Indigenous peoples of Brazil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Indigenous peoples in Brazil ( pt, povos indígenas no Brasil) or Indigenous Brazilians ( pt, indígenas brasileiros, links=no) once comprised an estimated 2000
 Questions about the original settlement of the Americas has produced a number of hypothetical models. The origins of these Indigenous people are still a matter of dispute among archaeologists.
Questions about the original settlement of the Americas has produced a number of hypothetical models. The origins of these Indigenous people are still a matter of dispute among archaeologists.

 Another study, focused on mitochondrial DNA ( mtDNA), inherited only through the maternal line, revealed that the maternal ancestry of the Indigenous people of the Americas traces back to a few founding lineages from Siberia, which would have arrived via the Bering strait. According to this study, the ancestors of Native Americans likely remained for a time near the Bering Strait, after which there would have been a rapid movement of settling of the Americas, taking the founding lineages to
Another study, focused on mitochondrial DNA ( mtDNA), inherited only through the maternal line, revealed that the maternal ancestry of the Indigenous people of the Americas traces back to a few founding lineages from Siberia, which would have arrived via the Bering strait. According to this study, the ancestors of Native Americans likely remained for a time near the Bering Strait, after which there would have been a rapid movement of settling of the Americas, taking the founding lineages to
 Brazilian native people, unlike those in
Brazilian native people, unlike those in
 On the eve of the Portuguese arrival in 1500, the coastal areas of Brazil had two major mega-groups – the '' Tupi'' (speakers of
On the eve of the Portuguese arrival in 1500, the coastal areas of Brazil had two major mega-groups – the '' Tupi'' (speakers of  With the exception of the
With the exception of the

 When the Portuguese explorers first arrived in Brazil in April 1500, they found, to their astonishment, a wide coastline rich in resources, teeming with hundreds of thousands of Indigenous people living in a "paradise" of natural riches. Pêro Vaz de Caminha, the official scribe of
When the Portuguese explorers first arrived in Brazil in April 1500, they found, to their astonishment, a wide coastline rich in resources, teeming with hundreds of thousands of Indigenous people living in a "paradise" of natural riches. Pêro Vaz de Caminha, the official scribe of

 Jesuit priests such as fathers José de Anchieta and Manuel da Nóbrega studied and recorded their language and founded mixed settlements, such as
Jesuit priests such as fathers José de Anchieta and Manuel da Nóbrega studied and recorded their language and founded mixed settlements, such as
 A number of wars between several tribes, such as the Tamoio Confederation, and the Portuguese ensued, sometimes with the Indians siding with enemies of Portugal, such as the French, in the famous episode of France Antarctique in
A number of wars between several tribes, such as the Tamoio Confederation, and the Portuguese ensued, sometimes with the Indians siding with enemies of Portugal, such as the French, in the famous episode of France Antarctique in
 In the 20th century, the Brazilian Government adopted a more humanitarian attitude and offered official protection to the indigenous people, including the establishment of the first indigenous reserves. Fortune brightened for the Indians around the turn of the 20th century when Cândido Rondon, a man of both Portuguese and Bororo ancestry, and an explorer and progressive officer in the Brazilian army, began working to gain the Indians' trust and establish peace. Rondon, who had been assigned to help bring telegraph communications into the Amazon, was a curious and natural explorer. In 1910, he helped found the '' Serviço de Proteção aos Índios – SPI'' (Service for the Protection of Indians, today the FUNAI, or '' Fundação Nacional do Índio'', National Foundation for Indians). SPI was the first federal agency charged with protecting Indians and preserving their culture. In 1914, Rondon accompanied
In the 20th century, the Brazilian Government adopted a more humanitarian attitude and offered official protection to the indigenous people, including the establishment of the first indigenous reserves. Fortune brightened for the Indians around the turn of the 20th century when Cândido Rondon, a man of both Portuguese and Bororo ancestry, and an explorer and progressive officer in the Brazilian army, began working to gain the Indians' trust and establish peace. Rondon, who had been assigned to help bring telegraph communications into the Amazon, was a curious and natural explorer. In 1910, he helped found the '' Serviço de Proteção aos Índios – SPI'' (Service for the Protection of Indians, today the FUNAI, or '' Fundação Nacional do Índio'', National Foundation for Indians). SPI was the first federal agency charged with protecting Indians and preserving their culture. In 1914, Rondon accompanied
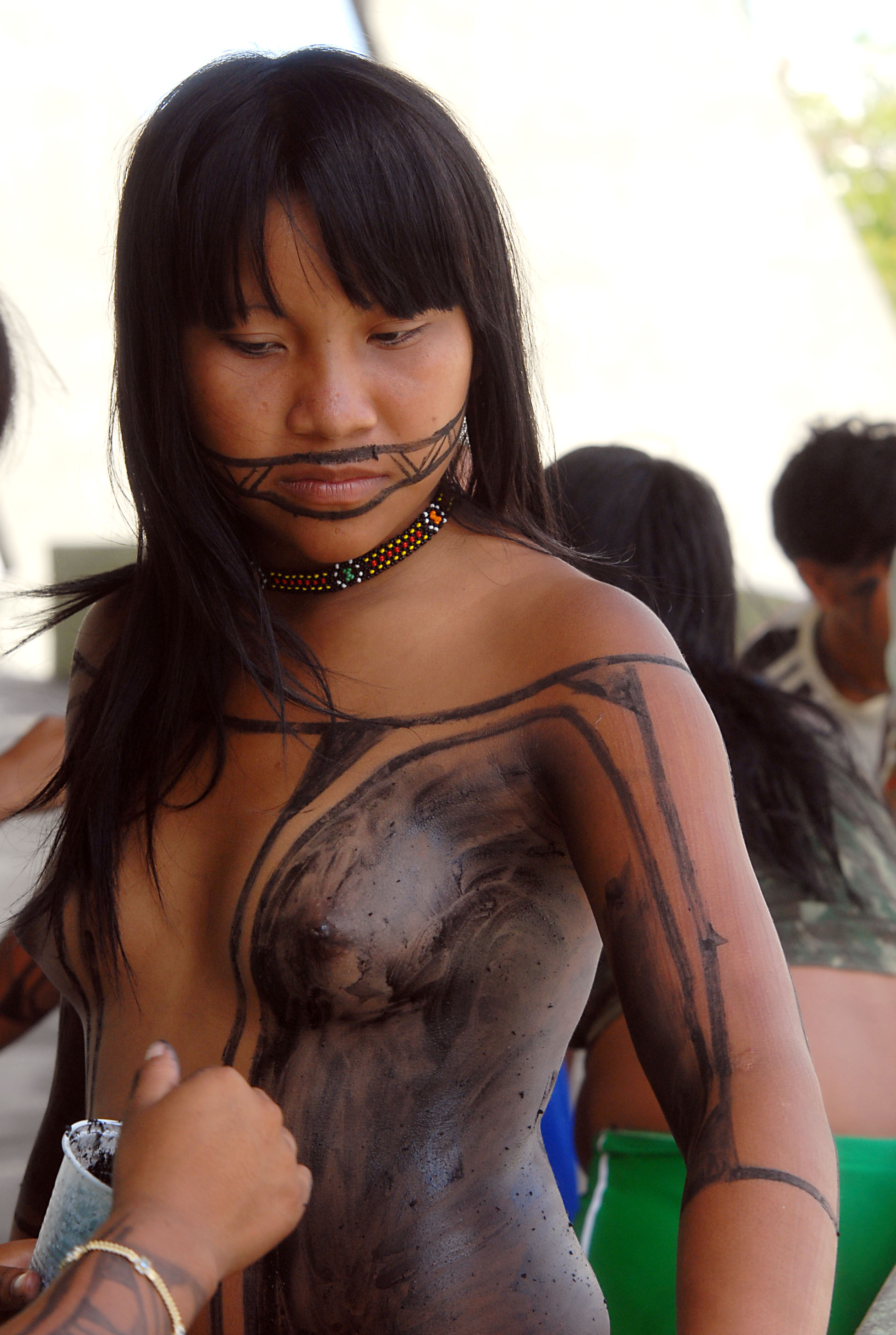 After Rondon's pioneering work, the SPI was turned over to bureaucrats and military officers and its work declined after 1957. The new officials did not share Rondon's deep commitment to the Indians. SPI sought to address tribal issues by transforming the tribes into mainstream Brazilian society. The lure of reservation riches enticed cattle ranchers and settlers to continue their assault on Indians lands – and the SPI eased the way. Between 1900 and 1967, an estimated 98 indigenous tribes were wiped out.
