The rule of the
Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
in Poland between 1386 and 1572 spans the
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
and the
Early Modern Period in European history. The
Lithuanian Grand Duke Jogaila (Władysław II Jagiełło) founded the dynasty; his marriage to Queen
Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Grea ...
in 1386 strengthened an ongoing
Polish–Lithuanian union. The partnership brought vast territories controlled by the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
into Poland's sphere of influence and proved beneficial for both the
Polish and
Lithuanian people
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Unite ...
, who coexisted and cooperated in one of the largest
political entities in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
for the next four centuries.
In the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
region, Poland engaged in ongoing conflict with the
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
. The struggles led to a major battle, the
Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
of 1410, but there was also the milestone
Peace of Thorn of 1466 under King
Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (in full Casimir IV Andrew Jagiellon; pl, Kazimierz IV Andrzej Jagiellończyk ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447, until his death. He was one of the m ...
; the treaty defined the basis of the future
Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
. In the south, Poland confronted the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and the
Crimean Tatars, and in the east Poles helped Lithuania fight the
Grand Duchy of Moscow. Poland's and Lithuania's territorial expansion included the far north region of
Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
.
In the Jagiellonian period,
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
developed as a
feudal state with a predominantly agricultural economy and an increasingly dominant
landed nobility Landed nobility or landed aristocracy is a category of nobility in the history of various countries, for which landownership was part of their noble privileges. Their character depends on the country.
*The notion of landed gentry in the United Kin ...
. The ''
Nihil novi
''Nihil novi nisi commune consensu'' ("Nothing new without the Consent of the governed, common consent") is the original Latin title of a 1505 Statute, act or constitution adopted by the Poland, Polish ''Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland, Sejm'' (parl ...
'' act adopted by the Polish
Sejm in 1505 transferred most of the
legislative power in the state from the
monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power i ...
to the Sejm. This event marked the beginning of the system known as the "
Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty ( la, Aurea Libertas; pl, Złota Wolność, lt, Auksinė laisvė), sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth ( pl, Rzeczpospolita Szlachecka or ''Złota wolność szlachecka'') was a pol ...
", when the "free and equal" members of the
Polish nobility ruled the state
and
elected the monarch.
The 16th century saw
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
movements deeply influencing Polish
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, resulting in unique policies of
religious tolerance
Religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, mistaken, or harmful". ...
for the Europe of that time. The European
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
as fostered by the last Jagiellonian Kings
Sigismund I the Old () and
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
() resulted in an immense
cultural flowering.
Late Middle Ages (14th–15th century)
Jagiellonian monarchy

In 1385, the
Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; be, Крэўская унія, translit=Kreŭskaja unija; pl, unia w Krewie; lt, Krėvos sutartis) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made ...
was signed between Queen
Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Grea ...
and
Jogaila, the
Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Kingdom of Lithuania, Lithuania, which was established as an Absolute monarchy, absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three Duke, ducal D ...
, the ruler of the last
pagan state in Europe. The act arranged for Jogaila's
baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
and the couple's marriage, which established the beginning of the
Polish–Lithuanian union. After Jogaila's baptism, he was known in Poland by his baptismal name Władysław and the Polish version of his Lithuanian name, Jagiełło. The union strengthened both nations in their shared opposition to the
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
and the growing threat of the
Grand Duchy of Moscow.
Vast expanses of
Rus' lands, including the
Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
basin and territories extending south to the
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, were at that time under Lithuanian control. In order to gain control of these vast holdings, Lithuanians and Ruthenians had fought the
Battle of Blue Waters in 1362 or 1363 against the invading
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
and had taken advantage of the power vacuum to the south and east that resulted from the
Mongol destruction of
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
. The population of the Grand Duchy's enlarged territory was accordingly heavily
Ruthenian and
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
. The territorial expansion led to a confrontation between Lithuania and the Grand Duchy of Moscow, which found itself emerging from the
Tatar
The Tatars ()[Tatar]
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different rule and itself in a process of expansion. Uniquely in Europe, the union connected two states geographically located on the opposite sides of the great civilizational divide between the
Western Christian
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic ...
or
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
world, and the
Eastern Christian
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and ...
or
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
world.
The intention of the union was to create a common state under Władysław Jagiełło, but the ruling oligarchy of Poland learned that their goal of incorporating Lithuania into Poland was unrealistic. Territorial disputes led to warfare between Poland and Lithuania or Lithuanian factions; the Lithuanians at times even found it expedient to conspire with the Teutonic Knights against the Poles. Geographic consequences of the
dynastic union
A dynastic union is a type of union with only two different states that are governed under the same dynasty, with their boundaries, their laws, and their interests remaining distinct from each other.
Historical examples
Union of Kingdom of Arag ...
and the preferences of the
Jagiellonian
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
kings instead created a process of orientating Polish territorial priorities to the east.
Between 1386 and 1572, the Polish–Lithuanian union was ruled by a succession of constitutional monarchs of the
Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
. The political influence of the Jagiellonian kings gradually diminished during this period, while the landed nobility took over an ever-increasing role in central government and national affairs. The royal dynasty, however, had a stabilizing effect on Poland's politics. The Jagiellonian Era is often regarded as a period of maximum political power, great prosperity, and in its later stage, a
Golden Age of Polish culture.
Social and economic developments

The feudal rent system prevalent in the 13th and 14th centuries, under which each
estate had well defined rights and obligations, degenerated around the 15th century as the nobility tightened their control over manufacturing, trade and other economic activities. This created many directly owned agricultural enterprises known as
folwark
''Folwark''; german: Vorwerk; uk, Фільварок; ''Filwarok''; be, Фальварак; ''Falwarak''; lt, Palivarkas is a Polish word for a primarily serfdom-based farm and agricultural enterprise (a type of ''latifundium''), often very ...
s in which feudal rent payments were replaced with forced labor on the lord's land. This limited the rights of cities and forced most of the
peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasant ...
s into
serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which deve ...
. Such practices were increasingly sanctioned by the law. For example, the
Piotrków Privilege of 1496, granted by King
John I Albert
John I Albert ( pl, Jan I Olbracht; 27 December 1459 – 17 June 1501) was King of Poland from 1492 until his death in 1501 and Duke of Głogów (Glogau) from 1491 to 1498. He was the fourth Polish sovereign from the Jagiellonian dynasty, the s ...
, banned rural land purchases by townspeople and severely limited the ability of peasant farmers to leave their villages. Polish towns, lacking national representation protecting their class interests, preserved some degree of self-government (city councils and jury courts), and the trades were able to organize and form
guilds. The nobility soon excused themselves from their principal duty: mandatory military service in case of war (
pospolite ruszenie
''Pospolite ruszenie'' (, lit. ''mass mobilization''; "Noble Host", lat, motio belli, the French term ''levée en masse'' is also used) is a name for the mobilisation of armed forces during the period of the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Li ...
). The division of the nobility into two main layers was institutionalized, but never legally formalized, in the ''
Nihil novi
''Nihil novi nisi commune consensu'' ("Nothing new without the Consent of the governed, common consent") is the original Latin title of a 1505 Statute, act or constitution adopted by the Poland, Polish ''Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland, Sejm'' (parl ...
'' "constitution" of 1505, which required the king to consult the
general sejm
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED O ...
, that is the
Senate, as well as the lower chamber of (regional) deputies, the Sejm proper, before enacting any changes. The masses of ordinary nobles
szlachta competed or tried to compete against the uppermost rank of their class, the
magnates, for the duration of Poland's independent existence.
Poland and Lithuania in personal union under Jagiełło

The first king of the new dynasty was Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, who was known as
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło ()He is known under a number of names: lt, Jogaila Algirdaitis; pl, Władysław II Jagiełło; be, Jahajła (Ягайла). See also: Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło. ...
in Poland. He was elected king of Poland in 1386 after his marriage to
Jadwiga of Anjou, the
King of Poland in her own right, and his conversion to
Roman Catholicism. The
Christianization of Lithuania
The Christianization of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos krikštas) occurred in 1387, initiated by King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania Władysław II Jagiełło and his cousin Vytautas the Great. It signified the official adoption of Christianity b ...
in the
Latin Rite
Latin liturgical rites, or Western liturgical rites, are Catholic rites of public worship employed by the Latin Church, the largest particular church '' sui iuris'' of the Catholic Church, that originated in Europe where the Latin language once ...
followed. Jogaila's rivalry in Lithuania with his cousin
Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
, who was opposed to Lithuania's domination by Poland, was settled in 1392 in the
Ostrów Agreement
The Ostrów or Astrava Agreement ( lt, Astravos sutartis, be, Востраўскае пагадненне, pl, Ugoda w Ostrowie) was a treaty between Jogaila (Władysław II Jagiełło), King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his cous ...
and in 1401 in the
Union of Vilnius and Radom: Vytautas became the Grand Duke of Lithuania for life under Jogaila's nominal supremacy. The agreement made possible a close cooperation between the two nations necessary to succeed in struggles with the Teutonic Order. The
Union of Horodło
The Union of Horodło or Pact of Horodło was a set of three acts signed in the town of Horodło on 2 October 1413. The first act was signed by Władysław II Jagiełło, King of Poland, and Vytautas, Grand Duke of Lithuania. The second and thir ...
of 1413 defined the relationship further and granted privileges to the
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
(as opposed to
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
) segment of the Lithuanian nobility.
Struggle with the Teutonic Knights

The
Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War
The Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War, also known as the Great War, occurred between 1409 and 1411 between the Teutonic Knights and the allied Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Inspired by the local Samogitian uprising, the war beg ...
of 1409–1411, precipitated by the
Samogitian uprisings in Lithuanian territories controlled by the
State of the Teutonic Order
The State of the Teutonic Order (german: Staat des Deutschen Ordens, ; la, Civitas Ordinis Theutonici; lt, Vokiečių ordino valstybė; pl, Państwo zakonu krzyżackiego), also called () or (), was a medieval Crusader state, located in Cent ...
, culminated in the
Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
(Tannenberg), in which the combined forces of the Polish and Lithuanian-Rus' armies completely defeated the
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
. The offensive that followed lost its impact with the ineffective siege of
Malbork (Marienburg). The failure to take the fortress and eliminate the Teutonic (later
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n) state had dire historic consequences for Poland in the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries. The
Peace of Thorn of 1411 gave Poland and Lithuania rather modest territorial adjustments, including Samogitia. Afterwards, there were more military campaigns and peace deals that did not hold. One unresolved arbitration took place at the
Council of Constance. In 1415,
Paulus Vladimiri,
rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
of the
Kraków Academy
The Jagiellonian University (Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
, presented his ''Treatise on the Power of the Pope and the Emperor in respect to Infidels'' at the council, in which he advocated tolerance, criticized the violent conversion methods of the Teutonic Knights, and postulated that pagans have the right to peaceful coexistence with Christians and political independence. This stage of the Polish-Lithuanian conflict with the Teutonic Order ended with the
Treaty of Melno
The Treaty of Melno ( lt, Melno taika; pl, Pokój melneński) or Treaty of Lake Melno (german: Friede von Melnosee) was a peace treaty ending the Gollub War. It was signed on 27 September 1422, between the Teutonic Knights and an alliance of th ...
in 1422. The
Polish-Teutonic War of 1431-35 (see
Battle of Wiłkomierz
The Battle of Wiłkomierz (see other names) took place on September 1, 1435, near Ukmergė in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. With the help of military units from the Kingdom of Poland, the forces of Grand Duke Sigismund Kęstutaitis soundly defea ...
) was concluded with the
Peace of Brześć Kujawski in 1435.
The Hussite movement and the Polish–Hungarian union
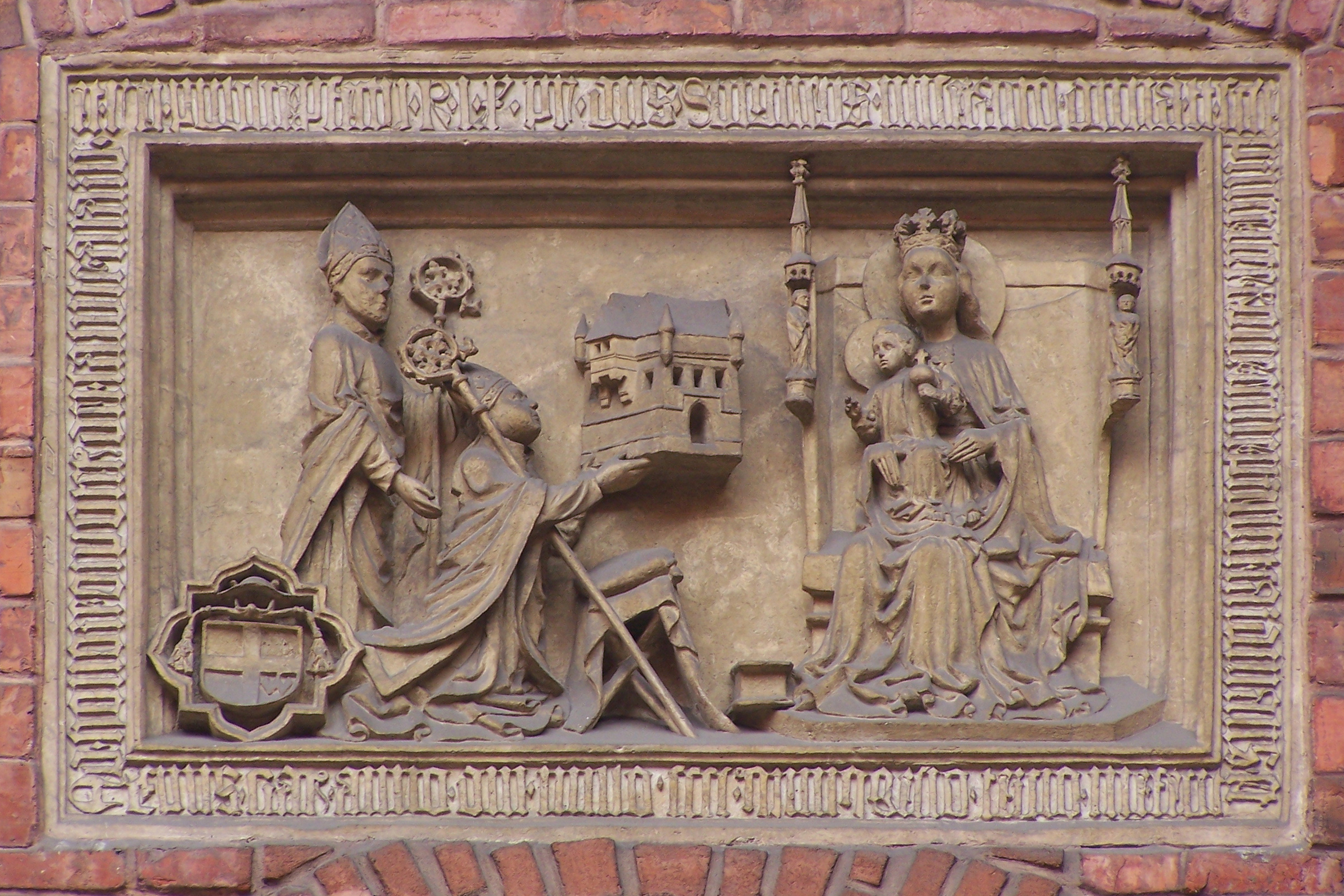

