', Latin for "provost-general", more commonly called Father General. He is elected by the General Congregation for life or until he resigns; he is confirmed by the pope and has absolute authority in running the Society. The current Superior General of the Jesuits is the Venezuelan
Arturo Sosa
Arturo Marcelino Sosa Abascal (born 12 November 1948) is a Venezuelan Catholic priest who serves as the 31st and present superior general of the Society of Jesus. He was elected Superior General by the Society's 36th General Congregation on ...
who was elected on 14 October 2016.
The Father General is assisted by "assistants", four of whom are "assistants for provident care" and serve as general advisors and a sort of inner council, and several other regional assistants, each of whom heads an "assistancy", which is either a geographic area (for instance the North American Assistancy) or an area of ministry (for instance higher education). The assistants normally reside with Father General in Rome and along with others form an advisory council to the General. A vicar general and secretary of the society run day-to-day administration. The General is also required to have an admonitor, a confidential advisor whose task is to warn the General honestly and confidentially when he might be acting imprudently or contrary to the church's magisterium. The central staff of the General is known as the Curia.
The society is divided into geographic areas called provinces, each of which is headed by a Provincial Superior, formally called Father Provincial, chosen by the Superior General. He has authority over all Jesuits and ministries in his area, and is assisted by a ''socius'' who acts as a sort of secretary and chief of staff. With the approval of the Superior General, the Provincial Superior appoints a novice master and a master of tertians to oversee formation, and rectors of local communities of Jesuits. For better cooperation and apostolic efficacy in each continent, the Jesuit provinces are grouped into six Jesuit Conferences worldwide.
Each Jesuit community within a province is normally headed by a rector who is assisted by a "minister", from the Latin word for "servant", a priest who helps oversee the community's day-to-day needs.
The General Congregation is a meeting of all of the assistants, provincials, and additional representatives who are elected by the professed Jesuits of each province. It meets irregularly and rarely, normally to elect a new superior general and/or to take up some major policy issues for the Order. The Superior General meets more regularly with smaller councils composed of just the provincials.
Statistics
, the Jesuits formed the largest single
religious order
A religious order is a lineage of communities and organizations of people who live in some way set apart from society in accordance with their specific religious devotion, usually characterized by the principles of its founder's religious pract ...
of priests and brothers in the Catholic Church. The Jesuits have experienced a decline in numbers in recent decades. As of 2020, the society had 14,839 members (10,721 priests and 4110 other Jesuits which includes brothers and scholastics). This represents a 59% percent decline since the Second Vatican Council (1965), when the society had a total membership of 36,038, of which 20,301 were priests. This decline is most pronounced in Europe and the Americas, with relatively modest membership gains occurring in Asia and Africa. According to Patrick Reilly of the ''National Catholic Register'', there seems to be no "Pope Francis effect" in counteracting the fall of vocations among the Jesuits. Twenty-eight novices took first vows in the Jesuits in the United States and Haiti in 2019. In September 2019, the superior general of the Jesuits,
Arturo Sosa
Arturo Marcelino Sosa Abascal (born 12 November 1948) is a Venezuelan Catholic priest who serves as the 31st and present superior general of the Society of Jesus. He was elected Superior General by the Society's 36th General Congregation on ...
, estimated that by 2034 the number would decrease to about 10,000 Jesuits, with a much younger average age than in 2019, and with a shift away from Europe and into Latin America, Africa, and India.
The society is divided into 83 provinces along with six independent regions and ten dependent regions.
On 1 January 2007, members served in 112 nations on six continents with the largest number in India and the US. Their average age was 57.3 years: 63.4 years for priests, 29.9 years for scholastics, and 65.5 years for brothers.
The current
Superior General
A superior general or general superior is the leader or head of a religious institute in the Catholic Church and some other Christian denominations. The superior general usually holds supreme executive authority in the religious community, while t ...
of the Jesuits is
Arturo Sosa
Arturo Marcelino Sosa Abascal (born 12 November 1948) is a Venezuelan Catholic priest who serves as the 31st and present superior general of the Society of Jesus. He was elected Superior General by the Society's 36th General Congregation on ...
. The society is characterized by its ministries in the fields of missionary work, human rights, social justice and, most notably, higher education. It operates colleges and universities in various countries around the world and is particularly active in the
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and India. In the United States the Jesuits have historical ties to Association of Jesuit Colleges and Universities, 27 colleges and universities and Jesuit Secondary Education Association, 61 high schools. The degree to which the Jesuits are involved in the administration of each institution varies. As of September 2018, 15 of the 27 Jesuit universities in the US had non-Jesuit lay presidents. According to a 2014 article in ''The Atlantic'', "the number of Jesuit priests who are active in everyday operations at the schools isn't nearly as high as it once was". Worldwide it runs 322 secondary schools and 172 colleges and University, universities. A typical conception of the mission of a Jesuit school will often contain such concepts as proposing Christ as the model of human life, the pursuit of excellence in teaching and learning, lifelong spiritual and intellectual growth, and training men and women for others.
Habit and dress
Jesuits do not have an official habit. The society's ''Constitutions'' gives the following instructions: "The clothing too should have three characteristics: first, it should be proper; second, conformed to the usage of the country of residence; and third, not contradictory to the poverty we profess." (Const. 577)
Historically, a Jesuit-style cassock which the Jesuits call Soutane became "standard issue": it is similar to a robe which is wrapped around the body and was tied with a cincture, rather than the customary buttoned front. A tuftless biretta (only diocesan clergy wore tufts) and a ferraiolo (cape) completed the look.
Today, most Jesuits in the United States wear the clerical collar and black clothing of ordinary priests.
Controversies
Power-seeking
The ''Monita Secreta'' (Secret Instructions of the Jesuits), published in 1612 and in 1614 in Kraków, is alleged to have been written by Claudio Acquaviva, the fifth general of the society, but was probably written by former Jesuit Jerome Zahorowski. It purports to describe the methods to be adopted by Jesuits for the acquisition of greater power and influence for the society and for the Catholic Church. The ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' states the book is a forgery, fabricated to ascribe a sinister reputation to the Society of Jesus.
Political intrigue
The Jesuits were temporarily banished from France in 1594 after a man named Jean Châtel tried to assassinate the king of France, Henry IV of France, Henri IV. Under questioning, Châtel revealed that he had been educated by the Jesuits of the Collège de Clermont. The Jesuits were accused of inspiring Châtel's attack. Two of his former teachers were exiled and a third was hanged. The Collège de Clermont was closed, and the building was confiscated. The Jesuits were banned from France, although this ban was quickly lifted.
In England, Henry Garnet, one of the leading English Jesuits, was hanged for misprision of treason because of his knowledge of the Gunpowder Plot (1605). The Plot was the attempted assassination of James VI and I, his family, and most of the Protestantism, Protestant aristocracy in a single attack, by exploding the Palace of Westminster, Houses of Parliament. Another Jesuit, Oswald Tesimond, managed to escape arrest for his involvement in this plot.
Casuistic justification
Jesuits have been accused of using casuistry to obtain justifications for unjustifiable actions (cf. formulary controversy and ''Lettres Provinciales'', by Blaise Pascal). Hence, the Concise Oxford Dictionary, Concise Oxford Dictionary of the English language lists "equivocating" as a secondary denotation of the word "Jesuit". Modern critics of the Society of Jesus include Avro Manhattan, Alberto Rivera (activist), Alberto Rivera, and Malachi Martin, the latter being the author of ''The Jesuits: The Society of Jesus and the Betrayal of the Roman Catholic Church'' (1987).
Exclusion of those of Jewish or Muslim ancestry
Although in the first 30 years of the existence of the Society of Jesus there were many Jesuits who were ''conversos'' (Catholic-convert Jews), an anti-''converso'' faction led to the ''Decree de genere'' (1593) which proclaimed that either Jewish or Muslim ancestry, no matter how distant, was an insurmountable impediment for admission to the Society of Jesus. This new rule was contrary to the original wishes of Ignatius who "said that he would take it as a special grace from our Lord to come from Jewish lineage". The 16th-century ''Decree de genere'' was repealed in 1946.
Theological debates
Within the Catholic Church, there has existed a sometimes tense relationship between Jesuits and the Holy See, due to questioning of official church teaching and papal directives, such as those on abortion, birth control, Catholic Church doctrine on the ordination of women#Deaconesses and female deacons, women deacons, homosexuality, and liberation theology. At the same time, Jesuits have been appointed to prominent doctrinal and theological positions in the church; under Pope Benedict XVI, Archbishop Luis Ladaria Ferrer was Secretary of the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith who is now, under Pope Francis, the Prefect of this Congregation.
Religious persecution
In the quest to evangelize, Jesuits persecuted people of other religions, including Hindus, Muslims and other Christians. The Goa Inquisition, Goan Inquisition was one among various persecutions that Jesuits were involved in. Voltaire wrote about the Goan Inquisition:
Nazi persecution
The Catholic Church faced Nazi persecution of the Catholic Church, persecution in Nazi Germany. Hitler was anticlerical and had particular disdain for the Jesuits. According to John Pollard, the Jesuits' "ethos represented the most intransigent opposition to the philosophy of Nazism", and so the Nazis considered them as one of their most dangerous enemies. A Jesuit college in the city of Innsbruck served as a center for anti-Nazi resistance and was closed down by the Nazis in 1938. Jesuits were a target for Gestapo persecution, and many Jesuit priests were deported to death camps. Jesuits made up the largest contingent of clergy imprisoned in the Priest Barracks of Dachau Concentration Camp. Vincent Lapomarda lists some 30 Jesuits as having died at Dachau. Of the total of 152 Jesuits murdered by the Nazis across Europe, 43 died in the death camps and an additional 27 died from captivity or its results.
