Irish Houses of Parliament on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Parliament House ( ga, Tithe na Parlaiminte) in

 In the 17th century, parliament settled at Chichester House, a townhouse in Hoggen Green (later College Green) formerly owned by Sir George Carew, Lord President of Munster and Lord High Treasurer of Ireland, which had been built on the site of a nunnery disbanded by King
In the 17th century, parliament settled at Chichester House, a townhouse in Hoggen Green (later College Green) formerly owned by Sir George Carew, Lord President of Munster and Lord High Treasurer of Ireland, which had been built on the site of a nunnery disbanded by King

 Much of the public ceremonies mirrored those of the British Houses of Parliament. Sessions were formally opened by a
Much of the public ceremonies mirrored those of the British Houses of Parliament. Sessions were formally opened by a
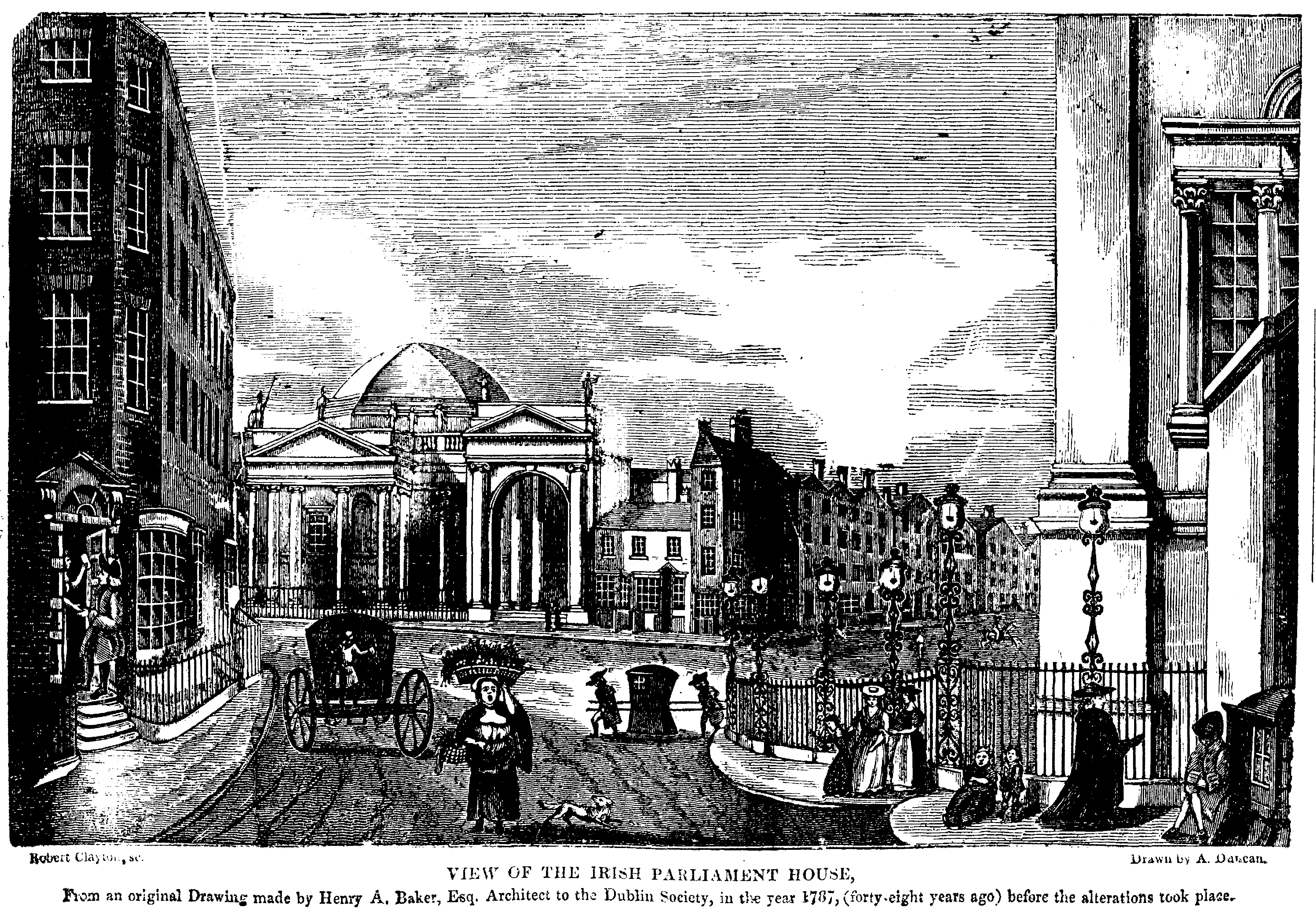 Initially, the former Parliament House was used for a variety of purposes, including as a military garrison and as an art gallery. In 1803 the fledgling
Initially, the former Parliament House was used for a variety of purposes, including as a military garrison and as an art gallery. In 1803 the fledgling

 The house is seen generally with affection by Dubliners. It was used as a symbol by generations of nationalist leaders from O'Connell to Parnell and Redmond in their own quest for Irish self-government. In a particular irony,
The house is seen generally with affection by Dubliners. It was used as a symbol by generations of nationalist leaders from O'Connell to Parnell and Redmond in their own quest for Irish self-government. In a particular irony,
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, was home to the Parliament of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland ( ga, Parlaimint na hÉireann) was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two ch ...
