Iberians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in
/ref> The Iberians lived in villages and oppida (fortified settlements) and their communities were based on a
 After the First Punic war, the massive war debt suffered by Carthage led them to attempt to expand their control over the Iberian peninsula. Hamilcar Barca began this conquest from his base at Cádiz by conquering the Tartessian
After the First Punic war, the massive war debt suffered by Carthage led them to attempt to expand their control over the Iberian peninsula. Hamilcar Barca began this conquest from his base at Cádiz by conquering the Tartessian
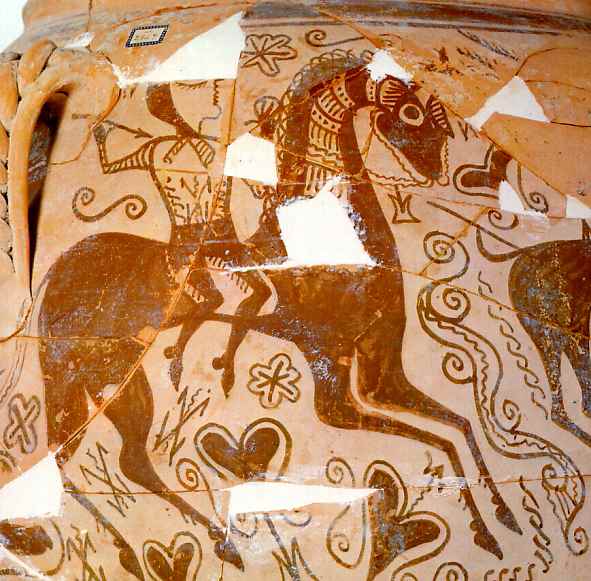 Iberian society was divided into different classes, including kings or chieftains (Latin: "regulus"), nobles, priests, artisans and slaves. Iberian aristocracy, often called a "senate" by the ancient sources, met in a council of nobles. Kings or chieftains would maintain their forces through a system of obligation or vassalage that the Romans termed "fides".Rafael Treviño Martinez, Rome's Enemies (4) : Spanish Armies 218-19 BC (Men at Arms Series, 180)
The Iberians adopted wine and olives from the Greeks. Horse breeding was particularly important to the Iberians and their nobility. Mining was also very important for their economy, especially the silver mines near Gader and Cartago Nova, the iron mines in the Ebro valley, as well as the exploitation of tin and
Iberian society was divided into different classes, including kings or chieftains (Latin: "regulus"), nobles, priests, artisans and slaves. Iberian aristocracy, often called a "senate" by the ancient sources, met in a council of nobles. Kings or chieftains would maintain their forces through a system of obligation or vassalage that the Romans termed "fides".Rafael Treviño Martinez, Rome's Enemies (4) : Spanish Armies 218-19 BC (Men at Arms Series, 180)
The Iberians adopted wine and olives from the Greeks. Horse breeding was particularly important to the Iberians and their nobility. Mining was also very important for their economy, especially the silver mines near Gader and Cartago Nova, the iron mines in the Ebro valley, as well as the exploitation of tin and
 Iberian soldiers were widely employed by Carthage and Rome as mercenaries and auxiliary troops. A large portion of Carthaginian forces during the Punic wars was made up of Iberians and Celtiberians. Iberian warfare was
Iberian soldiers were widely employed by Carthage and Rome as mercenaries and auxiliary troops. A large portion of Carthaginian forces during the Punic wars was made up of Iberians and Celtiberians. Iberian warfare was

 The Iberian language, like the rest of the paleohispanic languages, became extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD, after being gradually replaced by
The Iberian language, like the rest of the paleohispanic languages, became extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD, after being gradually replaced by
«La conformación del mundo ibérico septentrional»
''Palaeohispanica'' 5, pp. 333–358.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20081227095813/http://www.webpersonal.net/jrr/index.htm Iberian Epigraphy Page, by J.R. Ramos {{Authority control Pre-Indo-Europeans Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula History of Catalonia People by historical ethnicity
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Roman sources (among others, by Hecataeus of Miletus, Avienius
Postumius Rufius Festus Avienius (sometimes erroneously Avienus) was a Latin writer of the 4th century AD. He was a native of Volsinii in Etruria, from the distinguished family of the Rufii Festi.
Avienius is not identical with the historian ...
, Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
and Strabo). Roman sources also use the term ''Hispani'' to refer to the Iberians.
The term ''Iberian'', as used by the ancient authors, had two distinct meanings. One, more general, referred to all the populations of the Iberian peninsula without regard to ethnic differences ( Pre-Indo-European, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
and non-Celtic Indo-Europeans). The other, more restricted ethnic sense and the one dealt with in this article, refers to the people living in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, which by the 6th century BC had absorbed cultural influences from the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns and the Greeks. This pre-Indo-European cultural group spoke the Iberian language from the 7th to the 1st century BC. The rest of the peninsula, in the northern, central, and northwestern areas, was inhabited by Vascones, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
or Celtiberians groups and the possibly Pre-Celtic
The pre-Celtic period in the prehistory of Central Europe and Western Europe occurred before the expansion of the Celts or their culture in Iron Age Europe and Anatolia (9th to 6th centuries BC), but after the emergence of the Proto-Celtic lang ...
or Proto-Celtic Indo-European Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. ...
