Image gradient on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the
An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the
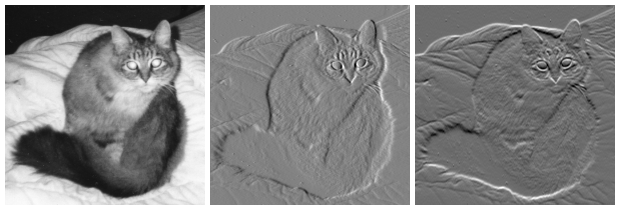 Image gradients can be used to extract information from images. Gradient images are created from the original image (generally by convolving with a filter, one of the simplest being the
Image gradients can be used to extract information from images. Gradient images are created from the original image (generally by convolving with a filter, one of the simplest being the
 An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the
An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the Canny edge detector
The Canny edge detector is an edge detection operator that uses a multi-stage algorithm to detect a wide range of edges in images. It was developed by John F. Canny in 1986. Canny also produced a ''computational theory of edge detection'' explai ...
uses image gradient for edge detection. In graphics software for digital image editing, the term gradient or color gradient is also used for a gradual blend of color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
which can be considered as an even gradation from low to high values, as used from white to black in the images to the right. Another name for this is ''color progression''.
Mathematically, the gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p is the "direction and rate of fastest increase". If the gr ...
of a two-variable function (here the image intensity function) at each image point is a 2D vector with the components given by the derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
s in the horizontal and vertical directions. At each image point, the gradient vector points in the direction of largest possible intensity increase, and the length of the gradient vector corresponds to the rate of change in that direction.
Since the intensity function of a digital image is only known at discrete points, derivatives of this function cannot be defined unless we assume that there is an underlying continuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous g ...
intensity function which has been sampled at the image points. With some additional assumptions, the derivative of the continuous intensity function can be computed as a function on the sampled intensity function, i.e., the digital image. Approximations of these derivative functions can be defined at varying degrees of accuracy. The most common way to approximate the image gradient is to convolve an image with a kernel, such as the Sobel operator
The Sobel operator, sometimes called the Sobel–Feldman operator or Sobel filter, is used in image processing and computer vision, particularly within edge detection algorithms where it creates an image emphasising edges. It is named after I ...
or Prewitt operator.
Image gradients are often utilized in maps and other visual representations of data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpret ...
in order to convey additional information. GIS tools use color progressions to indicate elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
and population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopu ...
, among others.
Computer vision
 Image gradients can be used to extract information from images. Gradient images are created from the original image (generally by convolving with a filter, one of the simplest being the
Image gradients can be used to extract information from images. Gradient images are created from the original image (generally by convolving with a filter, one of the simplest being the Sobel filter
The Sobel operator, sometimes called the Sobel–Feldman operator or Sobel filter, is used in image processing and computer vision, particularly within edge detection algorithms where it creates an image emphasising edges. It is named after I ...
) for this purpose. Each pixel of a gradient image measures the change in intensity of that same point in the original image, in a given direction. To get the full range of direction, gradient images in the x and y directions are computed.
One of the most common uses is in edge detection. After gradient images have been computed, pixels with large gradient values become possible edge pixels. The pixels with the largest gradient values in the direction of the gradient become edge pixels, and edges may be traced in the direction perpendicular to the gradient direction. One example of an edge detection algorithm that uses gradients is the Canny edge detector
The Canny edge detector is an edge detection operator that uses a multi-stage algorithm to detect a wide range of edges in images. It was developed by John F. Canny in 1986. Canny also produced a ''computational theory of edge detection'' explai ...
.
Image gradients can also be used for robust feature and texture matching. Different lighting or camera properties can cause two images of the same scene to have drastically different pixel values. This can cause matching algorithms to fail to match very similar or identical features. One way to solve this is to compute texture or feature signatures based on gradient images computed from the original images. These gradients are less susceptible to lighting and camera changes, so matching errors are reduced.
Mathematics
The gradient of an image is a vector of its partials: :, where: : is the derivative with respect to x (gradient in the x direction) : is the derivative with respect to y (gradient in the y direction). Thederivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
of an image can be approximated by finite differences. If central difference is used, to calculate we can apply a 1-dimensional filter to the image by convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' ...
:
:
where denotes the 1-dimensional convolution operation. This 2×1 filter will shift the image by half a pixel. To avoid this, the following 3×1 filter
:
can be used. The gradient direction can be calculated by the formula:
: