Jackson, Mississippi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jackson, officially the City of Jackson, is the capital of and the most populous city in the

 Located on the historic Natchez Trace trade route, created by Native Americans and used by European American settlers, and on the Pearl River, the city's first European American settler was Louis LeFleur, a French-Canadian trader. The village became known as LeFleur's Bluff. During the late 18th century and early 19th century, this site had a trading post. It was connected to markets in Tennessee. Soldiers returning to Tennessee from the military campaigns near in 1815 built a public road that connected Lake Pontchartrain in Louisiana to this district. A United States treaty with the Choctaw, the Treaty of Doak's Stand in 1820, formally opened the area for non-Native American settlers.
LeFleur's Bluff was developed when it was chosen as the site for the new state's
Located on the historic Natchez Trace trade route, created by Native Americans and used by European American settlers, and on the Pearl River, the city's first European American settler was Louis LeFleur, a French-Canadian trader. The village became known as LeFleur's Bluff. During the late 18th century and early 19th century, this site had a trading post. It was connected to markets in Tennessee. Soldiers returning to Tennessee from the military campaigns near in 1815 built a public road that connected Lake Pontchartrain in Louisiana to this district. A United States treaty with the Choctaw, the Treaty of Doak's Stand in 1820, formally opened the area for non-Native American settlers.
LeFleur's Bluff was developed when it was chosen as the site for the new state's
 Despite its small population, during the Civil War, Jackson became a strategic center of manufacturing for the Confederacy. In 1863, during the military campaign which ended in the capture of Vicksburg,
Despite its small population, during the Civil War, Jackson became a strategic center of manufacturing for the Confederacy. In 1863, during the military campaign which ended in the capture of Vicksburg,  Because of the siege and following destruction, few antebellum structures have survived in Jackson. The Governor's Mansion, built-in 1842, served as Sherman's headquarters and has been preserved. Another is the Old Capitol building, which served as the home of the Mississippi state legislature from 1839 to 1903. The Mississippi legislature passed the ordinance of secession from the Union on January 9, 1861, there, becoming the second state to secede from the United States. The Jackson City Hall, built in 1846 for less than $8,000, also survived. It is said that Sherman, a Mason, spared it because it housed a
Because of the siege and following destruction, few antebellum structures have survived in Jackson. The Governor's Mansion, built-in 1842, served as Sherman's headquarters and has been preserved. Another is the Old Capitol building, which served as the home of the Mississippi state legislature from 1839 to 1903. The Mississippi legislature passed the ordinance of secession from the Union on January 9, 1861, there, becoming the second state to secede from the United States. The Jackson City Hall, built in 1846 for less than $8,000, also survived. It is said that Sherman, a Mason, spared it because it housed a

 Author
Author
 The mass demonstrations of the 1960s were initiated with the arrival of more than 300 Freedom Riders on May 24, 1961. They were arrested in Jackson for disturbing the peace after they disembarked from their interstate buses. The interracial teams rode the buses from Washington, D.C. and sat together to demonstrate against segregation on public transportation, as the Constitution provides for unrestricted public transportation. Although the Freedom Riders had intended as their final destination, Jackson was the farthest that any managed to travel. New participants kept joining the movement, as they intended to fill the jails in Jackson with their protest. The riders had encountered extreme violence along the way, including a bus burning and physical assaults. They attracted national media attention to the struggle for constitutional rights.
After the Freedom Rides, students and activists of the Freedom Movement launched a series of merchant boycotts, sit-ins and protest marches, from 1961 to 1963. Businesses discriminated against black customers. For instance, at the time, department stores did not hire black salesclerks or allow black customers to use their fitting rooms to try on clothes, or lunch counters for meals while in the store, but they wanted them to shop in their stores.
In Jackson, shortly after midnight on June 12, 1963,
The mass demonstrations of the 1960s were initiated with the arrival of more than 300 Freedom Riders on May 24, 1961. They were arrested in Jackson for disturbing the peace after they disembarked from their interstate buses. The interracial teams rode the buses from Washington, D.C. and sat together to demonstrate against segregation on public transportation, as the Constitution provides for unrestricted public transportation. Although the Freedom Riders had intended as their final destination, Jackson was the farthest that any managed to travel. New participants kept joining the movement, as they intended to fill the jails in Jackson with their protest. The riders had encountered extreme violence along the way, including a bus burning and physical assaults. They attracted national media attention to the struggle for constitutional rights.
After the Freedom Rides, students and activists of the Freedom Movement launched a series of merchant boycotts, sit-ins and protest marches, from 1961 to 1963. Businesses discriminated against black customers. For instance, at the time, department stores did not hire black salesclerks or allow black customers to use their fitting rooms to try on clothes, or lunch counters for meals while in the store, but they wanted them to shop in their stores.
In Jackson, shortly after midnight on June 12, 1963,
, Goldring/Woldenberg Institute of Southern Jewish Life website, History Department, Digital Archive, Mississippi, Jackson, Beth Israel. Retrieved August 17, 2008. He and his congregation had supported civil rights. Gradually the old barriers came down. Since that period, both whites and African Americans in the state have had a consistently high rate of voter registration and turnout. Following the decades of the Great Migration, when more than one million black people left the rural South, since the 1930s the state has been majority white in total population. African Americans are a majority in the city of Jackson, although the metropolitan area is majority white. African Americans are also a majority in several cities and counties of the Mississippi Delta, which are included in the 2nd congressional district. The other three congressional districts are majority white.
 Jackson is located primarily in northeastern Hinds County, with small portions in Madison and Rankin counties. The city of Jackson also includes around 3,000 acres (12.1 km2) comprising Jackson-Medgar Evers International Airport in Rankin County and a small portion of Madison County. The
Jackson is located primarily in northeastern Hinds County, with small portions in Madison and Rankin counties. The city of Jackson also includes around 3,000 acres (12.1 km2) comprising Jackson-Medgar Evers International Airport in Rankin County and a small portion of Madison County. The
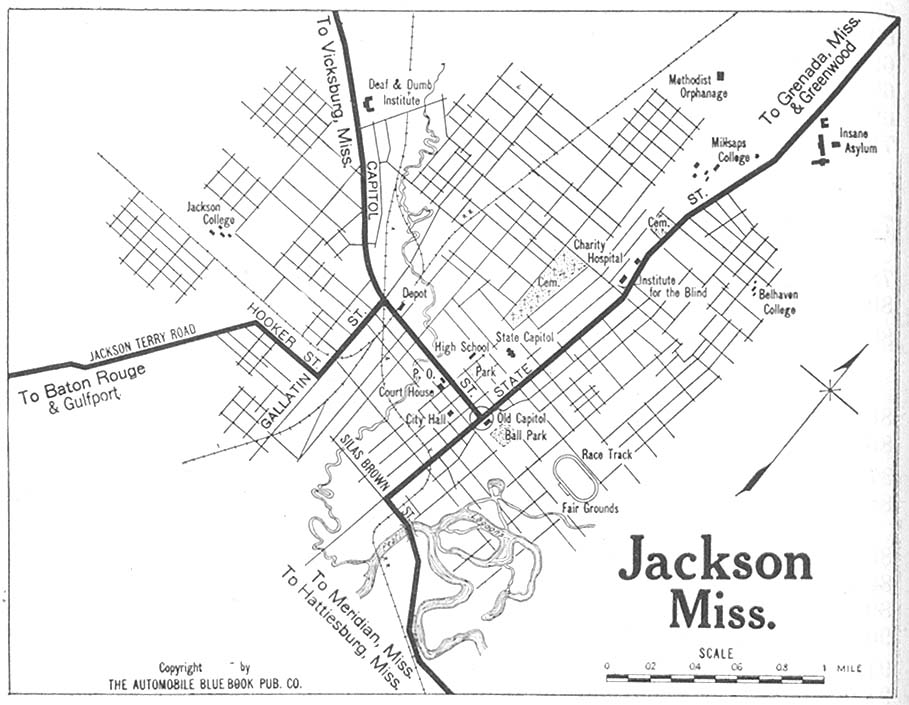
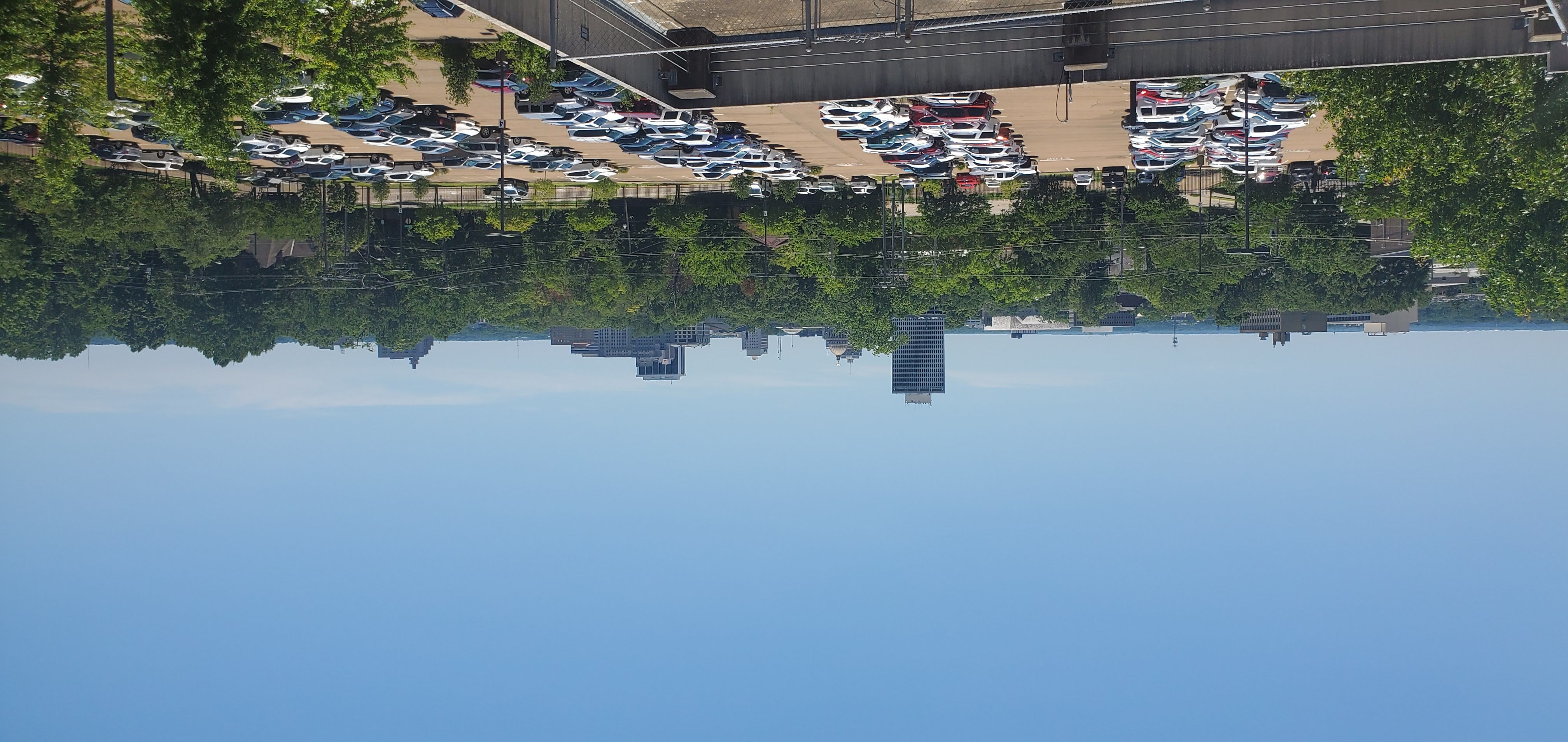 Downtown Jackson is situated directly on the banks of the Pearl River. The downtown district has direct connections to both Interstate 55 via Pearl Street and Pasagoula Street and Interstate 20 via State Street (US 51). Much of the downtown was constructed before the 1980s and only small additions to the skyline have been made since then.