, Vettones
The Vettones (Greek: ''Ouettones'') were a pre-Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula of possibly Celtic ethnicity.
Origins
Lujan (2007) concludes that some of the names of the Vettones show clearly western Hispano-Celtic features. Reissued i ...
, and the Turdetani.
Starting in the 5th century BC, Iberian soldiers were frequently deployed in battles in Italy, Greece and especially in Sicily due to their military qualities.
History
The Iberian culture developed from the 6th century BC, and perhaps as early as the fifth to the third millennium BC in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula.Spain: Historical Setting – Library of Congress Country Study – Iberia/ref> The Iberians lived in villages and oppida (fortified settlements) and their communities were based on a
tribal
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
organization. The Iberians in the Spanish Levant were more urbanized than their neighbors in the central and northwestern regions of the Iberian peninsula. The peoples in the central and northwest regions were mostly speakers of Celtic dialects, semi-pastoral and lived in scattered villages, though they also had a few fortified towns like Numantia
Numantia ( es, Numancia) is an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the current municipality of Garray ( Soria), Spain.
Numantia is famous for its role in the Celtiberian Wars. In ...
. They had a knowledge of writing, metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scal ...
, including bronze, and agricultural techniques.
Settlements
In the centuries preceding Carthaginian and Roman conquest, Iberian settlements grew insocial complexity
In sociology, social complexity is a conceptual framework used in the analysis of society. In the sciences, contemporary definitions of complexity are found in systems theory, wherein the phenomenon being studied has many parts and many possible ...
, exhibiting evidence of social stratification and urbanization. This process was probably aided by trading contacts with the Phoenicians, Greeks, and Carthaginians. By the late 5th and early 4th centuries BC a series of important social changes led to the consolidation of an aristocracy and the emergence of a clientele system. "This new political system led, among other things, to cities and towns that centered around these leaders, also known as territorial nucleation. In this context, the oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (plural ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretchi ...
or fortified Iberian town became the centre of reference in the landscape and the political space."
The settlement of ''Castellet de Banyoles'' in Tivissa was one of the most important ancient Iberian settlements in the north eastern part of the Iberian peninsula that was discovered in 1912. Also, the 'Treasure of Tivissa', a unique collection of silver Iberian votive offerings was found here in 1927.
Lucentum was another ancient Iberian settlement, as well as Castelldefels Castle.
Mausoleum of Pozo Moro near the town of Chinchilla de Monte-Aragón
Chinchillas are either of two species (''Chinchilla chinchilla'' and ''Chinchilla lanigera'') of crepuscular rodents of the parvorder Caviomorpha. They are slightly larger and more robust than ground squirrels, and are native to the Andes moun ...
in Castile-La Mancha seems to mark the location of another big settlement.
Sagunto is the location of an ancient Iberian and later Roman city of Saguntum, where a big fortress was built in the 5th century BC.
Greek colonists made the first historical reference to the Iberians in the 6th century BC. They defined Iberians as non-Celtic peoples south of the Ebro river (Iber). The Greeks also dubbed as "Iberians" another people in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
region, currently known as Caucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
ns. It is thought that there is no connection between the two peoples.
The Iberians traded extensively with other Mediterranean cultures. Iberian pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
and metalwork has been found in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. The Iberians had extensive contact with Greek colonists in the Spanish colonies of Emporion, Rhode, and Hemeroskopeion. The Iberians may have adopted some of the Greeks' artistic techniques. Statues such as the Lady of Baza and the Lady of Elx are thought to have been made by Iberians relatively well acquainted with Greek art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
. Thucydides stated that one of the three original tribes of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, the Sicani, were of Iberian origin, though "Iberian" at the time could have included what we think of as Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
The Iberians also had contacts with the Phoenicians, who had established various colonies in southern Andalucia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
. Their first colony on the Iberian Peninsula was founded in 1100 BC and was originally called ''Gadir'', later renamed by the Romans as ''Gades'' (modern Cádiz). Other Phoenician colonies in southern Iberia included Malaka ( Málaga), Sexi and Abdera.
According to Arrian, the Iberians sent emissaries to Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 324 BC, along with other embassies of Carthaginians, Italics and Gauls, to request his friendship.
Second Punic War and Roman conquest
Guadalquivir
The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from the Gul ...
river region, which was rich in silver. After Hamilcar's death, his son-in-law Hasdrubal the Fair
Hasdrubal the Fair ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , ''ʿAzrobaʿl''; –221BC) was a Carthaginian military leader and politician, governor in Iberia after Hamilcar Barca's death, and founder of Cartagena.
Family
Livy's ''History of Rome'' rec ...
continued his incursions into Iberia, founding the colony of Qart Hadasht (modern Cartagena) and extending his influence all the way to the southern bank of the river Ebro. After Hasdrubal's assassination in 221 BC, Hannibal assumed command of the Carthaginian forces and spent two years completing the conquest of the Iberians south of the Ebro. In his first campaign, Hannibal defeated the Olcades, the Vaccaei and the Carpetani expanding his control over the river Tagus region. Hannibal then laid siege to Roman ally of Saguntum
Sagunto ( ca-valencia, Sagunt) is a municipality of Spain, located in the province of Valencia, Valencian Community. It belongs to the modern fertile ''comarca'' of Camp de Morvedre. It is located c. 30 km north of the city of Valencia, cl ...
and this led to the beginning of the Second Punic War. The Iberian theater was a key battleground during this war and many Iberian and Celtiberian warriors fought for both Rome and Carthage, though most tribes sided with Carthage.
