Islamic science on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the
Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the
 The Islamic era began in 622. Islamic armies eventually conquered
The Islamic era began in 622. Islamic armies eventually conquered 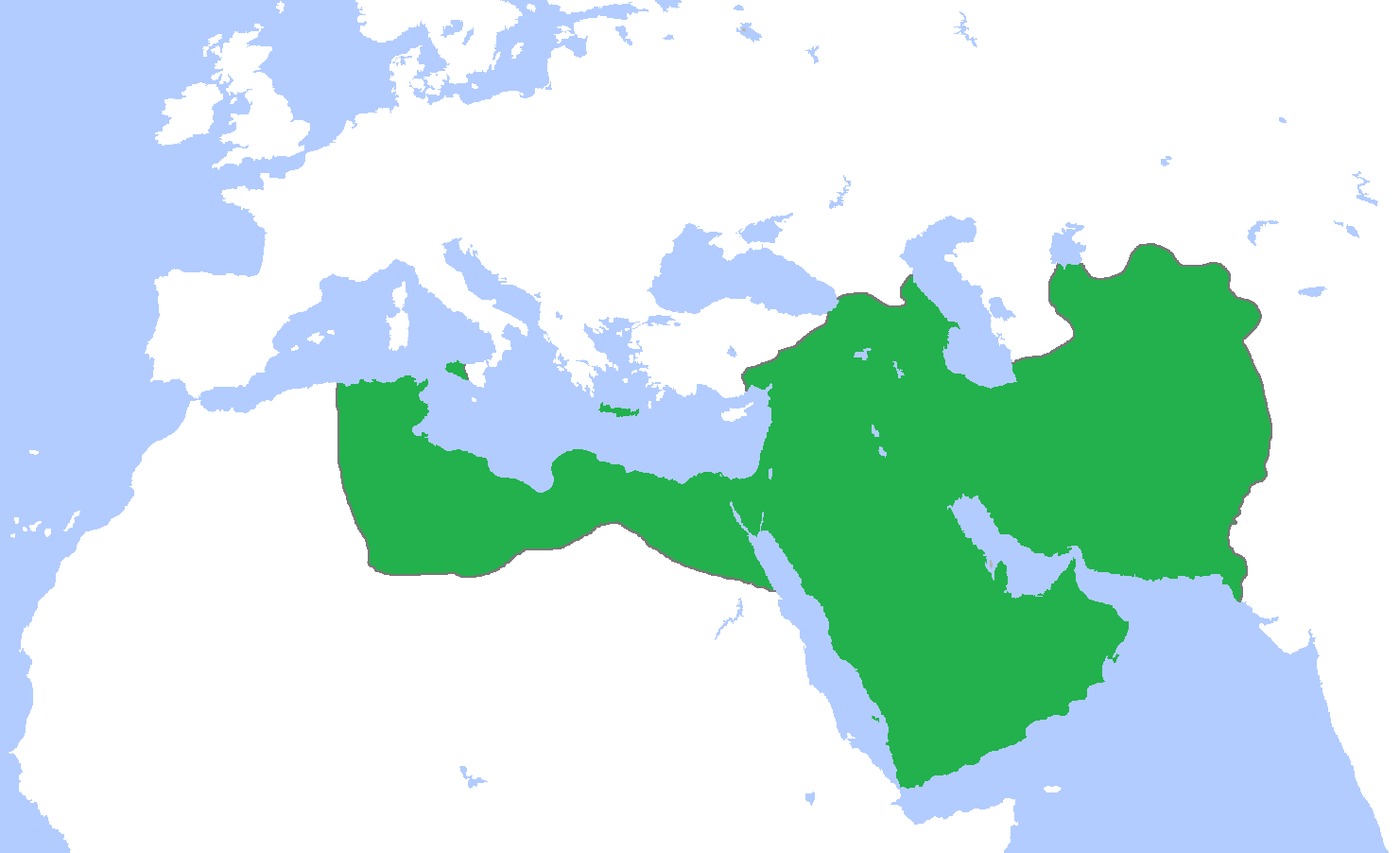 Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of
Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of
 Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was
Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was
 The study of the natural world extended to a detailed examination of plants. The work done proved directly useful in the unprecedented growth of pharmacology across the Islamic world. Al-Dinawari (815–896) popularised
The study of the natural world extended to a detailed examination of plants. The work done proved directly useful in the unprecedented growth of pharmacology across the Islamic world. Al-Dinawari (815–896) popularised
 The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources. Abu Zayd al-Balkhi (850–934), founder of the Balkhī school of cartography in Baghdad, wrote an atlas called ''Figures of the Regions'' (Suwar al-aqalim).
