Isle of Thanet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Isle of Thanet () is a
 Archaeological evidence shows that the area now known as the Isle of Thanet was one of the major areas of
Archaeological evidence shows that the area now known as the Isle of Thanet was one of the major areas of
peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on a ...
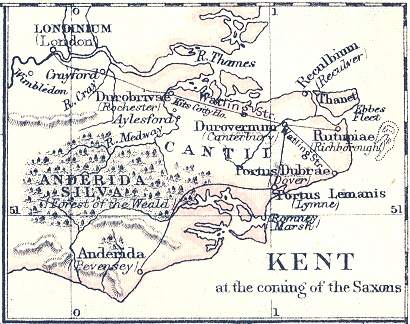
forming the easternmost part of Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. While in the past it was separated from the mainland by the Wantsum Channel, it is no longer an island.
Archaeological remains testify to its settlement in ancient times. Today, it is a tourist destination, and has an active agricultural base.
Etymology
The island of Thanet is mentioned as ''Tonetic'' (c. AD 150; the TON- of this form was misread as TOΛI-, hence it appears as ''Toliatis'' in the surviving manuscripts ofPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
); ''Tanat's'' (3rd C AD, Solinus Solinus may refer to:
* Gaius Julius Solinus, a 3rd century Latin author
* Solinus (horse), a British racehorse (1975–1979)
* Solinus, Duke of Ephesus, a character in William Shakespeare's play ''The Comedy of Errors''
See also
* Salinas (disam ...
); ''Tanatos'' (AD 731); ''Tenid'' in 679BEAUREPAIRE and ''Tenet'' (e.g. charters of AD 679, 689 and thereafter); and the Old Welsh forms ''Tanet'' and ''Danet'', found in the ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia B ...
'' (c. AD 829/30) and Armes Prydein
''Armes Prydein'' (, ''The Prophecy of Britain'') is an early 10th-century Welsh prophetic poem from the ''Book of Taliesin''.
In a rousing style characteristic of Welsh heroic poetry, it describes a future where all of Brythonic peoples are all ...
(c. AD 930).
Standard reference works for English place-names (such as Eilert Ekwall
Bror Oscar Eilert Ekwall (born 8 January 1877 in Vallsjö (now in Sävsjö, Jönköpings län), Sweden, died 23 November 1964 in Lund, Skåne län, Sweden), known as Eilert Ekwall, was Professor of English at Sweden's Lund University from 1909 t ...
's ''Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-Names'') state the name ''Tanet'' is known to be Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
in origin. Commonly the original meaning of Thanet is thought to be "fire" or "bright island" (''tân'' means fire in Modern Welsh and ''tan'' in Breton), and this has led to speculation the island was home to an ancient beacon or lighthouse.
Another theory states that ''Tanet'' is a common European toponymic creation of Celtic origin, based on the Celtic word ''*tanno-'' meaning "holm oak" (compare Breton ''tann'' "sort of oak", Cornish ''glastannen'' "holm oak") and the Celtic suffix ''*-etu'', to mean a collection of trees. Thanet would mean "place of the holm oaks", such as the Northern French Thenney (Eure, ''Thaneth'' ab. 1050); Tennie (Sarthe, ''Tanida'' 9th century) or the Italian Tanedo (Lombardy, ''Tanetum'', Tite-Live).
The 7th-century Archbishop Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
recorded an apocryphal folk-etymology in which the island's name is fancifully connected with the Greek word for death ( Thanatos/Θάνατος), stating that Thanet, "an island of the ocean separated from Britain by a narrow channel ... ascalled ''Tanatos'' from the death of serpents; for while it has none of its own, soil taken from it to any place whatsoever kills snakes there."
The ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia B ...
'', written in the 9th century, states that "''Tanet''" was the name used for the island by the legendary Jutes Hengist and Horsa, while its name in Old Welsh
Old Welsh ( cy, Hen Gymraeg) is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic ...
was "''Ruoi(c)hin''"; this name may be translated as "gift" (''rhwych'' in Modern Welsh).
History

 Archaeological evidence shows that the area now known as the Isle of Thanet was one of the major areas of
Archaeological evidence shows that the area now known as the Isle of Thanet was one of the major areas of Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with ...
settlement. A large hoard of Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
implements has been found at Minster-in-Thanet; and several Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
settlements have also come to light.
