Hydroponic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
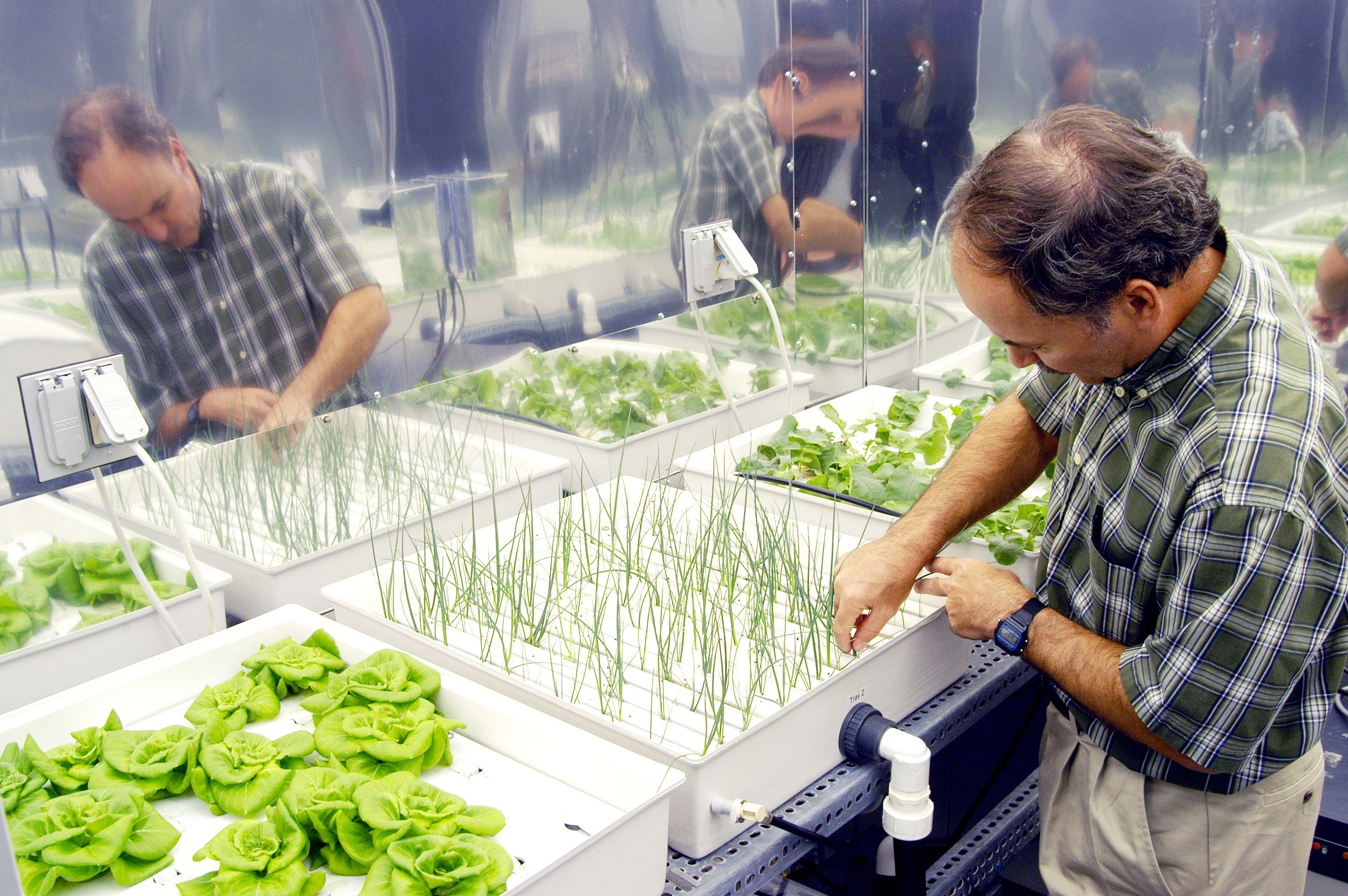 Hydroponics is a type of
Hydroponics is a type of
 The earliest published work on growing terrestrial plants without soil was the 1627 book ''Sylva Sylvarum'' or 'A Natural History' by
The earliest published work on growing terrestrial plants without soil was the 1627 book ''Sylva Sylvarum'' or 'A Natural History' by
"Daniel Arnon, 84, Researcher And Expert on Photosynthesis"
''
 In static solution culture, plants are grown in containers of nutrient solution, such as glass
In static solution culture, plants are grown in containers of nutrient solution, such as glass
 In continuous-flow solution culture, the nutrient solution constantly flows past the roots. It is much easier to automate than the static solution culture because sampling and adjustments to the temperature, pH, and nutrient concentrations can be made in a large storage tank that has potential to serve thousands of plants. A popular variation is the nutrient film technique or NFT, whereby a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth is recirculated in a thin layer past a bare root mat of plants in a watertight channel, with an upper surface exposed to air. As a consequence, an abundant supply of oxygen is provided to the roots of the plants. A properly designed NFT system is based on using the right channel slope, the right flow rate, and the right channel length. The main advantage of the NFT system over other forms of hydroponics is that the plant roots are exposed to adequate supplies of water, oxygen, and nutrients. In all other forms of production, there is a conflict between the supply of these requirements, since excessive or deficient amounts of one results in an imbalance of one or both of the others. NFT, because of its design, provides a system where all three requirements for healthy plant growth can be met at the same time, provided that the simple concept of NFT is always remembered and practised. The result of these advantages is that higher yields of high-quality produce are obtained over an extended period of cropping. A downside of NFT is that it has very little buffering against interruptions in the flow (e.g., power outages). But, overall, it is probably one of the more productive techniques.
The same design characteristics apply to all conventional NFT systems. While slopes along channels of 1:100 have been recommended, in practice it is difficult to build a base for channels that is sufficiently true to enable nutrient films to flow without ponding in locally depressed areas. As a consequence, it is recommended that slopes of 1:30 to 1:40 are used. This allows for minor irregularities in the surface, but, even with these slopes, ponding and water logging may occur. The slope may be provided by the floor, benches or racks may hold the channels and provide the required slope. Both methods are used and depend on local requirements, often determined by the site and crop requirements.
As a general guide, flow rates for each gully should be one liter per minute. At planting, rates may be half this and the upper limit of 2 L/min appears about the maximum. Flow rates beyond these extremes are often associated with nutritional problems. Depressed growth rates of many crops have been observed when channels exceed 12 meters in length. On rapidly growing crops, tests have indicated that, while oxygen levels remain adequate, nitrogen may be depleted over the length of the gully. As a consequence, channel length should not exceed 10–15 meters. In situations where this is not possible, the reductions in growth can be eliminated by placing another nutrient feed halfway along the gully and halving the flow rates through each outlet.
In continuous-flow solution culture, the nutrient solution constantly flows past the roots. It is much easier to automate than the static solution culture because sampling and adjustments to the temperature, pH, and nutrient concentrations can be made in a large storage tank that has potential to serve thousands of plants. A popular variation is the nutrient film technique or NFT, whereby a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth is recirculated in a thin layer past a bare root mat of plants in a watertight channel, with an upper surface exposed to air. As a consequence, an abundant supply of oxygen is provided to the roots of the plants. A properly designed NFT system is based on using the right channel slope, the right flow rate, and the right channel length. The main advantage of the NFT system over other forms of hydroponics is that the plant roots are exposed to adequate supplies of water, oxygen, and nutrients. In all other forms of production, there is a conflict between the supply of these requirements, since excessive or deficient amounts of one results in an imbalance of one or both of the others. NFT, because of its design, provides a system where all three requirements for healthy plant growth can be met at the same time, provided that the simple concept of NFT is always remembered and practised. The result of these advantages is that higher yields of high-quality produce are obtained over an extended period of cropping. A downside of NFT is that it has very little buffering against interruptions in the flow (e.g., power outages). But, overall, it is probably one of the more productive techniques.
The same design characteristics apply to all conventional NFT systems. While slopes along channels of 1:100 have been recommended, in practice it is difficult to build a base for channels that is sufficiently true to enable nutrient films to flow without ponding in locally depressed areas. As a consequence, it is recommended that slopes of 1:30 to 1:40 are used. This allows for minor irregularities in the surface, but, even with these slopes, ponding and water logging may occur. The slope may be provided by the floor, benches or racks may hold the channels and provide the required slope. Both methods are used and depend on local requirements, often determined by the site and crop requirements.
As a general guide, flow rates for each gully should be one liter per minute. At planting, rates may be half this and the upper limit of 2 L/min appears about the maximum. Flow rates beyond these extremes are often associated with nutritional problems. Depressed growth rates of many crops have been observed when channels exceed 12 meters in length. On rapidly growing crops, tests have indicated that, while oxygen levels remain adequate, nitrogen may be depleted over the length of the gully. As a consequence, channel length should not exceed 10–15 meters. In situations where this is not possible, the reductions in growth can be eliminated by placing another nutrient feed halfway along the gully and halving the flow rates through each outlet.
 Aeroponic techniques have proven to be commercially successful for propagation, seed germination, seed potato production, tomato production, leaf crops, and micro-greens. Since inventor Richard Stoner commercialized aeroponic technology in 1983, aeroponics has been implemented as an alternative to water intensive hydroponic systems worldwide. The limitation of hydroponics is the fact that of water can only hold of air, no matter whether aerators are utilized or not.
Another distinct advantage of aeroponics over hydroponics is that any species of plants can be grown in a true aeroponic system because the microenvironment of an aeroponic can be finely controlled. The limitation of hydroponics is that certain species of plants can only survive for so long in water before they become waterlogged. The advantage of aeroponics is that suspended aeroponic plants receive 100% of the available oxygen and carbon dioxide to the roots zone, stems, and leaves, thus accelerating biomass growth and reducing rooting times. NASA research has shown that aeroponically grown plants have an 80% increase in dry weight biomass (essential minerals) compared to hydroponically grown plants. Aeroponics used 65% less water than hydroponics. NASA also concluded that aeroponically grown plants require ¼ the nutrient input compared to hydroponics. Unlike hydroponically grown plants, aeroponically grown plants will not suffer transplant shock when transplanted to soil, and offers growers the ability to reduce the spread of disease and pathogens.