The Superior General of Jesuits at the outbreak of war was Wlodzimierz Ledóchowski, a Pole. The Nazi persecution of the Catholic Church in Poland was particularly severe. Lapomarda wrote that Ledóchowski helped "stiffen the general attitude of the Jesuits against the Nazis" and that he permitted Vatican Radio to carry on its campaign against the Nazis in Poland. Vatican Radio was run by the Jesuit Filippo Soccorsi and spoke out against Nazi oppression, particularly with regard to Poland and to Vichy-French anti-Semitism.

Several Jesuits were prominent in the small German resistance to Nazism, German Resistance. Among the central membership of the Kreisau Circle of the Resistance were the Jesuit priests Augustin Rösch, Alfred Delp, and Lothar König. The Bavarian Jesuit Provincial, Augustin Rosch, ended the war on death row for his role in the July Plot to overthrow Hitler. Another non-military German Resistance group, dubbed the Solf Circle, "Frau Solf Tea Party" by the Gestapo, included the Jesuit priest Friedrich Erxleben. The German Jesuit Robert Leiber acted as intermediary between Pius XII and the German Resistance.
[:de:Peter Hoffmann (Historiker, 1930), Peter Hoffmann; ''The History of the German Resistance 1933–1945''; 3rd Edn (First English Edn); McDonald & Jane's; London; 1977; p. 160]
Among the Jesuit victims of the Nazis, Germany's Rupert Mayer has been beatified. Mayer was a Bavarian Jesuit who clashed with the Nazis as early as 1923. Continuing his critique following Hitler's rise to power, Mayer was imprisoned in 1939 and sent to Sachsenhausen concentration camp, Sachsenhausen Extermination camp, death camp. As his health declined, the Nazis feared the creation of a martyr and sent him to the Abbey of Ettal in 1940. There he continued to give sermons and lectures against the evils of the Nazi régime, until his death in 1945.
Rescue efforts during the Holocaust
In his history of the heroes of the Holocaust, the Jewish historian Martin Gilbert notes that in every country under German occupation, priests played a major part in rescuing Jews, and that the Jesuits were one of the Catholic Orders that hid Jewish children in monasteries and schools to protect them from the Nazis.
[Martin Gilbert; ''The Righteous: the Unsung Heroes of the Holocaust''; Holt Paperback; New York; 2004; Preface] Fourteen Jesuit priests have been formally recognized by Yad Vashem, the Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority in Jerusalem, for risking their lives to save Jews during the Holocaust of World War II: Roger Braun (1910–1981) of France, Pierre Chaillet (1900–1972) of France, Jean-Baptist De Coster (Jesuit), Jean-Baptist De Coster (1896–1968) of Belgium, Jean Fleury (1905–1982) of France, Emile Gessler (1891–1958) of Belgium, Jean-Baptiste Janssens (1889–1964) of Belgium, Alphonse Lambrette (1884–1970) of Belgium, Emile Planckaert (1906–2006) of France, Jacob Raile (1894–1949) of Hungary, Henri Revol (1904–1992) of France, Adam Sztark (1907–1942) of Poland, Henri Van Oostayen (1906–1945) of Belgium, Ioannes Marangas (1901–1989) of Greece, and Raffaele de Chantuz Cubbe (1904–1983) of Italy.
Several other Jesuits are known to have rescued or given refuge to Jews during that period. A plaque commemorating the 152 Jesuit priests who gave their lives during the Holocaust was installed in April 2007 at the Jesuits' Rockhurst University in Kansas City, Missouri, United States.
In science

Between the sixteenth and eighteenth centuries, the teaching of science in Jesuit schools, as laid down in the
Ratio atque Institutio Studiorum Societatis Iesu' ("The Official Plan of studies for the Society of Jesus") of 1599, was almost entirely based on the works of Aristotle.
The Jesuits, nevertheless, have made numerous significant contributions to the development of science. For example, the Jesuits have dedicated significant study to fields from cosmology to seismology, the latter of which has been described as "the Jesuit science". The Jesuits have been described as "the single most important contributor to experimental physics in the seventeenth century". According to Jonathan Wright (historian), Jonathan Wright in his book ''God's Soldiers'', by the eighteenth century the Jesuits had "contributed to the development of pendulum clocks, pantographs, barometers, reflecting telescopes and microscopes – to scientific fields as various as magnetism, optics, and electricity. They observed, in some cases before anyone else, the colored bands on Jupiter's surface, the Andromeda Galaxy, Andromeda nebula, and Saturn's rings. They theorized about the circulation of the blood (independently of William Harvey, Harvey), the theoretical possibility of flight, the way the moon affected the tides, and the wave-like nature of light."
The Jesuit China missions of the 16th and 17th centuries introduced Western science and astronomy. One modern historian writes that in late Ming courts, the Jesuits were "regarded as impressive especially for their knowledge of astronomy, calendar-making, mathematics, hydraulics, and geography". The Society of Jesus introduced, according to Thomas Woods, "a substantial body of scientific knowledge and a vast array of mental tools for understanding the physical universe, including the Euclidean geometry that made planetary motion comprehensible".
Notable members
Notable Jesuits include missionaries, educators, scientists, artists, philosophers, and a pope. Among many distinguished early Jesuits was
Francis Xavier
Francis Xavier (born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta; Latin: ''Franciscus Xaverius''; Basque: ''Frantzisko Xabierkoa''; French: ''François Xavier''; Spanish: ''Francisco Javier''; Portuguese: ''Francisco Xavier''; 7 April 15063 December ...
, a missionary to Asia who converted more people to Catholicism than anyone before, and Robert Bellarmine, a Doctor of the Church. José de Anchieta and Manuel da Nóbrega, founders of the city of São Paulo, Brazil, were Jesuit priests. Another famous Jesuit was Jean de Brébeuf, a French missionary who was martyred during the 17th century in what was once New France (now
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
) in Canada.
In Spanish America,
José de Acosta
José de Acosta (1539 or 1540 in Medina del Campo, Spain – February 15, 1600 in Salamanca, Spain) was a sixteenth-century Spanish Jesuit missionary and naturalist in Latin America. His deductions regarding the ill effects of crossing over t ...
wrote a major work on early Peru and New Spain with important material on indigenous peoples. In South America, Peter Claver was notable for his mission to African slaves, building on the work of Alonso de Sandoval. Francisco Javier Clavijero was expelled from New Spain during the Suppression of the Society of Jesus in 1767 and wrote an important history of Mexico during his exile in Italy. Eusebio Kino is renowned in the southwestern United States and northern Mexico (an area then called the Pimería Alta). He founded numerous missions and served as the peace-bringer between the tribes and the government of New Spain. Antonio Ruiz de Montoya was an important missionary in the Jesuit reductions of Paraguay.
Baltasar Gracián was a 17th-century Spanish Jesuit and baroque prose writer and philosopher. He was born in Belmonte de Gracián, Belmonte, near Calatayud (Aragon). His writings, particularly ''El Criticón'' (1651–7) and ''Oráculo Manual y Arte de Prudencia'' ("The Art of Prudence", 1647) were lauded by Arthur Schopenhauer, Schopenhauer and Friedrich Nietzsche, Nietzsche.
In Scotland, John Ogilvie (saint), John Ogilvie, a Jesuit, is the nation's only post-Reformation saint.
Gerard Manley Hopkins was one of the first English poets to use sprung verse. Anthony de Mello was a Jesuit priest and psychotherapist who became widely known for his books which introduced Westerners to the South Asia, East Indian traditions of spirituality.
Cardinal Jorge Bergoglio of Argentina was elected Pope Francis on 13 March 2013 and is the first Jesuit to be elected pope.
The Feast of All Jesuit Saints and Blesseds is celebrated on 5 November.
Gallery: Jesuit churches
File:Church of the Gesù, Rome.jpg, The Church of the Gesù
, image = Church of the Gesù, Rome.jpg
, imagesize =
, caption = Giacomo della Porta's façade, precursor of Baroque
, mapframe = yes
, mapframe-caption = Click on the map for a full ...
in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, is the mother church
Mother church or matrice is a term depicting the Christian Church as a mother in her functions of nourishing and protecting the believer. It may also refer to the primary church of a Christian denomination or diocese, i.e. a cathedral or a metropo ...
of the Jesuits.
File:Iglesia de La Compañía, Quito, Ecuador, 2015-07-22, DD 128-130 HDR.JPG, ''Iglesia de La Compañía'', Quito, Ecuador, interior with gold leaf
File:StPierreParis.jpg, Church of Saint-Pierre de Montmartre, Paris, France
File:Church of the Society of Jesus (Cusco, Peru) 2013-03-31 002.JPG, Church of the Society of Jesus (Cusco, Peru), Jesuit church, Cuzco, Peru
File:Colegio de Belen. Havana, Cuba.jpg, Colegio de Belén, Havana, "The Palace of Education"
File:Ateneo de Naga University Church facade 02.jpg, Christ the King Church in the Ateneo de Naga University campus, Naga City, Philippines
File:Fordham University 08.JPG, Fordham University Church at Rose Hill, Bronx, New York, USA
File:St John, Creighton.jpg, St. John's Church in Creighton University campus, Omaha, Nebraska, USA
File:New Orleans (LA, USA) Holy Name of Jesus Church.jpg, Holy Name of Jesus Church in the Loyola University New Orleans campus, New Orleans Louisiana USA
File:Gesu Church Milwaukee.jpg, The Church of the Gesu in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA, is the school church of Marquette University.
File:XavierRockhurstcut.png, St. Francis Xavier Church, a Jesuit parish church across the street from the Rockhurst University campus, Kansas City, Missouri, USA
File:St. Francis Xavier College Church - St. Louis 01.jpg, St. Francis Xavier College Church in the Saint Louis University campus, St. Louis, Missouri, USA
File:Mission Santa Clara.jpg, The Mission Santa Clara de Asís, Santa Clara University's Mission Church is at the heart of Santa Clara University's historic campus Santa Clara, California, USA.