Al-Biruni (973–1048) measured the radius of the earth using a new method. It involved observing the height of a mountain at
The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources. Abu Zayd al-Balkhi (850–934), founder of the Balkhī school of cartography in Baghdad, wrote an atlas called ''Figures of the Regions'' (Suwar al-aqalim).
Al-Biruni (973–1048) measured the radius of the earth using a new method. It involved observing the height of a mountain at
File:TabulaRogeriana upside-down.jpg, Modern copy of al-Idrisi's 1154 '' Tabula Rogeriana'', upside-down, north at top
 Islamic mathematicians gathered, organised and clarified the mathematics they inherited from ancient Egypt, Greece, India, Mesopotamia and Persia, and went on to make innovations of their own. Islamic mathematics covered
Islamic mathematicians gathered, organised and clarified the mathematics they inherited from ancient Egypt, Greece, India, Mesopotamia and Persia, and went on to make innovations of their own. Islamic mathematics covered  Al-Khwarizmi (8th–9th centuries) was instrumental in the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system and the development of
Al-Khwarizmi (8th–9th centuries) was instrumental in the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system and the development of
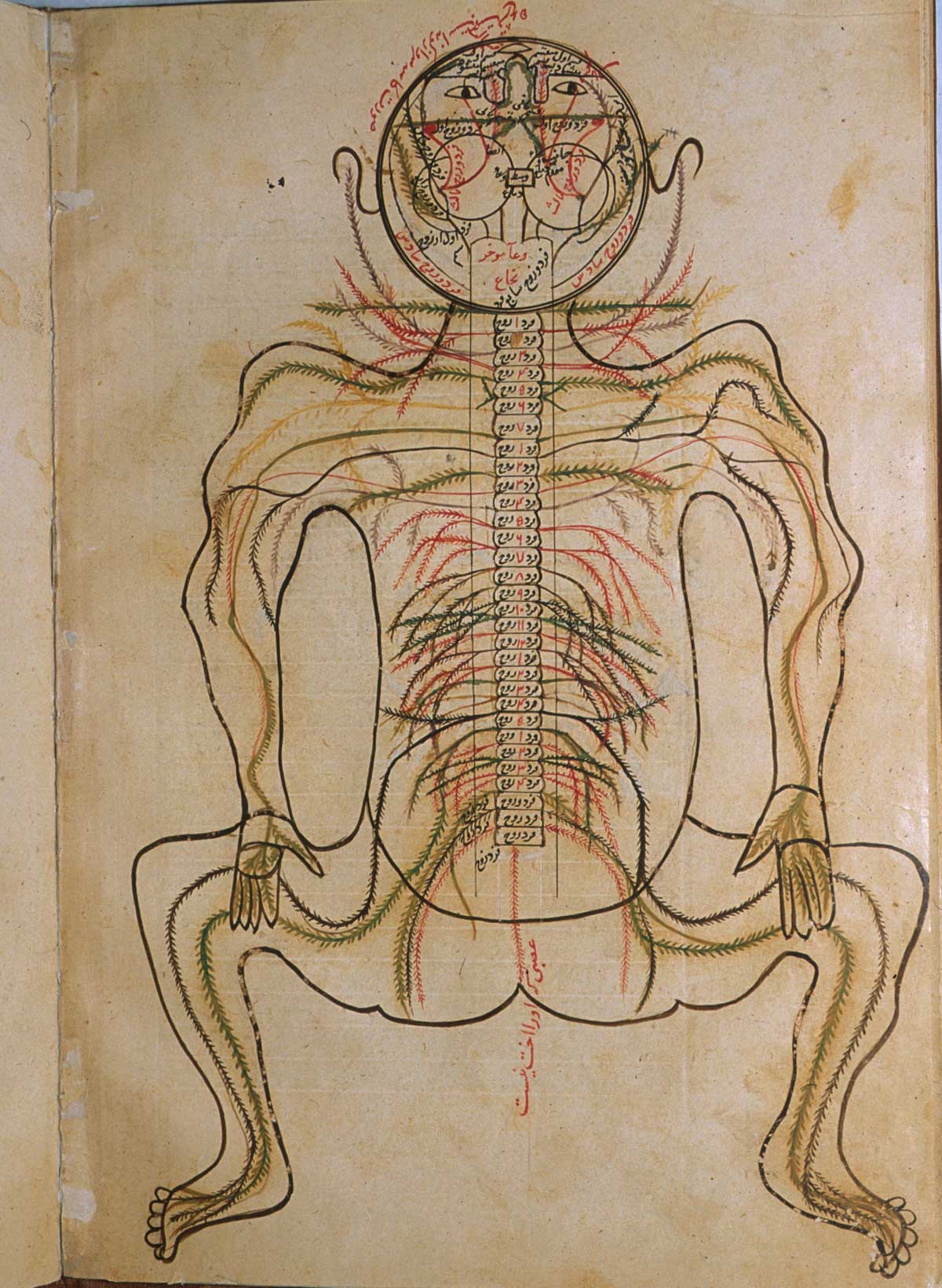 Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''
Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''

 Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Abbas ibn Firnas (810–887) developed lenses for magnification and the improvement of vision.