Aeroponics is also widely used in laboratory studies of plant physiology and plant pathology. Aeroponic techniques have been given special attention from
Aeroponic techniques have proven to be commercially successful for propagation, seed germination, seed potato production, tomato production, leaf crops, and micro-greens. Since inventor Richard Stoner commercialized aeroponic technology in 1983, aeroponics has been implemented as an alternative to water intensive hydroponic systems worldwide. The limitation of hydroponics is the fact that of water can only hold of air, no matter whether aerators are utilized or not.
Another distinct advantage of aeroponics over hydroponics is that any species of plants can be grown in a true aeroponic system because the microenvironment of an aeroponic can be finely controlled. The limitation of hydroponics is that certain species of plants can only survive for so long in water before they become waterlogged. The advantage of aeroponics is that suspended aeroponic plants receive 100% of the available oxygen and carbon dioxide to the roots zone, stems, and leaves, thus accelerating biomass growth and reducing rooting times. NASA research has shown that aeroponically grown plants have an 80% increase in dry weight biomass (essential minerals) compared to hydroponically grown plants. Aeroponics used 65% less water than hydroponics. NASA also concluded that aeroponically grown plants require ¼ the nutrient input compared to hydroponics. Unlike hydroponically grown plants, aeroponically grown plants will not suffer transplant shock when transplanted to soil, and offers growers the ability to reduce the spread of disease and pathogens.
Aeroponics is also widely used in laboratory studies of plant physiology and plant pathology. Aeroponic techniques have been given special attention from
 Passive sub-irrigation, also known as passive hydroponics, semi-hydroponics, or ''hydroculture'', is a method wherein plants are grown in an inert
Passive sub-irrigation, also known as passive hydroponics, semi-hydroponics, or ''hydroculture'', is a method wherein plants are grown in an inert
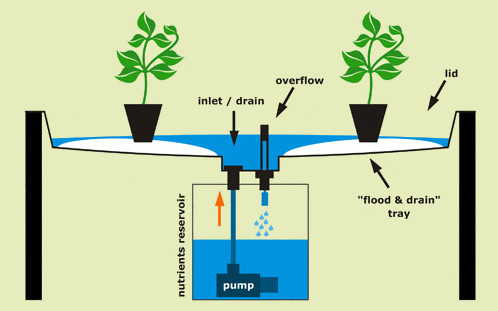 In its simplest form, there is a tray above a reservoir of nutrient solution. Either the tray is filled with growing medium (clay granules being the most common) and then plant directly or place the pot over medium, stand in the tray. At regular intervals, a simple timer causes a pump to fill the upper tray with nutrient solution, after which the solution drains back down into the reservoir. This keeps the medium regularly flushed with nutrients and air. Once the upper tray fills past the drain stop, it begins recirculating the water until the timer turns the pump off, and the water in the upper tray drains back into the reservoirs.
In its simplest form, there is a tray above a reservoir of nutrient solution. Either the tray is filled with growing medium (clay granules being the most common) and then plant directly or place the pot over medium, stand in the tray. At regular intervals, a simple timer causes a pump to fill the upper tray with nutrient solution, after which the solution drains back down into the reservoir. This keeps the medium regularly flushed with nutrients and air. Once the upper tray fills past the drain stop, it begins recirculating the water until the timer turns the pump off, and the water in the upper tray drains back into the reservoirs.
 This method can be set up in various configurations. In its simplest form, a nutrient-and-water solution is manually applied one or more times per day to a container of inert growing media, such as rockwool, perlite, vermiculite, coco fibre, or sand. In a slightly more complex system, it is automated with a delivery pump, a timer and irrigation tubing to deliver nutrient solution with a delivery frequency that is governed by the key parameters of plant size, plant growing stage, climate, substrate, and substrate conductivity, pH, and water content.
In a commercial setting, watering frequency is multi-factorial and governed by computers or PLCs.
Commercial hydroponics production of large plants like tomatoes, cucumber, and peppers uses one form or another of run-to-waste hydroponics.
In environmentally responsible uses, the nutrient-rich waste is collected and processed through an on-site filtration system to be used many times, making the system very productive.
This method can be set up in various configurations. In its simplest form, a nutrient-and-water solution is manually applied one or more times per day to a container of inert growing media, such as rockwool, perlite, vermiculite, coco fibre, or sand. In a slightly more complex system, it is automated with a delivery pump, a timer and irrigation tubing to deliver nutrient solution with a delivery frequency that is governed by the key parameters of plant size, plant growing stage, climate, substrate, and substrate conductivity, pH, and water content.
In a commercial setting, watering frequency is multi-factorial and governed by computers or PLCs.
Commercial hydroponics production of large plants like tomatoes, cucumber, and peppers uses one form or another of run-to-waste hydroponics.
In environmentally responsible uses, the nutrient-rich waste is collected and processed through an on-site filtration system to be used many times, making the system very productive.
 The hydroponic method of plant production by means of suspending the plant roots in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water. Traditional methods favor the use of plastic buckets and large containers with the plant contained in a net pot suspended from the centre of the lid and the roots suspended in the nutrient solution.
The solution is oxygen saturated by an air pump combined with porous stones. With this method, the plants grow much faster because of the high amount of oxygen that the roots receive. The Kratky Method is similar to deep water culture, but uses a non-circulating water reservoir.
The hydroponic method of plant production by means of suspending the plant roots in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water. Traditional methods favor the use of plastic buckets and large containers with the plant contained in a net pot suspended from the centre of the lid and the roots suspended in the nutrient solution.
The solution is oxygen saturated by an air pump combined with porous stones. With this method, the plants grow much faster because of the high amount of oxygen that the roots receive. The Kratky Method is similar to deep water culture, but uses a non-circulating water reservoir.
 A rotary hydroponic garden is a style of commercial hydroponics created within a circular frame which rotates continuously during the entire growth cycle of whatever plant is being grown.
While system specifics vary, systems typically rotate once per hour, giving a plant 24 full turns within the circle each 24-hour period. Within the center of each rotary hydroponic garden can be a high intensity grow light, designed to simulate sunlight, often with the assistance of a mechanized timer.
Each day, as the plants rotate, they are periodically watered with a hydroponic growth solution to provide all nutrients necessary for robust growth. Due to the plants continuous fight against gravity, plants typically mature much more quickly than when grown in soil or other traditional hydroponic growing systems. Because rotary hydroponic systems have a small size, they allow for more plant material to be grown per area of floor space than other traditional hydroponic systems.
Rotary hydroponic systems should be avoided in most circumstances, mainly because of their experimental nature and their high costs for finding, buying, operating, and maintaining them.
A rotary hydroponic garden is a style of commercial hydroponics created within a circular frame which rotates continuously during the entire growth cycle of whatever plant is being grown.
While system specifics vary, systems typically rotate once per hour, giving a plant 24 full turns within the circle each 24-hour period. Within the center of each rotary hydroponic garden can be a high intensity grow light, designed to simulate sunlight, often with the assistance of a mechanized timer.
Each day, as the plants rotate, they are periodically watered with a hydroponic growth solution to provide all nutrients necessary for robust growth. Due to the plants continuous fight against gravity, plants typically mature much more quickly than when grown in soil or other traditional hydroponic growing systems. Because rotary hydroponic systems have a small size, they allow for more plant material to be grown per area of floor space than other traditional hydroponic systems.
Rotary hydroponic systems should be avoided in most circumstances, mainly because of their experimental nature and their high costs for finding, buying, operating, and maintaining them.
 Rock wool ( mineral wool) is the most widely used medium in hydroponics. Rock wool is an inert substrate suitable for both run-to-waste and recirculating systems. Rock wool is made from molten rock, basalt or 'slag' that is spun into bundles of single filament fibres, and bonded into a medium capable of capillary action, and is, in effect, protected from most common microbiological degradation. Rock wool is typically used only for the seedling stage, or with newly cut clones, but can remain with the plant base for its lifetime. Rock wool has many advantages and some disadvantages. The latter being the possible skin irritancy (mechanical) whilst handling (1:1000). Flushing with cold water usually brings relief. Advantages include its proven efficiency and effectiveness as a commercial hydroponic substrate. Most of the rock wool sold to date is a non-hazardous, non-carcinogenic material, falling under Note Q of the European Union Classification Packaging and Labeling Regulation (CLP).
Mineral wool products can be engineered to hold large quantities of water and air that aid root growth and nutrient uptake in hydroponics; their fibrous nature also provides a good mechanical structure to hold the plant stable. The naturally high pH of mineral wool makes them initially unsuitable to plant growth and requires "conditioning" to produce a wool with an appropriate, stable pH.
Rock wool ( mineral wool) is the most widely used medium in hydroponics. Rock wool is an inert substrate suitable for both run-to-waste and recirculating systems. Rock wool is made from molten rock, basalt or 'slag' that is spun into bundles of single filament fibres, and bonded into a medium capable of capillary action, and is, in effect, protected from most common microbiological degradation. Rock wool is typically used only for the seedling stage, or with newly cut clones, but can remain with the plant base for its lifetime. Rock wool has many advantages and some disadvantages. The latter being the possible skin irritancy (mechanical) whilst handling (1:1000). Flushing with cold water usually brings relief. Advantages include its proven efficiency and effectiveness as a commercial hydroponic substrate. Most of the rock wool sold to date is a non-hazardous, non-carcinogenic material, falling under Note Q of the European Union Classification Packaging and Labeling Regulation (CLP).
Mineral wool products can be engineered to hold large quantities of water and air that aid root growth and nutrient uptake in hydroponics; their fibrous nature also provides a good mechanical structure to hold the plant stable. The naturally high pH of mineral wool makes them initially unsuitable to plant growth and requires "conditioning" to produce a wool with an appropriate, stable pH.
 Baked clay pellets are suitable for hydroponic systems in which all nutrients are carefully controlled in water solution. The clay pellets are inert, pH-neutral, and do not contain any nutrient value.
The clay is formed into round pellets and fired in rotary
Baked clay pellets are suitable for hydroponic systems in which all nutrients are carefully controlled in water solution. The clay pellets are inert, pH-neutral, and do not contain any nutrient value.