Rome sent Gnaeus and Publius Cornelius Scipio to conquer Iberia from Carthage. Gnaeus subsequently defeated the Iberian Ilergetes The Ilergetes were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania) who dwelt in the plains area of the rivers Segre and Cinca towards Iberus (Ebro) river, and in and around Ilerda/Iltrida, present-day Lleida/L ...
tribe north of the Ebro who were allied with Carthage, conquered the Iberian oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (plural ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretchi ...
of Tarraco and defeated the Carthaginian fleet. After the arrival of Publius Scipio, Tarraco was fortified and, by 211 BC, the Scipio brothers had overrun the Carthaginian and allied forces south of the Ebro. However, during this campaign, Publius Scipio was killed in battle and Gnaeus died in the retreat. The tide turned with the arrival of Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus in 210 BC. Scipio attacked and conquered Carthago Nova
Cartagena () is a Spanish city and a major naval station on the Mediterranean coast, south-eastern Iberia. As of January 2018, it has a population of 218,943 inhabitants, being the region's second-largest municipality and the country's sixth-la ...
and defeated the army of Hasdrubal Barca at the Battle of Baecula
The Battle of Baecula was a major field battle in Iberia during the Second Punic War. Roman Republican and Iberian auxiliary forces under the command of Scipio Africanus routed the Carthaginian army of Hasdrubal Barca.
Prelude
According to P ...
(209-208). The war dragged on with Carthage sending more reinforcements until the Battle of Ilipa (modern Alcalá del Río in Sevilla province), which was a decisive victory for Publius Scipio Africanus. The Carthaginians retreated to Gades, and Publius Scipio gained control over the entire south of the peninsula. After this victory, the Ilergetes and other Iberian tribes revolted and it was only after this revolt that the Romans conquered the rest of the Carthaginian territories in southern Spain.
After the Carthaginian defeat, the Iberian territories were divided into two major provinces, Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania ( ...
and Hispania Citerior. In 197 BC, the Iberian tribes revolted once again in the H. Citerior province. After securing these regions, Rome invaded and conquered Lusitania and Celtiberia
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
. The Romans fought a long and drawn out campaign for the conquest of Lusitania. Wars and campaigns in the northern regions of the Iberian peninsula would continue until 16 BC, when the final rebellions of the Cantabrian Wars were defeated.
Iberian culture
 Iberian society was divided into different classes, including kings or chieftains (Latin: "regulus"), nobles, priests, artisans and slaves. Iberian aristocracy, often called a "senate" by the ancient sources, met in a council of nobles. Kings or chieftains would maintain their forces through a system of obligation or vassalage that the Romans termed "fides".Rafael Treviño Martinez, Rome's Enemies (4) : Spanish Armies 218-19 BC (Men at Arms Series, 180)
The Iberians adopted wine and olives from the Greeks. Horse breeding was particularly important to the Iberians and their nobility. Mining was also very important for their economy, especially the silver mines near Gader and Cartago Nova, the iron mines in the Ebro valley, as well as the exploitation of tin and
Iberian society was divided into different classes, including kings or chieftains (Latin: "regulus"), nobles, priests, artisans and slaves. Iberian aristocracy, often called a "senate" by the ancient sources, met in a council of nobles. Kings or chieftains would maintain their forces through a system of obligation or vassalage that the Romans termed "fides".Rafael Treviño Martinez, Rome's Enemies (4) : Spanish Armies 218-19 BC (Men at Arms Series, 180)
The Iberians adopted wine and olives from the Greeks. Horse breeding was particularly important to the Iberians and their nobility. Mining was also very important for their economy, especially the silver mines near Gader and Cartago Nova, the iron mines in the Ebro valley, as well as the exploitation of tin and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
deposits. They produced fine metalwork and high quality iron weapons such as the falcata.
Art and religion
The Iberians produced sculpture in stone and bronze, most of which was much influenced by the Greeks and Phoenicians, and other cultures such as Assyrian, Hittite and Egyptian influences. The styles of Iberian sculpture are divided geographically into Levantine, Central, Southern, and Western groups, of which the Levantine group displays the most Greek influence. Iberian pottery and painting was also distinct and widespread throughout the region. A distinct feature of the culture, the pottery was primarily decorated with geometric forms in red but in some areas (fromMurcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the seventh largest city in the country. It has a population of 460,349 inhabitants in 2021 (about one ...
to the south of Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
) it also included figurative images.
The Iberian polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
religion was influenced by the Greek and Phoenician practices, as it is evident in their sculptures. The man-bull Bicha of Balazote (possibly a fertility deity) and various depictions of sphinxes and lions bear a resemblance to eastern Mediterranean mythological creatures. The Lady of Elche
The ''Lady of Elche'' (in Spanish, ''Dama de Elche'' in Valencian, ''Dama d'Elx'') is a limestone bust that was discovered in 1897, at ''La Alcudia'', an archaeological site on a private estate two kilometers south of Elche, Spain. It is curren ...
and Lady of Guardamar show clear Hellenistic influence. Phoenician and Greek deities like Tanit
Tanit ( Punic: 𐤕𐤍𐤕 ''Tīnīt'') was a Punic goddess. She was the chief deity of Carthage alongside her consort Baal-Hamon.