, and since 1803 has housed the Bank of Ireland
Bank of Ireland Group plc ( ga, Banc na hÉireann) is a commercial bank operation in Ireland and one of the traditional Big Four Irish banks. Historically the premier banking organisation in Ireland, the Bank occupies a unique position in Iris ...
. It was the world's first purpose-built bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single gr ...
parliament house. It is located at College Green.
History
Originally it was the site ofChichester House
Chichester House or Carew's House was a building in College Green (formerly Hoggen Green), Dublin, Ireland, used in the 17th century to house the Parliament of Ireland. Originally built to be a hospital, it was never used as such.
At one time ...
, which was built in the early 17th century by Sir Arthur Chichester. This building was adapted for use by the Irish Parliament in the 1670s, and was demolished to make way for a new parliamentary building. Chichester House was flanked by rows of narrow houses known as Dutch Billies, which were demolished and replaced during the Wide Streets Commission. Construction started in 1729. The building was home to the two Houses of Parliament, serving as the seat of both chambers (the Lords
Lords may refer to:
* The plural of Lord
Places
*Lords Creek, a stream in New Hanover County, North Carolina
*Lord's, English Cricket Ground and home of Marylebone Cricket Club and Middlesex County Cricket Club
People
*Traci Lords (born 19 ...
and Commons) of the Parliament of the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label= Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
for most of the 18th century until that parliament was abolished by the Act of Union of 1800, when Ireland became part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
.
The current parliament building is Leinster House
Leinster House ( ga, Teach Laighean) is the seat of the Oireachtas, the parliament of Ireland. Originally, it was the ducal palace of the Dukes of Leinster. Since 1922, it is a complex of buildings, of which the former ducal palace is the core ...
.
Plans for the new building

 In the 17th century, parliament settled at Chichester House, a townhouse in Hoggen Green (later College Green) formerly owned by Sir George Carew, Lord President of Munster and Lord High Treasurer of Ireland, which had been built on the site of a nunnery disbanded by King
In the 17th century, parliament settled at Chichester House, a townhouse in Hoggen Green (later College Green) formerly owned by Sir George Carew, Lord President of Munster and Lord High Treasurer of Ireland, which had been built on the site of a nunnery disbanded by King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
at the time of the dissolution of the monasteries. Carew's house, named Chichester House after its later owner Sir Arthur Chichester
Arthur Chichester, 1st Baron Chichester (May 1563 – 19 February 1625; known between 1596 and 1613 as Sir Arthur Chichester), of Carrickfergus in Ireland, was an English administrator and soldier who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland from 16 ...
, was a building of sufficient importance to have become the temporary home of the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label= Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
's law courts during the Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in some Western liturgical calendars on 29 September, a ...
law term in 1605. Most famously, the legal documentation facilitating the Plantation of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster ( gle, Plandáil Uladh; Ulster-Scots: ''Plantin o Ulstèr'') was the organised colonisation ('' plantation'') of Ulstera province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of th ...
had been signed there on 16 November 1612.
Chichester House was in a dilapidated state, allegedly haunted and unfit for official use. In 1727 parliament voted to spend £6,000 on a new building on the site. It was to be the world's first purpose-built two-chamber parliament building.