During the
Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Cat ...
of 1420–1434, Jagiełło, Vytautas and
Sigismund Korybut
Sigismund Korybut ( lt, Žygimantas Kaributaitis; be, Жыгімонт Карыбутавіч; pl, Zygmunt Korybutowicz; cz, Zikmund Korybutovič; uk, Жиґимонт Корибутович or Сигізмунд Корибутович, 1395 � ...
were involved in political and military intrigues with respect to the
Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
crown, which was offered by the
Hussite
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Huss ...
s to Jagiełło in 1420. Bishop
Zbigniew Oleśnicki became known as the leading opponent of a union with the Hussite Czech state.
The Jagiellonian dynasty was not entitled to automatic hereditary succession, rather each new king had to be approved by nobility consensus. Władysław Jagiełło had two sons late in life from his last wife
Sophia of Halshany. In 1430, the nobility agreed to the succession of the future
Władysław III only after the king consented to a series of concessions. In 1434, the old monarch died and his minor son Władysław was crowned; the Royal Council led by Bishop Oleśnicki undertook the regency duties.

In 1438, the Czech anti-
Habsburg opposition, mainly Hussite factions, offered the Czech crown to Jagiełło's younger son
Casimir
Casimir is classically an English, French and Latin form of the Polish name Kazimierz. Feminine forms are Casimira and Kazimiera. It means "proclaimer (from ''kazać'' to preach) of peace (''mir'')."
List of variations
*Belarusian: Казі ...
. The idea, accepted in Poland over Oleśnicki's objections, resulted in two unsuccessful Polish military expeditions to
Bohemia.
After Vytautas' death in 1430, Lithuania became embroiled in internal wars and conflicts with Poland. Casimir, sent as a boy by King Władysław on a mission there in 1440, was surprisingly proclaimed by the Lithuanians as their Grand Duke, and he remained in Lithuania.
Oleśnicki gained the upper hand again and pursued his long-term objective of Poland's union with Hungary. At that time, the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
embarked on a fresh round of European conquests and threatened Hungary, which needed the assistance of the powerful Polish–Lithuanian ally. In 1440, Władysław III assumed the Hungarian throne. Influenced by
Julian Cesarini
Julian Cesarini the Elder ( It.: ''Giuliano Cesarini, seniore'') (1398 in Rome – 10 November 1444 in Varna, Ottoman Empire) was one of the group of brilliant cardinals created by Pope Martin V on the conclusion of the Western Schism. His ...
, the young king led the Hungarian army against the Ottomans in 1443 and again in 1444. Like Cesarini, Władysław III was killed at the
Battle of Varna
The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman Army under Sultan Murad II (who did not actually rule the sultanate at the time) defeated the Hungarian– Polish and Wallachian armies commanded ...
.

Beginning near the end of Jagiełło's life, Poland was governed in practice by an oligarchy of magnates led by Bishop Oleśnicki. The rule of the dignitaries was actively opposed by various groups of ''
szlachta''. Their leader
Spytek of Melsztyn Spycimir, also Spyćmier, Spyćmir, Spyćmierz, Spićymierz, etc., is an old Polish masculine given name. Etymology: ''spyci-'': "in vain", ''-mir'': "peace". Diminutives: Spytko, Spytek. Its name day is 26 April.Bogdan Kupis, ''Nasze imiona'', 1991 ...
was killed at the
Battle of Grotniki
The Battle of Grotniki took place on 4 May 1439 in the vicinity of Grotniki Duże, a village near Nowy Korczyn, currently in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship.
The battle was fought between the Hussite confederates under Spytko III of Melsztyn aga ...
in 1439, which allowed Oleśnicki to purge Poland of the remaining Hussite sympathizers and pursue his other objectives without significant opposition.
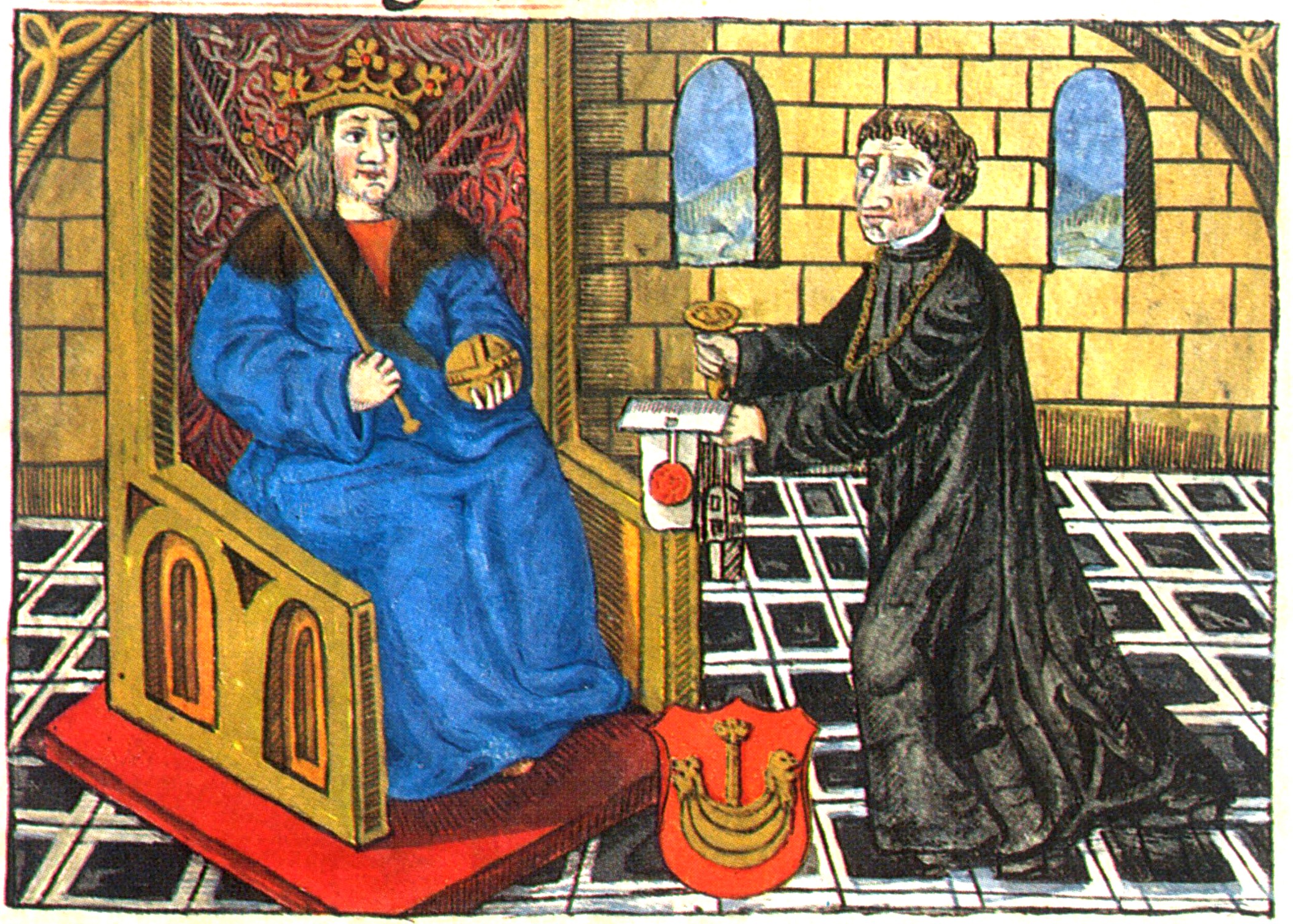
The accession of Casimir IV Jagiellon
In 1445,
Casimir
Casimir is classically an English, French and Latin form of the Polish name Kazimierz. Feminine forms are Casimira and Kazimiera. It means "proclaimer (from ''kazać'' to preach) of peace (''mir'')."
List of variations
*Belarusian: Казі ...
, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, was asked to assume the Polish throne vacated upon the death of his brother Władysław. Casimir was a tough negotiator and did not accept the Polish nobility's conditions for his election. He finally arrived in Poland and was crowned in 1447 on his own terms. His assumption of the Crown of Poland freed Casimir from the control that the Lithuanian oligarchy had imposed on him; in the
Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
Privilege of 1447, he declared the
Lithuanian nobility
The Lithuanian nobility or szlachta ( Lithuanian: ''bajorija, šlėkta'') was historically a legally privileged hereditary elite class in the Kingdom of Lithuania and Grand Duchy of Lithuania (including during period of foreign rule 1795–191 ...
to have equal rights with Polish ''szlachta''. In time, Casimir was able to wrest power from
Cardinal Oleśnicki and his group. He replaced their influence with a power base built on the younger middle nobility. Casimir was able to resolve a conflict with the pope and the local Church hierarchy over the right to fill vacant bishop positions in his favor.
War with the Teutonic Order and its resolution

