International recognition of Artsakh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The political status of Nagorno-Karabakh has remained unresolved since
The political status of Nagorno-Karabakh has remained unresolved since
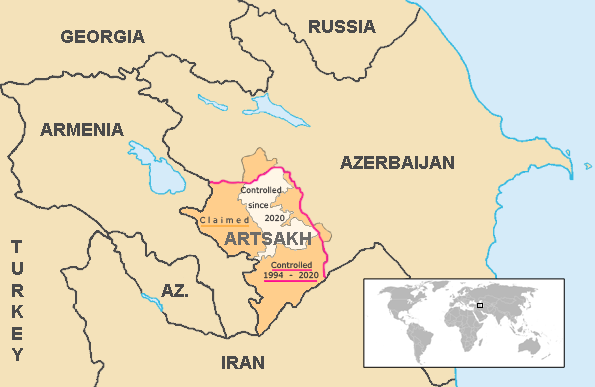 The sovereign status of the
The sovereign status of the
The conflict over the Nagorno-Karabakh region dealt with by the OSCE Minsk Conference
,
The conflict over the Nagorno-Karabakh region dealt with by the OSCE Minsk Conference
,
 Before California recognized Nagorno-Karabakh in May 2014, three places within the state had already recognized it:
*
Before California recognized Nagorno-Karabakh in May 2014, three places within the state had already recognized it:
*
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
's recognition as an independent state in 1991. During the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, it had been an ethnic Armenian autonomous oblast of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic
Azerbaijan ( az, Азәрбајҹан, Azərbaycan, italics=no), officially the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (Azerbaijan SSR; az, Азәрбајҹан Совет Сосиалист Республикасы, Azərbaycan Sovet Sosialist R ...
; however, the disintegration of the USSR was accompanied by the conflict between local Armenians who sought to join Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is m ...
to Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
, and local Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most nume ...
who opposed this. The conflict soon boiled over into open warfare in the First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War, referred to in Armenia as the Artsakh Liberation War ( hy, Արցախյան ազատամարտ, Artsakhyan azatamart) was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 t ...
and ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
, as a result of which Nagorno-Karabakh - as well as 7 surrounding regions of Azerbaijan - came to be occupied by an Armenia-allied de facto state, the Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
. Negotiations took place sporadically over the following decades, during which a ceasefire generally prevailed between Armenia / Artsakh and Azerbaijan (albeit without peacekeeping
Peacekeeping comprises activities intended to create conditions that favour lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as reduces the risk of renewed warfare.
Within the United ...
forces). Turkey and Azerbaijan closed their borders to Armenia and Artsakh, and took other diplomatic steps to isolate them. Meanwhile, the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, ...
, OSCE Minsk Group
The OSCE Minsk Group was created in 1992 by the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), now Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), to encourage a peaceful, negotiated resolution to the conflict between Az ...
, and other bodies made various statements and proposed dialogue initiatives; none of them successful. In the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved conflict over the region, involving Azerba ...
, Azerbaijani forces, backed by Turkey, entered the Artsakh-held territories and retook the southern half of the region, including Shusha
/ hy, Շուշի
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = ShushaCollection2021.jpg
, image_caption = Landmarks of Shusha, from top left:Ghazanchetsots Cathedral • Yukhari Govha ...
. Armenia was forced to concede additional territories in order to preserve Stepanakert and the northern half of the Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
under local Armenian control (and protected by Russian peacekeepers). The political status of this reduced region was not specified in the agreement, and remains unresolved.
Political ties with Armenia
In the case of Chiragov and others v. Armenia, theEuropean Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR or ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights. The court hears applications alleging that ...
decided that "the Republic of Armenia, from the early days of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, has had a significant and decisive influence over the “NKR”, that the two entities are highly integrated in virtually all important matters and that this situation persists to this day."
According to Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
, "from the beginning of the Karabakh conflict, Armenia provided aid, weapons, and volunteers. Armenian involvement in Karabakh escalated after a December 1993 Azerbaijani offensive. The Republic of Armenia began sending conscripts and regular Army and Interior Ministry troops to fight in Karabakh."
Positions and statements
 The sovereign status of the
The sovereign status of the Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
is not recognized by any United Nations member state (including Armenia), but has been recognized by Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
, Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which ...
and South Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated populat ...
; Transnistria is not recognized by any UN member state, while the latter two have international recognition from several UN member states. Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
is currently in an ongoing negotiation with Artsakh, where the end goal is either Artsakh independence recognition or Artsakh integration with Armenia, whatever the people of Artsakh would prefer. Three UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
Resolutions (853
__NOTOC__
Year 853 ( DCCCLIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Byzantine Empire
* May 22 – A Byzantine fleet (85 ships and 5,000 men) sacks and d ...