Ibn Sahl ( 940–1000) discovered the law of refraction known as Snell's law. He used the law to produce the first Aspheric lenses that focused light without geometric aberrations.
In the eleventh century
Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Abbas ibn Firnas (810–887) developed lenses for magnification and the improvement of vision.
Ibn Sahl ( 940–1000) discovered the law of refraction known as Snell's law. He used the law to produce the first Aspheric lenses that focused light without geometric aberrations.
In the eleventh century
 Advances in
Advances in
 The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of
The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of
 Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The ''
Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The ''
"How Greek Science Passed to the Arabs"
by De Lacy O'Leary * *Habibi, Golareh
is there such a thing as Islamic science? the influence of Islam on the world of science
''Science Creative Quarterly''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Science In Medieval Islam .Science Medieval history of the Middle East Islamic world
 Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the
Science in the medieval Islamic world was the science developed and practised during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
under the Umayyads of Córdoba, the Abbadids of Seville, the Samanids, the Ziyarids, the Buyids in Persia, the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
and beyond, spanning the period roughly between 786 and 1258. Islamic scientific achievements encompassed a wide range of subject areas, especially astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, and medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included alchemy and chemistry, botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
and agronomy, geography and cartography, ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a me ...
, pharmacology, physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
, and zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, an ...
.
Medieval Islamic science had practical purposes as well as the goal of understanding. For example, astronomy was useful for determining the '' Qibla'', the direction in which to pray, botany had practical application in agriculture, as in the works of Ibn Bassal and Ibn al-'Awwam, and geography enabled Abu Zayd al-Balkhi to make accurate maps. Islamic mathematicians such as Al-Khwarizmi, Avicenna and Jamshīd al-Kāshī made advances in algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary ...
, trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. ...
, geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
and Arabic numerals. Islamic doctors described diseases like smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
and measles, and challenged classical Greek medical theory. Al-Biruni, Avicenna and others described the preparation of hundreds of drugs made from medicinal plants and chemical compounds. Islamic physicists such as Ibn Al-Haytham
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham, Latinized as Alhazen (; full name ; ), was a medieval mathematician, astronomer, and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age from present-day Iraq.For the description of his main fields, see e.g. ("He is one of the pr ...
, Al-Bīrūnī and others studied optics and mechanics as well as astronomy, and criticised Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
's view of motion.
During the Middle Ages, Islamic science flourished across a wide area around the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
and further afield, for several centuries, in a wide range of institutions.
Context and history
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Pl ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, and successfully displaced the Persian and Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
s from the region within a few decades. Within a century, Islam had reached the area of present-day Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
in the west and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
in the east. The Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
(roughly between 786 and 1258) spanned the period of the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
(750–1258), with stable political structures and flourishing trade. Major religious and cultural works of the Islamic empire were translated into Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
and occasionally Persian. Islamic culture inherited Greek, Indic, Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n and Persian influences. A new common civilisation formed, based on Islam. An era of high culture and innovation ensued, with rapid growth in population and cities. The Arab Agricultural Revolution in the countryside brought more crops and improved agricultural technology, especially irrigation. This supported the larger population and enabled culture to flourish.McClellan and Dorn 2006, pp.103–115 From the 9th century onwards, scholars such as Al-Kindi translated India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n, Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n, Sasanian (Persian) and Greek knowledge, including the works of Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
, into Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
. These translations supported advances by scientists across the Islamic world.
 Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of
Islamic science survived the initial Christian reconquest of Spain, including the fall of Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
in 1248, as work continued in the eastern centres (such as in Persia). After the completion of the Spanish reconquest in 1492, the Islamic world went into an economic and cultural decline. The Abbasid caliphate was followed by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
( 1299–1922), centred in Turkey, and the Safavid Empire (1501–1736), centred in Persia, where work in the arts and sciences continued.
Fields of inquiry
Medieval Islamic scientific achievements encompassed a wide range of subject areas, especiallymathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, and medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which ...
, alchemy and chemistry, ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a me ...
, and geography and cartography.
Alchemy and chemistry
The early Islamic period saw the establishment of theoretical frameworks inalchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim wo ...
and chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
. The sulfur-mercury theory of metals
Abū Mūsā Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (Arabic: , variously called al-Ṣūfī, al-Azdī, al-Kūfī, or al-Ṭūsī), died 806−816, is the purported author of an enormous number and variety of works in Arabic, often called the Jabirian corpus. The ...