In 1454, the
Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (german: Preußischer Bund, pl, Związek Pruski) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Kwidzyn (then officially ''Marienwerder'') by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia (region), Prussi ...
, an alliance of Prussian cities and nobility opposed to the increasingly oppressive rule of the Teutonic Knights, asked King Casimir to take over Prussia and initiated an armed uprising against the Knights. Casimir declared a war on the Order and the formal incorporation of Prussia into the Polish Crown; those events led to the
Thirteen Years' War of 1454–66. The mobilization of the Polish forces (the
pospolite ruszenie
''Pospolite ruszenie'' (, lit. ''mass mobilization''; "Noble Host", lat, motio belli, the French term ''levée en masse'' is also used) is a name for the mobilisation of armed forces during the period of the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Li ...
) was weak at first, since the
szlachta would not cooperate without concessions from Casimir that were formalized in the
Statutes of Nieszawa The Nieszawa Statutes () were a set of laws enacted in the Kingdom of Poland in 1454, in the town of Nieszawa located in north-central Poland. The King Casimir IV Jagiellon made a number of concessions to the Polish nobility and the gentry (szlachta ...
promulgated in 1454. This prevented a takeover of all of Prussia, but in the
Second Peace of Thorn
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń ( pl, drugi pokój toruński; german: Zweiter Friede von Thorn), was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 betwe ...
in 1466, the Knights had to surrender the western half of their territory to the
Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
(the areas known afterwards as
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
, a semi-autonomous entity), and to accept Polish-Lithuanian
suzerainty over the remainder (the later
Ducal Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establishe ...
). Poland regained
Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
, with its access to the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, as well as
Warmia
Warmia ( pl, Warmia; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian: ''Warńija''; lt, Varmė; Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia. Its historic capital ...
. In addition to land warfare, naval battles took place in which ships provided by the City of
Danzig (Gdańsk) successfully fought
Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
and Teutonic fleets.
Other territories recovered by the Polish Crown in the 15th-century include the
Duchy of Oświęcim
The Duchy of Oświęcim ( pl, Księstwo Oświęcimskie), or the Duchy of Auschwitz (german: Herzogtum Auschwitz), was one of many Duchies of Silesia, formed in the aftermath of the fragmentation of Poland.
It was established about 1315 on the Le ...
and
Duchy of Zator
The Duchy of Zator was one of many Duchies of Silesia.
It was split off the Duchy of Oświęcim, when after eleven years of joint rule the sons of Duke Casimir I in 1445 finally divided the lands among themselves, whereby his eldest son Wenc ...
on
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
's border with
Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
, and there was notable progress regarding the incorporation of the Piast
Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
n duchies into the Crown.
Turkish and Tatar wars
The influence of the
Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
in
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
rose during the 15th century. In 1471, Casimir's son
Władysław became king of Bohemia, and in 1490, also of Hungary.
The southern and eastern outskirts of Poland and Lithuania became threatened by
Turkish invasions beginning in the late 15th century.
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
's involvement with Poland goes back to 1387, when
Petru I,
Hospodar
Hospodar or gospodar is a term of Slavonic origin, meaning "lord" or " master".
Etymology and Slavic usage
In the Slavonic language, ''hospodar'' is usually applied to the master/owner of a house or other properties and also the head of a family. ...
of Moldavia sought protection against the Hungarians by paying
homage to King Władysław II Jagiełło in
Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
. This move gave Poland access to
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
ports.
In 1485, King Casimir undertook an expedition into Moldavia after its seaports were overtaken by the
Ottoman Turks. The Turkish-controlled
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
raided the eastern territories in 1482 and 1487 until they were confronted by King
John Albert, Casimir's son and successor.
Poland was attacked in 1487–1491 by remnants of the
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
that invaded Poland as far as
Lublin before being beaten at
Zaslavl.
In 1497, King John Albert made an attempt to resolve the Turkish problem militarily, but his efforts were unsuccessful; he was unable to secure effective participation in the war by his brothers, King
Vladislas (Władysław) II of Bohemia and Hungary and
Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, and he also faced resistance on the part of
Stephen the Great, the ruler of Moldavia. More destructive
Tatar raids instigated by the Ottoman Empire took place in 1498, 1499 and 1500.
Diplomatic peace efforts initiated by John Albert were finalized after the king's death in 1503. They resulted in a territorial compromise and an unstable truce.
Invasions into Poland and Lithuania from the
Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
took place in 1502 and 1506 during the reign of King
Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
. In 1506, the Tatars were defeated at the
Battle of Kletsk
The Battle of Kletsk ( lt, Klecko mūšis, be, Бітва пад Клецкам) was a battle fought on 5 August 1506 near Kletsk (now in Belarus), between the Grand Ducal Lithuanian army, led by Court Marshal of Lithuania Michael Glinski, and ...
by
Michael Glinski
Michael Lvovich Glinsky ( lt, Mykolas Glinskis, russian: Михаил Львович Глинский, pl, Michał Gliński; 1460s – 24 September 1534) was a noble from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania of distant Tatar extraction, who was also a t ...
.
Moscow's threat to Lithuania; accession of Sigismund I

Lithuania was increasingly threatened by the growing power of the
Grand Duchy of Moscow in the 15th and 16th centuries. Moscow indeed took over many of Lithuania's eastern possessions in
military campaigns of 1471, 1492, and 1500. Grand Duke
Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
of Lithuania was elected King of Poland in 1501, after the death of John Albert. In 1506, he was succeeded by
Sigismund I the Old (''Zygmunt I Stary'') in both Poland and Lithuania as political realities were drawing the two states closer together. Prior to his accession to the Polish throne, Sigismund had been a Duke of
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
by the authority of his brother Vladislas II of
Bohemia, but like other Jagiellon rulers before him, he did not pursue the claim of the Polish Crown to Silesia.
Culture in the Late Middle Ages
The
culture of the 15th century Poland can be described as retaining typical medieval characteristics. Nonetheless, the crafts and industries in existence already in the preceding centuries became more highly developed under favorable social and economic conditions, and their products were much more widely disseminated. Paper production was one of the new industries that appeared, and printing developed during the last quarter of the century. In 1473,
Kasper Straube produced the first
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
print in
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
, whereas Kasper Elyan printed Polish texts for the first time in
Wrocław (Breslau) in 1475. The world's oldest prints in
Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
, namely religious texts in
Old Church Slavonic, appeared after 1490 from the press of
Schweipolt Fiol in Krakow.
Luxury items were in high demand among the increasingly prosperous nobility, and to a lesser degree among the wealthy town merchants. Brick and stone residential buildings became common, but only in cities. The mature
Gothic style
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
** Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken ...
was represented not only in architecture, but also in sacral wooden sculpture. The
Altar of Veit Stoss
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paganism ...
in
St. Mary's Basilica in Kraków is one of the most magnificent art works of its kind in Europe.
 Kraków University
Kraków University, which stopped functioning after the death of
Casimir the Great, was renewed and rejuvenated around 1400. Augmented by a
theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
department, the "academy" was supported and protected by Queen
Jadwiga
Jadwiga (; diminutives: ''Jadzia'' , ''Iga'') is a Polish feminine given name. It originated from the old German feminine given name ''Hedwig'' (variants of which include ''Hedwiga''), which is compounded from ''hadu'', "battle", and ''wig'', "fig ...
and the Jagiellonian dynasty members, which is reflected in its present name: the Jagiellonian University. Europe's oldest department of mathematics and astronomy was established in 1405. Among the university's prominent scholars were
Stanisław of Skarbimierz,
Paulus Vladimiri and
Albert of Brudzewo,
Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated ...
' teacher.
John of Ludzisko and Archbishop
Gregory of Sanok
Gregory of Sanok ( pl, Grzegorz z Sanoka; Sanok, 1403 or 1407 – 29 January 1477, Rohatyn) was a Polish bishop, a professor at the Kraków Academy, metropolitan archbishop of Lwów, scholar, philosopher and a major figure of Polish humanism.
L ...
, the precursors of Polish
humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and Agency (philosophy), agency of Human, human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical in ...
, were professors at the university. Gregory's court was the site of an early literary society at
Lwów (Lviv) after he became the archbishop there. Scholarly thought elsewhere was represented by Jan Ostroróg, a political publicist and reformist, and
Jan Długosz
Jan Długosz (; 1 December 1415 – 19 May 1480), also known in Latin as Johannes Longinus, was a Polish priest, chronicler, diplomat, soldier, and secretary to Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki of Kraków. He is considered Poland's first histo ...
, a historian, whose ''Annals'' is the largest history work of his time in Europe and a fundamental source for history of medieval Poland. Distinguished and influential foreign humanists were also active in Poland.
Filippo Buonaccorsi
Filippo Buonaccorsi, called Callimachus, Callimico, Bonacurarius, Caeculus, Geminianensis (Latin: ''Philippus Callimachus Experiens'', ''Bonacursius''; , 2 May 1437 – 1 November 1496) was an Italian humanist, writer and diplomat active in Pola ...
, a poet and diplomat, arrived from Italy in 1468 and stayed in Poland until his death in 1496. Known as Kallimach, he prepared biographies of Gregory of Sanok, Zbigniew Oleśnicki, and very likely Jan Długosz, besides establishing another literary society in Kraków. He tutored and mentored the sons of Casimir IV and postulated unrestrained royal power. In Kraków, the
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
humanist
Conrad Celtes
Conrad Celtes (german: Konrad Celtes; la, Conradus Celtis (Protucius); 1 February 1459 – 4 February 1508) was a German Renaissance humanist scholar and poet of the German Renaissance born in Franconia (nowadays part of Bavaria). He led the ...
organized the humanist literary and scholarly association ''
Sodalitas Litterarum Vistulana'', the first in this part of Europe.
Early Modern Era (16th century)
Agriculture-based economic expansion
The
folwark
''Folwark''; german: Vorwerk; uk, Фільварок; ''Filwarok''; be, Фальварак; ''Falwarak''; lt, Palivarkas is a Polish word for a primarily serfdom-based farm and agricultural enterprise (a type of ''latifundium''), often very ...
, a large-scale system of agricultural production based on
serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which deve ...
, was a dominant feature on Poland's economic landscape beginning in the late 15th century and for the next 300 years. This dependence on nobility-controlled agriculture in central-eastern Europe diverged from the western part of the continent, where elements of
capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
and
industrialization were developing to a much greater extent, with the attendant growth of a
bourgeoisie class and its political influence. The 16th-century agricultural trade
boom combined with free or very cheap peasant labor made the folwark economy very profitable.
Mining and metallurgy developed further during the 16th century, and technical progress took place in various commercial applications. Great quantities of exported agricultural and forest products floated down the rivers to be transported through ports and land routes. This resulted in a
positive trade balance for Poland throughout the 16th century. Imports from the West included industrial products, luxury products and fabrics.
[Józef Andrzej Gierowski – ''Historia Polski 1505–1764'' (History of Poland 1505–1764), p. 24-38]
Most of the exported
grain left Poland through
Gdańsk (Danzig), which became the wealthiest, most highly developed, and most autonomous of the Polish cities because of its location at the mouth of the
Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
River and access to the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
. It was also by far the largest center for manufacturing. Other towns were negatively affected by Gdańsk's near-monopoly in foreign trade, but profitably participated in transit and export activities. The largest of those were
Kraków (Cracow),
Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
,
Lwów (Lviv), and
Warszawa (Warsaw), and outside of the Crown,
Breslau (Wrocław).
Thorn (Toruń) and
Elbing (Elbląg) were the main cities in
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
after Gdańsk.
Burghers and nobles

During the 16th century, prosperous
patrician
Patrician may refer to:
* Patrician (ancient Rome), the original aristocratic families of ancient Rome, and a synonym for "aristocratic" in modern English usage
* Patrician (post-Roman Europe), the governing elites of cities in parts of medieval ...
families of merchants, bankers, or industrial investors, many of German origin, still conducted large-scale business operations in Europe or lent money to Polish noble interests, including the royal court. Some regions were highly urbanized in comparison to most of the rest of Europe. In
Greater Poland and
Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
at the end of the 16th century, for example, 30% of the population lived in cities.
256 towns were founded, most in
Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
. The townspeople's upper layer was ethnically multinational and tended to be well-educated. Numerous sons of burghers studied at the
Academy of Kraków and at foreign universities; members of their group are among the finest contributors to the culture of the
Polish Renaissance
The Renaissance in Poland ( pl, Renesans, Odrodzenie; literally: the Rebirth) lasted from the late 15th to the late 16th century and is widely considered to have been the Golden Age of Polish culture. Ruled by the Jagiellonian dynasty, the Crown ...
. Unable to form their own nationwide political class, many blended into the nobility in spite of the legal obstacles.
The nobility (or ''
szlachta'') in Poland constituted a greater proportion of the population than in other countries, up to 10%. In principle, they were all equal and politically empowered, but some had no property and were not allowed to hold offices or participate in
sejms or
sejmik
A sejmik (, diminutive of ''sejm'', occasionally translated as a ''dietine''; lt, seimelis) was one of various local parliaments in the history of Poland and history of Lithuania. The first sejmiks were regional assemblies in the Kingdom of ...
s, the legislative bodies. Of the "landed" nobility, some possessed a small patch of land that they tended themselves and lived like peasant families, while the magnates owned dukedom-like networks of estates with several hundred towns and villages and many thousands of subjects. Mixed marriages gave some peasants one of the few possible paths to nobility.
16th-century Poland was officially a "republic of nobles", and the "middle class" of the nobility (individuals at a lower social level than "magnates") formed the leading component during the later Jagiellonian period and afterwards. Nonetheless, members of the magnate families held the highest state and church offices. At that time, the ''szlachta'' in Poland and Lithuania was ethnically diversified and represented several religious denominations. During this period of tolerance, such factors had little bearing on one's economic status or career potential. Jealous of their class privilege ("
freedoms
Political freedom (also known as political autonomy or political agency) is a central concept in history and political thought and one of the most important features of democratic societies.Hannah Arendt, "What is Freedom?", ''Between Past and F ...
"), the Renaissance ''szlachta'' developed a sense of public service duties, educated their youth, took keen interest in current trends and affairs and traveled widely. The
Golden Age of Polish Culture adopted western
humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and Agency (philosophy), agency of Human, human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical in ...
and
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
patterns, and visiting foreigners often remarked on the splendor of their residencies and the conspicuous consumption of wealthy Polish nobles.
Reformation

In a situation analogous with that of other European countries, the progressive internal decay of the
Polish Church created conditions favorable for the dissemination of the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
ideas and currents. For example, there was a chasm between the lower clergy and the nobility-based Church hierarchy, which was quite laicized and preoccupied with temporal issues, such as power and wealth, and often corrupt. The middle nobility, which had already been exposed to the
Hussite
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Huss ...
reformist persuasion, increasingly looked at the Church's many privileges with envy and hostility.
The teachings of
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
were accepted most readily in the regions with strong German connections:
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
,
Greater Poland,
Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
and
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
. In
Gdańsk (Danzig) in 1525 a lower-class
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
social uprising took place and was bloodily subdued by
Sigismund I; after the reckoning he established a representation for the plebeian interests as a segment of the city government.
Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was name ...
and the
Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
under
Albrecht Hohenzollern became a strong center of
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
propaganda dissemination affecting all of northern Poland and
Lithuania. Sigismund quickly reacted against the "religious novelties", issuing his first related edict in 1520, banning any promotion of the Lutheran ideology, or even foreign trips to the Lutheran centers. Such attempted (poorly enforced) prohibitions continued until 1543.