File:Saint Ignatius Church (San Francisco).jpg, St. Ignatius Church, a Jesuit parish church in the University of San Francisco campus, San Francisco, California, USA
File:Phila ChurchoftheGesu02.jpg, the Church of the Gesu, Philadelphia is the school church of St. Joseph's Preparatory School, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
File:Eglise du Gèsu de Frascati.JPG, The Church of the Gesu in Frascati, province of Rome, Italy
File:Gesu Montreal 01.jpg, The Église du Gesù (Montreal), Église du Gesù in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, church and cultural venue
File:Jakarta Indonesia Jakarta-Cathedral-01.jpg, Jakarta Cathedral, Indonesia
Institutions
Educational institutions
Although the work of the Jesuits today embraces a wide variety of apostolates, ministries, and civil occupations, they are probably most well known for their educational work. Since the inception of the order, Jesuits have been teachers. Besides serving on the faculty of Catholic and secular schools, the Jesuits are the Catholic religious order with the List of Jesuit educational institutions, second highest number of schools which they run: 168 tertiary education, tertiary institutions in 40 countries and 324 secondary schools in 55 countries. (The Brothers of the Christian Schools have over 560 Lasallian educational institutions.) They also run elementary schools at which they are less likely to teach. Many of the schools are List of schools named after Francis Xavier, named after Francis Xavier and other prominent Jesuits.
After the
Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
, Jesuit schools had become a very controversial place of instruction as they abandoned teaching traditional Catholic education with things such as the mastery of
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and the Baltimore Catechism. Jesuit schools replaced classic theological instruction from people like Thomas Aquinas and Bonaventure to people like Karl Rahner and Pierre Teilhard de Chardin which was a very controversial move at the time.
Jesuit educational institutions aim to promote the values of Eloquentia Perfecta. This is a Jesuit tradition that focuses on cultivating a person as a whole, as one learns to speak and write for the common good.
File:AltaGracia.jpg, Jesuit Block and Estancias of Córdoba, Argentina
File:Université de Namur - rue de Bruxelles - 02.jpg, Université de Namur, Belgium
File:Biblioteca Unisinos.jpg, University of the Sinos Valley, Brazil
File:Saint Marys HFX.jpg, Saint Mary's University (Halifax), St. Mary's University, Halifax, Canada
File:Extremo Suroccidental ce la Javeriana cut.png, Pontifical Xavierian University, Pontifical Xaverian University, Bogota, Colombia
File:PUCEEcuador.png, Pontifical Catholic University of Ecuador, Pontifical Catholic University, Ecuador
File:Alte Anatomie Ingolstadt.JPG, University of Ingolstadt, Germany
File:Xaviers college.jpg, St. Xavier's College, Mumbai, St. Xavier's College, Mumbai, India
File:Building4sxc.JPG, St. Xavier's College, Kolkata, St. Xavier's College, Kolkata, India
File:Facciata small.jpg, Pontifical Gregorian University, Rome, Italy
File:Sophia University, Yotsuya Campus, Tokyo, Japan.jpg, Sophia University, Tokyo, Japan
File:Elisabeth University of Music Hiroshima-shi 01.jpg, Elisabeth University of Music, Hiroshima, Japan.
File:USJ Campus.jpg, Saint Joseph University, St. Joseph University, Beirut, Lebanon
File:Universidad del Pacifico plaza.jpg, Universidad del Pacífico (Peru), University of Pacific, Peru
File:WTNaga BAHALANA A2a.JPG, Ateneo de Naga University, Philippines
File:SogangCut.png, Sogang University, Seoul, South Korea
File:Deustuko Unibersitatea cut.jpg, University of Deusto, Bilbao, Spain
File:Universidad Pontificia de Comillas.jpg, Comillas Pontifical University, Spain
File:Keating Hall, Fordham University Rose Hill.jpg, Fordham University, New York City, United States
File:Bellarmine Hall at Fairfield University, CT.jpg, Fairfield University, Bellarmine Hall, Fairfield, Connecticut, United States
File:Sankt Georgen2.jpg, Sankt Georgen Graduate School of Philosophy and Theology, Frankfurt, Germany
File:Georgetown University -23.JPG, Georgetown University, Washington DC, United States
Social and development institutions
Jesuits have become increasingly involved in works directed primarily toward social and economic development for the poor and marginalized. Included in this would be research, training, advocacy, and action for human development, as well as direct services. Most Jesuit schools have an office that fosters social awareness and social service in the classroom and through extracurricular programs, usually detailed on their websites. The Jesuits also run over 500 notable or stand-alone social or economic development centres in 56 countries around the world.
Publications

Jesuits are also known for their involvement in publications. ''La Civiltà Cattolica'', a periodical produced in Rome by the Jesuits, has often been used as a semi-official platform for popes and Vatican officials to float ideas for discussion or hint at future statements or positions. In the United States, ''The Way'' is an international journal of contemporary Christian spirituality published by the British Jesuits. ''America (Jesuit magazine), America'' magazine has long had a prominent place in Catholic intellectual circles Most Jesuit colleges and universities have their own presses which produce a variety of books, book series, textbooks, and academic publications. Ignatius Press, founded by a Jesuit, is an independent publisher of Catholic books, most of which are of the popular academic or lay-intellectual variety. Manresa is a review of Ignatian spirituality published in Madrid, Spain.
In Australia, the Jesuits produce a number of magazines, including ''Eureka Street (magazine), Eureka Street'', ''Madonna'', ''Australian Catholics'', and ''Province Express''.
In Germany, the Jesuits publish ''Geist und Leben.''
In Sweden the Catholic cultural magazine ''Signum'', edited by the Newman Institute, covers a broad spectrum of issues concerning faith, culture, research, and society. The printed version of ''Signum'' is published eight times per year.
See also
* Ad maiorem Dei gloriam
* Apostleship of Prayer
* Blas Valera
* Bollandist
* Canadian Indian residential school system
* Jesuit conspiracy theories
* Jesuit Ivy
* Jesuit missions among the Guaraní
* Jesuit Missions of Chiquitos
* Jesuit Refugee Service
* List of Jesuit sites
* List of saints of the Society of Jesus
* Misiones Province
*Missionaries
* Monumenta Historica Societatis Iesu
* Igreja de São Roque
* Sexual abuse scandal in the Society of Jesus
* Thomas Weld (of Lulworth)
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Surveys
* Bangert, William V. ''A History of the Society of Jesus'' (2nd ed. 1958) 552 pp.
* Barthel, Manfred. ''Jesuits: History & Legend of the Society of Jesus'' (1984) 347 pp
online free* Chapple, Christopher. ''Jesuit Tradition in Education & Missions: A 450-Year Perspective'' (1993), 290 pp.
* Mitchell, David. ''Jesuits: A History'' (1981) 320 pp.
* Molina, J. Michelle. ''To Overcome Oneself: The Jesuit Ethic and Spirit of Global Expansion, 1520–1767'' (2013
online* O'Malley, John W. ''The Jesuits: A History from Ignatius to the Present'' (2014), 138 pp
* Worcester, Thomas. ed. ''The Cambridge Companion to the Jesuits'' (2008), to 1773
* Wright, Jonathan. ''God's Soldiers: Adventure, Politics, Intrigue & Power: A History of the Jesuits'' (2004) 368 p
online free
Specialized studies
* Alden, Dauril. ''Making of an Enterprise: The Society of Jesus in Portugal, Its Empire & Beyond, 1540–1750'' (1996).
* Brockey, Liam Matthew. ''Journey to the East: The Jesuit Mission to China, 1579–1724'' (2007).
* , Special Edition Published 1997 by Loyola University Press, US. .
* James Patrick Broderick, Brodrick, James. ''Saint Francis Xavier (1506–1552)'' (1952).
* James Patrick Broderick, Brodrick, James. ''Saint Ignatius Loyola: The Pilgrim Years 1491–1538'' (1998).
* Burson, Jeffrey D. and Jonathan Wright, eds. ''The Jesuit Suppression in Global Context: Causes, Events, and Consequences'' (Cambridge UP, 2015).
* Bygott, Ursula M. L. ''With Pen & Tongue: The Jesuits in Australia, 1865–1939'' (1980).
* Dalmases, Cándido de. ''Ignatius of Loyola, Founder of the Jesuits: His Life & Work'' (1985).
* Caraman, Philip. ''Ignatius Loyola: A Biography of the Founder of the Jesuits'' (1990).
* Edwards, Francis. ''Jesuits in England from 1580 to the Present Day'' (1985).
* Grendler, Paul F. "Jesuit Schools and Universities in Europe 1548–1773." ''Brill Research Perspectives in Jesuit Studies'' 1.1 (2019): 1–118
online* Healy, Róisin. ''Jesuit Specter in Imperial Germany'' (2003).
* Höpfl, Harro. ''Jesuit Political Thought: The Society of Jesus & the State, c. 1540–1640'' (2004).
* Hsia, Ronnie Po-chia. "Jesuit Foreign Missions. A Historiographical Essay." ''Journal of Jesuit Studies'' (2014) 1#1, pp. 47–65.
* Kaiser, Robert Blair. ''Inside the Jesuits: How Pope Francis is Changing the Church and the World'' (Rowman & Littlefield, 2014)
* Klaiber, Jeffrey. ''The Jesuits in Latin America: 1549–2000:: 450 Years of Inculturation, Defense of Human Rights, and Prophetic Witness''. St Louis, MO: Institute of Jesuit Sources 2009.
