Ibn Jubayr on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ibn Jubayr (1 September 1145 вҖ“ 29 November 1217; ar, Ш§ШЁЩҶ Ш¬ШЁЩҠШұ), also written Ibn Jubair, Ibn Jobair, and Ibn Djubayr, was an 
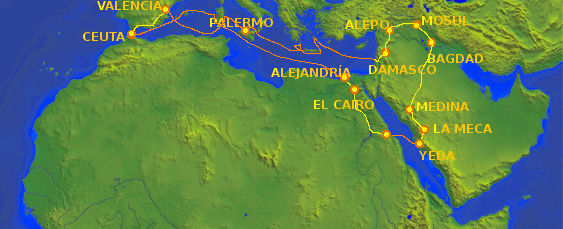
 Everywhere that Ibn Jubayr traveled in
Everywhere that Ibn Jubayr traveled in
 Ibn Jubayr also travelled to
Ibn Jubayr also travelled to
Ibn Jubair: Capturing the Decline of Islamic Power
muslimheritage.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Ibn Jubayr 1145 births 1217 deaths 12th-century Arabs 13th-century Arabs People from Valencia Geographers of the medieval Islamic world Travel writers of the medieval Islamic world People from the Almohad Caliphate Hajj accounts 13th-century geographers 12th-century Al-Andalus writers 13th-century Al-Andalus writers 13th-century travelers 12th-century travelers Saladin
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, Ш№ЩҺШұЩҺШЁЩҗЩҠЩҢЩ‘, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, Ш№ЩҺШұЩҺШЁ, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
, traveller and poet from al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-ГҒndalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, вҙ°вөҸвҙ·вҙ°вөҚвө“вөҷ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-ГҖndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al AndalГәs; pt, al-ГӮndalus; es, al-ГҒndalus () was the M ...
. His travel chronicle describes the pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
he made to Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
from 1183 to 1185, in the years preceding the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189вҖ“1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity (Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
. His chronicle describes Saladin's domains in Egypt and the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
which he passed through on his way to Mecca. Further, on his return journey, he passed through Christian Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, which had been recaptured from the Muslims only a century before, and he made several observations on the hybrid polyglot culture that flourished there.
Early life
Ibn Jubayr was born in 1145 AD inValencia
Valencia ( va, ValГЁncia) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
, Spain, to an Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, Ш№ЩҺШұЩҺШЁЩҗЩҠЩҢЩ‘, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, Ш№ЩҺШұЩҺШЁ, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
family of the Kinanah
The Kinana ( ar, ЩғЩҗЩҶЩҺШ§ЩҺЩҶЩҺШ©, KinДҒna) were an Arab tribe based around Mecca in the Tihama coastal area and the Hejaz mountains. The Quraysh of Mecca, the tribe of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, was an offshoot of the Kinana. A number of mod ...
tribe. He was a descendant of 'Abdal-Salam ibn Jabayr, who, in 740 AD, had accompanied an army sent by the caliph of Damascus to put down a Berber uprising in his Spanish provinces. Ibn Jubayr studied in the town of XГ tiva, where his father worked as a civil servant. He later became secretary to the Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, Ш®ЩҗЩ„ЩҺШ§ЩҒЩҺШ©ЩҸ ЩұЩ„Щ’Щ…ЩҸЩҲЩҺШӯЩҗЩ‘ШҜЩҗЩҠЩҶЩҺ or or from ar, ЩұЩ„Щ’Щ…ЩҸЩҲЩҺШӯЩҗЩ‘ШҜЩҸЩҲЩҶЩҺ, translit=al-MuwaбёҘбёҘidЕ«n, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fou ...
governor of Granada.
Ibn Jubayr does not explain the reason for his travels. It has been suggested that as secretary for the ruler of Granada in 1182, he was threatened into drinking seven cups of wine. Seized by remorse, the ruler then filled seven cups of gold Dinara, which he gave him. To expiate his godless act, although it had been forced upon him, Ibn Jubayr decided to perform the duty of Hajj to Mecca. Robert Irwin has recently argued that dubious provenance aside, this seems an unlikely explanation, as Hajj was rarely penitential.Ibn Jubayr & Irwin, R., (trans), The Travels of Ibn Jubayr: A Medieval Journey from Cordoba to Jerusalem, (London, 2019) p. 16
He left Granada on 3 February 1183 accompanied by a physician from the city.
Travels
Sea journey from Ceuta to Alexandria
Ibn Jubayr left Granada and crossed over the Strait of Gibraltar toCeuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, ШіЩҺШЁЩ’ШӘЩҺШ©, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territorie ...