The then ancient Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north b ...
, the seat of the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
(before 1707) and, later, British Parliament, was a converted building; the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
's odd seating arrangements were due to the chamber's previous existence as a chapel. Hence MPs faced each other from former pews.
The design of this building, one of two purpose-built Irish parliamentary buildings (along with Parliament Buildings, Stormont), was entrusted to an architect, Edward Lovett Pearce
Sir Edward Lovett Pearce (1699 – 7 December 1733) was an Irish architect, and the chief exponent of Palladianism in Ireland. He is thought to have initially studied as an architect under his father's first cousin, Sir John Vanbrugh. He is be ...
, who was a member of parliament and a protégé of the Speaker of the House of Commons, William Conolly of Castletown House. During construction, Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
moved into the Blue Coat Hospital on Dublin's Northside
Northside or North Side may refer to:
Music
* Northside (band), a musical group from Manchester, England
* NorthSide, an American record label
* NorthSide Festival (Denmark), a music festival in Aarhus, Denmark
* " Norf Norf", a 2015 song by Vinc ...
. The foundation stone for the new building was laid on 3February 1729 by Thomas Wyndham, 1st Baron Wyndham
Thomas Wyndham, 1st Baron Wyndham PC (27 December 1681 – 24 November 1745), was an Irish lawyer and politician. He served as Lord Chancellor of Ireland from 1726 to 1739.
Background
Wyndham was born in Wiltshire, the son of Colonel John Wyndh ...
, the Lord Chancellor of Ireland
The Lord High Chancellor of Ireland (commonly known as Lord Chancellor of Ireland) was the highest judicial office in Ireland until the establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922. From 1721 to 1801, it was also the highest political office of ...
.
Design
Pearce's design was revolutionary. The building was effectively semi-circular in shape, occupying nearly 6,000 m2 (1.5 acres). Unlike Chichester House, which was set far back from Hoggen Green, the new building opened directly onto the Green. The principal entrance consisted of a colonnade of Ionic columns extending around three sides of the entrance quadrangle, forming a letter E (see picture below). Three statues, representing Hibernia (theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
name for Ireland), Fidelity and Commerce (later carved by Edward Smyth) stood above the portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cul ...
. Over the main entrance, the royal coat of arms was cut in stone.
The building underwent extensions by architect James Gandon
James Gandon (20 February 1743 – 24 December 1823) was an English architect best known for his work in Ireland during the late 18th century and early 19th century. His better known works include The Custom House and the surrounding Beresford ...
, as Pearce had died. Gandon was responsible for three of Dublin's finest buildings, the Custom House, the Four Courts and the King's Inns
The Honorable Society of King's Inns ( ir, Cumann Onórach Óstaí an Rí) is the "Inn of Court" for the Bar of Ireland. Established in 1541, King's Inns is Ireland's oldest school of law and one of Ireland's significant historical environment ...
. Between 1785 and 1789 he added a new peers' entrance at the east of the building, facing onto Westmoreland Street. Unlike the main entrance to the south, which came to be known as the House of Commons entrance, the new peers' entrance used six Corinthian columns, at the request of peers who wished their entrance to be distinct from the Ionic columns of the main entrance. Over this, three statues by Edward Smyth were placed, representing Fortitude, Justice and Liberty. A curved wall joined the Pearce entrance to Gandon's extension. This masked the uneven joins of some of the extension, as shown below. The wall, built of granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
with inset alcoves, bears little resemblance to the building as it was in its parliamentary days.
Another extension was added on the west side into Foster Place, designed in 1787 by architect Robert Parke; while matching Gandon's portico, he tried a different solution, linking the other portico to the main Pearce one by a set of Ionic pillars. The result proved unattractive. When the Bank of Ireland
Bank of Ireland Group plc ( ga, Banc na hÉireann) is a commercial bank operation in Ireland and one of the traditional Big Four Irish banks. Historically the premier banking organisation in Ireland, the Bank occupies a unique position in Iris ...
took over the building, it created an architectural unity by replacing this set of Ionic columns by a curved wall similar to Gandon's east wall. Ionic columns were then added to both curved walls, giving the extensions an architectural and visual unity that had been lacking and producing the building's ultimate exterior.