* Lapomarda, Vincent A., ''The Catholic Bishops of Europe and the Nazi Persecutions of Catholics and Jews'', Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press (2012)
* McCoog, Thomas M., ed. ''Mercurian Project: Forming Jesuit Culture: 1573–1580'' (2004) (30 advanced essays by scholars).
* Martin, A. Lynn. ''Jesuit Mind. The Mentality of an Elite in Early Modern France'' (1988).
* O'Malley, John. "The Society of Jesus." in R. Po-chia Hsia, ed., ''A Companion to the Reformation World'' (2004), pp. 223–236.
* O'Malley, John W. ed. ''Saints or Devils Incarnate? Studies in Jesuit History'' (2013).
*
* Pomplun, Trent. ''Jesuit on the Roof of the World: Ippolito Desideri's Mission to Tibet.'' Oxford University Press (2010).
* Roberts, Ian D. ''Harvest of Hope: Jesuit Collegiate Education in England, 1794–1914'' (1996).
* Ronan, Charles E. and Bonnie B. C. Oh, eds. ''East Meets West: The Jesuits in China, 1582–1773'' (1988).
* Ross, Andrew C. ''Vision Betrayed: The Jesuits in Japan & China, 1542–1742'' (1994).
* Santich, Jan Joseph. ''Missio Moscovitica: The Role of the Jesuits in the Westernization of Russia, 1582–1689'' (1995).
* Schmiedl, Joachim (2011)
''Religious Orders as Transnational Networks of the Catholic Church''EGO – European History Online
Mainz
Institute of European History
retrieved: 25 March 2021
pdf
.
* Wright, Jonathan. "From Immolation to Restoration: The Jesuits, 1773–1814." ''Theological Studies'' (2014) 75#4 pp. 729–745.
* Zhang, Qiong. ''Making the New World their own: Chinese encounters with Jesuit science in the age of discovery'' (Brill, 2015).
United States
* Cushner, Nicholas P. ''Soldiers of God: The Jesuits in Colonial America, 1565–1767'' (2002) 402 pp.
* Garraghan, Gilbert J. ''The Jesuits Of The Middle United States'' (3 vol 1938) covers Midwest from 1800 to 191
vol 1 onlinevol 2vol 3
* McDonough, Peter. ''Men astutely trained : a history of the Jesuits in the American century'' (1994), covers 1900 to 1960s
online free
* Schroth, Raymond A. ''The American Jesuits: A History'' (2009)
Primary sources
* Desideri, Ippolito. "Mission to Tibet: The Extraordinary Eighteenth-Century Account of Father Ippolito Desideri." Translated by Michael J. Sweet. Edited by Leonard Zwilling. Boston: Wisdom Publications, 2010.
* Donnelly, John Patrick, ed. ''Jesuit Writings of the Early Modern Period: 1540–1640'' (2006)
In German
* Klaus Schatz. ''Geschichte der deutschen Jesuiten: Bd. 1: 1814–1872'' Münster: Aschendorff Verlag, 2013. XXX, 274 S.
online review
* Schatz. ''Geschichte der deutschen Jesuiten: Bd. 2: 1872–1917''
* Schatz. ''Geschichte der deutschen Jesuiten: Bd. 3: 1917–1945''
* Schatz. ''Geschichte der deutschen Jesuiten: Bd. 4: 1945–1983''
* Schatz. ''Geschichte der deutschen Jesuiten: Bd. 5: Quellen, Glossar, Biogramme, Gesamtregister''
External links
*
*
Catholic Church documents
* [https://www.vatican.va/holy_father/benedict_xvi/speeches/2006/november/documents/hf_ben-xvi_spe_20061103_gregoriana_en.html Benedict XVI's Visit to the Pontifical Gregorian University, 3 November 2006]
Jesuit documents
The Jesuit Ratio Studiorum of 1599
Letter of the Jesuit Social Justice Secretariat to the leaders of the G8, July 2005
Other links
The Jesuits
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Nigel Aston, Simon Ditchfield & Olwen Hutton (''In Our Time'', 18 January 2007)
*
*
Archives of Jezuïeten – Belgische (1832–1935) En Vlaamse (1935–) Provincie. 16de Eeuw–2012
i
ODIS – Online Database for Intermediary Structures
Institute for Advanced Jesuit Studies. Boston College.
{{Authority control
Society of Jesus,
Ignatius of Loyola
1540 establishments in Europe
Counter-Reformation
Religious organizations established in the 1540s
Catholic religious orders established in the 16th century

 In fulfilling the mission of the "Formula of the Institute of the Society", the first Jesuits concentrated on a few key activities. First, they founded schools throughout Europe. Jesuit teachers were trained in both
In fulfilling the mission of the "Formula of the Institute of the Society", the first Jesuits concentrated on a few key activities. First, they founded schools throughout Europe. Jesuit teachers were trained in both  The Jesuits were founded just before the
The Jesuits were founded just before the  After much training and experience in theology, Jesuits went across the globe in search of converts to Christianity. Despite their dedication, they had little success in Asia, except in the
After much training and experience in theology, Jesuits went across the globe in search of converts to Christianity. Despite their dedication, they had little success in Asia, except in the 

 The Jesuits first entered China through the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese settlement on Colonial Macau, Macau, where they settled on Ilha Verde, Green Island and founded St. Paul's College, Macau, St. Paul's College.
The Jesuit China missions of the 16th and 17th centuries introduced Western science and astronomy, then undergoing Scientific Revolution, its own revolution, to China. The Scientific Revolution, scientific revolution brought by the Jesuits coincided with a time when scientific innovation had declined in China:
For over a century, Jesuits like Michele Ruggieri, Matteo Ricci, Diego de Pantoja, Philippe Couplet, Michal Boym, and François Noël (missionary), François Noël refined translations and disseminated history of Chinese science, Chinese knowledge, Chinese culture, culture, history of China, history, and Chinese philosophy, philosophy to Europe. Their
The Jesuits first entered China through the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese settlement on Colonial Macau, Macau, where they settled on Ilha Verde, Green Island and founded St. Paul's College, Macau, St. Paul's College.
The Jesuit China missions of the 16th and 17th centuries introduced Western science and astronomy, then undergoing Scientific Revolution, its own revolution, to China. The Scientific Revolution, scientific revolution brought by the Jesuits coincided with a time when scientific innovation had declined in China:
For over a century, Jesuits like Michele Ruggieri, Matteo Ricci, Diego de Pantoja, Philippe Couplet, Michal Boym, and François Noël (missionary), François Noël refined translations and disseminated history of Chinese science, Chinese knowledge, Chinese culture, culture, history of China, history, and Chinese philosophy, philosophy to Europe. Their  During the French colonisation of New France in the 17th century, Jesuits played an active role in North America. When Samuel de Champlain established the foundations of the French colony at Québec, he was aware of native tribes who possessed their own languages, customs, and traditions. These natives that inhabited modern day Ontario, Québec, and the areas around Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay were the Montagnais, the Algonquins, and the Wyandot people, Huron. Champlain believed that these had souls to be saved, so in 1614 he initially obtained the Recollects, a reform branch of the Franciscans in France, to convert the native inhabitants. In 1624 the French Recollects realized the magnitude of their task and sent a delegate to France to invite the Society of Jesus to help with this mission. The invitation was accepted, and Jesuits Jean de Brébeuf, Ennemond Masse, and Charles Lalemant arrived in Quebec in 1625. Lalemant is considered to have been the first author of one of the The Jesuit Relations, ''Jesuit Relations of New France'', which chronicled their evangelization during the 17th century.
The Jesuits became involved in the Jesuit Missions amongst the Huron, Huron mission in 1626 and lived among the Huron peoples. Brébeuf learned the native language and created the first Huron language dictionary. Outside conflict forced the Jesuits to leave New France in 1629 when Quebec was Surrender of Quebec, surrendered to the Kingdom of England, English. But in 1632 Quebec was returned to the French under the Treaty of Saint Germain-en-Laye and the Jesuits returned to Huron territory, modern Huronia (region), Huronia.
In 1639, Jesuit Jerome Lalemant decided that the missionaries among the Hurons needed a local residence and established Sainte-Marie among the Hurons, Sainte-Marie, which expanded into a living replica of European society. It became the Jesuit headquarters and an important part of Canadian history. Throughout most of the 1640s the Jesuits had great success, establishing five chapels in Huronia and baptising over one thousand Huron natives. However, as the Jesuits began to expand westward they encountered more Iroquois natives, rivals of the Hurons. The Iroquois grew jealous of the Hurons' wealth and fur trade system, and began to attack Huron villages in 1648. They killed missionaries and burned villages, and the Hurons scattered. Both Jean de Brébeuf and Gabriel Lalemant were tortured and killed in the Iroquois raids; they have been canonized as martyrs in the Catholic Church. With the knowledge of the invading Iroquois, the Jesuit Paul Ragueneau burned down Sainte-Marie instead of allowing the Iroquois the satisfaction of destroying it. By late June 1649, the French and some Christian Hurons built Sainte-Marie II on Christian Island (Isle de Saint-Joseph). However, facing starvation, lack of supplies, and constant threats of Iroquois attack, the small Sainte-Marie II was abandoned in June 1650; the remaining Hurons and Jesuits departed for Quebec and Ottawa. After a series of epidemics, beginning in 1634, some Huron began to mistrust the Jesuits and accused them of being sorcerers casting spells from their books. As a result of the Iroquois raids and outbreak of disease, many missionaries, traders, and soldiers died. Today, the Huron tribe, also known as the Wyandot people, Wyandot, have a First Nations reserve in Quebec, Canada, and three major settlements in the United States.
