Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 ''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'', ''Siyuan yujian'' (), also referred to as ''Jade Mirror of the Four Origins'', is a 1303 mathematical monograph by Yuan dynasty mathematician
''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'', ''Siyuan yujian'' (), also referred to as ''Jade Mirror of the Four Origins'', is a 1303 mathematical monograph by Yuan dynasty mathematician
 The four quantities are ''x'', ''y'', ''z'', ''w'' can be presented with the following diagram
:::::::::::::x
::::::::::::y 太w
:::::::::::::z
The square of which is:
The four quantities are ''x'', ''y'', ''z'', ''w'' can be presented with the following diagram
:::::::::::::x
::::::::::::y 太w
:::::::::::::z
The square of which is:


 :
Successive elimination of unknowns to get
::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
Solve this and obtain 14 paces
:
Successive elimination of unknowns to get
::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
Solve this and obtain 14 paces


 ''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'', ''Siyuan yujian'' (), also referred to as ''Jade Mirror of the Four Origins'', is a 1303 mathematical monograph by Yuan dynasty mathematician
''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'', ''Siyuan yujian'' (), also referred to as ''Jade Mirror of the Four Origins'', is a 1303 mathematical monograph by Yuan dynasty mathematician Zhu Shijie
Zhu Shijie (, 1249–1314), courtesy name Hanqing (), pseudonym Songting (), was a Chinese mathematician and writer. He was a Chinese mathematician during the Yuan Dynasty. Zhu was born close to today's Beijing. Two of his mathematical works ha ...
. Zhu advanced Chinese algebra with this Magnum opus
A masterpiece, ''magnum opus'' (), or ''chef-d’œuvre'' (; ; ) in modern use is a creation that has been given much critical praise, especially one that is considered the greatest work of a person's career or a work of outstanding creativity, ...
.
The book consists of an introduction and three books, with a total of 288 problems. The first four problems in the introduction illustrate his method of the four unknowns. He showed how to convert a problem stated verbally into a system of polynomial equations (up to the 14th order), by using up to four unknowns: 天 Heaven, 地 Earth, 人 Man, 物 Matter, and then how to reduce the system to a single polynomial equation in one unknown by successive elimination of unknowns. He then solved the high-order equation by Southern Song dynasty mathematician Qin Jiushao
Qin Jiushao (, ca. 1202–1261), courtesy name Daogu (道古), was a Chinese mathematician, meteorologist, inventor, politician, and writer. He is credited for discovering Horner's method as well as inventing Tianchi basins, a type of rain gau ...
's "Ling long kai fang" method published in Shùshū Jiǔzhāng (“Mathematical Treatise in Nine Sections
The ''Mathematical Treatise in Nine Sections'' () is a mathematical text written by Chinese Southern Song dynasty mathematician Qin Jiushao in the year 1247. The mathematical text has a wide range of topics and is taken from all aspects of th ...
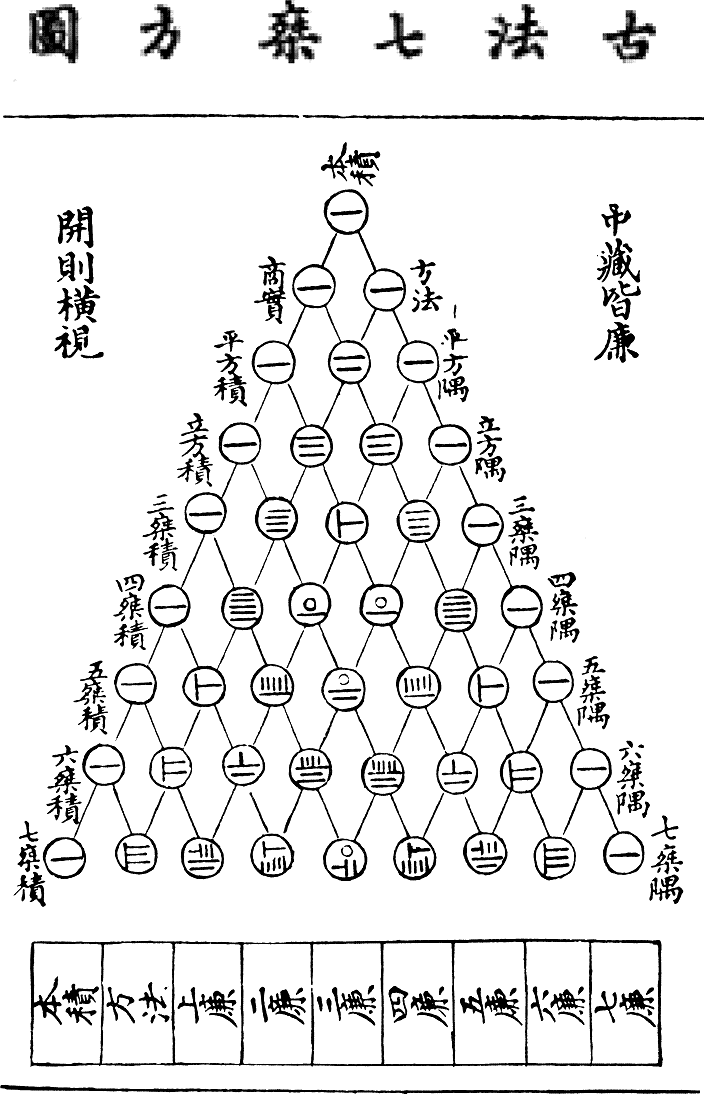
”) in 1247 (more than 570 years before English mathematician William Horner's method using synthetic division). To do this, he makes use of the Pascal triangle
In mathematics, Pascal's triangle is a triangular array of the binomial coefficients that arises in probability theory, combinatorics, and algebra. In much of the Western world, it is named after the French mathematician Blaise Pascal, although ...
, which he labels as the diagram of an ancient method first discovered by Jia Xian
Jia Xian (; ca. 1010–1070) was a Chinese mathematician from Kaifeng of the Song dynasty.
Biography
According to the history of the Song dynasty, Jia was a palace eunuch of the Left Duty Group. He studied under the mathematician Chu Yan, and ...
before 1050.
Zhu also solved square and cube roots problems by solving quadratic and cubic equations, and added to the understanding of series and progressions, classifying them according to the coefficients of the Pascal triangle. He also showed how to solve systems of linear equations by reducing the matrix of their coefficients to diagonal form
In mathematics, a diagonal form is an algebraic form (homogeneous polynomial) without cross-terms involving different indeterminates. That is, it is
:\sum_^n a_i ^m\
for some given degree ''m''.
Such forms ''F'', and the hypersurfaces ''F'' = ...
. His methods predate Blaise Pascal, William Horner, and modern matrix methods by many centuries. The preface of the book describes how Zhu travelled around China for 20 years as a teacher of mathematics.
''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'' consists of four books, with 24 classes and 288 problems, in which 232 problems deal with Tian yuan shu
''Tian yuan shu'' () is a Chinese system of algebra for polynomial equations. Some of the earliest existing writings were created in the 13th century during the Yuan dynasty. However, the tianyuanshu method was known much earlier, in the Song dy ...
, 36 problems deal with variable of two variables, 13 problems of three variables, and 7 problems of four variables.
Introduction
 The four quantities are ''x'', ''y'', ''z'', ''w'' can be presented with the following diagram
:::::::::::::x
::::::::::::y 太w
:::::::::::::z
The square of which is:
The four quantities are ''x'', ''y'', ''z'', ''w'' can be presented with the following diagram
:::::::::::::x
::::::::::::y 太w
:::::::::::::z
The square of which is:


The Unitary Nebuls
This section deals withTian yuan shu
''Tian yuan shu'' () is a Chinese system of algebra for polynomial equations. Some of the earliest existing writings were created in the 13th century during the Yuan dynasty. However, the tianyuanshu method was known much earlier, in the Song dy ...
or problems of one unknown.
:Question: Given the product of ''huangfan'' and ''zhi ji'' equals to 24 paces, and the sum of vertical and hypothenuse equals to 9 paces, what is the value of the base?
