Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an
Abrahamic
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
monotheistic religion centred primarily around the
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
, a religious text considered by
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
to be the direct word of
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
(or ''
Allah'') as it was revealed to
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
, the
main and final Islamic prophet.
[Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: ]Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. . (See also
quick reference
) " e Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the
world's second-largest religion behind
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, with its followers ranging between 1-1.8 billion globally, or around a quarter of the world's population.
Due to the average younger age and higher
fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were ...
,
Islam is the world's fastest growing major religious group, and is projected by ''
Pew Research Center'' to be the world's largest religion by the end of the 21st century, surpassing
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
.
It teaches that God is
merciful,
all-powerful, and
unique, and has guided humanity through
various prophets,
revealed scriptures, and
natural signs, with the Quran serving as the final and universal revelation and Muhammad serving as the "
Seal of the Prophets" (the last prophet of God).
The teachings and practices of Muhammad () documented in traditional collected accounts () provide a secondary constitutional model for Muslims to follow after the Quran.
Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a
primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier prophets such as
Adam,
Noah,
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
,
Moses, and
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
, among others; these earlier revelations are attributed to
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
and
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, which are regarded in Islam as
spiritual predecessor faiths. They also consider the Quran, when preserved in
Classical Arabic, to be the unaltered and final revelation of God to humanity. Like other Abrahamic religions, Islam also teaches of a "
Final Judgement
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
" wherein the righteous will be rewarded in
paradise
In religion, paradise is a place of exceptional happiness and delight. Paradisiacal notions are often laden with pastoral imagery, and may be cosmogonical or eschatological or both, often compared to the miseries of human civilization: in parad ...
() and the unrighteous will be punished in
hell (). The religious concepts and practices of Islam include the
Five Pillars of Islam
The Five Pillars of Islam (' ; also ' "pillars of the religion") are fundamental practices in Islam, considered to be obligatory acts of worship for all Muslims. They are summarized in the famous hadith of Gabriel. The Sunni and Shia agree o ...
—considered obligatory acts of worship —and following Islamic law, , which touches on virtually every aspect of life, from
banking and finance and
welfare
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifical ...
to
women's roles and the
environment.
[ (See also:]
sharia
via '' Lexico''.) The Five Pillars comprise ''
Shahada
The ''Shahada'' ( Arabic: ٱلشَّهَادَةُ , "the testimony"), also transliterated as ''Shahadah'', is an Islamic oath and creed, and one of the Five Pillars of Islam and part of the Adhan. It reads: "I bear witness that there i ...
'', the Islamic
oath
Traditionally an oath (from Anglo-Saxon ', also called plight) is either a statement of fact or a promise taken by a sacrality as a sign of verity. A common legal substitute for those who conscientiously object to making sacred oaths is to g ...
and
creed; ''
Salah'', daily
prayers
Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through deliberate communication. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication or intercession directed towards a deity or a deified ...
; ''
Zakat
Zakat ( ar, زكاة; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is ...
,'' forms of
almsgiving
Alms (, ) are money, food, or other material goods donated to people living in poverty. Providing alms is often considered an act of virtue or charity. The act of providing alms is called almsgiving, and it is a widespread practice in a numbe ...
;
''Sawm'', religious
fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
; and ''
Hajj'', a
mandated once-in-a-lifetime pilgrimage to
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
during the 12th month of the lunar calendar.
, the religious rite of
circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Top ...
, is seen as obligatory or recommendable for male followers.
Prominent
religious festivals include
Ramadan,
Eid al-Fitr, and
Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha () is the second and the larger of the two main holidays celebrated in Islam (the other being Eid al-Fitr). It honours the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to Allah's com ...
. The cities of Mecca,
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, and
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
are home to the
three holiest sites in Islam, in descending order:
Masjid al-Haram,
Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, and
Al-Aqsa Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situate ...
, respectively.
Islam originated in the 7th century at
Jabal al-Nour
Jabal an-Nour ( ar, جَبَل ٱلنُّوْر, Jabal an-Nūr, lit=Mountain of the Light or 'Hill of the Illumination') is a mountain near Mecca in the Hejaz region of Saudi Arabia. The mountain houses the grotto or cave of Hira' ( ar, غَار ...
, a mountain peak near Mecca where
Muhammad's first revelation
Muhammad's first revelation was an event described in Islamic tradition as taking place in AD 610, during which the Islamic prophet Muhammad was visited by the angel Gabriel, who revealed to him the beginnings of what would later become the Qur'a ...
is said to have taken place. Through various
caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
s, the religion later
spread outside of Arabia shortly after Muhammad's death, and by the 8th century, the
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
had imposed Islamic rule from the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
in the west to the
Indus Valley in the east. The
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
refers to the period traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century, during the reign of the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
, when much of the
Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
was experiencing a
scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
,
economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
, and
cultural flourishing. Islamic scientific achievements encompassed a wide range of subject areas especially
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
,
mathematics,
astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
,
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
as well as
physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
,
pharmacology,
engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
and
optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultrav ...
. The expansion of the Muslim world involved
various states and caliphates as well as extensive trade and religious conversion as a result of
Islamic missionary activities ().
There are two major
Islamic denominations:
Sunni Islam (85–90 percent)
[Denny, Frederick. 2010]
''Sunni Islam: Oxford Bibliographies Online Research Guide''
Oxford: Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. p. 3. "Sunni Islam is the dominant division of the global Muslim community, and throughout history it has made up a substantial majority (85 to 90 percent) of that community." and
Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
(10–15 percent);
combined, they make up a majority of the population in
49 countries. While
Sunni–Shia differences initially arose from disagreements over the
succession to Muhammad, they grew to cover a broader dimension both
theologically
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
and
juridically, with the divergence acquiring notable political significance.
Approximately 12 percent of the world's Muslims live in
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, the most populous Muslim-majority country; percent live in
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
; 20 percent live in the
Middle East–North Africa; and 15 percent live in
sub-Saharan Africa.
Sizable Muslim communities are also present in the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
,
China, and
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
.
Etymology
In Arabic, ''Islam'' ( ar, إسلام, lit=submission
o God
Oh God may refer to:
* An exclamation; similar to "oh no", "oh yes", "oh my", "aw goodness", "ah gosh", "ah gawd"; see interjection
''Oh, God!'' franchise
* ''Oh, God!'' (film) (1977 film) aka "Oh, God! 1"
* ''Oh, God! Book II'' (1980 film) aka ...
}) is the verbal noun of
Form IV originating from the verb (), from the
triliteral root
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or " radicals" (hence the term consonantal root). Such abstract consonantal roots are used in the formation of actual words by adding the vowe ...
(), which forms a large class of words mostly relating to concepts of submission, safeness, and peace. In a religious context, it refers to the total surrender to the will of
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
.
A ''
Muslim'' (), the word for a follower of Islam, is the
active participle of the same verb form, and means "submitter (to God)" or "one who surrenders (to God)". In the
Hadith of Gabriel, ''Islam'' is presented as one part of a triad that also includes (faith), and (excellence).
Islam itself was historically called
''Mohammedanism'' in the
English-speaking world
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest langua ...
. This term has fallen out of use and is sometimes said to be
offensive, as it suggests that a human being, rather than God, is central to Muslims' religion, parallel to
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
in
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
. Some authors, however, continue to use the term ''Mohammedanism'' as a
technical term
Jargon is the specialized terminology associated with a particular field or area of activity. Jargon is normally employed in a particular communicative context and may not be well understood outside that context. The context is usually a particu ...
for the religious system as opposed to the
theological
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the s ...
concept of Islam that exists within that system.
Articles of faith
The Islamic
creed (''
aqidah
''Aqidah'' ( (), plural ''ʿaqāʾid'', also rendered ''ʿaqīda'', ''aqeeda'', etc.) is an Islamic term of Arabic origin that literally means " creed". It is also called Islamic creed and Islamic theology.
''Aqidah'' go beyond concise stat ...
'') requires belief in
six articles: God, angels, revelation, prophets, the
Day of Resurrection
In Islam, "the promise and threat" () of Judgment Day ( ar, یوم القيامة, Yawm al-qiyāmah, Day of Resurrection or ar, یوم الدین, italic=no, Yawm ad-din, Day of Judgement),
when "all bodies will be resurrected" from the dead, ...
, and the divine decree.
God
The central concept of Islam is ''
tawḥīd'' ( ar, توحيد, link=no), the oneness of God. Usually thought of as a ''precise
monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfo ...
'', but also
panentheistic
Panentheism ("all in God", from the Greek grc, πᾶν, pân, all, label=none, grc, ἐν, en, in, label=none and grc, Θεός, Theós, God, label=none) is the belief that the divine intersects every part of the universe and also extends bey ...
in Islamic mystical teachings. God is seen as incomparable and without partners such as in the
Christian Trinity, and associating partners to God or attributing God's attributes to others is seen as
idolatory, called
''shirk''. God is seen as transcendent of creation and so is beyond comprehension. Thus, Muslims are not
iconodule
Iconodulism (also iconoduly or iconodulia) designates the religious service to icons (kissing and honourable veneration, incense, and candlelight). The term comes from Neoclassical Greek εἰκονόδουλος (''eikonodoulos'') (from el, ε ...
s and do not attribute forms to God. God is instead described and referred to by several
names or attributes, the most common being ''Ar-Rahmān'' () meaning "The Entirely Merciful," and ''Ar-Rahīm'' () meaning "The Especially Merciful" which are invoked at the beginning of most chapters of the Quran.
Islam teaches that the creation of everything in the
universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
was brought into being by God's command as expressed by the wording, "
Be, and it is
"Be, and it is" ( ) is a phrase that occurs several times in the Quran, referring to creation by Allah. In Arabic the imperative verb ''be'' ('' kun'') is spelled with the letters ''kāf'' and '' nūn''.
Kun fa-yakūnu has its reference in the Qur ...
,"
[ Q2:117 ] and that the
purpose of existence is to worship God. He is viewed as a personal god
and there are no intermediaries, such as
clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
, to contact God. Consciousness and awareness of God is referred to as
Taqwa
''Taqwa'' ( ar, تقوى '' / '')
is an Islamic term for being conscious and cognizant of God, of truth, "piety, fear of God."Nanji, Azim. "Islamic Ethics," in ''A Companion to Ethics'', Peter Singer. Oxford: Blackwells,n(1991), pp. 106– ...
. ''
Allāh'' is a term with no
plural
The plural (sometimes abbreviated pl., pl, or ), in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the default quantity represented by that noun. This de ...
or
gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures ...
being ascribed to it and is also used by Muslims and Arabic-speaking Christians and Jews in reference to God, whereas ' () is a term used for a deity or a god in general. Other non-Arab Muslims might use different names as much as Allah, for instance in Turkish or in Persian.
Angels
Angels ( ar, ملك, link=no, ') are beings described in the Quran and hadith. They are described as created to worship God and also to serve other specific duties such as communicating
revelation
In religion and theology, revelation is the revealing or disclosing of some form of truth or knowledge through communication with a deity or other supernatural entity or entities.
Background
Inspiration – such as that bestowed by God on the ...
s from God, recording every person's actions, and taking a person's
soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '' soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest atte ...
at the time of death. They are described as being created variously from 'light' (
''nūr'') or 'fire' (''nār''). Islamic angels are often represented in
anthropomorphic forms combined with
supernatural images, such as wings, being of great size or wearing heavenly articles. Common characteristics for angels are their missing needs for bodily desires, such as eating and drinking. Some of them, such as
Gabriel
In Abrahamic religions ( Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብ ...
and
Michael, are mentioned by name in the Quran. Angels play a significant role in the literature about the
Mi'raj
The Israʾ and Miʿraj ( ar, الإسراء والمعراج, ') are the two parts of a Night Journey that, according to Islam, the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632) took during a single night around the year 621 (1 BH – 0 BH). With ...
, where Muhammad encounters several angels during his journey through the heavens. Further angels have often been featured in
Islamic eschatology,
theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
and
philosophy.
Books

The Islamic holy books are the records that Muslims believe various prophets received from God through revelations, called ''
wahy''. Muslims believe that parts of the previously revealed scriptures, such as the ''
Tawrat
The Tawrat ( ar, ), also romanized as Tawrah or Taurat, is the Arabic-language name for the Torah within its context as an Islamic holy book believed by Muslims to have been given by God to the prophets and messengers amongst the Children of ...
'' (
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the ...
) and the ''
Injil
Injil ( ar, wikt:إنجيل, إنجيل, ʾInjīl, alternative spellings: ''Ingil'' or ''Injeel'') is the Arabic name for the Gospel of Jesus Jesus in Islam, (Isa). This ''Injil'' is described by the Quran as one of the four Islamic holy books w ...
'' (
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
), had become
distorted—either in interpretation, in text, or both,
while the Quran (lit. 'Recitation')
is viewed as the final, verbatim and unaltered word of God.
Muslims believe that the verses of the Quran were revealed to Muhammad by God, through the
archangel
Archangels () are the second lowest rank of angel in the hierarchy of angels. The word ''archangel'' itself is usually associated with the Abrahamic religions, but beings that are very similar to archangels are found in a number of other relig ...
Gabriel (''
Jibrīl''), on multiple occasions between 610 CE and 632, the year Muhammad died. While Muhammad was alive, these revelations were written down by his companions, although the prime method of transmission was orally through
memorization
Memorization is the process of committing something to memory. It is a mental process undertaken in order to store in memory for later recall visual, auditory, or tactical information.
The scientific study of memory is part of cognitive neuros ...
.
The Quran is divided into 114 chapters (
suras) which combined contain 6,236 verses (''
āyāt''). The chronologically earlier chapters, revealed at
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
, are concerned primarily with spiritual topics while the later
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
n chapters discuss more social and legal issues relevant to the Muslim community.
[
"The word ''Quran'' was invented and first used in the Qurʼan itself. There are two different theories about this term and its formation."] Muslim jurists consult the ''hadith'' ('accounts'), or the written record of Prophet Muhammad's life, to both supplement the Quran and assist with its interpretation. The science of Quranic commentary and exegesis is known as ''
tafsir
Tafsir ( ar, تفسير, tafsīr ) refers to exegesis, usually of the Quran. An author of a ''tafsir'' is a ' ( ar, مُفسّر; plural: ar, مفسّرون, mufassirūn). A Quranic ''tafsir'' attempts to provide elucidation, explanation, in ...
''. The set of rules governing proper
elocution of recitation is called
tajwid
In the context of the recitation of the Quran, ''tajwīd'' ( ar, تجويد ', , ' elocution') is a set of rules for the correct pronunciation of the letters with all their qualities and applying the various traditional methods of recitation (' ...
. In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in
Arabic literature
Arabic literature ( ar, الأدب العربي / ALA-LC: ''al-Adab al-‘Arabī'') is the writing, both as prose and poetry, produced by writers in the Arabic language. The Arabic word used for literature is '' Adab'', which is derived from ...
, and has influenced art and the Arabic language.
Prophets
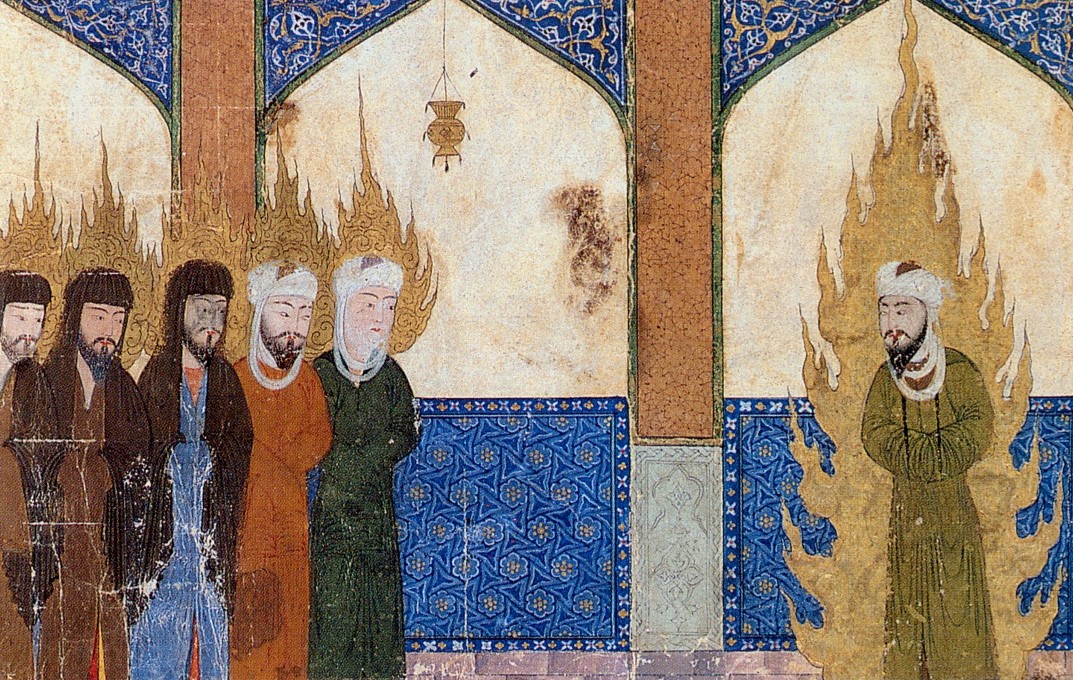

