Island of Montreal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Island of Montreal (french: Île de Montréal) is a large island in southwestern
 The first French name for the island was ''l'ille de Vilmenon'', noted by
The first French name for the island was ''l'ille de Vilmenon'', noted by
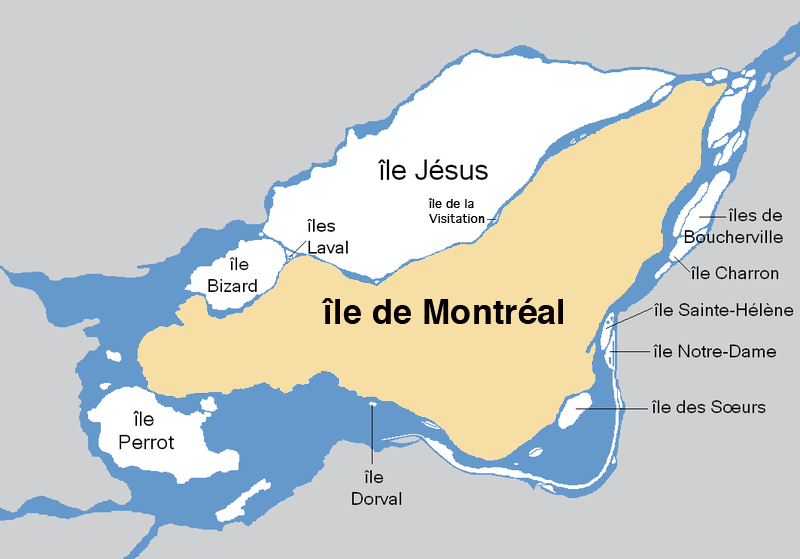 Near the Ottawa shore at the western end of island, the Ottawa River widens into Lac des Deux-Montagnes. A natural watercourse there, between the island and Île Perrot, has been improved by the island's Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue Canal. These waterways, connecting Lac des Deux-Montagnes with Lake Saint-Louis, constitute one of the places where the Ottawa flows into the St. Lawrence.
North of the island's western end, Lac des Deux-Montagnes flows into Rivière des Prairies, still part of the Ottawa. The Prairies separates the island from the other major part of the Hochelaga Archipelago including
Near the Ottawa shore at the western end of island, the Ottawa River widens into Lac des Deux-Montagnes. A natural watercourse there, between the island and Île Perrot, has been improved by the island's Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue Canal. These waterways, connecting Lac des Deux-Montagnes with Lake Saint-Louis, constitute one of the places where the Ottawa flows into the St. Lawrence.
North of the island's western end, Lac des Deux-Montagnes flows into Rivière des Prairies, still part of the Ottawa. The Prairies separates the island from the other major part of the Hochelaga Archipelago including  The
The
Jacques Cartier Bridge: 43 million
Champlain Bridge: 58 million

(Table of Contents)
/small> * Fisher, John. ''Memorial in Support of the Petition of the Inhabitants and Proprietors of the City and Island of Montreal Praying That the Ecclesiastics of St. Sulpice May Not Be Constituted a Body Corporate and Ecclesiastical, and Their Title Confirmed to Certain Valuable Seigniories and Estates''. Montreal?: s.n, 1840. * Mackay, Murdo. ''The Language Problem and School Board Reform on the Island of Montreal''. Ottawa: National Library of Canada, 1988. * Parks Canada. ''Montréal, a City Steeped in History Guide to Nationality Significant Places, Persons and Events on the Island of Montréal''. Québec: Parks Canada, 2004. * Russell, Ken. ''Metropolitan Government on the Island of Montreal''. Toronto: Osgoode Hall Law School, 1972. * Sancton, Andrew. ''Governing the Island of Montreal Language Differences and Metropolitan Politics''. Lane studies in regional government. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1985. * Savoie, Josée. ''Neighbourhood Characteristics and the Distribution of Crime on the Island of Montréal''. Crime and justice research paper series, no. 007. Ottawa: Statistics Canada, 2006. * Stansfield, John. ''The Pleistocene and Recent Deposits of the Island of Montreal''. Ottawa: Government Printing Bureau, 1915.
Municipalities of Montreal Island - City of Montreal
{{DEFAULTSORT:Montreal Hochelaga Archipelago River islands of Quebec Landforms of Montreal
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
, Canada, that is the site of a number of municipalities including most of the city of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
and is the most populous island in Canada. It is the main island of the Hochelaga Archipelago
The Hochelaga Archipelago (), also known as the Montreal Islands, is a group of islands at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa rivers in the southwestern part of the province of Quebec, Canada.
Population
On 1 July 2021, the Ho ...
at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
rivers.