The clay is formed into round pellets and fired in rotary
 Regardless of hydroponic demand, coconut coir is a natural byproduct derived from coconut processes. The outer husk of a coconut consists of fibers which are commonly used to make a myriad of items ranging from floor mats to brushes. After the long fibers are used for those applications, the dust and short fibers are merged to create coir. Coconuts absorb high levels of nutrients throughout their life cycle, so the coir must undergo a maturation process before it becomes a viable growth medium. This process removes salt, tannins and phenolic compounds through substantial water washing. Contaminated water is a byproduct of this process, as three hundred to six hundred liters of water per one cubic meter of coir is needed. Additionally, this maturation can take up to six months and one study concluded the working conditions during the maturation process are dangerous and would be illegal in North America and Europe. Despite requiring attention, posing health risks and environmental impacts, coconut coir has impressive material properties. When exposed to water, the brown, dry, chunky and fibrous material expands nearly three or four times its original size. This characteristic combined with coconut coir's water retention capacity and resistance to pests and diseases make it an effective growth medium. Used as an alternative to rock wool, coconut coir, also known as coir peat, offers optimized growing conditions.
Regardless of hydroponic demand, coconut coir is a natural byproduct derived from coconut processes. The outer husk of a coconut consists of fibers which are commonly used to make a myriad of items ranging from floor mats to brushes. After the long fibers are used for those applications, the dust and short fibers are merged to create coir. Coconuts absorb high levels of nutrients throughout their life cycle, so the coir must undergo a maturation process before it becomes a viable growth medium. This process removes salt, tannins and phenolic compounds through substantial water washing. Contaminated water is a byproduct of this process, as three hundred to six hundred liters of water per one cubic meter of coir is needed. Additionally, this maturation can take up to six months and one study concluded the working conditions during the maturation process are dangerous and would be illegal in North America and Europe. Despite requiring attention, posing health risks and environmental impacts, coconut coir has impressive material properties. When exposed to water, the brown, dry, chunky and fibrous material expands nearly three or four times its original size. This characteristic combined with coconut coir's water retention capacity and resistance to pests and diseases make it an effective growth medium. Used as an alternative to rock wool, coconut coir, also known as coir peat, offers optimized growing conditions.
 Parboiled rice husks (PBH) are an agricultural byproduct that would otherwise have little use. They decay over time, and allow drainage, and even retain less water than growstones. A study showed that rice husks did not affect the effects of plant growth regulators.
Parboiled rice husks (PBH) are an agricultural byproduct that would otherwise have little use. They decay over time, and allow drainage, and even retain less water than growstones. A study showed that rice husks did not affect the effects of plant growth regulators.
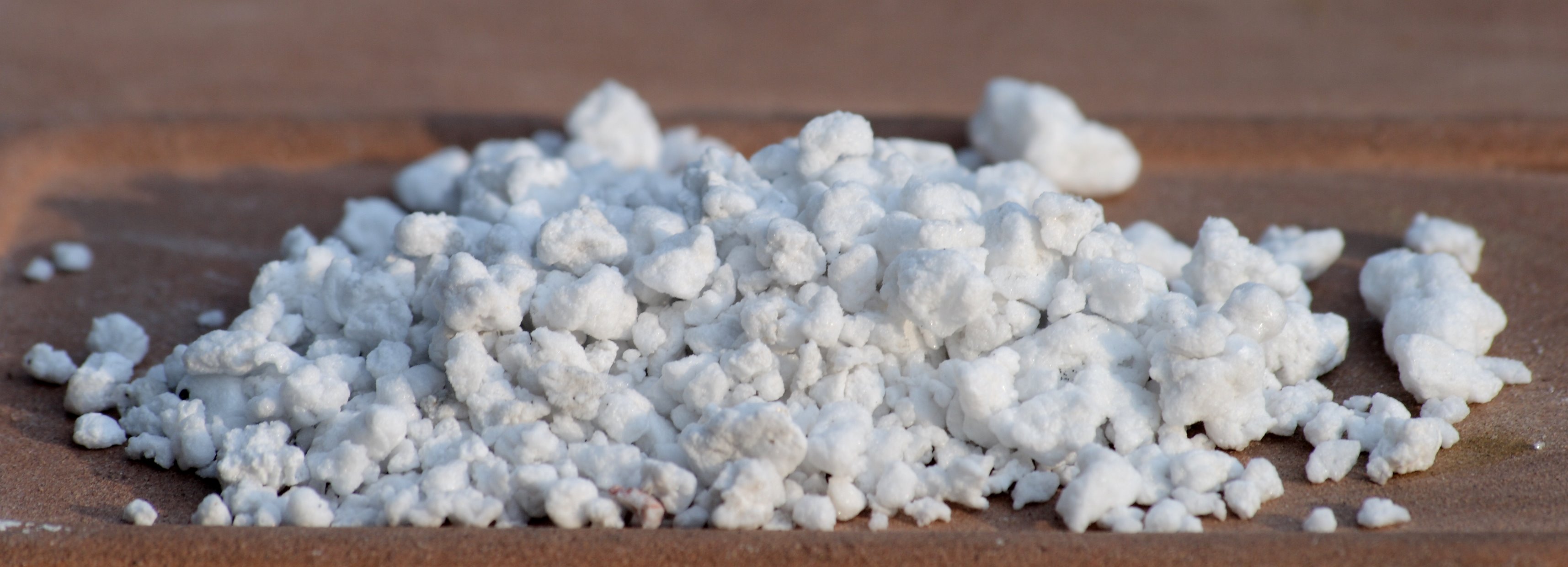
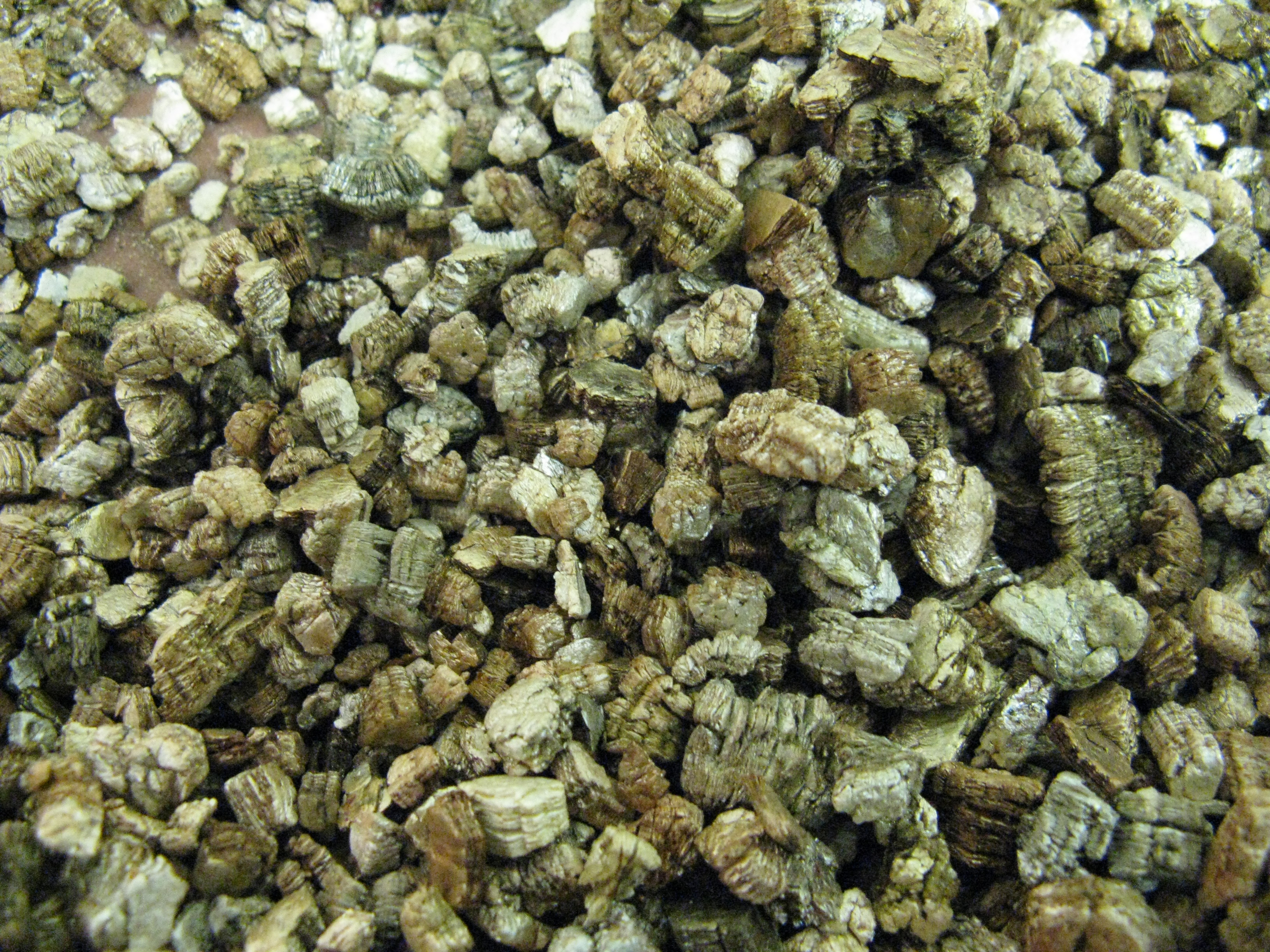
 Like perlite,
Like perlite,
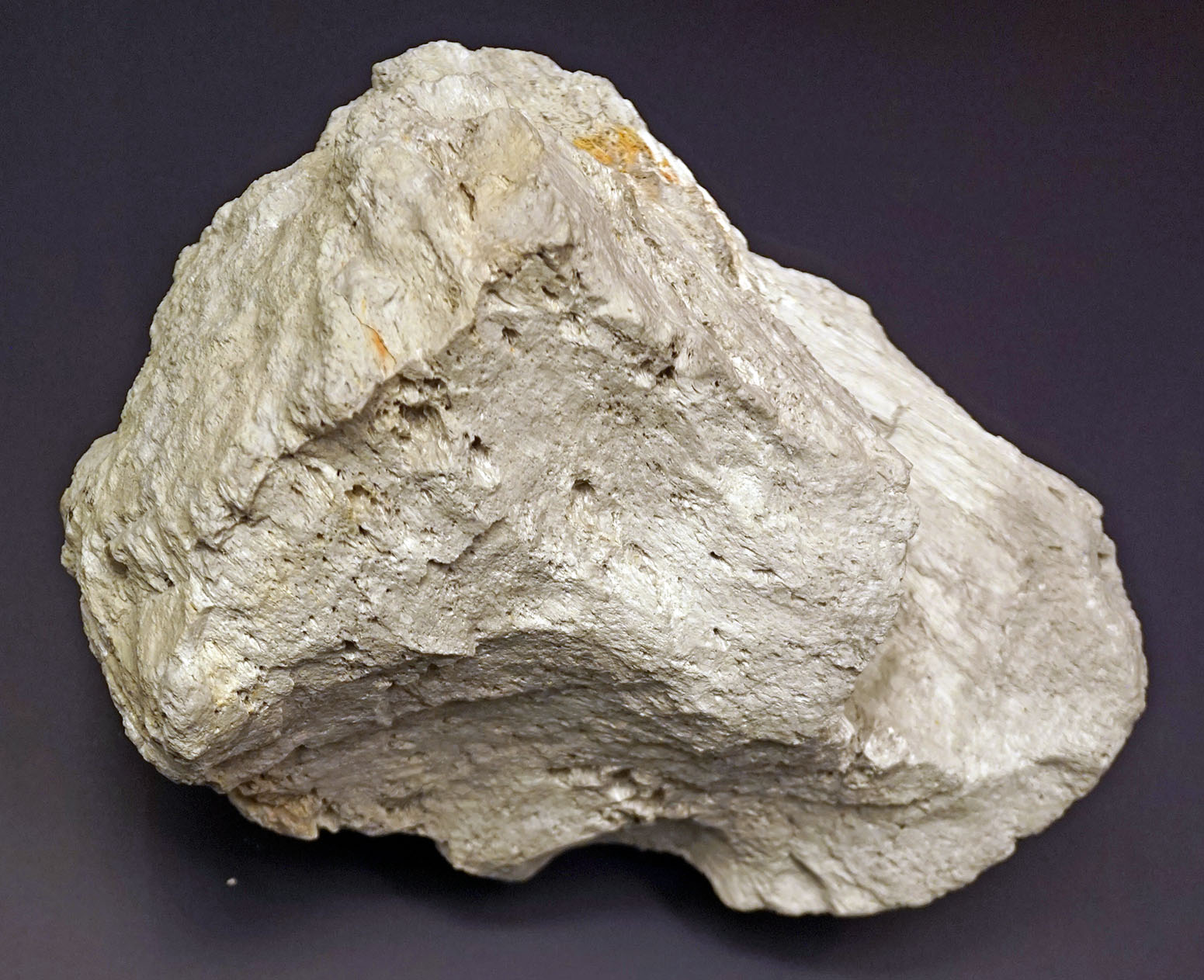 Like perlite,
Like perlite,
 Wood fibre, produced from steam friction of wood, is an efficient organic substrate for hydroponics. It has the advantage that it keeps its structure for a very long time.
Wood fibre, produced from steam friction of wood, is an efficient organic substrate for hydroponics. It has the advantage that it keeps its structure for a very long time.
 Polystyrene packing peanuts are inexpensive, readily available, and have excellent drainage. However, they can be too lightweight for some uses. They are used mainly in closed-tube systems. Note that non-biodegradable
Polystyrene packing peanuts are inexpensive, readily available, and have excellent drainage. However, they can be too lightweight for some uses. They are used mainly in closed-tube systems. Note that non-biodegradable

 Hydroponics is a type of
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
and a subset of hydroculture
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water-based mineral nutrient solutions in aqueous solvents. Terrestrial or aquatic plant ...
which involves growing plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s, usually crops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponi ...
or medicinal plants
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including defense and protection ag ...
, without soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
, by using water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
-based mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solutio ...
s in aqueous solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s. Terrestrial or aquatic plant
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments ( saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that ...
s may grow with their root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
s exposed to the nutritious liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
or in addition, the roots may be mechanically supported by an inert medium such as perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an industrial ...
, gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classifi ...
, or other substrates.
Despite inert media, roots can cause changes of the rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microo ...
pH and root exudate Plant root exudates are fluids emitted through the roots of plants. These secretions influence the rhizosphere around the roots to inhibit harmful microbes and promote the grow of self and kin plants.
Plant root systems can grow to be complex du ...
s can affect rhizosphere biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
and physiological balance of the nutrient solution by secondary metabolite
Secondary metabolites, also called specialised metabolites, toxins, secondary products, or natural products, are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the norma ...
s. Transgenic plants grown hydroponically allow the release of pharmaceutical proteins as part of the root exudate into the hydroponic medium.
The nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
used in hydroponic systems can come from many different organic
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ...
or inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemist ...
sources, including fish excrement
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of l ...
, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
manure
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the Soil fertility, fertility of soil by adding organic ma ...
, purchased chemical fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s, or artificial
Artificiality (the state of being artificial or manmade) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity.