Prophets (Arabic: ar, أنبياء, label=none, translit=anbiyāʾ) are believed to have been chosen by God to receive and preach a divine message. Additionally, a prophet delivering a new book to a nation is called a ''rasul'' ( ar, رسول, label=none, translit=rasūl), meaning "messenger". Muslims believe prophets are human and not divine. All of the prophets are said to have preached the same basic message of Islam – submission to the will of God – to various nations in the past and that this accounts for many similarities among religions. The Quran Qisas Al-Anbiya, recounts the names of numerous figures considered prophets in Islam, including
Adam,
Noah,
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
,
Moses and
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
, among others.
Muslims believe that God sent Muhammad as the final prophet ("Seal of the prophets") to convey the completed message of Islam. In Islam, the "normative" example of Muhammad's life is called the sunnah (literally "trodden path"). Muslims are encouraged to emulate Muhammad's moral behaviors in their daily lives, and the Sunnah is seen as crucial to guiding interpretation of the Quran. This example is preserved in traditions known as hadith, which are accounts of his words, actions, and personal characteristics. Hadith qudsi, Hadith Qudsi is a sub-category of hadith, regarded as God's verbatim words quoted by Muhammad that are not part of the Quran. A hadith involves two elements: a chain of narrators, called Hadith studies#Traditional importance of the sanad, ''sanad'', and the actual wording, called ''Hadith studies, matn''. There are various methodologies to classify the authenticity of hadiths, with the commonly used grading being: "authentic" or "correct" ( ar, صحيح, links=no, translit=Authentic hadith, ṣaḥīḥ, label=none); "good", ''hasan'' ( ar, حسن, links=no, label=none, translit=Hasan (hadith), ḥasan); or "weak" ( ar, ضعيف, label=none, translit=Da'if, ḍaʻīf), among others. The ''Kutub al-Sittah'' are a collection of six books, regarded as the most authentic reports in
Sunni Islam. Among them is ''Sahih al-Bukhari'', often considered by Sunnis to be one of the most Hadith terminology#Terminology relating to the authenticity of a hadith, authentic sources after the Quran.
[Aisha Abd al-Rahman, al-Rahman, Aisha Abd, ed. 1990. ''Introduction to the Science of Hadith, Muqaddimah Ibn al-Ṣalāḥ''. Cairo: Dar al-Ma'arif, 1990. pp. 160–69] Another famous source of hadiths is known as ''The Four Books'', which Shias consider as the most authentic hadith reference.
Resurrection and judgment
Belief in the "Day of Resurrection" or ''Qiyamah, Yawm al-Qiyāmah'' ( ar, يوم القيامة, link=no), is also crucial for Muslims. It is believed that the time of ''Qiyāmah'' is preordained by God but unknown to man. The Quran and the hadith, as well as in the commentaries of Ulama, scholars, describe the trials and Great Tribulation, tribulations preceding and during the ''Qiyāmah''. The Quran emphasizes universal resurrection, bodily resurrection, a break from the pre-Islamic Arabian understanding of death.
On Yawm al-Qiyāmah, Muslims believe all humankind will be judged by their good and bad deeds and consigned to ''Jannah'' (paradise) or ''Jahannam'' (hell). The Quran in Surat al-Zalzalah describes this as: "So whoever does an atom's weight of good will see it. And whoever does an atom's weight of evil will see it." The Quran Islamic views of sin, lists several sins that can condemn a person to
hell, such as Kafir, disbelief in God ( ar, كفر, translit=kufr, label=none), and dishonesty. However, the Quran makes it clear that God will forgive the Islamic views on sin, sins of those who repent if he wishes. Good deeds, like charity, prayer, and compassion towards animals, will be rewarded with entry to heaven. Muslims view heaven as a place of joy and blessings, with Quranic references describing its features. Mystical traditions in Islam place these heavenly delights in the context of an ecstatic awareness of God. ''Yawm al-Qiyāmah'' is also identified in the Quran as ''Yawm ad-Dīn'' ( "Day of Religion");
[;] ''as-Sāʿah'' ( "the Last Hour");
[;] and ''Al-Qaria, al-Qāriʿah'' ( "The Clatterer");
Divine predestination
The concept of Divinity, divine decree and destiny in Islam ( ar, القضاء والقدر, ') means that every matter, good or bad, is believed to have been decreed by God. ''Al-qadar'', meaning "power", derives from a root that means "to measure" or "calculating". Muslims often express this belief in divine destiny with the phrase Inshallah, "Insha-Allah" meaning "if God wills" when speaking on future events. In addition to loss, gain is also seen as a test of believers – whether they would still recognize that the gain originates only from God.
Acts of worship
There are five obligatory acts of worship – the
Shahada
The ''Shahada'' ( Arabic: ٱلشَّهَادَةُ , "the testimony"), also transliterated as ''Shahadah'', is an Islamic oath and creed, and one of the Five Pillars of Islam and part of the Adhan. It reads: "I bear witness that there i ...
declaration of faith, the five daily prayers, the
Zakat
Zakat ( ar, زكاة; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is ...
alms-giving, fasting during Ramadan and the
Hajj pilgrimage – collectively known as "The Pillars of Islam" (''Arkān al-Islām'').
Apart from these, Muslims also perform other supplemental religious acts.
Testimony

The Shahada, ''shahadah'', is an
oath
Traditionally an oath (from Anglo-Saxon ', also called plight) is either a statement of fact or a promise taken by a sacrality as a sign of verity. A common legal substitute for those who conscientiously object to making sacred oaths is to g ...
declaring belief in Islam. The expanded statement is "" ( ar, أشهد أن لا إله إلا الله وأشهد أن محمداً رسول الله, label=none), or, "I testify that there is no deity except
God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
and I testify that Muhammad is the messenger of God." Islam is sometimes argued to have a very simple creed with the shahada being the premise for the rest of the religion. Non-Muslims wishing to convert to Islam are required to recite the shahada in front of witnesses.
Prayer

Prayer in Islam, called salah, as-salah or aṣ-ṣalāt ( ar, الصلاة, link=no), is seen as a personal communication with God and consists of repeating units called rakat that include Ruku, bowing and Sujud, prostrating to God. Performing prayers five times a day is compulsory. The prayers are recited in the Arabic language and consist of verses from the Quran. The prayers are done in direction of the kaaba, Ka'bah. Salah requires ritual purity, which involves ''wudu'' (ritual wash) or occasionally, such as for new converts, ''ghusl'' (full body ritual wash). The means used to signal the prayer time is a vocal call called the ''adhan''.
A mosque is a places of worship, place of worship for Muslims, who often refer to it by its Arabic name masjid. Although the primary purpose of the mosque is to serve as a place of prayer, it is also important to the ummah, Muslim community as a place to meet and study with the Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, Masjid an-Nabawi ("Prophetic Mosque") in Medina, Saudi Arabia, having also served as a shelter for the poor. Minarets are towers used to call the adhan.
Charity
Zakat, Zakāt (Arabic language, Arabic: ar, زكاة, translit=zakāh, label=none) is a means of welfare in a Muslim society, characterized by the giving of a fixed portion (2.5% annually)
[Ahmed, Medani, and Sebastian Gianci. "Zakat." p. 479 in ''Encyclopedia of Taxation and Tax Policy''.] of Financial capital, accumulated wealth by those who can afford it to help the poor or needy, such as for freeing captives, those in bonded labour, debt, or for (stranded) travellers, and for those employed to collect zakat. It is considered a religious obligation that the well-off owe to the needy because their wealth is seen as a "trust from God's bounty" and is seen as a "purification" of one's excess wealth. The total annual value contributed due to zakat is 15 times greater then global humanitarian aid donations, using conservative estimates. ''Sadaqah'', as opposed to Zakat, is a much encouraged Supererogation, supererogatory charity. A waqf is a perpetual charitable trust, which financed hospitals and schools in Muslim societies.
Fasting

During the month of
Ramadan, it is obligatory for Muslims to fast. The Ramadan fast (Arabic language, Arabic: ar, صوم, translit=ṣawm, label=none) precludes food and drink, as well as other forms of consumption, such as smoking, and is performed from dawn to sunset. The fast is to encourage a feeling of nearness to God by restraining oneself for God's sake from what is otherwise permissible and to think of the needy. In addition, there are other days when fasting is supererogatory.
Pilgrimage
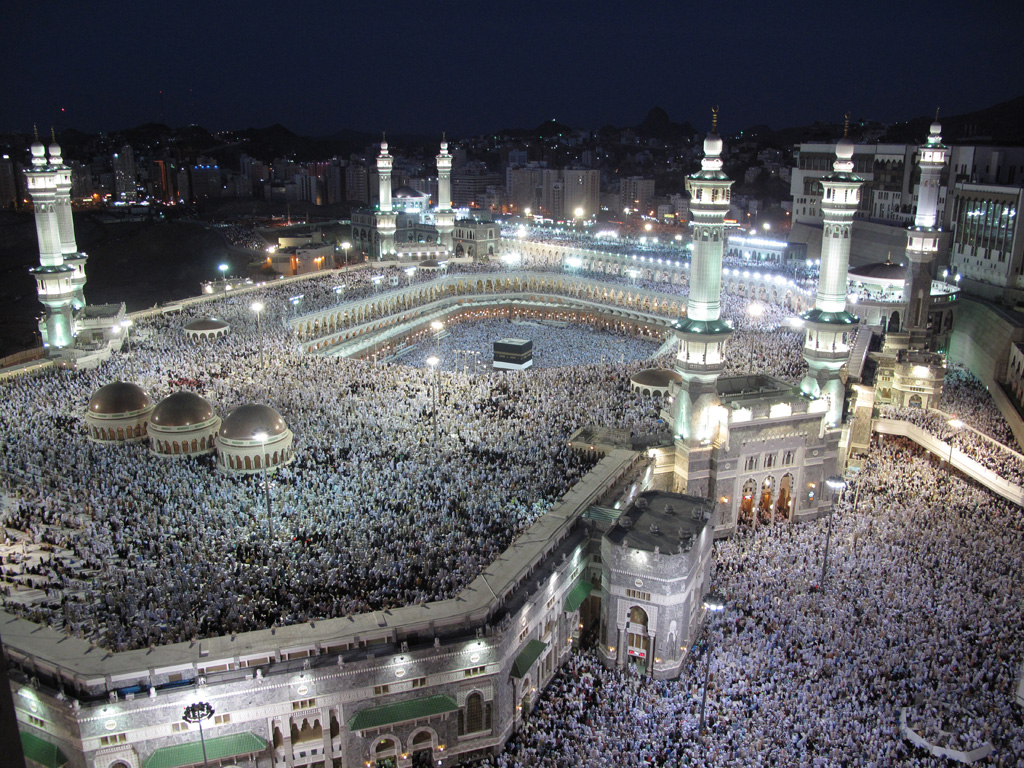

The obligatory Islamic pilgrimage, called the "" ( ar, حج, link=no), is to be done at least once a lifetime by every Muslim with the means to do so during the Islamic calendar, Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah. Rituals of the Hajj mostly imitate the story of the family of
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
. Pilgrims spend a day and a night on the plains of Mina, Saudi Arabia, Mina, then a day praying and worshipping in the plain of Mount Arafat, then spending a night on the plain of Muzdalifah; then moving to Jamaraat Bridge, Jamarat, symbolically Stoning of the Devil, stoning the Devil, then going to the city of
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
and walking seven times around the Kaaba, which Muslims believe Abraham built as a place of worship, then walking seven times between Al-Safa and Al-Marwah, Mount Safa and Mount Marwah recounting the steps of Abraham's wife, Hagar, while she was looking for water for her baby Ishmael in Islam, Ishmael in the desert before Mecca developed into a settlement. All Muslim men should wear only two simple white unstitched pieces of cloth called Ihram clothing, ihram, intended to bring continuity through generations and uniformity among pilgrims despite class or origin. Another form of pilgrimage, ''umrah'', is supererogatory and can be undertaken at any time of the year.
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
is also a site of Islamic pilgrimage and
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, the city of many Islamic prophets, contains the Temple Mount, Al-Aqsa Mosque, which used to be the qibla, direction of prayer before Mecca.
Quranic recitation and memorization
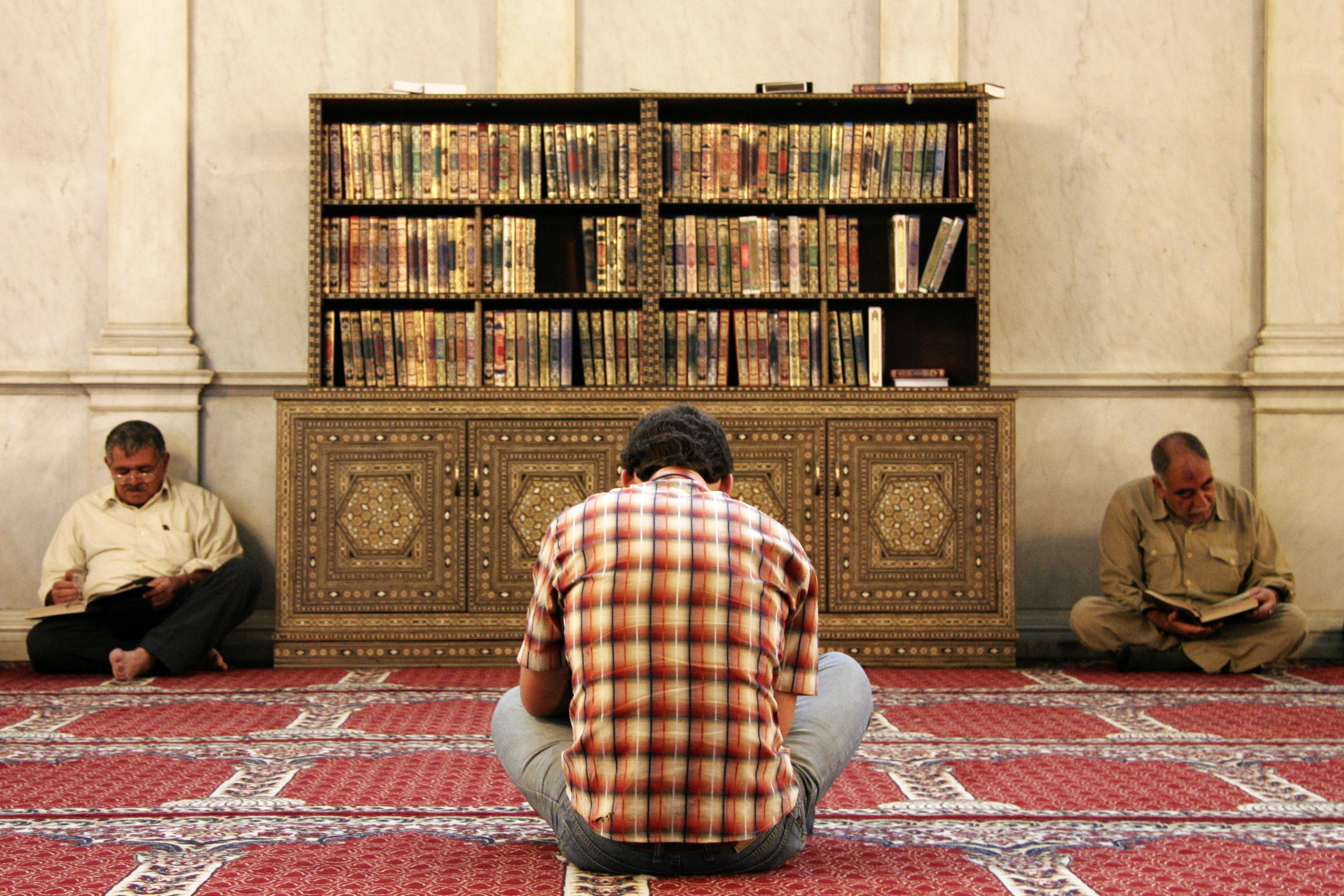