Sigismund's son
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
(''Zygmunt II August''), a monarch of a much more tolerant attitude, guaranteed the freedom of the Lutheran religion practice in all of
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
by 1559. Besides Lutheranism, which, within the Polish Crown, ultimately found substantial following mainly in the cities of Royal Prussia and western Greater Poland, the teachings of the persecuted
Anabaptists and
Unitarians, and in Greater Poland the
Czech Brothers, were met, at least among the ''szlachta'', with a more sporadic response.
In Royal Prussia, 41% of the parishes were counted as Lutheran in the second half of the 16th century, but that percentage kept increasing. According to
Kasper Cichocki, who wrote in the early 17th century, only remnants of Catholicism were left there in his time. Lutheranism was strongly dominant in Royal Prussia throughout the 17th century, with the exception of
Warmia
Warmia ( pl, Warmia; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian: ''Warńija''; lt, Varmė; Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia. Its historic capital ...
(Ermland).

Around 1570, of the at least 700 Protestant congregations in Poland–Lithuania, over 420 were
Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
and over 140 Lutheran, with the latter including 30-40 ethnically Polish. Protestants encompassed approximately ½ of the
magnate class, ¼ of other nobility and townspeople, and 1/20 of the non-Orthodox peasantry. The bulk of the Polish-speaking population had remained Catholic, but the proportion of Catholics became significantly diminished within the upper social ranks.
Calvinism gained many followers in the mid 16th century among both the ''szlachta'' and the magnates, especially in
Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
and Lithuania. The Calvinists, who led by
Jan Łaski
Jan Łaski or Johannes à Lasco (1499 – 8 January 1560) was a Polish Calvinist reformer. Owing to his influential work in England (1548–1553) during the English Reformation, he is known to the English-speaking world by the Anglicised form J ...
were working on unification of the Protestant churches, proposed the establishment of a Polish national church, under which all Christian denominations, including
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
(very numerous in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Ukraine), would be united. After 1555 Sigismund II, who accepted their ideas, sent an envoy to the pope, but the papacy rejected the various Calvinist postulates. Łaski and several other Calvinist scholars published in 1563 the
Bible of Brest, a complete Polish
Bible translation
The Bible has been translated into many languages from the biblical languages of Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. all of the Bible has been translated into 724 languages, the New Testament has been translated into an additional 1,617 languages, and ...
from the
original languages, an undertaking financed by
Mikołaj Radziwiłł the Black. After 1563–1565 (the abolishment of state enforcement of
the Church jurisdiction), full religious tolerance became the norm. The Polish
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
emerged from this critical period weakened but not badly damaged (the bulk of the Church property was preserved), which facilitated the later success of
Counter-Reformation.

Among the Calvinists, who also included the lower classes and their leaders, ministers of common background, disagreements soon developed, based on different views in the areas of religious and social doctrines. The official split took place in 1562, when two separate churches were officially established: the mainstream Calvinist and the smaller, more reformist,
Polish Brethren
The Polish Brethren (Polish: ''Bracia Polscy'') were members of the Minor Reformed Church of Poland, a Nontrinitarian Protestant church that existed in Poland from 1565 to 1658. By those on the outside, they were called " Arians" or " Socinians" ( ...
or
Arians
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God t ...
. The adherents of the radical wing of the Polish Brethren promoted, often by way of personal example, the ideas of social justice. Many Arians (such as
Piotr of Goniądz and
Jan Niemojewski
Janusz Jan Niemojewski (1531–1598) was a Polish nobleman, and theologian of the Polish Brethren.Kęstutis Daugirdas, "Die Anfänge des Sozinianismus", Göttingen, 2016, p. 91-94, 180-183
Works
* 1583 – "Odpowiedź na potwarz Wilkowskiego"
* 1 ...
) were pacifists opposed to private property, serfdom, state authority and military service; through communal living some had implemented the ideas of shared usage of the land and other property. A major Polish Brethren congregation and center of activities was established in 1569 in
Raków near
Kielce, and lasted until 1638, when Counter-Reformation had it closed. The notable
Sandomierz Agreement
The Sandomierz Agreement (or Sandomierz Consensus; lat. ''Consensus Sendomiriensis'') was an agreement reached in 1570 in Sandomierz between a number of Protestant groups in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was intended to unite different ...
of 1570, an act of compromise and cooperation among several Polish Protestant denominations, excluded the Arians, whose more moderate, larger faction toward the end of the century gained the upper hand within the movement.
The act of the
Warsaw Confederation
The Warsaw Confederation, signed on 28 January 1573 by the Polish national assembly (''sejm konwokacyjny'') in Warsaw, was one of the first European acts granting religious freedoms. It was an important development in the history of Poland and o ...
, which took place during the
convocation sejm
Royal elections in Poland ( Polish: ''wolna elekcja'', lit. ''free election'') were the elections of individual kings, rather than dynasties, to the Polish throne. Based on traditions dating to the very beginning of the Polish statehood, strengt ...
of 1573, provided guarantees, at least for the nobility, of religious freedom and peace. It gave the Protestant denominations, including the Polish Brethren, formal rights for many decades to come. Uniquely in 16th-century Europe, it turned the Commonwealth, in the words of Cardinal
Stanislaus Hosius
Stanislaus Hosius ( pl, Stanisław Hozjusz; 5 May 1504 – 5 August 1579) was a Polish Roman Catholic cardinal. From 1551 he was the Prince-Bishop of the Bishopric of Warmia in Royal Prussia and from 1558 he served as the papal legate to the H ...
, a Catholic reformer, into a "safe haven for heretics".
Culture of Polish Renaissance
Golden Age of Polish culture

The Polish "Golden Age", the period of the reigns of Sigismund I and Sigismund II, the last two Jagiellonian kings, or more generally the 16th century, is most often identified with the rise of the culture of
Polish Renaissance
The Renaissance in Poland ( pl, Renesans, Odrodzenie; literally: the Rebirth) lasted from the late 15th to the late 16th century and is widely considered to have been the Golden Age of Polish culture. Ruled by the Jagiellonian dynasty, the Crown ...
. The cultural flowering had its material base in the prosperity of the elites, both the landed nobility and urban
patriciate at such centers as
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
and
Gdańsk.
As was the case with other European nations, the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
inspiration came in the first place from
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, a process accelerated to some degree by Sigismund I's marriage to
Bona Sforza.
Many Poles traveled to Italy to study and to learn its culture. As imitating Italian ways became very trendy (the royal courts of the two kings provided the leadership and example for everybody else), many
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
artists and thinkers were coming to Poland, some settling and working there for many years. While the pioneering Polish
humanists
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humani ...
, greatly influenced by
Erasmus of Rotterdam
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (; ; English: Erasmus of Rotterdam or Erasmus;''Erasmus'' was his baptismal name, given after St. Erasmus of Formiae. ''Desiderius'' was an adopted additional name, which he used from 1496. The ''Roterodamus'' w ...
, accomplished the preliminary assimilation of the
antiquity culture, the generation that followed was able to put greater emphasis on the development of native elements, and because of its social diversity, advanced the process of national integration.
Literacy, education and patronage of intellectual endeavors

Beginning in 1473 in
Cracow (Kraków), the printing business kept growing. By the turn of the 16th/17th century there were about 20 printing houses within the Commonwealth, 8 in Cracow, the rest mostly in
Gdańsk (Danzig),
Thorn (Toruń) and
Zamość
Zamość (; yi, זאמאשטש, Zamoshtsh; la, Zamoscia) is a historical city in southeastern Poland. It is situated in the southern part of Lublin Voivodeship, about from Lublin, from Warsaw. In 2021, the population of Zamość was 62,021.
...
. The
Academy of Kraków and Sigismund II possessed well-stocked libraries; smaller collections were increasingly common at noble courts, schools and townspeople's households. Illiteracy levels were falling, as by the end of the 16th century almost every parish ran a school.
The
Lubrański Academy, an institution of higher learning, was established in
Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
in 1519. The
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
resulted in the establishment of a number of
gymnasiums, academically oriented secondary schools, some of international renown, as the
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
denominations wanted to attract supporters by offering high quality education. The
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
reaction was the creation of
Jesuit colleges of comparable quality. The
Kraków University in turn responded with
humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
program gymnasiums of its own.
The university itself experienced a period of prominence at the turn of the 15th/16th century, when especially the mathematics, astronomy and geography faculties attracted numerous students from abroad.
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
,
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
and their literatures were likewise popular. By the mid 16th century the institution entered a crisis stage, and by the early 17th century regressed into
Counter-reformational conformism. The Jesuits took advantage of the infighting and established in 1579 a
university college in Vilnius, but their efforts aimed at taking over the Academy of Kraków were unsuccessful. Under the circumstances many elected to pursue their studies abroad.
, who built the presently existing
Wawel
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established o ...
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
castle, and his son
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
, supported intellectual and artistic activities and surrounded themselves with the creative elite. Their patronage example was followed by ecclesiastic and lay feudal lords, and by patricians in major towns.
Science
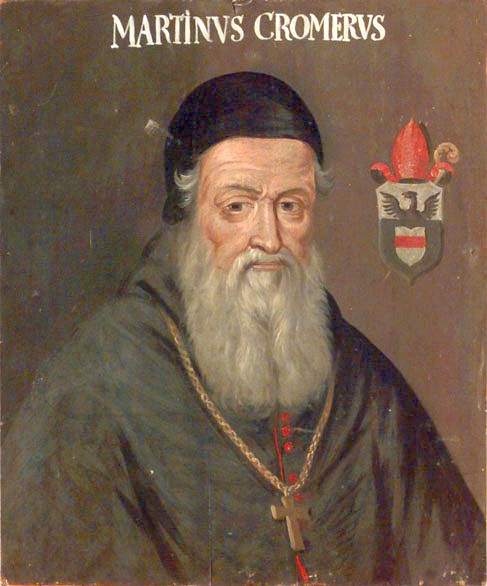