, 874, and 884
__NOTOC__
Year 884 ( DCCCLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* March 1 – Diego Rodríguez Porcelos, count of Castile, founds and repo ...
) and United Nations General Assembly resolution
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
General Assembly resolutions usually require a simple majority (50 percent of all votes plus ...
s 49/13 and 57/298 refer to Nagorno-Karabakh as a region of Azerbaijan. None of these resolutions were passed under Chapter VII (Action with Respect to Threats to the Peace, Breaches of the Peace, and Acts of Aggression) of the Charter. Certain politicians and legal scholars have expressed the view that resolutions are only legally binding if they are made under Chapter VII of the Charter. However, it does not mean that binding force of the UN Security Council Resolutions (822, 853, 874, and 884) is called into question.The language of these four Resolutions indicates that they are "not mere recommendations or exhortations, but legally binding decisions." According to a report prepared by British parliamentarian and rapporteur David Atkinson, presented to Political Affairs Committee of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) is the parliamentary arm of the Council of Europe, a 46-nation international organisation dedicated to upholding human rights, democracy and the rule of law.
The Assembly is made up ...
(PACE), "the borders of Azerbaijan were internationally recognised at the time of the country being recognised as independent state in 1991," and "the territory of Azerbaijan included the Nagorno-Karabakh region."Mr David Atkinson, United Kingdom, European Democrat Group, (RapporteurThe conflict over the Nagorno-Karabakh region dealt with by the OSCE Minsk Conference
,
Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) is the parliamentary arm of the Council of Europe, a 46-nation international organisation dedicated to upholding human rights, democracy and the rule of law.
The Assembly is made up ...
, 29 November 2004
The Resolution #1416, adopted by PACE in 2005, stated that "Considerable parts of the territory of Azerbaijan are still occupied by Armenian forces, still in control of the Nagorno-Karabakh region." The resolution further stated: "The Assembly reiterates that the occupation of foreign territory by a member state constitutes a grave violation of that state’s obligations as a member of the Council of Europe and reaffirms the right of displaced persons from the area of conflict to return to their homes safely and with dignity." Recalling the Resolutions 822, 853
__NOTOC__
Year 853 ( DCCCLIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Byzantine Empire
* May 22 – A Byzantine fleet (85 ships and 5,000 men) sacks and d ...
, 874, and 884
__NOTOC__
Year 884 ( DCCCLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place Europe
* March 1 – Diego Rodríguez Porcelos, count of Castile, founds and repo ...
(all 1993) of the UN Security Council, PACE urged "the parties concerned to comply with them, in particular by refraining from any armed hostilities and by withdrawing military forces from any occupied territories." The resolution also called on "the Government of Azerbaijan to establish contact, without preconditions, with the political representatives of both communities from the Nagorno-Karabakh region regarding the future status of the region."
The Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
called on the Nagorno-Karabakh de facto authorities to refrain from staging one-sided "local self-government elections" in Nagorno-Karabakh. "These so-called 'elections' cannot be legitimate," stressed Council of Europe Committee of Ministers' Chairman and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German language, German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constit ...
Foreign Minister Ernst Walch, Parliamentary Assembly President Lord Russell-Johnston
David Russell Russell-Johnston, Baron Russell-Johnston (born David Russell Johnston; 28 July 1932 – 27 July 2008), usually known as Russell Johnston, was a leading Scottish Liberal Democrat politician and was the Leader of the Scottish Libera ...
and Secretary General Walter Schwimmer
Walter Schwimmer (born 16 June 1942, Vienna) is a former politician and diplomat from Austria. Was Secretary General of the Council of Europe from September 1, 1999, to August 31, 2004.
Life
After being a member of the Austrian Parliament (Nation ...
. They recalled that following the 1991–1994 armed conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan, a substantial part of the region's population was forced to flee their homes and are still living as displaced person
Forced displacement (also forced migration) is an involuntary or coerced movement of a person or people away from their home or home region. The UNHCR defines 'forced displacement' as follows: displaced "as a result of persecution, conflict, g ...
s in those countries or as refugees abroad. This position was reiterated by Walter Schwimmer, Secretary General of the Council of Europe on 4 August 2004 with regard to the next elections, staged in the province, and by the Chair of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
’s Committee of Ministers
The Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe ( French: ''Comité des ministres du Conseil de l'Europe'') or Committee of Ministers ( French: ''Comité des ministres'') is the Council of Europe's decision-making body. It comprises the Forei ...
on 12 July 2007 with regard to the presidential elections organised in Nagorno-Karabakh. On 21 May 2010 Catherine Ashton
Catherine Margaret Ashton, Baroness Ashton of Upholland, (born 20 March 1956), is a Labour Party (UK), British Labour politician who served as the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and Vice-President of ...