, then under Muslim rule. He boarded a Genoese ship on February 24, 1183 and set sail for Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ЩұЩ„Щ’ШҘЩҗШіЩ’ЩғЩҺЩҶЩ’ШҜЩҺШұЩҗЩҠЩҺЩ‘Ш©ЩҸ ; grc-gre, О‘О»ОөОҫО¬ОҪОҙПҒОөО№Оұ, AlexГЎndria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
. His sea journey took him past the Balearic Islands and then across to the west coast of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
. Offshore, he heard of the fate of 80 Muslim men, women and children who had been abducted from North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and were being sold into slavery. Between Sardinia and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, the ship ran into a severe storm. He said of the Italians and Muslims on board who had experience of the sea that "all agreed that they had never in their lives seen such a tempest". After the storm, the ship went on past Sicily and Crete
Crete ( el, ОҡПҒО®П„О·, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
and turned south and crossed over to the North African coast. He arrived in Alexandria on March 26.
In Egypt
 Everywhere that Ibn Jubayr traveled in
Everywhere that Ibn Jubayr traveled in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, Щ…ШөШұ , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, he was full of praise for the new Sunni ruler, Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( вҖ“ 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, ШіЩҮвҖҢЩ„Ш§ШӯЩҮвҖҢШҜЫҢЩҶ, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
. For example, he said, "There is no congregational or ordinary mosque, no mausoleum built over a grave, nor hospital, nor theological college, where the bounty of the Sultan does not extend to all who seek shelter or live in them". He pointed out that when the Nile did not flood enough, Saladin remitted the land tax from the farmers. He also said that "such is his (Salahuddin's) justice, and the safety he has brought to his high-roads that men in his lands can go about their affairs by night and from its darkness apprehend no awe that should deter them". Ibn Jubayr, on the other hand, was very disparaging of the previous Shi'a dynasty of the Fatimids.
Of Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ЩҮШұШ©, al-QДҒhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
, Ibn Jubayr noted, the colleges and hostels that were erected for students and pious men of other lands by the Saladin. In those colleges, students found lodging and tutors to teach them the sciences that they desired as well as also allowances to cover their needs. The care of the sultan also granted them baths, hospitals, and the appointment of doctors, who could even come to visit them at their place of stay who would be answerable for their cure. One of Saladin's other generous acts was that every day, 2000 loaves of bread were distributed to the poor. Also impressing Ibn Jubayr in the city was the number of mosques, estimated at between 8,000 and 12,000, with four or five of them often in the same street.
In Alexandria
Upon arrival atAlexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ЩұЩ„Щ’ШҘЩҗШіЩ’ЩғЩҺЩҶЩ’ШҜЩҺШұЩҗЩҠЩҺЩ‘Ш©ЩҸ ; grc-gre, О‘О»ОөОҫО¬ОҪОҙПҒОөО№Оұ, AlexГЎndria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Ibn Jubayr was angered by the customs officials who insisted on taking zakat
Zakat ( ar, ШІЩғШ§Ш©; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is ...
from the pilgrims, regardless of whether or not they were obliged to pay. In the city, he visited the Lighthouse of Alexandria
The Lighthouse of Alexandria, sometimes called the Pharos of Alexandria (; Ancient Greek: бҪҒ ОҰО¬ПҒОҝПӮ П„бҝҶПӮ бјҲО»ОөОҫОұОҪОҙПҒОөОҜОұПӮ, contemporary Koine ), was a lighthouse built by the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, during the rei ...
, which was then still standing, and he was amazed by its size and splendor.
One of the greatest wonders that we saw in this city was the lighthouse which Great and Glorious God had erected by the hands of those who were forced to such labor as 'Indeed in that are signs for those who discern'He was also impressed by the free colleges, hostels for foreign students, baths and hospitals in the city. They were paid for by
Quran 15:75
and as a guide to voyagers, for without it they could not find the true course to Alexandria. It can be seen for more than seventy miles and is of great antiquity. It is most strongly built in all directions and competes with the skies in height. Description of it falls short, the eyes fail to comprehend it, and words are inadequate, so vast is the spectacle.
awqaf
A waqf ( ar, ЩҲЩҺЩӮЩ’ЩҒ; ), also known as hubous () or ''mortmain'' property is an inalienable charitable endowment under Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot of land or other assets for Muslim religious or charitabl ...
and taxes on the city's Jews
Jews ( he, ЧҷЦ°Ч”Ч•ЦјЧ“ЦҙЧҷЧқ, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''ChristГіs'' (О§ПҒ ...
. He noted that there were between 8,000 and 12,000 mosques in Alexandria. After a stay of eight days, he set off to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ЩҮШұШ©, al-QДҒhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
.
In Cairo
He reached Cairo three days later. In the city, he visited thecemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a buri ...
at al-Qarafah, which contained the graves of many important figures in the history of Islam
The history of Islam concerns the political, social, economic, military, and cultural developments of the Islamic civilization. Most historians believe that Islam originated in Mecca and Medina at the start of the 7th century CE. Muslims re ...