Muslims recite and memorize the whole or parts of the Quran as acts of virtue. Reciting the Quran with elocution (''tajwid'') has been described as an excellent act of worship. Pious Muslims recite the whole Quran during the month of Ramadan. In Muslim societies, any social program generally begins with the recitation of the Quran. One who has memorized the whole Quran is called a hafiz ("memorizer") who, it is said, will be able to intercede for ten people on the Last Judgment Day. Apart from this, almost every Muslim memorizes some portion of the Quran because they need to recite it during their prayers.

Supplication and remembrance
Supplication to God, called in Arabic ''ad-duʿāʾ'' ( ar, الدعاء ) has its own etiquette such as Raising hands in dua, raising hands as if begging or invoking with an extended index finger.
Remebrance of God ( ar, ذكر, translit=Dhikr', label=none) refers to phrases repeated referencing God. Commonly, this includes Tahmid, declaring Alhamdulillah, praise be due to God ( ar, الحمد لله, translit=al-Ḥamdu lillāh, label=none) during prayer or when feeling thankful, Tasbih, declaring glory to God during prayer or when in awe of something and saying 'Basmala, in the name of God' (, ) before starting an act such as eating.
History
Muhammad (610–632)
Born in
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
in 570, Muhammad was orphaned early in life. New trade routes rapidly transformed Meccan society from a semi-bedouin society to a commercial urban society, leaving out weaker segments of society without protection. He acquired the nickname "Amin (name), trustworthy" ( ar, الامين), and was sought after as a bank to safeguard valuables and an impartial arbitrator. Affected by the ills of society and after becoming financially secure through marrying his employer, the businesswoman Khadija bint Khuwaylid, Khadija, he began retreating to a Cave of Hira, cave to contemplate. During the last 22 years of his life, beginning at age 40 in 610 Common Era, CE, Muhammad reported receiving revelations from God, conveyed to him through the Holy Spirit (Islam), archangel Gabriel, thus becoming the seal of the prophets sent to mankind, according to Islamic tradition.
During this time, Muhammad in Mecca, while in Mecca, Muhammad preached first in secret and then in public, imploring his listeners to abandon polytheism and worship one God. Many early converts to Islam were women, the poor, foreigners, and slaves like the first muezzin Bilal ibn Rabah al-Habashi. The Meccan elite profited from the pilgrimages to the idols of the Kaaba and felt Muhammad was destabilizing their social order by preaching about one God, and that in the process he gave questionable ideas to the poor and slaves. Muhammad, who was accused of being a poet, a madman or possessed, presented the challenge of the Quran to imitate the like of the Quran in order to disprove him. The Meccan authorities persecuted Muhammad and his followers, including a boycott and banishment of Muhammad and his clan to starve them into withdrawing their protection of him. This resulted in the Migration to Abyssinia of some Muslims (to the Aksumite Empire).
After 12 years of the persecution of Muslims by the Meccans, Muhammad and his Sahaba, companions performed the ''Hegira, Hijra'' ("emigration") in 622 to the city of Yathrib (current-day Medina). There, with the Medinan converts (the ''Ansar (Islam), Ansar'') and the Meccan migrants (the ''Muhajirun''), Muhammad in Medina established his Theocracy, political and religious authority. The Constitution of Medina was signed by all the tribes of Medina establishing among the Muslim and non-Muslim communities religious freedoms and freedom to use their own laws and agreeing to bar weapons from Medina and to defend it from external threats. Meccan forces and their allies lost against the Muslims at the Battle of Badr in 624 and then fought an inconclusive battle in the Battle of Uhud before unsuccessfully besieging Medina in the Battle of the Trench (March–April 627). In 628, the Treaty of Hudaybiyyah was signed between Mecca and the Muslims, but it was broken by Mecca two years later. As more tribes converted to Islam, Meccan trade routes were cut off by the Muslims. By 629 Muhammad was victorious in the nearly bloodless conquest of Mecca, and by the time of his death in 632 (at age 62) he had united the tribes of Arabia into a single religious polity. Muhammad's closest companions, such as Abu Hureyrah, recorded and compiled what would constitute the hadith.
Caliphate and civil strife (632–750)


Muhammad died in 632 and the first successors, called Caliphs – Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman ibn al-Affan, Ali ibn Abi Talib and sometimes Hasan ibn Ali – are known in Sunni Islam as ''al-khulafā' ar-rāshidūn'' ("Rightly Guided Caliphs"). Some tribes left Islam and rebelled under leaders who declared themselves new prophets but were crushed by Abu Bakr in the Ridda wars. Local populations of Jews and indigenous Christians, persecuted as religious minorities and heretics and taxed heavily, often helped Muslims take over their lands, resulting in rapid expansion of the caliphate into the Sassanid Empire, Persian and Byzantine empires.
Uthman election of Uthman, was elected in 644 and his assassination by rebels led to Ali being elected the next Caliph. In the First Fitna, First Civil War, Muhammad's widow, Aisha, raised an army against Ali, asking to avenge the death of Uthman, but was defeated at the Battle of the Camel. Ali attempted to remove the governor of Syria, Mu'awiya, who was seen as corrupt. Mu'awiya then declared war on Ali and was defeated in the Battle of Siffin. Ali's decision to arbitrate angered the Kharijites, an extremist sect, who felt that by not fighting a sinner, Ali became a sinner as well. The Kharijites rebelled and were defeated in the Battle of Nahrawan but a Kharijite assassin later killed Ali. Ali's son, Hasan ibn Ali, was elected Caliph and signed a Hasan–Muawiya treaty, peace treaty to avoid further fighting, abdicating to Muawiyah I, Mu'awiyah in return for Mu'awiyah not appointing a successor. Mu'awiyah began the Umayyad dynasty with the appointment of his son Yazid I as successor, sparking the Second Fitna, Second Civil War. During the Battle of Karbala, Husayn ibn Ali was killed by Yazid's forces; the event has been Ashura, annually commemorated by Shia ever since. Sunnis, led by Ibn al-Zubayr, opposed to a dynastic caliphate were defeated in the Siege of Mecca (692), Siege of Mecca. These disputes over leadership would give rise to the Sunni-Shia schism,
with the Shia believing leadership belongs to Muhammad's family through Ali, called the ahl al-bayt. Political quietism in Islam, Quietist forms of Kharijites led to the third largest denomination in Islam, Ibadiyya.
Abu Bakr's leadership oversaw the beginning of the compilation of the Qur'an. The Caliph Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz set up the committee, The Seven Fuqaha of Medina, and Malik ibn Anas wrote one of the earliest books on Islamic jurisprudence, the ''Muwatta Imam Malik, Muwatta'', as a consensus of the opinion of those jurists. The Kharijites believed there is no compromised middle ground between good and evil, and any Muslim who commits a grave sin becomes an unbeliever. The term is also used to refer to later groups such as Islamic State, Isis. The Murji'ah taught that people's righteousness could be judged by God alone. Therefore, wrongdoers might be considered misguided, but not denounced as unbelievers. This attitude came to prevail into mainstream Islamic beliefs.
The Umayyad dynasty conquered the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Gallia Narbonensis, Narbonnese Gaul and Sindh. The Umayyads struggled with a lack of legitimacy and relied on a heavily patronized military. Since the jizya tax was a tax paid by non-Muslims which exempted them from military service, the Umayyads denied recognizing the conversion of non-Arabs as it reduced revenue. While the Rashidun Caliphate emphasized austerity, with Umar even requiring an inventory of each official's possessions, Umayyad luxury bred dissatisfaction among the pious. The Kharijites led the Berber Revolt leading to the first Muslim states independent of the Caliphate. In the Abbasid revolution, non-Arab converts (''mawali''), Arab clans pushed aside by the Umayyad clan, and some Shi'a rallied and overthrew the Umayyads, inaugurating the more cosmopolitan Abbasid dynasty in 750.
Classical era (750–1258)

Al-Shafi'i codified a method to determine the reliability of hadith. During the early Abbasid era, scholars such as Muhammad al-Bukhari, Bukhari and Muslim ibn al-Hajjaj, Muslim compiled the major Six major Hadith collections, Sunni hadith collections while scholars like Muhammad ibn Ya'qub al-Kulayni, Al-Kulayni and Ibn Babawayh compiled major Shia hadith collections. The four Sunni Madh'habs, the Hanafi, Hanbali, Maliki, and Shafi'i, were established around the teachings of Abū Ḥanīfa, Ahmad ibn Hanbal, Malik ibn Anas and al-Shafi'i. In contrast, the teachings of Ja'far al-Sadiq formed the Ja'fari jurisprudence. In the 9th century Al-Tabari completed the first commentary of the Quran, that became one of the most cited commentaries in Sunni Islam, the ''Tafsir al-Tabari''. Some Muslims began questioning the piety of indulgence in worldly life and emphasized poverty, humility, and avoidance of sin based on renunciation of bodily desires. Ascetics such as Hasan al-Basri would inspire a movement that would evolve into ''Tasawwuf'' or Sufism.
At this time, theological problems, notably on free will, were prominently tackled, with Hasan al Basri holding that although God knows people's actions, good and evil come from abuse of free will and the Iblis, devil. Greek rationalist philosophy influenced a speculative school of thought known as Muʿtazila, first originated by Wasil ibn Ata. Caliphs such as Mamun al Rashid and Al-Mu'tasim made it an official creed and unsuccessfully attempted to force their position on the majority. They carried out inquisitions with the traditionalist Ahmad ibn Hanbal notably refusing to conform to the Mutazila idea of the creation of the Quran and was tortured and kept in an unlit prison cell for nearly thirty months. However, other Schools of Islamic theology, schools of Kalam, speculative theology – Maturidi, Māturīdism founded by Abu Mansur al-Maturidi and Ash'ari founded by Al-Ash'ari – were more successful in being widely adopted. Philosophers such as Al-Farabi, Avicenna and Averroes sought to harmonize Aristotle's metaphysics within Islam, similar to later scholasticism within Christianity in Europe, and Maimonides' work within Judaism, while others like Al-Ghazali argued against such syncretism and ultimately prevailed.
This era is sometimes called the "
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
".
Avicenna was a pioneer in Medical research, experimental medicine,
[Jacquart, Danielle (2008). "Islamic Pharmacology in the Middle Ages: Theories and Substances". European Review (Cambridge University Press) 16: 219–227.] and his ''The Canon of Medicine'' was used as a standard medicinal text in the Islamic world and Europe for centuries. Rhazes was the first to distinguish the diseases smallpox and measles. Public hospitals of the time issued the first medical diplomas to license doctors.
Ibn al-Haytham is regarded as the father of the modern scientific method and often referred to as the "world's first true scientist", in particular regarding his work in optics.
[Nomanul Haq, Haq, Syed (2009). "Science in Islam". Oxford Dictionary of the Middle Ages. . Retrieved 22 October 2014] In engineering, the Banū Mūsā brothers' Automaton, automatic flute player is considered to have been the first Program (machine), programmable machine.
In Islamic mathematics, mathematics, the concept of the algorithm is named after Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi, who is considered a founder of algebra, which is named after his book The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, ''al-jabr'', while others developed the concept of a function (mathematics), function. The government paid scientists the equivalent salary of professional athletes today.
The Guinness World Records recognizes the University of Al Karaouine, founded in 859, as the world's oldest degree-granting university.
The vast Abbasid empire proved impossible to hold together. Soldiers established their own dynasties, such as the Tulunids, Samanid Empire, Samanid and Ghaznavid, Ghaznavid dynasty. Additionally, the millennialist Isma'ili Shi'a missionary movement rose with the Fatimid dynasty taking control of North Africa and with the Qarmatians sacking Mecca and stealing the Black Stone in their unsuccessful rebellion. In what is called the Shi'a Century, another Ismaili group, the Buyid dynasty conquered Baghdad and turned the Abbasids into a figurehead monarchy. The Sunni Seljuk dynasty, campaigned to Sunni Revival, reassert Sunni Islam by promulgating the accumulated scholarly opinion of the time notably with the construction of educational institutions known as Nezamiyeh, which are associated with Al-Ghazali and Saadi Shirazi. The Ismailis continued splintering over the legitimacy of successive imams with the Alawites and the Druze, offshoots of Shi'a Islam, dating to this time.
Religious missions converted Volga Bulgaria to Islam. The Delhi Sultanate reached deep into the Indian Subcontinent and many converted to Islam, in particular Dalit, low-caste Hindus whose descendents make up the vast majority of Indian Muslims. Many Muslims also went to
China to trade, virtually dominating the import and export industry of the Song dynasty.
Pre-Modern era (1258–18th century)