Connotations
Artificiality ...
nutrient solutions.
Plants are commonly grown hydroponically in a greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These ...
or contained environment on inert media, adapted to the controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) process. Plants commonly grown hydroponically include tomatoes, peppers
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
, cucumbers
Cucumber (''Cucumis sativus'') is a widely-cultivated creeping vine plant in the Cucurbitaceae family that bears usually cylindrical fruits, which are used as culinary vegetables.strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
, lettuces, and cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
, usually for commercial use, and ''Arabidopsis thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land.
A winter ...
'', which serves as a model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
in plant science
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek wo ...
and genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
.
Hydroponics offers many advantages, notably a decrease in water usage in agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. To grow of tomatoes using intensive farming
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ...
methods requires of water; using hydroponics, ; and only using aeroponics
Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in the air or mist environment without soil or an aggregate medium. The word "aeroponic" is derived from the Greek meanings of ''aer'' ("air") and ''ponos'' ("labour"). It is a subset of hydroponic ...
.
Hydroponic cultures lead to highest biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
production compared to other growth substrates, of plants cultivated in the same environmental conditions and supplied with equal amounts of nutrients.
Since hydroponics takes much less water and nutrients to grow produce and climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
threatens agricultural yields, it could be possible in the future for people in harsh environments with little accessible water to grow their own plant-based food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
.
Hydroponics is not only used on earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
, but has also proven itself in plant production experiments in space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consi ...
.
History
 The earliest published work on growing terrestrial plants without soil was the 1627 book ''Sylva Sylvarum'' or 'A Natural History' by
The earliest published work on growing terrestrial plants without soil was the 1627 book ''Sylva Sylvarum'' or 'A Natural History' by Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
, printed a year after his death. As a result of his work, water culture became a popular research technique. In 1699, John Woodward John Woodward or ''variant'', may refer to:
Sports
* John Woodward (English footballer) (born 1947), former footballer
* John Woodward (Scottish footballer) (born 1949), former footballer
* Johnny Woodward (1924–2002), English footballer
* Jo ...
published his water culture experiments with spearmint
Spearmint, also known as garden mint, common mint, lamb mint and mackerel mint, is a species of mint, ''Mentha spicata'' (, native to Europe and southern temperate Asia, extending from Ireland in the west to southern China in the east. It is nat ...
. He found that plants in less-pure water sources grew better than plants in distilled water. By 1842, a list of nine elements believed to be essential for plant growth had been compiled, and the discoveries of German botanists Julius von Sachs
Julius von Sachs (; 2 October 1832 – 29 May 1897) was a German botanist from Breslau, Prussian Silesia. He is considered the founder of experimental plant physiology and co-founder of modern water culture. Julius von Sachs and Wilhelm Knop a ...
and Wilhelm Knop
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Mount ...
, in the years 1859–1875, resulted in a development of the technique of soilless cultivation. To quote von Sachs directly: "In the year 1860, I published the results of experiments which demonstrated that land plants are capable of absorbing their nutritive matters out of watery solutions, without the aid of soil, and that it is possible in this way not only to maintain plants alive and growing for a long time, as had long been known, but also to bring about a vigorous increase of their organic substance, and even the production of seed capable of germination." Growth of terrestrial plants without soil in mineral nutrient solutions was later called "solution culture" in reference to "soil culture". It quickly became a standard research and teaching technique in the 19th and 20th centuries and is still widely used in plant nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element i ...
science.
Around the 1930s plant nutritionists investigated diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
of certain plants, and thereby, observed symptoms related to existing soil conditions such as salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
. In this context, water culture experiments were undertaken with the hope of delivering similar symptoms under controlled laboratory conditions. This approach forced by Dennis Robert Hoagland
Dennis Robert Hoagland (April 2, 1884 – September 5, 1949) was an American chemist and plant scientist working in the fields of plant nutrition, agricultural chemistry, and physiology. He was Professor of Plant Nutrition at the Universi ...
led to innovative model systems (e.g., green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
Nitella
''Nitella'' is a genus of charophyte green algae in the family Characeae
Characeae is a family of freshwater green algae in the order Charales, commonly known as stoneworts. They are also known as brittleworts or skunkweed, from the fragilit ...
) and standardized nutrient recipes playing an increasingly important role in modern plant physiology
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (b ...
. In 1929, William Frederick Gericke of the University of California at Berkeley began publicly promoting that the principles of solution culture be used for agricultural crop production. He first termed this cultivation method "aquiculture" created in analogy to "agriculture" but later found that the cognate term aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
was already applied to culture of aquatic organisms
Aquatic means relating to water; living in or near water or taking place in water; does not include groundwater, as "aquatic" implies an environment where plants and animals live.
Aquatic(s) may also refer to:
* Aquatic animal, either vertebrate ...
. Gericke created a sensation by growing tomato vines high in his back yard in mineral nutrient solutions rather than soil. He then introduced the term ''Hydroponics'', water culture, in 1937, proposed to him by W. A. Setchell, a phycologist with an extensive education in the classics. Hydroponics is derived from neologism
A neologism Ancient_Greek.html"_;"title="_from_Ancient_Greek">Greek_νέο-_''néo''(="new")_and_λόγος_/''lógos''_meaning_"speech,_utterance"is_a_relatively_recent_or_isolated_term,_word,_or_phrase_that_may_be_in_the_process_of_entering_com ...