The interior contained one unusual and highly symbolic feature. While in many converted parliamentary buildings where both houses met in the same building, the houses were given equality or indeed the upper house was given a more prominent location within the building, in the new Irish Houses of Parliament the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
was featured, with its octagonal
In geometry, an octagon (from the Greek ὀκτάγωνον ''oktágōnon'', "eight angles") is an eight-sided polygon or 8-gon.
A '' regular octagon'' has Schläfli symbol and can also be constructed as a quasiregular truncated square, t ...
parliamentary chamber located in the building's centre. The smaller House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
was given a lesser position nearby.
The original, domed House of Commons chamber was destroyed by fire in the 1790s, and a less elaborate new chamber, without a dome, was rebuilt in the same location and opened in 1796, four years before the Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
's ultimate abolition.
Pearce's design copied
Pearce's designs came to be studied and copied both at home and abroad. The Viceregal Apartments inDublin Castle
Dublin Castle ( ga, Caisleán Bhaile Átha Cliath) is a former Motte-and-bailey castle and current Irish government complex and conference centre. It was chosen for its position at the highest point of central Dublin.
Until 1922 it was the s ...
imitated his top-lit corridors. The British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
in Bloomsbury
Bloomsbury is a district in the West End of London. It is considered a fashionable residential area, and is the location of numerous cultural, intellectual, and educational institutions.
Bloomsbury is home of the British Museum, the largest ...
in London copied his colonnaded main entrance. His impact reached Washington, D.C., where Pearce's building, and in particular his octagonal House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
chamber, was studied as plans were made for the United States Capitol
The United States Capitol, often called The Capitol or the Capitol Building, is the seat of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, which is formally known as the United States Congress. It is located on Capitol Hill ...
building. While the shape of the chamber was not replicated, some of its decorative motifs were, with the ceiling structure in the Old Senate Chamber and old House of Representatives chamber (now the Statuary Hall) bearing a striking resemblance to Pearce's ceiling in the House of Commons.
The uniqueness of the building, the quality of its workmanship and its central location in College Green, across from Trinity College Dublin
, name_Latin = Collegium Sanctae et Individuae Trinitatis Reginae Elizabethae juxta Dublin
, motto = ''Perpetuis futuris temporibus duraturam'' (Latin)
, motto_lang = la
, motto_English = It will last i ...
, made it one of Dublin's most highly regarded structures.
Public ceremonies

 Much of the public ceremonies mirrored those of the British Houses of Parliament. Sessions were formally opened by a
Much of the public ceremonies mirrored those of the British Houses of Parliament. Sessions were formally opened by a Speech from the Throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened, outlining t ...
by the Lord Lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibilit ...
, who "used to sit, surrounded by more splendour than His Majesty on the throne of England". The Sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
's official representative, when he sat on the Throne
A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. "Throne" in an abstract sense can also refer to the mon ...
, sat beneath a canopy of crimson velvet.
As in the English and British parliaments, the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
was presided over by the Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
, who sat on the Woolsack, a large seat stuffed with wool, which was seen as a symbol of economic success and wealth. At the State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It includes a speech from the throne known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes plac ...
, Members were summoned from the nearby House of Commons chamber by White Rod
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, (as opposed to Black Rod
Black Rod (officially known as the Lady Usher of the Black Rod or, if male, the Gentleman Usher of the Black Rod) is an official in the parliaments of several Commonwealth countries. The position originates in the House of Lords of the Parlia ...
in Westminster).
In the Commons, business was presided over by the Speaker
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** In ...
, who in the absence of a government chosen from and answerable to the Commons was the dominant parliamentary figure. Speaker Conolly remains today one of the most widely known figures ever to be produced by an Irish parliament, for his role in Parliament and for the wealth that allowed him to build one of Ireland's greatest Georgian houses, Castletown House.
Sessions of parliament drew many of the wealthiest of Ireland's Anglo-Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the establis ...
Ascendancy to Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
, particularly as sessions often coincided with the Irish Social Season, running from January to 17 March ( St. Patrick's Day), when the Lord Lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibilit ...
presided in state over state balls and drawing rooms in the Viceregal Apartments in Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle ( ga, Caisleán Bhaile Átha Cliath) is a former Motte-and-bailey castle and current Irish government complex and conference centre. It was chosen for its position at the highest point of central Dublin.
Until 1922 it was the s ...