Through Muslim trade networks and the activity of Sufi orders, Islam spread into new areas. Under the Ottoman Empire, Islam spread to Southeast Europe. Conversion to Islam, however, was not a sudden abandonment of old religious practices; rather, it was typically a matter of "assimilating Islamic rituals, cosmologies, and literatures into... local religious systems", as illustrated by Muhammad's appearance in Hinduism, Hindu folklore. The Turks probably found similarities between Sufi rituals and Shaman practices. Muslim Turks incorporated elements of Tengrism, Turkish Shamanism beliefs to Islam. Islam during the Ming dynasty, Muslims in China, who were descended from earlier immigrants, were assimilated, sometimes by force, by adopting Chinese names and Chinese culture, culture while Nanjing became an important center of Islamic study.
While cultural influence used to radiate outward from Baghdad, after the Mongol invasions and conquests, Mongol destruction of the Abbasid Caliphate, Arab influence decreased. Iran and Central Asia, benefiting from increased cross-cultural access to East Asia under Pax Mongolica, Mongol rule, flourished and developed more distinctively from Arab influence, such as the Timurid Renaissance under the Timurid dynasty. Nasir al-Din al-Tusi (1201–1274) proposed the Tusi couple, mathematical model that was later adopted by Copernicus unrevised in his heliocentric model and Jamshīd al-Kāshī's estimate of pi would not be surpassed for 180 years. Many Muslim dynasties in India chose Persian as their court language.
The introduction of gunpowder weapons led to the rise of large centralized states and the Muslim Gunpowder empires consolidated much of the previously splintered territories. The Ottoman Caliphate, caliphate was claimed by the Ottoman dynasty of the Ottoman Empire since Murad I's Ottoman conquest of Adrianople, conquest of Edirne in 1362, and its claims were strengthened in 1517 as Selim I became the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques, ruler of Mecca and Medina. The Shia Safavid dynasty rose to power in 1501 and later conquered all of Iran. In South Asia, Babur founded the Mughal Empire. The Mughals compiled the Islamic legal text, the Fatwa Alamgiri.
The religion of the centralized states of the Gunpowder empires influenced the religious practice of their constituent populations. A symbiosis between list of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rulers and Sufism strongly influenced Islamic reign by the Ottomans from the beginning. The Mevlevi Order and Bektashi Order had a close relation to the sultans, as Sufi-mystical as well as heterodox and syncretic approaches to Islam flourished. The often forceful Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam, Safavid conversion of Iran to the Twelver Shia Islam of the Safavid Empire ensured the final dominance of the Twelver, Twelver sect within Shia Islam. Persian migrants to South Asia, as influential bureaucrats and landholders, help spread Shia Islam, forming some of the largest Shia populations outside Iran. Nader Shah, who overthrew the Safavids, attempted to improve relations with Sunnis by propagating the integration of Twelverism into Sunni Islam as a fifth ''madhhab'', called Ja'farism, which failed to gain recognition from the Ottomans.
Modern era (18th – 20th centuries)

Earlier in the 14th century, Ibn Taymiyya promoted a puritanical form of Islam,
[Mary Hawkesworth, Maurice Kogan ''Encyclopedia of Government and Politics: 2-volume set'' Routledge 2013 pp. 270–271] rejecting philosophical approaches in favor of simpler theology
and called to open the gates of itjihad rather than blind imitation of scholars. He called for a jihad against those he deemed heretics
[Richard Gauvain ''Salafi Ritual Purity: In the Presence of God'' Routledge 2013 p. 6] but his writings only played a marginal role during his lifetime. During the 18th century in Arabia, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, influenced by the works of Ibn Taymiyya and Ibn al-Qayyim, founded a movement, called Wahhabi with their self-designation as ''Muwahiddun'', to return to what he saw as unadultered Islam.
[Ga ́bor A ́goston, Bruce Alan Masters ''Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire'' Infobase Publishing 2010 p. 260] He condemned many local Islamic customs, such as visiting the grave of Muhammad or saints, as later bidah, innovations and sinful
and destroyed sacred rocks and trees, Sufi shrines, the Destruction of early Islamic heritage sites in Saudi Arabia, tombs of Muhammad and his companions and the tomb of Husayn at Karbala, a major Shia pilgrimage site. He formed an alliance with the House of Saud, Saud family, which, by the 1920s, completed their conquest of the area that would become Saudi Arabia. Ma Wanfu and Ma Debao promoted salafist movements in the nineteenth century such as Sailaifengye in China after returning from Mecca but were eventually persecuted and forced into hiding by Sufi groups. Other groups sought to reform Sufism rather than reject it, with the Senusiyya and Muhammad Ahmad both waging war and establishing states in Libya and Sudan respectively. In India, Shah Waliullah Dehlawi attempted a more conciliatory style against Sufism and influenced the Deobandi movement. In response to the Deobandi movement, the Barelwi movement was founded as a mass movement, defending popular Sufism and reforming its practices.
The
Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
was generally in political decline starting the 1800s, especially regarding non-Muslim European powers. Earlier, in the fifteenth century, the Reconquista succeeded in ending the Taifa, Muslim presence in Iberia. By the 19th century; the British Company rule in India, East India Company had formally annexed the Mughal dynasty in India. As a response to Imperialism, Western Imperialism, many intellectuals sought to Islamic revival, reform Islam. Islamic modernism, initially labelled by Western scholars as Salafi movement, ''Salafiyya'', embraced modern values and institutions such as democracy while being scripture-oriented.
[Robert Rabil ''Salafism in Lebanon: From Apoliticism to Transnational Jihadism'' Georgetown University Press 2014 chapter: "Doctrine"] Notable forerunners include Muhammad Abduh, Muhammad 'Abduh and Jamal al-Din al-Afghani.
[Henri Lauzière ''The Making of Salafism: Islamic Reform in the Twentieth Century'' Columbia University Press 2015 ] Abul A'la Maududi helped influence modern political Islam. Similar to contemporary Civil code, codification, Shariah was for the first time partially codified into law in 1869 in the Ottoman Empire's Mecelle code.
The Fall of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Empire disintegrated after World War I and the Caliphate was Abolition of the Caliphate, abolished in 1924 by the first List of Presidents of Turkey, President of the Turkish Republic, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, as part of his Atatürk's Reforms, secular reforms. Pan-Islamists attempted to unify Muslims and competed with growing nationalist forces, such as pan-Arabism. The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), consisting of Islam by country, Muslim-majority countries, was established in 1969 after the burning of the Qibli Mosque, Al-Aqsa Mosque in
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
.
Contact with industrialized nations brought Muslim populations to new areas through economic migration. Many Muslims migrated as indentured servants (mostly from India and Indonesia) to the Caribbean, forming the largest Muslim populations by percentage in the Americas. Migration from Syria and Lebanon was the biggest contributor to the Muslim population in Latin America. The resulting urbanization and increase in trade in sub-Saharan Africa brought Muslims to settle in new areas and spread their faith, likely doubling its Muslim population between 1869 and 1914. Muslim immigrants began arriving largely from former colonies in several Western European nations since the 1960s, many as guest workers.
Contemporary era (20th century–present)
Forerunners of Islamic modernism influenced Islamist political movements such as the Muslim Brotherhood and related parties in the Arab world, which performed well in elections following the Arab Spring, Jamaat-e-Islami in South Asia and the Justice and Development Party (Turkey), AK Party, which has democratically been in power in Turkey for decades. In Iran, Iranian Revolution, revolution replaced a secularism, secular monarchy with an Islamic state. Others such as Rashid Rida, Sayyid Rashid Rida broke away from Islamic modernists and pushed against embracing what he saw as Western influence.
In opposition to Islamic political movements, in 20th century Turkey, the military carried out 1997 Turkish military memorandum, coups to oust Islamist governments, and headscarves were legally restricted, as also happened in Tunisia. In other places religious power was co-opted, such as in Saudi Arabia, where the state monopolized religious scholarship and are often seen as puppets of the state
while Egypt nationalized Al-Azhar University, previously an independent voice checking state power. Salafism was funded for its quietism. Saudi Arabia campaigned against revolutionary Islamist movements in the Middle East, in opposition to Iran,
Turkey and Qatar.
Muslim minorities of various ethnicities have been persecuted as a religious group. This has been undertaken by communist forces like the Khmer Rouge, who viewed them as their primary enemy to be exterminated since they stood out and worshiped their own god and the Chinese Communist Party in Xinjiang internment camps, Xinjiang
and by nationalist forces such as during the Bosnian genocide.
The globalization of communication has increased dissemination of religious information. The adoption of the hijab has grown more common and some Muslim intellectuals are increasingly striving to separate scriptural Islamic beliefs from cultural traditions. Among other groups, this access to information has led to the rise of popular "televangelist" preachers, such as Amr Khaled, who compete with the traditional ulema in their reach and have decentralized religious authority. More "individualized" interpretations of Islam notably include Liberal Muslims who attempt to reconcile religious traditions with current secular governance and women's issues.
In the 21st century, the rise of Isil in 2013 presented a new breed of triumphalist extremist Islamist group that seized parts of Iraq and Syria and sought to declare a new medieval caliphate. Rejected as terrorists by the mainstream global Muslim community, the group was forced to resort to insurgency-like tactics in the face of Iranian intervention commanded by Qasem Soleimani in 2014
and a US-led military intervention in 2017 that by 2019 saw almost all of its territorial gains reversed.
Demographics
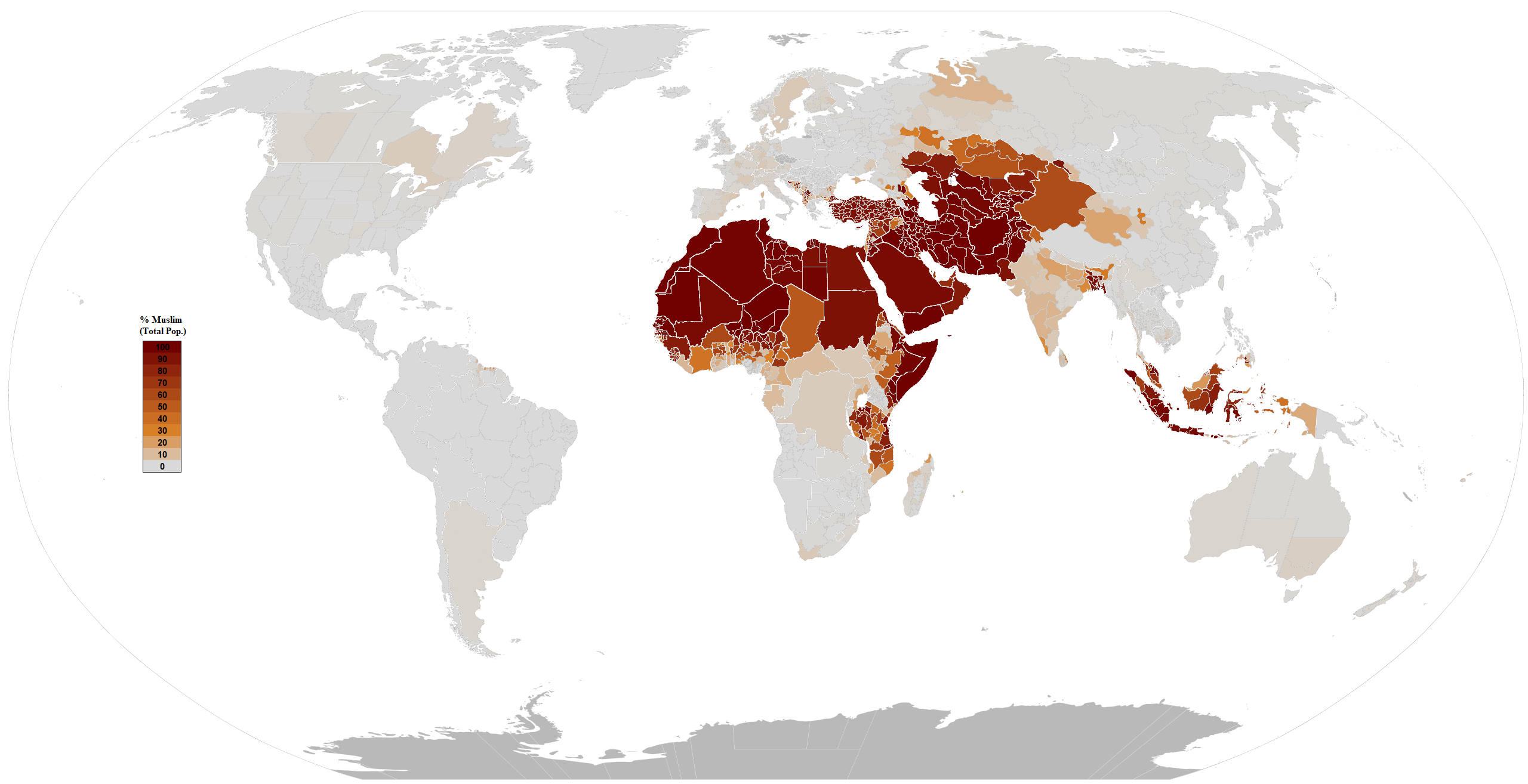
About 23.4% of the global population, or about 1.8 billion people, are Muslims.
[Lipka, Michael, and Conrad Hackett. [2015] 6 April 2017.]
Why Muslims are the world's fastest-growing religious group
(data analysis). ''Fact Tank''. Pew Research Center. In 1900, this estimate was 12.3%, in 1990 it was 19.9%
and projections suggest the proportion will be 29.7% by 2050.
It has been estimated that 87–90% of Muslims are Sunni and 10–13% are Shia, with a minority belonging to other sects. Approximately 49 countries are List of Muslim majority countries, Muslim-majority, with 62% of the world's Muslims living in Asia, and 683 million adherents in
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, Islam in Pakistan, Pakistan, Islam in India, India, and Islam in Bangladesh, Bangladesh alone.
[ Information provided by the International Population Center, Department of Geography, San Diego State University (2005).] Most estimates indicate
China has approximately 20 to 30 million Muslims (1.5% to 2% of the population). Islam in Europe is the second largest religion after
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
in many countries, with growth rates due primarily to immigration and higher birth rates of Muslims in 2005. Religious conversion has no net impact on the Muslim population growth as "the number of people who convert to Islam, become Muslims through conversion seems to be roughly equal to the number of Muslims who leave the faith".
By both percentage and total numbers, Islam is the world's fastest growing major religious group, and is projected to be the world's largest by the end of the 21st century, surpassing that of
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
.
It is estimated that, by 2050, the number of Muslims will nearly equal the number of Christians around the world, "due to the young age and high fertility rate, fertility-rate of Muslims relative to other religious groups".
[Pew Forum for Religion & Public Life. April 2015.]
The Future of World Religions: Population Growth Projections, 2010–2050
" Pew Research Center. p. 7
Article
Schools and branches
Sunni

Sunni Islam or Sunnism is the name for the largest denomination in Islam. The term is a contraction of the phrase "ahl as-sunna wa'l-jamaat", which means "people of the Sunnah, sunna (the traditions of the prophet Muhammad) and the community". Sunnis, or sometimes Sunnites, believe that the first four caliphs were the rightful successors to Muhammad and primarily reference Al-Kutub Al-Sittah, six major hadith works for legal matters, while following one of the four traditional schools of jurisprudence: Hanafi, Hanbali, Maliki or Shafi'i.
Sunni schools of theology encompass Asharism founded by Al-Ashʿarī (c. 874–936), Maturidi by Abu Mansur al-Maturidi (853–944 CE) and Traditionalist theology (Islam), traditionalist theology under the leadership of Ahmad ibn Hanbal (780–855 CE). Traditionalist theology is characterized by its adherence to a literal understanding of the Quran and the Sunnah, the belief in the Quran is uncreated and eternal, and opposition to reason (kalam) in religious and ethical matters. On the other hand, Maturidism asserts, scripture is not needed for basic ethics and that ''good'' and ''evil'' can be understood by reason alone, but people rely on revelation, for matters beyond human's comprehension. Asharism holds that ethics can derive just from divine revelation but not from human reason. However, Asharism accepts reason regarding exegetical matters and combines Muʿtazila approaches with traditionalist ideas.
In the 18th century, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab led a Salafi movement, referred by outsiders as Wahhabism, in modern-day Saudi Arabia. A similar movement called Ahl al-Hadith also de-emphasized the centuries' old Sunni legal tradition, preferring to directly follow the Quran and Hadith. The ''Nur movement, Nurcu'' Sunni movement was by Said Nursi (1877–1960);
[Svante E. Cornell ''Azerbaijan Since Independence'' M.E. Sharpe p. 283] it incorporates elements of Sufism and science,
and has given rise to the Gülen movement.
Shia

Shia Islam, or Shi'ism, is the second-largest Muslim denomination. Shias, or Shiites, split with Sunnis over Muhammad's Succession to Muhammad, successor as leader, who the Shia believed must be from certain descendants of Muhammad's family known as the Ahl al-Bayt and those leaders, referred to as Imamate in Shia doctrine, Imams, have additional spiritual authority. Some of the first Imams are revered by all Shia groups and Sunnis, such as Ali. Zaidism, Zaidi, the second-oldest branch, reject special powers of Imams and are sometimes considered a 'fifth school' of Sunni Islam rather than a Shia denomination.
The Twelvers, the first and the largest Shia branch, believe in twelve Imams, the last of whom went into Occultation (Islam), occultation to return one day. The Ismailism, Ismailis split with the Twelvers over who was the seventh Imam and have split into more groups over the status of successive Imams, with the largest group being the Nizari Isma'ilism, Nizaris.
Ibadi
Ibadi Islam or Ibadism is practised by 1.45 million Muslims around the world (~ 0.08% of all Muslims), most of them in Oman. Ibadism is often associated with and viewed as a moderate variation of the Khawarij movement, though Ibadis themselves object to this classification. Unlike most Kharijite groups, Ibadism does not regard sinful Muslims as unbelievers. Ibadi hadiths, such as the Jami Sahih collection, uses chains of narrators from early Islamic history they considered trustworthy but most Ibadi hadiths are also found in standard Sunni collections and contemporary Ibadis often approve of the standard Sunni collections.

