Igneous rock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Igneous rock (derived from the 

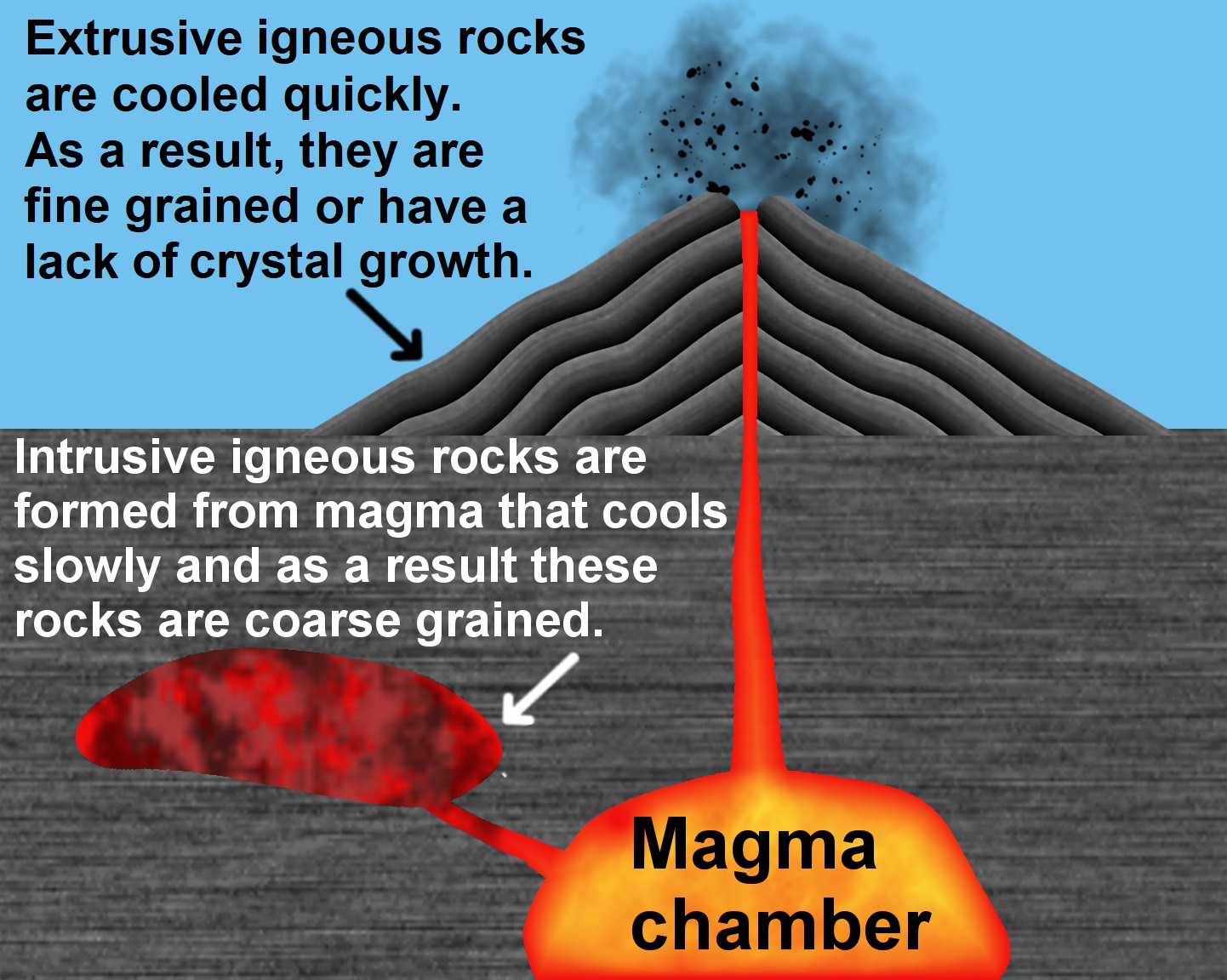 Igneous rocks can be either intrusive ( plutonic and hypabyssal) or
Igneous rocks can be either intrusive ( plutonic and hypabyssal) or
 Intrusive igneous rocks make up the majority of igneous rocks and are formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of a planet. Bodies of intrusive rock are known as '' intrusions'' and are surrounded by pre-existing rock (called '' country rock''). The country rock is an excellent thermal insulator, so the magma cools slowly, and intrusive rocks are coarse-grained ('' phaneritic''). The mineral grains in such rocks can generally be identified with the naked eye. Intrusions can be classified according to the shape and size of the intrusive body and its relation to the
Intrusive igneous rocks make up the majority of igneous rocks and are formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of a planet. Bodies of intrusive rock are known as '' intrusions'' and are surrounded by pre-existing rock (called '' country rock''). The country rock is an excellent thermal insulator, so the magma cools slowly, and intrusive rocks are coarse-grained ('' phaneritic''). The mineral grains in such rocks can generally be identified with the naked eye. Intrusions can be classified according to the shape and size of the intrusive body and its relation to the

 Extrusive igneous rock, also known as volcanic rock, is formed by the cooling of molten magma on the earth's surface. The magma, which is brought to the surface through fissures or
Extrusive igneous rock, also known as volcanic rock, is formed by the cooling of molten magma on the earth's surface. The magma, which is brought to the surface through fissures or
 Igneous rocks are classified according to mode of occurrence, texture, mineralogy, chemical composition, and the geometry of the igneous body.