υδρωπονικά (derived from Greek ύδωρ=water and πονέω=cultivate), constructed in analogy to γεωπονικά (derived from Greek γαία=earth and πονέω=cultivate), geoponica
The ''Geoponica'' or ''Geoponika'' ( el, Γεωπονικά) is a twenty-book collection of agricultural lore, compiled during the 10th century in Constantinople for the Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus. The Greek word ''Geoponica ...
, that which concerns agriculture, replacing, γεω-, earth, with ὑδρο-, water.
Despite initial successes, however, Gericke realized that the time was not yet ripe for the general technical application and commercial use of hydroponics for producing crops. He also wanted to make sure all aspects of hydroponic cultivation were researched and tested before making any of the specifics available to the public. Reports of Gericke's work and his claims that hydroponics would revolutionize plant agriculture prompted a huge number of requests for further information. Gericke had been denied use of the university's greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These ...
s for his experiments due to the administration's skepticism, and when the university tried to compel him to release his preliminary nutrient recipes developed at home, he requested greenhouse space and time to improve them using appropriate research facilities. While he was eventually provided greenhouse space, the university assigned Hoagland and Arnon to re-evaluate Gericke's claims and show his formula held no benefit over soil grown plant yields, a view held by Hoagland. Because of these irreconcilable conflicts, Gericke left his academic position in 1937 in a climate that was politically unfavorable and continued his research independently in his greenhouse. In 1940, Gericke, whose work is considered to be the basis for all forms of hydroponic growing, published the book, ''Complete Guide to Soilless Gardening''. Therein, for the first time, he published his basic formula involving the macro- and micronutrient salts for hydroponically-grown plants.
As a result of research of Gericke's claims by order of the Director of the ''California Agricultural Experiment Station'' of the University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public land-grant research university system in the U.S. state of California. The system is composed of the campuses at Berkeley, Davis, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, University of Califor ...
, Claude Hutchison, Dennis Hoagland and Daniel Arnon wrote a classic 1938 agricultural bulletin, ''The Water Culture Method for Growing Plants Without Soil'', one of the most important works on solution culture ever, which made the claim that hydroponic crop yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields.
Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the c ...
s were no better than crop yields obtained with good-quality soils. Ultimately, crop yields would be limited by factors other than mineral nutrients, especially light and aeration of the culture medium. However, in the introduction to his landmark book on soilless cultivation, published two years later, Gericke pointed out that the results published by Hoagland and Arnon in comparing the yields of experimental plants in sand, soil and solution cultures, were based on several systemic errors ("...these experimenters have made the mistake of limiting the productive capacity of hydroponics to that of soil. Comparison can be only by growing as great a number of plants in each case as the fertility of the culture medium can support").
For example, the Hoagland and Arnon study did not adequately appreciate that hydroponics has other key benefits compared to soil culture including the fact that the roots of the plant have constant access to oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and that the plants have access to as much or as little water and nutrients as they need. This is important as one of the most common errors when cultivating plants is over- and underwatering; and hydroponics prevents this from occurring as large amounts of water, which may drown root systems in soil, can be made available to the plant in hydroponics, and any water not used, drained away, recirculated, or actively aerated, eliminating anoxic
The term anoxia means a total depletion in the level of oxygen, an extreme form of hypoxia or "low oxygen". The terms anoxia and hypoxia are used in various contexts:
* Anoxic waters, sea water, fresh water or groundwater that are depleted of diss ...
conditions in the root area. In soil, a grower needs to be very experienced to know exactly with how much water to feed the plant. Too much and the plant will be unable to access oxygen because air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
in the soil pores is displaced, which can lead to root rot
Root rot is a condition in which anoxic conditions in the soil or potting media around the roots of a plant cause them to rot. This occurs due to excessive standing water around the roots. It is found in both indoor and outdoor plants, although ...
; too little and the plant will undergo water stress or lose the ability to absorb nutrients, which are typically moved into the roots while dissolved, leading to nutrient deficiency symptoms such as chlorosis
In botany, chlorosis is a condition in which leaves produce insufficient chlorophyll. As chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of leaves, chlorotic leaves are pale, yellow, or yellow-white. The affected plant has little or no ability to ...
. Eventually, Gericke's advanced ideas led to the implementation of hydroponics into commercial agriculture while Hoagland's views and helpful support by the University prompted Hoagland and his associates to develop several new formulas for mineral nutrient solutions, universally known as Hoagland solution.
One of the earliest successes of hydroponics occurred on Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
, a rocky atoll in the Pacific Ocean used as a refueling stop for Pan American Airlines. Hydroponics was used there in the 1930s to grow vegetables for the passengers. Hydroponics was a necessity on Wake Island because there was no soil, and it was prohibitively expensive to airlift in fresh vegetables.
From 1943 to 1946, Daniel I. Arnon
Daniel Israel Arnon (November 14, 1910 – December 20, 1994) was a Polish-born American plant physiologist and National Medal of Science recipient whose research led to greater insights into the operation of photosynthesis and nutrition in plan ...
served as a major in the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
and used his prior expertise with plant nutrition to feed troops stationed on barren Ponape Island
Pohnpei "upon (''pohn'') a stone altar (''pei'')" (formerly known as Ponape or Ascension, Proto-Chuukic-Pohnpeic: ''*Fawo ni pei)'' is an island of the Senyavin Islands which are part of the larger Caroline Islands group. It belongs to Pohnpei ...
in the western Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
by growing crops in gravel and nutrient-rich water because there was no arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
available.Sullivan, Walter"Daniel Arnon, 84, Researcher And Expert on Photosynthesis"
''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', December 23, 1994. Accessed April 7, 2020
In the 1960s, Allen Cooper of England developed the nutrient film technique. The Land Pavilion at Walt Disney World's EPCOT Center opened in 1982 and prominently features a variety of hydroponic techniques.
In recent decades, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
has done extensive hydroponic research for its Controlled Ecological Life Support System
Controlled (or closed) ecological life-support systems (acronym CELSS) are a self-supporting life support system for space stations and colonies typically through controlled closed ecological systems, such as the BioHome, BIOS-3, Biosphere 2, Ma ...
(CELSS). Hydroponics research mimicking a Martian environment uses LED lighting to grow in a different color spectrum with much less heat. Ray Wheeler, a plant physiologist at Kennedy Space Center's Space Life Science Lab, believes that hydroponics will create advances within space travel, as a bioregenerative life support system
Bioregenerative life support systems (BLSS) are artificial ecosystems consisting of many complex symbiotic relationships among higher plants, animals, and microorganisms. As the most advanced life support
Life support comprises the treatments a ...
.
As of 2017, Canada had hundreds of acres of large-scale commercial hydroponic greenhouses, producing tomatoes, peppers and cucumbers.
Due to technological advancements within the industry and numerous economic factors, the global hydroponics market is forecast to grow from US$226.45 million in 2016 to US$724.87 million by 2023.
Techniques
There are two main variations for each medium: sub-irrigation and topirrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
. For all techniques, most hydroponic reservoirs are now built of plastic, but other materials have been used, including concrete, glass, metal, vegetable solids, and wood. The containers should exclude light to prevent algae and fungal growth in the nutrient solution.
Static solution culture
 In static solution culture, plants are grown in containers of nutrient solution, such as glass
In static solution culture, plants are grown in containers of nutrient solution, such as glass Mason jar
A Mason jar, also known as a canning jar or fruit jar, is a glass jar used in home canning to preserve food. It was named after American tinsmith John Landis Mason, who patented it in 1858. The jar's mouth has a screw thread on its outer perime ...
s (typically, in-home applications), pots, buckets, tubs, or tanks. The solution is usually gently aerated but may be un-aerated. If un-aerated, the solution level is kept low enough that enough roots are above the solution so they get adequate oxygen. A hole is cut (or drilled) in the top of the reservoir for each plant; if it is a jar or tub, it may be its lid, but otherwise, cardboard, foil, paper, wood or metal may be put on top. A single reservoir can be dedicated to a single plant, or to various plants. Reservoir size can be increased as plant size increases. A home-made system can be constructed from food containers or glass canning jars with aeration
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration processes create additional surface area in ...
provided by an aquarium pump, aquarium airline tubing, aquarium valves or even a biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
of green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga ...
on the glass, through photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
. Clear containers can also be covered with aluminium foil, butcher paper, black plastic, or other material to eliminate the effects of negative phototropism
Phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. Phototropism is most often observed in plants, but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi. The cells on the plant that are farthest from the light contain a hor ...
. The nutrient solution is changed either on a schedule, such as once per week, or when the concentration drops below a certain level as determined with an electrical conductivity meter
An electrical conductivity meter (EC meter) measures the electrical conductivity in a solution. It has multiple applications in research and engineering, with common usage in hydroponics, aquaculture, aquaponics, and freshwater systems to moni ...
. Whenever the solution is depleted below a certain level, either water or fresh nutrient solution is added. A Mariotte's bottle
Mariotte's bottle is a device that delivers a constant rate of flow from closed bottles or tanks. It is named after French physicist Edme Mariotte (1620-1684). A picture of a bottle with a gas inlet is shown in the works of Mariotte, but this cons ...
, or a float valve, can be used to automatically maintain the solution level. In raft solution culture, plants are placed in a sheet of buoyant plastic that is floated on the surface of the nutrient solution. That way, the solution level never drops below the roots.
Continuous-flow solution culture
 In continuous-flow solution culture, the nutrient solution constantly flows past the roots. It is much easier to automate than the static solution culture because sampling and adjustments to the temperature, pH, and nutrient concentrations can be made in a large storage tank that has potential to serve thousands of plants. A popular variation is the nutrient film technique or NFT, whereby a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth is recirculated in a thin layer past a bare root mat of plants in a watertight channel, with an upper surface exposed to air. As a consequence, an abundant supply of oxygen is provided to the roots of the plants. A properly designed NFT system is based on using the right channel slope, the right flow rate, and the right channel length. The main advantage of the NFT system over other forms of hydroponics is that the plant roots are exposed to adequate supplies of water, oxygen, and nutrients. In all other forms of production, there is a conflict between the supply of these requirements, since excessive or deficient amounts of one results in an imbalance of one or both of the others. NFT, because of its design, provides a system where all three requirements for healthy plant growth can be met at the same time, provided that the simple concept of NFT is always remembered and practised. The result of these advantages is that higher yields of high-quality produce are obtained over an extended period of cropping. A downside of NFT is that it has very little buffering against interruptions in the flow (e.g., power outages). But, overall, it is probably one of the more productive techniques.