, first found in pseudo-Apollonius of Tyana's '' Sirr al-khalīqa'' ("The Secret of Creation", c. 750–850) and in the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan (written c. 850–950), remained the basis of theories of metallic composition until the 18th century. The '' Emerald Tablet'', a cryptic text that all later alchemists up to and including Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, Theology, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosophy, natural philosopher"), widely ...
saw as the foundation of their art, first occurs in the ''Sirr al-khalīqa'' and in one of the works attributed to Jabir. In practical chemistry, the works of Jabir, and those of the Persian alchemist and physician Abu Bakr al-Razi (c. 865–925), contain the earliest systematic classifications of chemical substances. Alchemists were also interested in artificially creating such substances. Jabir describes the synthesis of ammonium chloride ( sal ammoniac) from organic substances, and Abu Bakr al-Razi experimented with the heating of ammonium chloride, vitriol, and other salts, which would eventually lead to the discovery of the mineral acids
A mineral acid (or inorganic acid) is an acid derived from one or more inorganic compounds, as opposed to organic acids which are acidic, organic compounds. All mineral acids form hydrogen ions and the conjugate base when dissolved in water.
Char ...
by 13th-century Latin alchemists such as pseudo-Geber.
Astronomy and cosmology
 Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was
Astronomy became a major discipline within Islamic science. Astronomers devoted effort both towards understanding the nature of the cosmos and to practical purposes. One application involved determining the ''Qibla'', the direction to face during prayer. Another was astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, predicting events affecting human life and selecting suitable times for actions such as going to war or founding a city. Al-Battani
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Jābir ibn Sinān al-Raqqī al-Ḥarrānī aṣ-Ṣābiʾ al-Battānī ( ar, محمد بن جابر بن سنان البتاني) ( Latinized as Albategnius, Albategni or Albatenius) (c. 858 – 929) was an astron ...
(850–922) accurately determined the length of the solar year. He contributed to the Tables of Toledo, used by astronomers to predict the movements of the sun, moon and planets across the sky. Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulat ...
(1473-1543) later used some of Al-Battani's astronomic tables.
Al-Zarqali (1028–1087) developed a more accurate astrolabe, used for centuries afterwards. He constructed a water clock in Toledo, discovered that the Sun's apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
moves slowly relative to the fixed stars, and obtained a good estimate of its motion for its rate of change. Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (1201–1274) wrote an important revision to Ptolemy's 2nd-century celestial model. When Tusi became Helagu's astrologer, he was given an observatory and gained access to Chinese techniques and observations. He developed trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. ...
as a separate field, and compiled the most accurate astronomical tables available up to that time.
Botany and agronomy
 The study of the natural world extended to a detailed examination of plants. The work done proved directly useful in the unprecedented growth of pharmacology across the Islamic world. Al-Dinawari (815–896) popularised
The study of the natural world extended to a detailed examination of plants. The work done proved directly useful in the unprecedented growth of pharmacology across the Islamic world. Al-Dinawari (815–896) popularised botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
in the Islamic world with his six-volume ''Kitab al-Nabat'' (''Book of Plants''). Only volumes 3 and 5 have survived, with part of volume 6 reconstructed from quoted passages. The surviving text describes 637 plants in alphabetical order from the letters ''sin'' to ''ya'', so the whole book must have covered several thousand kinds of plants. Al-Dinawari described the phases of plant growth and the production of flowers and fruit. The thirteenth century encyclopedia compiled by Zakariya al-Qazwini
Zakariyya' al-Qazwini ( , ar, أبو يحيى زكرياء بن محمد بن محمود القزويني), also known as Qazvini ( fa, قزوینی), born in Qazvin (Iran) and died 1283, was a Persian cosmographer and geographer of Arab anc ...
(1203–1283) – ''ʿAjā'ib al-makhlūqāt'' (The Wonders of Creation) – contained, among many other topics, both realistic botany and fantastic accounts. For example, he described trees which grew birds on their twigs in place of leaves, but which could only be found in the far-distant British Isles., in Morelon & Rashed 1996, pp.813–852Turner 1997, pp.138–139 The use and cultivation of plants was documented in the 11th century by Muhammad bin Ibrāhīm Ibn Bassāl of Toledo in his book ''Dīwān al-filāha'' (The Court of Agriculture), and by Ibn al-'Awwam al-Ishbīlī (also called Abū l-Khayr al-Ishbīlī) of Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
in his 12th century book ''Kitāb al-Filāha'' (Treatise on Agriculture). Ibn Bassāl had travelled widely across the Islamic world, returning with a detailed knowledge of agronomy that fed into the Arab Agricultural Revolution. His practical and systematic book describes over 180 plants and how to propagate and care for them. It covered leaf- and root-vegetables, herbs, spices and trees.
Geography and cartography
 The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources. Abu Zayd al-Balkhi (850–934), founder of the Balkhī school of cartography in Baghdad, wrote an atlas called ''Figures of the Regions'' (Suwar al-aqalim).