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
made two attempts to invade Britain, in both 55 and 54 BC. In 2017 archaeologists from the University of Leicester
, mottoeng = So that they may have life
, established =
, type = public research university
, endowment = £20.0 million
, budget = £326 million
, chancellor = David Willetts
, vice_chancellor = Nishan Canagarajah
, head_lab ...
excavated a Roman fort
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
covering up to at Ebbsfleet, and dated it to around 55–50 BC. They further linked it to Caesar's invasion of Britain
The term Invasion of England may refer to the following planned or actual invasions of what is now modern England, successful or otherwise.
Pre-English Settlement of parts of Britain
* The 55 and 54 BC Caesar's invasions of Britain.
* The 43 A ...
in 54 BC, and suggested that the invading force arrived in nearby Pegwell Bay
Pegwell Bay is a shallow inlet in the English Channel coast astride the estuary of the River Stour north of Sandwich Bay, between Ramsgate and Sandwich in Kent. Part of the bay is a nature reserve, with seashore habitats including mudflats and ...
. Nearly a century later, in 43 AD, Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor ...
sent four legions to Britain, where the Romans were to remain for the next 400 years. During that time the port of Richborough, on the opposite side of the Wantsum Channel, became one of the chief ports of Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
.
According to the eighth-century ecclesiastical historian Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom ...
, Vortigern, King of the Britons
The title King of the Britons ( cy, Brenin y Brythoniaid, la, Rex Britannorum) was used (often retrospectively) to refer to the most powerful ruler among the Celtic Britons, both before and after the period of Roman Britain up until the Norma ...
, was under attack from other tribes and called for assistance. Among those who came were the Jutes Hengist and Horsa; Vortigern is said to have rewarded them with the Isle of Thanet in return for their services. As the following extract from the ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia B ...
'' (first written sometime shortly after 833) testifies:
This story, however, is an example of non-historical founding myths, though one constructed with political objectives in mind. In reality, it appears to have been settled by Jutes under Visigothic
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
authority between 476-517 AD,though they may have been present earlier as Foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
. These were followed by Ingaevones
The Ingaevones were a West Germanic cultural group living in the Northern Germania along the North Sea coast in the areas of Jutland, Holstein, and Frisia in classical antiquity. Tribes in this area included the Angles, Frisii, Chauci, S ...
in the sixth century.
Throughout this time the Isle remained an island. The Wantsum Channel allowed ships to sail between the mainland and the island in calm waters. Gradually this silted up, and the last ship sailed through the Channel in 1672.
In 597 Augustine of Canterbury
Augustine of Canterbury (early 6th century – probably 26 May 604) was a monk who became the first Archbishop of Canterbury in the year 597. He is considered the "Apostle to the English" and a founder of the English Church.Delaney ''D ...
is said, by Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom ...
, to have landed with 40 men at Ebbsfleet, in the parish of Minster-in-Thanet, before founding Britain's second Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
monastery in Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of t ...
(the first was founded fifty years earlier by Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is tod ...
on Eileach an Naoimh
Eileach an Naoimh, also known as Holy Isle, is an uninhabited island in the Inner Hebrides of the west coast of Scotland. It is the southernmost of the Garvellachs archipelago and lies in the Firth of Lorne between Mull and Argyll. The name is ...
in the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
): a cross marks the spot.
Following the raids on the Isle of Sheppey
The Isle of Sheppey is an island off the northern coast of Kent, England, neighbouring the Thames Estuary, centred from central London. It has an area of . The island forms part of the local government district of Swale. ''Sheppey'' is deriv ...
, Thanet became a regular target for Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
attacks, its vulnerable coastal monasteries providing convenient targets for the invaders. By 851 and again in 854, the Vikings overwintered in Thanet and continued their raids in spring. Thanet's monasteries were subsequently used by the Danes as feasting halls or general headquarters.
In 865, the Great Heathen Army
The Great Heathen Army,; da, Store Hedenske Hær also known as the Viking Great Army,Hadley. "The Winter Camp of the Viking Great Army, AD 872–3, Torksey, Lincolnshire", ''Antiquaries Journal''. 96, pp. 23–67 was a coalition of Scandin ...
encamped in Thanet and was promised by the people of Kent danegeld in exchange for peace. Regardless, the Vikings did not abide by this agreement and proceeded to rampage across eastern Kent.