The same design characteristics apply to all conventional NFT systems. While slopes along channels of 1:100 have been recommended, in practice it is difficult to build a base for channels that is sufficiently true to enable nutrient films to flow without ponding in locally depressed areas. As a consequence, it is recommended that slopes of 1:30 to 1:40 are used. This allows for minor irregularities in the surface, but, even with these slopes, ponding and water logging may occur. The slope may be provided by the floor, benches or racks may hold the channels and provide the required slope. Both methods are used and depend on local requirements, often determined by the site and crop requirements.
As a general guide, flow rates for each gully should be one liter per minute. At planting, rates may be half this and the upper limit of 2 L/min appears about the maximum. Flow rates beyond these extremes are often associated with nutritional problems. Depressed growth rates of many crops have been observed when channels exceed 12 meters in length. On rapidly growing crops, tests have indicated that, while oxygen levels remain adequate, nitrogen may be depleted over the length of the gully. As a consequence, channel length should not exceed 10–15 meters. In situations where this is not possible, the reductions in growth can be eliminated by placing another nutrient feed halfway along the gully and halving the flow rates through each outlet.
In continuous-flow solution culture, the nutrient solution constantly flows past the roots. It is much easier to automate than the static solution culture because sampling and adjustments to the temperature, pH, and nutrient concentrations can be made in a large storage tank that has potential to serve thousands of plants. A popular variation is the nutrient film technique or NFT, whereby a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth is recirculated in a thin layer past a bare root mat of plants in a watertight channel, with an upper surface exposed to air. As a consequence, an abundant supply of oxygen is provided to the roots of the plants. A properly designed NFT system is based on using the right channel slope, the right flow rate, and the right channel length. The main advantage of the NFT system over other forms of hydroponics is that the plant roots are exposed to adequate supplies of water, oxygen, and nutrients. In all other forms of production, there is a conflict between the supply of these requirements, since excessive or deficient amounts of one results in an imbalance of one or both of the others. NFT, because of its design, provides a system where all three requirements for healthy plant growth can be met at the same time, provided that the simple concept of NFT is always remembered and practised. The result of these advantages is that higher yields of high-quality produce are obtained over an extended period of cropping. A downside of NFT is that it has very little buffering against interruptions in the flow (e.g., power outages). But, overall, it is probably one of the more productive techniques.
The same design characteristics apply to all conventional NFT systems. While slopes along channels of 1:100 have been recommended, in practice it is difficult to build a base for channels that is sufficiently true to enable nutrient films to flow without ponding in locally depressed areas. As a consequence, it is recommended that slopes of 1:30 to 1:40 are used. This allows for minor irregularities in the surface, but, even with these slopes, ponding and water logging may occur. The slope may be provided by the floor, benches or racks may hold the channels and provide the required slope. Both methods are used and depend on local requirements, often determined by the site and crop requirements.
As a general guide, flow rates for each gully should be one liter per minute. At planting, rates may be half this and the upper limit of 2 L/min appears about the maximum. Flow rates beyond these extremes are often associated with nutritional problems. Depressed growth rates of many crops have been observed when channels exceed 12 meters in length. On rapidly growing crops, tests have indicated that, while oxygen levels remain adequate, nitrogen may be depleted over the length of the gully. As a consequence, channel length should not exceed 10–15 meters. In situations where this is not possible, the reductions in growth can be eliminated by placing another nutrient feed halfway along the gully and halving the flow rates through each outlet.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in the air or mist environment without soil or an aggregate medium. The word "aeroponic" is derived from the Greek meanings of ''aer'' ("air") and ''ponos'' ("labour"). It is a subset of hydroponic ...
is a system wherein roots are continuously or discontinuously kept in an environment saturated with fine drops (a mist
Mist is a phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in the cold air, usually by condensation. Physically, it is an example of a dispersion. It is most commonly seen where water vapor in warm, moist air meets sudden cooling, such a ...
or aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogen ...
) of nutrient solution. The method requires no substrate and entails growing plants with their roots suspended in a deep air or growth chamber with the roots periodically wetted with a fine mist of atomized nutrients. Excellent aeration is the main advantage of aeroponics.
 Aeroponic techniques have proven to be commercially successful for propagation, seed germination, seed potato production, tomato production, leaf crops, and micro-greens. Since inventor Richard Stoner commercialized aeroponic technology in 1983, aeroponics has been implemented as an alternative to water intensive hydroponic systems worldwide. The limitation of hydroponics is the fact that of water can only hold of air, no matter whether aerators are utilized or not.
Another distinct advantage of aeroponics over hydroponics is that any species of plants can be grown in a true aeroponic system because the microenvironment of an aeroponic can be finely controlled. The limitation of hydroponics is that certain species of plants can only survive for so long in water before they become waterlogged. The advantage of aeroponics is that suspended aeroponic plants receive 100% of the available oxygen and carbon dioxide to the roots zone, stems, and leaves, thus accelerating biomass growth and reducing rooting times. NASA research has shown that aeroponically grown plants have an 80% increase in dry weight biomass (essential minerals) compared to hydroponically grown plants. Aeroponics used 65% less water than hydroponics. NASA also concluded that aeroponically grown plants require ¼ the nutrient input compared to hydroponics. Unlike hydroponically grown plants, aeroponically grown plants will not suffer transplant shock when transplanted to soil, and offers growers the ability to reduce the spread of disease and pathogens.
Aeroponics is also widely used in laboratory studies of plant physiology and plant pathology. Aeroponic techniques have been given special attention from
Aeroponic techniques have proven to be commercially successful for propagation, seed germination, seed potato production, tomato production, leaf crops, and micro-greens. Since inventor Richard Stoner commercialized aeroponic technology in 1983, aeroponics has been implemented as an alternative to water intensive hydroponic systems worldwide. The limitation of hydroponics is the fact that of water can only hold of air, no matter whether aerators are utilized or not.
Another distinct advantage of aeroponics over hydroponics is that any species of plants can be grown in a true aeroponic system because the microenvironment of an aeroponic can be finely controlled. The limitation of hydroponics is that certain species of plants can only survive for so long in water before they become waterlogged. The advantage of aeroponics is that suspended aeroponic plants receive 100% of the available oxygen and carbon dioxide to the roots zone, stems, and leaves, thus accelerating biomass growth and reducing rooting times. NASA research has shown that aeroponically grown plants have an 80% increase in dry weight biomass (essential minerals) compared to hydroponically grown plants. Aeroponics used 65% less water than hydroponics. NASA also concluded that aeroponically grown plants require ¼ the nutrient input compared to hydroponics. Unlike hydroponically grown plants, aeroponically grown plants will not suffer transplant shock when transplanted to soil, and offers growers the ability to reduce the spread of disease and pathogens.
Aeroponics is also widely used in laboratory studies of plant physiology and plant pathology. Aeroponic techniques have been given special attention from NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
since a mist is easier to handle than a liquid in a zero-gravity environment.
Fogponics
Fogponics is a derivation of aeroponics wherein the nutrient solution is aerosolized by a diaphragm vibrating at ultrasonic frequencies. Solution droplets produced by this method tend to be 5–10 µm in diameter, smaller than those produced by forcing a nutrient solution through pressurized nozzles, as in aeroponics. The smaller size of the droplets allows them to diffuse through the air more easily, and deliver nutrients to the roots without limiting their access to oxygen.Passive sub-irrigation
 Passive sub-irrigation, also known as passive hydroponics, semi-hydroponics, or ''hydroculture'', is a method wherein plants are grown in an inert
Passive sub-irrigation, also known as passive hydroponics, semi-hydroponics, or ''hydroculture'', is a method wherein plants are grown in an inert porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
medium that moves water and fertilizer to the roots by capillary action
Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, any external forces li ...
from a separate reservoir as necessary, reducing labor and providing a constant supply of water to the roots. In the simplest method, the pot sits in a shallow solution of fertilizer and water or on a capillary mat saturated with nutrient solution. The various hydroponic media available, such as expanded clay and coconut husk
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the f ...
, contain more air space than more traditional potting mixes, delivering increased oxygen to the roots, which is important in epiphytic plants such as orchids
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
and bromeliads, whose roots are exposed to the air in nature. Additional advantages of passive hydroponics are the reduction of root rot and the additional ambient humidity provided through evaporations.
Hydroculture compared to traditional farming in terms of crops yield per area in a controlled environment was roughly 10 times more efficient than traditional farming, uses 13 times less water in one crop cycle than traditional farming, but on average uses 100 times more kilojoules per kilogram of energy than traditional farming.
Ebb and flow (flood and drain) sub-irrigation
 In its simplest form, there is a tray above a reservoir of nutrient solution. Either the tray is filled with growing medium (clay granules being the most common) and then plant directly or place the pot over medium, stand in the tray. At regular intervals, a simple timer causes a pump to fill the upper tray with nutrient solution, after which the solution drains back down into the reservoir. This keeps the medium regularly flushed with nutrients and air. Once the upper tray fills past the drain stop, it begins recirculating the water until the timer turns the pump off, and the water in the upper tray drains back into the reservoirs.
In its simplest form, there is a tray above a reservoir of nutrient solution. Either the tray is filled with growing medium (clay granules being the most common) and then plant directly or place the pot over medium, stand in the tray. At regular intervals, a simple timer causes a pump to fill the upper tray with nutrient solution, after which the solution drains back down into the reservoir. This keeps the medium regularly flushed with nutrients and air. Once the upper tray fills past the drain stop, it begins recirculating the water until the timer turns the pump off, and the water in the upper tray drains back into the reservoirs.