Mostly due to the efforts of the Villas-Bôas brothers, Brazil's first Indian reserve, the Xingu National Park, was established by the Federal Government in 1961.
During the social and political upheaval in the 1960s, reports of mistreatment of Indians increasingly reached
After Rondon's pioneering work, the SPI was turned over to bureaucrats and military officers and its work declined after 1957. The new officials did not share Rondon's deep commitment to the Indians. SPI sought to address tribal issues by transforming the tribes into mainstream Brazilian society. The lure of reservation riches enticed cattle ranchers and settlers to continue their assault on Indians lands – and the SPI eased the way. Between 1900 and 1967, an estimated 98 indigenous tribes were wiped out.
Mostly due to the efforts of the Villas-Bôas brothers, Brazil's first Indian reserve, the Xingu National Park, was established by the Federal Government in 1961.
During the social and political upheaval in the 1960s, reports of mistreatment of Indians increasingly reached
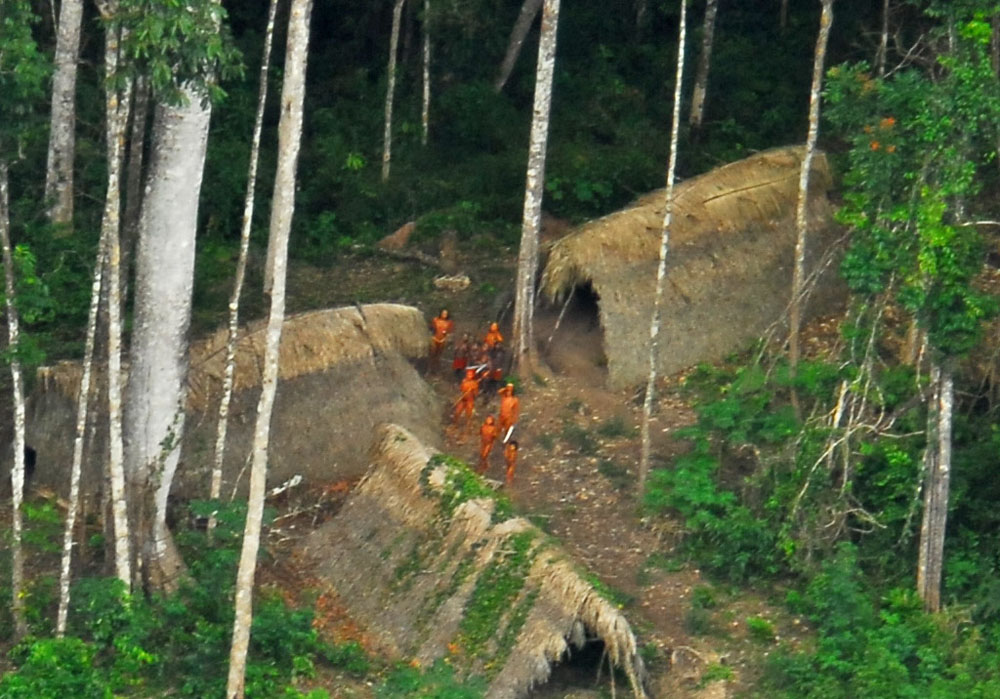 The 1988 Brazilian Constitution recognizes indigenous people' right to pursue their traditional ways of life and to the permanent and exclusive possession of their "traditional lands", which are demarcated as Indigenous Territories.Federal Constitution of Brazil
The 1988 Brazilian Constitution recognizes indigenous people' right to pursue their traditional ways of life and to the permanent and exclusive possession of their "traditional lands", which are demarcated as Indigenous Territories.Federal Constitution of Brazil
Chapter VII Article 231
. In practice, however, Brazil's indigenous people still face a number of external threats and challenges to their continued existence and cultural heritage. The process of demarcation is slow—often involving protracted legal battles—and FUNAI do not have sufficient resources to enforce the legal protection on indigenous land. Since the 1980s there has been a boom in the exploitation of the Amazon Rainforest for mining, logging and cattle ranching, posing a severe threat to the region's indigenous population. Settlers illegally encroaching on indigenous land continue to destroy the environment necessary for indigenous people' traditional ways of life, provoke violent confrontations and spread disease. People such as the Akuntsu and Kanoê have been brought to the brink of extinction within the last three decades. Deforestation for mining also affects the daily lives of indigenous tribes in Brazil. For instance, the Munduruku Indians have higher levels of mercury poisoning due to gold production in the area. On 13 November 2012, the national indigenous people association from Brazil APIB submitted to the United Nation a human rights document that complaints about new proposed laws in Brazil that would further undermine their rights if approved. Much of the language has been incorporated into the official Within hours of taking office in January 2019, Bolsonaro made two major changes to FUNAI, affecting its responsibility to identify and demarcate indigenous lands: He moved FUNAI from under the Ministry of Justice to be under the newly created ''Ministry of Human Rights, Family and Women,'' and he delegated the identification of the traditional habitats of indigenous people and their designation as inviolable protected territories − a task attributed to FUNAI by the constitution – to the Agriculture Ministry. He argued that those territories have tiny isolated populations and proposed to integrate them into the larger Brazilian society. Critics feared that such integration would lead the Brazilian natives to suffer
Within hours of taking office in January 2019, Bolsonaro made two major changes to FUNAI, affecting its responsibility to identify and demarcate indigenous lands: He moved FUNAI from under the Ministry of Justice to be under the newly created ''Ministry of Human Rights, Family and Women,'' and he delegated the identification of the traditional habitats of indigenous people and their designation as inviolable protected territories − a task attributed to FUNAI by the constitution – to the Agriculture Ministry. He argued that those territories have tiny isolated populations and proposed to integrate them into the larger Brazilian society. Critics feared that such integration would lead the Brazilian natives to suffer
 * Amanyé
* Atikum
* Awá-Guajá
*
* Amanyé
* Atikum
* Awá-Guajá
*
Fundação Nacional do Índio, National Foundation of the Native AmericanEncyclopedia of Indigenous people in Brazil. Instituto SocioambientalEtnolinguistica.Org: discussion list on South American languagesIndigenous people Issues and Resources: BrazilIndigenous people in Brazil
at Google Videos
New photos of Uncontacted Brazilian tribeGoogle Video on Indigenous People of BrazilChildren of the Amazon, a documentary on indigenous people in Brazil
by ''
tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
and nations inhabiting what is now the country of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, before Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an contact around 1500. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
thought he had reached the East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around ...
, but Portuguese Vasco da Gama had already reached India via the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
route, when Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
was colonized by Portugal.
Nevertheless, the word ("Indians") was by then established to designate the people of the New World and continues to be used in the Portuguese language to designate these people, while a person from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
is called in order to distinguish the two.
At the time of European contact, some of the Indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
were traditionally semi- nomadic tribes who subsisted on hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
, fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. ...
, gathering
Gather, gatherer, or gathering may refer to:
Anthropology and sociology
*Hunter-gatherer, a person or a society whose subsistence depends on hunting and gathering of wild foods
*Intensive gathering, the practice of cultivating wild plants as a st ...
and migrant agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. Many tribes suffered extinction as a consequence of the European settlement and many were assimilated into the Brazilian population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction usi ...
.
The Indigenous population was decimated by European diseases, declining from a pre-Columbian high of 2 to 3 million to some 300,000 , distributed among 200 tribes. By the 2010 IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics ( pt, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística; IBGE) is the agency responsible for official collection of statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental informat ...
census, 817,000 Brazilians classified themselves as Indigenous, the same census registered 274 indigenous languages of 304 different indigenous ethnic groups.