The classification of the many types of igneous rocks can provide important information about the conditions under which they formed. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends on the cooling history, and the mineral composition of the rock. Feldspars, quartz or feldspathoids, olivines, pyroxenes, amphiboles, and micas are all important minerals in the formation of almost all igneous rocks, and they are basic to the classification of these rocks. All other minerals present are regarded as nonessential in almost all igneous rocks and are called ''accessory minerals''. Types of igneous rocks with other essential minerals are very rare, but include
Igneous rocks are classified according to mode of occurrence, texture, mineralogy, chemical composition, and the geometry of the igneous body.
The classification of the many types of igneous rocks can provide important information about the conditions under which they formed. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends on the cooling history, and the mineral composition of the rock. Feldspars, quartz or feldspathoids, olivines, pyroxenes, amphiboles, and micas are all important minerals in the formation of almost all igneous rocks, and they are basic to the classification of these rocks. All other minerals present are regarded as nonessential in almost all igneous rocks and are called ''accessory minerals''. Types of igneous rocks with other essential minerals are very rare, but include
 Texture is an important criterion for the naming of volcanic rocks. The
Texture is an important criterion for the naming of volcanic rocks. The 
 When it is impractical to classify a volcanic rock by mineralogy, the rock must be classified chemically.
There are relatively few minerals that are important in the formation of common igneous rocks, because the magma from which the minerals crystallize is rich in only certain elements: silicon,
When it is impractical to classify a volcanic rock by mineralogy, the rock must be classified chemically.
There are relatively few minerals that are important in the formation of common igneous rocks, because the magma from which the minerals crystallize is rich in only certain elements: silicon,
 :
Most magmas are fully melted only for small parts of their histories. More typically, they are mixes of melt and crystals, and sometimes also of gas bubbles. Melt, crystals, and bubbles usually have different densities, and so they can separate as magmas evolve.
As magma cools, minerals typically
:
Most magmas are fully melted only for small parts of their histories. More typically, they are mixes of melt and crystals, and sometimes also of gas bubbles. Melt, crystals, and bubbles usually have different densities, and so they can separate as magmas evolve.
As magma cools, minerals typically
File:Kanaga Volcano (22432739869).jpg, Kanaga volcano in the
USGS Igneous Rocks
The IUGS systematics of igneous rocks
{{DEFAULTSORT:Igneous Rock 01 Igneous petrology Volcanology
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contra ...
rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses.
Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust.

Geological significance
Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rocks form about 15% of the Earth's current land surface. Most of the Earth's oceanic crust is made of igneous rock. Igneous rocks are also geologically important because: * their minerals and global chemistry give information about the composition of the lower crust or upper mantle from which their parent magma was extracted, and the temperature and pressure conditions that allowed this extraction; * their absolute ages can be obtained from various forms of radiometric dating and can be compared to adjacent geological strata, thus permitting calibration of the geological time scale; * their features are usually characteristic of a specific tectonic environment, allowing tectonic reconstructions (see plate tectonics); * in some special circumstances they host important mineral deposits (ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 Apr ...
s): for example, tungsten, tin, and uranium are commonly associated with granites and diorites, whereas ores of chromium and platinum are commonly associated with gabbros.
Geological setting
 Igneous rocks can be either intrusive ( plutonic and hypabyssal) or
Igneous rocks can be either intrusive ( plutonic and hypabyssal) or extrusive
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contra ...
( volcanic).
Intrusive
bedding
Bedding, also known as bedclothes or bed linen, is the materials laid above the mattress of a bed for hygiene, warmth, protection of the mattress, and decorative effect. Bedding is the removable and washable portion of a human sleeping environm ...
of the country rock into which it intrudes. Typical intrusive bodies are batholiths, stocks, laccolith
A laccolith is a body of intrusive rock with a dome-shaped upper surface and a level base, fed by a conduit from below. A laccolith forms when magma (molten rock) rising through the Earth's crust begins to spread out horizontally, prying apar ...
s, sills and dikes. Common intrusive rocks are granite, gabbro, or diorite.
The central cores of major mountain ranges consist of intrusive igneous rocks. When exposed by erosion, these cores (called '' batholiths'') may occupy huge areas of the Earth's surface.
Intrusive igneous rocks that form at depth within the crust are termed plutonic (or ''abyssal'') rocks and are usually coarse-grained. Intrusive igneous rocks that form near the surface are termed '' subvolcanic'' or ''hypabyssal'' rocks and they are usually much finer-grained, often resembling volcanic rock. Hypabyssal rocks are less common than plutonic or volcanic rocks and often form dikes, sills, laccoliths, lopolith
A lopolith is a large igneous intrusion which is lenticular in shape with a depressed central region. Lopoliths are generally concordant with the intruded strata with dike or funnel-shaped feeder bodies below the body. The term was first defin ...
s, or phacoliths.