Downtown Jackson is situated directly on the banks of the Pearl River. The downtown district has direct connections to both Interstate 55 via Pearl Street and Pasagoula Street and Interstate 20 via State Street (US 51). Much of the downtown was constructed before the 1980s and only small additions to the skyline have been made since then.

 Interstate 20
*
Interstate 20
* Interstate 220
*
Interstate 220
* US 51
*
US 51
* US 49
*
US 49
*
 Jackson sits atop the extinct Jackson Volcano, located underground. It is the only capital city in the United States to have this feature. The buried peak of the volcano is located directly below the Mississippi Coliseum.
The municipality is drained on the west by tributaries of the Big Black River and on the east by the Pearl River, which is higher than the Big Black near Canton. The artesian groundwater flow is not as extensive in Jackson for this reason. The first large-scale well was drilled in the city in 1896, and the city water supply has relied on surface water resources.
Jackson sits atop the extinct Jackson Volcano, located underground. It is the only capital city in the United States to have this feature. The buried peak of the volcano is located directly below the Mississippi Coliseum.
The municipality is drained on the west by tributaries of the Big Black River and on the east by the Pearl River, which is higher than the Big Black near Canton. The artesian groundwater flow is not as extensive in Jackson for this reason. The first large-scale well was drilled in the city in 1896, and the city water supply has relied on surface water resources.
 According to the 2010 census, the racial and ethnic makeup of the city was predominantly Black and African American, and non-Hispanic white; in 2020, they remained the largest racial and ethnic composition for the city. With white demographic decline and white flight, its non-Hispanic white population has declined; this was also due to the increase in other traditional minorities within the city, state, and nation.
According to the 2010 census, the racial and ethnic makeup of the city was predominantly Black and African American, and non-Hispanic white; in 2020, they remained the largest racial and ethnic composition for the city. With white demographic decline and white flight, its non-Hispanic white population has declined; this was also due to the increase in other traditional minorities within the city, state, and nation.
 Jackson is home to a number of cultural and artistic attractions, including the following:
* Ballet Mississippi
* Celtic Heritage Society of Mississippi
* Crossroads Film Society and its annual Film Festival
* International Museum of Muslim Cultures
* Jackson State University Botanical Garden
* Jackson Zoo
* Light and Glass Studio
* Margaret Walker Center
* Mississippi Agriculture and Forestry Museum
* Mississippi Arts Center
* Mississippi Chorus
* Mississippi Civil Rights Museum
* Mississippi Department of Archives and History, which contains the state archives and records
* Mississippi Heritage Trust
* Mississippi Hispanic Association
* Mississippi Metropolitan Ballet
* Mississippi Museum of Art
* Mississippi Opera
* Mississippi Symphony Orchestra (MSO), formerly the Jackson Symphony Orchestra, founded in 1944
* Municipal Art Gallery
* Museum of Mississippi History
* Mynelle Gardens
* New Stage Theatre
*
Jackson is home to a number of cultural and artistic attractions, including the following:
* Ballet Mississippi
* Celtic Heritage Society of Mississippi
* Crossroads Film Society and its annual Film Festival
* International Museum of Muslim Cultures
* Jackson State University Botanical Garden
* Jackson Zoo
* Light and Glass Studio
* Margaret Walker Center
* Mississippi Agriculture and Forestry Museum
* Mississippi Arts Center
* Mississippi Chorus
* Mississippi Civil Rights Museum
* Mississippi Department of Archives and History, which contains the state archives and records
* Mississippi Heritage Trust
* Mississippi Hispanic Association
* Mississippi Metropolitan Ballet
* Mississippi Museum of Art
* Mississippi Opera
* Mississippi Symphony Orchestra (MSO), formerly the Jackson Symphony Orchestra, founded in 1944
* Municipal Art Gallery
* Museum of Mississippi History
* Mynelle Gardens
* New Stage Theatre
*
 The city of Jackson and its metropolitan area are home to collegiate and semi-professional sports teams; Major League Baseball's Atlanta Braves minor affiliate, the
The city of Jackson and its metropolitan area are home to collegiate and semi-professional sports teams; Major League Baseball's Atlanta Braves minor affiliate, the


 Jackson is home to the most collegiate institutions in Mississippi.
Jackson is home to the most collegiate institutions in Mississippi.
, Jackson Convention and Visitors Bureau In the song "
Jackson Convention & Visitors BureauMetro Jackson Chamber of Commerce
{{Authority control Cities in Mississippi Cities in Hinds County, Mississippi Cities in Madison County, Mississippi Cities in Rankin County, Mississippi 1792 establishments in the United States Andrew Jackson County seats in Mississippi Cities in Jackson metropolitan area, Mississippi Mississippi Blues Trail Planned cities in the United States Populated places established in 1792
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
. The city is also one of two county seats of Hinds County, along with Raymond. The city had a population of 153,701 at the 2020 census, down from 173,514 at the 2010 census. Jackson's population declined more between 2010 and 2020 (11.42%) than any major city in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. Jackson is the anchor for the Jackson metropolitan statistical area, the largest metropolitan area completely within the state. With a 2020 population estimated around 600,000, metropolitan Jackson is home to over one-fifth of Mississippi's population. The city sits on the Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
and is located in the greater Jackson Prairie region of Mississippi.
Founded in 1821 as the site for a new state capital, the city is named after General Andrew Jackson, who was honored for his role in the Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the Frenc ...
during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
and would later serve as U.S. president. Following the nearby Battle of Vicksburg
The siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mis ...
in 1863 during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
, Union forces under the command of General William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
began the siege of Jackson
The Jackson Expedition, also known as the Siege of Jackson, occurred in the aftermath of the surrender of Vicksburg, Mississippi, in July 1863. Union Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman led the expedition to clear General Joseph E. Johnston ...
and the city was subsequently burned.
During the 1920s, Jackson surpassed Meridian to become the most populous city in the state following a speculative natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
boom in the region. The current slogan for the city is "The City with Soul". It has had numerous musicians prominent in blues, gospel, folk, and jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
. The city is located in the deep south halfway between Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
and on Interstate 55
Interstate 55 (I-55) is a major Interstate Highway in the central United States. As with most primary Interstates that end in a five, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, connecting the Gulf of Mexico to the Great Lakes. The h ...
and Shreveport, Louisiana and Birmingham, Alabama on Interstate 20. Being at this location has given the city the nickname the "crossroads of the south".