, High Representative of the European Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy
The High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy (HR/VP) is the chief co-ordinator and representative of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) within the European Union (EU). The position is currently held b ...
, stated: "I would like to recall that the European Union does not recognise the constitutional and legal framework within which the "parliamentary elections" in Nagorno Karabakh will be held this Sunday. This event should not prejudice the peaceful settlement of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict". OSCE Minsk Group
The OSCE Minsk Group was created in 1992 by the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), now Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), to encourage a peaceful, negotiated resolution to the conflict between Az ...
Co-Chairs stated that "Although the Co-Chairs understand the need for the de facto authorities in NK to try to organize democratically the public life of their population with such a procedure, they underscore again that Nagorno-Karabakh is not recognized as an independent and sovereign state by any of their three countries, nor by any other country, including Armenia. The Co-Chairs consider that this procedure should not preempt the determination of the final legal status of Nagorno-Karabakh in the broader framework of the peaceful settlement of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict".
In January 2016, the PACE adopted the Resolution #2085 entitled "Inhabitants of frontier regions of Azerbaijan are deliberately deprived of water" which stated that "the occupation by Armenia of Nagorno-Karabakh and other adjacent areas of Azerbaijan creates similar humanitarian and environmental problems for the citizens of Azerbaijan living in the Lower Karabakh valley". The resolution also requested "the immediate withdrawal of Armenian armed forces from the region" and "the Armenian authorities to cease using water resources as tools of political influence or an
instrument of pressure".
The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
declared that "The European Union confirms its support for the territorial integrity of Azerbaijan, and recalls that it does not recognise the independence of Nagorno Karabakh. The European Union cannot consider legitimate the 'presidential elections' that were scheduled to take place on 11 August 2002 in Nagorno Karabakh". The European Union reiterated this position with regard to the presidential elections, held in the region in 2007.
The US Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other nat ...
's annual Country Reports on Human Rights Practices Country Reports on Human Rights Practices are annual publications on the human rights conditions in countries and regions outside the United States, mandated by U.S. law to be submitted annually by the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor
...
– 2006, released on 6 March 2007 stated that "Armenia continues to occupy the Azerbaijani territory of Nagorno-Karabakh and seven surrounding Azerbaijani territories. During the year incidents along the militarized line of contact separating the sides again resulted in numerous casualties on both sides".
A background paper prepared by the Directorate General of Political Affairs of the Council of Europe for the seminar "Youth and Conflict Resolution" (Strasbourg, 31 March – 2 April 2003) states, "The Armenian side maintains that the N-K independence referendum was conducted in accordance with the USSR law on the 'Procedure for Solving Issues of Secession of a Soviet Republic from the USSR' of 3 April 1990. Article 3 of this law provided autonomous regions within the Soviet republics with the right to determine independently, by referendum, whether they wished to remain within the USSR or join the republic seceding from the USSR. It would however seem that according to this law N-K would have the choice of two options – to remain within the USSR or to join independent Azerbaijan; N-K independence does not seem possible".Mr David Atkinson, United Kingdom, European Democrat Group, (RapporteurThe conflict over the Nagorno-Karabakh region dealt with by the OSCE Minsk Conference
,
Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) is the parliamentary arm of the Council of Europe, a 46-nation international organisation dedicated to upholding human rights, democracy and the rule of law.
The Assembly is made up ...
, 29 November 2004. See the section: AS/POL (2004) 24 Appendix IV 8 September 2004: subsection "The legal side of the dispute"
According to the article in "The Journal of Conflict Resolution", the Armenian side "justified its claim by Article 70 of the Soviet Constitution, which affirms the right to self-determination of the peoples of the USSR. In fact, this recognition of the principle of self-determination is only part of a general declaratory statement about the nature of the Soviet federation: “The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics is an integral, federal, multi-national state formed on the principle of socialist federalism as a result of the free self-determination of nations and the voluntary association of equal Soviet Socialist Republics. The USSR embodies the state unity of the Soviet people and draws all its nations and nationalities together for the purpose of jointly building communism.” There is no mechanism, other than the right of the union republics to secede (Article 72 of the constitution), through which to express the right of self-determination".