Extrusive

 Extrusive igneous rock, also known as volcanic rock, is formed by the cooling of molten magma on the earth's surface. The magma, which is brought to the surface through fissures or
Extrusive igneous rock, also known as volcanic rock, is formed by the cooling of molten magma on the earth's surface. The magma, which is brought to the surface through fissures or volcanic eruptions
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ...
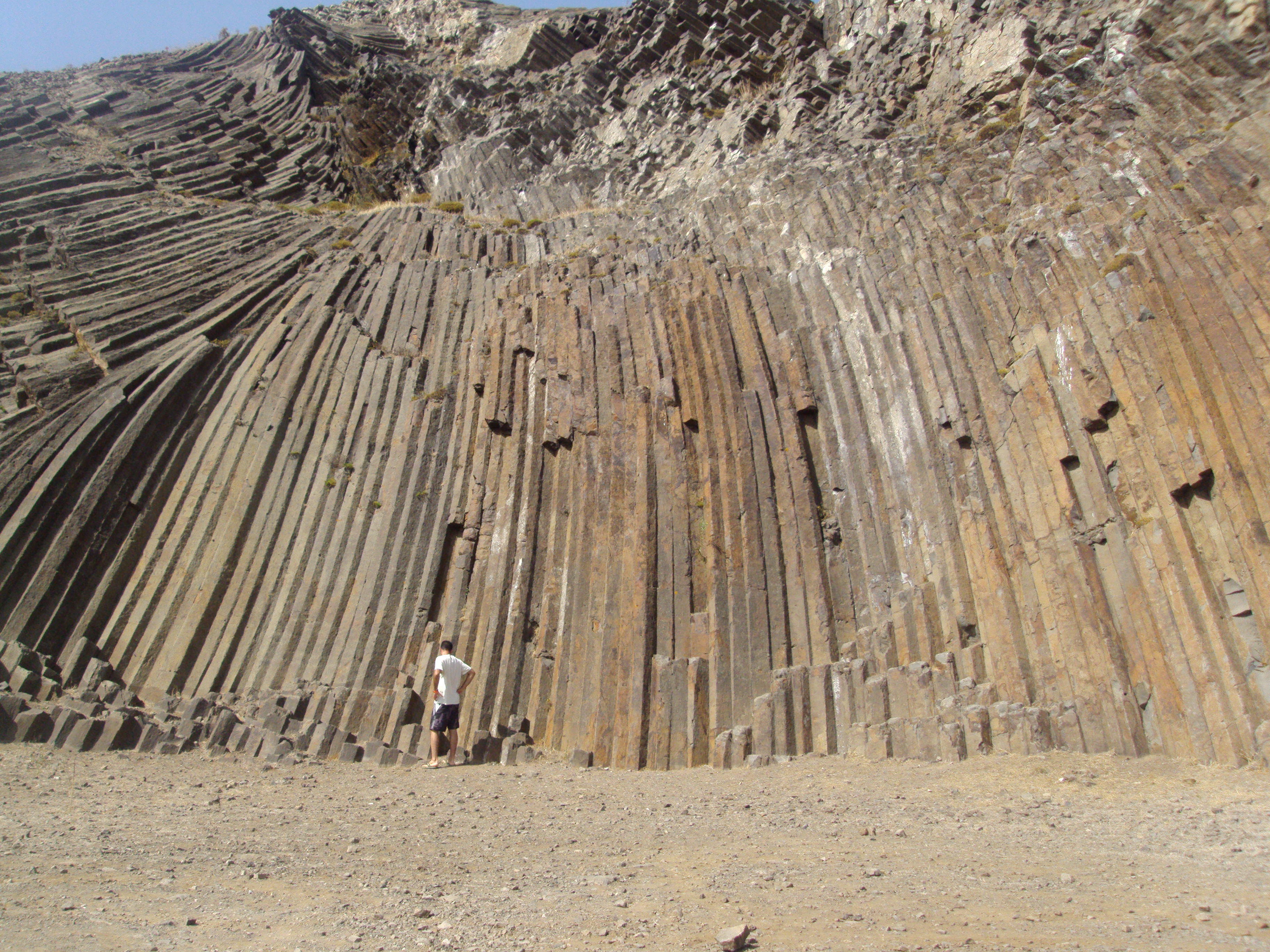
, rapidly solidifies. Hence such rocks are fine-grained ( aphanitic) or even glassy. Basalt is the most common extrusive igneous rock and forms lava flows, lava sheets and lava plateaus. Some kinds of basalt solidify to form long polygonal columns. The Giant's Causeway
The Giant's Causeway is an area of about 40,000 interlocking basalt columns, the result of an ancient volcanic fissure eruption. It is located in County Antrim on the north coast of Northern Ireland, about three miles (5 km) northeast of ...
in Antrim, Northern Ireland is an example.