Name
 The first French name for the island was ''l'ille de Vilmenon'', noted by
The first French name for the island was ''l'ille de Vilmenon'', noted by Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; Fichier OrigineFor a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December 1635) was a Fr ...
in a 1616 map, and derived from the sieur
Lord of the Manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England, referred to the landholder of a rural estate. The lord enjoyed manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seigno ...
de Vilmenon, a patron of the founders of Quebec at the court of Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crow ...
. However, by 1632 Champlain referred to the ''Isle de Mont-real'' in another map. The island derived its name from Mount Royal (French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
''Mont Royal'', then pronounced ), and gradually spread its name to the town, which had originally been called Ville-Marie.
In Kanien’kéha, the island is called Tiohtià:ke tsi ionhwéntsare ('broken in two', referring to the Lachine Rapids to the island's southwest) or Otsirà:ke (meaning 'on the fire'). In Anishninaabemowin, the land is called Mooniyaang, named for the first stop in the great Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawa ...
migration from Dawnland (the Maritimes
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of C ...
) to the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
.
Physical geography
The island is approximately 50 km (30 miles) long and 16 km (10 miles) wide at its widest point, and has a shoreline of 266 km (165 miles). It is the second largest island in theSaint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
, after Anticosti Island in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The Island of Montreal is the largest island in the Hochelaga Archipelago
The Hochelaga Archipelago (), also known as the Montreal Islands, is a group of islands at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa rivers in the southwestern part of the province of Quebec, Canada.
Population
On 1 July 2021, the Ho ...
, which is formed by the confluence of the Ottawa and St. Lawrence rivers.
 Near the Ottawa shore at the western end of island, the Ottawa River widens into Lac des Deux-Montagnes. A natural watercourse there, between the island and Île Perrot, has been improved by the island's Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue Canal. These waterways, connecting Lac des Deux-Montagnes with Lake Saint-Louis, constitute one of the places where the Ottawa flows into the St. Lawrence.
North of the island's western end, Lac des Deux-Montagnes flows into Rivière des Prairies, still part of the Ottawa. The Prairies separates the island from the other major part of the Hochelaga Archipelago including
Near the Ottawa shore at the western end of island, the Ottawa River widens into Lac des Deux-Montagnes. A natural watercourse there, between the island and Île Perrot, has been improved by the island's Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue Canal. These waterways, connecting Lac des Deux-Montagnes with Lake Saint-Louis, constitute one of the places where the Ottawa flows into the St. Lawrence.
North of the island's western end, Lac des Deux-Montagnes flows into Rivière des Prairies, still part of the Ottawa. The Prairies separates the island from the other major part of the Hochelaga Archipelago including Île Bizard
Île Bizard is an island near the Island of Montreal in the Hochelaga Archipelago region.
History
Historically named Île Bonaventure, by 1723 it had come to be named Île Bizard, after Jacques Bizard, to whom it was conceded as a fief in 1678 ...
and Île Jésus. After coursing about 55km (35 miles), the Prairie, at the northeastern tip of the island, joins the St. Lawrence.
The St. Lawrence coast of the island faces a variable waterway. In the southwest, the St. Lawrence River widens into Lake Saint-Louis as it approaches the island. Around a southern point near the center of the island, the St. Lawrence narrows into the Lachine Rapids, then widens into the Bassin de La Prairie past that southern point, and narrows again at the Montreal neighborhood of Cite Du Havre before flowing towards Quebec City
Quebec City ( or ; french: Ville de Québec), officially Québec (), is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is t ...
and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. The Lachine Canal on the island bypasses this complex part of the river. Neighboring islands in the St. Lawrence include Saint Helen's Island, Notre Dame Island, and Nuns' Island.
 The
The topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
of the island has been significantly altered by human activity, as evidenced by historical maps that name a lake St. Pierre in the island. This lake, and several other watercourses, have been drained or covered over as the city developed, while areas on the island's shores have been reclaimed and extended. The southwest of the island is separated by the Lachine Canal between Lachine and Montreal's Old Port; this portion of the island is partially divided further by the Canal de l'Aqueduc, running roughly parallel to the Lachine Canal, beginning in the borough of LaSalle and continuing between the boroughs of Le Sud-Ouest and Verdun.
Most of the bedrock of the island consists of Chazy limestone, with some Utica shale
The Utica Shale is a stratigraphical unit of Upper Ordovician age in the Appalachian Basin. It
underlies much of the northeastern United States and adjacent parts of Canada.
It takes the name from the city of Utica, New York, as it was first ...
. At the centre of the island stand the three peaks of Mount Royal
Mount Royal (french: link=no, Mont Royal, ) is a large intrusive rock hill or small mountain in the city of Montreal, immediately west of Downtown Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The best-known hypothesis for the origin of the name Montreal is the ...
, a volcanic intrusion (not an extinct volcano, contrary to popular belief). This short mountain (elevation 233 metres, 765') is a member of, and gives its name to, the Monteregian Hills
The Monteregian Hills (french: Collines Montérégiennes) is a linear chain of isolated hills in Montreal and Montérégie, between the Laurentians and the Appalachians.