. He noted that under Saladin, the walls of the citadel were being extended with the object of reinforcing the entire city from any future siege by Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
. Another work that he saw being built was a bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
over the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: ГҒman DawЕ« is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
, which would be high enough not to be submerged in the annual flooding of the river. He saw a spacious free hospital, which was divided into three sections: for men, women and the insane. He saw the pyramids, but he was unaware for whom they had been built, and the Sphinx
A sphinx ( , grc, ПғПҶОҜОіОҫ , Boeotian: , plural sphinxes or sphinges) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of a falcon.
In Greek tradition, the sphinx has the head of a woman, the haunches of ...
. He also saw a device that was used to measure the height of the Nile flood.
In Sicily
InSicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, at the very late stages of his travels (December 1184 to January 1185), Ibn Jubayr recounted other experiences. He commented on the activity of the volcanoes:
At the close of night a red flame appeared, throwing up tongues into the air. It was the celebrated volcano ( Stromboli). We were told that a fiery blast of great violence bursts out from air-holes in the two mountains and makes the fire. Often a great stone is cast up and thrown into the air by the force of the blast and prevented thereby from falling and settling at the bottom. This is one of the most remarkable of stories, and it is true. As for the great mountain in the island, known as the Jabal al-Nar ountain of Fire it also presents a singular feature in that some years a fire pours from it in the manner of the `bursting of the dam'. It passes nothing it does not burn until, coming to the sea, it rides out on its surface and then subsides beneath it. Let us praise the Author of all things for His marvelous creations. There is no God but He.Also striking Ibn Jubayr was the city of Palermo, which he described as follows:
It is the metropolis of these islands, combining the benefits of wealth and splendor, and having all that you could wish of beauty, real or apparent, and all the needs of subsistence, mature and fresh. It is an ancient and elegant city, magnificent and gracious, and seductive to look upon. Proudly set between its open spaces and plains filled with gardens, with broad roads and avenues, it dazzles the eyes with its perfection. It is a wonderful place, built in the Cordova style, entirely from cut stone known as kadhan soft limestone A river splits the town, and four springs gush in its suburbs.... The King roams through the gardens and courts for amusement and pleasure... The Christian women of this city follow the fashion of Muslim women, are fluent of speech, wrap their cloaks about them, and are veiled.
Further journeys
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i MГјnevvere) and also commonly simplified as MadД«nah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
, Damascus, Mosul
Mosul ( ar, Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҲШөЩ„, al-Mawб№Јil, ku, Щ…ЩҲЩҲШіЪө, translit=MГ»sil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ЬЎЬҳЬЁЬ , MДҒwб№Јil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
, Acre and Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, ШЁЩҺШәЩ’ШҜЩҺШ§ШҜ , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
. At Basra
Basra ( ar, ЩұЩ„Щ’ШЁЩҺШөЩ’ШұЩҺШ©, al-Baб№Јrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
, he saw how Indian timber was carefully used to make Lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
sail ships. He returned in 1185 by way of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. His path was not without troubles, including a shipwreck. On both occasions, he travelled on Genoese ships.
Frequently quoted is Ibn Jubayr's famous description of Muslims prospering under the Christian Crusaders' Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
:
We moved from Tibnin - may God destroy it - at daybreak on Monday. Our way lay through continuous farms and ordered settlements, whose inhabitants were all Muslims, living comfortably within the Franks.... They surrender half their crops to the Franks at harvest time, and pay as well a poll-tax of one dinar and five qirat for each person. Other than that they are not interfered with, save for a light tax on the fruit of their trees. The houses and all their effects are left to their full possession. All the coastal cities occupied by the Franks are managed in this fashion, their rural districts, the villages and farms, belong to the Muslims. But their hearts have been seduced, for they observe how unlike them in ease and comfort are their brethren in the Muslim regions under their (Muslim) governors. This is one of the misfortunes afflicting the Muslims. The Muslim community bewails the injustice of the landlord of its own faith, and applauds the conduct of its opponent and enemy, the Frankish landlord, and is accustomed to justice from him.
Later life
Jubayr traveled to the East on two further occasions (1189вҖ“1191 and 1217) without leaving an account. He died on 29 November 1217 in Alexandria, during the second trip.Overview and publication
Ibn Jubayr provides a highly-detailed and graphic description of the places he visited during his travels. The book differs from other contemporary accounts in not being a mere collection of toponyms and descriptions of monuments but containing observation of geographical details as well as cultural, religious and political matters. Particularly interesting are his notes about the declining faith of his fellow Muslims in Palermo after the recentNorman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
and about what he perceived as the Muslim-influenced customs of King William II of Sicily under the Norman-Arab-Byzantine culture.