On 18 January 2007, FUNAI reported 67 remaining uncontacted tribes in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, up from 40 known in 2005. With this addition Brazil passed New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
, becoming the country with the largest number of uncontacted peoples in the world.
History
Origins
 Questions about the original settlement of the Americas has produced a number of hypothetical models. The origins of these Indigenous people are still a matter of dispute among archaeologists.
Questions about the original settlement of the Americas has produced a number of hypothetical models. The origins of these Indigenous people are still a matter of dispute among archaeologists.
Migration into the continents
Anthropological
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
and genetic evidence indicates that most Amerindian people descended from migrant peoples from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
who entered the Americas across the Bering Strait and along the western coast of North America in at least three separate waves. In Brazil, particularly, most native tribes who were living in the land by 1500 are thought to be descended from the first Siberian wave of migrants, who are believed to have crossed the Bering Land Bridge at the end of the last Ice Age, between 13,000 and 17,000 years before the present. A migrant wave would have taken some time after initial entry to reach present-day Brazil, probably entering the Amazon River basin from the Northwest. (The second and third migratory waves from Siberia, which are thought to have generated the Athabaskan, Aleut
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the ...
, Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
, and Yupik people, apparently did not reach farther than the southern United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, respectively.)
Genetic studies

= Y-chromosome DNA
= An analysis of AmerindianY-chromosome DNA
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of s ...
indicates specific clustering of much of the South American population. The micro-satellite diversity and distributions of the Y lineage specific to South America indicates that certain Amerindian populations have been isolated since the initial colonization of the region.
= Autosomal DNA
= According to anautosomal DNA
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
genetic study from 2012, Native Americans descend from at least three main migrant waves from Siberia. Most of it is traced back to a single ancestral population, called 'First Americans'. However, those who speak Inuit languages
The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and adjacent subarctic, reaching farthest south in Labrador. The related Yupik languages (spoken in weste ...
from the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
inherited almost half of their ancestry from a second Siberia migrant wave. And those who speak Na-dene, on the other hand, inherited a tenth of their ancestry from a third migrant wave. The initial settling of the Americas was followed by a rapid expansion south down the coast, with little gene flow later, especially in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. One exception to this are the Chibcha speakers, whose ancestry comes from both North and South America.
= mtDNA
= Another study, focused on mitochondrial DNA ( mtDNA), inherited only through the maternal line, revealed that the maternal ancestry of the Indigenous people of the Americas traces back to a few founding lineages from Siberia, which would have arrived via the Bering strait. According to this study, the ancestors of Native Americans likely remained for a time near the Bering Strait, after which there would have been a rapid movement of settling of the Americas, taking the founding lineages to
Another study, focused on mitochondrial DNA ( mtDNA), inherited only through the maternal line, revealed that the maternal ancestry of the Indigenous people of the Americas traces back to a few founding lineages from Siberia, which would have arrived via the Bering strait. According to this study, the ancestors of Native Americans likely remained for a time near the Bering Strait, after which there would have been a rapid movement of settling of the Americas, taking the founding lineages to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
.
According to a 2016 study, focused on mtDNA lineages, "a small population entered the Americas via a coastal route around 16.0 ka, following previous isolation in eastern Beringia for ~2.4 to 9 thousand years after separating from eastern Siberian populations. After rapidly spreading throughout the Americas, limited gene flow in South America resulted in a marked phylogeographic structure of populations, which persisted through time. All of the ancient mitochondrial lineages detected in this study were absent from modern data sets, suggesting a high extinction rate. To investigate this further, we applied a novel principal components multiple logistic regression
test to Bayesian serial coalescent simulations. The analysis supported a scenario in which European colonization caused a substantial loss of pre-Columbian lineages".
= Linguistic comparison with Siberia
= Linguistic studies have backed up genetic studies, with ancient patterns having been found between the languages spoken inSiberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
and those spoken in the Americas.
= Oceanic component in the Amazon region
= Two 2015 autosomal DNA genetic studies confirmed the Siberian origins of the Natives of the Americas. However an ancient signal of shared ancestry with the Natives of Australia and Melanesia was detected among the Natives of the Amazon region. The migration coming out ofSiberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
would have happened 23,000 years ago.
Archaeological remains
 Brazilian native people, unlike those in
Brazilian native people, unlike those in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
and the Andean civilizations, did not keep written records or erect stone monuments, and the humid climate and acidic soil have destroyed almost all traces of their material culture, including wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
and bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s. Therefore, what is known about the region's history before 1500 has been inferred and reconstructed from small-scale archaeological evidence, such as ceramics and stone arrowheads.
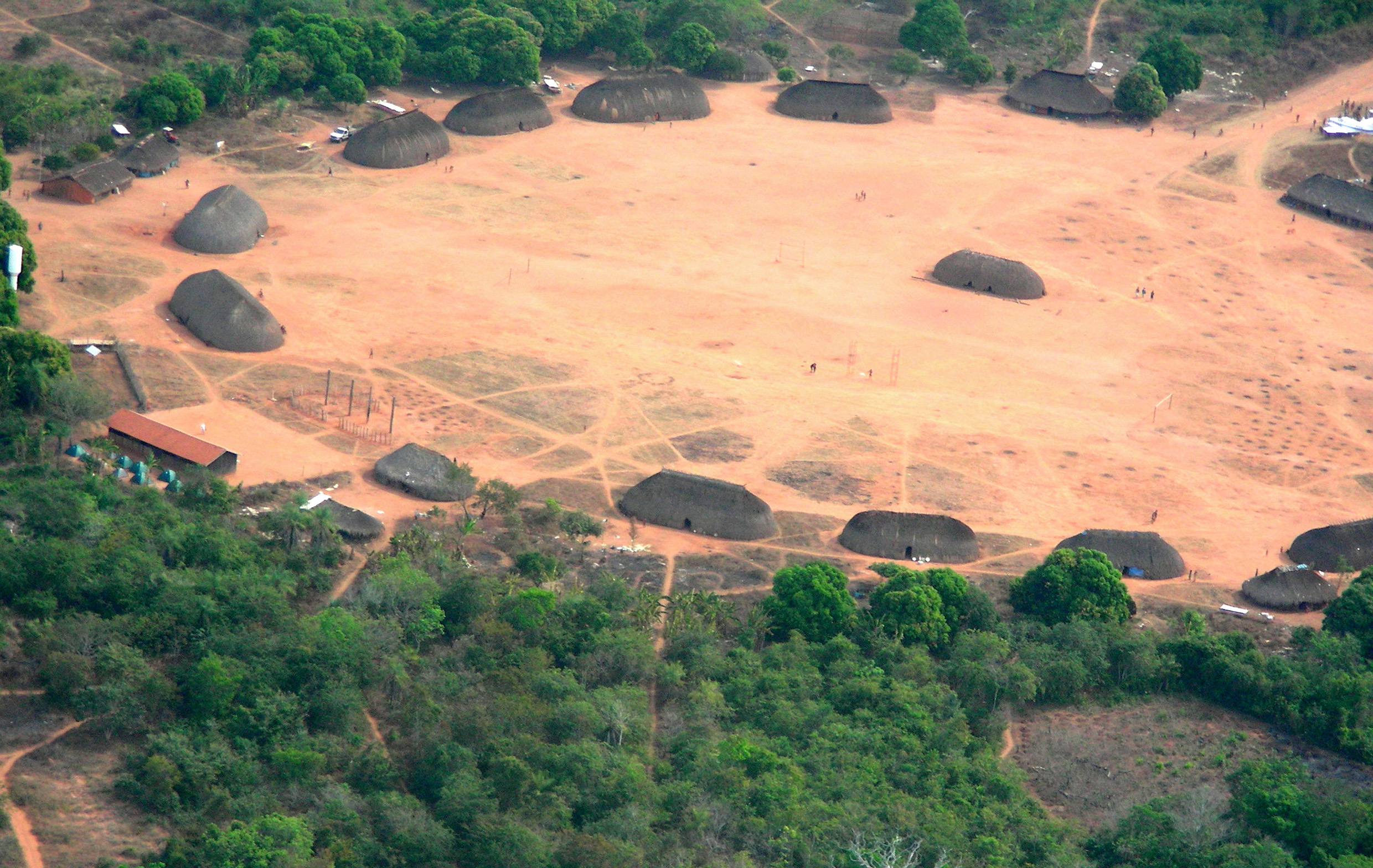
The most conspicuous remains of these societies are very large mounds of discarded shellfish (''sambaquis'') found in some coastal sites which were continuously inhabited for over 5,000 years; and the substantial "black earth" (''terra preta
''Terra preta'' (, locally , literally "black soil" in Portuguese) is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil (anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its ful ...