Quranism
The Quranism, Quranists are Muslims who generally believe that Islamic law and guidance should only be based on the Qur'an, rejecting the Sunnah, thus partially or completely doubting the Criticism of hadith, religious authority, reliability or authenticity of the Hadith literature, which they claim are fabricated.
There were first critics of the hadith traditions as early as the time of the scholar Al-Shafi'i; however, their arguments did not find much favor among Muslims. From the 19th century onwards, reformist thinkers like Syed Ahmad Khan, Sayyid Ahmad Khan, Abdullah Chakralawi, and later Ghulam Ahmed Perwez, Ghulam Ahmad Parwez in India began to systematically question the hadith and the Islamic tradition. At the same time, there was a long-standing discussion on the sole authority of the Quran in Egypt, initiated by an article by Muhammad Tawfiq Sidqi named "Islam is the Quran alone" (''al-Islām huwa l-Qurʾān waḥda-hū)'' in the magazine al-Manār. Quranism also took on a political dimension in the 20th century when Muammar Gaddafi, Muammar al-Gaddafi declared the Quran to be the constitution of Libya. In America, Rashad Khalifa, an Egyptian-American biochemist and discoverer of the Quran code (Code 19), which is a hypothetical mathematical code in the Quran, founded the organization "United Submitters International".
The rejection of the hadith leads in some cases to differences in the way religion is practiced for example in the ritual prayer. While some Quranists traditionally pray five times a day, others reduce the number to three or even two daily prayers. There are also different views on the details of prayer or other pillars of Islam such as zakāt, fasting, or the Hajj.
Other denominations
* Alevism, Bektashi Alevism is a Syncretism, syncretic and Heterodoxy, heterodox local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical (Batin (Islam), bāṭenī) teachings of Ali and Haji Bektash Veli. Alevism incorporates Turkish beliefs present during the 14th century,
[Jorgen S Nielsen Muslim ''Political Participation in Europe'' Edinburgh University Press 2013 page 255] such as Tengrism, Shamanism and Animism, mixed with Shias and Sufi beliefs, adopted by some Turkish tribes. It has been estimated that there are 10 million to over 20 million (~0.5%–1% of all Muslims) Alevis worldwide.
* The Ahmadiyya movement was founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad in India in 1889. Ahmad claimed to be the "Promised Messiah" or "Imam Mahdi" of prophecy. Today the group has 10 to 20 million practitioners, but is rejected by most Muslims as heretical, and Ahmadis have been subject to religious persecution and discrimination since the movement's inception.
Non-denominational Muslims
Non-denominational Muslims is an umbrella term that has been used for and by Muslims who do not belong to or do not self-identify with a specific Islamic denomination.
Recent surveys report that large proportions of Muslims in some parts of the world self-identify as "just Muslim", although there is little published analysis available regarding the motivations underlying this response. The
Pew Research Center reports that respondents self-identifying as "just Muslim" make up a majority of Muslims in seven countries (and a plurality in three others), with the highest proportion in Kazakhstan at 74%. At least one in five Muslims in at least 22 countries self-identify in this way.
Mysticism

Sufism (Arabic: ar, تصوف, translit=tasawwuf, label=none), is a mystical-ascetic approach to Islam that seeks to find a direct Divine presence, personal experience of God. Classical Sufi scholars defined ''Tasawwuf'' as "a science whose objective is the reparation of the heart and turning it away from all else but God", through "intuitive and emotional faculties" that one must be trained to use.
[Ahmad Zarruq, Zarruq, Ahmed, Zaineb Istrabadi, and Hamza Yusuf, Hamza Yusuf Hanson. 2008. ''The Principles of Sufism''. Amal Press.] It is not a sect of Islam and its adherents belong to the various Muslim denominations. Ismaili Shias, whose teachings root in Gnosticism and Neoplatonism, as well as by the Illuminationism, Illuminationist and School of Isfahan, Isfahan schools of Islamic philosophy have developed mystical interpretations of Islam. Hasan al-Basri, the early Sufi ascetic often portrayed as one of the earliest Sufis, emphasized fear of failing God's expectations of obedience. In contrast, later prominent Sufis, such as Mansur Al-Hallaj and Rumi, Jalaluddin Rumi, emphasized religiosity based on love towards God. Such devotion would also have an impact on the arts, with Rumi, still one of the best selling poets in America, writing his Persian poem Masnawi and the works of Hafez (1315–1390) are often considered the pinnacle of Persian poetry.
Sufis reject ''materialism'' and ''ego'' and regard everything as if it was sent by god alone, Sufi strongly believes in the oneness of god.
Sufis see ''tasawwuf'' as an inseparable part of Islam, just like the ''sharia''. Traditional Sufis, such as Bayazid Bastami, Jalaluddin Rumi, Haji Bektash Veli, Junaid Baghdadi, and Al-Ghazali, argued for Sufism as being based upon the tenets of Islam and the teachings of the prophet. Historian Nile Green argued that Islam in the Medieval period, was more or less ''Sufism''.
Popular devotional practices such as the veneration of Sufi saints have been viewed as innovations from the original religion from followers of salafism, who have sometimes physically attacked Sufis, leading to a deterioration in Sufi–Salafi relations.
Sufi congregations form orders (''tariqa'') centered around a teacher (''wali'') who traces a spiritual chain back to Muhammad. Sufis played an important role in the formation of Muslim societies through their missionary and educational activities.
Sufi influenced Ahle Sunnat movement or Barelvi movement defends Sufi practices and beliefs with over 200 million followers in south Asia. Sufism is prominent in Central Asia, as well as in African countries like Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Senegal, Chad and Niger.
Law and jurisprudence
Sharia is the religious law forming part of the Islamic tradition.
It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam, particularly the Quran and the Hadith. In Arabic, the term sharīʿah refers to God's divine law and is contrasted with ''fiqh'', which refers to its scholarly interpretations.
[Vikør, Knut S. 2014.]
Sharīʿah
" In ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Islam and Politics'', edited by Emad Shahin, E. Shahin. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. Archived from th
original
on 4 June 2014. Retrieved 25 May 2020. The manner of its application in modern times has been a subject of dispute between Muslim traditionalists and reformists.
Traditional Principles of Islamic jurisprudence, theory of Islamic jurisprudence recognizes four sources of sharia: the Quran, sunnah (''Hadith'' and prophetic biography, ''Sira''), qiyas (analogical reasoning), and ''ijma'' (juridical consensus).
[ Quote: "[...], by the ninth century, the classical theory of law fixed the sources of Islamic law at four: the ''Quran'', the ''Sunnah'' of the Prophet, ''qiyas'' (analogical reasoning), and ''ijma'' (consensus)."] Different Madhhab, legal schools developed methodologies for deriving sharia rulings from scriptural sources using a process known as ''ijtihad''.
Traditional jurisprudence distinguishes two principal branches of law,''Ibadah, ʿibādāt'' (rituals) and ''Muamalat, muʿāmalāt'' (social relations), which together comprise a wide range of topics.
Its rulings assign actions to one of five categories called ahkam: mandatory (''fard''), recommended (''mustahabb''), permitted (''mubah''), abhorred (''makruh''), and prohibited (''haram'').
Forgiveness is much celebrated in Islam and, in criminal law, while imposing a penalty on an offender in proportion to their offense is considered permissible; forgiving the offender is better. To go one step further by offering a favor to the offender is regarded as the peak of excellence. Some areas of sharia overlap with the Western notion of law while others correspond more broadly to living life in accordance with God's will.
Historically, sharia was interpreted by independent jurists (muftis). Their legal opinions (fatwa) were taken into account by ruler-appointed Qadi, judges who presided over Qadi, qāḍī's courts, and by ''Mazalim, maẓālim'' courts, which were controlled by the ruler's council and administered criminal law.
In the modern era, sharia-based criminal laws were widely replaced by statutes inspired by European models.
The Ottoman Empire's 19th-century Tanzimat reforms lead to the Mecelle civil code and represented the first attempt to Codification (law), codify sharia. While the constitutions of most Muslim-majority states contain references to sharia, its classical rules were largely retained only in Status (law), personal status (family) laws.
Legislative bodies which codified these laws sought to modernize them without abandoning their foundations in traditional jurisprudence.
[Mayer, Ann Elizabeth. 2009.]
Law. Modern Legal Reform
" In ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Islamic World'', edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. The Islamic revival of the late 20th century brought along calls by Islamist movements for complete implementation of sharia.
The role of sharia has become a contested topic around the world. There are ongoing debates whether sharia is compatible with secular forms of government, human rights, freedom of thought, and women's rights.
Schools of jurisprudence

A school of jurisprudence is referred to as a ''madhhab'' ( ar, مذهب). The four major Sunni schools are the Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i, Hanbali madhahs while the three major Shia schools are the Ja'fari, Zaidiyyah, Zaidi and Isma'ilism, Isma'ili madhahib. Each differs in their methodology, called ''Usul al-fiqh'' ("principles of jurisprudence"). The following of decisions by a religious expert without necessarily examining the decision's reasoning is called ''taqlid''. The term ''Salafi movement, ghair muqallid'' literally refers to those who do not use taqlid and, by extension, do not have a madhab. The practice of an individual interpreting law with independent reasoning is called ''ijtihad''.
Society
Religious personages
Islam, like Judaism, has no clergy in the sacerdotalism, sacerdotal sense, such as priests who mediate between God and people. ''Imam'' ( ar, إمام, label=none) is the religious title used to refer to an Islamic leadership position, often in the context of conducting an Islamic worship service.
Religious interpretation is presided over by the ''‘ulama'' (Arabic: علماء), a term used describe the body of Muslim scholars who have received training in Islamic studies. A scholar of the hadith is called a ''muhaddith'', a scholar of jurisprudence is called a ''faqih'' ( ar, فقيه, label=none), a jurist who is qualified to issue legal opinions or ''fatwas'' is called a mufti, and a ''qadi'' is an Islamic judge. Honorific titles given to scholars include sheikh, mullah and ''Mawlawi (Islamic title), mawlawi''.
Some Muslims also venerate Saints in Islam, saints associated with Islamic view of miracles, miracles ( ar, كرامات, translit=karāmāt, label=none). The practice of visiting the tombs of prophets and saints is known as ''ziyarat''. Unlike saints in Christianity, Muslim saints are usually acknowledged informally by the consensus of common people, not by scholars.
Governance
Mainstream Islamic law does not distinguish between "matters of church" and "matters of state"; the ulema, scholars function as both jurists and theologians. Various forms of Islamic jurisprudence therefore rule on matters than in other societal context might be considered the preserve of the state. Terms traditionally used to refer to Muslim leaders include Caliph and Sultan, and terms associated with traditionally Muslim states include Caliphate, Emirate, Imamate and Khanate (List of Latin phrases (E), e.g. the United Arab Emirates).
In Islamic economic jurisprudence, hoarding of wealth is reviled and thus monopoly, monopolistic behavior is frowned upon. Attempts to comply with shariah has led to the development of Islamic banking. Islam prohibits ''riba'', usually translated as usury, which refers to any unfair gain in trade and is most commonly used to mean interest. Instead, Islamic banks go into partnership with the borrower and both share from the profits and any losses from the venture. Another feature is the avoidance of uncertainty, which is seen as gambling and Islamic banks traditionally avoid derivative instruments such as futures or options which substantially protected them from the 2008 financial crisis. The state used to be involved in distribution of charity from the treasury, known as Bayt al-mal, before it became a largely individual pursuit. The first Caliph, Abu Bakr, distributed zakat as one of the first examples of a guaranteed minimum income, with each man, woman and child getting 10 to 20 dirhams annually. During the reign of the second Caliph Umar, child support was introduced and the old and disabled were entitled to stipends, while the Umayyad Caliph Umar II assigned a servant for each blind person and for every two chronically ill persons.
Jihad means "to strive or struggle [in the way of God]" and, in its broadest sense, is "exerting one's utmost power, efforts, endeavors, or ability in contending with an object of wikt:disapprobation, disapprobation". This could refer to one's striving to attain religious and moral perfection
with the Shia and Sufis in particular, distinguishing between the "greater jihad", which pertains to spiritual self-improvement, self-perfection, and the "lesser jihad", defined as warfare.
[. ] When used without a qualifier, jihad is often understood in its military form.
Jihad is the only form of warfare permissible in Islamic law and may be declared against illegal works, terrorists, criminal groups, rebels, Apostasy in Islam, apostates, and leaders or states who oppress Muslims.
Most Muslims today interpret Jihad as only a defensive form of warfare. Jihad only becomes an individual duty for those vested with authority. For the rest of the populace, this happens only in the case of a general mobilization.
For most Twelver, Twelver Shias, offensive jihad can only be declared by a Imamate in Twelver doctrine, divinely appointed leader of the Muslim community, and as such, is suspended since Muhammad al-Mahdi's occultation (Islam), occultation is 868 CE.
Daily and family life