. Leading peers flocked to Dublin, where they lived in enormous and richly decorated townhouses, initially on the Northside
Northside or North Side may refer to:
Music
* Northside (band), a musical group from Manchester, England
* NorthSide, an American record label
* NorthSide Festival (Denmark), a music festival in Aarhus, Denmark
* " Norf Norf", a 2015 song by Vinc ...
of Dublin, later in new Georgian residences around Merrion Square
Merrion Square () is a Georgian garden square on the southside of Dublin city centre.
History
The square was laid out in 1752 by the estate of Viscount FitzWilliam and was largely complete by the beginning of the 19th century. The demand f ...
and Fitzwilliam Square. Their presence in Dublin, along with large numbers of servants, provided a regular boost to the city's economy.
The abolition of Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
in 1800 had a major economic impact. Within a decade, many of the finest mansions (including Leinster House
Leinster House ( ga, Teach Laighean) is the seat of the Oireachtas, the parliament of Ireland. Originally, it was the ducal palace of the Dukes of Leinster. Since 1922, it is a complex of buildings, of which the former ducal palace is the core ...
, Powerscourt House, and Aldborough House) had been sold, often to government agencies. Though Parliament itself was based on the exclusion of the vast Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland whose members are both Catholic and Irish. They have a large diaspora, which includes over 36 million American citizens and over 14 million British citizens (a quarter of the Briti ...
majority in Ireland, many nationalist historians and writers blamed the absence of Parliament for Dublin's increased impoverishment, with many of the large mansions in areas like Henrietta Street sold to property developers and landlords who reduced them to tenements.
The draw of the Viceregal Court and its social season was no longer enough to encourage most Irish peers and their entourages to come to Dublin. Their absence, with all their collective spending, severely damaged the Dublin economy, which went into dramatic decline. By the 1830s and 1840s, nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell
Daniel O'Connell (I) ( ga, Dónall Ó Conaill; 6 August 1775 – 15 May 1847), hailed in his time as The Liberator, was the acknowledged political leader of Ireland's Roman Catholic majority in the first half of the 19th century. His mobilizat ...
was leading demand for the Repeal of the Act of Union and the re-establishment of an Irish parliament in Dublin, only this time one to which Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
could be elected, in contrast with the earlier Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
-only assembly.
Abolition
In the last thirty years of the Irish parliament, a series of crises and reforms changed its role. In 1782, following agitation by major parliamentary figures, but most notably Henry Grattan, the severe restrictions such as Poynings' Law that effectively controlled the Irish Parliament's ability to control its own legislative agenda were removed, producing what was known as theConstitution of 1782
The Constitution of 1782 was a group of Acts passed by the Parliament of Ireland and the Parliament of Great Britain in 1782–83 which increased the legislative and judicial independence of the Kingdom of Ireland by reducing the ability of ...
. A little over a decade later, Roman Catholics, who were by far the demographic majority, were allowed to cast votes in elections to Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
, though they were still barred from office. The crisis over the "madness" of King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great B ...
produced a major strain in Anglo-Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the establis ...
relations, as the King's parliaments possessed the theoretical right to nominate a regent without the requirement that they choose the same person. However, they in fact chose The Prince of Wales, who served as The Prince Regent in both the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
and the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label= Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
.
The British Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
decided the entire relationship between Britain and Ireland should be changed, with the merger of both kingdoms and their parliaments. After one failed attempt, this finally was achieved, albeit with mass bribery of members of both Houses, who were awarded British and United Kingdom peerages and other "encouragements". In August 1800 Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
held its last session in the Irish Houses of Parliament. On 1January 1801, the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label= Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
and its Parliament officially ceased to exist, with the new United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
coming into being, with a united parliament meeting in Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
, to which Ireland sent approximately 100 members, while peers in the Peerage of Ireland
The Peerage of Ireland consists of those titles of nobility created by the English monarchs in their capacity as Lord or King of Ireland, or later by monarchs of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It is one of the five divisi ...
had the constant right to elect a number of fellow Irish peers as representative peer
In the United Kingdom, representative peers were those peers elected by the members of the Peerage of Scotland and the Peerage of Ireland to sit in the British House of Lords. Until 1999, all members of the Peerage of England held the right t ...
s to represent Ireland in the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
, on the model already introduced for Scottish peers.