'') deposits in several places along the Amazon, which are believed to be ancient garbage dumps (midden
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and eco ...
s). Recent excavations of such deposits in the middle and upper course of the Amazon have uncovered remains of some very large settlements, containing tens of thousands of homes, indicating a complex social and economic structure.
Studies of the wear patterns of the prehistoric inhabitants of coastal Brazil found that the surfaces of anterior teeth facing the tongue were more worn than surfaces facing the lips, which researchers believe was caused by using teeth to peel and shred abrasive plants.
Marajoara culture
Marajoara culture flourished onMarajó island
Marajó () is a large coastal island in the Pará, state of Pará, Brazil. It is the main and largest of the islands in the Marajó Archipelago. Marajó Island is separated from the mainland by Marajó Bay, Pará River, smaller rivers (especi ...
at the mouth of the Amazon River. Archeologists have found sophisticated pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
in their excavations on the island. These pieces are large, and elaborately painted and incised with representations of plants and animals. These provided the first evidence that a complex society had existed on Marajó. Evidence of mound building further suggests that well-populated, complex and sophisticated settlements developed on this island, as only such settlements were believed capable of such extended projects as major earthworks.
The extent, level of complexity, and resource interactions of the Marajoara culture have been disputed. Working in the 1950s in some of her earliest research, American Betty Meggers
Betty Jane Meggers (December 5, 1921 – July 2, 2012) was an American archaeologist best known for her work in South America. She was considered influential at the Smithsonian Institution, where she was long associated in research,Anna Curtenius Roosevelt
Anna Curtenius Roosevelt (born 1946) is an American archaeologist and Professor of Anthropology at the University of Illinois Chicago. She studies human evolution and long-term human-environment interaction. She is one of the leading American ar ...
, led excavations and geophysical surveys of the mound Teso dos Bichos. She concluded that the society that constructed the mounds originated on the island itself.
The pre-Columbian culture of Marajó may have developed social stratification
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and politi ...
and supported a population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction usi ...
as large as 100,000 people. The Native Americans of the Amazon rain forest may have used their method of developing and working in Terra preta
''Terra preta'' (, locally , literally "black soil" in Portuguese) is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil (anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its ful ...
to make the land suitable for the large-scale agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
needed to support large populations and complex social formations such as chiefdoms
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
.
Xinguano Civilisation
The Xingu peoples built large settlements connected by roads and bridges, often bearing moats. The apex of their development was between 1200 CE to 1600 CE, their population inflating to the tens of thousands.Native people after the European colonisation
Distribution
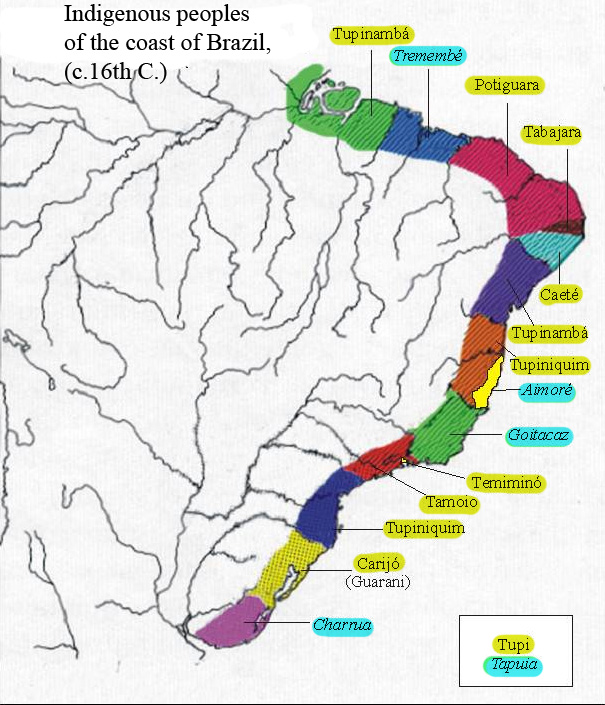
 On the eve of the Portuguese arrival in 1500, the coastal areas of Brazil had two major mega-groups – the '' Tupi'' (speakers of
On the eve of the Portuguese arrival in 1500, the coastal areas of Brazil had two major mega-groups – the '' Tupi'' (speakers of Tupi–Guarani languages
Tupi–Guarani () is the most widely distributed subfamily of the Tupian languages of South America. It consists of about fifty languages, including Guarani and Old Tupi.
The words ''petunia, jaguar, piranha, ipecac, tapioca, jacaranda, a ...
), who dominated practically the entire length of the Brazilian coast, and the ''Tapuia'' (a catch-all term for non-Tupis, usually Jê language people), who resided primarily in the interior. The Portuguese arrived in the final days of a long pre-colonial struggle between Tupis and Tapuias, which had resulted in the defeat and expulsion of the Tapuias from most coastal areas.
Although the coastal Tupi were broken down into sub-tribes, frequently hostile to each other, they were culturally and linguistically homogeneous. The fact that the early Europeans encountered practically the same people and language all along the Brazilian coast greatly simplified early communication and interaction.
Coastal Sequence c. 1500 (north to south):
# Tupinambá (Tupi, from the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
delta to Maranhão
Maranhão () is a state in Brazil. Located in the country's Northeast Region, it has a population of about 7 million and an area of . Clockwise from north, it borders on the Atlantic Ocean for 2,243 km and the states of Piauí, Tocantins a ...
)
# Tremembé
Tremembé is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Vale do Paraíba e Litoral Norte. The population is 47,714 (2020 est.) in an area of 191.09 km². The elevation is 560 m.
A ...
(Tapuia, coastal tribe, ranged from São Luis Island (south Maranhão) to the mouth of the Acaraú River
The Acaraú River is a river of Ceará state in eastern Brazil.
See also
*List of rivers of Ceará
List of rivers in Ceará (Brazilian State).
The list is arranged by drainage basin from east to west, with respective tributaries indented unde ...
in north Ceará; French traders cultivated an alliance with them)
# Potiguara
The Potiguara (also Potyguara or Pitiguara) are an indigenous people of Brazil. The Potiguara people live in Paraíba, in the municipalities of Marcação, Baía da Traição and Rio Tinto. Their population numbers sixteen thousand individua ...
(Tupi, literally "shrimp-eaters"; they had a reputation as great canoeists and aggressively expansionist, inhabited a great coastal stretch from Acaraú River
The Acaraú River is a river of Ceará state in eastern Brazil.
See also
*List of rivers of Ceará
List of rivers in Ceará (Brazilian State).
The list is arranged by drainage basin from east to west, with respective tributaries indented unde ...
to Itamaracá island, covering the modern states of southern Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte and Paraíba.)
# Tabajara (tiny Tupi tribe between Itamaracá island and Paraíba River; neighbors and frequent victims of the Potiguara)
# Caeté
Caeté is a Brazilian municipality located in the state of Minas Gerais. The city belongs to the mesoregion Metropolitana de Belo Horizonte and to the microregion of Belo Horizonte.
The name ''Caeté'' is derived from the local term for some Mar ...
(Tupi group in Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the ...
and Alagoas
Alagoas (, ) is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil and is situated in the eastern part of the Northeast Region. It borders: Pernambuco (N and NW); Sergipe (S); Bahia (SW); and the Atlantic Ocean (E). Its capital is the city of Maceió. ...
, ranged from Paraíba River to the São Francisco River; after killing and eating a Portuguese bishop, they were subjected to Portuguese extermination raids and the remnant pushed into the Pará interior)
# Tupinambá again (Tupi par excellence, ranged from the São Francisco River to the Bay of All Saints, population estimated as high as 100,000; hosted Portuguese castaway Caramuru
Caramuru (-1557) was the Tupi name of the Portuguese colonist Diogo Álvares Correia, who is notable for being the first European to establish contact with the native Tupinambá population in modern-day Brazil and was instrumental in the early ...