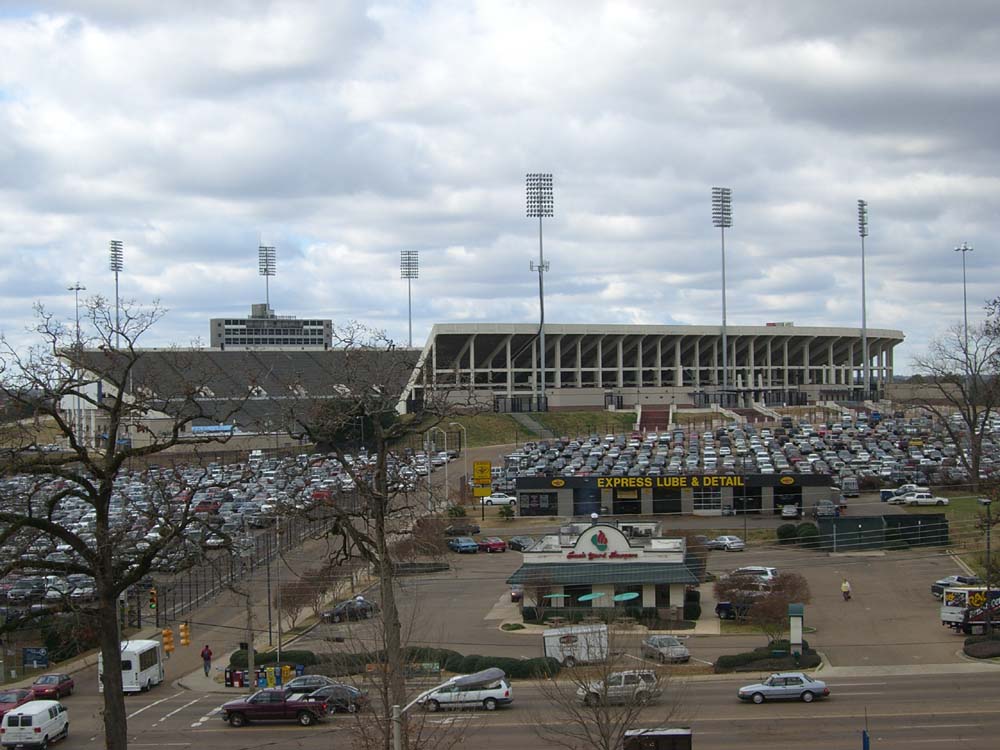
The city has a number of museums and cultural institutions, including the Mississippi Childrens Museum, Mississippi Museum of Natural Science, Mississippi Civil Rights Museum, Mississippi Museum of Art, Old Capital Museum, Museum of Mississippi History. Other notable locations are the Mississippi Coliseum and the Mississippi Veterans Memorial Stadium, home of the Jackson State Tigers Football
The Jackson State Tigers football team represents Jackson State University in college football at the NCAA Division I Football Championship Subdivision (FCS) level as a member of the Southwestern Athletic Conference (SWAC).
After joining the So ...
Team.
The Jackson metropolitan statistical area is the state's second largest metropolitan area overall, due to four counties in northern Mississippi being part of the Memphis, Tennessee metropolitan area. In 2020, the Jackson metropolitan area held a GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
of 30 billion dollars, accounting for 29% of the state's total GDP of 104.1 billion dollars.
History

Native Americans
The region that is now the city of Jackson was historically part of the large territory occupied by the Choctaw Nation. The Choctaw name for the locale was ''Chisha Foka''. The area now called Jackson was obtained by the United States under the terms of the Treaty of Doak's Stand in 1820, by which the United States acquired the land owned by the Choctaw Native Americans. After the treaty was ratified, American settlers moved into the area, encroaching on remaining Choctaw communal lands. One of the original Choctaw members, in 1849, described what he and his people experienced during this turbulent time when the Europeans had come to take their land. "We have had our habitations torn down and burned" as well as their "fences burned" while they constantly faced personal abuse and have been "scoured, manacled and fettered". Under pressure from the U.S. government, the Choctaw Native Americans agreed to removal after 1830 from all of their lands east of theMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
under the terms of several treaties. Although most of the Choctaw moved to Indian Territory in present-day Oklahoma, along with the other of the Five Civilized Tribes
The term Five Civilized Tribes was applied by European Americans in the colonial and early federal period in the history of the United States to the five major Native American nations in the Southeast—the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek ...
, a significant number chose to stay in their homeland, citing Article XIV of the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek. They gave up their tribal membership and became state and United States citizens at the time. Today, most Choctaw in Mississippi have reorganized and are part of the federally recognized Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians. They live in several majority- Indian communities located throughout the state. The largest community is located in Choctaw northeast of Jackson.
Founding and antebellum period (to 1860)
 Located on the historic Natchez Trace trade route, created by Native Americans and used by European American settlers, and on the Pearl River, the city's first European American settler was Louis LeFleur, a French-Canadian trader. The village became known as LeFleur's Bluff. During the late 18th century and early 19th century, this site had a trading post. It was connected to markets in Tennessee. Soldiers returning to Tennessee from the military campaigns near in 1815 built a public road that connected Lake Pontchartrain in Louisiana to this district. A United States treaty with the Choctaw, the Treaty of Doak's Stand in 1820, formally opened the area for non-Native American settlers.
LeFleur's Bluff was developed when it was chosen as the site for the new state's
Located on the historic Natchez Trace trade route, created by Native Americans and used by European American settlers, and on the Pearl River, the city's first European American settler was Louis LeFleur, a French-Canadian trader. The village became known as LeFleur's Bluff. During the late 18th century and early 19th century, this site had a trading post. It was connected to markets in Tennessee. Soldiers returning to Tennessee from the military campaigns near in 1815 built a public road that connected Lake Pontchartrain in Louisiana to this district. A United States treaty with the Choctaw, the Treaty of Doak's Stand in 1820, formally opened the area for non-Native American settlers.
LeFleur's Bluff was developed when it was chosen as the site for the new state's capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
. The Mississippi General Assembly decided in 1821 that the state needed a centrally located capital (the legislature was then located in Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
). They commissioned Thomas Hinds, James Patton, and William Lattimore to look for a suitable site. The absolute center of the state was a swamp, so the group had to widen their search.
After surveying areas north and east of Jackson, they proceeded southwest along with the Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
until they reached LeFleur's Bluff in today's Hinds County. Their report to the General Assembly stated that this location had beautiful and healthful surroundings, good water, abundant timber, navigable waters, and proximity to the Natchez Trace. The Assembly passed an act on November 28, 1821, authorizing the site as the permanent seat of the government of the state of Mississippi. On the same day, it passed a resolution to instruct the Washington delegation to press Congress for a donation of public lands on the river for improved navigation to the Gulf of Mexico. One Whig politician lamented the new capital as a "serious violation of principle" because it was not at the absolute center of the state.
The capital was named for General Andrew Jackson, to honor his (January 1815) victory at the Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the Frenc ...
during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
. He was later elected as the seventh president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
.
The city of Jackson was originally planned, in April 1822, by Peter Aaron Van Dorn in a " checkerboard" pattern advocated by Thomas Jefferson. City blocks alternated with parks and other open spaces. Over time, many of the park squares have been developed rather than maintained as green space. The state legislature first met in Jackson on December 23, 1822. In 1839, the Mississippi Legislature passed the first state law in the U.S. to permit married women to own and administer their own property.
Jackson was connected by public road to Vicksburg and Clinton in 1826. Jackson was first connected by railroad to other cities in 1840. An 1844 map shows Jackson linked by an east–west rail line running between Vicksburg, Raymond, and Brandon
Brandon may refer to:
Names and people
*Brandon (given name), a male given name
*Brandon (surname), a surname with several different origins
Places
Australia
*Brandon, a farm and 19th century homestead in Seaham, New South Wales
*Brandon, Q ...
. Unlike Vicksburg, Greenville, and Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
, Jackson is not located on the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
, and it did not develop during the antebellum era as those cities did from major river commerce. The construction of railroad lines to the city sparked its growth in the decades following the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
.
American Civil War
 Despite its small population, during the Civil War, Jackson became a strategic center of manufacturing for the Confederacy. In 1863, during the military campaign which ended in the capture of Vicksburg,
Despite its small population, during the Civil War, Jackson became a strategic center of manufacturing for the Confederacy. In 1863, during the military campaign which ended in the capture of Vicksburg, Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
forces captured Jackson during two battles—once before the fall of Vicksburg and once after the fall of Vicksburg.
On May 13, 1863, Union forces won the first Battle of Jackson, forcing Confederate forces to flee northward towards Canton. On May 14, Union troops under the command of William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
burned and looted key facilities in Jackson, a strategic manufacturing and railroad center for the Confederacy. After driving the Confederate forces out of Jackson, Union forces turned west and engaged the Vicksburg defenders at the Battle of Champion Hill in nearby Edwards. The Union forces began their siege of Vicksburg soon after their victory at Champion Hill. Confederate forces began to reassemble in Jackson in preparation for an attempt to break through the Union lines surrounding Vicksburg and end the siege. The Confederate forces in Jackson built defensive fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
s encircling the city while preparing to march west to Vicksburg.
Confederate forces marched out of Jackson in early July 1863 to break the siege of Vicksburg. But, unknown to them, Vicksburg had already surrendered on July 4, 1863. General Ulysses S. Grant dispatched General Sherman to meet the Confederate forces heading west from Jackson. Upon learning that Vicksburg had already surrendered, the Confederates retreated into Jackson. Union forces began the siege of Jackson
The Jackson Expedition, also known as the Siege of Jackson, occurred in the aftermath of the surrender of Vicksburg, Mississippi, in July 1863. Union Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman led the expedition to clear General Joseph E. Johnston ...
, which lasted for approximately one week. Union forces encircled the city and began an artillery bombardment. One of the Union artillery emplacements has been preserved on the grounds of the University of Mississippi Medical Center
University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC) is the health sciences campus of the University of Mississippi (Ole Miss) and is located in Jackson, Mississippi, United States. UMMC, also referred to as the Medical Center, is the state's only aca ...
in Jackson. Another Federal position is preserved on the campus of Millsaps College. John C. Breckinridge, former United States vice president, served as one of the Confederate generals defending Jackson. On July 16, 1863, Confederate forces slipped out of Jackson during the night and retreated across the Pearl River.
Union forces completely burned the city after its capture this second time. The city was called "Chimneyville" because only the chimneys of houses were left standing. The northern line of Confederate defenses in Jackson during the siege was located along a road near downtown Jackson, now known as Fortification Street.