Al-Biruni (973–1048) measured the radius of the earth using a new method. It involved observing the height of a mountain at
The spread of Islam across Western Asia and North Africa encouraged an unprecedented growth in trade and travel by land and sea as far away as Southeast Asia, China, much of Africa, Scandinavia and even Iceland. Geographers worked to compile increasingly accurate maps of the known world, starting from many existing but fragmentary sources. Abu Zayd al-Balkhi (850–934), founder of the Balkhī school of cartography in Baghdad, wrote an atlas called ''Figures of the Regions'' (Suwar al-aqalim).
Al-Biruni (973–1048) measured the radius of the earth using a new method. It involved observing the height of a mountain at Nandana
Nandana or Nandna ( pnb, ) was a fort built at strategic location on a hilly range on the eastern flanks of the Salt Range in Punjab Pakistan. Its ruins, including those of a town and a temple, are present. It was ruled by the Hindu Shahi king ...
(now in Pakistan). Al-Idrisi (1100–1166) drew a map of the world for Roger
Roger is a given name, usually masculine, and a surname. The given name is derived from the Old French personal names ' and '. These names are of Germanic origin, derived from the elements ', ''χrōþi'' ("fame", "renown", "honour") and ', ' ( ...
, the Norman King of Sicily (ruled 1105-1154). He also wrote the '' Tabula Rogeriana'' (Book of Roger), a geographic study of the peoples, climates, resources and industries of the whole of the world known at that time. The Ottoman admiral Piri Reis ( 1470–1553) made a map of the New World and West Africa in 1513. He made use of maps from Greece, Portugal, Muslim sources, and perhaps one made by Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
. He represented a part of a major tradition of Ottoman cartography.
Mathematics
 Islamic mathematicians gathered, organised and clarified the mathematics they inherited from ancient Egypt, Greece, India, Mesopotamia and Persia, and went on to make innovations of their own. Islamic mathematics covered
Islamic mathematicians gathered, organised and clarified the mathematics they inherited from ancient Egypt, Greece, India, Mesopotamia and Persia, and went on to make innovations of their own. Islamic mathematics covered algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary ...
, geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
and arithmetic
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers— addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th ...
. Algebra was mainly used for recreation: it had few practical applications at that time. Geometry was studied at different levels. Some texts contain practical geometrical rules for surveying and for measuring figures. Theoretical geometry was a necessary prerequisite for understanding astronomy and optics, and it required years of concentrated work. Early in the Abbasid caliphate (founded 750), soon after the foundation of Baghdad in 762, some mathematical knowledge was assimilated by al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ar, أبو جعفر عبد الله بن محمد المنصور; 95 AH – 158 AH/714 CE – 6 October 775 CE) usually known simply as by his laqab Al-Manṣūr (المنصور) ...
's group of scientists from the pre-Islamic Persian tradition in astronomy. Astronomers from India were invited to the court of the caliph in the late eighth century; they explained the rudimentary trigonometrical techniques used in Indian astronomy. Ancient Greek works such as Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's '' Almagest'' and Euclid's ''Elements'' were translated into Arabic. By the second half of the ninth century, Islamic mathematicians were already making contributions to the most sophisticated parts of Greek geometry. Islamic mathematics reached its apogee in the Eastern part of the Islamic world between the tenth and twelfth centuries. Most medieval Islamic mathematicians wrote in Arabic, others in Persian.
 Al-Khwarizmi (8th–9th centuries) was instrumental in the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system and the development of
Al-Khwarizmi (8th–9th centuries) was instrumental in the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system and the development of algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary ...
, introduced methods of simplifying equations, and used Euclidean geometry in his proofs. He was the first to treat algebra as an independent discipline in its own right,, page 263–277: "In a sense, al-Khwarizmi is more entitled to be called "the father of algebra" than Diophantus because al-Khwarizmi is the first to teach algebra in an elementary form and for its own sake, Diophantus is primarily concerned with the theory of numbers". and presented the first systematic solution of linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship ('' function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear ...
and quadratic equation
In algebra, a quadratic equation () is any equation that can be rearranged in standard form as
ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,,
where represents an unknown value, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and then the equation is linear, not qu ...
s.Maher, P. (1998). From Al-Jabr to Algebra. Mathematics in School, 27(4), 14–15.
Ibn Ishaq al-Kindi
Abū Yūsuf Yaʻqūb ibn ʼIsḥāq aṣ-Ṣabbāḥ al-Kindī (; ar, أبو يوسف يعقوب بن إسحاق الصبّاح الكندي; la, Alkindus; c. 801–873 AD) was an Arab Muslim philosopher, polymath, mathematician, physician ...