)
# Tupiniquim (Tupi, covered Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-larges ...
n discovery coast, from around Camamu
Camamu is a municipality in the state of Bahia, Brazil. Politically, it is in the Valença subregion of the Sul Baiano region. It is located on the southern coast of Bahia state, the Costa do Dendê (Palm Coast), along the BA-001 highway. The muni ...
to São Mateus River; these were the first indigenous people encountered by the Portuguese, having met the landing of captain Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human ...
in April 1500)
# Aimoré (Tapuia (Jê) tribe; concentrated on a sliver of coast in modern Espírito Santo state)
# Goitacá
The Goitacá (or Goytacazes, among other variant spellings "Waytaquazes" "Ouetacá", "Waitaká") were an indigenous people of Brazil. They are now extinct.
The Goitacá were a "Tapuia" (i.e. non- Tupi) people, one of the few that still remained ...
(Tapuia tribe; once dominated the coast from São Mateus River (in Espírito Santo state) down to the Paraíba do Sul river (in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
state); hunter-gatherers and fishermen, they were a shy people that avoided all contact with foreigners; estimated at 12,000; they had a fearsome reputation and were eventually annihilated by European colonists)
# Temiminó (small Tupi tribe, centered on Governador Island in Guanabara Bay; frequently at war with the Tamoio around them)
# Tamoio (Tupi, old branch of the Tupinambá, ranged from the western edge of Guanabara bay to Ilha Grande)
# Tupinambá again (Tupi, indistinct from the Tamoio. Inhabited the Paulist coast, from Ilha Grande to Santos; main enemies of the Tupiniquim to their west. Numbered between six and ten thousand).
# Tupiniquim again (Tupi, on the São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaW ...
coast from Santos/Bertioga down to Cananéia
Cananéia is the southernmost city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, near to where the Tordesilhas Line passed. The population in 2020 was 12,541 and the area is 1,242.010 km². The elevation is 8 m.
The city of Cananéia is host to the ...
; aggressively expansionist, they were recent arrivals imposing themselves on the Paulist coast and the Piratininga plateau at the expense of older Tupinambá and Carijó neighbors; hosted Portuguese castaways João Ramalho
João Ramalho () (1493–1582) was a Portuguese explorer and adventurer known as the first bandeirante. He lived much of his life among Tupiniquim natives in Brazil after he arrived there in 1515. He even became the leader of an Indian village ...
('Tamarutaca') and António Rodrigues in the early 1500s; the Tupiniquim were the first formal allies of the Portuguese colonists, helped establish the Portuguese Captaincy of São Vicente
The Captaincy of São Vicente (1534–1709) was a land grant and colonial administration in the far southern part of the colonial Portuguese Empire in Colonial Brazil.
History
In 1534 King John III of Portugal granted the Captaincy to Martim ...
in the 1530s; sometimes called "Guaianá" in old Portuguese chronicles, a Tupi term meaning "friendly" or "allied")
# Carijó (Guarani (Tupi) tribe, ranged from Cananeia all the way down to Lagoa dos Patos (in Rio Grande do Sul state); victims of the Tupiniquim and early European slavers; they hosted the mysterious '' degredado'' known as the ' Bachelor of Cananeia')
# Charrúa (Tapuia (Jê) tribe in modern Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
coast, with an aggressive reputation against intruders; killed Juan Díaz de Solís in 1516)
 With the exception of the
With the exception of the hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
Goitacases, the coastal Tupi and Tapuia tribes were primarily agriculturalists. The subtropical Guarani cultivated maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
, tropical Tupi cultivated manioc (cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
), highland Jês cultivated peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small an ...
, as the staple of their diet. Supplementary crops included beans, sweet potatoes, cará ( yam), ''jerimum'' ( pumpkin), and ''cumari'' (capsicum
''Capsicum'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae, native to the Americas, cultivated worldwide for their chili pepper or bell pepper fruit.
Etymology and names
The generic name may come from Latin , me ...
pepper).
Behind these coasts, the interior of Brazil was dominated primarily by Tapuia (Jê) people, although significant sections of the interior (notably the upper reaches of the Xingu, Teles Pires
The Teles Pires ( pt, Rio São Manuel) is a long river in Brazil. The river flows through the state of Mato Grosso and its lower part marks the border between the states of Mato Grosso and Pará. At its mouth it joins Juruena River and together ...
and Juruena River
The Juruena River ( pt, Rio Juruena) is a long river in west-central Brazil, in the state of Mato Grosso.
Course
The Juruena originates in the Parecis plateau.
Within Mato Grosso the river defines the eastern boundary of the Igarapés do Jurue ...
s – the area now covered roughly by modern Mato Grosso state) were the original pre-migration Tupi-Guarani homelands. Besides the Tupi and Tapuia, it is common to identify two other indigenous mega-groups in the interior: the Caribs, who inhabited much of what is now northwestern Brazil, including both shores of the Amazon River up to the delta and the Nuaraque group, whose constituent tribes inhabited several areas, including most of the upper Amazon (west of what is now Manaus
Manaus () is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian state of Amazonas. It is the seventh-largest city in Brazil, with an estimated 2020 population of 2,219,580 distributed over a land area of about . Located at the east center of the s ...
) and also significant pockets in modern Amapá and Roraima states.
The names by which the different Tupi tribes were recorded by Portuguese and French authors of the 16th century are poorly understood. Most do not seem to be proper names, but descriptions of relationship, usually familial – e.g. ''tupi'' means "first father", ''tupinambá'' means "relatives of the ancestors", ''tupiniquim'' means "side-neighbors", ''tamoio'' means "grandfather", ''temiminó'' means "grandson", ''tabajara'' means "in-laws" and so on. Some etymologists believe these names reflect the ordering of the migration waves of Tupi people from the interior to the coasts, e.g. first Tupi wave to reach the coast being the "grandfathers" (Tamoio), soon joined by the "relatives of the ancients" (Tupinamba), by which it could mean relatives of the Tamoio, or a Tamoio term to refer to relatives of the old Tupi back in the upper Amazon basin. The "grandsons" (Temiminó) might be a splinter. The "side-neighbors" (Tupiniquim) meant perhaps recent arrivals, still trying to jostle their way in. However, by 1870 the Tupi tribes population had declined to 250,000 indigenous people and by 1890 had diminished to an approximate 100,000.
First contacts

 When the Portuguese explorers first arrived in Brazil in April 1500, they found, to their astonishment, a wide coastline rich in resources, teeming with hundreds of thousands of Indigenous people living in a "paradise" of natural riches. Pêro Vaz de Caminha, the official scribe of
When the Portuguese explorers first arrived in Brazil in April 1500, they found, to their astonishment, a wide coastline rich in resources, teeming with hundreds of thousands of Indigenous people living in a "paradise" of natural riches. Pêro Vaz de Caminha, the official scribe of Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human ...
, the commander of the discovery fleet which landed in the present state of Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-larges ...
, wrote a letter to the King of Portugal describing in glowing terms the beauty of the land.
In "Histoire des découvertes et conquestes des Portugais dans le Nouveau Monde", Lafiatau described the natives as people who wore no clothing but rather painted their whole bodies with red. Their ears, noses, lips and cheeks were pierced. The men would shave the front, the top of the head and over the ears, while the women would typically wear their hair loose or in braids. Both men and women would accessorize themselves with noisy porcelain collars and bracelets, feathers dried fruits. He describes the ritualistic nature of how they practiced cannibalism, and he even mentions the importance of the role of the women in a household.