The actual declaration of establishment of the Nagorno Karabakh Republic
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
, issued on 2 September 1991, states that the republic is proclaimed pursuant to the USSR law of secession, and that it "enjoys the authorities given to Republics by the USSR Constitution and legislation and reserves the right to decide independently the issue of its state-legal status based on political consultations and negotiations with the leadership of Union and Republics." The Declaration further states that "the USSR Constitution and legislation, as well as other laws currently in force, which do not contradict the goals and principles of this Declaration and peculiarities of the Republic apply on the territory of the Nagorno Karabakh Republic, until the NKR Constitution and laws are adopted."
However, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Azerbaijan states that "according to this Law, in a Union republic containing autonomous republics, autonomous provinces and autonomous regions, the referendum had to be held separately in each autonomous unit, the people of which retained the right to decide independently the question of staying in the USSR or in the seceding Union republic, as well as to raise the question of their own state-legal status. It is important to emphasize that the secession of a Union republic from the USSR could be regarded valid only after the fulfillment of complicated and multi-staged procedure and, finally, the adoption of the relevant decision by the Congress of the USSR People's Deputies. However, until the Soviet Union ceased to exist as international person, the mentioned Law was without legal effect, since no Union republic, including Azerbaijan and Armenia, had used the procedure for secession stipulated in it".
The OSCE Minsk Group
The OSCE Minsk Group was created in 1992 by the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), now Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), to encourage a peaceful, negotiated resolution to the conflict between Az ...
has allowed the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (referring to it as the "leadership of Nagorny Karabakh"), as well as Armenia and Azerbaijan, to participate in the peace process as "parties to the conflict," and the Azerbaijani community of the region – as an "interested party". The Chairman of the CSCE Minsk Conference mentioned that "the terms 'party to the conflict' and 'leadership of Nagorny Karabakh' do not imply recognition of any diplomatic or political status under domestic or international law". The Azerbaijani community is led by Tural Ganjaliyev, the head of the executive power of Shusha region.
At a 2007 press conference in Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and i ...
, Yuri Merzlyakov
Yuri Nikolayevich Merzlyakov (russian: Юрий Николаевич Мерзляков; born 9 April 1949) is a Russian diplomat, who was one of the 3 co-chairmen of the OSCE Minsk Group.
Yuri Merzlyakov graduated from MGIMO in 1971 and Diploma ...
, the OSCE Minsk Group Russian Co-Chair stated, "At the press conference in Baku, I underlined that Nagorno Karabakh was a part of Azerbaijani SSR and not of Azerbaijan. I perfectly know that till 1917 Nagorno Karabakh was a part of the Russian Empire. The history is necessary in order to settle conflicts, but it is necessary to proceed from international law". Meanwhile, on 10 June 2007 after US-Azerbaijani security consultations in Washington D.C. with Azerbaijani Deputy Foreign Minister Araz Azimov
, image = File:Araz Azimov February 2016 (24932626176).jpg
, order =
, title = Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs of Azerbaijan
, term_start = 1994
, predecessor =
, president ...
, Deputy Assistant Secretary of US Department of State, US Co-Chairman of OSCE Minsk group Matthew Bryza
Matthew James Bryza (born February 16, 1964) is a former United States diplomat. His last post in the United States foreign service was the United States Ambassador to Azerbaijan.
Education
Bryza graduated from Stanford University with a Bache ...
in a joint press conference announced: "In the circles of international law there is no universal formula for the supremacy of territorial integrity over the right of self-determination of people.".
On 14 March 2008, the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
passed a non-binding resolution by a vote of 39 to 7, with 100 abstentions, reaffirming Azerbaijan's territorial integrity, expressing support for that country's internationally recognized borders and demanding the immediate withdrawal of all Armenian forces from all occupied territories there. The resolution was supported mainly by members of the OIC and GUAM
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, both of which Azerbaijan is a member, as well as other nations facing breakaway regions. The resolution was opposed by all three co-chairs of the OSCE Minsk Group.