By 1334–1335 Thanet had the highest population density in Kent according to King Edward III's lay subsidy rolls. Margate is mentioned in 1349, in a dispute about the land of Westgate Manor. Thanet acted as a granary for Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
and documents towards the end of that century refer to turreted walls beneath the cliffs needing maintenance. Coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landwar ...
has long since destroyed these structures.
Governance
Margate was incorporated as amunicipal borough
Municipal boroughs were a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1835 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in S ...
in 1857 and Ramsgate in 1884. Broadstairs and St Peter's Urban District and the Isle of Thanet Rural District covered the rest of the island from 1894 until 1974. By 1974, however, all these boroughs and districts had been abolished, and since that year the Isle of Thanet has formed the major part of the District
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivision ...
of Thanet.
Geology
The Isle is formed almost wholly ofchalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
, a soft pure white limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
of Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
age, specifically the Margate Chalk Member (Santonian to Campanian) traditionally referred to simply as the 'Margate Chalk', and sometimes as the ‘Margate Member’. It is a sub-division of the Newhaven Chalk Formation. Beneath this and outcropping around the margins of the Isle is the Seaford Chalk Formation which contains relatively more flint nodules and seams. It has also been referred to as the ‘Broadstairs Member’. The Seaford Chalk is of Coniacian
The Coniacian is an age or stage in the geologic timescale. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series and spans the time between 89.8 ± 1 Ma and 86.3 ± 0.7 Ma (million years ago). The Coniacian is preceded ...
to Santonian
The Santonian is an age in the geologic timescale or a chronostratigraphic stage. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 86.3 ± 0.7 mya (million years ago) and 83.6 ± 0.7 mya. ...
age whilst the Margate Chalk is of Santonian to Campanian age. Both were traditionally referred to the ‘Upper Chalk’ but are now classed as parts of the ‘White Chalk Subgroup’ as part of the broader Chalk Group
The Chalk Group (often just called the Chalk) is the lithostratigraphic unit (a certain number of rock strata) which contains the Upper Cretaceous limestone succession in southern and eastern England. The same or similar rock sequences occur acro ...
.
Overlying the chalk both within the Wantsum Channel and in patches on the surface of the Isle itself are the 100 m thick sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class ...
s, silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
s and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
s of the Palaeogene
The Paleogene ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning ...
age Thanet Formation (formerly the Thanet Beds). The area gives its name to the internationally recognised Thanetian
The Thanetian is, in the ICS Geologic timescale, the latest age or uppermost stratigraphic stage of the Paleocene Epoch or Series. It spans the time between . The Thanetian is preceded by the Selandian Age and followed by the Ypresian Age ( ...
, descriptive of rocks of this particular part of the Palaeocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pala ...
throughout the world. Brickearth head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals ...
deposits lie within many of the shallow chalk valleys and across some areas of flatter ground within the Isle.
Geography
The Isle of Thanet first came into being when sea levels rose after the last glacial period, around5000 BC
The 5th millennium BC spanned the years 5000 BC to 4001 BC (c. 7 ka to c. 6 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological an ...
. The North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
encroached on the land which is now the estuary of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
, and southwards to reach the higher land of the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills ...
, leaving behind an island composed of chalk in its wake. Eventually the sea broke through river valleys in the North Downs to the south (Middle Chalk) and finally today's English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
was opened up. The proto- River Stour then formed part of the intervening water, with a new tributary, the River Wantsum, completing it; it became known as the Wantsum Channel.
The Wantsum Channel gradually narrowed as pebble beaches built up at the southern end of the strait, blocking silt coming down the Stour. Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom ...
, in the 8th century, said that the Channel was then three furlong
A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one eighth of a mile, equivalent to 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in hor ...
s wide (). A map of 1414 showed a ferry crossing at Sarre. The first bridge over the channel was built there in 1485. Until the mid 18th century there was a ferry between Sandwich
A sandwich is a food typically consisting of vegetables, sliced cheese or meat, placed on or between slices of bread, or more generally any dish wherein bread serves as a container or wrapper for another food type. The sandwich began as a po ...
and the island; in 1755 a wooden drawbridge was built, and the ferry was closed.
Today the Isle is an island no longer and the erstwhile channel is now flat marshland criss-crossed by drainage ditches. Meanwhile, the exposed chalk cliffs are gradually being worn down by the sea, particularly at the North Foreland
North Foreland is a chalk headland on the Kent coast of southeast England, specifically in Broadstairs.