 Because of the siege and following destruction, few antebellum structures have survived in Jackson. The Governor's Mansion, built-in 1842, served as Sherman's headquarters and has been preserved. Another is the Old Capitol building, which served as the home of the Mississippi state legislature from 1839 to 1903. The Mississippi legislature passed the ordinance of secession from the Union on January 9, 1861, there, becoming the second state to secede from the United States. The Jackson City Hall, built in 1846 for less than $8,000, also survived. It is said that Sherman, a Mason, spared it because it housed a
Because of the siege and following destruction, few antebellum structures have survived in Jackson. The Governor's Mansion, built-in 1842, served as Sherman's headquarters and has been preserved. Another is the Old Capitol building, which served as the home of the Mississippi state legislature from 1839 to 1903. The Mississippi legislature passed the ordinance of secession from the Union on January 9, 1861, there, becoming the second state to secede from the United States. The Jackson City Hall, built in 1846 for less than $8,000, also survived. It is said that Sherman, a Mason, spared it because it housed a Masonic Lodge
A Masonic lodge, often termed a private lodge or constituent lodge, is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. It is also commonly used as a term for a building in which such a unit meets. Every new lodge must be warranted or chartered ...
, though a more likely reason is that it housed an army hospital.
Reconstruction
During Reconstruction, Republicans granted African Americans civil rights. Schools were established and African Americans held political offices. Eugene Welborne, Charles Reese, Weldon Hicks, and George Caldwell Granberry were among the legislators who represented Hinds County in the legislature. African Americans also served in local offices, as judges, and as marshalls. Mississippi had considerable insurgent action, as whites struggled to maintain white supremacy. Jackson’s appointed mayorJoseph G. Crane
Joseph G. Crane was a Union Army officer who was appointed mayor of Jackson, Mississippi (the state capitol) in 1869. He was stabbed to death on the capitol steps by Edward M. Yerger, a former Confederate Army officer who edited a newspaper. After ...
was stabbed to death in 1869. The assailant, Edward M. Yerger
Edward M. Yerger (1828 – April 22, 1875) was an American newspaper editor and military officer. After a career in the newspaper industry, Yerger was arrested for the stabbing death of the provisional mayor of Jackson, Mississippi. His claim of ...
, was arrested by military authorities but, after a U.S. Supreme Court case (Ex parte Yerger
''Ex parte Yerger'', 75 U.S. (8 Wall.) 85 (1869), was a case heard by the Supreme Court of the United States in which the court held that, under the Judiciary Act of 1789, it is authorized to issue writs of habeas corpus.
Background
In June 1869 ...
), he was bonded out, moved to Baltimore and was never tried.
The economic recovery from the Civil War was slow through the start of the 20th century, but there were some developments in transportation. In 1871, the city introduced mule-drawn streetcars which ran on State Street, which were replaced by electric ones in 1899. In 1875, the Red Shirts were formed, one of the second waves of insurgent paramilitary organizations that essentially operated as "the military arm of the Democratic Party" to take back political power from the Republicans and to drive black people from the polls ( Mississippi Plan).
Post-Reconstruction
Democrats regained control of the state legislature in 1876. The constitutional convention of 1890, which produced Mississippi's Constitution of 1890, was held at the capitol. This was the first of new constitutions or amendments ratified in each Southern state through 1908 that effectivelydisenfranchised
Disfranchisement, also called disenfranchisement, or voter disqualification is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing a person exercising the right to vote. D ...
most African Americans and many poor whites, through provisions making voter registration more difficult: such as poll taxes
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources.
Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments f ...
, residency requirements, and literacy tests. These provisions survived a Supreme Court challenge in 1898. As 20th-century Supreme Court decisions later ruled such provisions were unconstitutional, Mississippi and other Southern states rapidly devised new methods to continue disfranchisement of most black people, who comprised a majority in the state until the 1930s. Their exclusion from politics was maintained into the late 1960s.
The so-called New Capitol replaced the older structure upon its completion in 1903. Today the Old Capitol is operated as a historical museum.
Early 20th century (1901–1960)

 Author
Author Eudora Welty
Eudora Alice Welty (April 13, 1909 – July 23, 2001) was an American short story writer, novelist and photographer who wrote about the American South. Her novel '' The Optimist's Daughter'' won the Pulitzer Prize in 1973. Welty received numerou ...
was born in Jackson in 1909, lived most of her life in the Belhaven section of the city, and died there in 2001. Her memoir
A memoir (; , ) is any nonfiction narrative writing based in the author's personal memories. The assertions made in the work are thus understood to be factual. While memoir has historically been defined as a subcategory of biography or autobiog ...
of development as a writer, '' One Writer's Beginnings'' (1984), presented a picture of the city in the early 20th century. She won the Pulitzer Prize in 1973 for her novel, '' The Optimist's Daughter,'' and is best known for her novels and short stories. The main library of the Jackson/Hinds Library System was named in her honor, and her home has been designated as a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
.
Richard Wright, a highly acclaimed African-American author, lived in Jackson as an adolescent and young man in the 1910s and 1920s. He related his experience in his memoir '' Black Boy'' (1945). He described the harsh and largely terror-filled life most African Americans experienced in the South and Northern ghettos such as Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
under segregation Segregation may refer to:
Separation of people
* Geographical segregation, rates of two or more populations which are not homogenous throughout a defined space
* School segregation
* Housing segregation
* Racial segregation, separation of humans ...
in the early 20th century. Jackson had significant growth in the early 20th century, which produced dramatic changes in the city's skyline. Jackson's new Union Station
A union station (also known as a union terminal, a joint station in Europe, and a joint-use station in Japan) is a railway station at which the tracks and facilities are shared by two or more separate railway companies, allowing passengers to ...
downtown reflected the city's service by multiple rail lines, including the Illinois Central.
Across the street, the new, luxurious King Edward Hotel opened its doors in 1923, having been built according to a design by New Orleans architect William T. Nolan. It became a center for prestigious events held by Jackson society and Mississippi politicians. Nearby, the 18-story Standard Life Building, designed in 1929 by Claude Lindsley, was the largest reinforced concrete structure in the world upon its completion.
Jackson's economic growth was further stimulated in the 1930s by the discovery of natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
fields nearby. Speculators had begun searching for oil and natural gas in Jackson beginning in 1920. The initial drilling attempts came up empty. This failure did not stop Ella Render from obtaining a lease from the state's insane asylum to begin a well on its grounds in 1924, where he found natural gas. (Render eventually lost the rights when courts determined that the asylum did not have the right to lease the state's property.) Businessmen jumped on the opportunity and dug wells in the Jackson area. The continued success of these ventures attracted further investment. By 1930, there were 14 derricks in the Jackson skyline.
Mississippi Governor Theodore Bilbo
Theodore Gilmore Bilbo (October 13, 1877 – August 21, 1947) was an American politician who twice served as governor of Mississippi (1916–1920, 1928–1932) and later was elected a U.S. Senator (1935–1947). A lifelong Democrat, he was a fil ...
stated:
This enthusiasm was subdued when the first wells failed to produce oil of a sufficiently high gravity for commercial success. The barrels of oil had considerable amounts of saltwater, which lessened the quality. The governor's prediction was wrong in hindsight, but the oil and natural gas industry did provide an economic boost for the city and state. The effects of the Great Depression were mitigated by the industry's success. At its height in 1934, there were 113 producing wells in the state. The overwhelming majority were closed by 1955.
Due to provisions in the federal Rivers and Harbors Act
Rivers and Harbors Act may refer to one of many pieces of legislation and appropriations passed by the United States Congress since the first such legislation in 1824. At that time Congress appropriated $75,000 to improve navigation on the Ohio and ...
, on October 25, 1930, city leaders met with U.S. Army engineers to ask for federal help to alleviate Jackson flooding. J.J. Halbert, city engineer, proposed a straightening and dredging of the Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
below Jackson.
Jackson's Gold Coast
During Mississippi's extendedProhibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
period, from the 1920s until the 1960s, illegal drinking and gambling casinos flourished on the east side of the Pearl River, in Flowood along with the original U.S. Route 80 just across from the city of Jackson. Those illegal casinos, bootleg liquor stores, and nightclubs made up the Gold Coast, a strip of mostly black-market
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the ...
businesses that operated for decades along Flowood Road. Although outside the law, the Gold Coast was a thriving center of nightlife and music, with many local blues musicians appearing regularly in the clubs.
The Gold Coast declined and businesses disappeared after Mississippi's prohibition laws were repealed in 1966, allowing Hinds County, including Jackson, to go "wet". In addition, integration drew off business from establishments that earlier had catered to African Americans, such as the Summers Hotel. When it opened in 1943 on Pearl Street, it was one of two hotels in the city that served black clients. For years its Subway Lounge was a prime performance spot for black musicians playing jazz and blues.
In another major change, in 1990 the state-approved gaming on riverboats. Numerous casinos have been developed on riverboats, mostly in Mississippi Delta towns such as Tunica Resorts
Tunica Resorts, formerly known as Robinsonville until 2005,
, Greenville, and Vicksburg, as well as Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in and one of two county seats of Harrison County, Mississippi, United States (the other being the adjacent city of Gulfport). The 2010 United States Census recorded the population as 44,054 and in 2019 the estimated popu ...
on the Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coast, coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The list of U.S. states and territories by coastline, coastal states that have a shor ...
. Before the damage and losses due to Hurricane Katrina in 2005, the state ranked second nationally in gambling revenues.
World War II and later development
DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Hawkins Field
Hawkins Field is a baseball stadium in Nashville, Tennessee. It is the home field of the Vanderbilt Commodores college baseball team.
(at that time, also known as the Jackson Army Airbase) the American 21st, 309th, and 310th Bomber Groups that were stationed at the base were re-deployed for combat. Following the German invasion of the Netherlands
The German invasion of the Netherlands ( nl, Duitse aanval op Nederland), otherwise known as the Battle of the Netherlands ( nl, Slag om Nederland), was a military campaign part of Case Yellow (german: Fall Gelb), the Nazi German invasion of t ...
and the Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies, between 688 and 800 members of the Dutch Airforce escaped to the UK or Australia for training and, out of necessity, were eventually given permission by the United States to make use of Hawkins Field.