Etymology
The first definition of the Monteregian Hills came about in 19 ...
.
Human geography
The island of Montreal is the major component of the territory of the city ofMontreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
, along with Île Bizard, Saint Helen's Island, Notre Dame Island, Nuns' Island, and some 69 smaller islands. With a population of 2,014,221 inhabitants (22% of the population of Québec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
), it is by far the most populous island in Canada. It is also the 6th most populous island of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
and the 37th most populated island on Earth. In addition, it is the world's most populous island surrounded by fresh water. Montreal and the other municipalities on the island compose the administrative region
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
of Montréal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-p ...
. The area of the Urban agglomeration of Montreal, which includes the Island of Montreal and several other smaller islands, is 499 km2 (193 sq. mi.).
The crossings which connect the island to its surroundings are some of the busiest bridges in the country and the world. The Champlain Bridge and the Jacques Cartier Bridge together accommodate 101 million vehicle crossings a year.Champlain Bridge: 58 million
Municipalities
* Baie-d'Urfé *Beaconsfield
Beaconsfield ( ) is a market town and civil parish within the unitary authority of Buckinghamshire, England, west-northwest of central London and south-southeast of Aylesbury. Three other towns are within : Gerrards Cross, Amersham and High W ...
* Côte-Saint-Luc
* Dollard-des-Ormeaux
*Dorval
Dorval () is an on-island suburban city on the island of Montreal in southwestern Quebec, Canada. In 2016, the Canadian Census indicated that the population increased by 4.2% to 18,980. Although the city has the largest surface area in Montr ...
*Dorval Island
Dorval () is an Greater Montreal, on-island suburban City (Quebec), city on the island of Montreal in southwestern Quebec, Canada. In 2016, the Canadian Census indicated that the population increased by 4.2% to 18,980. Although the city has the ...
*Hampstead
Hampstead () is an area in London, which lies northwest of Charing Cross, and extends from the A5 road (Roman Watling Street) to Hampstead Heath, a large, hilly expanse of parkland. The area forms the northwest part of the London Borough o ...
* Kirkland
*Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
* Montréal-Est
* Montréal-Ouest
*Mount Royal
Mount Royal (french: link=no, Mont Royal, ) is a large intrusive rock hill or small mountain in the city of Montreal, immediately west of Downtown Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The best-known hypothesis for the origin of the name Montreal is the ...
*Pointe-Claire
Pointe-Claire (, ) is a Quebec local municipality within the Urban agglomeration of Montreal on the Island of Montreal in Canada. It is entirely developed, and land use includes residential, light manufacturing, and retail. As of the 2021 cen ...
* Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue
* Senneville
* Westmount
Demographics

See also
*List of islands of Quebec
This is an incomplete list of islands of Canada.
Arctic islands
Queen Elizabeth Islands
* Adams Island
* Alexander Island
*Baillie-Hamilton Island
* Bathurst Island
*Borden Island
* Brock Island
* Buckingham Island
* Byam Martin Island
* Camero ...
* List of rivers and water bodies of Montreal Island
Note
References
Further reading
* Adams, Frank D., and O. E. LeRoy. ''The Artesian and Other Deep Wells on the Island of Montreal''. Montreal: .n. 1906. * Bosworth, Newton. ''Hochelaga Depicta The Early History and Present State of the City and Island of Montreal''. Toronto: Coles Pub. Co, 1974./small> * Fisher, John. ''Memorial in Support of the Petition of the Inhabitants and Proprietors of the City and Island of Montreal Praying That the Ecclesiastics of St. Sulpice May Not Be Constituted a Body Corporate and Ecclesiastical, and Their Title Confirmed to Certain Valuable Seigniories and Estates''. Montreal?: s.n, 1840. * Mackay, Murdo. ''The Language Problem and School Board Reform on the Island of Montreal''. Ottawa: National Library of Canada, 1988. * Parks Canada. ''Montréal, a City Steeped in History Guide to Nationality Significant Places, Persons and Events on the Island of Montréal''. Québec: Parks Canada, 2004. * Russell, Ken. ''Metropolitan Government on the Island of Montreal''. Toronto: Osgoode Hall Law School, 1972. * Sancton, Andrew. ''Governing the Island of Montreal Language Differences and Metropolitan Politics''. Lane studies in regional government. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1985. * Savoie, Josée. ''Neighbourhood Characteristics and the Distribution of Crime on the Island of Montréal''. Crime and justice research paper series, no. 007. Ottawa: Statistics Canada, 2006. * Stansfield, John. ''The Pleistocene and Recent Deposits of the Island of Montreal''. Ottawa: Government Printing Bureau, 1915.
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Montreal Hochelaga Archipelago River islands of Quebec Landforms of Montreal