After the collapse of the Huron nation, the Jesuits were to undertake the task of converting the Iroquois, something they had attempted in 1642 with little success. In 1653 the Iroquois nation had a fallout with the Dutch. They then signed a peace treaty with the French and a mission was established. The Iroquois took the treaty lightly and soon turned on the French again. In 1658, the Jesuits were having very little success and were under constant threat of being tortured or killed, but continued their effort until 1687 when they abandoned their permanent posts in the Iroquois homeland.
By 1700, Jesuits turned to maintaining Quebec, Montreal, and Ottawa without establishing new posts. During the Seven Years' War, Quebec was Conquest of New France (1758–1760), captured by the British in 1759 and New France came under British control. The British barred the immigration of more Jesuits to New France, and by 1763, there were only 21 Jesuits stationed in New France. By 1773 only 11 Jesuits remained. During the same year the British crown laid claim to New France and declared that the Society of Jesus in New France was dissolved.
The dissolution of the Order left in place substantial estates and investments, amounting to an income of approximately £5,000 a year, and the Council for the Affairs of the Province of Quebec, later succeeded by the Legislative Assembly of Quebec, assumed the task of allocating the funds to suitable recipients, chiefly schools.
The Jesuit mission in Quebec was re-established in 1842. There were a number of Jesuit colleges founded in the decades following; one of these colleges evolved into present-day Université Laval, Laval University.
During the French colonisation of New France in the 17th century, Jesuits played an active role in North America. When Samuel de Champlain established the foundations of the French colony at Québec, he was aware of native tribes who possessed their own languages, customs, and traditions. These natives that inhabited modern day Ontario, Québec, and the areas around Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay were the Montagnais, the Algonquins, and the Wyandot people, Huron. Champlain believed that these had souls to be saved, so in 1614 he initially obtained the Recollects, a reform branch of the Franciscans in France, to convert the native inhabitants. In 1624 the French Recollects realized the magnitude of their task and sent a delegate to France to invite the Society of Jesus to help with this mission. The invitation was accepted, and Jesuits Jean de Brébeuf, Ennemond Masse, and Charles Lalemant arrived in Quebec in 1625. Lalemant is considered to have been the first author of one of the The Jesuit Relations, ''Jesuit Relations of New France'', which chronicled their evangelization during the 17th century.
The Jesuits became involved in the Jesuit Missions amongst the Huron, Huron mission in 1626 and lived among the Huron peoples. Brébeuf learned the native language and created the first Huron language dictionary. Outside conflict forced the Jesuits to leave New France in 1629 when Quebec was Surrender of Quebec, surrendered to the Kingdom of England, English. But in 1632 Quebec was returned to the French under the Treaty of Saint Germain-en-Laye and the Jesuits returned to Huron territory, modern Huronia (region), Huronia.
In 1639, Jesuit Jerome Lalemant decided that the missionaries among the Hurons needed a local residence and established Sainte-Marie among the Hurons, Sainte-Marie, which expanded into a living replica of European society. It became the Jesuit headquarters and an important part of Canadian history. Throughout most of the 1640s the Jesuits had great success, establishing five chapels in Huronia and baptising over one thousand Huron natives. However, as the Jesuits began to expand westward they encountered more Iroquois natives, rivals of the Hurons. The Iroquois grew jealous of the Hurons' wealth and fur trade system, and began to attack Huron villages in 1648. They killed missionaries and burned villages, and the Hurons scattered. Both Jean de Brébeuf and Gabriel Lalemant were tortured and killed in the Iroquois raids; they have been canonized as martyrs in the Catholic Church. With the knowledge of the invading Iroquois, the Jesuit Paul Ragueneau burned down Sainte-Marie instead of allowing the Iroquois the satisfaction of destroying it. By late June 1649, the French and some Christian Hurons built Sainte-Marie II on Christian Island (Isle de Saint-Joseph). However, facing starvation, lack of supplies, and constant threats of Iroquois attack, the small Sainte-Marie II was abandoned in June 1650; the remaining Hurons and Jesuits departed for Quebec and Ottawa. After a series of epidemics, beginning in 1634, some Huron began to mistrust the Jesuits and accused them of being sorcerers casting spells from their books. As a result of the Iroquois raids and outbreak of disease, many missionaries, traders, and soldiers died. Today, the Huron tribe, also known as the Wyandot people, Wyandot, have a First Nations reserve in Quebec, Canada, and three major settlements in the United States.
After the collapse of the Huron nation, the Jesuits were to undertake the task of converting the Iroquois, something they had attempted in 1642 with little success. In 1653 the Iroquois nation had a fallout with the Dutch. They then signed a peace treaty with the French and a mission was established. The Iroquois took the treaty lightly and soon turned on the French again. In 1658, the Jesuits were having very little success and were under constant threat of being tortured or killed, but continued their effort until 1687 when they abandoned their permanent posts in the Iroquois homeland.
By 1700, Jesuits turned to maintaining Quebec, Montreal, and Ottawa without establishing new posts. During the Seven Years' War, Quebec was Conquest of New France (1758–1760), captured by the British in 1759 and New France came under British control. The British barred the immigration of more Jesuits to New France, and by 1763, there were only 21 Jesuits stationed in New France. By 1773 only 11 Jesuits remained. During the same year the British crown laid claim to New France and declared that the Society of Jesus in New France was dissolved.
The dissolution of the Order left in place substantial estates and investments, amounting to an income of approximately £5,000 a year, and the Council for the Affairs of the Province of Quebec, later succeeded by the Legislative Assembly of Quebec, assumed the task of allocating the funds to suitable recipients, chiefly schools.
The Jesuit mission in Quebec was re-established in 1842. There were a number of Jesuit colleges founded in the decades following; one of these colleges evolved into present-day Université Laval, Laval University.

 The Jesuits in New Spain distinguished themselves in several ways. They had high standards for acceptance to the order and many years of training. They attracted the patronage of elite families whose sons they educated in rigorous newly founded Jesuit ("colleges"), including San Pedro y San Pablo College (Museum of Light), Colegio de San Pedro y San Pablo, San Ildefonso College, Colegio de San Ildefonso, and the Museo Nacional del Virreinato, Colegio de San Francisco Javier, Tepozotlan. Those same elite families hoped that a son with a vocation to the priesthood would be accepted as a Jesuit. Jesuits were also zealous in evangelization of the indigenous, particularly on the northern frontiers.
To support their and members of the Society of Jesus, the Jesuits acquired landed estates that were run with the best-practices for generating income in that era. A number of these haciendas were donated by wealthy
elites. The donation of a hacienda to the Jesuits was the spark igniting a conflict between 17th-century bishop of Puebla Juan de Palafox y Mendoza, Don Juan de Palafox and the Jesuit colegio in that city. Since the Jesuits resisted paying the tithe on their estates, this donation effectively took revenue out of the church hierarchy's pockets by removing it from the tithe rolls.
Many of Jesuit haciendas were huge, with Palafox asserting that just two colleges owned 300,000 head of sheep, whose wool was transformed locally in Puebla to cloth; six sugar plantations worth a million pesos and generating an income of 100,000 pesos. The immense Jesuit hacienda of Santa Lucía produced , the fermented juice of the agave cactus whose main consumers were the lower classes and indigenous peoples in Spanish cities. Although most haciendas had a free work force of permanent or seasonal labourers, the Jesuit haciendas in Mexico had a significant number of black slaves.
The Jesuits operated their properties as an integrated unit with the larger Jesuit order; thus revenues from haciendas funded their . Jesuits did significantly expand missions to the indigenous in the northern frontier area and a number were martyred, but the crown supported those missions. Mendicant orders that had real estate were less economically integrated, so that some individual houses were wealthy while others struggled economically. The Franciscans, who were founded as an order embracing poverty, did not accumulate real estate, unlike the Augustinians and Dominicans in Mexico.
The Jesuits engaged in conflict with the episcopal hierarchy over the question of payment of tithes, the ten percent tax on agriculture levied on landed estates for support of the church hierarchy from bishops and cathedral chapters to parish priests. Since the Jesuits were the largest religious order holding real estate, surpassing the Dominicans and Augustinians who had accumulated significant property, this was no small matter. They argued that they were exempt, due to special pontifical privileges. In the mid-17th century, bishop of Puebla, Don Juan de Palafox took on the Jesuits over this matter and was so soundly defeated that he was recalled to Spain, where he became the bishop of the minor diocese of Osma.
As elsewhere in the Spanish empire, the Jesuits were expelled from Mexico in 1767. Their haciendas were sold off and their colegios and Spanish missions in Baja California, missions in Baja California were taken over by other orders. Exiled Mexican-born Jesuit Francisco Javier Clavijero wrote an important history of Mexico while in Italy, a basis for creole patriotism. Andrés Cavo also wrote an important text on Mexican history that Carlos María de Bustamante published in the early nineteenth-century. An earlier Jesuit who wrote about the history of Mexico was Diego Luis de Motezuma (1619–99), a descendant of the Aztec monarchs of Tenochtitlan. Motezuma's was completed in 1696. He "aimed to show that Mexican emperors were a legitimate dynasty in the 17th-century in the European sense".
The Jesuits were allowed to return to Mexico in 1840 when General Antonio López de Santa Anna was once more president of Mexico. Their re-introduction to Mexico was "to assist in the education of the poorer classes and much of their property was restored to them".
The Jesuits in New Spain distinguished themselves in several ways. They had high standards for acceptance to the order and many years of training. They attracted the patronage of elite families whose sons they educated in rigorous newly founded Jesuit ("colleges"), including San Pedro y San Pablo College (Museum of Light), Colegio de San Pedro y San Pablo, San Ildefonso College, Colegio de San Ildefonso, and the Museo Nacional del Virreinato, Colegio de San Francisco Javier, Tepozotlan. Those same elite families hoped that a son with a vocation to the priesthood would be accepted as a Jesuit. Jesuits were also zealous in evangelization of the indigenous, particularly on the northern frontiers.