From May 1942 until the end of the war, all Dutch military aircrews trained at the base and went on to serve in either the British or Australian Air Forces.
In 1949, the poet Margaret Walker began teaching at Jackson State University
Jackson State University (Jackson State or JSU) is a public historically black research university in Jackson, Mississippi. It is one of the largest HBCUs in the United States and the fourth largest university in Mississippi in terms of studen ...
, a historically black college. She taught there until 1979 and founded the university's Center for African-American Studies. Her poetry collection won a Yale Younger Poets Prize
The Yale Series of Younger Poets is an annual event of Yale University Press aiming to publish the debut collection of a promising American poet. Established in 1918, the Younger Poets Prize is the longest-running annual literary award in the Uni ...
. Her second novel, ''Jubilee
A jubilee is a particular anniversary of an event, usually denoting the 25th, 40th, 50th, 60th, and the 70th anniversary. The term is often now used to denote the celebrations associated with the reign of a monarch after a milestone number of y ...
'' (1966), is considered a major work of African-American literature. She has influenced many younger writers.
Civil rights movement in Jackson
Thecivil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the Unite ...
had been active for decades, particularly mounting legal challenges to Mississippi's constitution and laws that disfranchised black people. Beginning in 1960, Jackson as the state capital became the site for dramatic non-violent protests in a new phase of activism that brought in a wide variety of participants in the performance of mass demonstrations.
In 1960, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Jackson's population as 64.3% white and 35.7% black. At the time, public facilities were segregated and Jim Crow was in effect. Efforts to desegregate Jackson facilities began when nine Tougaloo College
Tougaloo College is a private historically black college in the Tougaloo area of Jackson, Mississippi. It is affiliated with the United Church of Christ and Christian Church (Disciples of Christ). It was originally established in 1869 by New Yor ...
students tried to read books in the "white only" public library and were arrested. Founded as a historically black college (HBCU) by the American Missionary Association after the Civil War, Tougaloo College
Tougaloo College is a private historically black college in the Tougaloo area of Jackson, Mississippi. It is affiliated with the United Church of Christ and Christian Church (Disciples of Christ). It was originally established in 1869 by New Yor ...
helped organize both black and white students of the region to work together for civil rights. It created partnerships with the neighboring mostly white Millsaps College to work with student activists. It has been recognized as a site on the "Civil Rights Trail" by the National Park Service.
 The mass demonstrations of the 1960s were initiated with the arrival of more than 300 Freedom Riders on May 24, 1961. They were arrested in Jackson for disturbing the peace after they disembarked from their interstate buses. The interracial teams rode the buses from Washington, D.C. and sat together to demonstrate against segregation on public transportation, as the Constitution provides for unrestricted public transportation. Although the Freedom Riders had intended as their final destination, Jackson was the farthest that any managed to travel. New participants kept joining the movement, as they intended to fill the jails in Jackson with their protest. The riders had encountered extreme violence along the way, including a bus burning and physical assaults. They attracted national media attention to the struggle for constitutional rights.
After the Freedom Rides, students and activists of the Freedom Movement launched a series of merchant boycotts, sit-ins and protest marches, from 1961 to 1963. Businesses discriminated against black customers. For instance, at the time, department stores did not hire black salesclerks or allow black customers to use their fitting rooms to try on clothes, or lunch counters for meals while in the store, but they wanted them to shop in their stores.
In Jackson, shortly after midnight on June 12, 1963,
The mass demonstrations of the 1960s were initiated with the arrival of more than 300 Freedom Riders on May 24, 1961. They were arrested in Jackson for disturbing the peace after they disembarked from their interstate buses. The interracial teams rode the buses from Washington, D.C. and sat together to demonstrate against segregation on public transportation, as the Constitution provides for unrestricted public transportation. Although the Freedom Riders had intended as their final destination, Jackson was the farthest that any managed to travel. New participants kept joining the movement, as they intended to fill the jails in Jackson with their protest. The riders had encountered extreme violence along the way, including a bus burning and physical assaults. They attracted national media attention to the struggle for constitutional rights.
After the Freedom Rides, students and activists of the Freedom Movement launched a series of merchant boycotts, sit-ins and protest marches, from 1961 to 1963. Businesses discriminated against black customers. For instance, at the time, department stores did not hire black salesclerks or allow black customers to use their fitting rooms to try on clothes, or lunch counters for meals while in the store, but they wanted them to shop in their stores.
In Jackson, shortly after midnight on June 12, 1963, Medgar Evers
Medgar Wiley Evers (; July 2, 1925June 12, 1963) was an American civil rights activist and the NAACP's first field secretary in Mississippi, who was murdered by Byron De La Beckwith. Evers, a decorated U.S. Army combat veteran who had served i ...
, civil rights activist and leader of the Mississippi chapter of the NAACP, was assassinated by Byron De La Beckwith, a white supremacist associated with the White Citizens' Council. Thousands marched in Evers' funeral procession to protest the killing. Two trials at the time both resulted in hung juries. A portion of U.S. Highway 49, all of Delta Drive, a library, the central post office for the city, and Jackson–Evers International Airport were named in honor of Medgar Evers. In 1994, prosecutors Ed Peters and Bobby DeLaughter Robert Burt DeLaughter Sr. (born February 28, 1954 in Vicksburg, Mississippi) is a former state prosecutor and then Hinds County Circuit Judge. He prosecuted and secured the conviction in 1994 of Byron De La Beckwith, charged with the murder of the ...
finally obtained a murder conviction in a state trial of De La Beckwith based on new evidence.
During 1963 and 1964, civil rights organizers gathered residents for voter education and voter registration
In electoral systems, voter registration (or enrollment) is the requirement that a person otherwise eligible to vote must register (or enroll) on an electoral roll, which is usually a prerequisite for being entitled or permitted to vote.
The r ...
. Black people had been essentially disfranchised since 1890. In a pilot project in 1963, activists rapidly registered 80,000 voters across the state, demonstrating the desire of African Americans to vote. In 1964 they created the Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party as an alternative to the all-white state Democratic Party, and sent an alternate slate of candidates to the national Democratic Party convention in Atlantic City, New Jersey, that year.
Segregation and the disfranchisement of African Americans gradually ended after the Civil Rights Movement gained Congressional passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965. In June 1966, Jackson was the terminus of the James Meredith March, organized by James Meredith, the first African American to enroll at the University of Mississippi. The march, which began in Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
, Tennessee, was an attempt to garner support for full implementation of civil rights in practice, following the legislation. It was accompanied by a new drive to register African Americans to vote in Mississippi. In this latter goal, it succeeded in registering between 2,500 and 3,000 black Mississippians to vote. The march ended on June 26 after Meredith, who had been wounded by a sniper's bullet earlier on the march, addressed a large rally of some 15,000 people in Jackson.
In September 1967 a Ku Klux Klan chapter bombed the synagogue of the Beth Israel Congregation in Jackson, and in November bombed the house of its rabbi, Dr. Perry Nussbaum. History of Beth Israel, Jackson, Mississippi, Goldring/Woldenberg Institute of Southern Jewish Life website, History Department, Digital Archive, Mississippi, Jackson, Beth Israel. Retrieved August 17, 2008. He and his congregation had supported civil rights. Gradually the old barriers came down. Since that period, both whites and African Americans in the state have had a consistently high rate of voter registration and turnout. Following the decades of the Great Migration, when more than one million black people left the rural South, since the 1930s the state has been majority white in total population. African Americans are a majority in the city of Jackson, although the metropolitan area is majority white. African Americans are also a majority in several cities and counties of the Mississippi Delta, which are included in the 2nd congressional district. The other three congressional districts are majority white.
Mid-1960s to present
The first successful cadaveric lung transplant was performed at theUniversity of Mississippi Medical Center
University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC) is the health sciences campus of the University of Mississippi (Ole Miss) and is located in Jackson, Mississippi, United States. UMMC, also referred to as the Medical Center, is the state's only aca ...
in Jackson in June 1963 by Dr. James Hardy. Hardy transplanted the cadaveric lung into a patient suffering from lung cancer. The patient survived for eighteen days before dying of kidney failure.
In 1966 it was estimated that recurring flood damage at Jackson from the Pearl River averaged nearly a million dollars per year. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers spent $6.8 million on levees and a new channel in 1966 before the project completion to prevent a flood equal to the December 1961 event plus an additional foot.
Since 1968, Jackson has been the home of Malaco Records
Malaco Records is an American independent record label based in Jackson, Mississippi, United States, that has been the home of various major blues and gospel acts, such as Johnnie Taylor, Bobby Bland, Mel Waiters, Z. Z. Hill, Denise LaSalle, ...
, one of the leading record companies for gospel, blues, and soul music
Soul music is a popular music genre that originated in the African American community throughout the United States in the late 1950s and early 1960s. It has its roots in African-American gospel music and rhythm and blues. Soul music became ...
in the United States. In January 1973, Paul Simon recorded the songs "Learn How to Fall" and "Take Me to the Mardi Gras", found on the album '' There Goes Rhymin' Simon'', in Jackson at the Malaco Recording Studios. Many well-known Southern artists recorded on the album, including the Muscle Shoals Rhythm Section
The Muscle Shoals Rhythm Section is a group of American session musicians based in the northern Alabama town of Muscle Shoals. One of the most prominent American studio house bands from the 1960s to the 1980s, these musicians, individually or a ...
(David Hood, Jimmy Johnson, Roger Hawkins, Barry Beckett), Carson Whitsett
James Carson Whitsett (May 1, 1945 – May 8, 2007) was an American keyboardist, songwriter, and record producer.