(801–873) worked on cryptography for the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
, and gave the first known recorded explanation of cryptanalysis and the first description of the method of frequency analysis.
Avicenna ( 980–1037) contributed to mathematical techniques such as casting out nines.Masood 2009, pp.104–105 Thābit ibn Qurra (835–901) calculated the solution to a chessboard problem involving an exponential series.
Al-Farabi
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned early Isl ...
( 870–950) attempted to describe, geometrically, the repeating patterns popular in Islamic decorative motifs in his book ''Spiritual Crafts and Natural Secrets in the Details of Geometrical Figures''. Omar Khayyam (1048–1131), known in the West as a poet, calculated the length of the year to within 5 decimal places, and found geometric solutions to all 13 forms of cubic equations, developing some quadratic equation
In algebra, a quadratic equation () is any equation that can be rearranged in standard form as
ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,,
where represents an unknown value, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and then the equation is linear, not qu ...
s still in use. Jamshīd al-Kāshī ( 1380–1429) is credited with several theorems of trigonometry, including the law of cosines, also known as Al-Kashi's Theorem. He has been credited with the invention of decimal fractions, and with a method like Horner's to calculate roots. He calculated π correctly to 17 significant figures.
Sometime around the seventh century, Islamic scholars adopted the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, describing their use in a standard type of text ''fī l-ḥisāb al hindī'', (On the numbers of the Indians). A distinctive Western Arabic variant of the Eastern Arabic numerals began to emerge around the 10th century in the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
and Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
(sometimes called ''ghubar'' numerals, though the term is not always accepted), which are the direct ancestor of the modern Arabic numerals used throughout the world.
Medicine
 Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''
Islamic society paid careful attention to medicine, following a ''hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
'' enjoining the preservation of good health. Its physicians inherited knowledge and traditional medical beliefs from the civilisations of classical Greece, Rome, Syria, Persia and India. These included the writings of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
such as on the theory of the four humours, and the theories of Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be o ...
. al-Razi ( 865–925) identified smallpox and measles, and recognized fever as a part of the body's defenses. He wrote a 23-volume compendium of Chinese, Indian, Persian, Syriac and Greek medicine. al-Razi questioned the classical Greek medical theory of how the four humours regulate life processes. He challenged Galen's work on several fronts, including the treatment of bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily f ...
, arguing that it was effective.
al-Zahrawi
Abū al-Qāsim Khalaf ibn al-'Abbās al-Zahrāwī al-Ansari ( ar, أبو القاسم خلف بن العباس الزهراوي; 936–1013), popularly known as al-Zahrawi (), Latinised as Albucasis (from Arabic ''Abū al-Qāsim''), was ...
(936–1013) was a surgeon whose most important surviving work is referred to as ''al-Tasrif
The ''Kitāb al-Taṣrīf'' ( ar, كتاب التصريف لمن عجز عن التأليف, lit=The Arrangement of Medical Knowledge for One Who is Not Able to Compile a Book for Himself), known in English as The Method of Medicine, is a 30-volume ...
'' (Medical Knowledge). It is a 30-volume set mainly discussing medical symptoms, treatments, and pharmacology. The last volume, on surgery, describes surgical instruments, supplies, and pioneering procedures. Avicenna ( 980–1037) wrote the major medical textbook, '' The Canon of Medicine''. Ibn al-Nafis (1213–1288) wrote an influential book on medicine; it largely replaced Avicenna's ''Canon'' in the Islamic world. He wrote commentaries on Galen and on Avicenna's works. One of these commentaries, discovered in 1924, described the circulation of blood through the lungs.
Optics and ophthalmology

 Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Abbas ibn Firnas (810–887) developed lenses for magnification and the improvement of vision.
Ibn Sahl ( 940–1000) discovered the law of refraction known as Snell's law. He used the law to produce the first Aspheric lenses that focused light without geometric aberrations.
In the eleventh century
Optics developed rapidly in this period. By the ninth century, there were works on physiological, geometrical and physical optics. Topics covered included mirror reflection.
Hunayn ibn Ishaq (809–873) wrote the book ''Ten Treatises on the Eye''; this remained influential in the West until the 17th century.
Abbas ibn Firnas (810–887) developed lenses for magnification and the improvement of vision.
Ibn Sahl ( 940–1000) discovered the law of refraction known as Snell's law. He used the law to produce the first Aspheric lenses that focused light without geometric aberrations.
In the eleventh century Ibn al-Haytham
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham, Latinized as Alhazen (; full name ; ), was a medieval mathematician, astronomer, and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age from present-day Iraq.For the description of his main fields, see e.g. ("He is one of the pr ...