:Answer: 3 paces
:Set up ''unitary tian'' as the base( that is let the base be the unknown quantity ''x'')
Since the product of ''huangfang'' and ''zhi ji'' = 24
in which
:huangfan is defined as:
:''zhi ji'':
:therefore
:Further, the sum of vertical and hypothenuse is
::
:Set up the unknown ''unitary tian'' as the vertical
We obtain the following equation
:::::::::: ()
:::::::::::: 太
:::::::::::
::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
::::::::::::::
Solve it and obtain x=3
The Mystery of Two Natures
::::::::::::太 Unitary :::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: equation: ; from the given ::::::::::::太 :::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: equation: ; we get: ::::::::::::::太 :::::::::::::: :::::::::::::: :::: and :::::::::::::::太 ::::::::::::::: ::::::::::::::: ::::::::::::::: :::: by method of elimination, we obtain a quadratic equation ::::::::::::::: ::::::::::::::: ::::::::::::::: :::: solution: .The Evolution of Three Talents
Template for solution of problem of three unknowns Zhu Shijie explained the method of elimination in detail. His example has been quoted frequently in scientific literature. Set up three equations as follows :::::::::::太 :::::::::::: :::::::::: ::::::::::: .... I ::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: ::::::::::::::.....II :::::::::::太 ::::::::::::: ::::::::::::: :::::::::::::::....III Elimination of unknown between II and III by manipulation of exchange of variables We obtain :::::::::::: 太 :::::::::::: :::::::::::: ::::::::::::: ...IV and ::::::::::::太 :::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: .... V Elimination of unknown between IV and V we obtain a 3rd order equation :::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: :::::::::::: Solve to this 3rd order equation to obtain ; Change back the variables We obtain the hypothenus =5 pacesSimultaneous of the Four Elements
This section deals with simultaneous equations of four unknowns. :
Successive elimination of unknowns to get
::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
Solve this and obtain 14 paces
:
Successive elimination of unknowns to get
::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
:::::::::::::
Solve this and obtain 14 paces
Book I

Problems of Right Angle Triangles and Rectangles
There are 18 problems in this section. Problem 18 Obtain a tenth order polynomial equation: : The root of which is ''x'' = 3, multiply by 4, getting 12. That is the final answer.Problems of Plane Figures
There are 18 problems in this sectionProblems of Piece Goods
There are 9 problems in this sectionProblems on Grain Storage
There are 6 problems in this sectionProblems on Labour
There are 7 problems in this sectionProblems of Equations for Fractional Roots
There are 13 problems in this sectionBook II
Mixed Problems
Containment of Circles and Squares
Problems on Areas
Surveying with Right Angle Triangles
There are eight problems in this section ;Problem 1: Let tian yuan unitary as half of the length, we obtain a 4th order equation : solve it and obtain =240 paces, hence length =2x= 480 paces=1 li and 120paces. Similarity, let tian yuan unitary(x) equals to half of width we get the equation: : Solve it to obtain =180 paces, length =360 paces =one li. ;Problem 7: Identical to ''The depth of a ravine (using hence-forward cross-bars)'' inHaidao Suanjing
''Haidao Suanjing'' (; ''The Sea Island Mathematical Manual'') was written by the Chinese mathematician Liu Hui of the Three Kingdoms era (220–280) as an extension of chapter 9 of ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art''.
L. van. He ...
.
;Problem 8: Identical to ''The depth of a transparent pool'' in Haidao Suanjing
''Haidao Suanjing'' (; ''The Sea Island Mathematical Manual'') was written by the Chinese mathematician Liu Hui of the Three Kingdoms era (220–280) as an extension of chapter 9 of ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art''.
L. van. He ...
.
Hay Stacks
Bundles of Arrows
Land Measurement
Summon Men According to Need
Problem No 5 is the earliest 4th order interpolation formula in the world men summoned :孔国平 440-441。 In which * =1st order difference * =2nd order difference * =3rd order difference * =4th order differenceBook III
Fruit pile
This section contains 20 problems dealing with triangular piles, rectangular piles Problem 1 Find the sum of triangular pile : and value of the fruit pile is: : Zhu Shijie use Tian yuan shu to solve this problem by letting x=n and obtained the formular : From given condition , hence : Solve it to obtain . Therefore, :。Figures within Figure
Simultaneous Equations
Equation of two unknowns
Left and Right
Equation of Three Unknowns
Equation of Four Unknowns
Six problems of four unknowns. Question 2 Yield a set of equations in four unknowns: .Zhu Shijie, Siyuan yujian, annotated by Li Zhaohua , Science Press pp246-249 2007 :References
Sources * Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns, tr. into English by Professor Chen Zhaixin, Former Head of Mathematics Department, Yenching University (in 1925),Translated into modern Chinese by Guo Shuchun, Volume I & II, Library of Chinese Classics, Chinese-English, Liaoning Education Press 2006 https://www.scribd.com/document/357204551/Siyuan-yujian-2, https://www.scribd.com/document/357204728/Siyuan-yujian-1 *Collected Works in the History of Sciences by Li Yan and Qian Baocong, Volume 1 《李俨钱宝琮科学史全集》 第一卷 钱宝琮 《中国算学史 上编》 *Zhu Shijie Siyuan yujian Book 1–4, Annotated by Qin Dyasty mathematician Luo Shilin, Commercial Press *J. Hoe, Les systèmes d'équations polynômes dans le Siyuan yujian (1303), Institut des Hautes Études Chinoises, Paris, 1977 *J. Hoe, A study of the fourteenth-century manual on polynomial equations "The jade mirror of the four unknowns" by Zhu Shijie, Mingming Bookroom, P.O. Box 29-316, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2007 {{refend Chinese mathematics 1303 books Mathematics books