At the time of European arrival, the territory of current day Brazil had as many as 2,000 nations and tribes (which equated to 11 million Indians). During the first 100 years of contact, the Indian population was reduced by 90%. This was mainly due to disease and illness spread by the colonists, furthered by slavery and European-brought violence. The indigenous people were traditionally mostly semi-nomadic tribes who subsisted on hunting, fishing, gathering, and migrant agriculture. For hundreds of years, the indigenous people of Brazil lived a semi-nomadic life, managing the forests to meet their needs. When the Portuguese arrived in 1500, the natives were living mainly on the coast and along the banks of major rivers. Initially, the Europeans saw native people as noble savage
A noble savage is a literary stock character who embodies the concept of the indigene, outsider, wild human, an " other" who has not been "corrupted" by civilization, and therefore symbolizes humanity's innate goodness. Besides appearing in m ...
s, and miscegenation of the population began right away. Portuguese claims of tribal warfare, cannibalism, and the pursuit of Amazonian brazilwood
''Paubrasilia echinata'' is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. It is a Brazilian timber tree commonly known as Pernambuco wood or brazilwood ( pt, pau-de-pernambuco, ; ...
for its treasured red dye convinced the Portuguese that they should "civilize" the natives (originally, colonists called Brazil Terra de Santa Cruz
The name '' Brazil'' is a shortened form of ''Terra do Brasil'' ("Land of Brazil"), a reference to the brazilwood tree. The name was given in the early 16th century to the territories leased to the merchant consortium led by Fernão de Loronha, to ...
, until later it acquired its name (see List of meanings of countries' names
This list covers English-language country names with their etymologies. Some of these include notes on indigenous names and their etymologies. Countries in ''italics'' are endonyms or no longer exist as sovereign political entities.
A
Afgh ...
) from brazilwood
''Paubrasilia echinata'' is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. It is a Brazilian timber tree commonly known as Pernambuco wood or brazilwood ( pt, pau-de-pernambuco, ; ...
). But the Portuguese, like the Spanish in their North American territories, had brought diseases with them against which many Indians were helpless due to lack of immunity. Measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
, and influenza killed tens of thousands. The diseases spread quickly along the indigenous trade routes, and it is likely that whole tribes were annihilated without ever coming in direct contact with Europeans.
Slavery and the bandeiras
The mutual feeling of wonderment and good relationship was to end in the succeeding years. The Portuguesecolonist
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
s, all males, started to have children with female Amerindians, creating a new generation of mixed-race people who spoke Indian languages (a Tupi language called Nheengatu). The children of these Portuguese men and Indian women formed the majority of the population. Groups of fierce pathfinders organized expeditions called " bandeiras" (flags) into the backlands to claim them for the Portuguese crown and to look for gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and precious stones.
Intending to profit from the sugar trade
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or doubl ...
, the Portuguese decided to plant sugar cane in Brazil, and to use indigenous slaves as the workforce, as the Spanish colonies were successfully doing. But the indigenous people were hard to capture. They were soon infected by diseases brought by the Europeans against which they had no natural immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity de ...
, and began dying in great numbers.
The Jesuits

Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
priests arrived with the first Governor General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy ...
as clerical assistants to the colonists, with the intention of converting the indigenous people to Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. They presented arguments in support of the notion that the indigenous people should be considered human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
, and extracted a Papal bull ('' Sublimis Deus'') proclaiming that, irrespective of their beliefs, they should be considered fully rational human beings, with rights to freedom and private property, who must not be enslaved.
 Jesuit priests such as fathers José de Anchieta and Manuel da Nóbrega studied and recorded their language and founded mixed settlements, such as
Jesuit priests such as fathers José de Anchieta and Manuel da Nóbrega studied and recorded their language and founded mixed settlements, such as São Paulo dos Campos de Piratininga
São Paulo dos Campos de Piratininga (''Saint Paul of the Fields of Piratininga'' in Portuguese) was the village that developed as São Paulo, Brazil in the region known as Campos de Piratininga. It was founded as a religious mission and a ...
, where colonists and Indians lived side by side, speaking the same ''Língua Geral
Língua Geral (, ''General Language'') is the name of two distinct lingua francas, spoken in Brazil: the '' Língua Geral Paulista'' (''Tupi Austral'', or Southern Tupi), which was spoken in the region of Paulistania but is now dead, and the '' L� ...
'' (common language), and freely intermarried. They began also to establish more remote villages peopled only by "civilized" Indians, called ''Missions'', or reductions (see the article on the Guarani people for more details).
By the middle of the 16th century, Catholic Jesuit priests, at the behest of Portugal's monarchy, had established missions throughout the country's colonies. They worked to both Europeanize them and convert them to Catholicism. Some historians argue that the Jesuits provided a period of relative stability for the Indians. Indeed, the Jesuits argued against using indigenous Brazilians for slave labour. However, the Jesuits still contributed to European imperialism. Many historians regard Jesuit involvement to be an ethnocide of indigenous culture where the Jesuit's attempted to 'Europeanise' the Indigenous Peoples of Brazil.
In the mid-1770s, the indigenous peoples' fragile co-existence with the colonists was again threatened. Because of a complex diplomatic web between Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and the Vatican, the Jesuits were expelled from Brazil and the missions confiscated and sold.
By 1800, the population of Colonial Brazil had reached approximately 2.21 million, among whom only approximately 100,858 were indigenous. By 1850, that number had dwindled to an estimated 52,126 people, out of 1.86 million.
Wars
 A number of wars between several tribes, such as the Tamoio Confederation, and the Portuguese ensued, sometimes with the Indians siding with enemies of Portugal, such as the French, in the famous episode of France Antarctique in
A number of wars between several tribes, such as the Tamoio Confederation, and the Portuguese ensued, sometimes with the Indians siding with enemies of Portugal, such as the French, in the famous episode of France Antarctique in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, sometimes allying themselves to Portugal in their fight against other tribes. At approximately the same period, a German soldier, Hans Staden
Hans Staden (c. 1525 – c. 1576) was a German soldier and explorer who voyaged to South America in the middle of the sixteenth century, where he was captured by the Tupinambá people of Brazil. He managed to survive and return safe to Europe. ...
, was captured by the Tupinambá and released after a while. He described it in a famous book, ''Warhaftige Historia und beschreibung eyner Landtschafft der Wilden Nacketen, Grimmigen Menschfresser-Leuthen in der Newenwelt America gelegen'' (True Story and Description of a Country of Wild, Naked, Grim, Man-eating People in the New World, America) (1557)
There are various documented accounts of smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
being knowingly used as a biological weapon by New Brazilian villagers that wanted to get rid of nearby Indian tribes (not always aggressive ones). The most "classical", according to Anthropologist, Mércio Pereira Gomes, happened in Caxias, in south Maranhão, where local farmers, wanting more land to extend their cattle farms, gave clothing owned by ill villagers (that normally would be burned to prevent further infection) to the Timbira. The clothing infected the entire tribe, and they had neither immunity nor cure. Similar things happened in other villages throughout South America.
The rubber trade
The 1840s brought trade and wealth to theAmazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
. The process for vulcanizing rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
was developed, and worldwide demand for the product skyrocketed. The best rubber trees in the world grew in the Amazon, and thousands of rubber tappers began to work the plantations. When the Indians proved to be a difficult labor force, peasants from surrounding areas were brought into the region. In a dynamic that continues to this day, the indigenous population was at constant odds with the peasants, who the Indians felt had invaded their lands in search of treasure.
The legacy of Cândido Rondon
 In the 20th century, the Brazilian Government adopted a more humanitarian attitude and offered official protection to the indigenous people, including the establishment of the first indigenous reserves. Fortune brightened for the Indians around the turn of the 20th century when Cândido Rondon, a man of both Portuguese and Bororo ancestry, and an explorer and progressive officer in the Brazilian army, began working to gain the Indians' trust and establish peace. Rondon, who had been assigned to help bring telegraph communications into the Amazon, was a curious and natural explorer. In 1910, he helped found the '' Serviço de Proteção aos Índios – SPI'' (Service for the Protection of Indians, today the FUNAI, or '' Fundação Nacional do Índio'', National Foundation for Indians). SPI was the first federal agency charged with protecting Indians and preserving their culture. In 1914, Rondon accompanied
In the 20th century, the Brazilian Government adopted a more humanitarian attitude and offered official protection to the indigenous people, including the establishment of the first indigenous reserves. Fortune brightened for the Indians around the turn of the 20th century when Cândido Rondon, a man of both Portuguese and Bororo ancestry, and an explorer and progressive officer in the Brazilian army, began working to gain the Indians' trust and establish peace. Rondon, who had been assigned to help bring telegraph communications into the Amazon, was a curious and natural explorer. In 1910, he helped found the '' Serviço de Proteção aos Índios – SPI'' (Service for the Protection of Indians, today the FUNAI, or '' Fundação Nacional do Índio'', National Foundation for Indians). SPI was the first federal agency charged with protecting Indians and preserving their culture. In 1914, Rondon accompanied Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
on Roosevelt's famous expedition to map the Amazon and discover new species. During these travels, Rondon was appalled to see how settlers and developers treated the indigenes, and he became their lifelong friend and protector.