Tanit is also called Tinnit. The name appears to have originated in Carthage (modern day Tunisia), though it doe ...
, Baal, Melkart, Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified wit ...
, Demeter and Asclepius were known in the region and worshiped. Currently few native Iberian gods are known, though the oracular healing deity "Betatun" is known from a Latin inscription at Fuertes del Rey.Lisbeth Bredholt Christensen, et al. The Handbook of Religions in Ancient Europe There was clearly an important female deity associated with the earth and regeneration as depicted by the Lady of Baza and linked with birds, flowers and wheat. The horse was also an important religious figure and an important sanctuary dedicated to Horses has been found in Mula (Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the seventh largest city in the country. It has a population of 460,349 inhabitants in 2021 (about one ...
). There are many depictions of a "horse taming god" or "lord of the horses" (''despotes hippon''). The female goddess Ataegina is also widely attested in the inscriptions.
Iberians performed their rites in the open and also maintained sanctuaries in holy places like groves, springs and caves. Archaeological evidence suggests the existence of a priestly class and Silius Italicus mentions priests in the region of Tartessos
Tartessos ( es, Tarteso) is, as defined by archaeological discoveries, a historical civilization settled in the region of Southern Spain characterized by its mixture of local Paleohispanic and Phoenician traits. It had a proper writing system ...
at a temple of Melqart. Evidence from pottery reveals some information about Iberian myth and ritual. Common themes are a celebratory ritual dance described by Strabo .f. 3.3.7.and seen in a relief from Fuerte del Rey known as the "Bastetania dance" and the confrontation between the deceased and a wolf figure.Lisbeth Bredholt Christensen, et al. The Handbook of Religions in Ancient Europe, page Ritual sacrifice of animals was also common.
In Iberian eschatology, "death was seen as the starting point for a journey symbolised by a crossing of the sea, the land or even the sky. Supernatural and mythical beings, such as the Sphinx or the wolf, and sometimes Divinity itself, accompanied and guided the deceased on this journey". The Iberians incinerated their dead and placed their ashes in ceremonial urns, the remains were then placed in stone tombs.
Iberians venerated the war god Cariocecus.
Indalo
The Indalo is a prehistoric magical symbol found in the cave of "Los Letreros" ("The Signboards") in Sierra de María-Los Vélez Natural Park in Vélez Blanco, Almería, Andalusia, Spain. It has been customary to paint the Indalo symbol on the fron ...
was an Iberian god from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
.
Warfare
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
and based on intertribal raiding and pillaging. In set piece battle, Iberians were known to regularly charge and retreat, throwing javelins and shouting at their opponents without actually committing to full contact combat. This sort of fighting was termed ''concursare'' by the Romans. The Iberians were particularly fond of ambushes
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mount ...
and guerrilla tactics.
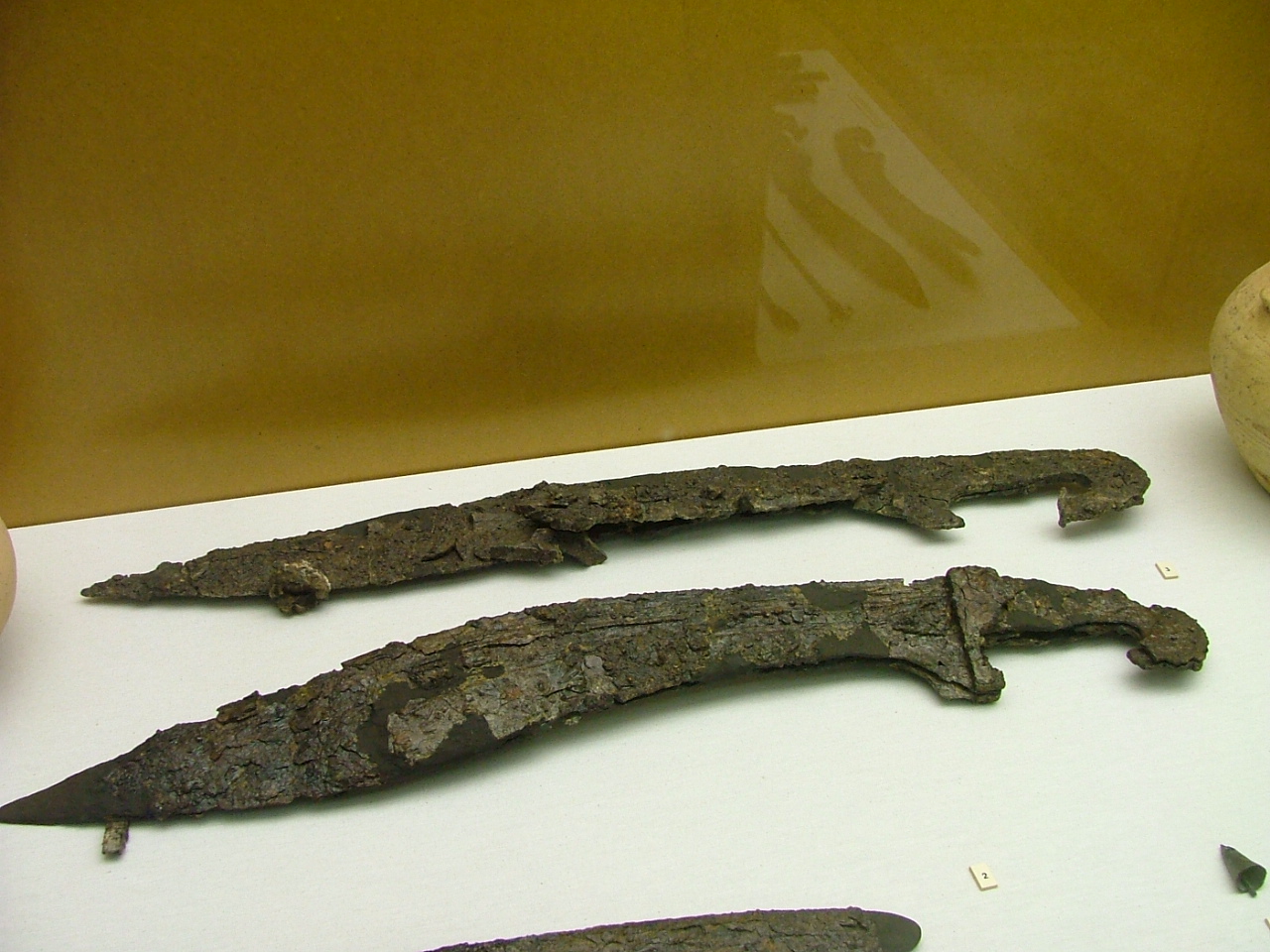
Ancient sources mention two major types of Iberian infantry, ''scutati'' and ''caetrati''. ''Scutati'' were heavily armored and carried large Italic style scutum shields. The ''caetrati'' carried the caetra, a small Iberian buckler
A buckler (French ''bouclier'' 'shield', from Old French ''bocle, boucle'' 'boss') is a small shield, up to 45 cm (up to 18 in) in diameter, gripped in the fist with a central handle behind the boss. While being used in Europe since ant ...