Armenia
Armenia does not officially recognize the sovereign status of Artsakh. Armenia's government has stated that it would unilaterally recognize Artsakh only as an option of last resort to be used only if Azerbaijan resorted to military activity. In 2010, President Armen Sarkissian said "We wanted for Artsakh’s independence to be recognized as a result of the negotiations, and only after that Armenia would recognize it. At the same time, if the war goes on and there is no chance for the negotiations to resume, Armenia will most probably will have no choice but to recognize rtsakh..We believe that there is no military solution to this problem." When the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War started, Prime Minister Pashinyan stated that the Armenian government was considering unilaterally recognizing the independence of Nagorno-Karabach. Responding to instances where Armenian farmers in Nagorno-Karabakh were killed or shot by Azerbaijani forces, Pashinyan tweeted “Azerbaijan calls Armenians of Nagorno-Karabakh ‘our citizens’ and, at the same time, shoots at them while they are doing agricultural work."Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan does not officially recognize the sovereign status of Artsakh; however, in a 2016 interview, current Azerbaijani President Aliyev referred to “an autonomous republic” of Nagorno-Karabakh. This was the first time that an Azerbaijani leader had used the word "republic" to refer to the Armenian-controlled enclave. The U.S. Co-Chair of the OSCE Minsk Group praised these remarks as move to open "discussions on status."European Parliament
On 20 May 2010, theEuropean Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the Legislature, legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven Institutions of the European Union, institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and in ...
adopted a resolution "on the need for an EU strategy for the South Caucasus", which states that EU must pursue a strategy to promote stability, prosperity and conflict resolution in the South Caucasus. The resolution "calls on the parties to intensify their peace talk efforts for the purpose of a settlement in the coming months, to show a more constructive attitude and to abandon preferences to perpetuate the status quo created by force and with no international legitimacy, creating in this way instability and prolonging the suffering of the war-affected populations; condemns the idea of a military solution and the heavy consequences of military force already used, and calls on both parties to avoid any further breaches of the 1994 ceasefire". The resolution also calls for withdrawal of Armenian forces from all occupied territories of Azerbaijan, accompanied by deployment of international forces to be organised with respect of the UN Charter in order to provide the necessary security guarantees in a period of transition, which will ensure the security of the population of Nagorno-Karabakh and allow the displaced persons to return to their homes and further conflicts caused by homelessness to be prevented; and states that the EU believes that the position according to which Nagorno-Karabakh includes all occupied Azerbaijani lands surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh should rapidly be abandoned. It also notes "that an interim status for Nagorno-Karabakh could offer a solution until the final status is determined and that it could create a transitional framework for peaceful coexistence and cooperation of Armenian and Azerbaijani populations in the region."
In October 2013, the European Parliament adopted the Resolution on the European Neighbourhood Policy in which it is stated that the occupation by one country of the Eastern Partnership (which includes Armenia and Azerbaijan) of the territory of another "violates the fundamental principles and objectives of the Eastern Partnership and that the resolution of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict should comply with UN Security Council resolutions 822, 853, 874 and 884 of 1993 and the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) Minsk Group Basic Principles, enshrined in the L’Aquila joint statement of 10 July 2009". This same document also states that "Parliament fully subscribes to the principles of sovereignty, territorial integrity and the right to self-determination of nations;"
On 15 November 2017, the European Parliament adopted a resolution "reaffirming its support to the OSCE Minsk Group co-chairs' efforts to solve the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict and to their 2009 Basic Principles, which include territorial integrity, self-determination and the non-use of force".
OSCE Minsk Group
On 26 June 2010, the presidents of the OSCE Minsk Group's Co-Chair countries, France, the Russian Federation, and the United States of America made a joint statement, reaffirming their "commitment to support the leaders of Armenia and Azerbaijan as they finalize the Basic Principles for the peaceful settlement of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict".Independence recognition efforts
Non-UN member states
U.S. states and communities
Fresno County
Fresno County (), officially the County of Fresno, is a county located in the central portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 1,008,654. The county seat is Fresno, the fifth-most populous city in Cali ...
(April 2013)
* Highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
(November 2013)
* Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world ...
(January 2014)
In addition, Highland is twinned with Lachin
Lachin ( az, Laçın, , ; hy, Բերձոր, translit=Berdzor; ku, Laçîn) is a town in Azerbaijan and the administrative center of the Lachin District. It is located within the strategic Lachin corridor, which links the disputed region of N ...
and Montebello is twinned with Stepanakert.Wright, Pam. "Montebello's newest Sister City program has come under fire from an ambassador for the Republic of Azerbaijan." ''Whittier Daily News
The ''Whittier Daily News'' is a paid local daily newspaper for Whittier, California, United States. Coverage area includes Whittier, South Whittier, Pico Rivera, La Habra Heights, Santa Fe Springs and La Mirada. The ''Whittier Daily News'' i ...
''. November 19, 2005.
On 20 April 2016, the city of Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
, Hawaii recognized Artsakh. On 21 September 2016, the city of Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Colorado recognized the independence of Artsakh.
In 2020, the Artsakh Republic was recognized by:
* Fitchburg, Massachusetts
Fitchburg is a city in northern Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The third-largest city in the county, its population was 41,946 at the 2020 census. Fitchburg is home to Fitchburg State University as well as 17 public and private e ...
