Interferon beta 1a on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a
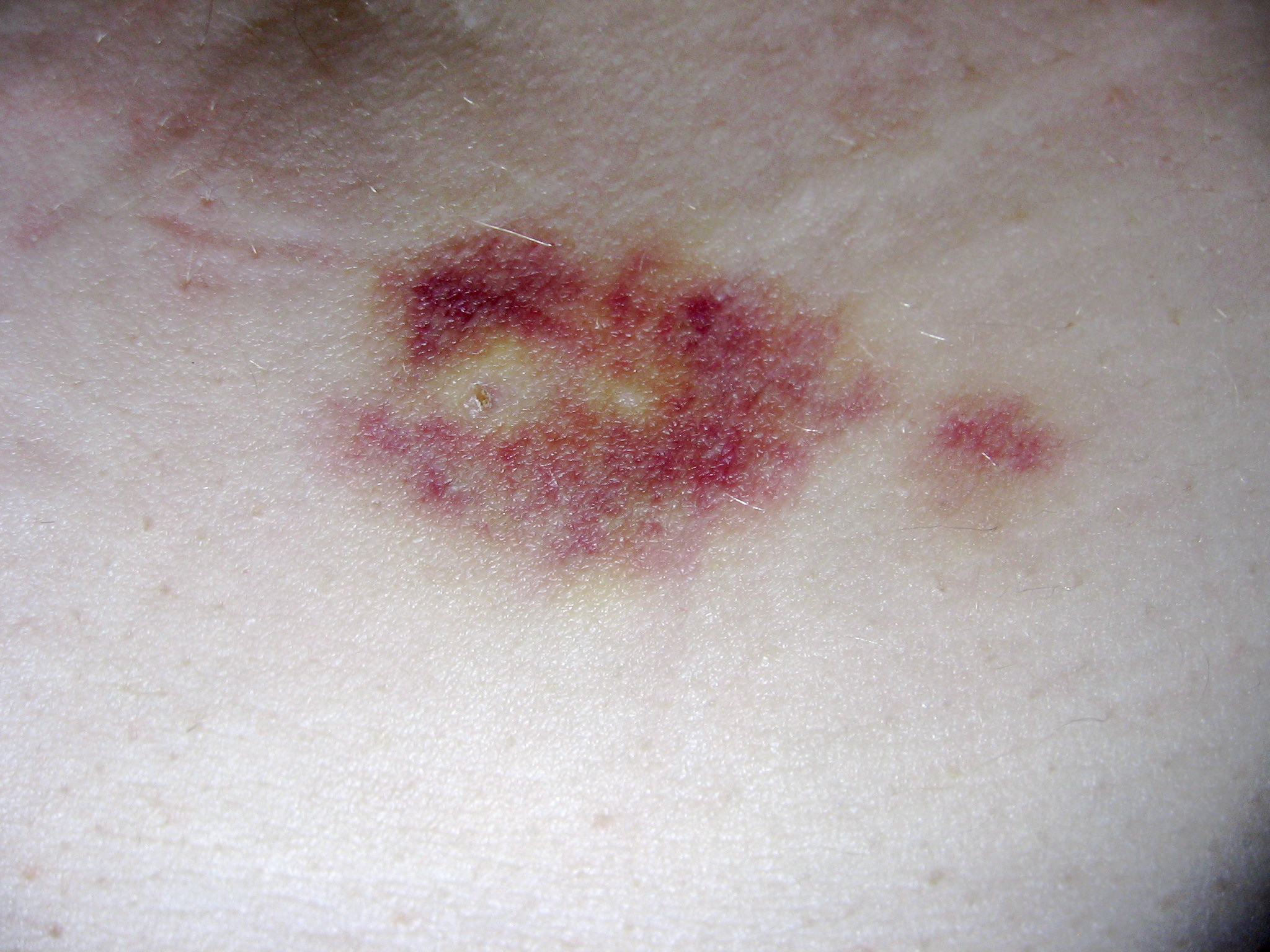 Interferon beta-1a is available only in injectable forms, and can cause skin reactions at the injection site that may include cutaneous necrosis. Skin reactions with interferon beta are more common with subcutaneous administration and vary greatly in their clinical presentation. They usually appear within the first month of treatment albeit their frequence and importance diminish after six months of treatment. Skin reactions are more prevalent in women. Mild skin reactions usually do not impede treatment whereas necroses appear in around 5% of patients and lead to the discontinuation of the therapy. Also over time, a visible dent at the injection site due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as
Interferon beta-1a is available only in injectable forms, and can cause skin reactions at the injection site that may include cutaneous necrosis. Skin reactions with interferon beta are more common with subcutaneous administration and vary greatly in their clinical presentation. They usually appear within the first month of treatment albeit their frequence and importance diminish after six months of treatment. Skin reactions are more prevalent in women. Mild skin reactions usually do not impede treatment whereas necroses appear in around 5% of patients and lead to the discontinuation of the therapy. Also over time, a visible dent at the injection site due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as

cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified '' E. coli''. Some research indicates that interferon injections may result in an 18–38% reduction in the rate of MS relapses.
Interferon beta has not been shown to slow the advance of disability. Interferons are not a cure for MS (there is no known cure); the claim is that interferons may slow the progress of the disease if started early and continued for the duration of the disease.
Medical uses
Clinically isolated syndrome
The earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), that is, a single attack of a single symptom. During a CIS, there is a subacute attack suggestive ofdemyelination
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency i ...
which should be included in the spectrum of MS phenotypes. Treatment with interferons after an initial attack decreases the risk of developing clinical definite MS.
Relapsing-remitting MS
Medications are modestly effective at decreasing the number of attacks in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and in reducing the accumulation of brain lesions, which is measured usinggadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
- enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Interferons reduce relapses by approximately 30% and their safe profile make them the first-line treatments. Nevertheless, not all the patients are responsive to these therapies. It is known that 30% of MS patients are non-responsive to Beta interferon. They can be classified in genetic, pharmacological and pathogenetic non-responders. One of the factors related to non-respondance is the presence of high levels of interferon beta neutralizing antibodies. Interferon therapy, and specially interferon beta 1b, induces the production of neutralizing antibodies, usually in the second 6 months of treatment, in 5 to 30% of treated patients. Moreover, a subset of RRMS patients with specially active MS, sometimes called "rapidly worsening MS" are normally non-responders to interferon beta 1a.
While more studies of the long-term effects of the drugs are needed, existing data on the effects of interferons indicate that early-initiated long-term therapy is safe and it is related to better outcomes.
Side effects
 Interferon beta-1a is available only in injectable forms, and can cause skin reactions at the injection site that may include cutaneous necrosis. Skin reactions with interferon beta are more common with subcutaneous administration and vary greatly in their clinical presentation. They usually appear within the first month of treatment albeit their frequence and importance diminish after six months of treatment. Skin reactions are more prevalent in women. Mild skin reactions usually do not impede treatment whereas necroses appear in around 5% of patients and lead to the discontinuation of the therapy. Also over time, a visible dent at the injection site due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as
Interferon beta-1a is available only in injectable forms, and can cause skin reactions at the injection site that may include cutaneous necrosis. Skin reactions with interferon beta are more common with subcutaneous administration and vary greatly in their clinical presentation. They usually appear within the first month of treatment albeit their frequence and importance diminish after six months of treatment. Skin reactions are more prevalent in women. Mild skin reactions usually do not impede treatment whereas necroses appear in around 5% of patients and lead to the discontinuation of the therapy. Also over time, a visible dent at the injection site due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as lipoatrophy
Lipoatrophy is the term describing the localized loss of fat tissue. This may occur as a result of subcutaneous injections of insulin in the treatment of diabetes, from the use of human growth hormone or from subcutaneous injections of copaxone us ...