(Alhazen, 965–1040) rejected the Greek ideas about vision, whether the Aristotelian tradition that held that the form of the perceived object entered the eye (but not its matter), or that of Euclid and Ptolemy which held that the eye emitted a ray. Al-Haytham proposed in his ''Book of Optics'' that vision occurs by way of light rays forming a cone with its vertex at the center of the eye. He suggested that light was reflected from different surfaces in different directions, thus causing objects to look different. He argued further that the mathematics of reflection and refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
needed to be consistent with the anatomy of the eye.Masood 2009, pp.173–175 He was also an early proponent of the scientific method
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientifi ...
, the concept that a hypothesis must be proved by experiments based on confirmable procedures or mathematical evidence, five centuries before Renaissance scientists.
Pharmacology
 Advances in
Advances in botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
and chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
in the Islamic world encouraged developments in pharmacology. Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi (Rhazes) (865–915) promoted the medical uses of chemical compounds. Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi (Abulcasis) (936–1013) pioneered the preparation of medicines by sublimation and distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the he ...
. His ''Liber servitoris'' provides instructions for preparing "simples" from which were compounded the complex drugs then used. Sabur Ibn Sahl (died 869) was the first physician to describe a large variety of drugs and remedies for ailments. Al-Muwaffaq, in the 10th century, wrote ''The foundations of the true properties of Remedies'', describing chemicals such as arsenious oxide and silicic acid. He distinguished between sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate, and drew attention to the poisonous nature of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
compounds, especially copper vitriol, and also of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
compounds. Al-Biruni (973–1050) wrote the ''Kitab al-Saydalah'' (''The Book of Drugs''), describing in detail the properties of drugs, the role of pharmacy and the duties of the pharmacist. Ibn Sina (Avicenna) described 700 preparations, their properties, their mode of action and their indications. He devoted a whole volume to simples in '' The Canon of Medicine''. Works by Masawaih al-Mardini ( 925–1015) and by Ibn al-Wafid (1008–1074) were printed in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
more than fifty times, appearing as ''De Medicinis universalibus et particularibus'' by Mesue the Younger
Masawaih al-Mardini (Yahyā ibn Masawaih al-Mardini; known as Mesue the Younger) was a Assyrian physician. He was born in Mardin, Upper Mesopotamia. After working in Baghdad, he entered to the service of the Fatimid caliph Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah. ...
(died 1015) and as the ''Medicamentis simplicibus'' by Abenguefit
ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥusayn ibn al-Wāfid al-Lakhmī () (c. 1008 – 1074), known in Latin Europe as , was an Andalusian Arab pharmacologist and physician from Toledo. He was the vizier of Al-Mamun of Toledo. His main work is ''Kitāb al-adwiya al ...
( 997 – 1074) respectively. Peter of Abano
Pietro d'Abano, also known as Petrus de Apono, Petrus Aponensis or Peter of Abano (Premuda, Loris. "Abano, Pietro D'." in '' Dictionary of Scientific Biography.'' (1970). New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. Vol. 1: p.4-5.1316), was an Italian phil ...
(1250–1316) translated and added a supplement to the work of al-Mardini under the title ''De Veneris''. Ibn al-Baytar
Diyāʾ al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Aḥmad al-Mālaqī, commonly known as Ibn al-Bayṭār () (1197–1248 AD) was an Andalusian Arab physician, botanist, pharmacist and scientist. His main contribution was to systematically record ...
(1197–1248), in his ''Al-Jami fi al-Tibb'', described a thousand simples and drugs based directly on Mediterranean plants collected along the entire coast between Syria and Spain, for the first time exceeding the coverage provided by Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of '' De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vo ...
in classical times. Islamic physicians such as Ibn Sina described clinical trials for determining the efficacy of medical drugs and substances.
Physics
 The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of
The fields of physics studied in this period, apart from optics and astronomy which are described separately, are aspects of mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objec ...
: statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque (also called moment) acting on physical systems that do not experience an acceleration (''a''=0), but rather, are in static equilibrium with ...
, dynamics, kinematics and motion. In the sixth century John Philoponus ( 490 – 570) rejected the Aristotelian view of motion. He argued instead that an object acquires an inclination to move when it has a motive power impressed on it. In the eleventh century Ibn Sina adopted roughly the same idea, namely that a moving object has force which is dissipated by external agents like air resistance. Ibn Sina distinguished between "force" and "inclination" (''mayl''); he claimed that an object gained ''mayl'' when the object is in opposition to its natural motion. He concluded that continuation of motion depends on the inclination that is transferred to the object, and that the object remains in motion until the ''mayl'' is spent. He also claimed that a projectile in a vacuum would not stop unless it is acted upon. That view accords with Newton's first law of motion, on inertia. As a non-Aristotelian suggestion, it was essentially abandoned until it was described as "impetus" by Jean Buridan ( 1295–1363), who was influenced by Ibn Sina's ''Book of Healing''.