* Fort Lee Borough
* Glendale, California
Glendale is a city in the San Fernando Valley and Verdugo Mountains regions of Los Angeles County, California, United States. At the 2020 U.S. Census the population was 196,543, up from 191,719 at the 2010 census, making it the fourth-larges ...
* Fowler
* Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Englewood Cliffs is a borough in Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey, whose population at the 2010 United States census was 5,281.Clark County, Nevada
Clark County is located in the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,265,461. Most of the county population resides in the Las Vegas Census County Divisions, which hold 1,771,945 people as of the 2010 Census, acros ...
* Ridgefield, New Jersey
}
Ridgefield is a borough in Bergen County, New Jersey, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough's population was 11,032,Cliffside Park, New Jersey
* Orange County
In 2021, the Artsakh Republic was recognized by:
*
 Independence of Artsakh is recognized by the cities of Alfortville,
Independence of Artsakh is recognized by the cities of Alfortville,
Government of the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
*
Twin Falls, Idaho
Twin Falls is the county seat and largest city of Twin Falls County, Idaho, United States. The city had a population of 51,807 as of the 2020 census. In the Magic Valley region, Twin Falls is the largest city in a radius, and is the regiona ...
* West Hollywood
West Hollywood is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. Incorporated in 1984, it is home to the Sunset Strip. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, its population was 35,757. It is considered one of the most prominent gay villages ...
* Burbank, California
Burbank is a city in the southeastern end of the San Fernando Valley in Los Angeles County, California, United States. Located northwest of downtown Los Angeles, Burbank has a population of 107,337. The city was named after David Burbank, who ...
* Oxford, Ohio
Oxford is a city in Butler County, Ohio, United States. The population was 23,035 at the 2020 census. A college town, Oxford was founded as a home for Miami University and lies in the southwestern portion of the state approximately northwest ...
* Rancho Cordova, California
Rancho Cordova is a city in Sacramento County, California, United States which was incorporated in 2003. It is part of the Sacramento Metropolitan Area. The population was 64,776 at the 2010 census. In 2010 and 2019, Rancho Cordova was named ...
Australia
In October 2012, theAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
n state of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
recognized Nagorno-Karabakh however, the Australian Foreign Minister
A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between co ...
reaffirmed in November 2015 that the federal government of the Commonwealth of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
does not, and supports Azerbaijan's claim to the state. In 2017, The Australian Greens
The Australian Greens, commonly known as The Greens, are a confederation of Green state and territory political parties in Australia. As of the 2022 federal election, the Greens are the third largest political party in Australia by vote and t ...
announced that they recognize the Republic of Artsakh (Nagorno-Karabakh).
In October 2020, the New South Wales Legislative Assembly
The New South Wales Legislative Assembly is the lower of the two houses of the Parliament of New South Wales, an Australian state. The upper house is the New South Wales Legislative Council. Both the Assembly and Council sit at Parliament Ho ...
recognized Artsakh. On 9 November 2020, the city of Willoughby recognized the independence of Artsakh.
In February 2021, the state of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh.
Canada
Following the outbreak of the2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of an unresolved conflict over the region, involving Azerba ...
, Senator Leo Housakos called for a motion for Canada to recognize Nagorno-Karabakh as an independent country.
On 5 November 2020, the city of Laval in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh.
On 8 December 2020, the Senate of Canada
The Senate of Canada (french: region=CA, Sénat du Canada) is the upper house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the House of Commons, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada.
The Senate is modelled after the ...
rejected a motion on "condemning the Azerbaijani-Turkish aggression" and recognizing the independence of Artsakh.
Czech Republic
On 27 October 2020, the municipal district of Řeporyje,Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh.
France
 Independence of Artsakh is recognized by the cities of Alfortville,
Independence of Artsakh is recognized by the cities of Alfortville, Limonest
Limonest () is a commune in the Metropolis of Lyon in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in eastern France.
Geography
Limonest is located northwest of Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the ...
, and Vienne. A Bill on recognition of the Artsakh Republic was submitted to the French National Assembly
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are kn ...
on 14 October 2020.
On 6 November 2020, the Assembly of Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
adopted a resolution on the recognition of the Artsakh Republic.
On 18 November 2020, the Council of Paris
The Council of Paris (French: ''Conseil de Paris'') is the deliberative body responsible for governing Paris, the capital of France. It possesses both the powers of a municipal council (''conseil municipal'') and those of a departmental counci ...
, the legislative body governing Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, recognized the independence of Artsakh and called on the French government to follow.