, may develop, however, this rarely occurs with interferon treatment.
Interferons, a subclass of cytokines, are produced in the body during illnesses such as influenza in order to help fight the infection. They are responsible for many of the symptoms of influenza infections, including fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, muscle aches, fatigue, and headaches. Many patients report influenza-like symptoms hours after taking interferon beta that usually improve within 24 hours, being such symptoms related to the temporary increase of cytokines. This reaction tends to disappear after 3 months of treatment and its symptoms can be treated with over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, that reduce fever and pain. Another common transient secondary effect with interferon-beta is a functional deterioration of already existing symptoms of the disease. Such deterioration is similar to the one produced in MS patients due to heat, fever or stress (Uhthoff's phenomenon
Uhthoff's phenomenon (also known as Uhthoff's syndrome, Uhthoff's sign, and Uhthoff's symptom) is the worsening of neurologic symptoms in multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases when the body is overheated. This may occur due to ...
), usually appears within 24 hours of treatment, is more common in the initial months of treatment, and may last several days. A symptom specially sensitive to worsening is spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles ...
. Interferon-beta can also reduce numbers of white blood cells (leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of leukocytes (WBC). Found in the blood, they are the white blood cells, and are the body's primary defense against an infection. Thus the condition of leukopenia places individuals at increased risk of in ...
), lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s (lymphopenia
Lymphocytopenia is the condition of having an abnormally low level of lymphocytes in the blood. Lymphocytes are a white blood cell with important functions in the immune system. It is also called lymphopenia. The opposite is lymphocytosis, which ...
) and neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s ( neutropenia), as well as affect liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
function. In most cases these effects are non-dangerous and reversible after cessation or reduction of treatment. Nevertheless, recommendation is that all patients should be monitored through laboratory blood analyses, including liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
, to ensure safe use of interferons.
To help prevent injection-site reactions, patients are advised to rotate injection sites and use an aseptic injection technique. Injection devices are available to optimize the injection process. Side effects are often onerous enough that many patients ultimately discontinue taking interferons (or glatiramer acetate
Glatiramer acetate (also known as Copolymer 1, Cop-1), sold under the brand name Copaxone among others, is an immunomodulator medication used to treat multiple sclerosis. Glatiramer acetate is approved in the United States to reduce the frequenc ...
, a comparable disease-modifying therapy requiring regular injections).
Mechanism of action
Interferon beta balances the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory agents in the brain, and reduces the number of inflammatory cells that cross theblood brain barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
. Overall, therapy with interferon beta leads to a reduction of neuron inflammation. Moreover, it is also thought to increase the production of nerve growth factor and consequently improve neuronal survival. In vitro, interferon beta reduces production of Th17 cells which are a subset of T lymphocytes believed to have a role in the pathophysiology of MS.
Society and culture
Brand names
Avonex
Avonex was approved in the US in 1996, and in the European Union in 1997, and is registered in more than 80 countries worldwide. It is the leading MS therapy in the US, with around 40% of the overall market, and in the European Union, with around 30% of the overall market. It is produced by theBiogen
Biogen Inc. is an American multinational biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, specializing in the discovery, development, and delivery of therapies for the treatment of neurological diseases to patients worldwide.
History
...
biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
company, originally under competition protection in the US under the Orphan Drug Act
The Orphan Drug Act of 1983 is a law passed in the United States to facilitate development of orphan drugs—drugs for rare diseases such as Huntington's disease, myoclonus, ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neu ...
.
Avonex is sold in three formulations, a lyophilized powder requiring reconstitution, a pre-mixed liquid syringe kit, and a pen; it is administered via intramuscular injection.