. Iberian armaments included the famed Gladius Hispaniensis, a curved sword called the falcata, straight swords, spears, javelins and an all iron spear called the Soliferrum
Soliferrum or Soliferreum (Latin: ''solus'', "only" + ''ferrum'', "Iron") was the Roman name for an ancient Iberian ranged pole weapon made entirely of iron. The soliferrum was a heavy hand-thrown javelin, designed to be thrown to a distance of u ...
. Iberian horsemen were a key element of Iberian forces as well as Carthaginian armies. Spain was rich with excellent wild horses and Iberian cavalry was some of the best in the ancient Mediterranean.
Iberian tribes
Iberians dwelt along eastern and southern coastal regions of the Iberian Peninsula, that corresponds to the northwestern shores of theMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
(see the map), roughly in today's Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
, Eastern, Northeastern and Northern Aragon, Valencian Community, Murcia Region, Eastern Andalucia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
, and the Balearic Islands (in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
), and also in today's Roussillon and parts of Languedoc (in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
).
The peninsula has this name because ancient Greeks, Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and other mediterranean peoples first contacted with peoples (tribes or tribal confederacies) that were Iberians in the ethnic and linguistic sense, although the majority of the Iberian Peninsula's peoples, that dwelt in the Northern, Central and Western regions (the majority of the peninsula's area), were not Iberians themselves in the ethnic and linguistic sense (they could only be considered Iberians in the geographical sense, i.e. they dwelt in the Iberian Peninsula).
The Iberian tribes or tribal confederacies were:
*Andosini - in the mountains of East Pyrenees southern slopes, in the high Segre river basin, area of modern Andorra.
*Ausetani
The Ausetani were an ancient Iberian (pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language. They lived in the eponymous region of Ausona and gave their name to the Roman city of '' ...
- in the Osona
Osona () is a comarca situated in Catalonia, Northeast Spain. Its capital is Vic. Its population in 2001 was 129,543. Osona covers roughly the same area as the historic Catalan county of Osona. The name Osona comes from ''Ausetans'', a group of ...
region (old County of Osona), in the middle Ter river
The Ter is a river in Catalonia, Spain, that rises at an approximate elevation of near the Ulldeter refuge at the foot of a glacial cirque delimited by the nearby peaks of el Bastiments, el Gra de Fajol, or el Pic de la Dona. It runs throug ...
basin. Ausa (today's Vic) was their main centre.
* Bastetani/ Bastitani/Bastuli
The Bastetani or Bastuli were an ancient Iberian (pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language. The relationship between the Iberian Bastetani and the Tartessian Mastieni ( ...
- The biggest iberian tribal confederation in area, they dwelt in a territory that included large areas of the mediterranean coast and the Sierra Nevada, in what are today parts of the modern provinces of Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the seventh largest city in the country. It has a population of 460,349 inhabitants in 2021 (about one ...
, Albacete, Jaén, Almería
Almería (, , ) is a city and municipality of Spain, located in Andalusia. It is the capital of the province of the same name. It lies on southeastern Iberia on the Mediterranean Sea. Caliph Abd al-Rahman III founded the city in 955. The city g ...