After 1800: Bank
 Initially, the former Parliament House was used for a variety of purposes, including as a military garrison and as an art gallery. In 1803 the fledgling
Initially, the former Parliament House was used for a variety of purposes, including as a military garrison and as an art gallery. In 1803 the fledgling Bank of Ireland
Bank of Ireland Group plc ( ga, Banc na hÉireann) is a commercial bank operation in Ireland and one of the traditional Big Four Irish banks. Historically the premier banking organisation in Ireland, the Bank occupies a unique position in Iris ...
bought the building from the British Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
for £40,000 for use as its headquarters. As a result, the chamber was broken up to form small offices and by a magnificent cash office. Architect Francis Johnston (then the most prominent architect working in Ireland) was employed to oversee the conversion. However, the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ...
chamber survived almost unscathed. It was used as the bank's board room until the 1970s when the bank moved its headquarters. The chamber is now open to the public and is used for various public functions, including music recitals.
Continuing Symbolism
Some of the building's contents survived. Theceremonial mace
A ceremonial mace is a highly ornamented staff of metal or wood, carried before a sovereign or other high officials in civic ceremonies by a mace-bearer, intended to represent the official's authority. The mace, as used today, derives from the or ...
of the House of Commons remained in the family of the last Speaker of the House of Commons, John Foster, MP. The Bank of Ireland bought the Mace at a sale in Christie's
Christie's is a British auction house founded in 1766 by James Christie. Its main premises are on King Street, St James's in London, at Rockefeller Center in New York City and at Alexandra House in Hong Kong. It is owned by Groupe Artémi ...
in London in 1937. The Chair of the Speaker of the House of Commons is now in the possession of the Royal Dublin Society
The Royal Dublin Society (RDS) ( ga, Cumann Ríoga Bhaile Átha Cliath) is an Irish philanthropic organisation and members club which was founded as the 'Dublin Society' on 25 June 1731 with the aim to see Ireland thrive culturally and economi ...
, while a bench from the Commons is in the Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ga, Acadamh Ríoga na hÉireann), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the sciences, humanities and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier learned society and one its leading cultural ...
. Two original tapestries remain in the House of Lords. Designed by Dutch landscape painter William Van der Hagen, and woven by John Van Beaver, dating from circa 1733, the tapestries are unique. One represents the "Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ga, Cath na Bóinne ) was a battle in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II of England and Ireland, VII of Scotland, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and J ...
" and the other the " Defence of Londonderry". Each tapestry has five portrait and narrative medallions around the central scene that depict, narrate and name central characters and events in the battles. Both also have "trophies of arms and figures of Fame below enclosed by fringed curtains". The chandelier of the House of Commons now hangs in the Examination Hall of Trinity College Dublin
, name_Latin = Collegium Sanctae et Individuae Trinitatis Reginae Elizabethae juxta Dublin
, motto = ''Perpetuis futuris temporibus duraturam'' (Latin)
, motto_lang = la
, motto_English = It will last i ...
. The Woolsack, on which the Lord Chancellor of Ireland
The Lord High Chancellor of Ireland (commonly known as Lord Chancellor of Ireland) was the highest judicial office in Ireland until the establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922. From 1721 to 1801, it was also the highest political office of ...
sat when chairing sessions of the House of Lords, is now back on display in the chamber. Copies of debates of the old Irish Parliament are now kept in Leinster House
Leinster House ( ga, Teach Laighean) is the seat of the Oireachtas, the parliament of Ireland. Originally, it was the ducal palace of the Dukes of Leinster. Since 1922, it is a complex of buildings, of which the former ducal palace is the core ...
, keeping a direct link between the two eras.
Re-establishment of a Parliament in Dublin
From the 1830s underDaniel O'Connell
Daniel O'Connell (I) ( ga, Dónall Ó Conaill; 6 August 1775 – 15 May 1847), hailed in his time as The Liberator, was the acknowledged political leader of Ireland's Roman Catholic majority in the first half of the 19th century. His mobilizat ...