To support their and members of the Society of Jesus, the Jesuits acquired landed estates that were run with the best-practices for generating income in that era. A number of these haciendas were donated by wealthy
elites. The donation of a hacienda to the Jesuits was the spark igniting a conflict between 17th-century bishop of Puebla Juan de Palafox y Mendoza, Don Juan de Palafox and the Jesuit colegio in that city. Since the Jesuits resisted paying the tithe on their estates, this donation effectively took revenue out of the church hierarchy's pockets by removing it from the tithe rolls.
Many of Jesuit haciendas were huge, with Palafox asserting that just two colleges owned 300,000 head of sheep, whose wool was transformed locally in Puebla to cloth; six sugar plantations worth a million pesos and generating an income of 100,000 pesos. The immense Jesuit hacienda of Santa Lucía produced , the fermented juice of the agave cactus whose main consumers were the lower classes and indigenous peoples in Spanish cities. Although most haciendas had a free work force of permanent or seasonal labourers, the Jesuit haciendas in Mexico had a significant number of black slaves.
The Jesuits operated their properties as an integrated unit with the larger Jesuit order; thus revenues from haciendas funded their . Jesuits did significantly expand missions to the indigenous in the northern frontier area and a number were martyred, but the crown supported those missions. Mendicant orders that had real estate were less economically integrated, so that some individual houses were wealthy while others struggled economically. The Franciscans, who were founded as an order embracing poverty, did not accumulate real estate, unlike the Augustinians and Dominicans in Mexico.
The Jesuits engaged in conflict with the episcopal hierarchy over the question of payment of tithes, the ten percent tax on agriculture levied on landed estates for support of the church hierarchy from bishops and cathedral chapters to parish priests. Since the Jesuits were the largest religious order holding real estate, surpassing the Dominicans and Augustinians who had accumulated significant property, this was no small matter. They argued that they were exempt, due to special pontifical privileges. In the mid-17th century, bishop of Puebla, Don Juan de Palafox took on the Jesuits over this matter and was so soundly defeated that he was recalled to Spain, where he became the bishop of the minor diocese of Osma.
As elsewhere in the Spanish empire, the Jesuits were expelled from Mexico in 1767. Their haciendas were sold off and their colegios and Spanish missions in Baja California, missions in Baja California were taken over by other orders. Exiled Mexican-born Jesuit Francisco Javier Clavijero wrote an important history of Mexico while in Italy, a basis for creole patriotism. Andrés Cavo also wrote an important text on Mexican history that Carlos María de Bustamante published in the early nineteenth-century. An earlier Jesuit who wrote about the history of Mexico was Diego Luis de Motezuma (1619–99), a descendant of the Aztec monarchs of Tenochtitlan. Motezuma's was completed in 1696. He "aimed to show that Mexican emperors were a legitimate dynasty in the 17th-century in the European sense".
The Jesuits were allowed to return to Mexico in 1840 when General Antonio López de Santa Anna was once more president of Mexico. Their re-introduction to Mexico was "to assist in the education of the poorer classes and much of their property was restored to them".
 The Jesuits arrived in the Viceroyalty of Peru by 1571; it was a key area of the Spanish empire, with not only dense indigenous populations but also huge deposits of silver at Potosí. A major figure in the first wave of Jesuits was
The Jesuits arrived in the Viceroyalty of Peru by 1571; it was a key area of the Spanish empire, with not only dense indigenous populations but also huge deposits of silver at Potosí. A major figure in the first wave of Jesuits was  To minister to newly arrived African slaves, Alonso de Sandoval (1576–1651) worked at the port of Cartagena de Indias. Sandoval wrote about this ministry in (1627), describing how he and his assistant Peter Claver, Pedro Claver, later canonized, met slave transport ships in the harbour, went below decks where 300–600 slaves were chained, and gave physical aid with water, while introducing the Africans to Christianity. In his treatise, he did not condemn slavery or the ill-treatment of slaves, but sought to instruct fellow Jesuits to this ministry and describe how he catechized the slaves.
Rafael Ferrer (Jesuit), Rafael Ferrer was the first Jesuit of Quito to explore and found missions in the upper Amazon River, Amazon regions of South America from 1602 to 1610, which belonged to the Audiencia Real, Audiencia (high court) of Quito that was a part of the Viceroyalty of Peru until it was transferred to the newly created Viceroyalty of New Granada in 1717. In 1602, Ferrer began to explore the Aguarico, Napo, and Marañon rivers (Sucumbios region, in what is today Ecuador and Peru), and between 1604 and 1605 set up missions among the Cofane natives. He was martyred by an apostate native in 1610.
In 1639, the Audiencia of Quito organized an expedition to renew its exploration of the Amazon river and the Quito Jesuit (Jesuita Quiteño) Cristóbal de Acuña was a part of this expedition. The expedition disembarked from the Napo river 16 February 1639 and arrived in what is today Pará Brazil on the banks of the Amazon river on 12 December 1639. In 1641, Acuña published in Madrid a memoir of his expedition to the Amazon river entitled , which for academics became a fundamental reference on the Amazon region.
In 1637, the Jesuits Gaspar Cugia and Lucas de la Cueva from Quito began establishing the Mainas missions in territories on the banks of the Marañón River, around the Pongo de Manseriche region, close to the Spanish settlement of Borja, Peru, Borja. Between 1637 and 1652 there were 14 missions established along the Marañón River and its southern tributaries, the Huallaga River, Huallaga and the Ucayali River, Ucayali rivers. Jesuit Lucas de la Cueva and Raimundo de Santacruz opened up two new routes of communication with Quito, through the Pastaza River, Pastaza and Napo River, Napo rivers.
Between 1637 and 1715, Samuel Fritz founded 38 missions along the length of the Amazon river, between the Napo and Negro rivers, that were called the Omagua Missions. These missions were continually attacked by the Brazilian Bandeirantes beginning in the year 1705. In 1768, the only Omagua mission that was left was San Joaquin de Omaguas, since it had been moved to a new location on the Napo river away from the Bandeirantes.
In the immense territory of Maynas, the Jesuits of Quito made contact with a number of indigenous tribes which spoke 40 different languages, and founded a total of 173 Jesuit missions encompassing 150,000 inhabitants. Because of the constant epidemics (smallpox and measles) and warfare with other tribes and the Bandeirantes, the total number of Jesuit Missions were reduced to 40 by 1744. The Jesuit missions offered the indigenous people Christianity, iron tools, and a small degree of protection from the slavers and the colonists. In exchange, the indigenous had to submit to Jesuit discipline and adopt, at least superficially, a life style foreign to their experience. The population of the missions was only sustained by frequent expeditions into the jungle by Jesuits, soldiers, and Christian Indians to capture indigenous people and force them to return or to settle in the missions. At the time when the Jesuits were expelled from Spanish America in 1767, the Jesuits of Quito registered 36 missions run by 25 Jesuits of Quito in the Audiencia of Quito – 6 in the Napo and Aguarico Missions and 19 in the Pastaza and Iquitos Missions, with the population at 20,000 inhabitants.
To minister to newly arrived African slaves, Alonso de Sandoval (1576–1651) worked at the port of Cartagena de Indias. Sandoval wrote about this ministry in (1627), describing how he and his assistant Peter Claver, Pedro Claver, later canonized, met slave transport ships in the harbour, went below decks where 300–600 slaves were chained, and gave physical aid with water, while introducing the Africans to Christianity. In his treatise, he did not condemn slavery or the ill-treatment of slaves, but sought to instruct fellow Jesuits to this ministry and describe how he catechized the slaves.
Rafael Ferrer (Jesuit), Rafael Ferrer was the first Jesuit of Quito to explore and found missions in the upper Amazon River, Amazon regions of South America from 1602 to 1610, which belonged to the Audiencia Real, Audiencia (high court) of Quito that was a part of the Viceroyalty of Peru until it was transferred to the newly created Viceroyalty of New Granada in 1717. In 1602, Ferrer began to explore the Aguarico, Napo, and Marañon rivers (Sucumbios region, in what is today Ecuador and Peru), and between 1604 and 1605 set up missions among the Cofane natives. He was martyred by an apostate native in 1610.
In 1639, the Audiencia of Quito organized an expedition to renew its exploration of the Amazon river and the Quito Jesuit (Jesuita Quiteño) Cristóbal de Acuña was a part of this expedition. The expedition disembarked from the Napo river 16 February 1639 and arrived in what is today Pará Brazil on the banks of the Amazon river on 12 December 1639. In 1641, Acuña published in Madrid a memoir of his expedition to the Amazon river entitled , which for academics became a fundamental reference on the Amazon region.
In 1637, the Jesuits Gaspar Cugia and Lucas de la Cueva from Quito began establishing the Mainas missions in territories on the banks of the Marañón River, around the Pongo de Manseriche region, close to the Spanish settlement of Borja, Peru, Borja. Between 1637 and 1652 there were 14 missions established along the Marañón River and its southern tributaries, the Huallaga River, Huallaga and the Ucayali River, Ucayali rivers. Jesuit Lucas de la Cueva and Raimundo de Santacruz opened up two new routes of communication with Quito, through the Pastaza River, Pastaza and Napo River, Napo rivers.
Between 1637 and 1715, Samuel Fritz founded 38 missions along the length of the Amazon river, between the Napo and Negro rivers, that were called the Omagua Missions. These missions were continually attacked by the Brazilian Bandeirantes beginning in the year 1705. In 1768, the only Omagua mission that was left was San Joaquin de Omaguas, since it had been moved to a new location on the Napo river away from the Bandeirantes.