, Granada and Málaga. Basti (today's Baza) was their main centre.
**Mastieni - in and around Mastia territory ( Cartagena).
*Bergistani The Bergistani ( la, Bargusii, grc, Βαργουσίοι, ''Bargousíoi''), were an ancient Iberian or Pre-Roman people of the Iberian peninsula. They were related to the Ilergetes and were not numerous. They inhabited the valley of the Saiarra ...
/ Bergusii - in the high Llobregat river basin, roughly in today's Barcelona province. Berga was their main centre. North of the Lacetani.
* Castellani - in the high Ter river
The Ter is a river in Catalonia, Spain, that rises at an approximate elevation of near the Ulldeter refuge at the foot of a glacial cirque delimited by the nearby peaks of el Bastiments, el Gra de Fajol, or el Pic de la Dona. It runs throug ...
basin, East Pyrenees southern slopes. North of the Ausetani
The Ausetani were an ancient Iberian (pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language. They lived in the eponymous region of Ausona and gave their name to the Roman city of '' ...
.
* Cessetani/ Cossetani - in the Tarraco region (roughly in today's central and east Tarragona province
Tarragona (, ) is a province of eastern Spain, in the southern part of the autonomous community of Catalonia. It is bordered by the provinces of Castellón, Teruel, Zaragoza, Lérida and Barcelona and by the Mediterranean Sea.
The province's p ...
), in the mediterranean coastal region. Kese ( Tarraco in Roman times, that would become the Hispania Tarraconensis capital), was their main centre.
* Ceretani/ Cerretani - in Cerretana (today's Cerdanya/ Cerdaña) and other East Pyrenees mountains southern slopes, also in the high Segre and Noguera rivers basins (tributaries of the Iberus - Ebro river), in the east part of Ribagorça. Libyca or Julia Libyca (today's Llivia) was their main centre. North of the Ilergetes The Ilergetes were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania) who dwelt in the plains area of the rivers Segre and Cinca towards Iberus (Ebro) river, and in and around Ilerda/Iltrida, present-day Lleida/L ...
and the Bergistani The Bergistani ( la, Bargusii, grc, Βαργουσίοι, ''Bargousíoi''), were an ancient Iberian or Pre-Roman people of the Iberian peninsula. They were related to the Ilergetes and were not numerous. They inhabited the valley of the Saiarra ...
.
* Contestani - South of the Sucro ( Xúquer) river and north of the Thader (Segura
Segura (, ; la, Thader; ar, شقورة, Shaqūrah, or ) is a medium-sized river in southeastern Spain. It has its source in the Sierra de Segura.
Course
The river begins at Santiago Pontones ( province of Jaén), passes Calasparra, C ...
) river, in an area that today is roughly part of the Alicante/Alacant
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a city and municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city was 337,482 , the second-largest in the ...
, Valencia, Murcia
Murcia (, , ) is a city in south-eastern Spain, the capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the seventh largest city in the country. It has a population of 460,349 inhabitants in 2021 (about one ...
and Albacete provinces. A tribal confederation. East of the Bastetani. Centres included Saetabi (modern Xàtiva) and la Bastida de les Alcusses.
**Deitani - in and around Ilici territory (today's Elx/ Elche)
* Edetani - North of the Sucro ( Xúquer/ Júcar) river and south of the Millars river, roughly in today's Valencia province. One of the biggest iberian tribes or tribal confederations. Edeta (Roman times Lauro, today's Lliria), to the northwest of Valencia, was their main centre, Arse
Arse or ARSE may refer to:
* A Commonwealth English slang term for the buttocks
* Arse, the name for the Iberian settlement of modern-day Sagunto
* Arse (district), a district in the South Tapanuli Regency, North Sumatra province, Sumatra, Indone ...
(Saguntum
Sagunto ( ca-valencia, Sagunt) is a municipality of Spain, located in the province of Valencia, Valencian Community. It belongs to the modern fertile ''comarca'' of Camp de Morvedre. It is located c. 30 km north of the city of Valencia, cl ...
in Roman times, today's Sagunto/Sagunt
Sagunto ( ca-valencia, Sagunt) is a municipality of Spain, located in the province of Valencia, Valencian Community. It belongs to the modern fertile ''comarques of the Valencian Community, comarca'' of Camp de Morvedre. It is located c. 30&nbs ...
) was also in their territory. North of the Contestani and the Bastetani and south of the Ilercavones.
* Elisyces/ Helisyces - a tribe that dwelt in the region of Narbo (Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the ...
) and modern northern Roussillon. May have been either Iberian or Ligurian or a Ligurian-Iberian tribe.
* Ilercavones - in the low Iberus ( Ebro) river basin to the Millars river along the mediterranean coast and to the inland towards the Sierra de Gúdar, in Ilercavonia. One of the biggest iberian tribes or tribal confederations. Hibera
Hibera is an ancient city, known for being a strategic point from which the Second Punic War is said to have originated. It was fought over by the Carthaginians and the Roman Republic, Romans during this period. According to the texts, most of th ...
(Roman time Dertusa or Dertosa, modern time Tortosa
Tortosa (; ) is the capital of the '' comarca'' of Baix Ebre, in Catalonia, Spain.