Polish science reached its culmination in the first half of the 16th century, in which the medieval point of view was criticized and more rational explanations were formulated.
Copernicus' ''
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium
''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' (English translation: ''On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres'') is the seminal work on the heliocentric theory of the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543) of the Polish Renaissance. The book, ...
'', published in
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
in 1543, shook up the traditional value system extended into an understanding of the physical universe, doing away with its Christianity-adopted
Ptolemaic anthropocentric
Anthropocentrism (; ) is the belief that human beings are the central or most important entity in the universe. The term can be used interchangeably with humanocentrism, and some refer to the concept as human supremacy or human exceptionalism. ...
model and setting free the explosion of scientific inquiry. Generally the prominent scientists of the period resided in many different regions of the country, and increasingly, the majority were of urban, rather than noble origin.
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated ...
, a son of a
Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
trader from Kraków, made many contributions to science and the arts. His scientific creativity was inspired at the University of Kraków, at the institution's height; he also studied at Italian universities later. Copernicus wrote Latin poetry, developed an
economic theory
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes ...
, functioned as a cleric-administrator, political activist in Prussian
sejmik
A sejmik (, diminutive of ''sejm'', occasionally translated as a ''dietine''; lt, seimelis) was one of various local parliaments in the history of Poland and history of Lithuania. The first sejmiks were regional assemblies in the Kingdom of ...
s, and led the
defense of Olsztyn against the forces of
Albrecht Hohenzollern. As an
astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either ...
, he worked on his scientific theory for many years at
Frombork
Frombork (; german: Frauenburg ) is a town in northern Poland, situated on the Vistula Lagoon in Braniewo County, within Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. As of December 2021, it has a population of 2,260.
The town was first mentioned in a 13th-centur ...
, where he died.
Josephus Struthius
Josephus Struthius ( Polish: Józef Struś; 1510 in Poznań – between 27 July 1568 and 26 January 1569 in Poznań) was a Polish professor of medicine in Padua (1535–1537) and personal doctor of Polish kings. He also served as mayor of Poznań ...
became famous as a physician and medical researcher.
Bernard Wapowski was a pioneer of Polish
cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
.
Maciej Miechowita
Maciej Miechowita (also known as ''Maciej z Miechowa, Maciej of Miechów, Maciej Karpiga, Matthias de Miechow''; 1457 – 8 September 1523) was a Polish renaissance scholar, professor of Jagiellonian University, historian, chronicler, geogra ...
, a
rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
at the
Cracow Academy
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
, published in 1517 ''Tractatus de duabus Sarmatiis'', a treatise on the geography of the East, an area in which Polish investigators provided first-hand expertise for the rest of Europe.
was one of the greatest theorists of political thought in Renaissance Europe. His most famous work, ''On the Improvement of the Commonwealth'', was published in Kraków in 1551. Modrzewski criticized the feudal societal relations and proposed broad realistic reforms. He postulated that all social classes should be subjected to the law to the same degree, and wanted to moderate the existing inequities. Modrzewski, an influential and often translated author, was a passionate proponent of the peaceful resolution of international conflicts.
Bishop
Wawrzyniec Goślicki (Goslicius), who wrote and published in 1568 a study entitled ''
De optimo senatore'' (''The Counsellor'' in the 1598 English translation), was another popular and influential in the West political thinker.
Historian
Marcin Kromer
Marcin Kromer (Latin: ''Martinus Cromerus''; 11 November 1512 – 23 March 1589) was Prince-Bishop of Warmia (Ermland), a Polish cartographer, diplomat and historian in the Kingdom of Poland and later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. H ...
wrote ''De origine et rebus gestis Polonorum'' (On the origin and deeds of Poles) in 1555 and in 1577 ''
Polonia'', a treatise highly regarded in Europe.
Marcin Bielski
Marcin Bielski (or ''Wolski''; 1495 – 18 December 1575) was a Polish soldier, historian, chronicler, renaissance satirical poet, writer and translator. His son, , royal secretary to king Sigismund III Vasa, was also a historian and poet. He wa ...
's ''Chronicle of the Whole World'', a
universal history
A universal history is a work aiming at the presentation of a history of all of mankind as a whole, coherent unit. A universal chronicle or world chronicle typically traces history from the beginning of written information about the past up to t ...
, was written ca. 1550. The chronicle of
Maciej Stryjkowski
Maciej Stryjkowski (also referred to as Strykowski and Strycovius;Nowa encyklopedia powszechna PWN. t. 6, 1997 – ) was a Polish historian, writer and a poet, known as the author of ''Chronicle of Poland, Lithuania, Samogitia and all of Rutheni ...
(1582) covered the history of Eastern Europe.
Literature

Modern
Polish literature
Polish literature is the literary tradition of Poland. Most Polish literature has been written in the Polish language, though other languages used in Poland over the centuries have also contributed to Polish literary traditions, including Latin, ...
begins in the 16th century. At that time the
Polish language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In a ...
, common to all educated groups, matured and penetrated all areas of public life, including municipal institutions, the legal code, the Church, and other official uses, coexisting for a while with
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
.
Klemens Janicki
Klemens Janicki (Janiciusz, Januszkowski, from Januszkowo) ( la, 'Clemens Ianicius') (1516–1543) was one of the most outstanding Latin poets of the 16th century.
Biography
Janicki was born in Januszkowo, a village near Żnin, Poland, to a peasa ...
, one of the Renaissance Latin language poets and a laureate of a papal distinction, was of peasant origin. Another plebeian author,
Biernat of Lublin, wrote his own version of
Aesop
Aesop ( or ; , ; c. 620–564 BCE) was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as ''Aesop's Fables''. Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous tales c ...
's fables in Polish, permeated with his socially radical views.
A Literary Polish language breakthrough came under the influence of the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
with the writings of
Mikołaj Rej
Mikołaj Rej or Mikołaj Rey of Nagłowice (4 February 1505 – between 8 September/5 October 1569) was a Polish poet and prose writer of the emerging Renaissance in Poland as it succeeded the Middle Ages, as well as a politician and musician. ...
. In his ''Brief Discourse'', a satire published in 1543, he defends a serf from a priest and a noble, but in his later works he often celebrates the joys of the peaceful but privileged life of a country gentleman. Rej, whose legacy is his unbashful promotion of the Polish language, left a great variety of literary pieces.
Łukasz Górnicki
Łukasz Ogończyk Górnicki (1527 in Oświęcim – 22 July 1603 in Lipniki by Tykocin), was a Polish Renaissance, poet, humanist, political commentator as well as secretary and chancellor of king Sigismund Augustus of Poland.
He wrote a numbe ...
, an author and translator, perfected the Polish prose of the period. His contemporary and friend
Jan Kochanowski
Jan Kochanowski (; 1530 – 22 August 1584) was a Polish Renaissance poet who established poetic patterns that would become integral to the Polish literary language. He is commonly regarded as the greatest Polish poet before Adam Mickiewicz.
...
became one of the greatest Polish poets of all time.
 Kochanowski
Kochanowski was born in 1530 into a prosperous noble family. In his youth he studied at the universities of Kraków,
Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was name ...
and
Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
and traveled extensively in Europe. He worked for a time as a royal secretary, and then settled in the village of
Czarnolas, a part of his family inheritance. Kochanowski's multifaceted creative output is remarkable for both the depth of thoughts and feelings that he shares with the reader, and for its beauty and classic perfection of form. Among Kochanowski's best known works are bucolic ''Frascas'' (trifles),
epic poetry
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants.
...
, religious
lyrics
Lyrics are words that make up a song, usually consisting of verses and choruses. The writer of lyrics is a lyricist. The words to an extended musical composition such as an opera are, however, usually known as a " libretto" and their writer, ...
, drama-tragedy ''The Dismissal of the Greek Envoys'', and the most highly regarded ''
Threnodies'' or
laments
A lament or lamentation is a passionate expression of grief, often in music, poetry, or song form. The grief is most often born of regret, or mourning. Laments can also be expressed in a verbal manner in which participants lament about something ...
, written after the death of his young daughter.
The poet
Mikołaj Sęp Szarzyński
Mikołaj Sęp Szarzyński (c. 1550 – c. 1581) was an influential Polish poet of the late Renaissance who wrote in both Polish and Latin. He was a pioneer of the Baroque and the greatest representative of the metaphysical movement of the e ...
, an intellectually refined master of small forms, bridges the late Renaissance and early
Baroque artistic periods.
Music
Following the European and Italian in particular musical trends, the
Renaissance music was developing in Poland, centered around the royal court patronage and branching from there. Sigismund I kept from 1543 a permanent choir at the Wawel castle, while the Reformation brought large scale group Polish language church singing during the services.
Jan of Lublin wrote a comprehensive
tablature
Tablature (or tabulature, or tab for short) is a form of musical notation indicating instrument fingering rather than musical pitches.
Tablature is common for fretted stringed instruments such as the guitar, lute or vihuela, as well as many fr ...
for the
organ and other
keyboard instrument
A keyboard instrument is a musical instrument played using a keyboard, a row of levers which are pressed by the fingers. The most common of these are the piano, organ, and various electronic keyboards, including synthesizers and digital p ...
s. Among the composers, who often permeated their music with national and folk elements, were
Wacław of Szamotuły,
Mikołaj Gomółka, who wrote music to Kochanowski translated
psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
, and
Mikołaj Zieleński
Mikołaj Zieleński (Zelenscius, fl. 1611) was a Polish composer, organist and '' Kapellmeister'' to the primate Baranowski, Archbishop of Gniezno.
Neither the date of his birth nor of his death are known; documents from Płock Cathedral state h ...
, who enriched the Polish music by adopting the
Venetian School polyphonic style.
Architecture, sculpture and painting

Architecture, sculpture and painting developed also under Italian influence from the beginning of the 16th century. A number of professionals from
Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
arrived and worked as royal artists in Kraków.
Francesco Fiorentino worked on the tomb of
John Albert already from 1502, and then together with
Bartolommeo Berrecci
Bartolomeo Berrecci (1480 Pontassieve, Italy - 1537 Kraków, Poland) was an Italian Renaissance architect who spent most of his career in Poland.
Studies and career in Poland
He learned architecture in Florence, first through apprenticeship ...
and
Benedykt from Sandomierz
Benedykt of Sandomierz (Polish: Benedykt z Sandomierza) was a Polish Renaissance architect, who together with Bartolommeo Berrecci rebuilt the Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków under the rule of Sigismund I of Poland after it burnt down in 1499.
Fi ...
rebuilt the
royal castle, which was accomplished between 1507 and 1536. Berrecci also built
Sigismund's Chapel at
Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral ( pl, Katedra Wawelska), formally titled the Royal Archcathedral Basilica of Saints Stanislaus and Wenceslaus, is a Roman Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it is part of the ...
. Polish magnates,
Silesian Piast
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his her ...
princes in
Brzeg
Brzeg (; Latin: ''Alta Ripa'', German: ''Brieg'', Silesian German: ''Brigg'', , ) is a town in southwestern Poland with 34,778 inhabitants (December 2021) and the capital of Brzeg County. It is situated in Silesia in the Opole Voivodeship on t ...
, and even Kraków merchants (by the mid 16th century their class economically gained strength nationwide) built or rebuilt their residencies to make them resemble the Wawel Castle. Kraków's
Sukiennice and
Poznań City Hall are among numerous buildings rebuilt in the Renaissance manner, but
Gothic construction continued alongside for a number of decades.
Between 1580 and 1600
Jan Zamoyski
Jan Sariusz Zamoyski ( la, Ioannes Zamoyski de Zamoscie; 19 March 1542 – 3 June 1605) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, and the 1st '' ordynat'' of Zamość. He served as the Royal Secretary from 1565, Deputy Chancellor from 1576, Grand Cha ...
commissioned the Venetian architect
Bernardo Morando to build the city of
Zamość
Zamość (; yi, זאמאשטש, Zamoshtsh; la, Zamoscia) is a historical city in southeastern Poland. It is situated in the southern part of Lublin Voivodeship, about from Lublin, from Warsaw. In 2021, the population of Zamość was 62,021.
...
. The town and its fortifications were designed to consistently implement the Renaissance and
Mannerism aesthetic paradigms.
Tombstone sculpture, often inside churches, is richly represented on graves of clergy and lay dignitaries and other wealthy individuals.
Jan Maria Padovano and
Jan Michałowicz of Urzędów count among the prominent artists.
Painted illuminations in
Balthasar Behem Codex
The Balthasar Behem Codex, also known as ''Codex Picturatus'', is a collection of the charters, privileges and statutes of the burghers of the city of Kraków. Compiled in 1505, the codex was named for the chancellor at the time, Balthasar Behe ...
are of exceptional quality, but draw their inspiration largely from
Gothic art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern, Southern and ...
.
Stanisław Samostrzelnik, a monk in the
Cistercian monastery in Mogiła near Kraków, painted miniatures and
polychrome
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery or sculpture in multiple colors.
Ancient Egypt
Colossal statu ...
d wall
frescos.
Republic of middle nobility; execution movement

The Polish political system in the 16th century was contested terrain as the middle gentry ''(
szlachta)'' sought power. Kings
Sigismund I the Old and
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
manipulated political institutions to block the gentry. The kings used their appointment power and influence on the elections to the Sejm. They issued propaganda upholding the royal position and provided financing to favoured leaders of the gentry. Seldom did the kings resort to repression or violence. Compromises were reached so that in the second half of the 16th century—for the only time in Polish history—the "democracy of the gentry" was implemented.
During the reign of Sigismund I, ''szlachta'' in the lower chamber of
general sejm
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED O ...
(from 1493 a bicameral legislative body), initially decidedly outnumbered by their more privileged colleagues from the
senate (which is what the appointed for life prelates and barons of the royal council were being called now), acquired a more numerous and fully elected representation. Sigismund however preferred to rule with the help of the
magnates, pushing ''szlachta'' into the "opposition".
After the ''
Nihil novi
''Nihil novi nisi commune consensu'' ("Nothing new without the Consent of the governed, common consent") is the original Latin title of a 1505 Statute, act or constitution adopted by the Poland, Polish ''Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland, Sejm'' (parl ...
'' act of 1505, a collection of laws known as
Łaski's Statute
Łaski's Statute(s) ( pl, Statut(y) Łaskiego, lat, Commune Incliti Poloniae regni privilegium constitutionum et indultuum publicitus decretorum approbatorumque), of 1505, was the first codification of law published in the Kingdom of Poland. Th ...
s was published in 1506 and distributed to Polish courts. The legal pronouncements, intended to facilitate the functioning of a uniform and centralized state, with ordinary ''szlachta'' privileges strongly protected, were frequently ignored by the kings, beginning with Sigismund I, and the upper nobility or church interests. This situation became the basis for the formation around 1520 of the ''szlachtas
execution movement, for the complete codification and execution, or enforcement, of the laws.
In 1518 Sigismund I married
Bona Sforza d'Aragona, a young, strong-minded Italian princess. Bona's sway over the king and the magnates, her efforts to strengthen the monarch's political position, financial situation, and especially the measures she took to advance her personal and dynastic interests, including the forced royal election of the minor
Sigismund Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
in 1529 and his
premature coronation in 1530, increased the discontent among ''szlachta'' activists.
The opposition middle ''szlachta'' movement came up with a constructive reform program during the Kraków sejm of 1538/1539. Among the movement's demands were termination of the kings' practice of alienation of
royal domain
Crown land (sometimes spelled crownland), also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it ...
, giving or selling land estates to great lords at the monarch' discretion, and a ban on concurrent holding of multiple state offices by the same person, both legislated initially in 1504. Sigismund I's unwillingness to move toward the implementation of the reformers' goals negatively affected the country's financial and defensive capabilities.
The relationship with ''szlachta'' had only gotten worse during the early years of the reign of Sigismund II Augustus and remained bad until 1562. Sigismund Augustus' secret marriage with
Barbara Radziwiłł in 1547, before his accession to the throne, was strongly opposed by his mother Bona and by the magnates of the Crown. Sigismund, who took over the reign after his father's death in 1548, overcame the resistance and had Barbara crowned in 1550; a few months later the new queen died. Bona, estranged from her son returned to Italy in 1556, where she died soon afterwards.