In the ''Shadows'', Abū Rayḥān al-Bīrūnī (973–1048) describes non-uniform motion as the result of acceleration. Ibn-Sina's theory of ''mayl'' tried to relate the velocity and weight of a moving object, a precursor of the concept of momentum. Aristotle's theory of motion stated that a constant force produces a uniform motion; Abu'l-Barakāt al-Baghdādī ( 1080 – 1164/5) disagreed, arguing that velocity and acceleration are two different things, and that force is proportional to acceleration, not to velocity.
Ibn Bajjah
Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyà ibn aṣ-Ṣā’igh at-Tūjībī ibn Bājja ( ar, أبو بكر محمد بن يحيى بن الصائغ التجيبي بن باجة), best known by his Latinised name Avempace (; – 1138), was an A ...
(Avempace, 1085–1138) proposed that for every force there is a reaction force. While he did not specify that these forces be equal, this was still an early version of Newton's third law of motion.
The Banu Musa brothers, Jafar-Muhammad, Ahmad and al-Hasan ( early 9th century) invented automated devices described in their Book of Ingenious Devices. Advances on the subject were also made by al-Jazari
Badīʿ az-Zaman Abu l-ʿIzz ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ar-Razāz al-Jazarī (1136–1206, ar, بديع الزمان أَبُ اَلْعِزِ إبْنُ إسْماعِيلِ إبْنُ الرِّزاز الجزري, ) was a polymath: a scholar, ...
and Ibn Ma'ruf.
Zoology
 Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The ''
Many classical works, including those of Aristotle, were transmitted from Greek to Syriac, then to Arabic, then to Latin in the Middle Ages. Aristotle's zoology remained dominant in its field for two thousand years. The ''Kitāb al-Hayawān
The ''Kitāb al-Ḥayawān'' ( ar, كتاب الحيوان, , ''LINA saadouni'') is an Arabic translation for hayawan (Arabic: , maqālāt).
'' Historia Animalium'': treatises 1–10;
'' De Partibus Animalium'': treatises 11–14;
''De Generation ...
'' (كتاب الحيوان, English: ''Book of Animals'') is a 9th-century Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
translation of ''History of Animals'': 1–10, ''On the Parts of Animals'': 11–14, and ''Generation of Animals'': 15–19.
The book was mentioned by Al-Kindī (died 850), and commented on by Avicenna (Ibn Sīnā) in his '' The Book of Healing''. Avempace (Ibn Bājja) and Averroes (Ibn Rushd) commented on and criticised ''On the Parts of Animals'' and ''Generation of Animals''.
Significance
Muslim scientists helped in laying the foundations for anexperiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
al science with their contributions to the scientific method
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientifi ...
and their empirical, experimental and quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis
...
approach to scientific inquiry. Durant, Will (1980). ''The Age of Faith ( The Story of Civilization, Volume 4)'', p. 162–186. Simon & Schuster. . Garrison, Fielding H., ''An Introduction to the History of Medicine: with Medical Chronology, Suggestions for Study and Bibliographic Data'', p. 86. In a more general sense, the positive achievement of Islamic science was simply to flourish, for centuries, in a wide range of institutions from observatories to libraries, madrasas to hospitals and courts, both at the height of the Islamic golden age and for some centuries afterwards. It did not lead to a scientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transforme ...
like that in Early modern Europe, but such external comparisons are probably to be rejected as imposing "chronologically and culturally alien standards" on a successful medieval culture.
See also
*Continuity thesis In the history of ideas, the continuity thesis is the hypothesis that there was no radical discontinuity between the intellectual development of the Middle Ages and the developments in the Renaissance and early modern period. Thus the idea of an in ...
* Indian influence on Islamic science
* History of scientific method
* History of Islamic economics
* Islamic philosophy
Islamic philosophy is philosophy that emerges from the Islamic tradition. Two terms traditionally used in the Islamic world are sometimes translated as philosophy—falsafa (literally: "philosophy"), which refers to philosophy as well as logic, ...
* Islamic attitudes towards science
Muslim scholars have developed a spectrum of viewpoints on science within the context of Islam.Seyyed Hossein Nasr. "Islam and Modern Science" The Quran and Islam allows for much interpretation when it comes to science. Scientists of medieval Mu ...
* Scholasticism
* Timeline of science and engineering in the Muslim world
This timeline of science and engineering in the Muslim world covers the time period from the eighth century AD to the introduction of European science to the Muslim world in the nineteenth century. All year dates are given according to the Gr ...
References
Sources
* * * * *Further reading
* * * * * *External links
"How Greek Science Passed to the Arabs"
by De Lacy O'Leary * *Habibi, Golareh
is there such a thing as Islamic science? the influence of Islam on the world of science
''Science Creative Quarterly''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Science In Medieval Islam .Science Medieval history of the Middle East Islamic world