Tortosa is located at above sea level, by the Ebro river, protected on its northern side by the mountains of the Cardó Massif, of which Buinaca, one of the hig ...
) was their main centre. North of the Edetani, south of the Ilergetes The Ilergetes were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania) who dwelt in the plains area of the rivers Segre and Cinca towards Iberus (Ebro) river, and in and around Ilerda/Iltrida, present-day Lleida/L ...
, east of the Sedetani and west of the Cessetani.
*Ilergetes The Ilergetes were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania) who dwelt in the plains area of the rivers Segre and Cinca towards Iberus (Ebro) river, and in and around Ilerda/Iltrida, present-day Lleida/L ...
/ Ilergetae - in the plains area of the middle and low Segre and Cinca rivers towards the Iberus ( Ebro) river margins. One of the biggest iberian tribes or tribal confederations. Iltrida ( Ilerda in Roman times, today's Lérida
Lleida (, ; Spanish: Lérida ) is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital city of the province of Lleida.
Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It is also the capital city of the Segrià comarca, as ...
/ Lleida) was their main centre.
*Indigetes
The Indigetes (Latin: ''indigetes'' or ''indigetae'' or ''Indiketes'') were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the eastern side of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language.
They occu ...
/ Indigetae - in the low Ter river
The Ter is a river in Catalonia, Spain, that rises at an approximate elevation of near the Ulldeter refuge at the foot of a glacial cirque delimited by the nearby peaks of el Bastiments, el Gra de Fajol, or el Pic de la Dona. It runs throug ...
basin, East Pyrenees southern slopes, they occupied the far north east area of the Iberian Peninsula known as Hispania Tarraconensis, in the gulf of Empodrae ( Empúries) and Rhoda (Roses), stretching up into the Pyrenees though the regions of Empordà
Emporda (from the official name in ca, Empordà, , name in es, Ampurdán, ) is a natural and historical region of Catalonia, Spain, divided since 1936 into two ''comarques'', Alt Empordà and Baix Empordà.
The city of Figueres, an important ...
, Selva
Selva () is a coastal comarque (county) in Catalonia, Spain, located between the mountain range known as the Serralada Transversal or Puigsacalm and the Costa Brava (part of the Mediterranean coast). Unusually, it is divided between the provinc ...
and perhaps as far as Gironès
Gironès (; es, Gironés) is a comarca (county) in eastern Catalonia, Spain, bordering Selva, Baix Empordà, Alt Empordà, Pla de l'Estany and Garrotxa. , more than half of the comarca's 175,148 inhabitants live in the capital, Girona, which ...
, in what is roughly today's Girona Province. Indika/Indiga or Undika was their main centre. A confederation was formed by four tribes.
* Lacetani - in the middle Llobregat river basin and surrounding hills. Northwest of the Laietani The Laietani were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They inhabited the area occupied by the city of Barcelona. One of the main thoroughfares of the city, Via Laietana, is named after the Laietan ...
.
*Laietani The Laietani were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the Iberian peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They inhabited the area occupied by the city of Barcelona. One of the main thoroughfares of the city, Via Laietana, is named after the Laietan ...
- in the low Llobregat river basin, along a part of the mediterranean coast roughly in what is today a part of the Barcelona province and Barcelona city. Laieta (Barcino in Roman times and Barcelona in modern times) was their main centre.
*Oretani
The Oretani or Oretanii (Greek: ''Orissioi'') were a pre-Roman ancient Iberian people (in the geographical sense) of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania), that lived in northeastern Andalusia, in the upper Baetis (Guadalquivir) river valley, ...
- In the high Baetis (Guadalquivir
The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from the Gul ...
) river valley, eastern Marianus Mons ( Sierra Morena) and southern area of today's La Mancha
La Mancha () is a natural and historical region located in the Spanish provinces of Albacete, Cuenca, Ciudad Real, and Toledo. La Mancha is an arid but fertile plateau (610 m or 2000 ft) that stretches from the mountains of Toledo to th ...
. They could have been an Iberian tribe, a Celtic one, or a mixed Celtic and Iberian tribe or tribal confederacy (and hence related to the Celtiberians). The Mantesani/Mentesani/Mantasani of today's La Mancha
La Mancha () is a natural and historical region located in the Spanish provinces of Albacete, Cuenca, Ciudad Real, and Toledo. La Mancha is an arid but fertile plateau (610 m or 2000 ft) that stretches from the mountains of Toledo to th ...
and the Germani (of Oretania) in eastern Marianus Mons ( Sierra Morena) and west Jabalón river valley, sometimes are included in the Oretani but it is not certain if they were Oretani tribes.
* Sedetani - south of the Iberus ( Ebro) river and west of the Guadalope river, roughly in the middle basin of the Iberus ( Ebro). Salduie (Roman time Salduba and Caesaraugusta and modern time Zaragoza) was in their territory. May have been more closely related to the Edetani. West of the Ilercavones.
* Sordones - in the Roussillon territory ( Pyrénées Orientales Départment, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
), Ruscino (today's Château-Roussillon near Perpignan) was their main centre.