The
Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
, until 1573 summoned by the king at his discretion (for example when he needed funds to wage a war), composed of the two chambers presided over by the monarch, became in the course of the 16th century the main organ of the state power. The reform-minded
execution movement had its chance to take on the magnates and the church hierarchy (and take steps to restrain their abuse of power and wealth) when Sigismund Augustus switched sides and lent them his support at the sejm of 1562. During this and several more sessions of parliament, within the next decade or so, the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
inspired ''szlachta'' was able to push through a variety of reforms, which resulted in a fiscally more sound, better governed, more centralized and territorially unified Polish state. Some of the changes were too modest, other had never become completely implemented (e. g. recovery of the usurped
Crown land), but nevertheless for the time being the middle ''szlachta'' movement was victorious.
, a Protestant activist, was a parliamentary leader of the execution movement and one of the organizers of the
Warsaw Confederation
The Warsaw Confederation, signed on 28 January 1573 by the Polish national assembly (''sejm konwokacyjny'') in Warsaw, was one of the first European acts granting religious freedoms. It was an important development in the history of Poland and o ...
.
Resources and strategic objectives
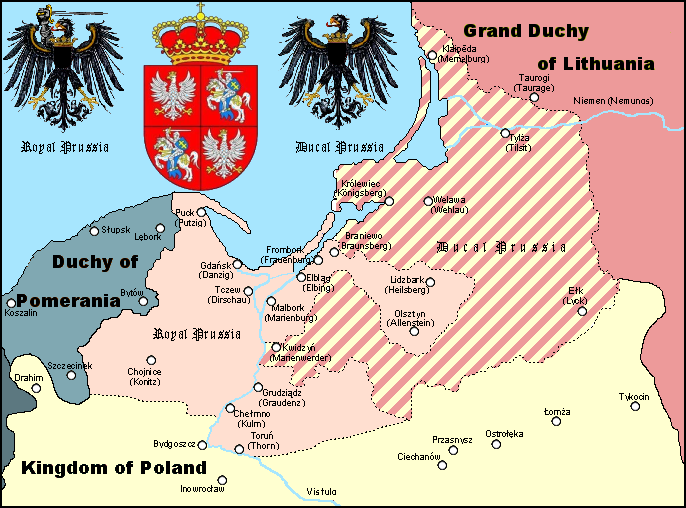
Despite the favorable economic development, the military potential of 16th century Poland was modest in relation to the challenges and threats coming from several directions, which included the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the
Teutonic state, the
Habsburgs, and
Muscovy. Given the declining military value and willingness of
pospolite ruszenie
''Pospolite ruszenie'' (, lit. ''mass mobilization''; "Noble Host", lat, motio belli, the French term ''levée en masse'' is also used) is a name for the mobilisation of armed forces during the period of the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Li ...
, the bulk of the forces available consisted of professional and mercenary soldiers. Their number and provision depended on ''szlachta''-approved funding (self-imposed taxation and other sources) and tended to be insufficient for any combination of adversaries. The quality of the forces and their command was good, as demonstrated by victories against a seemingly overwhelming enemy. The attainment of strategic objectives was supported by a well-developed service of knowledgeable diplomats and emissaries. Because of the limited resources at the state's disposal, the Jagiellonian Poland had to concentrate on the area most crucial for its security and economic interests, which was the strengthening of Poland's position along the
Baltic coast.
Prussia; struggle for Baltic area domination

The
Peace of Thorn of 1466 reduced the
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
, but brought no lasting solution to the problem they presented for Poland and their state avoided paying the prescribed
tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
. The chronically difficult relations had gotten worse after the 1511 election of
Albrecht as
Grand Master of the
Order. Faced with Albrecht's rearmament and hostile alliances,
Poland waged a war in 1519; the war ended in 1521, when mediation by
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infa ...
resulted in a truce. As a compromise move Albrecht, persuaded by
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
, initiated a process of secularization of the Order and the establishment of a lay duchy of Prussia, as Poland's dependency, ruled by Albrecht and afterwards by his descendants. The terms of the proposed pact immediately improved Poland's Baltic region situation, and at that time also appeared to protect the country's long-term interests. The
treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pe ...
was concluded in 1525 in Kraków; the remaining state of the Teutonic Knights (East Prussia centered on
Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was name ...
) was converted into the Protestant (
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
)
Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
under the King of Poland and the
homage act of the new Prussian duke in Kraków followed.
In reality the
House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenbu ...
, of which Albrecht was a member, the ruling family of the
Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
, had been actively expanding its territorial influence; for example already in the 16th century in
Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
and Silesia. Motivated by a current political expediency, Sigismund Augustus in 1563 allowed the
Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
elector
Elector may refer to:
* Prince-elector or elector, a member of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Holy Roman Emperors
* Elector, a member of an electoral college
** Confederate elector, a member of ...
branch of the Hohenzollerns, excluded under the 1525 agreement,
to inherit the
Prussian fief rule. The decision, confirmed by the 1569 sejm, made the future union of Prussia with Brandenburg possible. Sigismind II, unlike his successors, was however careful to assert his supremacy. The
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
, ruled after 1572 by elective kings, was even less able to counteract the growing importance of the dynastically active Hohenzollerns.
In 1568 Sigismund Augustus, who had already embarked on a war fleet enlargement program, established the Maritime Commission. A conflict with the City of
Gdańsk (Danzig), which felt that its monopolistic trade position was threatened, ensued. In 1569
Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
had its legal autonomy largely taken away, and in 1570 Poland's supremacy over Danzig and the Polish King's authority over the
Baltic shipping trade were regulated and received statutory recognition (
Karnkowski's Statutes).
Wars with Moscow
In the 16th century the
Grand Duchy of Moscow continued activities aimed at unifying the old
Rus' lands still under Lithuanian rule. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania had insufficient resources to counter Moscow's advances, already having to control the
Rus' population within its borders and not being able to count on loyalty of Rus' feudal lords. As a result of the protracted war at the turn of the 15th and 16th centuries, Moscow acquired large tracts of territory east of the
Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
. Polish assistance and involvement were increasingly becoming a necessary component of the balance of power in the eastern reaches of the Lithuanian domain.
Under
Vasili III
Vasili III Ivanovich (russian: Василий III Иванович, 25 March 14793 December 1533) was the Grand Prince of Moscow from 1505 to 1533. He was the son of Ivan III Vasiliyevich and Sophia Paleologue and was christened with the nam ...
Moscow fought a
war with Lithuania and Poland between 1512 and 1522, during which in 1514 the Russians took
Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
. That same year the Polish-Lithuanian rescue expedition fought the victorious
Battle of Orsha
The Battle of Orsha ( be, Бітва пад Оршай, translit=Bitva pad Oršaj, lt, Oršos mūšis, pl, bitwa pod Orszą, uk, Битва під Оршею), was a battle fought on 8 September 1514, between the allied forces of the Grand Du ...
under Hetman
Konstanty Ostrogski
Konstanty Iwanowicz Ostrogski (c. 1460 – 10 August 1530; lt, Konstantinas Ostrogiškis; uk, Костянтин Іванович Острозький, translit=Kostiantyn Ivanovych Ostrozkyi; be, Канстантын Іванавіч Ас� ...
and stopped the Duchy of Moscow's further advances. An armistice implemented in 1522 left Smolensk land and
Severia
Severia or Siveria ( orv, Сѣверія, russian: Северщина, translit=Severshchina, uk, Сіверія or , translit. ''Siveria'' or ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, eastern ...
in Russian hands. Another round of fighting took place during 1534–1537, when the Polish aid led by Hetman
Jan Tarnowski
Jan Amor Tarnowski (Latin: Joannes Tarnovius; 1488 – 16 May 1561) was a Polish nobleman, knight, military commander, military theoretician, and statesman of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. He was Grand Crown Hetman from 1527, and was ...
made possible the taking of
Gomel
Gomel (russian: Гомель, ) or Homiel ( be, Гомель, ) is the administrative centre of Gomel Region and the second-largest city in Belarus with 526,872 inhabitants (2015 census).
Etymology
There are at least six narratives of the o ...
and fiercely defeated
Starodub
Starodub ( rus, links=no, Староду́б, p=stərɐˈdup, ''old oak'') is a town in Bryansk Oblast, Russia, on the Babinets River (the Dnieper basin), southwest of Bryansk. Population: 16,000 (1975).
History
Starodub has been known ...
. New truce (Lithuania kept only Gomel), stabilization of the border and over two decades of peace followed.
The Jagiellons and the Habsburgs; Ottoman Empire expansion
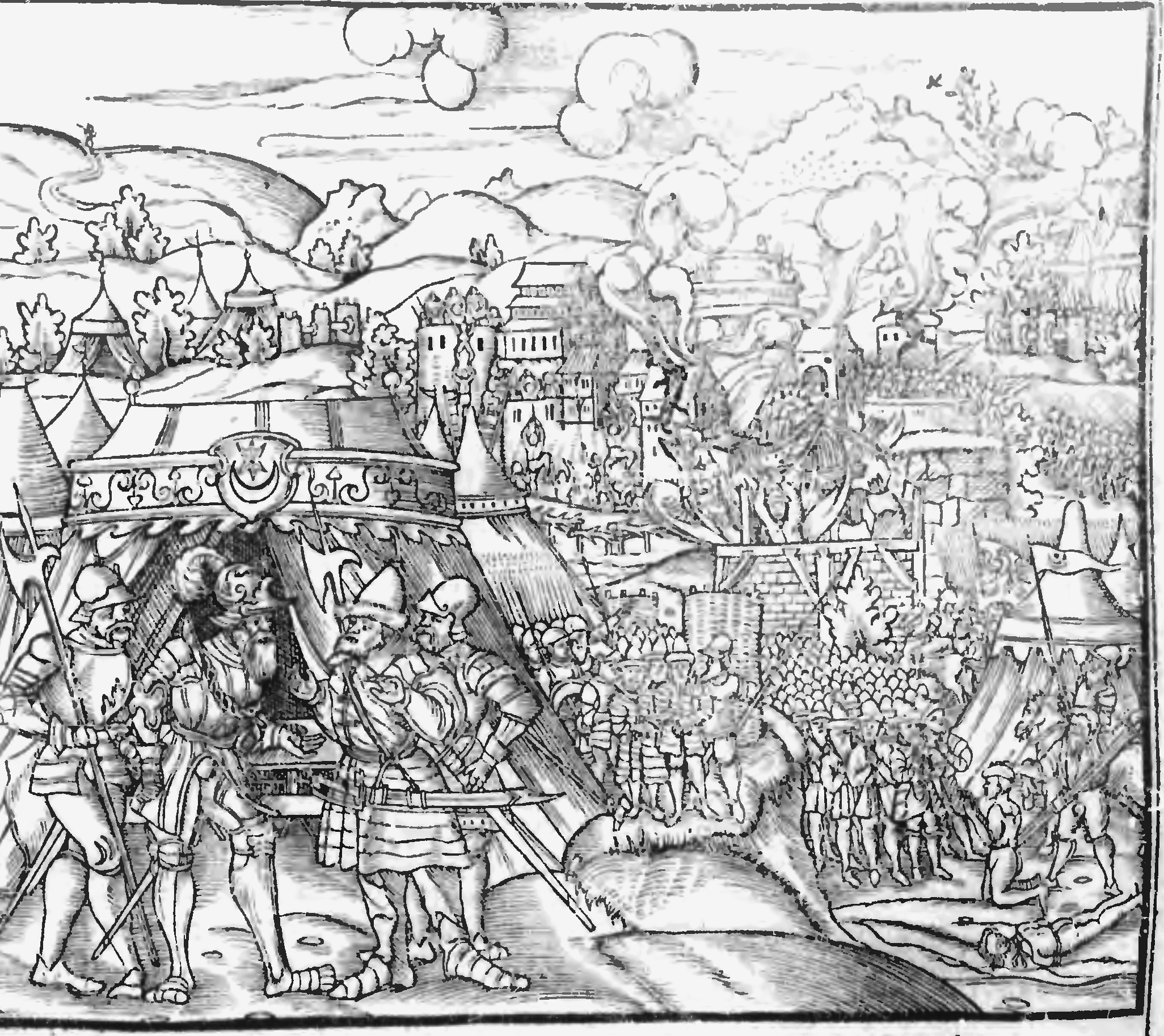