In the immense territory of Maynas, the Jesuits of Quito made contact with a number of indigenous tribes which spoke 40 different languages, and founded a total of 173 Jesuit missions encompassing 150,000 inhabitants. Because of the constant epidemics (smallpox and measles) and warfare with other tribes and the Bandeirantes, the total number of Jesuit Missions were reduced to 40 by 1744. The Jesuit missions offered the indigenous people Christianity, iron tools, and a small degree of protection from the slavers and the colonists. In exchange, the indigenous had to submit to Jesuit discipline and adopt, at least superficially, a life style foreign to their experience. The population of the missions was only sustained by frequent expeditions into the jungle by Jesuits, soldiers, and Christian Indians to capture indigenous people and force them to return or to settle in the missions. At the time when the Jesuits were expelled from Spanish America in 1767, the Jesuits of Quito registered 36 missions run by 25 Jesuits of Quito in the Audiencia of Quito – 6 in the Napo and Aguarico Missions and 19 in the Pastaza and Iquitos Missions, with the population at 20,000 inhabitants.
 In addition to recurrent epidemics, the Guaraní were threatened by the slave-raiding Bandeirantes from Brazil, who captured natives and sold them as slaves to work in sugar plantations or as concubines and household servants. Having depleted native populations near São Paulo, they discovered the richly populated Jesuit missions. Initially, the missions had few defenses against the slavers and thousands of Guaraní were captured and enslaved. Beginning in 1631, the Jesuits moved their missions from the Guayrá province (present day Brazil and Paraguay), about southwest to the three borders region of Paraguay, Argentina, and Brazil. About 10,000 of 30,000 Guaraní in the missions chose to accompany the Jesuits. In 1641 and 1642, armed by the Jesuits, Guaraní armies defeated the Bandeirantes and ended the worst of the slave trade in their region. From this point on the Jesuit missions enjoyed growth and prosperity, punctuated by epidemics. At the peak of their importance in 1732, the Jesuits presided over 141,000 Guaraní (including a sprinkling of other peoples) who lived in about 30 missions.
The opinions of historians differ with regard to the Jesuit missions. The missions are much-romanticized with the Guaraní portrayed as innocent children of nature and the Jesuits as their wise and benevolent guides to an earthly utopia. "Proponents...highlight that the Jesuits protected the Indians from exploitation and preserved the Guaraní language and other aspects of indigenous culture." "By means of religion," wrote the 18th century philosopher d'Alembert, "the Jesuits established a monarchical authority in Paraguay, founded solely on their powers of persuasion and on their lenient methods of government. Masters of the country, they rendered happy the people under their sway." Voltaire called the Jesuit missions "a triumph of humanity".
To the contrary the detractors say that 'the Jesuits took away the Indians' freedom, forced them to radically change their lifestyle, physically abused them, and subjected them to disease." Moreover, the missions were inefficient and their economic success "depended on subsidies from the Jesuit order, special protection and privileges from the Crown, and the lack of competition" The Jesuits are portrayed as "exploiters" who "sought to create a kingdom independent of the Spanish and Portuguese Crowns."
The Revolt of the Comuneros (Paraguay), Comunero Revolt (1721 to 1735) was a serious protest by Spanish and mestizo Paraguayans against the Jesuit missions. The residents of Paraguay violently protested the pro-Jesuit government of Paraguay, Jesuit control of Guaraní labor, and what they regarded as unfair competition for the market for products such as yerba mate. Although the revolt ultimately failed and the missions remained intact, the Jesuits were expelled from institutions they had created in Asunción. In 1756, the Guaraní protested the relocation of seven missions, fighting (and losing) a brief war with both the Spanish and Portuguese. The Jesuits were accused of inciting the Guaraní to rebel. In 1767, Charles III of Spain (1759–88) expelled the Jesuits from the Americas. The expulsion was part of an effort in the Bourbon Reforms to assert more Spanish control over its American colonies. Edited by Michael Meyer and William Beezley. In total, 78 Jesuits departed from the missions leaving behind 89,000 Guaraní in 30 missions.
In addition to recurrent epidemics, the Guaraní were threatened by the slave-raiding Bandeirantes from Brazil, who captured natives and sold them as slaves to work in sugar plantations or as concubines and household servants. Having depleted native populations near São Paulo, they discovered the richly populated Jesuit missions. Initially, the missions had few defenses against the slavers and thousands of Guaraní were captured and enslaved. Beginning in 1631, the Jesuits moved their missions from the Guayrá province (present day Brazil and Paraguay), about southwest to the three borders region of Paraguay, Argentina, and Brazil. About 10,000 of 30,000 Guaraní in the missions chose to accompany the Jesuits. In 1641 and 1642, armed by the Jesuits, Guaraní armies defeated the Bandeirantes and ended the worst of the slave trade in their region. From this point on the Jesuit missions enjoyed growth and prosperity, punctuated by epidemics. At the peak of their importance in 1732, the Jesuits presided over 141,000 Guaraní (including a sprinkling of other peoples) who lived in about 30 missions.
The opinions of historians differ with regard to the Jesuit missions. The missions are much-romanticized with the Guaraní portrayed as innocent children of nature and the Jesuits as their wise and benevolent guides to an earthly utopia. "Proponents...highlight that the Jesuits protected the Indians from exploitation and preserved the Guaraní language and other aspects of indigenous culture." "By means of religion," wrote the 18th century philosopher d'Alembert, "the Jesuits established a monarchical authority in Paraguay, founded solely on their powers of persuasion and on their lenient methods of government. Masters of the country, they rendered happy the people under their sway." Voltaire called the Jesuit missions "a triumph of humanity".
To the contrary the detractors say that 'the Jesuits took away the Indians' freedom, forced them to radically change their lifestyle, physically abused them, and subjected them to disease." Moreover, the missions were inefficient and their economic success "depended on subsidies from the Jesuit order, special protection and privileges from the Crown, and the lack of competition" The Jesuits are portrayed as "exploiters" who "sought to create a kingdom independent of the Spanish and Portuguese Crowns."
The Revolt of the Comuneros (Paraguay), Comunero Revolt (1721 to 1735) was a serious protest by Spanish and mestizo Paraguayans against the Jesuit missions. The residents of Paraguay violently protested the pro-Jesuit government of Paraguay, Jesuit control of Guaraní labor, and what they regarded as unfair competition for the market for products such as yerba mate. Although the revolt ultimately failed and the missions remained intact, the Jesuits were expelled from institutions they had created in Asunción. In 1756, the Guaraní protested the relocation of seven missions, fighting (and losing) a brief war with both the Spanish and Portuguese. The Jesuits were accused of inciting the Guaraní to rebel. In 1767, Charles III of Spain (1759–88) expelled the Jesuits from the Americas. The expulsion was part of an effort in the Bourbon Reforms to assert more Spanish control over its American colonies. Edited by Michael Meyer and William Beezley. In total, 78 Jesuits departed from the missions leaving behind 89,000 Guaraní in 30 missions.

 Tomé de Sousa, first Governorate General of Brazil, Governor General of Brazil, brought the first group of Jesuits to the colony. The Jesuits were officially supported by the King, who instructed Tomé de Sousa to give them all the support needed to Christianize the indigenous peoples.
The first Jesuits, guided by Manuel da Nóbrega, Juan de Azpilcueta Navarro, Leonardo Nunes, and later José de Anchieta, established the first Jesuit missions in Salvador and in São Paulo dos Campos de Piratininga, the settlement that gave rise to the city of São Paulo. Nóbrega and Anchieta were instrumental in the defeat of the French colonists of France Antarctique by managing to pacify the Tamoio natives, who had previously fought the Portuguese. The Jesuits took part in the foundation of the city of Rio de Janeiro in 1565.
The success of the Jesuits in converting the indigenous peoples is linked to their efforts to understand the native cultures, especially their languages. The first grammar of the Tupian languages, Tupi language was compiled by José de Anchieta and printed in Coimbra in 1595. The Jesuits often gathered the aborigines in communities (the Jesuit Reductions) where the natives worked for the community and were evangelised.
The Jesuits had frequent disputes with other colonists who wanted to enslave the natives. The action of the Jesuits saved many natives from being enslaved by Europeans, but also disturbed their ancestral way of life and inadvertently helped spread infectious diseases against which the aborigines had no natural defenses. Slave labor and trade were essential for the economy of Brazil and other American colonies, and the Jesuits usually did not object to the enslavement of African peoples, but rather critiqued the conditions of slavery. In cases where individual Jesuit priests criticised the institution of African slavery, they were censored and sent back to Europe.
Tomé de Sousa, first Governorate General of Brazil, Governor General of Brazil, brought the first group of Jesuits to the colony. The Jesuits were officially supported by the King, who instructed Tomé de Sousa to give them all the support needed to Christianize the indigenous peoples.
The first Jesuits, guided by Manuel da Nóbrega, Juan de Azpilcueta Navarro, Leonardo Nunes, and later José de Anchieta, established the first Jesuit missions in Salvador and in São Paulo dos Campos de Piratininga, the settlement that gave rise to the city of São Paulo. Nóbrega and Anchieta were instrumental in the defeat of the French colonists of France Antarctique by managing to pacify the Tamoio natives, who had previously fought the Portuguese. The Jesuits took part in the foundation of the city of Rio de Janeiro in 1565.
The success of the Jesuits in converting the indigenous peoples is linked to their efforts to understand the native cultures, especially their languages. The first grammar of the Tupian languages, Tupi language was compiled by José de Anchieta and printed in Coimbra in 1595. The Jesuits often gathered the aborigines in communities (the Jesuit Reductions) where the natives worked for the community and were evangelised.