Run-to-waste
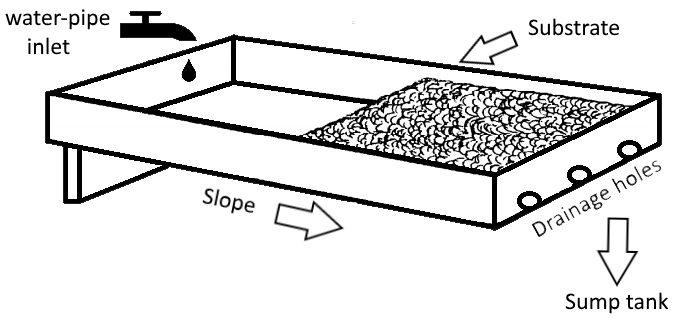
In a run-to-waste system, nutrient and water solution is periodically applied to the medium surface. The method was invented inBengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
in 1946; for this reason it is sometimes referred to as "The Bengal System".
 This method can be set up in various configurations. In its simplest form, a nutrient-and-water solution is manually applied one or more times per day to a container of inert growing media, such as rockwool, perlite, vermiculite, coco fibre, or sand. In a slightly more complex system, it is automated with a delivery pump, a timer and irrigation tubing to deliver nutrient solution with a delivery frequency that is governed by the key parameters of plant size, plant growing stage, climate, substrate, and substrate conductivity, pH, and water content.
In a commercial setting, watering frequency is multi-factorial and governed by computers or PLCs.
Commercial hydroponics production of large plants like tomatoes, cucumber, and peppers uses one form or another of run-to-waste hydroponics.
In environmentally responsible uses, the nutrient-rich waste is collected and processed through an on-site filtration system to be used many times, making the system very productive.
This method can be set up in various configurations. In its simplest form, a nutrient-and-water solution is manually applied one or more times per day to a container of inert growing media, such as rockwool, perlite, vermiculite, coco fibre, or sand. In a slightly more complex system, it is automated with a delivery pump, a timer and irrigation tubing to deliver nutrient solution with a delivery frequency that is governed by the key parameters of plant size, plant growing stage, climate, substrate, and substrate conductivity, pH, and water content.
In a commercial setting, watering frequency is multi-factorial and governed by computers or PLCs.
Commercial hydroponics production of large plants like tomatoes, cucumber, and peppers uses one form or another of run-to-waste hydroponics.
In environmentally responsible uses, the nutrient-rich waste is collected and processed through an on-site filtration system to be used many times, making the system very productive.
Deep water culture
Top-fed deep water culture
''Top-fed'' deep water culture is a technique involving delivering highly oxygenated nutrient solution direct to the root zone of plants. While deep water culture involves the plant roots hanging down into a reservoir of nutrient solution, in top-fed deep water culture the solution is pumped from the reservoir up to the roots (top feeding). The water is released over the plant's roots and then runs back into the reservoir below in a constantly recirculating system. As with deep water culture, there is an airstone in the reservoir that pumps air into the water via a hose from outside the reservoir. The airstone helps add oxygen to the water. Both the airstone and the water pump run 24 hours a day. The biggest advantage of top-fed deep water culture over standard deep water culture is increased growth during the first few weeks. With deep water culture, there is a time when the roots have not reached the water yet. With top-fed deep water culture, the roots get easy access to water from the beginning and will grow to the reservoir below much more quickly than with a deep water culture system. Once the roots have reached the reservoir below, there is not a huge advantage with top-fed deep water culture over standard deep water culture. However, due to the quicker growth in the beginning, grow time can be reduced by a few weeks.Rotary
 A rotary hydroponic garden is a style of commercial hydroponics created within a circular frame which rotates continuously during the entire growth cycle of whatever plant is being grown.
While system specifics vary, systems typically rotate once per hour, giving a plant 24 full turns within the circle each 24-hour period. Within the center of each rotary hydroponic garden can be a high intensity grow light, designed to simulate sunlight, often with the assistance of a mechanized timer.
Each day, as the plants rotate, they are periodically watered with a hydroponic growth solution to provide all nutrients necessary for robust growth. Due to the plants continuous fight against gravity, plants typically mature much more quickly than when grown in soil or other traditional hydroponic growing systems. Because rotary hydroponic systems have a small size, they allow for more plant material to be grown per area of floor space than other traditional hydroponic systems.
Rotary hydroponic systems should be avoided in most circumstances, mainly because of their experimental nature and their high costs for finding, buying, operating, and maintaining them.
A rotary hydroponic garden is a style of commercial hydroponics created within a circular frame which rotates continuously during the entire growth cycle of whatever plant is being grown.
While system specifics vary, systems typically rotate once per hour, giving a plant 24 full turns within the circle each 24-hour period. Within the center of each rotary hydroponic garden can be a high intensity grow light, designed to simulate sunlight, often with the assistance of a mechanized timer.
Each day, as the plants rotate, they are periodically watered with a hydroponic growth solution to provide all nutrients necessary for robust growth. Due to the plants continuous fight against gravity, plants typically mature much more quickly than when grown in soil or other traditional hydroponic growing systems. Because rotary hydroponic systems have a small size, they allow for more plant material to be grown per area of floor space than other traditional hydroponic systems.
Rotary hydroponic systems should be avoided in most circumstances, mainly because of their experimental nature and their high costs for finding, buying, operating, and maintaining them.
Substrates (growing support materials)
One of the most obvious decisions hydroponic farmers have to make is which medium they should use. Different media are appropriate for different growing techniques.Rock wool
 Rock wool ( mineral wool) is the most widely used medium in hydroponics. Rock wool is an inert substrate suitable for both run-to-waste and recirculating systems. Rock wool is made from molten rock, basalt or 'slag' that is spun into bundles of single filament fibres, and bonded into a medium capable of capillary action, and is, in effect, protected from most common microbiological degradation. Rock wool is typically used only for the seedling stage, or with newly cut clones, but can remain with the plant base for its lifetime. Rock wool has many advantages and some disadvantages. The latter being the possible skin irritancy (mechanical) whilst handling (1:1000). Flushing with cold water usually brings relief. Advantages include its proven efficiency and effectiveness as a commercial hydroponic substrate. Most of the rock wool sold to date is a non-hazardous, non-carcinogenic material, falling under Note Q of the European Union Classification Packaging and Labeling Regulation (CLP).
Mineral wool products can be engineered to hold large quantities of water and air that aid root growth and nutrient uptake in hydroponics; their fibrous nature also provides a good mechanical structure to hold the plant stable. The naturally high pH of mineral wool makes them initially unsuitable to plant growth and requires "conditioning" to produce a wool with an appropriate, stable pH.
Rock wool ( mineral wool) is the most widely used medium in hydroponics. Rock wool is an inert substrate suitable for both run-to-waste and recirculating systems. Rock wool is made from molten rock, basalt or 'slag' that is spun into bundles of single filament fibres, and bonded into a medium capable of capillary action, and is, in effect, protected from most common microbiological degradation. Rock wool is typically used only for the seedling stage, or with newly cut clones, but can remain with the plant base for its lifetime. Rock wool has many advantages and some disadvantages. The latter being the possible skin irritancy (mechanical) whilst handling (1:1000). Flushing with cold water usually brings relief. Advantages include its proven efficiency and effectiveness as a commercial hydroponic substrate. Most of the rock wool sold to date is a non-hazardous, non-carcinogenic material, falling under Note Q of the European Union Classification Packaging and Labeling Regulation (CLP).
Mineral wool products can be engineered to hold large quantities of water and air that aid root growth and nutrient uptake in hydroponics; their fibrous nature also provides a good mechanical structure to hold the plant stable. The naturally high pH of mineral wool makes them initially unsuitable to plant growth and requires "conditioning" to produce a wool with an appropriate, stable pH.
Expanded clay aggregate
 Baked clay pellets are suitable for hydroponic systems in which all nutrients are carefully controlled in water solution. The clay pellets are inert, pH-neutral, and do not contain any nutrient value.
The clay is formed into round pellets and fired in rotary
Baked clay pellets are suitable for hydroponic systems in which all nutrients are carefully controlled in water solution. The clay pellets are inert, pH-neutral, and do not contain any nutrient value.
The clay is formed into round pellets and fired in rotary kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay int ...
s at . This causes the clay to expand, like popcorn, and become porous. It is light in weight, and does not compact over time. The shape of an individual pellet can be irregular or uniform depending on brand and manufacturing process. The manufacturers consider expanded clay to be an ecologically sustainable and re-usable growing medium because of its ability to be cleaned and sterilized, typically by washing in solutions of white vinegar, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color (whitening) from a fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically, to ...
, or hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
(), and rinsing completely.
Another view is that clay pebbles are best not re-used even when they are cleaned, due to root growth that may enter the medium. Breaking open a clay pebble after a crop has been shown to reveal this growth.
Growstones
Growstones, made from glass waste, have both more air and water retention space than perlite and peat. This aggregate holds more water thanparboiled rice hulls
Rice hulls (or rice husks) are the hard protecting coverings of grains of rice. In addition to protecting rice during the growing season, rice hulls can be put to use as building material, fertilizer, insulation material, or fuel. Rice hulls are pa ...
. Growstones by volume consist of 0.5 to 5% calcium carbonate – for a standard 5.1 kg bag of Growstones that corresponds to 25.8 to 258 grams of calcium carbonate. The remainder is soda-lime glass.
Coconut Coir
 Regardless of hydroponic demand, coconut coir is a natural byproduct derived from coconut processes. The outer husk of a coconut consists of fibers which are commonly used to make a myriad of items ranging from floor mats to brushes. After the long fibers are used for those applications, the dust and short fibers are merged to create coir. Coconuts absorb high levels of nutrients throughout their life cycle, so the coir must undergo a maturation process before it becomes a viable growth medium. This process removes salt, tannins and phenolic compounds through substantial water washing. Contaminated water is a byproduct of this process, as three hundred to six hundred liters of water per one cubic meter of coir is needed. Additionally, this maturation can take up to six months and one study concluded the working conditions during the maturation process are dangerous and would be illegal in North America and Europe. Despite requiring attention, posing health risks and environmental impacts, coconut coir has impressive material properties. When exposed to water, the brown, dry, chunky and fibrous material expands nearly three or four times its original size. This characteristic combined with coconut coir's water retention capacity and resistance to pests and diseases make it an effective growth medium. Used as an alternative to rock wool, coconut coir, also known as coir peat, offers optimized growing conditions.