Many daily practices fall in the category of ''adab'', or etiquette and this includes greeting others with "''As-Salamu Alaykum, as-salamu 'alaykum''" ("peace be unto you"), saying ''Basmala, bismillah'' ("in Names of God, the name of God") before meals, and using only the right hand for eating and drinking.
Specific prohibited foods include pork products, blood and carrion. Health is viewed as a trust from God and khamr, intoxicants, such as alcoholic drinks, are prohibited.
All meat must come from a herbivorous animal slaughtered in the name of God by a Muslim, Jew, or Christian, except for game that one has hunted or fished for themself. Beards are often encouraged among men as something natural and body modifications, such as Religious perspectives on tattooing#Islam, permanent tattoos, are usually forbidden as violating the creation. Gold and silk for men are prohibited and are seen as extravagant. ''Haya (Islam), Haya'', often translated as "shame" or "modesty", is sometimes described as the innate character of Islam and informs much of Muslim daily life. For example, Islamic clothing, clothing in Islam emphasizes a standard of modesty, which has included the hijab for women. Similarly, Islamic hygienical jurisprudence, personal hygiene is encouraged with certain requirements.
In Marriage in Islam, Islamic marriage, the groom is required to pay a bridal gift (''mahr'').
Most families in the Islamic world are monogamous. However, Muslim men are allowed to practice polygyny and can have up to four wives at the same time. There are also cultural variations in weddings. Polyandry, a practice wherein a woman takes on two or more husbands, is prohibited in Islam.
After the birth of a child, the Adhan is pronounced in the right ear. On the seventh day, the ''aqiqah'' ceremony is performed, in which an animal is sacrificed and its meat is distributed among the poor. The child's head is shaved, and an amount of money equaling the weight of its hair is donated to the poor. Khitan (circumcision), Male circumcision is practised. Respecting and obeying one's parents, and taking care of them especially in their old age is a religious obligation.
A Islamic view of death, dying Muslim is encouraged to pronounce the ''
Shahada
The ''Shahada'' ( Arabic: ٱلشَّهَادَةُ , "the testimony"), also transliterated as ''Shahadah'', is an Islamic oath and creed, and one of the Five Pillars of Islam and part of the Adhan. It reads: "I bear witness that there i ...
'' as their last words. Paying respects to the dead and attending funerals in the community are considered among the virtuous acts. In Islamic funeral, Islamic burial rituals, burial is encouraged as soon as possible, usually within 24 hours. The body is washed, except for martyrs, by members of the same gender and enshrouded in a garment that must not be elaborate called ''kafan''. A "funeral prayer" called ''Salat al-Janazah'' is performed. Wailing, or loud, mournful outcrying, is discouraged. Coffins are often not preferred and graves are often unmarked, even for kings. Regarding inheritance, a son's share is double that of a daughter's.
[.]
''Khitan (circumcision), Khitan'', the Islamic religious rite of
circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Top ...
, is near-universal in the
Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
.
It is seen as obligatory or is highly recommended by all Fiqh, Islamic schools of jurisprudence.
It is considered a sign of belonging to the wider Ummah, Muslim community (''Ummah'').
Arts and culture
The term "Islamic culture" can be used to mean aspects of culture that pertain to the religion, such as festivals and dress code. It is also controversially used to denote the cultural aspects of traditionally Muslim people. Finally, "Islamic civilization" may also refer to the aspects of the synthesized culture of the early Caliphates, including that of non-Muslims, sometimes referred to as "wikt:Islamicate, Islamicate".
Islamic art encompasses the visual arts including fields as varied as architecture, calligraphy, painting, and Ceramics (art), ceramics, among others. While the making of images of animate beings has often been frowned upon in connection with Aniconism in Islam, laws against idolatry, this rule has been interpreted in different ways by different scholars and in different historical periods. This stricture has been used to explain the prevalence of Islamic calligraphy, calligraphy, tessellation, and pattern as key aspects of Islamic artistic culture. In Islamic architecture, varying cultures show influence such as North African and Spanish Islamic architecture such as the Great Mosque of Kairouan containing marble and Porphyry (geology), porphyry columns from Roman and Byzantine buildings, while mosques in Indonesia often have multi-tiered roofs from local Javanese styles.
The Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar that begins with the Hegira, Hijra of 622 CE, a date that was reportedly chosen by Caliph Umar as it was an important turning point in Muhammad's fortunes. Islamic Muslim holidays, holy days fall on fixed dates of the lunar calendar, meaning they occur in seasons, different seasons in different years in the Gregorian calendar. The most important Islamic festivals are ''
Eid al-Fitr'' ( ar, عيد الف) on the 1st of ''Shawwal'', marking the end of the fasting month ''Ramadan'', and ''
Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha () is the second and the larger of the two main holidays celebrated in Islam (the other being Eid al-Fitr). It honours the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to Allah's com ...
'' () on the 10th of ''Dhu al-Hijjah'', coinciding with the end of the
Hajj (pilgrimage).
Derived religions
Some movements, such as the Druze, Berghouata and Ha-Mim, either emerged from Islam or came to share certain beliefs with Islam, and whether each is a separate religion or a sect of Islam is sometimes controversial. Yazdânism is seen as a blend of local Kurdish beliefs and Islamic Sufi doctrine introduced to Kurdistan by Sheikh Adi ibn Musafir in the 12th century. Bábism stems from Twelver Shia passed through Siyyid 'Ali Muhammad i-Shirazi al-Bab while one of his followers Mirza Husayn 'Ali Nuri Baha'u'llah founded the Baháʼí Faith. Sikhism, founded by Guru Nanak in late-fifteenth-century Punjab, primarily incorporates aspects of Hinduism, with some Islamic influences.
Criticism

Criticism of Islam has existed since Islam's formative stages. Early criticism came from Christian authors, many of whom viewed Islam as a Medieval Christian views on Muhammad, Christian heresy or a form of idolatry, often explaining it in apocalyptic terms. Later, criticism from the Muslim world itself appeared, as well as from Jewish writers and from Ecclesiology, ecclesiastical Christians.
Christian writers criticized Islamic salvation optimism and its carnality. Islam's sensual descriptions of paradise led many Christians to conclude that Islam was not a spiritual religion. Although sensual pleasure was also present in early Christianity, as seen in the writings of Irenaeus, the doctrines of the former Manichaeism, Manichaean, Augustine of Hippo, led to the broad repudiation of bodily pleasure in both life and the afterlife. Ali ibn Sahl Rabban al-Tabari defended the Quranic description of paradise by asserting that the Bible also implies such ideas, such as drinking wine in the Gospel of Matthew.
Defamatory images of medieval Christian views on Muhammad, Muhammad, derived from early 7th century depictions of the Eastern Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Church,
[Minou Reeves, Reeves, Minou, and P. J. Stewart. 2003. ''Muhammad in Europe: A Thousand Years of Western Myth-Making''. New York University Press, NYU Press. . p. 93–96.] appear in the 14th-century epic poem ''Divine Comedy'' by Dante Alighieri.
[Stone, G. 2006. ''Dante's Pluralism and the Islamic Philosophy of Religion''. Springer Publishing. . p. 132.] Here, Muhammad appears in the eighth circle of hell, along with Ali. Dante does not blame Islam as a whole but accuses Muhammad of schism, by establishing another religion after Christianity.
Other criticisms focus on the question of human rights in modern Muslim-majority countries, and the treatment of women in Islamic law and practice. In the wake of the recent multiculturalism trend, Islam's influence on the ability of Muslim immigrants in the West to assimilate has been criticism of multiculturalism, criticized. Both in his public and personal life, others objected to the morality of Muhammad, therefore also the sunnah as a role model.
See also
* Glossary of Islam
* Index of Islam-related articles
* Islamic mythology
* Islamic studies
* Major religious groups
* Outline of Islam
References
Footnotes
Qur'an and hadith
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Lay summary*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Overview
*
*
*
*
* Siljander, Mark D., and John David Mann (2008). ''A Deadly Misunderstanding: a Congressman's Quest to Bridge the Muslim-Christian Divide'' (1st ed.). New York: HarperOne.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Encyclopedias and dictionaries
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* – via Oxford Reference.
*
*
Further reading
Encyclopedia of Sahih Al-Bukhariby Arabic Virtual Translation Center (New York 2019, Barnes & Noble ). The foundation of Islam: from revelation to tawhid.
* Abdul-Haqq, Abdiyah Akbar (1980). ''Sharing Your Faith with a Muslim''. Minneapolis: Bethany House Publishers. ''N.B''. Presents the genuine doctrines and concepts of Islam and of the Holy Qur'an, and this religion's affinities with Christianity and its Sacred Scriptures, in order to "dialogue" on the basis of what both faiths really teach.
*
*
*
* Cragg, Kenneth (1975). ''The House of Islam'', in ''The Religious Life of Man Series''. Second ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing Company 1975. xiii, 145 p. .
* Hourani, Albert (1991). ''Islam in European Thought''. First pbk. ed. Cambridge, Eng.: Cambridge University Press, 1992, cop. 1991. xi, 199 p. ; alternative ISBN on back cover, 0-521-42120-0.
*
* Khanbaghi, A, (2006). ''The Fire, the Star and the Cross: Minority Religions in Medieval and Early Modern Iran''. I. B. Tauris.
* Khavari, Farid A. (1990). ''Oil and Islam: the Ticking Bomb''. First ed. Malibu, Calif.: Roundtable Publications. viii, 277 p., ill. with maps and charts. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Prepublication text available at:
*
{{Authority control
Islam,
610 establishments
Abrahamic religions
Religious organizations established in the 7th century
 The Islamic holy books are the records that Muslims believe various prophets received from God through revelations, called '' wahy''. Muslims believe that parts of the previously revealed scriptures, such as the ''
The Islamic holy books are the records that Muslims believe various prophets received from God through revelations, called '' wahy''. Muslims believe that parts of the previously revealed scriptures, such as the '' Prophets (Arabic: ar, أنبياء, label=none, translit=anbiyāʾ) are believed to have been chosen by God to receive and preach a divine message. Additionally, a prophet delivering a new book to a nation is called a ''rasul'' ( ar, رسول, label=none, translit=rasūl), meaning "messenger". Muslims believe prophets are human and not divine. All of the prophets are said to have preached the same basic message of Islam – submission to the will of God – to various nations in the past and that this accounts for many similarities among religions. The Quran Qisas Al-Anbiya, recounts the names of numerous figures considered prophets in Islam, including Adam, Noah,
Prophets (Arabic: ar, أنبياء, label=none, translit=anbiyāʾ) are believed to have been chosen by God to receive and preach a divine message. Additionally, a prophet delivering a new book to a nation is called a ''rasul'' ( ar, رسول, label=none, translit=rasūl), meaning "messenger". Muslims believe prophets are human and not divine. All of the prophets are said to have preached the same basic message of Islam – submission to the will of God – to various nations in the past and that this accounts for many similarities among religions. The Quran Qisas Al-Anbiya, recounts the names of numerous figures considered prophets in Islam, including Adam, Noah,  The Shahada, ''shahadah'', is an
The Shahada, ''shahadah'', is an  Prayer in Islam, called salah, as-salah or aṣ-ṣalāt ( ar, الصلاة, link=no), is seen as a personal communication with God and consists of repeating units called rakat that include Ruku, bowing and Sujud, prostrating to God. Performing prayers five times a day is compulsory. The prayers are recited in the Arabic language and consist of verses from the Quran. The prayers are done in direction of the kaaba, Ka'bah. Salah requires ritual purity, which involves ''wudu'' (ritual wash) or occasionally, such as for new converts, ''ghusl'' (full body ritual wash). The means used to signal the prayer time is a vocal call called the ''adhan''.
A mosque is a places of worship, place of worship for Muslims, who often refer to it by its Arabic name masjid. Although the primary purpose of the mosque is to serve as a place of prayer, it is also important to the ummah, Muslim community as a place to meet and study with the Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, Masjid an-Nabawi ("Prophetic Mosque") in Medina, Saudi Arabia, having also served as a shelter for the poor. Minarets are towers used to call the adhan.
Prayer in Islam, called salah, as-salah or aṣ-ṣalāt ( ar, الصلاة, link=no), is seen as a personal communication with God and consists of repeating units called rakat that include Ruku, bowing and Sujud, prostrating to God. Performing prayers five times a day is compulsory. The prayers are recited in the Arabic language and consist of verses from the Quran. The prayers are done in direction of the kaaba, Ka'bah. Salah requires ritual purity, which involves ''wudu'' (ritual wash) or occasionally, such as for new converts, ''ghusl'' (full body ritual wash). The means used to signal the prayer time is a vocal call called the ''adhan''.
A mosque is a places of worship, place of worship for Muslims, who often refer to it by its Arabic name masjid. Although the primary purpose of the mosque is to serve as a place of prayer, it is also important to the ummah, Muslim community as a place to meet and study with the Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, Masjid an-Nabawi ("Prophetic Mosque") in Medina, Saudi Arabia, having also served as a shelter for the poor. Minarets are towers used to call the adhan.
 During the month of Ramadan, it is obligatory for Muslims to fast. The Ramadan fast (Arabic language, Arabic: ar, صوم, translit=ṣawm, label=none) precludes food and drink, as well as other forms of consumption, such as smoking, and is performed from dawn to sunset. The fast is to encourage a feeling of nearness to God by restraining oneself for God's sake from what is otherwise permissible and to think of the needy. In addition, there are other days when fasting is supererogatory.
During the month of Ramadan, it is obligatory for Muslims to fast. The Ramadan fast (Arabic language, Arabic: ar, صوم, translit=ṣawm, label=none) precludes food and drink, as well as other forms of consumption, such as smoking, and is performed from dawn to sunset. The fast is to encourage a feeling of nearness to God by restraining oneself for God's sake from what is otherwise permissible and to think of the needy. In addition, there are other days when fasting is supererogatory.
 The obligatory Islamic pilgrimage, called the "" ( ar, حج, link=no), is to be done at least once a lifetime by every Muslim with the means to do so during the Islamic calendar, Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah. Rituals of the Hajj mostly imitate the story of the family of
The obligatory Islamic pilgrimage, called the "" ( ar, حج, link=no), is to be done at least once a lifetime by every Muslim with the means to do so during the Islamic calendar, Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah. Rituals of the Hajj mostly imitate the story of the family of  Muslims recite and memorize the whole or parts of the Quran as acts of virtue. Reciting the Quran with elocution (''tajwid'') has been described as an excellent act of worship. Pious Muslims recite the whole Quran during the month of Ramadan. In Muslim societies, any social program generally begins with the recitation of the Quran. One who has memorized the whole Quran is called a hafiz ("memorizer") who, it is said, will be able to intercede for ten people on the Last Judgment Day. Apart from this, almost every Muslim memorizes some portion of the Quran because they need to recite it during their prayers.
Muslims recite and memorize the whole or parts of the Quran as acts of virtue. Reciting the Quran with elocution (''tajwid'') has been described as an excellent act of worship. Pious Muslims recite the whole Quran during the month of Ramadan. In Muslim societies, any social program generally begins with the recitation of the Quran. One who has memorized the whole Quran is called a hafiz ("memorizer") who, it is said, will be able to intercede for ten people on the Last Judgment Day. Apart from this, almost every Muslim memorizes some portion of the Quran because they need to recite it during their prayers.