On 21 November 2020, the city council of Saint-Étienne
Saint-Étienne (; frp, Sant-Etiève; oc, Sant Estève, ) is a city and the prefecture of the Loire department in eastern-central France, in the Massif Central, southwest of Lyon in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region.
Saint-Étienne is the ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh, while on the same date, the Aix-Marseille-Provence Metropolis
The Aix-Marseille-Provence Metropolis (french: métropole d'Aix-Marseille-Provence) is the ''métropole'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the cities of Marseille and Aix-en-Provence. It is located in the Bouches-du-Rhône, Var and Vauclu ...
called for the French government to recognize Artsakh. On 24 November 2020, the city of Décines-Charpieu and the Grenoble-Alpes Métropole both called for the recognition of Artsakh by the French government.
On 25 November 2020, the French Senate
The Senate (french: Sénat, ) is the upper house of the French Parliament, with the lower house being the National Assembly, the two houses constituting the legislature of France. The French Senate is made up of 348 senators (''sénateurs'' a ...
adopted a resolution calling for recognition of the independence of Artsakh. However, following the resolution adopted by France's Senate, a French Foreign Ministry spokesperson stated “France does not recognize the self-proclaimed Nagorno-Karabakh Republic.”
On 1 December 2020, the Asnières-sur-Seine
Asnières-sur-Seine () is a commune in the Hauts-de-Seine department and Île-de-France region of north-central France. It lies on the left bank of the river Seine, some eight kilometres from the centre of Paris in the north-western suburbs of ...
and Métropole Nice Côte d'Azur
Métropole Nice Côte d'Azur is the ''métropole'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the city of Nice. It is located in the Alpes-Maritimes department, in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, southeastern France. It was created in Decem ...
municipal council's called on the French Government to recognize Artsakh.
On 3 December 2020, the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the r ...
of France adopted a resolution urging the French Government to recognize Artsakh.
Between 17 and 21 December 2020, the commune of Issy-les-Moulineaux
Issy-les-Moulineaux () is a commune in the southwestern suburban area of Paris, France, lying on the left bank of the river Seine. Its citizens are called ''Isséens'' in French. It is one of Paris' entrances and is located from Notre-Dame Cat ...
, the department of Hauts-de-Seine
Hauts-de-Seine (; ) is a département in the Île-de-France region, Northern France. It covers Paris's western inner suburbs. It is bordered by Paris, Seine-Saint-Denis and Val-de-Marne to the east, Val-d'Oise to the north, Yvelines to the west ...
, and the cities of Sarcelles, Clamart
Clamart () is a commune in the southwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the centre of Paris.
The town is divided into two parts, separated by a forest: ''bas Clamart'', the historical centre, and ''petit Clamart'' with urbani ...
, and Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
adopted resolutions calling for the recognition of Artsakh. Meanwhile, the city of Valence recognized Artsakh's independence.
Guatemala
The City Hall ofSayaxché
Sayaxché () is a municipality in the El Petén department of Guatemala, on the Río La Pasión river. It covers an area of , and had 55,578 inhabitants at the 2002 Census; the latest official estimate (as at mid-2012) was 114,781 inhabitants.
Th ...
, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
has officially recognized the right to self-determination of the Armenians of Artsakh and is supporting the creation of a free and sovereign state.
Italy
On 15 October 2020, theItalian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
city of Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
became the first ever large European city to recognize the Republic of Artsakh. Recognitions by Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its ...
, Asolo
Asolo () is a town and '' comune'' in the Veneto Region of northern Italy. It is known as "The Pearl of the province of Treviso", and also as "The City of a Hundred Horizons" for its mountain settings.
History
The town was originally a settlem ...
, Cerchiara di Calabria
Cerchiara di Calabria is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Cosenza, part of the Calabria region of southern Italy.
Located in the Pollino National Park, Cercharia occupies the ancient site of ''Arponium'' in Magna Graecia, later known a ...
, and the Italian region of Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
followed within a fortnight. On 4 November 2020, the city of Campobasso
Campobasso (, ; nap, label= Campobassan, Cambuàsce ) is a city and '' comune'' in southern Italy, the capital of the region of Molise and of the province of Campobasso. It is located in the high basin of the Biferno river, surrounded by ...
recognized Artsakh. The following day, similar motions recognizing Artsakh was passed by the municipalities of Bleggio Superiore
Bleggio Superiore (''Blécc de Sóra'' in local dialect) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in Trentino in the northern Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about west of Trento.
Bleggio Superiore borders the following municipali ...
and Drena
Drena (''Dréna'' in local dialect) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in Trentino in the northern Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about southwest of Trento. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 476 and an area of .Al ...
.
On 18 November 2020, the city of Viareggio
Viareggio () is a city and ''comune'' in northern Tuscany, Italy, on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea. With a population of over 62,000, it is the second largest city within the province of Lucca, after Lucca.
It is known as a seaside resort as ...
recognized Artsakh's independence. On 19 November 2020, Aprilia
Aprilia is an Italian motorcycle manufacturer founded immediately after World War II in Noale, Italy, by Alberto Beggio. The company started as a manufacturer of bicycles and moved on to manufacture scooters and small-capacity motorcycles ...
and Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the ci ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh. On 25 November 2020, the city of Schio
Schio is a town and comune in the province of Vicenza (region of Veneto, northern Italy) situated north of Vicenza and east of the Lake Garda. It is surrounded by the Little Dolomites (Italian Prealps) and Mount Pasubio.
History
Its name comes ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh.
On 26 November 2020, the municipality of San Giorgio di Nogaro
San Giorgio di Nogaro ( fur, Sant Zorç di Noiâr, Central Eastern Friulian: ''San Zorz'') is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Udine in the Italian region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, located about northwest of Trieste and about south of ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh. On 2 December 2020, the municipality of Malo announced its recognition of Artsakh, followed by the towns of Ariccia
Ariccia (Latin: ''Aricia'') is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Rome, central Italy, southeast of Rome. It is in the Alban Hills of the Lazio (Latium) region and could be considered an extension of Rome's southeastern suburbs. One ...
on 11 December 2020 and San Pietro Vernotico on 31 December 2020.
On 2 April 2021, the municipality of San Vito dei Normanni recognized the independence of Artsakh.
On 26 May 2021, the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria
Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria ( it, Città metropolitana di Reggio Calabria) is an area of local government at the level of metropolitan city in the Calabria region of the Republic of Italy. It comprises the territory of the city of Reg ...
also recognized the Republic of Artsakh.
Spain
In September 2014, the Basque parliament adopted a motion supporting Nagorno-Karabakh's right to self-determination. On 22 October 2020, the Parliament ofCatalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
adopted a motion supporting the Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire and the recognition of the Artsakh Republic.
On 30 October 2020, the Catalan city of Amposta
Amposta () is the capital of the '' comarca'' of Montsià, in the province of Tarragona, Catalonia, Spain, 190 km south of Barcelona on the Mediterranean Coast. It is located at 8 metres above sea level, on the Ebre river, not far from its ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh.
On 6 November 2020, the city of Berga
Berga () is the capital of the ''comarca'' (county) of Berguedà, in the province of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is bordered by the municipalities of Cercs, Olvan, Avià, Capolat and Castellar del Riu.
History
Berga derives its name ...
in Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
recognized the independence of Artsakh. On 21 December 2020, Santa Pau
Santa Pau is a village and municipality in the province of Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The cit ...
recognized the sovereignty of Artsakh.
United Kingdom
On 25 November 2020, theDerby City Council
Derby City Council is the local government unitary authority for Derby, a city in the East Midlands region of England. It comprises 51 councillors, three for each of the 17 electoral wards of Derby. Currently there is no overall control of the co ...
unanimously passed a resolution to recognize the independence of the Republic of Artsakh. The city of Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby g ...
thus becoming the first city in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
to adopt such a resolution.
Uruguay
On 13 November 2020, the legislature ofUruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
's Montevideo Department
Montevideo () is a department (''departamento'') of Uruguay.
It is by far the smallest department in area, but also by far the most populated. Its capital is the city of Montevideo, which is also the national capital. While most of the departmen ...
unanimously recognized the independence of the Republic of Artsakh.
See also
*Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh
The Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh were areas of Azerbaijan, situated outside the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO), which were occupied by the ethnic Armenian military forces of the breakaway Republ ...
* Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations
The Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations (russian: Сообщество за демократию и права народов), also commonly and colloquially known as the Commonwealth of Unrecognized States, rarely as CIS-2 (), is a ...
* Foreign relations of Artsakh
The Republic of Artsakh is a republic with limited recognition in the South Caucasus region. The Republic of Artsakh controls most of the territory of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (before the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, it also co ...
* List of representative offices of Artsakh
* Madrid Principles
* Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
* Visa policy of Artsakh
Visitors to Artsakh must obtain a visa unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries.
Visa policy
Citizens of the following countries, including those from the Commonwealth of Independent States and all Eurasian Union member states, ...
References
{{reflist, 30emExternal links
Government of the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
*