Jawless fish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Agnatha (,
 Although a minor element of modern marine
Although a minor element of modern marine
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
Chordata
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These fi ...
, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present ( cyclostomes) and extinct (conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, whi ...
s and ostracoderm
Ostracoderms () are the armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic (excluding jawed fishes) (may also be polyphyletic if anaspids are closer to cyclostomes) and ...
s) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostome
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living ...
s.
Recent molecular data, both from rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribos ...
and from mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gr ...
.
The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata
A craniate is a member of the Craniata (sometimes called the Craniota), a proposed clade of chordate animals with a skull of hard bone or cartilage. Living representatives are the Myxini (hagfishes), Hyperoartia (including lampreys), and the m ...
was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates.
While a few scientists still regard the living agnathans as only superficially similar, and argue that many of these similarities are probably shared basal characteristics of ancient vertebrates, recent taxonomic studies clearly place hagfish (the Myxini or Hyperotreti) with the lampreys
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like su ...
(Hyperoartii) as being more closely related to each other than either is to the jawed fishes.
Metabolism
Agnathans are ectothermic, meaning they do not regulate their own body temperature. Agnathan metabolism is slow in cold water, and therefore they do not have to eat very much. They have no distinct stomach, but rather a long gut, more or less homogeneous throughout its length. Lampreys feed on other fish and mammals.Anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where t ...
fluids preventing blood clotting are injected into the host, causing the host to yield more blood. Hagfish are scavengers, eating mostly dead animals. They use a row of sharp teeth to break down the animal. The fact that Agnathan teeth are unable to move up and down limits their possible food types.
Morphology
In addition to the absence ofjaws
Jaws or Jaw may refer to:
Anatomy
* Jaw, an opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth
** Mandible, the lower jaw
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Jaws (James Bond), a character in ''The Spy Who Loved Me'' and ''Moonraker''
* ...
, modern agnathans are characterised by absence of paired fins; the presence of a notochord
In anatomy, the notochord is a flexible rod which is similar in structure to the stiffer cartilage. If a species has a notochord at any stage of its life cycle (along with 4 other features), it is, by definition, a chordate. The notochord consi ...
both in larvae and adults; and seven or more paired gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
pouches. Lampreys have a light sensitive pineal eye (homologous to the pineal gland
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cy ...
in mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s). All living and most extinct Agnatha do not have an identifiable stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
or any appendages. Fertilization and development are both external. There is no parental care in the Agnatha class. The Agnatha are ectothermic or cold blooded, with a cartilaginous skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
, and the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
contains 2 chambers.
Body covering
In modern agnathans, the body is covered in skin, with neither dermal or epidermalscales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
. The skin of hagfish has copious slime glands, the slime constituting their defense mechanism. The slime can sometimes clog up enemy fishes' gills, causing them to die. In direct contrast, many extinct agnathans sported extensive exoskeletons composed of either massive, heavy dermal armour
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or f ...
or small mineralized scales.
Appendages
Almost all agnathans, including all extant agnathans, have no paired appendages, although most do have a dorsal or acaudal fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
. Some fossil agnathans, such as osteostracans and pituriaspids, did have paired fins, a trait inherited in their jawed descendants. Romer, A.S. & Parsons, T.S. (1985): ''The Vertebrate Body.'' (6th ed.) Saunders, Philadelphia.
Reproduction
Fertilization in lampreys is external. Mode of fertilization in hagfishes is not known. Development in both groups probably is external. There is no known parental care. Not much is known about the hagfish reproductive process. It is believed that hagfish only have 30 eggs over a lifetime. There is very little of the larval stage that characterizes the lamprey. Lamprey are only able to reproduce once. After external fertilization, the lamprey'scloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, ...
s remain open, allowing a fungus to enter their intestines, killing them. Lampreys reproduce in freshwater riverbeds, working in pairs to build a nest and burying their eggs about an inch beneath the sediment. The resulting hatchlings go through four years of larval development before becoming adults.
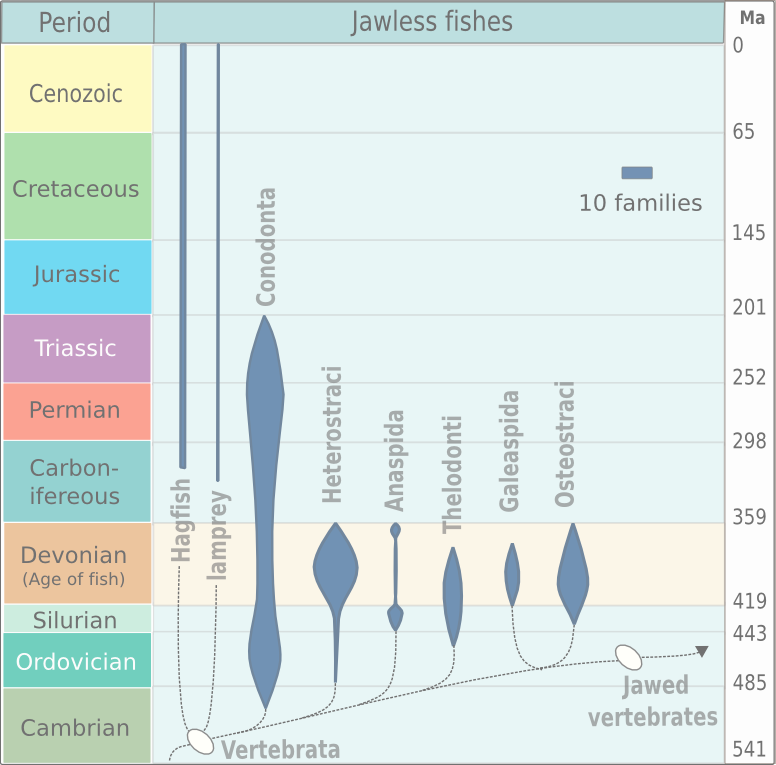
Evolution
 Although a minor element of modern marine
Although a minor element of modern marine fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is '' flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. ...