The molten rock, which typically contains suspended crystals and dissolved gases, is called magma. It rises because it is less dense than the rock from which it was extracted. When magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. Eruptions of volcanoes into air are termed '' subaerial'', whereas those occurring underneath the ocean are termed '' submarine''. Black smokers and mid-ocean ridge basalt are examples of submarine volcanic activity.
The volume of extrusive rock erupted annually by volcanoes varies with plate tectonic setting. Extrusive rock is produced in the following proportions:
* divergent boundary: 73%
* convergent boundary ( subduction zone): 15%
* hotspot: 12%.
The behaviour of lava depends upon its viscosity, which is determined by temperature, composition, and crystal content. High-temperature magma, most of which is basaltic in composition, behaves in a manner similar to thick oil and, as it cools, treacle. Long, thin basalt flows with pahoehoe
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or und ...
surfaces are common. Intermediate composition magma, such as andesite, tends to form cinder cones of intermingled ash, tuff and lava, and may have a viscosity similar to thick, cold molasses or even rubber when erupted. Felsic magma, such as rhyolite, is usually erupted at low temperature and is up to 10,000 times as viscous as basalt. Volcanoes with rhyolitic magma commonly erupt explosively, and rhyolitic lava flows are typically of limited extent and have steep margins because the magma is so viscous.
Felsic and intermediate magmas that erupt often do so violently, with explosions driven by the release of dissolved gases—typically water vapour, but also carbon dioxide. Explosively erupted pyroclastic material is called tephra and includes tuff, agglomerate and ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surro ...
. Fine volcanic ash is also erupted and forms ash tuff deposits, which can often cover vast areas.
Because volcanic rocks are mostly fine-grained or glassy, it is much more difficult to distinguish between the different types of extrusive igneous rocks than between different types of intrusive igneous rocks. Generally, the mineral constituents of fine-grained extrusive igneous rocks can only be determined by examination of thin section
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section (or petrographic thin section) is a thin slice of a rock or mineral sample, prepared in a laboratory, for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron ...
s of the rock under a microscope, so only an approximate classification can usually be made in the field. Although classification by mineral makeup is preferred by the IUGS, this is often impractical, and chemical classification is done instead using the TAS classification
The TAS classification can be used to assign names to many common types of volcanic rocks based upon the relationships between the combined alkali content and the silica content. These chemical parameters are useful, because the relative proportio ...
.
Classification
 Igneous rocks are classified according to mode of occurrence, texture, mineralogy, chemical composition, and the geometry of the igneous body.
The classification of the many types of igneous rocks can provide important information about the conditions under which they formed. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends on the cooling history, and the mineral composition of the rock. Feldspars, quartz or feldspathoids, olivines, pyroxenes, amphiboles, and micas are all important minerals in the formation of almost all igneous rocks, and they are basic to the classification of these rocks. All other minerals present are regarded as nonessential in almost all igneous rocks and are called ''accessory minerals''. Types of igneous rocks with other essential minerals are very rare, but include
Igneous rocks are classified according to mode of occurrence, texture, mineralogy, chemical composition, and the geometry of the igneous body.
The classification of the many types of igneous rocks can provide important information about the conditions under which they formed. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends on the cooling history, and the mineral composition of the rock. Feldspars, quartz or feldspathoids, olivines, pyroxenes, amphiboles, and micas are all important minerals in the formation of almost all igneous rocks, and they are basic to the classification of these rocks. All other minerals present are regarded as nonessential in almost all igneous rocks and are called ''accessory minerals''. Types of igneous rocks with other essential minerals are very rare, but include carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive or extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geochemical verification.
Carbonati ...
s, which contain essential carbonates.
In a simplified classification, igneous rock types are separated on the basis of the type of feldspar present, the presence or absence of quartz, and in rocks with no feldspar or quartz, the type of iron or magnesium minerals present. Rocks containing quartz (silica in composition) are ''silica-oversaturated''. Rocks with feldspathoids are ''silica-undersaturated'', because feldspathoids cannot coexist in a stable association with quartz.
Igneous rocks that have crystals large enough to be seen by the naked eye are called phaneritic; those with crystals too small to be seen are called aphanitic. Generally speaking, phaneritic implies an intrusive origin; aphanitic an extrusive one.
An igneous rock with larger, clearly discernible crystals embedded in a finer-grained matrix is termed porphyry. Porphyritic texture develops when some of the crystals grow to considerable size before the main mass of the magma crystallizes as finer-grained, uniform material.
Igneous rocks are classified on the basis of texture and composition. Texture refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of the mineral grains or crystals of which the rock is composed.