His writing is a foundation of the genre of work called Rihla
''RiбёҘla'' ( ar, ШұШӯЩ„Ш©) refers to both a journey and the written account of that journey, or travelogue. It constitutes a genre of Arabic literature. Associated with the medieval Islamic notion of "travel in search of knowledge" (Ш§Щ„ШұШӯЩ„Ш© ...
, or the creative travelogue. It is a mix of personal narrative, description of the areas traveled and personal anecdotes.
Ibn Jubayr's travel chronicle served as a model for later authors, some of whom copied from it without attribution. Ibn Juzayy
Abu al-Qasim, Muhammad b. Ahmad b. Muhammad b. 'Abd Allah, Ibn Juzayy al-Kalbi al-Gharnati () was an Andalusian Maliki-Ash'ari scholar and poet of Arab origin.
Works
He wrote many religious works such as his ''al-Qawanin al-Fiqhiyyah'' or "T ...
, who wrote the account of Ibn Battuta's travels in around 1355 AD, copied passages that had been written 170 years earlier by Ibn Jubayr that described Damascus, Mecca, Medina and other places in the Middle East. Passages copied from Ibn Jubayr are also found in the writings of al-Sharishi, al-Abdari and Al-Maqrizi.
A surviving copy of Ibn Jubayr's manuscript is preserved in the collection of the Leiden University Library. The 210-page manuscript was produced in Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
in 875 AH (1470 AD) and appears to have been written at high speed: diacritic marks are often missing, words are omitted and there is confusion between certain pairs of letters. The complete Arabic text was first published in 1852 by the orientalist William Wright. An updated edition was published in 1907 by Michael Jan de Goeje
Michael Jan de Goeje (August 13, 1836 – May 17, 1909) was a Dutch orientalist focusing on Arabia and Islam.
Early life
Michael Jan de Goeje was born in Dronrijp, Friesland. He devoted himself at an early age to the study of oriental lan ...
. A translation into Italian by Celestino Schiaparelli was published in 1906, a translation into English by Ronald Broadhurst was published in 1952, and a translation into French by Maurice Gaudefroy-Demombynes
Maurice Gaudefroy-Demombynes (15 December 1862 вҖ“ 12 August 1957) was a French Arabist, a specialist in Islam and the history of religions.
His best known works are his historical and religious studies on Hajj and Muslim institutions. He also tr ...
appeared in three volumes between 1949 and 1956.
See also
* Ghurabiyya Shia *Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''ШұЩҸШ¬Ш§Шұ'', ''RujДҒr''; Maltese: ''RuДЎДЎieru'', вҖ“ 22 June 1101), nicknamed Roger Bosso and The Great, was a Norman nobleman who became the first Count of Sicily from 1071 to 1101. He was a member of the ...
Notes
References
* * First published in 1986, . * * * * Revision of the 1852 edition of Wright. This is the Arabic text translated by Broadhurst. * * *Further reading
* * Biographical information on Ibn Jubayr given byAhmed Mohammed al-Maqqari
AбёҘmad ibn MuбёҘammad al-MaqqarД« al-TilmisДҒnД« (or al-MaбёібёіarД«) (), (1577-1632) was an Algerian scholar, biographer and historian who is best known for his , a compendium of the history of Al-Andalus which provided a basis for the scholar ...
(c. 1578вҖ“1632) and Ibn al-Khatib
Lisan ad-Din Ibn al-Khatib ( ar, Щ„ШіШ§ЩҶ Ш§Щ„ШҜЩҠЩҶ Ш§ШЁЩҶ Ш§Щ„Ш®Ш·ЩҠШЁ, LisДҒn ad-DД«n Ibn al-Khaб№ӯД«b) (Born 16 November 1313, LojaвҖ“ died 1374, Fes; full name in ar, Щ…ШӯЩ…ШҜ ШЁЩҶ Ш№ШЁШҜ Ш§Щ„Щ„ЩҮ ШЁЩҶ ШіШ№ЩҠШҜ ШЁЩҶ Ш№ШЁШҜ Ш§Щ„Щ„ЩҮ ШЁЩҶ Ш ...
( (1313вҖ“1374).
* Originally published as ''Les CroisГ©s'', Hachette, 1959.
External links
Ibn Jubair: Capturing the Decline of Islamic Power
muslimheritage.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Ibn Jubayr 1145 births 1217 deaths 12th-century Arabs 13th-century Arabs People from Valencia Geographers of the medieval Islamic world Travel writers of the medieval Islamic world People from the Almohad Caliphate Hajj accounts 13th-century geographers 12th-century Al-Andalus writers 13th-century Al-Andalus writers 13th-century travelers 12th-century travelers Saladin