, agnathans were prominent among the early fish in the early Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
. Two types of Early Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
animal apparently having fins, vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
musculature, and gills are known from the early Cambrian Maotianshan shales of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
: ''Haikouichthys
''Haikouichthys'' is an extinct genus of craniate (animals with notochords and distinct heads) that lived 518 million years ago, during the Cambrian explosion of multicellular life. ''Haikouichthys'' had a defined skull and other characteristi ...
'' and ''Myllokunmingia
''Myllokunmingia'' is a genus of basal chordate from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shales of China 518 to 490 mya and is thought to be a vertebrate, although this is not conclusively proven. The species M. fengjiaoa is 28 mm long and 6&nbs ...
''. They have been tentatively assigned to Agnatha by Janvier. A third possible agnathid from the same region is '' Haikouella''. A possible agnathid that has not been formally described was reported by Simonetti from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
. Conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, whi ...
s, a class of agnathans which arose in the early Cambrian, remained common enough until their extinction in the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest per ...
that their teeth (the only parts of them that were usually fossilized) are often used as index fossils from the late Cambrian to the Triassic.
Many Ordovician, Silurian, and Devonian agnathans were armored with heavy bony-spiky plates. The first armored agnathans—the Ostracoderm
Ostracoderms () are the armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic (excluding jawed fishes) (may also be polyphyletic if anaspids are closer to cyclostomes) and ...
s, precursors to the bony fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartil ...
and hence to the tetrapods
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct therapsi ...
(including human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s)—are known from the middle Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
, and by the Late Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleoz ...
the agnathans had reached the high point of their evolution. Most of the ostracoderms, such as thelodont
Thelodonti (from Greek: "feeble teeth")Maisey, John G., Craig Chesek, and David Miller. Discovering fossil fishes. New York: Holt, 1996. is a class of extinct jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor.
There is mu ...
s, osteostracans, and galeaspid
Galeaspida (from Latin, 'Helmet shields') is an extinct taxon of jawless marine and freshwater fish. The name is derived from ''galea'', the Latin word for ''helmet'', and refers to their massive bone shield on the head. Galeaspida lived in shallo ...
s, were more closely related to the gnathostomes than to the surviving agnathans, known as cyclostomes. Cyclostomes apparently split from other agnathans before the evolution of dentine and bone, which are present in many fossil agnathans, including conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, whi ...
s. Agnathans declined in the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
and never recovered.
Approximately 500 million years ago, two types of recombinatorial adaptive immune systems (AISs) arose in vertebrates. The jawed vertebrates diversify their repertoire of immunoglobulin domain-based T and B cell antigen receptors mainly through the rearrangement of V(D)J gene segments and somatic hypermutation, but none of the fundamental AIS recognition elements in jawed vertebrates have been found in jawless vertebrates. Instead, the AIS of jawless vertebrates is based on variable lymphocyte receptors (VLRs) that are generated through recombinatorial usage of a large panel of highly diverse leucine-rich-repeat (LRR) sequences. Three VLR genes (VLRA, VLRB, and VLRC) have been identified in lampreys and hagfish, and are expressed on three distinct lymphocytes lineages. VLRA+ cells and VLRC+ cells are T-cell-like and develop in a thymus-like lympho-epithelial structure, termed thymoids. VLRB+ cells are B-cell-like, develop in hematopoietic organs, and differentiate into “VLRB antibody”-secreting plasma cells.
Classification
Groups
Phylogeny based on the work of Mikko Haaramo and Delsuc et al. The new phylogeny from Miyashita ''et al''. (2019) is considered compatible with both morphological and molecular evidence.See also
*Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, livi ...
* Amphirhina
Amphirhina are animals, a phylogenetic classification within the subphylum vertebrata. They are more commonly known as the Branch Gnathostomata, and are described as having double nasal chambers, or nostrils, and jaws. The parallel branch in this n ...
, an alternate name for the above parallel, or sister, classification
* Cyclostomata
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q161095 Paraphyletic groups Infraphyla Terreneuvian first appearances Extant Cambrian first appearances