Texture
 Texture is an important criterion for the naming of volcanic rocks. The
Texture is an important criterion for the naming of volcanic rocks. The texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Surface texture, the texture means smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness
* Texture ...
of volcanic rocks, including the size, shape, orientation, and distribution of mineral grains and the intergrain relationships, will determine whether the rock is termed a tuff, a pyroclastic lava or a simple lava. However, the texture is only a subordinate part of classifying volcanic rocks, as most often there needs to be chemical information gleaned from rocks with extremely fine-grained groundmass or from airfall tuffs, which may be formed from volcanic ash.
Textural criteria are less critical in classifying intrusive rocks where the majority of minerals will be visible to the naked eye or at least using a hand lens, magnifying glass or microscope. Plutonic rocks also tend to be less texturally varied and less prone to showing distinctive structural fabrics. Textural terms can be used to differentiate different intrusive phases of large plutons, for instance porphyritic margins to large intrusive bodies, porphyry stocks and subvolcanic dikes. Mineralogical classification is most often used to classify plutonic rocks. Chemical classifications are preferred to classify volcanic rocks, with phenocryst species used as a prefix, e.g. "olivine-bearing picrite" or "orthoclase-phyric rhyolite".
Mineralogical classification
The IUGS recommends classifying igneous rocks by their mineral composition whenever possible. This is straightforward for coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock, but may require examination of thin sections under a microscope for fine-grained volcanic rock, and may be impossible for glassy volcanic rock. The rock must then be classified chemically. Mineralogical classification of an intrusive rock begins by determining if the rock is ultramafic, a carbonatite, or a lamprophyre. An ultramafic rock contains more than 90% of iron- and magnesium-rich minerals such as hornblende, pyroxene, or olivine, and such rocks have their own classification scheme. Likewise, rocks containing more than 50% carbonate minerals are classified as carbonatites, while lamprophyres are rare ultrapotassic rocks. Both are further classified based on detailed mineralogy. In the great majority of cases, the rock has a more typical mineral composition, with significant quartz, feldspars, or feldspathoids. Classification is based on the percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid out of the total fraction of the rock composed of these minerals, ignoring all other minerals present. These percentages place the rock somewhere on the QAPF diagram, which often immediately determines the rock type. In a few cases, such as the diorite-gabbro-anorthite field, additional mineralogical criteria must be applied to determine the final classification. Where the mineralogy of an volcanic rock can be determined, it is classified using the same procedure, but with a modified QAPF diagram whose fields correspond to volcanic rock types.Chemical classification and petrology
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, aluminium, sodium, potassium, calcium, iron, and magnesium. These are the elements that combine to form the silicate minerals, which account for over ninety percent of all igneous rocks. The chemistry of igneous rocks is expressed differently for major and minor elements and for trace elements. Contents of major and minor elements are conventionally expressed as weight percent oxides (e.g., 51% SiO2, and 1.50% TiO2). Abundances of trace elements are conventionally expressed as parts per million by weight (e.g., 420 ppm Ni, and 5.1 ppm Sm). The term "trace element" is typically used for elements present in most rocks at abundances less than 100 ppm or so, but some trace elements may be present in some rocks at abundances exceeding 1,000 ppm. The diversity of rock compositions has been defined by a huge mass of analytical data—over 230,000 rock analyses can be accessed on the web through a site sponsored by the U. S. National Science Foundation (see the External Link to EarthChem).
The single most important component is silica, SiO2, whether occurring as quartz or combined with other oxides as feldspars or other minerals. Both intrusive and volcanic rocks are grouped chemically by total silica content into broad categories.
* '' Felsic'' rocks have the highest content of silica, and are predominantly composed of the ''felsic minerals'' quartz and feldspar. These rocks (granite, rhyolite) are usually light coloured, and have a relatively low density.
* '' Intermediate'' rocks have a moderate content of silica, and are predominantly composed of feldspars. These rocks (diorite, andesite) are typically darker in colour than felsic rocks and somewhat more dense.
* '' Mafic'' rocks have a relatively low silica content and are composed mostly of pyroxenes, olivines and calcic plagioclase. These rocks (basalt, gabbro) are usually dark coloured, and have a higher density than felsic rocks.
* '' Ultramafic'' rock is very low in silica, with more than 90% of mafic minerals (komatiite, dunite).
This classification is summarized in the following table:
The percentage of alkali metal oxide
The alkali metals react with oxygen to form several different compounds: suboxides, oxides, peroxides, sesquioxides, superoxides, and ozonides. They all react violently with water.
Alkali metal suboxides
* Hexarubidium monoxide (Rb6O) h
* No ...
s ( Na2O plus K2O) is second only to silica in its importance for chemically classifying volcanic rock. The silica and alkali metal oxide percentages are used to place volcanic rock on the TAS diagram, which is sufficient to immediately classify most volcanic rocks. Rocks in some fields, such as the trachyandesite field, are further classified by the ratio of potassium to sodium (so that potassic trachyandesites are latites and sodic trachyandesites are benmoreites). Some of the more mafic fields are further subdivided or defined by normative mineralogy
Normative mineralogy is a calculation of the composition of a rock sample that estimates the ''idealised mineralogy'' of a rock based on a quantitative chemical analysis according to the principles of geochemistry.