 Muhammad died in 632 and the first successors, called Caliphs – Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman ibn al-Affan, Ali ibn Abi Talib and sometimes Hasan ibn Ali – are known in Sunni Islam as ''al-khulafā' ar-rāshidūn'' ("Rightly Guided Caliphs"). Some tribes left Islam and rebelled under leaders who declared themselves new prophets but were crushed by Abu Bakr in the Ridda wars. Local populations of Jews and indigenous Christians, persecuted as religious minorities and heretics and taxed heavily, often helped Muslims take over their lands, resulting in rapid expansion of the caliphate into the Sassanid Empire, Persian and Byzantine empires. Uthman election of Uthman, was elected in 644 and his assassination by rebels led to Ali being elected the next Caliph. In the First Fitna, First Civil War, Muhammad's widow, Aisha, raised an army against Ali, asking to avenge the death of Uthman, but was defeated at the Battle of the Camel. Ali attempted to remove the governor of Syria, Mu'awiya, who was seen as corrupt. Mu'awiya then declared war on Ali and was defeated in the Battle of Siffin. Ali's decision to arbitrate angered the Kharijites, an extremist sect, who felt that by not fighting a sinner, Ali became a sinner as well. The Kharijites rebelled and were defeated in the Battle of Nahrawan but a Kharijite assassin later killed Ali. Ali's son, Hasan ibn Ali, was elected Caliph and signed a Hasan–Muawiya treaty, peace treaty to avoid further fighting, abdicating to Muawiyah I, Mu'awiyah in return for Mu'awiyah not appointing a successor. Mu'awiyah began the Umayyad dynasty with the appointment of his son Yazid I as successor, sparking the Second Fitna, Second Civil War. During the Battle of Karbala, Husayn ibn Ali was killed by Yazid's forces; the event has been Ashura, annually commemorated by Shia ever since. Sunnis, led by Ibn al-Zubayr, opposed to a dynastic caliphate were defeated in the Siege of Mecca (692), Siege of Mecca. These disputes over leadership would give rise to the Sunni-Shia schism, with the Shia believing leadership belongs to Muhammad's family through Ali, called the ahl al-bayt. Political quietism in Islam, Quietist forms of Kharijites led to the third largest denomination in Islam, Ibadiyya.
Abu Bakr's leadership oversaw the beginning of the compilation of the Qur'an. The Caliph Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz set up the committee, The Seven Fuqaha of Medina, and Malik ibn Anas wrote one of the earliest books on Islamic jurisprudence, the ''Muwatta Imam Malik, Muwatta'', as a consensus of the opinion of those jurists. The Kharijites believed there is no compromised middle ground between good and evil, and any Muslim who commits a grave sin becomes an unbeliever. The term is also used to refer to later groups such as Islamic State, Isis. The Murji'ah taught that people's righteousness could be judged by God alone. Therefore, wrongdoers might be considered misguided, but not denounced as unbelievers. This attitude came to prevail into mainstream Islamic beliefs.
The Umayyad dynasty conquered the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Gallia Narbonensis, Narbonnese Gaul and Sindh. The Umayyads struggled with a lack of legitimacy and relied on a heavily patronized military. Since the jizya tax was a tax paid by non-Muslims which exempted them from military service, the Umayyads denied recognizing the conversion of non-Arabs as it reduced revenue. While the Rashidun Caliphate emphasized austerity, with Umar even requiring an inventory of each official's possessions, Umayyad luxury bred dissatisfaction among the pious. The Kharijites led the Berber Revolt leading to the first Muslim states independent of the Caliphate. In the Abbasid revolution, non-Arab converts (''mawali''), Arab clans pushed aside by the Umayyad clan, and some Shi'a rallied and overthrew the Umayyads, inaugurating the more cosmopolitan Abbasid dynasty in 750.
Muhammad died in 632 and the first successors, called Caliphs – Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman ibn al-Affan, Ali ibn Abi Talib and sometimes Hasan ibn Ali – are known in Sunni Islam as ''al-khulafā' ar-rāshidūn'' ("Rightly Guided Caliphs"). Some tribes left Islam and rebelled under leaders who declared themselves new prophets but were crushed by Abu Bakr in the Ridda wars. Local populations of Jews and indigenous Christians, persecuted as religious minorities and heretics and taxed heavily, often helped Muslims take over their lands, resulting in rapid expansion of the caliphate into the Sassanid Empire, Persian and Byzantine empires. Uthman election of Uthman, was elected in 644 and his assassination by rebels led to Ali being elected the next Caliph. In the First Fitna, First Civil War, Muhammad's widow, Aisha, raised an army against Ali, asking to avenge the death of Uthman, but was defeated at the Battle of the Camel. Ali attempted to remove the governor of Syria, Mu'awiya, who was seen as corrupt. Mu'awiya then declared war on Ali and was defeated in the Battle of Siffin. Ali's decision to arbitrate angered the Kharijites, an extremist sect, who felt that by not fighting a sinner, Ali became a sinner as well. The Kharijites rebelled and were defeated in the Battle of Nahrawan but a Kharijite assassin later killed Ali. Ali's son, Hasan ibn Ali, was elected Caliph and signed a Hasan–Muawiya treaty, peace treaty to avoid further fighting, abdicating to Muawiyah I, Mu'awiyah in return for Mu'awiyah not appointing a successor. Mu'awiyah began the Umayyad dynasty with the appointment of his son Yazid I as successor, sparking the Second Fitna, Second Civil War. During the Battle of Karbala, Husayn ibn Ali was killed by Yazid's forces; the event has been Ashura, annually commemorated by Shia ever since. Sunnis, led by Ibn al-Zubayr, opposed to a dynastic caliphate were defeated in the Siege of Mecca (692), Siege of Mecca. These disputes over leadership would give rise to the Sunni-Shia schism, with the Shia believing leadership belongs to Muhammad's family through Ali, called the ahl al-bayt. Political quietism in Islam, Quietist forms of Kharijites led to the third largest denomination in Islam, Ibadiyya.
Abu Bakr's leadership oversaw the beginning of the compilation of the Qur'an. The Caliph Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz set up the committee, The Seven Fuqaha of Medina, and Malik ibn Anas wrote one of the earliest books on Islamic jurisprudence, the ''Muwatta Imam Malik, Muwatta'', as a consensus of the opinion of those jurists. The Kharijites believed there is no compromised middle ground between good and evil, and any Muslim who commits a grave sin becomes an unbeliever. The term is also used to refer to later groups such as Islamic State, Isis. The Murji'ah taught that people's righteousness could be judged by God alone. Therefore, wrongdoers might be considered misguided, but not denounced as unbelievers. This attitude came to prevail into mainstream Islamic beliefs.
The Umayyad dynasty conquered the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Gallia Narbonensis, Narbonnese Gaul and Sindh. The Umayyads struggled with a lack of legitimacy and relied on a heavily patronized military. Since the jizya tax was a tax paid by non-Muslims which exempted them from military service, the Umayyads denied recognizing the conversion of non-Arabs as it reduced revenue. While the Rashidun Caliphate emphasized austerity, with Umar even requiring an inventory of each official's possessions, Umayyad luxury bred dissatisfaction among the pious. The Kharijites led the Berber Revolt leading to the first Muslim states independent of the Caliphate. In the Abbasid revolution, non-Arab converts (''mawali''), Arab clans pushed aside by the Umayyad clan, and some Shi'a rallied and overthrew the Umayyads, inaugurating the more cosmopolitan Abbasid dynasty in 750.
 Al-Shafi'i codified a method to determine the reliability of hadith. During the early Abbasid era, scholars such as Muhammad al-Bukhari, Bukhari and Muslim ibn al-Hajjaj, Muslim compiled the major Six major Hadith collections, Sunni hadith collections while scholars like Muhammad ibn Ya'qub al-Kulayni, Al-Kulayni and Ibn Babawayh compiled major Shia hadith collections. The four Sunni Madh'habs, the Hanafi, Hanbali, Maliki, and Shafi'i, were established around the teachings of Abū Ḥanīfa, Ahmad ibn Hanbal, Malik ibn Anas and al-Shafi'i. In contrast, the teachings of Ja'far al-Sadiq formed the Ja'fari jurisprudence. In the 9th century Al-Tabari completed the first commentary of the Quran, that became one of the most cited commentaries in Sunni Islam, the ''Tafsir al-Tabari''. Some Muslims began questioning the piety of indulgence in worldly life and emphasized poverty, humility, and avoidance of sin based on renunciation of bodily desires. Ascetics such as Hasan al-Basri would inspire a movement that would evolve into ''Tasawwuf'' or Sufism.
At this time, theological problems, notably on free will, were prominently tackled, with Hasan al Basri holding that although God knows people's actions, good and evil come from abuse of free will and the Iblis, devil. Greek rationalist philosophy influenced a speculative school of thought known as Muʿtazila, first originated by Wasil ibn Ata. Caliphs such as Mamun al Rashid and Al-Mu'tasim made it an official creed and unsuccessfully attempted to force their position on the majority. They carried out inquisitions with the traditionalist Ahmad ibn Hanbal notably refusing to conform to the Mutazila idea of the creation of the Quran and was tortured and kept in an unlit prison cell for nearly thirty months. However, other Schools of Islamic theology, schools of Kalam, speculative theology – Maturidi, Māturīdism founded by Abu Mansur al-Maturidi and Ash'ari founded by Al-Ash'ari – were more successful in being widely adopted. Philosophers such as Al-Farabi, Avicenna and Averroes sought to harmonize Aristotle's metaphysics within Islam, similar to later scholasticism within Christianity in Europe, and Maimonides' work within Judaism, while others like Al-Ghazali argued against such syncretism and ultimately prevailed.
This era is sometimes called the "
Al-Shafi'i codified a method to determine the reliability of hadith. During the early Abbasid era, scholars such as Muhammad al-Bukhari, Bukhari and Muslim ibn al-Hajjaj, Muslim compiled the major Six major Hadith collections, Sunni hadith collections while scholars like Muhammad ibn Ya'qub al-Kulayni, Al-Kulayni and Ibn Babawayh compiled major Shia hadith collections. The four Sunni Madh'habs, the Hanafi, Hanbali, Maliki, and Shafi'i, were established around the teachings of Abū Ḥanīfa, Ahmad ibn Hanbal, Malik ibn Anas and al-Shafi'i. In contrast, the teachings of Ja'far al-Sadiq formed the Ja'fari jurisprudence. In the 9th century Al-Tabari completed the first commentary of the Quran, that became one of the most cited commentaries in Sunni Islam, the ''Tafsir al-Tabari''. Some Muslims began questioning the piety of indulgence in worldly life and emphasized poverty, humility, and avoidance of sin based on renunciation of bodily desires. Ascetics such as Hasan al-Basri would inspire a movement that would evolve into ''Tasawwuf'' or Sufism.
At this time, theological problems, notably on free will, were prominently tackled, with Hasan al Basri holding that although God knows people's actions, good and evil come from abuse of free will and the Iblis, devil. Greek rationalist philosophy influenced a speculative school of thought known as Muʿtazila, first originated by Wasil ibn Ata. Caliphs such as Mamun al Rashid and Al-Mu'tasim made it an official creed and unsuccessfully attempted to force their position on the majority. They carried out inquisitions with the traditionalist Ahmad ibn Hanbal notably refusing to conform to the Mutazila idea of the creation of the Quran and was tortured and kept in an unlit prison cell for nearly thirty months. However, other Schools of Islamic theology, schools of Kalam, speculative theology – Maturidi, Māturīdism founded by Abu Mansur al-Maturidi and Ash'ari founded by Al-Ash'ari – were more successful in being widely adopted. Philosophers such as Al-Farabi, Avicenna and Averroes sought to harmonize Aristotle's metaphysics within Islam, similar to later scholasticism within Christianity in Europe, and Maimonides' work within Judaism, while others like Al-Ghazali argued against such syncretism and ultimately prevailed.
This era is sometimes called the " Earlier in the 14th century, Ibn Taymiyya promoted a puritanical form of Islam,Mary Hawkesworth, Maurice Kogan ''Encyclopedia of Government and Politics: 2-volume set'' Routledge 2013 pp. 270–271 rejecting philosophical approaches in favor of simpler theology and called to open the gates of itjihad rather than blind imitation of scholars. He called for a jihad against those he deemed hereticsRichard Gauvain ''Salafi Ritual Purity: In the Presence of God'' Routledge 2013 p. 6 but his writings only played a marginal role during his lifetime. During the 18th century in Arabia, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, influenced by the works of Ibn Taymiyya and Ibn al-Qayyim, founded a movement, called Wahhabi with their self-designation as ''Muwahiddun'', to return to what he saw as unadultered Islam.Ga ́bor A ́goston, Bruce Alan Masters ''Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire'' Infobase Publishing 2010 p. 260 He condemned many local Islamic customs, such as visiting the grave of Muhammad or saints, as later bidah, innovations and sinful and destroyed sacred rocks and trees, Sufi shrines, the Destruction of early Islamic heritage sites in Saudi Arabia, tombs of Muhammad and his companions and the tomb of Husayn at Karbala, a major Shia pilgrimage site. He formed an alliance with the House of Saud, Saud family, which, by the 1920s, completed their conquest of the area that would become Saudi Arabia. Ma Wanfu and Ma Debao promoted salafist movements in the nineteenth century such as Sailaifengye in China after returning from Mecca but were eventually persecuted and forced into hiding by Sufi groups. Other groups sought to reform Sufism rather than reject it, with the Senusiyya and Muhammad Ahmad both waging war and establishing states in Libya and Sudan respectively. In India, Shah Waliullah Dehlawi attempted a more conciliatory style against Sufism and influenced the Deobandi movement. In response to the Deobandi movement, the Barelwi movement was founded as a mass movement, defending popular Sufism and reforming its practices.
The
Earlier in the 14th century, Ibn Taymiyya promoted a puritanical form of Islam,Mary Hawkesworth, Maurice Kogan ''Encyclopedia of Government and Politics: 2-volume set'' Routledge 2013 pp. 270–271 rejecting philosophical approaches in favor of simpler theology and called to open the gates of itjihad rather than blind imitation of scholars. He called for a jihad against those he deemed hereticsRichard Gauvain ''Salafi Ritual Purity: In the Presence of God'' Routledge 2013 p. 6 but his writings only played a marginal role during his lifetime. During the 18th century in Arabia, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, Muhammad ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab, influenced by the works of Ibn Taymiyya and Ibn al-Qayyim, founded a movement, called Wahhabi with their self-designation as ''Muwahiddun'', to return to what he saw as unadultered Islam.Ga ́bor A ́goston, Bruce Alan Masters ''Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire'' Infobase Publishing 2010 p. 260 He condemned many local Islamic customs, such as visiting the grave of Muhammad or saints, as later bidah, innovations and sinful and destroyed sacred rocks and trees, Sufi shrines, the Destruction of early Islamic heritage sites in Saudi Arabia, tombs of Muhammad and his companions and the tomb of Husayn at Karbala, a major Shia pilgrimage site. He formed an alliance with the House of Saud, Saud family, which, by the 1920s, completed their conquest of the area that would become Saudi Arabia. Ma Wanfu and Ma Debao promoted salafist movements in the nineteenth century such as Sailaifengye in China after returning from Mecca but were eventually persecuted and forced into hiding by Sufi groups. Other groups sought to reform Sufism rather than reject it, with the Senusiyya and Muhammad Ahmad both waging war and establishing states in Libya and Sudan respectively. In India, Shah Waliullah Dehlawi attempted a more conciliatory style against Sufism and influenced the Deobandi movement. In response to the Deobandi movement, the Barelwi movement was founded as a mass movement, defending popular Sufism and reforming its practices.
The  About 23.4% of the global population, or about 1.8 billion people, are Muslims.Lipka, Michael, and Conrad Hackett. [2015] 6 April 2017.
About 23.4% of the global population, or about 1.8 billion people, are Muslims.Lipka, Michael, and Conrad Hackett. [2015] 6 April 2017. Sunni Islam or Sunnism is the name for the largest denomination in Islam. The term is a contraction of the phrase "ahl as-sunna wa'l-jamaat", which means "people of the Sunnah, sunna (the traditions of the prophet Muhammad) and the community". Sunnis, or sometimes Sunnites, believe that the first four caliphs were the rightful successors to Muhammad and primarily reference Al-Kutub Al-Sittah, six major hadith works for legal matters, while following one of the four traditional schools of jurisprudence: Hanafi, Hanbali, Maliki or Shafi'i.
Sunni schools of theology encompass Asharism founded by Al-Ashʿarī (c. 874–936), Maturidi by Abu Mansur al-Maturidi (853–944 CE) and Traditionalist theology (Islam), traditionalist theology under the leadership of Ahmad ibn Hanbal (780–855 CE). Traditionalist theology is characterized by its adherence to a literal understanding of the Quran and the Sunnah, the belief in the Quran is uncreated and eternal, and opposition to reason (kalam) in religious and ethical matters. On the other hand, Maturidism asserts, scripture is not needed for basic ethics and that ''good'' and ''evil'' can be understood by reason alone, but people rely on revelation, for matters beyond human's comprehension. Asharism holds that ethics can derive just from divine revelation but not from human reason. However, Asharism accepts reason regarding exegetical matters and combines Muʿtazila approaches with traditionalist ideas.
In the 18th century, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab led a Salafi movement, referred by outsiders as Wahhabism, in modern-day Saudi Arabia. A similar movement called Ahl al-Hadith also de-emphasized the centuries' old Sunni legal tradition, preferring to directly follow the Quran and Hadith. The ''Nur movement, Nurcu'' Sunni movement was by Said Nursi (1877–1960);Svante E. Cornell ''Azerbaijan Since Independence'' M.E. Sharpe p. 283 it incorporates elements of Sufism and science, and has given rise to the Gülen movement.
Sunni Islam or Sunnism is the name for the largest denomination in Islam. The term is a contraction of the phrase "ahl as-sunna wa'l-jamaat", which means "people of the Sunnah, sunna (the traditions of the prophet Muhammad) and the community". Sunnis, or sometimes Sunnites, believe that the first four caliphs were the rightful successors to Muhammad and primarily reference Al-Kutub Al-Sittah, six major hadith works for legal matters, while following one of the four traditional schools of jurisprudence: Hanafi, Hanbali, Maliki or Shafi'i.
Sunni schools of theology encompass Asharism founded by Al-Ashʿarī (c. 874–936), Maturidi by Abu Mansur al-Maturidi (853–944 CE) and Traditionalist theology (Islam), traditionalist theology under the leadership of Ahmad ibn Hanbal (780–855 CE). Traditionalist theology is characterized by its adherence to a literal understanding of the Quran and the Sunnah, the belief in the Quran is uncreated and eternal, and opposition to reason (kalam) in religious and ethical matters. On the other hand, Maturidism asserts, scripture is not needed for basic ethics and that ''good'' and ''evil'' can be understood by reason alone, but people rely on revelation, for matters beyond human's comprehension. Asharism holds that ethics can derive just from divine revelation but not from human reason. However, Asharism accepts reason regarding exegetical matters and combines Muʿtazila approaches with traditionalist ideas.
In the 18th century, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab led a Salafi movement, referred by outsiders as Wahhabism, in modern-day Saudi Arabia. A similar movement called Ahl al-Hadith also de-emphasized the centuries' old Sunni legal tradition, preferring to directly follow the Quran and Hadith. The ''Nur movement, Nurcu'' Sunni movement was by Said Nursi (1877–1960);Svante E. Cornell ''Azerbaijan Since Independence'' M.E. Sharpe p. 283 it incorporates elements of Sufism and science, and has given rise to the Gülen movement.
 Shia Islam, or Shi'ism, is the second-largest Muslim denomination. Shias, or Shiites, split with Sunnis over Muhammad's Succession to Muhammad, successor as leader, who the Shia believed must be from certain descendants of Muhammad's family known as the Ahl al-Bayt and those leaders, referred to as Imamate in Shia doctrine, Imams, have additional spiritual authority. Some of the first Imams are revered by all Shia groups and Sunnis, such as Ali. Zaidism, Zaidi, the second-oldest branch, reject special powers of Imams and are sometimes considered a 'fifth school' of Sunni Islam rather than a Shia denomination. The Twelvers, the first and the largest Shia branch, believe in twelve Imams, the last of whom went into Occultation (Islam), occultation to return one day. The Ismailism, Ismailis split with the Twelvers over who was the seventh Imam and have split into more groups over the status of successive Imams, with the largest group being the Nizari Isma'ilism, Nizaris.
Shia Islam, or Shi'ism, is the second-largest Muslim denomination. Shias, or Shiites, split with Sunnis over Muhammad's Succession to Muhammad, successor as leader, who the Shia believed must be from certain descendants of Muhammad's family known as the Ahl al-Bayt and those leaders, referred to as Imamate in Shia doctrine, Imams, have additional spiritual authority. Some of the first Imams are revered by all Shia groups and Sunnis, such as Ali. Zaidism, Zaidi, the second-oldest branch, reject special powers of Imams and are sometimes considered a 'fifth school' of Sunni Islam rather than a Shia denomination. The Twelvers, the first and the largest Shia branch, believe in twelve Imams, the last of whom went into Occultation (Islam), occultation to return one day. The Ismailism, Ismailis split with the Twelvers over who was the seventh Imam and have split into more groups over the status of successive Imams, with the largest group being the Nizari Isma'ilism, Nizaris.