Biography
Carson Whitsett was born in Jackson, Mississippi. He joined his older brother Tim's band, Tim Whitsett & The Imperials ( ...
, the Onward Brass Band from New Orleans, and others. The label has recorded many leading soul and blues artists, including Bobby Bland
Robert Calvin Bland (born Robert Calvin Brooks; January 27, 1930 – June 23, 2013), known professionally as Bobby "Blue" Bland, was an American blues singer.
Bland developed a sound that mixed gospel with the blues and R&B. He was descr ...
, ZZ Hill, Latimore, Shirley Brown
Shirley Brown (born January 6, 1947, West Memphis, Arkansas) is an American R&B singer, best known for her million-selling single " Woman to Woman", which was nominated for a Grammy Award in 1975.
Biography
Brown was born in West Memphis, but ...
, Denise LaSalle, and Tyrone Davis.
On May 15, 1970, Jackson police killed two students and wounded twelve at Jackson State College after a protest of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
included students' overturning and burning some cars. These killings occurred eleven days after the National Guard
National Guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
Nat ...
killed four students in an anti-war protest at Kent State University in Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, and were part of national social unrest. ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print magazine in 1933, it was widely ...
'' cited the Jackson State killings in its issue of May 18 when it suggested that U.S. President Richard Nixon faced a new home front.
The influx of illegal drugs occurred nationally as smugglers used the highways, seaports, and airports of the Gulf region. The 1980s in Jackson were dominated by Mayor Dale Danks Jr. until he was unseated by lawyer and legislator J. Kane Ditto
John Kane Ditto (born May 18, 1944) is an American politician and formerly the mayor of Jackson, Mississippi. He was born in Bowling Green, Kentucky.
Ditto, a Democrat, served as Mayor of the City of Jackson from July 3, 1989 until July 1997. D ...
, who criticized the deficit funding and the politicized police department of the city. Federal investigations of drug trafficking at Jackson's Hawkins Field airport were a part of the ''Kerry Report,'' the 1986 U.S. Senate investigation of public corruption and foreign relations.
As Jackson has become the medical and legal center of the state, it has attracted Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
professionals in both fields. Since the late 20th century, it has developed the largest Jewish community
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
in the state.
In 1997, Harvey Johnson, Jr. was elected as Jackson's first African-American mayor. During his term, he proposed the development of a convention center to attract more business to the city. In 2004, during his second term, 66 percent of the voters passed a referendum for a tax to build the Convention Center.
Mayor Johnson was replaced by Frank Melton on July 4, 2005. Melton generated controversy through his unconventional behavior, which included acting as a law enforcement officer. A dramatic spike in crime ensued during his term, despite Melton's efforts to reduce crime. The lack of jobs contributed to crime. In 2006 a young African-American businessman, Starsky Darnell Redd, was convicted of money laundering in federal court along with his mother, other associates, and Billy Tucker, the former airport security chief.
In 2007, Hinds County sheriff Malcolm McMillin was appointed as the new police chief in Jackson, setting a historic precedent. McMillin was both the county sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
and city police chief until 2009, when he stepped down due to disagreements with the mayor. Mayor Frank Melton died in May 2009, and City Councilman Leslie McLemore served as acting mayor of Jackson until July 2009, when former Mayor Harvey Johnson was elected and assumed the position.
On June 26, 2011, 49-year-old James Craig Anderson was killed in Jackson after being beaten, robbed, and run over by a group of white teenagers. The district attorney described it as a " hate crime", and the FBI investigated it as a civil rights violation.
On March 18, 2013, a severe hailstorm hit the Jackson metro area. The hail caused major damage to roofs, vehicles, and building siding. Hail ranged in size from golfball to softball. There were more than 40,000 hailstorm claims of homeowner and automobile damage.
In 2013, Jackson was named as one of the top 10 friendliest cities in the United States by ''CN Traveler''. The capital city was tied with Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
as Number 7. The city was noticed for friendly people, great food, and green and pretty public places.
On July 1, 2013, Chokwe Lumumba was sworn into office as mayor of the city. After eight months in office, Lumumba died on February 25, 2014. Lumumba was a popular yet controversial figure due to his prior membership in the Republic of New Afrika, as well as being a co-founder of the National Coalition of Blacks for Reparations in America.
Lumumba's son, Chokwe Antar Lumumba
Chokwe Antar Lumumba (born March 29, 1983) is an American attorney, activist, and politician serving as the 53rd mayor of Jackson, Mississippi, the 7th consecutive African-American to hold the position.
He was first elected in 2017. In the prim ...
, ran for the mayoral seat following his father's death, but lost to Councillor Tony Yarber on April 22, 2014. In 2017, however, Chokwe Antar Lumumba ran for mayor again, and won. Following his victory, on June 26 he was interviewed by Amy Goodman on ''Democracy Now!
''Democracy Now!'' is an hour-long American TV, radio, and Internet news program hosted by journalists Amy Goodman (who also acts as the show's executive producer), Juan González, and Nermeen Shaikh. The show, which airs live each weekday at ...
'', at which time he declared a commitment to make Jackson the "Most Radical City on the Planet".
For several years, the city water supply failed to meet federal drinking water standards and was subject to many boil water orders in 2021 and 2022. Due to deteriorating water infrastructure, some parts of the city experienced low water pressure, and in some neighborhoods residents reported untreated sewage flowing in city streets. In August 2022, Jackson lost access to water when its largest water treatment plant failed, leaving tap water untreated.
Geography
 Jackson is located primarily in northeastern Hinds County, with small portions in Madison and Rankin counties. The city of Jackson also includes around 3,000 acres (12.1 km2) comprising Jackson-Medgar Evers International Airport in Rankin County and a small portion of Madison County. The
Jackson is located primarily in northeastern Hinds County, with small portions in Madison and Rankin counties. The city of Jackson also includes around 3,000 acres (12.1 km2) comprising Jackson-Medgar Evers International Airport in Rankin County and a small portion of Madison County. The Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
forms most of the eastern border of the city. A small portion of the city containing Tougaloo College
Tougaloo College is a private historically black college in the Tougaloo area of Jackson, Mississippi. It is affiliated with the United Church of Christ and Christian Church (Disciples of Christ). It was originally established in 1869 by New Yor ...
is the portion of Jackson that lies in Madison County, bounded on the west by Interstate 220 and on the east by the U.S. Route 51
U.S. Route 51 or U.S. Highway 51 (US 51) is a major south-north United States highway that extends from the western suburbs of New Orleans, Louisiana, to within of the Wisconsin–Michigan state line. As most of the United States Numbered Highw ...
and Interstate 55
Interstate 55 (I-55) is a major Interstate Highway in the central United States. As with most primary Interstates that end in a five, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, connecting the Gulf of Mexico to the Great Lakes. The h ...
. In the 2010 census, only 622 of the city's residents lived in Madison County, and only 1 lived within the city limits in Rankin County. The city is bordered to the north by Ridgeland in Madison County, to the northeast by Ross Barnett Reservoir on the Pearl River, to the east by Flowood and Richland in Rankin County, to the south by Byram in Hinds County, and to the west by Clinton in Hinds County.
According to the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of t ...
, the city has a total area of , of which are land and , or 1.94% of the total, are water.
Cityscape
 Downtown Jackson is situated directly on the banks of the Pearl River. The downtown district has direct connections to both Interstate 55 via Pearl Street and Pasagoula Street and Interstate 20 via State Street (US 51). Much of the downtown was constructed before the 1980s and only small additions to the skyline have been made since then.
Downtown Jackson is situated directly on the banks of the Pearl River. The downtown district has direct connections to both Interstate 55 via Pearl Street and Pasagoula Street and Interstate 20 via State Street (US 51). Much of the downtown was constructed before the 1980s and only small additions to the skyline have been made since then.
Major highways
*Interstate 55
Interstate 55 (I-55) is a major Interstate Highway in the central United States. As with most primary Interstates that end in a five, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, connecting the Gulf of Mexico to the Great Lakes. The h ...
*US 80
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Geology
For the most part, Jackson is built on acidic, variably drained silt loamsoil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debri ...
. Loess forms the topsoil in western sections, where the Loring soil series is common. The Tippo series, also a silt loam, is found in the central flood plain. Farther east, common soil series include Guyton silt loam, Providence silt loam and Smithdale fine sandy loam.
 Jackson sits atop the extinct Jackson Volcano, located underground. It is the only capital city in the United States to have this feature. The buried peak of the volcano is located directly below the Mississippi Coliseum.
The municipality is drained on the west by tributaries of the Big Black River and on the east by the Pearl River, which is higher than the Big Black near Canton. The artesian groundwater flow is not as extensive in Jackson for this reason. The first large-scale well was drilled in the city in 1896, and the city water supply has relied on surface water resources.
Jackson sits atop the extinct Jackson Volcano, located underground. It is the only capital city in the United States to have this feature. The buried peak of the volcano is located directly below the Mississippi Coliseum.
The municipality is drained on the west by tributaries of the Big Black River and on the east by the Pearl River, which is higher than the Big Black near Canton. The artesian groundwater flow is not as extensive in Jackson for this reason. The first large-scale well was drilled in the city in 1896, and the city water supply has relied on surface water resources.
Climate
Jackson is located in the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Cfa''). Rain occurs throughout the year, though the winter and spring are the wettest seasons, while September and October are usually the driest months. Snow is rare, and accumulation very seldom lasts more than a day. Average annual precipitation is , see climate table. Much of Jackson's rainfall occurs during thunderstorms. Thunder is heard on roughly 70 days each year. Jackson lies in a region prone to severe thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are somet ...
s which can produce large hail, damaging winds, and tornadoes. Among the most notable tornado events was the F5 Candlestick Park tornado on March 3, 1966, which destroyed the shopping center of the same name and surrounding businesses and residential areas, killing 19 in South Jackson.