Normative mineral calculations ...
, in which an idealized mineral composition is calculated for the rock based on its chemical composition. For example, basanite is distinguished from tephrite
Tephrite is an igneous, volcanic (extrusive) rock, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. Mineral content is usually abundant feldspathoids (leucite or nepheline), plagioclase, and lesser alkali feldspar. Pyroxenes (clinopyroxenes) are common ...
by having a high normative olivine content.
Other refinements to the basic TAS classification include:
* Ultrapotassic – rocks containing molar K2O/Na2O >3.
* Peralkaline
Peralkaline rocks include those igneous rocks which have a deficiency of aluminium such that sodium and potassium are in excess of that needed for feldspar. The presence of aegerine (sodium pyroxene) and riebeckite (sodium amphibole) are indicati ...
– rocks containing molar (K2O + Na2O)/Al2O3 >1.
* Peraluminous
Peraluminous rocks are igneous rocks that have a molecular proportion of aluminium oxide higher than the combination of sodium oxide, potassium oxide and calcium oxide.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy, ''Petrology,'' Freeman, 2nd ed., 1995, p. ...
– rocks containing molar (K2O + Na2O + CaO)/Al2O3 <1.
In older terminology, silica oversaturated rocks were called '' silicic'' or ''acidic'' where the SiO2 was greater than 66% and the family term ''quartzolite'' was applied to the most silicic. A normative feldspathoid classifies a rock as silica-undersaturated; an example is nephelinite
Nephelinite is a fine-grained or aphanitic igneous rock made up almost entirely of nepheline and clinopyroxene (variety augite). If olivine is present, the rock may be classified as an olivine nephelinite. Nephelinite is dark in color and may res ...
.
Magmas are further divided into three series:
* The ''tholeiitic
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma ...
'' series – basaltic andesites and andesites.
* The calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic m ...
series – andesites.
* The alkaline series – subgroups of alkaline basalts and the rare, very high potassium-bearing (i.e. shoshonitic) lavas.
The alkaline series is distinguishable from the other two on the TAS diagram, being higher in total alkali oxides for a given silica content, but the tholeiitic and calc-alkaline series occupy approximately the same part of the TAS diagram. They are distinguished by comparing total alkali with iron and magnesium content.
These three magma series occur in a range of plate tectonic settings. Tholeiitic magma series rocks are found, for example, at mid-ocean ridges, back-arc basins, oceanic islands formed by hotspots, island arcs and continental large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s.
All three series are found in relatively close proximity to each other at subduction zones where their distribution is related to depth and the age of the subduction zone. The tholeiitic magma series is well represented above young subduction zones formed by magma from relatively shallow depth. The calc-alkaline and alkaline series are seen in mature subduction zones, and are related to magma of greater depths. Andesite and basaltic andesite are the most abundant volcanic rock in island arc which is indicative of the calc-alkaline magmas. Some island arcs have distributed volcanic series as can be seen in the Japanese island arc system where the volcanic rocks change from tholeiite—calc-alkaline—alkaline with increasing distance from the trench.
History of classification
Some igneous rock names date to before the modern era of geology. For example, ''basalt'' as a description of a particular composition of lava-derived rock dates toGeorgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire ...
in 1546 in his work ''De Natura Fossilium
''De Natura Fossilium'' is a scientific text written by Georg Bauer also known as Georgius Agricola, first published in 1546. The book represents the first scientific attempt to categorize minerals, rocks and sediments since the publication of ...
''. The word ''granite'' goes back at least to the 1640s and is derived either from French ''granit'' or Italian ''granito'', meaning simply "granulate rock". The term ''rhyolite'' was introduced in 1860 by the German traveler and geologist Ferdinand von Richthofen The naming of new rock types accelerated in the 19th century and peaked in the early 20th century.
Much of the early classification of igneous rocks was based on the geological age and occurrence of the rocks. However, in 1902, the American petrologists Charles Whitman Cross
Charles Whitman Cross (September 1, 1854 – April 20, 1949) was an American geologist. He was educated at Amherst College, the University of Göttingen, and Leipzig University. A petrologist, much of his field work concerned rocks in Colorado. ...
, Joseph P. Iddings, Louis V. Pirsson, and Henry Stephens Washington
Henry Stephens Washington (January 15, 1867 – January 7, 1934) was an American geologist.
Biography
Washington was born in Newark, New Jersey on January 15, 1867. He attended Yale University, graduating in 1886, and took his masters there two y ...
proposed that all existing classifications of igneous rocks should be discarded and replaced by a "quantitative" classification based on chemical analysis. They showed how vague, and often unscientific, much of the existing terminology was and argued that as the chemical composition of an igneous rock was its most fundamental characteristic, it should be elevated to prime position.