Rebif
Rebif is a disease-modifying drug (DMD) used to treat multiple sclerosis in cases of clinically isolated syndromes as well as relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis and is similar to the interferon beta protein produced by the human body. It is co-marketed byMerck Serono
Merck Serono (EMD Serono in the United States and Canada) is a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Darmstadt, Germany, and a brand and division of Merck focused on biopharmaceuticals.
In September 2006, Merck KGaA announced its intent to p ...
and Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer ...
in the US under an exception to the Orphan Drug Act
The Orphan Drug Act of 1983 is a law passed in the United States to facilitate development of orphan drugs—drugs for rare diseases such as Huntington's disease, myoclonus, ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neu ...
. It was approved in the European Union in 1998, and in the US in 2002; it has since been approved in more than 90 countries worldwide including Canada and Australia. EMD Serono has had sole rights to Rebif in the US since January 2016. Rebif is administered via subcutaneous injection.
Cinnovex
Cinnovex is the brand name of recombinant Interferon beta-1a, which is manufactured as biosimilar/biogeneric inIran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. It is produced in a lyophilized form and sold with distilled water
Distilled water is water that has been boiled into vapor and condensed back into liquid in a separate container. Impurities in the original water that do not boil below or near the boiling point of water remain in the original container. Thus, di ...
for injection. Cinnovex was developed at the Fraunhofer Society
The Fraunhofer Society (german: Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V., lit=Fraunhofer Society for the Advancement of Applied Research) is a German research organization with 76institutes spread throughout Germany ...
in collaboration with CinnaGen, and is the first therapeutic protein from a Fraunhofer laboratory to be approved as biogeneric / biosimilar medicine. There are several clinical studies to prove the similarity of CinnoVex and Avonex. A more water-soluble variant is currently being investigated by the Vakzine Projekt Management (VPM) GmbH in Braunschweig, Germany.
Plegridy
Plegridy is a brand name of apegylated
PEGylation (or pegylation) is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol (PEG, in pharmacy called macrogol) polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein ...
form of Interferon beta-1a. Plegridy's advantage is it only needs injecting once every two weeks.
Betaferon (interferon beta-1b)
Closely related to interferon beta-1a is interferon beta-1b, which is also indicated for MS, but is formulated with a different dose and administered with a different frequency. Each drug has a different safety/efficacy profile. Interferon beta-1b is marketed only by Bayer in the US as Betaseron, and outside the US as Betaferon.Economics
In the United States, , the cost is between US$1,284 and US$1,386 per 30 mcg vial. As of 2020, the National Average Drug Acquisition Cost (NADAC) in the United States for Avonex was $6,872.94 for a 30 mcg kit. Avonex and Rebif are on the top ten best-selling multiple sclerosis drugs of 2013: It is an example of a specialty drug that would only be available through aspecialty pharmacy Specialty pharmacy refers to distribution channels designed to handle specialty drugs — pharmaceutical therapies that are either high cost, high complexity and/or high touch. High touch refers to higher degree of complexity in terms of distributi ...
. This is because it requires a refrigerated chain of distribution and costs $17,000-a-year.
Research
COVID-19
Interferon beta-1a administered subcutaneously or intravenously was investigated since March 2020 as a potential treatment in patients hospitalized withCOVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly ...
in a multinational Solidarity trial
The Solidarity trial for treatments is a multinational Phase III-IV clinical trial organized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and partners to compare four untested treatments for hospitalized people with severe COVID-19 illness. The tria ...
(initially in combination with lopinavir
Lopinavir is an anti retroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir).
It was patented in 1995 and approved for medical ...
) but it did not reduce in-hospital mortality compared to local standard of care.
SNG001, an inhalation formulation of interferon beta-1a, is being developed as a treatment for COVID-19 by Synairgen. A pilot trial in hospitalized patients showed higher odds of clinical improvement with SNG001 compared to placebo and in January 2021 a phase 3 trial in this population started.
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Interferon Beta-1a Cytokines Pfizer brands Merck brands Immunostimulants Specialty drugs