The record low temperature is , set on January 27, 1940, and the record high is , last recorded August 30, 2000.
Demographics
Jackson remained a small town for much of the 19th century. Before the American Civil War, Jackson's population remained small, particularly in contrast to the river towns along the commerce-ladenMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
. Despite the city's status as the state capital, the 1850 census counted only 1,881 residents, and by 1900 the population of Jackson was still less than 8,000. Although it expanded rapidly, during this period Meridian became Mississippi's largest city, based on trade, manufacturing, and access to transportation via railroad and highway.
In the early 20th century, Jackson had its largest rates of growth but ranked second to Meridian in Mississippi. By 1944, Jackson's population had risen to some 70,000 inhabitants, and it became the largest city in the state. It has maintained its position, achieving a peak population in the 1980 census of more than 200,000 residents in the city. Since then, Jackson has steadily declined in population, while its suburbs have boomed. This change has occurred in part due to white flight after the desegregation
Desegregation is the process of ending the separation of two groups, usually referring to races. Desegregation is typically measured by the index of dissimilarity, allowing researchers to determine whether desegregation efforts are having impact o ...
of public schools in 1970 but also demonstrates the national suburbanization
Suburbanization is a population shift from central urban areas into suburbs, resulting in the formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urba ...
trend, in which wealthier residents moved out to newer housing. This decline slowed in the first decade of the 21st century.
Race and ethnicity
''Note: the US Census treats Hispanic/Latino as an ethnic category. This table excludes Latinos from the racial categories and assigns them to a separate category. Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race.'' According to the 2010 census, the racial and ethnic makeup of the city was predominantly Black and African American, and non-Hispanic white; in 2020, they remained the largest racial and ethnic composition for the city. With white demographic decline and white flight, its non-Hispanic white population has declined; this was also due to the increase in other traditional minorities within the city, state, and nation.
According to the 2010 census, the racial and ethnic makeup of the city was predominantly Black and African American, and non-Hispanic white; in 2020, they remained the largest racial and ethnic composition for the city. With white demographic decline and white flight, its non-Hispanic white population has declined; this was also due to the increase in other traditional minorities within the city, state, and nation.
Income
According to census statistics in 2000, the median income for a household in the city was $30,414, and the median income for a family was $36,003. Males had a median income of $29,166 versus $23,328 for females. The per capita income for the city was $17,116. About 19.6% of families and 23.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 33.7% of those under age 18 and 15.7% of those age 65 or over. At the publication of the 2020 American Community Survey, the city's median household income increased to $35,070; families had a median income of $44,348, married-couple families $74,893, and non-families $22,061.Crime
In 1993 Jackson had the nation's 12th highest homicide rate among cities with more than 100,000 residents, according to the FBI. The 87 slayings in the city in 1993 gave Jackson a homicide rate of 41.9 per 100,000 residents, the FBI reported, and set a new record for the most violent deaths in one year. 1994 had higher homicides, with 91, and the record would be broken again in 1995 with a total of 92. In 2020, the city's homicide rate reached its highest in history with 79.69 homicides per 100,000 residents, with a total of 128 homicides. Of major U.S. cities, onlySt. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
surpassed Jackson's homicide rate. The homicide rate in 2020 represented a significant spike after years of declining homicide rates in the early 2000s. Property crime remains much lower than in the 1990s and overall violent crime has not increased as significantly as homicide in recent years and is below the peak in 1994 as of 2020. In 2021, a record number of homicides were recorded - 155 - and at a rate of 101 per 100,000 amongst the highest in the world.
In late 2020, Police Chief James Davis along with the Mayor and other city leaders unveiled the virtual policing concept. After months of struggling to move the concept forward Chief Davis began discussions with Eric B. Fox
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization).
The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* ain ...
, a veteran Jackson Police Officer to return to the department. Fox returned officially in January 2022 and launched a new concept, the Real Time Command Center.
Economy
Jackson is home to several major industries; these include electrical equipment and machinery, processed food, and primary and fabricated metal products. The surrounding area supports the agricultural development of livestock, soybeans, cotton, and poultry. According to the city's government, its top three employers are theUniversity of Mississippi Medical Center
University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC) is the health sciences campus of the University of Mississippi (Ole Miss) and is located in Jackson, Mississippi, United States. UMMC, also referred to as the Medical Center, is the state's only aca ...
, Jackson Public Schools, and Nissan North America
, trading as Nissan Motor Corporation and often shortened to Nissan, is a Japanese multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan. The company sells its vehicles under the Nissan, Infiniti, and Datsun brands ...
as of 2020. Other notable corporations with a large presence in the city and area have included or currently include Amazon (in nearby Madison County), Burlington, and Walmart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores from the United States, headquarter ...
.
The city is home to Cooperation Jackson, which is an economic development vehicle for worker-owned cooperative
A worker cooperative is a cooperative owned and self-managed by its workers. This control may mean a firm where every worker-owner participates in decision-making in a democratic fashion, or it may refer to one in which management is elected by ...
business. The organization has led to the creation of several businesses including lawn care provider The Green Team, organic farm Freedom Farms, print shop The Center for Community Production, and The Balagoon Center, which is a cooperative business incubator.
Arts and culture
 Jackson is home to a number of cultural and artistic attractions, including the following:
* Ballet Mississippi
* Celtic Heritage Society of Mississippi
* Crossroads Film Society and its annual Film Festival
* International Museum of Muslim Cultures
* Jackson State University Botanical Garden
* Jackson Zoo
* Light and Glass Studio
* Margaret Walker Center
* Mississippi Agriculture and Forestry Museum
* Mississippi Arts Center
* Mississippi Chorus
* Mississippi Civil Rights Museum
* Mississippi Department of Archives and History, which contains the state archives and records
* Mississippi Heritage Trust
* Mississippi Hispanic Association
* Mississippi Metropolitan Ballet
* Mississippi Museum of Art
* Mississippi Opera
* Mississippi Symphony Orchestra (MSO), formerly the Jackson Symphony Orchestra, founded in 1944
* Municipal Art Gallery
* Museum of Mississippi History
* Mynelle Gardens
* New Stage Theatre
*
Jackson is home to a number of cultural and artistic attractions, including the following:
* Ballet Mississippi
* Celtic Heritage Society of Mississippi
* Crossroads Film Society and its annual Film Festival
* International Museum of Muslim Cultures
* Jackson State University Botanical Garden
* Jackson Zoo
* Light and Glass Studio
* Margaret Walker Center
* Mississippi Agriculture and Forestry Museum
* Mississippi Arts Center
* Mississippi Chorus
* Mississippi Civil Rights Museum
* Mississippi Department of Archives and History, which contains the state archives and records
* Mississippi Heritage Trust
* Mississippi Hispanic Association
* Mississippi Metropolitan Ballet
* Mississippi Museum of Art
* Mississippi Opera
* Mississippi Symphony Orchestra (MSO), formerly the Jackson Symphony Orchestra, founded in 1944
* Municipal Art Gallery
* Museum of Mississippi History
* Mynelle Gardens
* New Stage Theatre
* Russell C. Davis Planetarium
Russell may refer to:
People
* Russell (given name)
* Russell (surname)
* Lady Russell (disambiguation)
* Lord Russell (disambiguation)
Places Australia
*Russell, Australian Capital Territory
*Russell Island, Queensland (disambiguation)
**Russ ...
* Smith-Robertson Museum and Cultural Center
* USA International Ballet Competition
Sports
 The city of Jackson and its metropolitan area are home to collegiate and semi-professional sports teams; Major League Baseball's Atlanta Braves minor affiliate, the
The city of Jackson and its metropolitan area are home to collegiate and semi-professional sports teams; Major League Baseball's Atlanta Braves minor affiliate, the Mississippi Braves
The Mississippi Braves, or M-Braves as they are referred to locally, are a Minor League Baseball team based in Pearl, Mississippi, a suburb of Jackson. The team is the Double-A affiliate of the Atlanta Braves and plays in the Southern League. ...
, plays in the area. Mississippi Brilla of USL League Two also operates in the area.
Government and infrastructure

Municipal government
In 1985, Jackson voters opted to replace the three-person mayor-commissioner system with a city council and mayor. This electoral system enables a wider representation of residents on the city council. City council members are elected from each of the city's seven wards, considered single-member districts. The mayor is elected at-large citywide. Jackson's mayor isChokwe Antar Lumumba
Chokwe Antar Lumumba (born March 29, 1983) is an American attorney, activist, and politician serving as the 53rd mayor of Jackson, Mississippi, the 7th consecutive African-American to hold the position.
He was first elected in 2017. In the prim ...
( D). Who was elected on July 3, 2017.
Jackson's City Council members are:
*Ward 1: Ashby Foote
*Ward 2: Melvin Priester, Jr.
*Ward 3: Kenneth Stokes
*Ward 4: De'Keither Stamps
*Ward 5: Charles H. Tillman
*Ward 6: Aaron Banks
*Ward 7: Virgi Lindsay
State government
TheMississippi Department of Corrections
The Mississippi Department of Corrections (MDOC) is a state agency of Mississippi that operates prisons. It has its headquarters in Jackson. Burl Cain is the commissioner.
History
In 1843 a penitentiary in four city squares in central Jackson ...
(MDOC) operates the Jackson Probation & Parole Office in Jackson. The MDOC Central Mississippi Correctional Facility
The Central Mississippi Correctional Facility for Women (CMCF) is a Mississippi Department of Corrections (MDOC) prison for men and women located in an unincorporated area in Rankin County, Mississippi, near the city of Pearl.unincorporated Unincorporated may refer to:
* Unincorporated area, land not governed by a local municipality
* Unincorporated entity, a type of organization
* Unincorporated territories of the United States, territories under U.S. jurisdiction, to which Congress ...