Geological occurrence, structure, mineralogical constitution—the hitherto accepted criteria for the discrimination of rock species—were relegated to the background. The completed rock analysis is first to be interpreted in terms of the rock-forming minerals which might be expected to be formed when the magma crystallizes, e.g., quartz feldspars, olivine, akermannite, Feldspathoids, magnetite, corundum, and so on, and the rocks are divided into groups strictly according to the relative proportion of these minerals to one another. This new classification scheme created a sensation, but was criticized for its lack of utility in fieldwork, and the classification scheme was abandoned by the 1960s. However, the concept of normative mineralogy has endured, and the work of Cross and his coinvestigators inspired a flurry of new classification schemes.
Among these was the classification scheme of M.A. Peacock, which divided igneous rocks into four series: the alkalic, the alkali-calcic, the calc-alkali, and the calcic series. His definition of the alkali series, and the term calc-alkali, continue in use as part of the widely used Irvine-Barager classification, along with W.Q. Kennedy's tholeiitic series.
By 1958, there were some 12 separate classification schemes and at least 1637 rock type names in use. In that year, Albert Streckeisen Albert Streckeisen (8 November 1901 – 29 September 1998) was a Swiss petrographer and petrologist, the son of Basel forensic scientist Adolf Streckeisen.
Biography
He studied geology, mineralogy and petrology in Basel, Zürich and Berne. He su ...
wrote a review article on igneous rock classification that ultimately led to the formation of the IUGG Subcommission of the Systematics of Igneous Rocks. By 1989 a single system of classification had been agreed upon, which was further revised in 2005. The number of recommended rock names was reduced to 316. These included a number of new names promulgated by the Subcommission.
Origin of magmas
The Earth's crust averages about thick under the continents, but averages only some beneath the oceans. The continental crust is composed primarily of sedimentary rocks resting on a crystalline '' basement'' formed of a great variety of metamorphic and igneous rocks, includinggranulite
Granulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated ...
and granite. Oceanic crust is composed primarily of basalt and gabbro. Both continental and oceanic crust rest on peridotite of the mantle.
Rocks may melt in response to a decrease in pressure, to a change in composition (such as an addition of water), to an increase in temperature, or to a combination of these processes.
Other mechanisms, such as melting from a meteorite impact
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or m ...
, are less important today, but impacts during the accretion of the Earth led to extensive melting, and the outer several hundred kilometers of our early Earth was probably an ocean of magma. Impacts of large meteorites in the last few hundred million years have been proposed as one mechanism responsible for the extensive basalt magmatism of several large igneous provinces.
Decompression
Decompression melting occurs because of a decrease in pressure. Thesolidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin), a Roman coin of nearly solid gold
* Solidus (punctuation), or slash, a punctuation mark
* Solidus (chemistry), the line on a phase diagram below which a substance is completely solid
* ...
temperatures of most rocks (the temperatures below which they are completely solid) increase with increasing pressure in the absence of water. Peridotite at depth in the Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate rock between the crust and the outer core. It has a mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg and thus makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly so ...
may be hotter than its solidus temperature at some shallower level. If such rock rises during the convection of solid mantle, it will cool slightly as it expands in an adiabatic process, but the cooling is only about 0.3 °C per kilometer. Experimental studies of appropriate peridotite samples document that the solidus temperatures increase by 3 °C to 4 °C per kilometer. If the rock rises far enough, it will begin to melt. Melt droplets can coalesce into larger volumes and be intruded upwards. This process of melting from the upward movement of solid mantle is critical in the evolution of the Earth.
Decompression melting creates the ocean crust at mid-ocean ridges
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a diverg ...
. It also causes volcanism in intraplate regions, such as Europe, Africa and the Pacific sea floor. There, it is variously attributed either to the rise of mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
s (the "Plume hypothesis") or to intraplate extension (the "Plate hypothesis").
Effects of water and carbon dioxide
The change of rock composition most responsible for the creation of magma is the addition of water. Water lowers the solidus temperature of rocks at a given pressure. For example, at a depth of about 100 kilometers, peridotite begins to melt near 800 °C in the presence of excess water, but near or above about 1,500 °C in the absence of water. Water is driven out of the oceanic lithosphere in subduction zones, and it causes melting in the overlying mantle. Hydrous magmas composed of basalt and andesite are produced directly and indirectly as results of dehydration during the subduction process. Such magmas, and those derived from them, build upisland arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
s such as those in the Pacific Ring of Fire. These magmas form rocks of the calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic m ...
series, an important part of the continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' be ...
.
The addition of carbon dioxide is relatively a much less important cause of magma formation than the addition of water, but genesis of some silica-undersaturated magmas has been attributed to the dominance of carbon dioxide over water in their mantle source regions. In the presence of carbon dioxide, experiments document that the peridotite solidus temperature decreases by about 200 °C in a narrow pressure interval at pressures corresponding to a depth of about 70 km. At greater depths, carbon dioxide can have more effect: at depths to about 200 km, the temperatures of initial melting of a carbonated peridotite composition were determined to be 450 °C to 600 °C lower than for the same composition with no carbon dioxide. Magmas of rock types such as nephelinite
Nephelinite is a fine-grained or aphanitic igneous rock made up almost entirely of nepheline and clinopyroxene (variety augite). If olivine is present, the rock may be classified as an olivine nephelinite. Nephelinite is dark in color and may res ...
, carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive or extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geochemical verification.
Carbonati ...
, and kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of S ...
are among those that may be generated following an influx of carbon dioxide into mantle at depths greater than about 70 km.
Temperature increase
Increase in temperature is the most typical mechanism for formation of magma within continental crust. Such temperature increases can occur because of the upward intrusion of magma from the mantle. Temperatures can also exceed the solidus of a crustal rock in continental crust thickened by compression at a plate boundary. The plate boundary between the Indian and Asian continental masses provides a well-studied example, as the Tibetan Plateau just north of the boundary has crust about 80 kilometers thick, roughly twice the thickness of normal continental crust. Studies of electricalresistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
deduced from magnetotelluric data have detected a layer that appears to contain silicate melt and that stretches for at least 1,000 kilometers within the middle crust along the southern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Granite and rhyolite are types of igneous rock commonly interpreted as products of the melting of continental crust because of increases in temperature. Temperature increases also may contribute to the melting of lithosphere dragged down in a subduction zone.
Magma evolution
crystallize
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposi ...
from the melt at different temperatures ( fractional crystallization). As minerals crystallize, the composition of the residual melt typically changes. If crystals separate from the melt, then the residual melt will differ in composition from the parent magma. For instance, a magma of gabbroic composition can produce a residual melt of granitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz- ...
composition if early formed crystals are separated from the magma. Gabbro may have a liquidus temperature near 1,200 °C, and the derivative granite-composition melt may have a liquidus temperature as low as about 700 °C. Incompatible element In petrology and geochemistry, an incompatible element is one that is unsuitable in size and/or charge to the cation sites of the minerals of which it is included. It is defined by the partition coefficient between rock-forming minerals and melt b ...
s are concentrated in the last residues of magma during fractional crystallization and in the first melts produced during partial melting: either process can form the magma that crystallizes to pegmatite, a rock type commonly enriched in incompatible elements. Bowen's reaction series is important for understanding the idealised sequence of fractional crystallisation of a magma. Clinopyroxene thermobarometry is used to determine temperature and pressure conditions at which magma differentiation occurred for specific igneous rocks.
Magma composition can be determined by processes other than partial melting and fractional crystallization. For instance, magmas commonly interact with rocks they intrude, both by melting those rocks and by reacting with them. Magmas of different compositions can mix with one another. In rare cases, melts can separate into two immiscible melts of contrasting compositions.
Etymology
- The word '' igneous'' rock means ''composed of fire''. and is derived from the Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...root words of ''igni-'', meaning ''fire'', and ''-eous'' meaning ''composed of''.
- The word ''volcanic rock Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic ...'' is derived from theLatin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...root words of ''Vulcan Vulcan may refer to: Mythology * Vulcan (mythology), the god of fire, volcanoes, metalworking, and the forge in Roman mythology Arts, entertainment and media Film and television * Vulcan (''Star Trek''), name of a fictional race and their home p ...'', the Roman the god of fire, and ''-ic'', meaning ''having some characteristics of''.
- The word '' plutonic'' rock, another name for intrusive igneous rock, is derived from the Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...root words of '' Pluto'', the Roman god of the underworld, and ''-ic'', meaning ''having some characteristics of''.
Gallery
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large v ...
with a 1906 lava flow in the foreground
File:Molten Lava in Pahoehoe Skylight.jpg, A "skylight" hole, about across, in a solidified lava crust reveals molten lava below (flowing towards the top right) in an eruption of Kīlauea in Hawaii
File:"This means something. This is important" (19967592275).jpg, Devils Tower, an eroded laccolith in the Black Hills of Wyoming
File:Happy Anniversary Hawaii (14802198589).jpg, A cascade of molten lava flowing into Aloi Crater during the 1969-1971 Mauna Ulu eruption of Kilauea volcano
File:Columnar jointing in the Alcantara Gorge, Sicily.jpg, Columnar jointing in the Alcantara Gorge, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
File:Cretaceous sedimentary rocks intruded by a Miocene granite laccolith.jpg, A laccolith of granite (light-coloured) that was intruded into older sedimentary rocks (dark-coloured) at Cuernos del Paine, Torres del Paine National Park
Torres del Paine National Park ( es, Parque Nacional Torres del Paine) is a national park encompassing mountains, glaciers, lakes, and rivers in southern Chilean Patagonia. The Cordillera del Paine is the centerpiece of the park. It lies in a tr ...
, Chile
File:Multiple Igneous Intrusion Phases Kosterhavet Sweden.jpg, An igneous intrusion cut by a pegmatite dike, which in turn is cut by a dolerite dike
See also
* * * * *Notes
References
External links
USGS Igneous Rocks
The IUGS systematics of igneous rocks
{{DEFAULTSORT:Igneous Rock 01 Igneous petrology Volcanology