Rondon, who died in 1958, is a national hero in Brazil. The Brazilian state of Rondônia is named after him.
SPI failure and FUNAI
 After Rondon's pioneering work, the SPI was turned over to bureaucrats and military officers and its work declined after 1957. The new officials did not share Rondon's deep commitment to the Indians. SPI sought to address tribal issues by transforming the tribes into mainstream Brazilian society. The lure of reservation riches enticed cattle ranchers and settlers to continue their assault on Indians lands – and the SPI eased the way. Between 1900 and 1967, an estimated 98 indigenous tribes were wiped out.
Mostly due to the efforts of the Villas-Bôas brothers, Brazil's first Indian reserve, the Xingu National Park, was established by the Federal Government in 1961.
During the social and political upheaval in the 1960s, reports of mistreatment of Indians increasingly reached
After Rondon's pioneering work, the SPI was turned over to bureaucrats and military officers and its work declined after 1957. The new officials did not share Rondon's deep commitment to the Indians. SPI sought to address tribal issues by transforming the tribes into mainstream Brazilian society. The lure of reservation riches enticed cattle ranchers and settlers to continue their assault on Indians lands – and the SPI eased the way. Between 1900 and 1967, an estimated 98 indigenous tribes were wiped out.
Mostly due to the efforts of the Villas-Bôas brothers, Brazil's first Indian reserve, the Xingu National Park, was established by the Federal Government in 1961.
During the social and political upheaval in the 1960s, reports of mistreatment of Indians increasingly reached Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
's urban centers and began to affect Brazilian thinking. In 1967, following the publication of the '' Figueiredo Report'', commissioned by the Ministry of the Interior, the military government launched an investigation into SPI. It soon came to light that the SPI was corrupt and failing to protect natives, their lands, and, culture. The 5,000-page report catalogued atrocities including slavery, sexual abuse, torture, and mass murder.
It has been charged that agency officials, in collaboration with land speculators, were systematically slaughtering the Indians by intentionally circulating disease-laced clothes. Criminal prosecutions followed, and the SPI was disbanded. The same year the government established Fundação Nacional do Índio (''National Indian Foundation''), known as FUNAI which is responsible for protecting the interests, cultures, and rights of the Brazilian indigenous populations. Some tribes have become significantly integrated into Brazilian society. The unacculturated tribes which have been contacted by FUNAI, are supposed to be protected and accommodated within Brazilian society in varying degrees. By 1987 it was recognized that unessential contact with the tribes was causing illness and social disintegration. The uncontacted tribes are now supposed to be protected from intrusion and interference in their life style and territory. However, the exploitation of rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
and other Amazonic natural resources has led to a new cycle of invasion, expulsion, massacres and death, which continues to this day.
The military government
Also in 1964, in a seismic political shift, the Brazilian military took control of the government and abolished all existing political parties, creating a two-party system. For the next two decades, Brazil was ruled by a series of generals. The country's mantra was "Brazil, the Country of the Future," which the military government used as justification for a giant push into the Amazon to exploit its resources, thereby beginning to transform Brazil into one of the leading economies of the world. Construction began on a transcontinental highway across the Amazon basin, aimed to encourage migration to theAmazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
and to open up the region to more trade. With funding from World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, thousands of square miles of forest were cleared without regard for reservation status. After the highway projects came giant hydroelectric projects, then swaths of forest were cleared for cattle ranches. As a result, reservation lands suffered massive deforestation and flooding. The public works projects attracted very few migrants, but those few – and largely poor – settlers brought new diseases that further devastated the Indians population.
Contemporary situation
 The 1988 Brazilian Constitution recognizes indigenous people' right to pursue their traditional ways of life and to the permanent and exclusive possession of their "traditional lands", which are demarcated as Indigenous Territories.Federal Constitution of Brazil
The 1988 Brazilian Constitution recognizes indigenous people' right to pursue their traditional ways of life and to the permanent and exclusive possession of their "traditional lands", which are demarcated as Indigenous Territories.Federal Constitution of BrazilChapter VII Article 231
. In practice, however, Brazil's indigenous people still face a number of external threats and challenges to their continued existence and cultural heritage. The process of demarcation is slow—often involving protracted legal battles—and FUNAI do not have sufficient resources to enforce the legal protection on indigenous land. Since the 1980s there has been a boom in the exploitation of the Amazon Rainforest for mining, logging and cattle ranching, posing a severe threat to the region's indigenous population. Settlers illegally encroaching on indigenous land continue to destroy the environment necessary for indigenous people' traditional ways of life, provoke violent confrontations and spread disease. People such as the Akuntsu and Kanoê have been brought to the brink of extinction within the last three decades. Deforestation for mining also affects the daily lives of indigenous tribes in Brazil. For instance, the Munduruku Indians have higher levels of mercury poisoning due to gold production in the area. On 13 November 2012, the national indigenous people association from Brazil APIB submitted to the United Nation a human rights document that complaints about new proposed laws in Brazil that would further undermine their rights if approved. Much of the language has been incorporated into the official
Brazilian Portuguese
Brazilian Portuguese (' ), also Portuguese of Brazil (', ) or South American Portuguese (') is the set of varieties of the Portuguese language native to Brazil and the most influential form of Portuguese worldwide. It is spoken by almost all of ...
language. For example, 'Carioca' the word used to describe people born in the city of Rio de Janeiro, is from the indigenous word for 'house of the white (people)'.
 Within hours of taking office in January 2019, Bolsonaro made two major changes to FUNAI, affecting its responsibility to identify and demarcate indigenous lands: He moved FUNAI from under the Ministry of Justice to be under the newly created ''Ministry of Human Rights, Family and Women,'' and he delegated the identification of the traditional habitats of indigenous people and their designation as inviolable protected territories − a task attributed to FUNAI by the constitution – to the Agriculture Ministry. He argued that those territories have tiny isolated populations and proposed to integrate them into the larger Brazilian society. Critics feared that such integration would lead the Brazilian natives to suffer
Within hours of taking office in January 2019, Bolsonaro made two major changes to FUNAI, affecting its responsibility to identify and demarcate indigenous lands: He moved FUNAI from under the Ministry of Justice to be under the newly created ''Ministry of Human Rights, Family and Women,'' and he delegated the identification of the traditional habitats of indigenous people and their designation as inviolable protected territories − a task attributed to FUNAI by the constitution – to the Agriculture Ministry. He argued that those territories have tiny isolated populations and proposed to integrate them into the larger Brazilian society. Critics feared that such integration would lead the Brazilian natives to suffer cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
The different types of cultural ass ...
. Several months later, Brazil's National Congress overturned these changes.
The European Union–Mercosur free trade agreement
The European Union–Mercosur free trade agreement is a proposed free trade agreement on which the European Union and Mercosur reached agreement in principle in 2019. The planned deal was announced on 28 June at the 2019 G20 Osaka summit after t ...
, which would form one of the world's largest free trade areas, has been denounced by environmental activists and indigenous rights campaigners. The fear is that the deal could lead to more deforestation of the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest is the largest rainforest in the world, covering an area of 3,000,000 km2 (2,316,612.95 square miles). It represents over half of the planet's rainforests and comprises the largest and most biodiverse tract of tropic ...
as it expands market access to Brazilian beef.
A 2019 report by the Indigenous Missionary Council on Violence against Indigenous Peoples in Brazil documented an increase in the number of invasions of indigenous lands by loggers, miners and land grabbers, recording 160 cases in the first nine months of 2019, up from 96 cases in the entirety of 2017. The number of reported killings in 2018, 135, had also increased from 110 recorded in 2017.