, generations of leaders campaigned for the creation of a new Irish parliament, convinced that the Act of Union had been a great mistake. While O'Connell campaigned for full-scale repeal, leaders like Isaac Butt and Charles Stewart Parnell
Charles Stewart Parnell (27 June 1846 – 6 October 1891) was an Irish nationalist politician who served as a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1875 to 1891, also acting as Leader of the Home Rule League from 1880 to 1882 and then Leader of t ...
sought a more modest form of Home Rule
Home rule is government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance wi ...
within the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, rather than an independent Irish state. Leaders from O'Connell to Parnell and later John Redmond
John Edward Redmond (1 September 1856 – 6 March 1918) was an Irish nationalist politician, barrister, and MP in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. He was best known as leader of the moderate Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP) from ...
spoke of the proud day on which an Irish parliament might once again meet in what they called '' Grattan's Parliament'' in College Green. When, in 1911, King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother ...
and his consort Queen Mary visited Dublin (where they attracted mass crowds), street sellers sold drawings of the King and Queen arriving in the not too distant future at the Old Houses of Parliament in College Green.
Their advocacy resulted in several legislative attempts to re-establish an Irish Parliament. The first attempt in 1886 did not pass the British House of Commons
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England.
The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 65 ...
, while the second in 1893 was blocked by the massive unionist majority in the British House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster ...
. Finally, the passage of the Parliament Act in 1911, which restricted the veto powers of the House of Lords, created space in 1914 for an Irish Home Rule Bill to pass both Houses, receive the Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in oth ...
and become law.
However, the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
injected what proved to be a fatal delay for Home Rule and in late April 1916, a small band of radical Republicans under Patrick Pearse staged the Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with t ...
, in which they seized a number of prominent Irish buildings, mainly in Dublin, and proclaimed an Irish Republic
The Irish Republic ( ga, Poblacht na hÉireann or ) was an unrecognised revolutionary state that declared its independence from the United Kingdom in January 1919. The Republic claimed jurisdiction over the whole island of Ireland, but by ...
. One building they did not take over was the old Parliament House. Perhaps they feared that, as a bank, it would be heavily protected. Perhaps, expecting that the Rising would ultimately fail and that the reaction to the Rising and what Pearse called their "blood sacrifice", rather than the Rising itself, would reawaken Irish nationalism and produce independence, they did not seek to use the building for fear that it, like the GPO, would be destroyed in the British counter-attack. Or perhaps, because of its association with a former Ascendancy parliament, it carried little symbolism for them. The rising eventually lead to the partitioning of Ireland and the establishment of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
, which was a British Dominion rather than a form of Home Rule.
The Dáil
In January 1919, Irish republican MPs elected in the 1918 general election assembled to form the First Dáil and issued a Unilateral Declaration of Independence. They chose the Round Room of the Mansion House, the official residence of theLord Mayor of Dublin
The Lord Mayor of Dublin ( ga, Ardmhéara Bhaile Átha Cliath) is the honorary title of the chairperson ( ga, Cathaoirleach, links=no ) of Dublin City Council which is the local government body for the city of Dublin, the capital of Ireland. Th ...
for their home. (The Round Room had more royal connections than the old Parliament House; it had been built for the visit of King George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten y ...
in 1821.)
It is highly unlikely that the Bank of Ireland
Bank of Ireland Group plc ( ga, Banc na hÉireann) is a commercial bank operation in Ireland and one of the traditional Big Four Irish banks. Historically the premier banking organisation in Ireland, the Bank occupies a unique position in Iris ...
, then with a largely Unionist board (some of whom were directly descended from members of the former Irish Parliament), would have supplied the building for such a use. The building was also a working bank and headquarters. In 1921 the British Government created a House of Commons of Southern Ireland through the Government of Ireland Act 1920 (also known as the Fourth Home Rule Act), though only four MPs (all unionists) assembled for the State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of a session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It includes a speech from the throne known as the King's (or Queen's) Speech. The event takes plac ...
by the Lord Lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibilit ...
, which was held in the Royal College of Science rather than the old Parliament House. Section 66 of the 1920 Act stated that once the Government of Southern Ireland had provided alternative accommodation for the bank and compensation for moving, the old Parliament House would become vested in "His Majesty for the use of the Parliament of Southern Ireland". However, the House of Commons of Southern Ireland failed to operate, no Government of Southern Ireland was ever formed, superseded by the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between ...
.