 Sufism (Arabic: ar, تصوف, translit=tasawwuf, label=none), is a mystical-ascetic approach to Islam that seeks to find a direct Divine presence, personal experience of God. Classical Sufi scholars defined ''Tasawwuf'' as "a science whose objective is the reparation of the heart and turning it away from all else but God", through "intuitive and emotional faculties" that one must be trained to use.Ahmad Zarruq, Zarruq, Ahmed, Zaineb Istrabadi, and Hamza Yusuf, Hamza Yusuf Hanson. 2008. ''The Principles of Sufism''. Amal Press. It is not a sect of Islam and its adherents belong to the various Muslim denominations. Ismaili Shias, whose teachings root in Gnosticism and Neoplatonism, as well as by the Illuminationism, Illuminationist and School of Isfahan, Isfahan schools of Islamic philosophy have developed mystical interpretations of Islam. Hasan al-Basri, the early Sufi ascetic often portrayed as one of the earliest Sufis, emphasized fear of failing God's expectations of obedience. In contrast, later prominent Sufis, such as Mansur Al-Hallaj and Rumi, Jalaluddin Rumi, emphasized religiosity based on love towards God. Such devotion would also have an impact on the arts, with Rumi, still one of the best selling poets in America, writing his Persian poem Masnawi and the works of Hafez (1315–1390) are often considered the pinnacle of Persian poetry.
Sufis reject ''materialism'' and ''ego'' and regard everything as if it was sent by god alone, Sufi strongly believes in the oneness of god.
Sufis see ''tasawwuf'' as an inseparable part of Islam, just like the ''sharia''. Traditional Sufis, such as Bayazid Bastami, Jalaluddin Rumi, Haji Bektash Veli, Junaid Baghdadi, and Al-Ghazali, argued for Sufism as being based upon the tenets of Islam and the teachings of the prophet. Historian Nile Green argued that Islam in the Medieval period, was more or less ''Sufism''. Popular devotional practices such as the veneration of Sufi saints have been viewed as innovations from the original religion from followers of salafism, who have sometimes physically attacked Sufis, leading to a deterioration in Sufi–Salafi relations.
Sufi congregations form orders (''tariqa'') centered around a teacher (''wali'') who traces a spiritual chain back to Muhammad. Sufis played an important role in the formation of Muslim societies through their missionary and educational activities. Sufi influenced Ahle Sunnat movement or Barelvi movement defends Sufi practices and beliefs with over 200 million followers in south Asia. Sufism is prominent in Central Asia, as well as in African countries like Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Senegal, Chad and Niger.
Sufism (Arabic: ar, تصوف, translit=tasawwuf, label=none), is a mystical-ascetic approach to Islam that seeks to find a direct Divine presence, personal experience of God. Classical Sufi scholars defined ''Tasawwuf'' as "a science whose objective is the reparation of the heart and turning it away from all else but God", through "intuitive and emotional faculties" that one must be trained to use.Ahmad Zarruq, Zarruq, Ahmed, Zaineb Istrabadi, and Hamza Yusuf, Hamza Yusuf Hanson. 2008. ''The Principles of Sufism''. Amal Press. It is not a sect of Islam and its adherents belong to the various Muslim denominations. Ismaili Shias, whose teachings root in Gnosticism and Neoplatonism, as well as by the Illuminationism, Illuminationist and School of Isfahan, Isfahan schools of Islamic philosophy have developed mystical interpretations of Islam. Hasan al-Basri, the early Sufi ascetic often portrayed as one of the earliest Sufis, emphasized fear of failing God's expectations of obedience. In contrast, later prominent Sufis, such as Mansur Al-Hallaj and Rumi, Jalaluddin Rumi, emphasized religiosity based on love towards God. Such devotion would also have an impact on the arts, with Rumi, still one of the best selling poets in America, writing his Persian poem Masnawi and the works of Hafez (1315–1390) are often considered the pinnacle of Persian poetry.
Sufis reject ''materialism'' and ''ego'' and regard everything as if it was sent by god alone, Sufi strongly believes in the oneness of god.
Sufis see ''tasawwuf'' as an inseparable part of Islam, just like the ''sharia''. Traditional Sufis, such as Bayazid Bastami, Jalaluddin Rumi, Haji Bektash Veli, Junaid Baghdadi, and Al-Ghazali, argued for Sufism as being based upon the tenets of Islam and the teachings of the prophet. Historian Nile Green argued that Islam in the Medieval period, was more or less ''Sufism''. Popular devotional practices such as the veneration of Sufi saints have been viewed as innovations from the original religion from followers of salafism, who have sometimes physically attacked Sufis, leading to a deterioration in Sufi–Salafi relations.
Sufi congregations form orders (''tariqa'') centered around a teacher (''wali'') who traces a spiritual chain back to Muhammad. Sufis played an important role in the formation of Muslim societies through their missionary and educational activities. Sufi influenced Ahle Sunnat movement or Barelvi movement defends Sufi practices and beliefs with over 200 million followers in south Asia. Sufism is prominent in Central Asia, as well as in African countries like Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Senegal, Chad and Niger.
 A school of jurisprudence is referred to as a ''madhhab'' ( ar, مذهب). The four major Sunni schools are the Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i, Hanbali madhahs while the three major Shia schools are the Ja'fari, Zaidiyyah, Zaidi and Isma'ilism, Isma'ili madhahib. Each differs in their methodology, called ''Usul al-fiqh'' ("principles of jurisprudence"). The following of decisions by a religious expert without necessarily examining the decision's reasoning is called ''taqlid''. The term ''Salafi movement, ghair muqallid'' literally refers to those who do not use taqlid and, by extension, do not have a madhab. The practice of an individual interpreting law with independent reasoning is called ''ijtihad''.
A school of jurisprudence is referred to as a ''madhhab'' ( ar, مذهب). The four major Sunni schools are the Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi'i, Hanbali madhahs while the three major Shia schools are the Ja'fari, Zaidiyyah, Zaidi and Isma'ilism, Isma'ili madhahib. Each differs in their methodology, called ''Usul al-fiqh'' ("principles of jurisprudence"). The following of decisions by a religious expert without necessarily examining the decision's reasoning is called ''taqlid''. The term ''Salafi movement, ghair muqallid'' literally refers to those who do not use taqlid and, by extension, do not have a madhab. The practice of an individual interpreting law with independent reasoning is called ''ijtihad''.
 Many daily practices fall in the category of ''adab'', or etiquette and this includes greeting others with "''As-Salamu Alaykum, as-salamu 'alaykum''" ("peace be unto you"), saying ''Basmala, bismillah'' ("in Names of God, the name of God") before meals, and using only the right hand for eating and drinking.
Specific prohibited foods include pork products, blood and carrion. Health is viewed as a trust from God and khamr, intoxicants, such as alcoholic drinks, are prohibited. All meat must come from a herbivorous animal slaughtered in the name of God by a Muslim, Jew, or Christian, except for game that one has hunted or fished for themself. Beards are often encouraged among men as something natural and body modifications, such as Religious perspectives on tattooing#Islam, permanent tattoos, are usually forbidden as violating the creation. Gold and silk for men are prohibited and are seen as extravagant. ''Haya (Islam), Haya'', often translated as "shame" or "modesty", is sometimes described as the innate character of Islam and informs much of Muslim daily life. For example, Islamic clothing, clothing in Islam emphasizes a standard of modesty, which has included the hijab for women. Similarly, Islamic hygienical jurisprudence, personal hygiene is encouraged with certain requirements.
In Marriage in Islam, Islamic marriage, the groom is required to pay a bridal gift (''mahr'').
Most families in the Islamic world are monogamous. However, Muslim men are allowed to practice polygyny and can have up to four wives at the same time. There are also cultural variations in weddings. Polyandry, a practice wherein a woman takes on two or more husbands, is prohibited in Islam.
After the birth of a child, the Adhan is pronounced in the right ear. On the seventh day, the ''aqiqah'' ceremony is performed, in which an animal is sacrificed and its meat is distributed among the poor. The child's head is shaved, and an amount of money equaling the weight of its hair is donated to the poor. Khitan (circumcision), Male circumcision is practised. Respecting and obeying one's parents, and taking care of them especially in their old age is a religious obligation.
A Islamic view of death, dying Muslim is encouraged to pronounce the ''
Many daily practices fall in the category of ''adab'', or etiquette and this includes greeting others with "''As-Salamu Alaykum, as-salamu 'alaykum''" ("peace be unto you"), saying ''Basmala, bismillah'' ("in Names of God, the name of God") before meals, and using only the right hand for eating and drinking.
Specific prohibited foods include pork products, blood and carrion. Health is viewed as a trust from God and khamr, intoxicants, such as alcoholic drinks, are prohibited. All meat must come from a herbivorous animal slaughtered in the name of God by a Muslim, Jew, or Christian, except for game that one has hunted or fished for themself. Beards are often encouraged among men as something natural and body modifications, such as Religious perspectives on tattooing#Islam, permanent tattoos, are usually forbidden as violating the creation. Gold and silk for men are prohibited and are seen as extravagant. ''Haya (Islam), Haya'', often translated as "shame" or "modesty", is sometimes described as the innate character of Islam and informs much of Muslim daily life. For example, Islamic clothing, clothing in Islam emphasizes a standard of modesty, which has included the hijab for women. Similarly, Islamic hygienical jurisprudence, personal hygiene is encouraged with certain requirements.
In Marriage in Islam, Islamic marriage, the groom is required to pay a bridal gift (''mahr'').
Most families in the Islamic world are monogamous. However, Muslim men are allowed to practice polygyny and can have up to four wives at the same time. There are also cultural variations in weddings. Polyandry, a practice wherein a woman takes on two or more husbands, is prohibited in Islam.
After the birth of a child, the Adhan is pronounced in the right ear. On the seventh day, the ''aqiqah'' ceremony is performed, in which an animal is sacrificed and its meat is distributed among the poor. The child's head is shaved, and an amount of money equaling the weight of its hair is donated to the poor. Khitan (circumcision), Male circumcision is practised. Respecting and obeying one's parents, and taking care of them especially in their old age is a religious obligation.
A Islamic view of death, dying Muslim is encouraged to pronounce the ''