Rankin County, is located in proximity to Jackson.
Federal representation
The larger portion of Jackson is part of Mississippi's 2nd congressional district. U.S. Representative Bennie Gordon Thompson, a Democrat, has served since 1993. Until 2011 he was Chairman of the Committee on Homeland Security and has been the ranking member since 2011. The United States Postal Service operates the Jackson Main Post Office and several smaller post offices.Education
Higher education

 Jackson is home to the most collegiate institutions in Mississippi.
Jackson is home to the most collegiate institutions in Mississippi. Jackson State University
Jackson State University (Jackson State or JSU) is a public historically black research university in Jackson, Mississippi. It is one of the largest HBCUs in the United States and the fourth largest university in Mississippi in terms of studen ...
is the largest collegiate institution in Jackson, fourth largest in Mississippi, and the only doctoral-granting research institution based in its region.
Colleges and universities
*Jackson State University
Jackson State University (Jackson State or JSU) is a public historically black research university in Jackson, Mississippi. It is one of the largest HBCUs in the United States and the fourth largest university in Mississippi in terms of studen ...
*Tougaloo College
Tougaloo College is a private historically black college in the Tougaloo area of Jackson, Mississippi. It is affiliated with the United Church of Christ and Christian Church (Disciples of Christ). It was originally established in 1869 by New Yor ...
* Millsaps College
*Belhaven University
Belhaven University (Belhaven or BU) is a private evangelical Christian university in Jackson, Mississippi. Founded in 1883, the university offers traditional majors, programs of general studies, and pre-professional programs in Christian Minis ...
*University of Mississippi Medical Center
University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC) is the health sciences campus of the University of Mississippi (Ole Miss) and is located in Jackson, Mississippi, United States. UMMC, also referred to as the Medical Center, is the state's only aca ...
* Mississippi College School of Law
* Hinds Community College
Primary and secondary schools
Public schools
Jackson Public School District (JPS) operates 60 public schools. It is one of the largest school districts in the state with about 30,000 students in thirty-eight elementary schools, thirteen middle schools, seven high schools, and two special schools. Jackson Public Schools is the only urban school district in the state. the public schools have few children who are middle or upper class, as 99% of the students in JPS qualify for free or reduced school lunches. In 2017 Susan Womack, president of the Parents for Public Schools Jackson (PPSJ) from 2000 to 2012, stated that middle to upper-class families in Jackson tended to leave public school after elementary school, with parents who remained in Jackson enrolling their children in private school, and those who wished to continue enrolling their children in public schools moving to Madison County. The PPSJ decided circa the mid-2000s that it was not feasible to encourage middle and upper-class parents to put their children in JPS schools. The district's high schools include: * Callaway High School *Capital City Alternative School
Capital City Alternative School is an alternative school in Jackson, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gul ...
* Career Development Center
* Forest Hill High School
* Jim Hill High School
* Lanier High School
* Murrah High School
* Provine High School
* Wingfield High School
While most of Jackson is in Jackson PSD, there are parts in Hinds County that are instead in Hinds County School District. This part is zoned to Terry High School in Terry
Terry is a unisex given name, derived from French Thierry and Theodoric. It can also be used as a diminutive nickname for the names Teresa or Theresa (feminine) or Terence (given name), Terence or Terrier (masculine).
People
Male
* Terry Albrit ...
. The portion of Jackson in Madison County is within the Madison County School District.
There are state-operated K-12 public schools for special purposes;
* Mississippi School for the Blind
Mississippi School for the Blind (MSB) is a state-operated K-12 public school for blind children located in Jackson, Mississippi, United States.
The Mississippi State Legislature
The Mississippi Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. ...
* Mississippi School for the Deaf
The Mississippi School for the Deaf (MSD) is a school for the deaf and hard of hearing in Jackson, Mississippi accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS). It offers elementary and secondary education (K-12), covering stud ...
Private schools
Private secondary schools include: * Christ Missionary & Industrial (CM&I) College High School * Hillcrest Christian School * Jackson Academy * Woodland Hills Academy (closed) Some schools are in nearby municipalities: * St. Andrew's Episcopal School (the elementary school is in Jackson but the secondary school campus is in Ridgeland) *Jackson Preparatory School
Jackson Preparatory School (Jackson Prep) is an independent, coeducational, day school enrolling 700 students in grades five through twelve. The school is located in Flowood, Mississippi
Flowood is a city in Rankin County, Mississippi, United S ...
( Flowood)
* The Veritas School ( Ridgeland)
* St. Joseph Catholic School St. Joseph's School, St. Joseph's Catholic School, St Joseph's School, St Joseph's Catholic School, and variants are frequently used school names, and may refer to:
Africa
*St Joseph's School, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Asia
*St Joseph Higher Seconda ...
( Madison), of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Jackson
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Jackson is a diocese in the ecclesiastical province of Mobile, in the southern United States of America. Its ecclesiastical jurisdiction includes the northern and central parts of the state of Mississippi, an a ...
* Hartfield Academy ( Flowood)
* Canton Academy
Canton Academy, officially known as the Canton Academic Foundation, is a segregation academy in Canton, Mississippi, the county seat of Madison County. It serves 285 students in grades K-12.
History
Canton opened in January 1970 as a segregatio ...
( Canton)
* Tri-County Academy ( Flora)
Private primary schools include:
* Jackson Academy
* First Presbyterian Day School
* Magnolia Speech School
* St. Andrew's Episcopal Lower School – South Campus
* St. Richard Catholic School
* St. Therese Catholic School
Public libraries
Jackson/Hinds Library System is the library system of Jackson.Infrastructure
On March 27, 2015, Jackson Mayor Tony Yarber issued a state of emergency for transportation (potholes) and water infrastructure (breaks in water mains). The quality of Jackson's water infrastructure system decreased after the severe winter weather of 2014–2015. Jackson's office estimated the cost to fix the roads and water pipes at $750 million to $1 billion. After issuing the state of emergency, the City of Jackson filed a letter of intent to Department of Health to borrow $2.5 million to repair broken water pipes. The Jackson City Council must approve the mayor's proposal. Additionally, Mayor Yarber asked for help from both FEMA and the state Governor's office. Calling for a state of emergency increases the likelihood that the U.S. Department of Transportation would give the city money from a "quick release" funding account. In late August 2022, the Pearl River overflowed, flooding much of the city and contaminating the water supply. Mayor Lumumba declared a state of emergency and shut down all businesses and schools.Transportation
In 2015, 11 percent of the city of Jackson households lacked a car, which decreased to 7.6 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Jackson averaged 1.68 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8. Jackson has an increasing number of bicycle lanes. Jackson–Medgar Wiley Evers International Airport is located east of city in Rankin County.In popular culture
In 2011, theUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
named the USS ''Jackson'' (LCS-6) in honor of the city.
In 2002, the Subway Lounge (of the Summers Hotel on the Gold Coast) was featured as the subject of the film documentary entitled ''Last of the Mississippi Jukes.''
The popular film '' The Help'' (2011), based on the bestselling novel by the same name by Kathryn Stockett
Kathryn Stockett is an American novelist. She is known for her 2009 debut novel, '' The Help'', which is about African-American maids working in white households in Jackson, Mississippi, during the 1960s.
Career
Stockett worked in magazine publ ...
, was filmed in Jackson. The city has a two-part, self-guided tour of areas featured in the film and the book."'The Help' in Belhaven Neighborhood Tour", Jackson Convention and Visitors Bureau In the song "
Uptown Funk
"Uptown Funk" is a song by British record producer Mark Ronson from his fourth studio album, ''Uptown Special'' (2015), featuring American singer and songwriter Bruno Mars. It was released as the album's lead single on 10 November 2014 via dow ...
" by Mark Ronson and featuring Bruno Mars
Peter Gene Hernandez (born October 8, 1985), known professionally as Bruno Mars, is an American singer, songwriter, and record producer. He is known for his stage performances, retro showmanship, and for performing in a wide range of musical ...
Jackson is mentioned in the lines "Julio! Get the Stretch! Ride to Harlem; Hollywood, Jackson, Mississippi."
'' Get on Up'', a movie released in August 2014, had some scenes filmed in Jackson, and nearby Natchez. The movie is based on the life of James Brown.
The movie ''Speech & Debate
''Speech & Debate'' is a 2017 American film directed by Dan Harris. The film is an adaptation of the play of the same name and was released on April 7, 2017, by Vertical Entertainment.
Plot
The film features three misfit students in a high s ...
'', an adaptation of the stage play of the same name of Broadway theatre
Broadway theatre,Although ''theater'' is generally the spelling for this common noun in the United States (see American and British English spelling differences), 130 of the 144 extant and extinct Broadway venues use (used) the spelling ''Th ...
, was filmed entirely in Jackson.
Notable people
:''See:List of people from Mississippi
This list contains people who were born or lived in the U.S. state of Mississippi.
Activists and advocates
* Ruby Bridges (born 1954), first African-American child to attend an all-white school in the South ( Tylertown)
* Will D. Campbell ...
''
Further reading
*'' Jackson Rising: The Struggle for Economic Democracy and Black Self-Determination in Jackson, Mississippi'', edited by Kali Akuno and Ajamu Nangwaya. (2017) Daraja Press. .Notes
References
Bibliography
External links
*Jackson Convention & Visitors Bureau
{{Authority control Cities in Mississippi Cities in Hinds County, Mississippi Cities in Madison County, Mississippi Cities in Rankin County, Mississippi 1792 establishments in the United States Andrew Jackson County seats in Mississippi Cities in Jackson metropolitan area, Mississippi Mississippi Blues Trail Planned cities in the United States Populated places established in 1792