In 1922, when the Provisional Government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
under W. T. Cosgrave made its plans for independence, it gave little thought to the old Parliament House. In addition to dealing with the bank, it lacked room around it for additional buildings to be used for governmental purposes. Directly behind it, was a major street called Fleet Street. In front of it, at both the Lords and Commons entrances, were major thoroughfares, College Green and Westmoreland Street, leaving the only space for expansion on its Foster Place side, which also had little space for offices. Finally, in the Ireland of 1922 with a civil war raging, the building was not secure enough to be used as a modern-day parliament.
As a result, the Free State initially hired Leinster House from its then owner, the Royal Dublin Society
The Royal Dublin Society (RDS) ( ga, Cumann Ríoga Bhaile Átha Cliath) is an Irish philanthropic organisation and members club which was founded as the 'Dublin Society' on 25 June 1731 with the aim to see Ireland thrive culturally and economi ...
, in 1922, before buying it in 1924. Longer-term plans either to convert the Royal Hospital Kilmainham, into a national parliament, or to build a new parliament house, all fell through, leaving Leinster House as the accidental result.
Modern view

 The house is seen generally with affection by Dubliners. It was used as a symbol by generations of nationalist leaders from O'Connell to Parnell and Redmond in their own quest for Irish self-government. In a particular irony,
The house is seen generally with affection by Dubliners. It was used as a symbol by generations of nationalist leaders from O'Connell to Parnell and Redmond in their own quest for Irish self-government. In a particular irony, Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin ( , ; en, " eOurselves") is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active throughout both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The original Sinn Féin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur Gr ...
, which as a republican party fought for Irish independence during the Anglo-Irish War, was founded by a man, Arthur Griffith
Arthur Joseph Griffith ( ga, Art Seosamh Ó Gríobhtha; 31 March 1871 – 12 August 1922) was an Irish writer, newspaper editor and politician who founded the political party Sinn Féin. He led the Irish delegation at the negotiations that pro ...
, who sought to restore the King, Lords and Commons of Ireland and the 1782 constitution to the centre of Irish governance, and the College Green Houses of Parliament to its position as the home of an Irish parliament.
To this day some still lobby for the re-establishment of the College Green House of Parliament. In 2006, the Minister for Communications, Energy and Natural Resources, Eamon Ryan, met with Bank of Ireland's chief executive and chair to propose the building for an electronic library. In 2010, Minister of State
Minister of State is a title borne by politicians in certain countries governed under a parliamentary system. In some countries a Minister of State is a Junior Minister of government, who is assigned to assist a specific Cabinet Minister. I ...
, Seán Haughey
Seán Haughey (born 8 November 1961) is an Irish Fianna Fáil politician who has been a Teachta Dála (TD) for the Dublin Bay North constituency since 2016, and previously from 1992 to 2011 for the Dublin North-Central constituency. He serve ...
, proposed that the building be handed over to the state in return for the Irish state's bailout of the bank during the Irish banking crisis. Both suggestions were rejected by the bank.
Other suggestions included that the building be used to house the bank's former art collection, that it be used as an office for an elected Lord Mayor of Dublin
The Lord Mayor of Dublin ( ga, Ardmhéara Bhaile Átha Cliath) is the honorary title of the chairperson ( ga, Cathaoirleach, links=no ) of Dublin City Council which is the local government body for the city of Dublin, the capital of Ireland. Th ...
or that it house the Dáil or Seanad and act as a parliament building again. In 2011, Jimmy Deenihan
Jimmy Deenihan (born 11 September 1952) is an Irish former Fine Gael politician who served as Minister of State for the Diaspora from 2014 to 2016, Minister for Arts, Heritage and the Gaeltacht from 2011 to 2014 and Minister of State at the D ...
, Minister for Arts, Heritage and the Gaeltacht, wrote to the bank setting out proposals to acquire the building as a venue for the state to use as a cultural venue and requesting a meeting with the bank's Governor. TD Kevin Humphreys in 2012 also called for the bank to return the building to the state.
References and sources
Notes
Sources
* * * History of the Irish Parliament 1692–1800 by E.M. Johnston-Liik (Ulster Historical Foundation, 2002) * Volume 2 of "The Unreformed House of Commons" by Edward and Annie G. Porritt (Cambridge University Press, 1903)External links
{{Authority control 1789 establishments in Ireland Buildings and structures in Dublin (city) Government buildings completed in 1789 Government buildings in the Republic of Ireland Legislative buildings in Europe Parliament of Ireland Seats of national legislatures Edward Lovett Pearce buildings