On 5 May 2020, post HRW's investigation, Brazilian lawmakers released a report examining the violence against Indigenous people, Afro-Brazilian rural communities and others engaged in illegal logging, mining, and land grabbing.
Indigenous Rights Movements
Urban Rights Movement
The urban rights movement is a recent development in the rights of indigenous peoples. Brazil has one of the highest income inequalities in the world, and much of that population includes indigenous tribes migrating toward urban areas both by choice and by displacement. Beyond the urban rights movement, studies have shown that the suicide risk among the indigenous population is 8.1 times higher than the non-indigenous population. Many indigenous rights movements have been created through the meeting of many indigenous tribes in urban areas. For example, in Barcelos, an indigenous rights movement arose because of "local migratory circulation." This is how many alliances form to create a stronger network for mobilization. Indigenous populations also living in urban areas have struggles regarding work. They are pressured into doing cheap labor. Programs like Oxfam have been used to help indigenous people gain partnerships to begin grassroots movements. Some of their projects overlap with environmental activism as well. Many Brazilian youths are mobilizing through the increased social contact, since some indigenous tribes stay isolated while others adapt to the change. Access to education also affects these youths, and therefore, more groups are mobilizing to fight for indigenous rights.Environmental and Territorial Rights Movement
Dynamics favouring recognition
Many of the indigenous tribes' rights and rights claims parallel the environmental and territorial rights movement. Although indigenous people have gained 21% of the Brazilian Amazon as part of indigenous land, many issues still affect the sustainability of Indigenous territories today. Climate change is one issue that indigenous tribes attribute as a reason to keep their territory. Some indigenous peoples and conservation organizations in the Brazilian Amazon have formed alliances, such as the alliance of the A'ukre Kayapo village and the Instituto SocioAmbiental (ISA) environmental organization. They focus on environmental, education and developmental rights. For example, Amazon Watch collaborates with various indigenous organizations in Brazil to fight for both territorial and environmental rights. "Access to natural resources by indigenous and peasant communities in Brazil has been considerably less and much more insecure," so activists focus on more traditional conservation efforts, and expanding territorial rights for indigenous people. Territorial rights for the indigenous populations of Brazil largely fall under socio-economic issues. There have been violent conflicts regarding rights to land between the government and the indigenous population, and political rights have done little to stop them. There have been movements of the landless (MST) that help keep land away from the elite living in Brazil.Dynamics opposing recognition
Environmentalists and indigenous peoples have been viewed as opponents to economic growth and barriers to development due to the fact that much of the land that indigenous tribes live on could be used for development projects, including dams, and more industrialization. Groups self-identifying as indigenous may lack intersubjective recognition, thus claims to TIs, which can involve the demarcation of large areas of territory and threaten to dispossess established local communities, can be challenged by others, even neighbouring kinship groups, on the grounds that those making the claims are not 'real Indians', due to factors such as historical intermarriage ( miscegenation),cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
The different types of cultural ass ...
, and stigma against self-identifying as indigenous. Claims to TIs can also be opposed by major landowning families from the rubber era, or by the peasants that work the land, who may instead prefer to support the concept of the extractive reserve.
Education
The Afro-Brazilian and Indigenous History and Culture Law (Law No. 11.645/2008) is a Brazilian law mandating the teaching of Afro-Brazilian and Indigenous History and Culture which was passed and entered into effectiveness on 10 March 2008. It amends Law No. 9.394, of 20 December 1996, modified by Law No. 10.639, of 9 January 2003, which established the guidelines and bases of Brazilian national education, to include in the official curriculum of the education system the mandatory theme of Afro-Brazilian and Indigenous History and Culture.Major ethnic groups
For complete list see List of Indigenous peoples in Brazil * Amanyé
* Atikum
* Awá-Guajá
*
* Amanyé
* Atikum
* Awá-Guajá
* Baniwa
Baniwa (also known with local variants as Baniva, Baniua, Curipaco, Vaniva, Walimanai, Wakuenai) are indigenous South Americans, who speak the Baniwa language belonging to the Maipurean (Arawak) language family. They live in the Amazon Region, ...
* Botocudo
* Bará
* Enawene Nawe
* Guaraní
* Kadiwéu
* Kaingang
The Kaingang (also spelled ''caingangue'' in Portuguese or ''kanhgág'' in the Kaingang language) people are an Indigenous Brazilian ethnic group spread out over the three southern Brazilian states of Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande ...
* Kamayurá (Kamaiurá)
* Karajá
The Karajá, also known as Iny, are an indigenous tribe located in Brazil.Karaja Indians.
''Hands Ar ...
* Kayapo
* Kubeo
* Kaxinawá
* Kokama
* Korubo
* Kulina Madihá
* Mbya
* Makuxi
* Matsés
* Mayoruna
* Munduruku
* ''Hands Ar ...
Mura people
The Muras are an indigenous people who live in the central and eastern parts of Amazonas, Brazil, along the Amazon river from the Madeira to the Purus. They played an important part in Brazilian history during colonial times and were known for ...
* Nambikwara
* Ofayé
* Pai Tavytera
* Panará
* Pankararu
* Pataxó
* Pirahã
* Paiter
* Potiguara
The Potiguara (also Potyguara or Pitiguara) are an indigenous people of Brazil. The Potiguara people live in Paraíba, in the municipalities of Marcação, Baía da Traição and Rio Tinto. Their population numbers sixteen thousand individua ...
* Sateré Mawé
* Suruí do Pará
* Tapirape
* Terena
The Trans-European Research and Education Networking Association (TERENA, ) was a not-for-profit association of European national research and education networks (NRENs) incorporated in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. The association was originally ...
* Ticuna
* Tremembé
Tremembé is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Vale do Paraíba e Litoral Norte. The population is 47,714 (2020 est.) in an area of 191.09 km². The elevation is 560 m.
A ...
* Tupi
* Waorani
* Wapixana
The Wapishana or Wapichan (or Wapisiana, Wapitxana, Vapidiana, Wapixana) are an indigenous group found in the Roraima area of northern Brazil and southern Guyana.
Location
Currently the Wapishana are located in the State of Roraima, Brazil, no ...
* Wauja
The Waura or Wauja (waujá) are an indigenous people of Brazil. Their language, Waura, is an Arawakan language. They live in the region near the Upper Xingu River, in the Xingu Indigenous Park, and had a population of 487 in 2010.
History
The W ...
* Witoto
* Xakriabá
* Xavante
* Xukuru
* Yanomami
See also
* Amazon Watch * Amerindians * Archaeology of the Americas * Agriculture in Brazil *Bandeirantes
The ''Bandeirantes'' (), literally "flag-carriers", were slavers, explorers, adventurers, and fortune hunters in early Colonial Brazil. They are largely responsible for Brazil's great expansion westward, far beyond the Tordesillas Line of 1494 ...
* Belo Monte Dam
The Belo Monte Dam (''formerly known as'' Kararaô) is a hydroelectric dam complex on the northern part of the Xingu River in the state of Pará, Brazil. After its completion, with the installation of its 18th turbine, in November 2019, the ins ...
* Bering Land Bridge
* Camarão indians' letters
* Darcy Ribeiro
* Encyclopedia of Indigenous Peoples in Brazil
* Ecotourism in the Amazon rainforest
* Chief Raoni
* COIAB
* Ceibo Alliance
* Brazilians
Brazilians ( pt, Brasileiros, ) are the citizens of Brazil. A Brazilian can also be a person born abroad to a Brazilian parent or legal guardian as well as a person who acquired Brazilian citizenship. Brazil is a multiethnic society, which ...
* Fundação Nacional do Índio
* Indian Day
* Índia pega no laço
* Indigenous peoples of South America
* Man of the Hole
* Museu do Índio
* Uncontacted peoples
* Percy Fawcett
* Sydney Possuelo
* Villas Boas brothers
References
External links
Fundação Nacional do Índio, National Foundation of the Native American
at Google Videos
New photos of Uncontacted Brazilian tribe
by ''
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large n ...
''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous Peoples in Brazil
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
Ethnic groups in Brazil
Race in Brazil