In 1515, during a
congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
in
Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, a dynastic succession arrangement was agreed to between
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death. He was never crowned by the pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed himself E ...
and the Jagiellon brothers,
Vladislas II of Bohemia and Hungary
Vladislaus II, also known as Vladislav, Władysław or Wladislas ( hu, II. Ulászló; 1 March 1456 – 13 March 1516), was King of Bohemia from 1471 to 1516, and King of Hungary and Croatia from 1490 to 1516. As the eldest son of Casimir IV Jagi ...
and Sigismund I of Poland and Lithuania. It was supposed to end the Emperor's support for Poland's enemies, the Teutonic and Russian states, but after the election of
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infa ...
, Maximilian's successor in 1519, the relations with Sigismund had worsened.
The
Jagiellon rivalry with the
House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
in central Europe was ultimately resolved to the Habsburgs' advantage. The decisive factor that damaged or weakened the monarchies of the last Jagiellons was the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's Turkish expansion. Hungary's vulnerability greatly increased after
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳ ...
took the
Belgrade fortress in 1521. To prevent Poland from extending military aid to Hungary, Suleiman had a
Tatar
The Tatars ()[Tatar]
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different -Turkish force raid southeastern Poland–Lithuania in 1524. The Hungarian army was defeated in 1526 at the
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and thos ...
, where the young
Louis II Jagiellon, son of Vladislas II, was killed. Subsequently, after a period of internal strife and external intervention, Hungary was partitioned between the Habsburgs and the Ottomans.
The 1526 death of
Janusz III of Masovia
Janusz III of Masovia (pl: ''Janusz III mazowiecki''; ca. 27 September 1502 – 9/10 March 1526), was a Polish prince member of the House of Piast in the Masovian branch. He was a Duke of Czersk, Warsaw, Liw, Zakroczym and Nur during 1503-15 ...
, the last of the
Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
n
Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branche ...
dukes line (a remnant of the
fragmentation period divisions), enabled Sigismund I to finalize the incorporation of Masovia into the
Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
in 1529.
From the early 16th century the
Pokuttya
Pokuttia, also known as Pokuttya or Pokutia ( uk, Покуття, Pokuttya; pl, Pokucie; german: Pokutien; ro, Pocuția), is a historical area of East-Central Europe, situated between the Dniester and Cheremosh rivers and the Carpathian Moun ...
border region was contested by Poland and
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and for ...
(see
Battle of Obertyn
The Battle of Obertyn (August 22, 1531) was fought between Moldavian Voivode Petru Rareş and Polish forces under hetman Jan Tarnowski, in the town of Obertyn, south of the Dniester River, now in Ukraine. The battle ended with a Polish victory and ...
). A peace with Moldavia took effect in 1538 and Pokuttya remained Polish. An "eternal peace" with the Ottoman Empire was negotiated by Poland in 1533 to secure frontier areas. Moldavia had fallen under Turkish domination, but Polish-Lithuanian magnates remained actively involved there.
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
even claimed "jurisdiction" and in 1569 accepted a formal, short-lived
suzerainty over Moldavia.
Livonia; struggle for Baltic area domination

In the 16th century the Grand Duchy of Lithuania became increasingly interested in extending its territorial rule to
Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
, especially to gain control of Baltic seaports, such as
Riga, and for other economic benefits. Livonia was by the 1550s largely
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
, traditionally ruled by the
Brothers of the Sword knightly order. This put Poland and Lithuania on a collision course with Moscow and other regional powers, which had also attempted expansion in that area.
Soon after the
Treaty of Kraków
The Treaty of Kraków was signed on 8 April 1525 between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. It officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War.John Freely Celestial Revolutionary: Copernicus, the Man and His Universe ...
of 1525,
Albrecht (Albert) of Hohenzollern planned a Polish–Lithuanian fief in Livonia, seeking a dominant position for his brother
Wilhelm
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Mount ...
, the Archbishop of Riga. What happened instead was the establishment of a Livonian pro-Polish–Lithuanian party or faction. Internal fighting in Livonia took place when the Grand Master of the Brothers concluded a treaty with Moscow in 1554, declaring his state's neutrality regarding the Russian–Lithuanian conflict. Supported by Albrecht and the magnates, Sigismund II declared a war on the Order. Grand Master
Wilhelm von Fürstenberg accepted the Polish–Lithuanian conditions without a fight, and according to the 1557
Treaty of Pozvol, a military alliance obliged the Livonian state to support Lithuania against Moscow.

Other powers aspiring to the Livonian Baltic access responded by partitioning the
Livonian state, which triggered the lengthy
Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) was the Russian invasion of Old Livonia, and the prolonged series of military conflicts that followed, in which Tsar Ivan the Terrible of Russia (Muscovy) unsuccessfully fought for control of the region (pr ...
, fought between 1558 and 1583.
Ivan IV of Russia
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584.
Iva ...
took
Dorpat
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after the Northern European country's political and financial capital, Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 91,407 (as of 2021). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of ...
(Tartu) and
Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru county, at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia international border. With 54 ...
in 1558, and soon the
Danes and
Swedes had occupied other parts of the country. To protect the integrity of their country, the Livonians now sought a union with the Polish–Lithuanian state.
Gotthard Kettler
Gotthard Kettler, Duke of Courland (also ''Godert'', ''Ketteler'', german: Gotthard Kettler, Herzog von Kurland; 2 February 1517 – 17 May 1587) was the last Master of the Livonian Order and the first Duke of Courland and Semigallia.
Biography
...
, the new Grand Master, met in
Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
(Vilna, Wilno) with Sigismund Augustus in 1561 and declared Livonia a vassal state under the Polish king. The
Union of Vilnius
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''U ...
called for secularization of the Brothers of the Sword Order and incorporation of the newly established
Duchy of Livonia
The Duchy of Livonia ( or ; lt, Livonijos kunigaikštystė; la, Ducatus Ultradunensis; et, Liivimaa hertsogkond; lv, Pārdaugavas hercogiste; german: Herzogtum Livland), also referred to as Polish Livonia or Livonia ( pl, link=no, Inflanty) ...
into the ''
Rzeczpospolita
() is the official name of Poland and a traditional name for some of its predecessor states. It is a compound of "thing, matter" and "common", a calque of Latin ''rés pública'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. ''republic'', in Engli ...
'' ("Republic") as an autonomous entity. The
Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was also created as a separate fief, to be ruled by Kettler. Sigismund II obliged himself to recover the parts of Livonia lost to Moscow and the Baltic powers, which had led to grueling wars with Russia (
1558–1570 and
1577–1582) and
heavy struggles also concerning the fundamental issues of
control of the Baltic trade and freedom of navigation.
The Baltic region policies of the last Jagiellon king and his advisors were the most mature of 16th-century Poland's strategic programs. The outcome of the efforts in that area was to a considerable extent successful for the Commonwealth. The wars concluded during the reign of King
Stephen Báthory
Stephen Báthory ( hu, Báthory István; pl, Stefan Batory; ; 27 September 1533 – 12 December 1586) was Voivode of Transylvania (1571–1576), Prince of Transylvania (1576–1586), King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania (1576–1586) ...
.
Poland and Lithuania in real union under Sigismund II

Sigismund II's childlessness added urgency to the idea of turning the
personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
between Poland and the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
into a more permanent and tighter relationship; it was also a priority for the execution movement.
Lithuania's laws were codified and reforms enacted in 1529, 1557, 1565–1566 and 1588, gradually making its social, legal and economic system similar to that of Poland, with the expanding role of the middle and lower nobility.
Fighting wars with
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
under Ivan IV and the threat perceived from that direction provided additional motivation for the
real union
Real union is a union of two or more states, which share some state institutions in contrast to personal unions; however, they are not as unified as states in a political union. It is a development from personal union and has historically be ...
for both Poland and Lithuania.
The process of negotiating the actual arrangements turned out to be difficult and lasted from 1563 to 1569, with the Lithuanian magnates, worried about losing their dominant position, being at times uncooperative. It took Sigismunt II's unilateral declaration of the
incorporation into the Polish Crown of substantial disputed border regions, including most of Lithuanian
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, to make the Lithuanian magnates rejoin the process, and participate in the swearing of the act of the
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
on July 1, 1569. Lithuania for the near future was becoming more secure on the eastern front. Its increasingly
Polonized
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
nobility made in the coming centuries great contributions to the
Commonwealth's culture, but at the cost of Lithuanian national development.
The
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 mill ...
survived as a peasant
vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
and also as a written language in religious use, from the publication of the Lithuanian Catechism by
Martynas Mažvydas
Martynas Mažvydas (1510 – 21 May 1563) was a Protestant author who edited the first printed book in the Lithuanian language.
Variants of his name include Martinus Masvidius, Martinus Maszwidas, M. Mossuids Waytkūnas, Mastwidas, Mažvyda ...
in 1547. The
Ruthenian language was and remained in the Grand Duchy's official use even after the Union, until the takeover of
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
.
The Commonwealth: multicultural, magnate dominated