With the rest of Broadstairs and part of Ramsgate it is the eastern side of Kent's largest peninsula, the Isle of Thanet. It presents a ...
. Much else of the coast is a built-up area. The Wantsum area is still liable to flooding: during the North Sea flood of 1953
The 1953 North Sea flood was a major flood caused by a heavy storm surge that struck the Netherlands, north-west Belgium, England and Scotland. Most sea defences facing the surge were overwhelmed, causing extensive flooding.
The storm and flo ...
Thanet was cut off for a few days, but the sea defences have been strengthened since then.
The soil and equable climate of the Isle have always encouraged arable farming.
Today there are still farms inland, but the coast is nearly all covered in settlements, most of which have come into being in the 19th and 20th centuries.
As the popularity of the seaside resort
A seaside resort is a town, village, or hotel that serves as a vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, such as in the Germa ...
grew, so did that of the Isle of Thanet. At first the holidaymakers came by boat from London; after the coming of the railways in the mid-1840s, that became the preferred mode of transport. The population grew, as the following population statistics show:
Landmarks
The principal landmarks on the Isle are the North Foreland, and all the bays around the coastline, the principal ones of which are Minnis Bay, Palm Bay,Botany Bay
Botany Bay ( Dharawal: ''Kamay''), an open oceanic embayment, is located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, south of the Sydney central business district. Its source is the confluence of the Georges River at Taren Point and the Cook ...
, Joss Bay, and Pegwell Bay: the latter being part of the estuary of the River Stour. In 2007, seven of those beaches met stringent quality standards and were awarded as Blue Flag beach
The Blue Flag is a certification by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE) that a beach, marina, or sustainable boating tourism operator meets its standards.
The Blue Flag is a trademark owned by FEE, which is a not-for-profit non-go ...
es: Minnis Bay, Botany Bay (Broadstairs), Margate Main Sands, St Mildreds Bay (Westgate), Stone Bay (Broadstairs), West Bay (Westgate), and Westbrook Bay. In 2008, this had risen to 10 beaches.
Transport
The rail connections are via theChatham Main Line
The Chatham Main Line is a railway line in England that links London VictoriaQuail Map 5 – England South ages 2–13Sept 2002 (Retrieved 14 December 2011) and Dover Priory / Ramsgate, travelling via Medway (of which the town of Chatham is ...
through Margate to Ramsgate, and the Ashford to Ramsgate (via Canterbury West) Line Ashford may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Ashford, New South Wales
*Ashford, South Australia
*Electoral district of Ashford, South Australia
Ireland
*Ashford, County Wicklow
*Ashford Castle, County Galway
United Kingdom
*Ashford, Kent, a town
**B ...
. A high-speed rail link from London to Thanet began in December 2009, and forms part of the UK's first true high-speed commuter service, according to the South Eastern Railway Company. The Thanet Loop bus service connects Margate, Ramsgate, and Broadstairs. Main road links are the A28, which brings traffic from Canterbury and Ashford; and the A299, north coast route. The Thanet Coastal Path skirts the coast.
There is an airport at Manston, formerly RAF Manston, but since renamed by its commercial operators as Manston Airport. The airport is no longer in operation.
Ferry services (predominantly freight and car with passengers) were operated by Transeuropa Ferries to Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
from the Port of Ramsgate but ceased in 2013.
A tramway was once operated by the Isle of Thanet Electric Tramways and Lighting Company from Westbrook to Ramsgate from 1901 to 1937. The tramway had a narrow gauge of .
Cultural references
* The Isle of Thanet is mentioned in the 1977 Ian Dury song " Billericay Dickie": "I'd rendezvous with Janet, quite near the Isle of Thanet, she looked more like a gannet, she wasn't half a prannet". * It is also mentioned in the 2002 song "She's in Broadstairs" byHalf Man Half Biscuit
Half Man Half Biscuit are an English rock band, formed in 1984 in Birkenhead, Merseyside. Known for their satirical, sardonic, and sometimes surreal songs, the band comprises lead singer and guitarist Nigel Blackwell, bassist and singer Neil ...
on their album '' Cammell Laird Social Club'': "I'm on another planet, She's on the Isle of Thanet".
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Isle Of Thanet Thanet Thanet History of Kent Ancient Greek geography of Britain