*Vescetani/Oscenses - In today's northern Aragon, east of Gállego river, in Sobrarbe, in and around Bolskan, later Osca (Huesca
Huesca (; an, Uesca) is a city in north-eastern Spain, within the autonomous community of Aragon. It is also the capital of the Spanish province of the same name and of the comarca of Hoya de Huesca. In 2009 it had a population of 52,059, almo ...
), and high Cinca River valley, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. They could also be related to the Vascones and therefore be related to the Aquitani speaking the Aquitanian language.
*Unknown named tribe or tribes in the Balearic Islands (formed by the Pityusic Islands
(islands)
, image_name =
, image_caption =
, image_size =
, map_image = Localització de les Pitiüses respecte les Illes Balears.svg
, local_name =
, native_name_link = Spanish/Catalan language
, nickname ...
and Gymnesian islands), may have been Iberians.
Iberian language

 The Iberian language, like the rest of the paleohispanic languages, became extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD, after being gradually replaced by
The Iberian language, like the rest of the paleohispanic languages, became extinct by the 1st to 2nd centuries AD, after being gradually replaced by Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
. The Iberian language remains an unclassified non-Indo European language. A 1978 study claimed many similarities between Iberian and the Messapic language. Iberian languages also share some elements with the Basque language. Links have also been found with the Etruscan language and Minoan Linear A
Linear A is a writing system that was used by the Minoans of Crete from 1800 to 1450 BC to write the hypothesized Minoan language or languages. Linear A was the primary script used in palace and religious writings of the Minoan civi ...
.
There are different theories about the origin of the Iberian language. According to the ''Catalan'' theory, the Iberian language originated in northern Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
, from where it expanded north and south.Velaza, Javier (2006) ''Lengua vs. cultura material: el (viejo) problema de la lengua indígena de Cataluña, Actes de la III Reunió Internacional d'Arqueologia de Calafell (Calafell, 25 to 27 November 2004), Arqueo Mediterrània 9, pp. 273-280
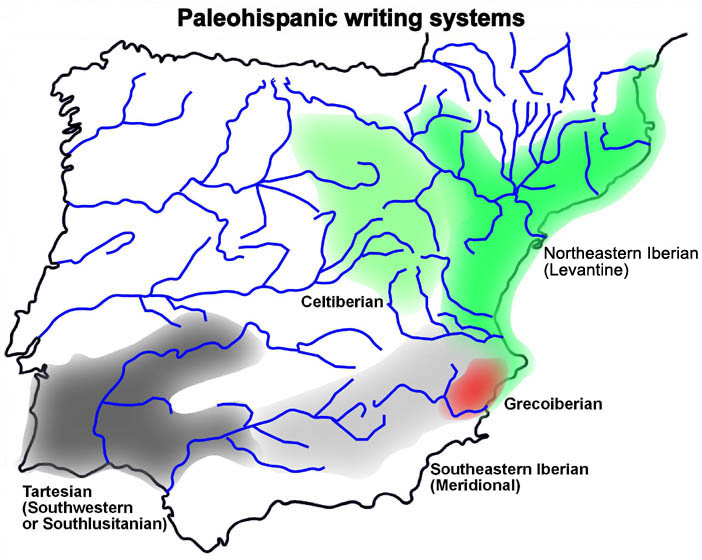
Iberian scripts
The Iberians use three different scripts to represent the Iberian language. *Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and the Greco-Iberian alphabet ...
** Dual variant (4th century BC and 3rd century BC)
** Non-dual variant (2nd century BC and 1st century BC)
* Southeastern Iberian script
* Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the paleohispanic scripts that present ...
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and the Greco-Iberian alphabet ...
and southeastern Iberian script share a common distinctive typological characteristic, also present in other paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the main script. Most of them are unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic, despite having su ...
: they present signs with syllabic value for the occlusive
In phonetics, an occlusive, sometimes known as a stop, is a consonant sound produced by occluding (i.e. blocking) airflow in the vocal tract, but not necessarily in the nasal tract. The duration of the block is the ''occlusion'' of the consonan ...
s and signs with monofonematic value for the rest of consonants
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced wit ...
and vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (len ...
. From a writing systems point of view, they are neither alphabets
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllab ...
nor syllabaries, they are mixed scripts that normally are identified as semi-syllabaries. About this common origin, there is no agreement between researchers: for some this origin is only linked to the Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.
The Phoenician a ...
while for others the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as w ...
had participated too.
See also
* Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula * Iberian language *Iberian scripts
The Iberian scripts are the Paleohispanic scripts that were used to represent the extinct Iberian language. Most of them are typologically unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic.Ferrer, J., Moncunill, N., V ...
* Ancient Iberian coinage
References
Further reading
* Beltrán, Miguel (1996): ''Los iberos en Aragón'', Zaragoza. * Ruiz, Arturo; Molinos, Manuel (1993): ''Los iberos'', Barcelona. * Sanmartí, Joan; Santacana, Joan (2005): ''Els ibers del nord'', Barcelona. * Sanmartí, Joan (2005)«La conformación del mundo ibérico septentrional»
''Palaeohispanica'' 5, pp. 333–358.
External links
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20081227095813/http://www.webpersonal.net/jrr/index.htm Iberian Epigraphy Page, by J.R. Ramos {{Authority control Pre-Indo-Europeans Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula History of Catalonia People by historical ethnicity