By the Union of Lublin a unified
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
(''
Rzeczpospolita
() is the official name of Poland and a traditional name for some of its predecessor states. It is a compound of "thing, matter" and "common", a calque of Latin ''rés pública'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. ''republic'', in Engli ...
'') was created, stretching from the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
and the
Carpathian mountains to present-day
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and western and central
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
(which earlier had been
Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
principalities). Within the new federation some degree of formal separateness of Poland and
Lithuania was retained (distinct state offices, armies, treasuries and judicial systems), but the union became a multinational entity with a common monarch,
parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
, monetary system and foreign-military policy, in which only the nobility enjoyed full citizenship rights. Moreover, the nobility's uppermost stratum was about to assume the dominant role in the Commonwealth, as magnate factions were acquiring the ability to manipulate and control the rest of ''szlachta'' to their clique's private advantage. This trend, facilitated further by the liberal settlement and land acquisition consequences of the union, was becoming apparent at the time of, or soon after the 1572 death of Sigismund Augustus, the last monarch of the Jagiellonian dynasty.
One of the most salient characteristics of the newly established Commonwealth was its
multiethnicity, and accordingly diversity of religious faiths and denominations. Among the peoples represented were
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
(about 50% or less of the total population),
Lithuanians,
Latvians
Latvians ( lv, latvieši) are a Baltic ethnic group and nation native to Latvia and the immediate geographical region, the Baltics. They are occasionally also referred to as Letts, especially in older bibliography. Latvians share a common La ...
,
Rus' people (corresponding to today's
Belarusians,
Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
,
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
or their
East Slavic ancestors),
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
,
Estonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic ethnic group native to Estonia who speak the Estonian language.
The Estonian language is spoken as the first language by the vast majority of Estonians; it is closely related to oth ...
,
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
,
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
,
Tatars
The Tatars ()[Tatar]
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different and
Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
, among others, for example smaller
West European
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
groups. As for the main social segments in the early 17th century, nearly 70% of the Commonwealth's population were
peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasant ...
s, over 20% residents of towns, and less than 10% nobles and clergy combined. The total population, estimated at 8–10 million, kept growing dynamically until the middle of the century.
The Slavic populations of the eastern lands,
Rus' or
Ruthenia, were solidly, except for the Polish colonizing nobility (and
Polonized
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
elements of local nobility),
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
, which portended future trouble for the Commonwealth.
Jewish settlement
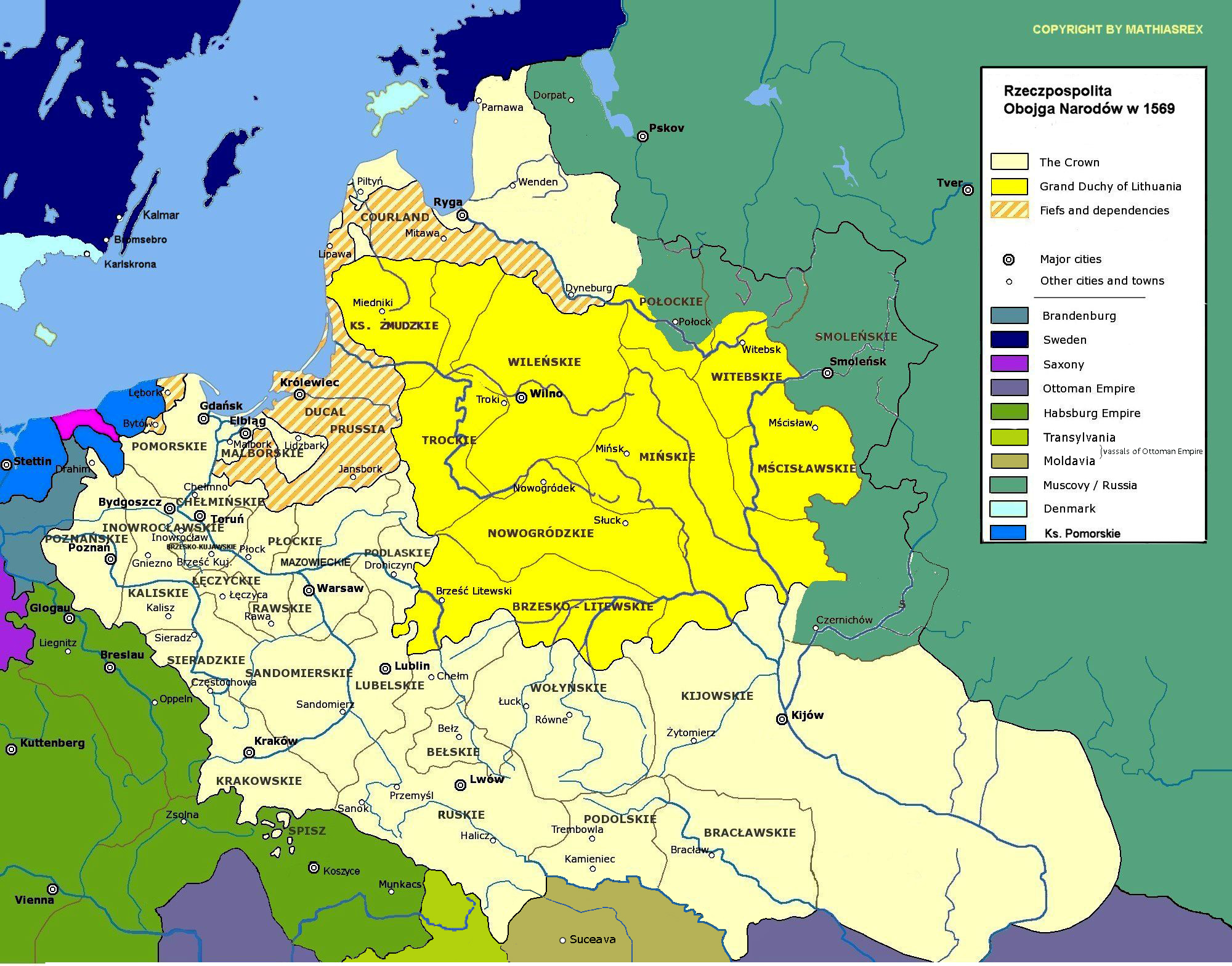
Poland had become the home to
Europe's largest Jewish population, as royal edicts guaranteeing Jewish safety and religious freedom, issued during the 13th century (
Bolesław the Pious,
Statute of Kalisz of 1264), contrasted with bouts of persecution in Western Europe. This persecution intensified following the
Black Death of 1348–1349, when some in the West blamed the outbreak of the plague on the Jews. As scapegoats were sought, the increased
Jewish persecution led to
pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russia ...
s and mass killings in a number of German cities, which caused an exodus of survivors heading east. Much of Poland was spared from the Black Death, and Jewish immigration brought their valuable contributions and abilities to the rising state. The number of Jews in Poland kept increasing throughout the Middle Ages; the population had reached about 30,000 toward the end of the 15th century, and, as refugees escaping further persecution elsewhere kept streaming in, 150,000 in the 16th century.
A royal privilege issued in 1532 granted the Jews freedom to trade anywhere within the kingdom.
Massacres and expulsions from many German states continued until 1552–1553.
[ Richard Overy (2010), ''The Times Complete History of the World'', Eights Edition, p. 116–117. London: Times Books. .] By the mid-16th century, 80% of the world's Jews lived and flourished in Poland and in Lithuania; most of western and central Europe was by that time closed to Jews.
In Poland–Lithuania the Jews were increasingly finding employment as managers and intermediaries, facilitating the functioning of and collecting revenue in huge magnate-owned land estates, especially in the eastern borderlands, developing into an indispensable mercantile and administrative class. Despite the partial resettlement of Jews in Western Europe following the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
(1618–1648), a great majority of world Jewry had lived in Eastern Europe (in the Commonwealth and in the regions further east and south, where many migrated), until the 1940s.
See also
*
History of Lithuania
The history of Lithuania dates back to settlements founded many thousands of years ago, but the first written record of the name for the country dates back to 1009 AD. Lithuanians, one of the Baltic peoples, later conquered neighboring lands an ...
*
History of Poland during the Piast dynasty
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th cen ...
*
History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1648)
The history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1648) covers a period in the history of Poland and Lithuania, before their joint state was subjected to devastating wars in the middle of the 17th century. The Union of Lublin of 1569 ...
*
Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, includi ...
Notes
''a.''This is true especially regarding legislative matters and legal framework. Despite the restrictions the nobility imposed on the monarchs, the Polish kings had never become figureheads. In practice they wielded considerable executive power, up to and including the last king,
Stanisław August Poniatowski. Some were at times even accused of absolutist tendencies, and it may be for the lack of sufficiently strong personalities or favorable circumstances that none of the kings had succeeded in significant and lasting strengthening of the monarchy.
''b.'' 13 in
Greater Poland, 59 in
Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
, 32 in
Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
, and 153 in
Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
.
[A. Janeczek. "Town and country in the Polish Commonwealth, 1350-1650." In: S. R. Epstein. ''Town and Country in Europe, 1300-1800''. ]Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
. 2004. p. 164.
References
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
{{Main, Bibliography of the history of Poland
* ''The Cambridge History of Poland'' (two vols., 1941–1950
online edition vol 1 to 1696* Butterwick, Richard, ed. ''The Polish-Lithuanian Monarchy in European Context, c. 1500-1795.'' Palgrave, 2001. 249 pp.
online edition* Davies, Norman. ''Heart of Europe: A Short History of Poland.'' Oxford University Press, 1984.
* Davies, Norman. ''God's Playground: A History of Poland.'' 2 vol. Columbia U. Press, 1982.
* Pogonowski, Iwo Cyprian. ''Poland: A Historical Atlas.'' Hippocrene, 1987. 321 pp.
* Sanford, George. ''Historical Dictionary of Poland.'' Scarecrow Press, 2003. 291 pp.
* Stone, Daniel. ''The Polish-Lithuanian State, 1386-1795.'' U. of Washington Press, 2001.
* Zamoyski, Adam. ''The Polish Way''. Hippocrene Books, 1987. 397 pp.
History of Lithuania (1219–1569)
 In 1385, the
In 1385, the  The feudal rent system prevalent in the 13th and 14th centuries, under which each estate had well defined rights and obligations, degenerated around the 15th century as the nobility tightened their control over manufacturing, trade and other economic activities. This created many directly owned agricultural enterprises known as
The feudal rent system prevalent in the 13th and 14th centuries, under which each estate had well defined rights and obligations, degenerated around the 15th century as the nobility tightened their control over manufacturing, trade and other economic activities. This created many directly owned agricultural enterprises known as  The first king of the new dynasty was Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, who was known as
The first king of the new dynasty was Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, who was known as  The
The  During the
During the  In 1438, the Czech anti- Habsburg opposition, mainly Hussite factions, offered the Czech crown to Jagiełło's younger son
In 1438, the Czech anti- Habsburg opposition, mainly Hussite factions, offered the Czech crown to Jagiełło's younger son  Beginning near the end of Jagiełło's life, Poland was governed in practice by an oligarchy of magnates led by Bishop Oleśnicki. The rule of the dignitaries was actively opposed by various groups of '' szlachta''. Their leader
Beginning near the end of Jagiełło's life, Poland was governed in practice by an oligarchy of magnates led by Bishop Oleśnicki. The rule of the dignitaries was actively opposed by various groups of '' szlachta''. Their leader  In 1454, the
In 1454, the  Kraków University, which stopped functioning after the death of Casimir the Great, was renewed and rejuvenated around 1400. Augmented by a
Kraków University, which stopped functioning after the death of Casimir the Great, was renewed and rejuvenated around 1400. Augmented by a  The
The  During the 16th century, prosperous
During the 16th century, prosperous  In a situation analogous with that of other European countries, the progressive internal decay of the Polish Church created conditions favorable for the dissemination of the
In a situation analogous with that of other European countries, the progressive internal decay of the Polish Church created conditions favorable for the dissemination of the  Sigismund's son
Sigismund's son  Around 1570, of the at least 700 Protestant congregations in Poland–Lithuania, over 420 were
Around 1570, of the at least 700 Protestant congregations in Poland–Lithuania, over 420 were  Among the Calvinists, who also included the lower classes and their leaders, ministers of common background, disagreements soon developed, based on different views in the areas of religious and social doctrines. The official split took place in 1562, when two separate churches were officially established: the mainstream Calvinist and the smaller, more reformist,
Among the Calvinists, who also included the lower classes and their leaders, ministers of common background, disagreements soon developed, based on different views in the areas of religious and social doctrines. The official split took place in 1562, when two separate churches were officially established: the mainstream Calvinist and the smaller, more reformist,  The Polish "Golden Age", the period of the reigns of Sigismund I and Sigismund II, the last two Jagiellonian kings, or more generally the 16th century, is most often identified with the rise of the culture of
The Polish "Golden Age", the period of the reigns of Sigismund I and Sigismund II, the last two Jagiellonian kings, or more generally the 16th century, is most often identified with the rise of the culture of  Beginning in 1473 in Cracow (Kraków), the printing business kept growing. By the turn of the 16th/17th century there were about 20 printing houses within the Commonwealth, 8 in Cracow, the rest mostly in Gdańsk (Danzig), Thorn (Toruń) and
Beginning in 1473 in Cracow (Kraków), the printing business kept growing. By the turn of the 16th/17th century there were about 20 printing houses within the Commonwealth, 8 in Cracow, the rest mostly in Gdańsk (Danzig), Thorn (Toruń) and 
 Polish science reached its culmination in the first half of the 16th century, in which the medieval point of view was criticized and more rational explanations were formulated. Copernicus' ''
Polish science reached its culmination in the first half of the 16th century, in which the medieval point of view was criticized and more rational explanations were formulated. Copernicus' '' Modern
Modern  Kochanowski was born in 1530 into a prosperous noble family. In his youth he studied at the universities of Kraków,
Kochanowski was born in 1530 into a prosperous noble family. In his youth he studied at the universities of Kraków,  Architecture, sculpture and painting developed also under Italian influence from the beginning of the 16th century. A number of professionals from
Architecture, sculpture and painting developed also under Italian influence from the beginning of the 16th century. A number of professionals from  The
The  Despite the favorable economic development, the military potential of 16th century Poland was modest in relation to the challenges and threats coming from several directions, which included the
Despite the favorable economic development, the military potential of 16th century Poland was modest in relation to the challenges and threats coming from several directions, which included the  The Peace of Thorn of 1466 reduced the
The Peace of Thorn of 1466 reduced the  Other powers aspiring to the Livonian Baltic access responded by partitioning the Livonian state, which triggered the lengthy
Other powers aspiring to the Livonian Baltic access responded by partitioning the Livonian state, which triggered the lengthy  Sigismund II's childlessness added urgency to the idea of turning the
Sigismund II's childlessness added urgency to the idea of turning the  By the Union of Lublin a unified
By the Union of Lublin a unified  Poland had become the home to Europe's largest Jewish population, as royal edicts guaranteeing Jewish safety and religious freedom, issued during the 13th century ( Bolesław the Pious, Statute of Kalisz of 1264), contrasted with bouts of persecution in Western Europe. This persecution intensified following the Black Death of 1348–1349, when some in the West blamed the outbreak of the plague on the Jews. As scapegoats were sought, the increased Jewish persecution led to
Poland had become the home to Europe's largest Jewish population, as royal edicts guaranteeing Jewish safety and religious freedom, issued during the 13th century ( Bolesław the Pious, Statute of Kalisz of 1264), contrasted with bouts of persecution in Western Europe. This persecution intensified following the Black Death of 1348–1349, when some in the West blamed the outbreak of the plague on the Jews. As scapegoats were sought, the increased Jewish persecution led to