The Jesuits had frequent disputes with other colonists who wanted to enslave the natives. The action of the Jesuits saved many natives from being enslaved by Europeans, but also disturbed their ancestral way of life and inadvertently helped spread infectious diseases against which the aborigines had no natural defenses. Slave labor and trade were essential for the economy of Brazil and other American colonies, and the Jesuits usually did not object to the enslavement of African peoples, but rather critiqued the conditions of slavery. In cases where individual Jesuit priests criticised the institution of African slavery, they were censored and sent back to Europe.
 In April 2005, Thomas J. Reese, editor of the American Jesuit weekly magazine '' America (Jesuit magazine), America'', resigned at the request of the society. The move was widely published in the media as the result of pressure from the Vatican, following years of criticism by the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith on articles touching subjects such as AIDS, HIV/AIDS, religious pluralism, Catholic Church and homosexuality, homosexuality, and the right of life for the unborn. Following his resignation, Reese spent a year-long sabbatical at Santa Clara University before being named a fellow at the Woodstock Theological Center in Washington, D.C., and later Senior Analyst for the ''National Catholic Reporter''. President Barack Obama appointed him to the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom in 2014 and again in 2016.
On 2 February 2006, Peter Hans Kolvenbach informed members of the Society of Jesus that, with the consent of Pope Benedict XVI, he intended to step down as Superior General in 2008, the year he would turn 80.
On 22 April 2006, Feast of Our Lady, Mother of the Society of Jesus, Pope Benedict XVI greeted thousands of Jesuits on Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage to Rome, and took the opportunity to thank God "for having granted to your Company the gift of men of extraordinary sanctity and of exceptional apostolic zeal such as St Ignatius of Loyola, St Francis Xavier, and Beatification, Bl
In April 2005, Thomas J. Reese, editor of the American Jesuit weekly magazine '' America (Jesuit magazine), America'', resigned at the request of the society. The move was widely published in the media as the result of pressure from the Vatican, following years of criticism by the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith on articles touching subjects such as AIDS, HIV/AIDS, religious pluralism, Catholic Church and homosexuality, homosexuality, and the right of life for the unborn. Following his resignation, Reese spent a year-long sabbatical at Santa Clara University before being named a fellow at the Woodstock Theological Center in Washington, D.C., and later Senior Analyst for the ''National Catholic Reporter''. President Barack Obama appointed him to the United States Commission on International Religious Freedom in 2014 and again in 2016.
On 2 February 2006, Peter Hans Kolvenbach informed members of the Society of Jesus that, with the consent of Pope Benedict XVI, he intended to step down as Superior General in 2008, the year he would turn 80.
On 22 April 2006, Feast of Our Lady, Mother of the Society of Jesus, Pope Benedict XVI greeted thousands of Jesuits on Christian pilgrimage, pilgrimage to Rome, and took the opportunity to thank God "for having granted to your Company the gift of men of extraordinary sanctity and of exceptional apostolic zeal such as St Ignatius of Loyola, St Francis Xavier, and Beatification, Bl  In 2013, Jesuit Cardinal Jorge Bergoglio became Pope Francis. Before he became pope, he was appointed bishop when he was in "virtual estrangement from the Jesuits" since he was seen as "an enemy of liberation theology" and viewed by others as "still far too orthodox". He was criticised for colluding with the National Reorganization Process, Argentine junta, while biographers characterised him as working to save the lives of other Jesuits. As a Jesuit pope, he has been stressing discernment over following rules, changing the culture of the clergy to steer away from clericalism and to move toward an ethic of service, i.e to have the "smell of sheep," staying close to the people. After his papal election, the Superior General of the Jesuits Adolfo Nicolás praised Pope Francis as a "brother among brothers".
On 2 October 2016, General Congregation 36 convened in Rome, convoked by Superior General Adolfo Nicolás, who had announced his intention to resign at age 80. On 14 October, the 36th General Congregation of the Society of Jesus elected
In 2013, Jesuit Cardinal Jorge Bergoglio became Pope Francis. Before he became pope, he was appointed bishop when he was in "virtual estrangement from the Jesuits" since he was seen as "an enemy of liberation theology" and viewed by others as "still far too orthodox". He was criticised for colluding with the National Reorganization Process, Argentine junta, while biographers characterised him as working to save the lives of other Jesuits. As a Jesuit pope, he has been stressing discernment over following rules, changing the culture of the clergy to steer away from clericalism and to move toward an ethic of service, i.e to have the "smell of sheep," staying close to the people. After his papal election, the Superior General of the Jesuits Adolfo Nicolás praised Pope Francis as a "brother among brothers".
On 2 October 2016, General Congregation 36 convened in Rome, convoked by Superior General Adolfo Nicolás, who had announced his intention to resign at age 80. On 14 October, the 36th General Congregation of the Society of Jesus elected  Several Jesuits were prominent in the small German resistance to Nazism, German Resistance. Among the central membership of the Kreisau Circle of the Resistance were the Jesuit priests Augustin Rösch, Alfred Delp, and Lothar König. The Bavarian Jesuit Provincial, Augustin Rosch, ended the war on death row for his role in the July Plot to overthrow Hitler. Another non-military German Resistance group, dubbed the Solf Circle, "Frau Solf Tea Party" by the Gestapo, included the Jesuit priest Friedrich Erxleben. The German Jesuit Robert Leiber acted as intermediary between Pius XII and the German Resistance.:de:Peter Hoffmann (Historiker, 1930), Peter Hoffmann; ''The History of the German Resistance 1933–1945''; 3rd Edn (First English Edn); McDonald & Jane's; London; 1977; p. 160
Among the Jesuit victims of the Nazis, Germany's Rupert Mayer has been beatified. Mayer was a Bavarian Jesuit who clashed with the Nazis as early as 1923. Continuing his critique following Hitler's rise to power, Mayer was imprisoned in 1939 and sent to Sachsenhausen concentration camp, Sachsenhausen Extermination camp, death camp. As his health declined, the Nazis feared the creation of a martyr and sent him to the Abbey of Ettal in 1940. There he continued to give sermons and lectures against the evils of the Nazi régime, until his death in 1945.
Several Jesuits were prominent in the small German resistance to Nazism, German Resistance. Among the central membership of the Kreisau Circle of the Resistance were the Jesuit priests Augustin Rösch, Alfred Delp, and Lothar König. The Bavarian Jesuit Provincial, Augustin Rosch, ended the war on death row for his role in the July Plot to overthrow Hitler. Another non-military German Resistance group, dubbed the Solf Circle, "Frau Solf Tea Party" by the Gestapo, included the Jesuit priest Friedrich Erxleben. The German Jesuit Robert Leiber acted as intermediary between Pius XII and the German Resistance.:de:Peter Hoffmann (Historiker, 1930), Peter Hoffmann; ''The History of the German Resistance 1933–1945''; 3rd Edn (First English Edn); McDonald & Jane's; London; 1977; p. 160
Among the Jesuit victims of the Nazis, Germany's Rupert Mayer has been beatified. Mayer was a Bavarian Jesuit who clashed with the Nazis as early as 1923. Continuing his critique following Hitler's rise to power, Mayer was imprisoned in 1939 and sent to Sachsenhausen concentration camp, Sachsenhausen Extermination camp, death camp. As his health declined, the Nazis feared the creation of a martyr and sent him to the Abbey of Ettal in 1940. There he continued to give sermons and lectures against the evils of the Nazi régime, until his death in 1945.
 Between the sixteenth and eighteenth centuries, the teaching of science in Jesuit schools, as laid down in the
Between the sixteenth and eighteenth centuries, the teaching of science in Jesuit schools, as laid down in the  Jesuits are also known for their involvement in publications. ''La Civiltà Cattolica'', a periodical produced in Rome by the Jesuits, has often been used as a semi-official platform for popes and Vatican officials to float ideas for discussion or hint at future statements or positions. In the United States, ''The Way'' is an international journal of contemporary Christian spirituality published by the British Jesuits. ''America (Jesuit magazine), America'' magazine has long had a prominent place in Catholic intellectual circles Most Jesuit colleges and universities have their own presses which produce a variety of books, book series, textbooks, and academic publications. Ignatius Press, founded by a Jesuit, is an independent publisher of Catholic books, most of which are of the popular academic or lay-intellectual variety. Manresa is a review of Ignatian spirituality published in Madrid, Spain.
In Australia, the Jesuits produce a number of magazines, including ''Eureka Street (magazine), Eureka Street'', ''Madonna'', ''Australian Catholics'', and ''Province Express''.
In Germany, the Jesuits publish ''Geist und Leben.''
In Sweden the Catholic cultural magazine ''Signum'', edited by the Newman Institute, covers a broad spectrum of issues concerning faith, culture, research, and society. The printed version of ''Signum'' is published eight times per year.
Jesuits are also known for their involvement in publications. ''La Civiltà Cattolica'', a periodical produced in Rome by the Jesuits, has often been used as a semi-official platform for popes and Vatican officials to float ideas for discussion or hint at future statements or positions. In the United States, ''The Way'' is an international journal of contemporary Christian spirituality published by the British Jesuits. ''America (Jesuit magazine), America'' magazine has long had a prominent place in Catholic intellectual circles Most Jesuit colleges and universities have their own presses which produce a variety of books, book series, textbooks, and academic publications. Ignatius Press, founded by a Jesuit, is an independent publisher of Catholic books, most of which are of the popular academic or lay-intellectual variety. Manresa is a review of Ignatian spirituality published in Madrid, Spain.
In Australia, the Jesuits produce a number of magazines, including ''Eureka Street (magazine), Eureka Street'', ''Madonna'', ''Australian Catholics'', and ''Province Express''.
In Germany, the Jesuits publish ''Geist und Leben.''
In Sweden the Catholic cultural magazine ''Signum'', edited by the Newman Institute, covers a broad spectrum of issues concerning faith, culture, research, and society. The printed version of ''Signum'' is published eight times per year.