Regardless of hydroponic demand, coconut coir is a natural byproduct derived from coconut processes. The outer husk of a coconut consists of fibers which are commonly used to make a myriad of items ranging from floor mats to brushes. After the long fibers are used for those applications, the dust and short fibers are merged to create coir. Coconuts absorb high levels of nutrients throughout their life cycle, so the coir must undergo a maturation process before it becomes a viable growth medium. This process removes salt, tannins and phenolic compounds through substantial water washing. Contaminated water is a byproduct of this process, as three hundred to six hundred liters of water per one cubic meter of coir is needed. Additionally, this maturation can take up to six months and one study concluded the working conditions during the maturation process are dangerous and would be illegal in North America and Europe. Despite requiring attention, posing health risks and environmental impacts, coconut coir has impressive material properties. When exposed to water, the brown, dry, chunky and fibrous material expands nearly three or four times its original size. This characteristic combined with coconut coir's water retention capacity and resistance to pests and diseases make it an effective growth medium. Used as an alternative to rock wool, coconut coir, also known as coir peat, offers optimized growing conditions.
Rice husks
 Parboiled rice husks (PBH) are an agricultural byproduct that would otherwise have little use. They decay over time, and allow drainage, and even retain less water than growstones. A study showed that rice husks did not affect the effects of plant growth regulators.
Parboiled rice husks (PBH) are an agricultural byproduct that would otherwise have little use. They decay over time, and allow drainage, and even retain less water than growstones. A study showed that rice husks did not affect the effects of plant growth regulators.
Perlite

Perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an industrial ...
is a volcanic rock that has been superheated into very lightweight expanded glass pebbles. It is used loose or in plastic sleeves immersed in the water. It is also used in potting soil mixes to decrease soil density. It does contain a high amount of fluorine which could be harmful to some plants. Perlite has similar properties and uses to vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently, and commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the we ...
but, in general, holds more air and less water and is buoyant.
Vermiculite
 Like perlite,
Like perlite, vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently, and commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the we ...
is a mineral that has been superheated until it has expanded into light pebbles. Vermiculite holds more water than perlite and has a natural "wicking" property that can draw water and nutrients in a passive hydroponic system. If too much water and not enough air surrounds the plants roots, it is possible to gradually lower the medium's water-retention capability by mixing in increasing quantities of perlite.
Pumice
 Like perlite,
Like perlite, pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
is a lightweight, mined volcanic rock that finds application in hydroponics.
Sand
Sand is cheap and easily available. However, it is heavy, does not hold water very well, and it must be sterilized between uses.Gravel
The same type that is used in aquariums, though any small gravel can be used, provided it is washed first. Indeed, plants growing in a typical traditional gravel filter bed, with water circulated using electric powerhead pumps, are in effect being grown using gravel hydroponics, also termed "nutriculture". Gravel is inexpensive, easy to keep clean, drains well and will not become waterlogged. However, it is also heavy, and, if the system does not provide continuous water, the plant roots may dry out.Wood fiber
 Wood fibre, produced from steam friction of wood, is an efficient organic substrate for hydroponics. It has the advantage that it keeps its structure for a very long time.
Wood fibre, produced from steam friction of wood, is an efficient organic substrate for hydroponics. It has the advantage that it keeps its structure for a very long time. Wood wool
Wood wool, known primarily as excelsior in North America, is a product made of wood slivers cut from logs. It is mainly used in packaging, for cooling pads in home evaporative cooling systems known as swamp coolers, for erosion control mats, and ...
(i.e. wood slivers) have been used since the earliest days of the hydroponics research. However, more recent research suggests that wood fibre may have detrimental effects on "plant growth regulators".
Sheep wool
Wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool. ...
from shearing sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticate ...
is a little-used yet promising renewable growing medium. In a study comparing wool with peat slabs, coconut fibre slabs, perlite and rockwool slabs to grow cucumber plants, sheep wool had a greater air capacity of 70%, which decreased with use to a comparable 43%, and water capacity that increased from 23% to 44% with use. Using sheep wool resulted in the greatest yield out of the tested substrates, while application of a biostimulator consisting of humic acid, lactic acid and Bacillus subtilis improved yields in all substrates.
Brick shards
Brick shards have similar properties to gravel. They have the added disadvantages of possibly altering the pH and requiring extra cleaning before reuse.Polystyrene packing peanuts
 Polystyrene packing peanuts are inexpensive, readily available, and have excellent drainage. However, they can be too lightweight for some uses. They are used mainly in closed-tube systems. Note that non-biodegradable
Polystyrene packing peanuts are inexpensive, readily available, and have excellent drainage. However, they can be too lightweight for some uses. They are used mainly in closed-tube systems. Note that non-biodegradable polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the Aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin pe ...
peanuts must be used; biodegradable packing peanuts will decompose into a sludge. Plants may absorb styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen ...
and pass it to their consumers; this is a possible health risk.
Nutrient solutions
Inorganic hydroponic solutions
Theformulation
Formulation is a term used in various senses in various applications, both the material and the abstract or formal. Its fundamental meaning is the putting together of components in appropriate relationships or structures, according to a formul ...
of hydroponic solutions is an application of plant nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element i ...
, with nutrient deficiency symptoms mirroring those found in traditional soil based agriculture. However, the underlying chemistry of hydroponic solutions can differ from soil chemistry
Soil chemistry is the study of the chemical characteristics of soil. Soil chemistry is affected by mineral composition, organic matter and environmental factors. In the early 1850s a consulting chemist to the Royal Agricultural Society in England ...
in many significant ways. Important differences include:
* Unlike soil, hydroponic nutrient solutions do not have cation-exchange capacity
Cation-exchange capacity (CEC) is a measure of how many cations can be retained on soil particle surfaces. Negative charges on the surfaces of soil particles bind positively-charged atoms or molecules (cations), but allow these to exchange with ot ...
(CEC) from clay particles or organic matter. The absence of CEC and soil pores means the pH, oxygen saturation, and nutrient concentrations can change much more rapidly in hydroponic setups than is possible in soil.
* Selective absorption of nutrients by plants often imbalances the amount of counterion
160px, Polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin, is typically supplied with as the counterion.">cation-exchange_resin.html" ;"title="Polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin">Polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin, is typical ...
s in solution. This imbalance can rapidly affect solution pH and the ability of plants to absorb nutrients of similar ionic charge (see article membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges ...
). For instance, nitrate anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s are often consumed rapidly by plants to form protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, leaving an excess of cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
s in solution. This cation imbalance can lead to deficiency symptoms in other cation based nutrients (e.g. Mg2+) even when an ideal quantity of those nutrients are dissolved in the solution.
* Depending on the pH or on the presence of water contaminants, nutrients such as iron can precipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the process of transforming a dissolved substance into an insoluble solid from a super-saturated solution. The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading ...
from the solution and become unavailable to plants. Routine adjustments to pH, buffering the solution, or the use of chelating agent
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands a ...
s is often necessary.
* Unlike soil type
A soil type is a taxonomic unit in soil science. All soils that share a certain set of well-defined properties form a distinctive soil type. Soil type is a technical term of soil classification, the science that deals with the systematic categori ...
s, which can vary greatly in their composition, hydroponic solutions are often standardized and require routine maintenance for plant cultivation. Under controlled conditions hydroponic solutions are periodically pH adjusted to near neutral (pH 6.0) and are aerated with oxygen. Also, water levels must be refilled to account for transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth ...
losses and nutrient solutions require re-fortification to correct the nutrient imbalances that occur as plants grow and deplete nutrient reserves. Sometimes the regular measurement of nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolu ...
ions is used as a key parameter to estimate the remaining proportions and concentrations of other essential nutrient ions to restore a balanced solution.
* Well-known examples of standardized, balanced nutrient solutions are the Hoagland solution, the Long Ashton nutrient solution, or the Knop solution.
As in conventional agriculture, nutrients should be adjusted to satisfy Liebig's law of the minimum for each specific plant variety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
. Nevertheless, generally acceptable concentrations for nutrient solutions exist, with minimum and maximum concentration ranges for most plants being somewhat similar. Most nutrient solutions are mixed to have concentrations between 1,000 and 2,500 ppm. Acceptable concentrations for the individual nutrient ions, which comprise that total ppm figure, are summarized in the following table. For essential nutrients, concentrations below these ranges often lead to nutrient deficiencies while exceeding these ranges can lead to nutrient toxicity. Optimum nutrition concentrations for plant varieties are found empirically by experience or by plant tissue test
The nutrient content of a plant can be assessed by testing a sample of tissue from that plant. These tests are important in agriculture since fertilizer application can be fine-tuned if the plants nutrient status is known. Nitrogen most commonly l ...
s.
Organic hydroponic solutions
Organic fertilizer
Organic fertilizers are fertilizers that are naturally produced. Fertilizers are materials that can be added to soil or plants, in order to provide nutrients and sustain growth. Typical organic fertilizers include all animal waste including me ...
s can be used to supplement or entirely replace the inorganic compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemis ...
s used in conventional hydroponic solutions. However, using organic fertilizers introduces a number of challenges that are not easily resolved. Examples include:
* organic fertilizers are highly variable in their nutritional compositions in terms of minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed ...
and different chemical species
A chemical species is a chemical substance or ensemble composed of chemically identical molecular entities that can explore the same set of molecular energy levels on a characteristic or delineated time scale. These energy levels determine the wa ...
. Even similar materials can differ significantly based on their source (e.g. the quality of manure
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the Soil fertility, fertility of soil by adding organic ma ...
varies based on an animal's diet).
* organic fertilizers are often sourced from animal byproducts, making disease transmission a serious concern for plants grown for human consumption or animal forage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also use ...
.
* organic fertilizers are often particulate
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The te ...
and can clog substrates or other growing equipment. Sieving
A sieve, fine mesh strainer, or sift, is a device for separating wanted elements from unwanted material or for controlling the particle size distribution of a sample, using a screen such as a woven mesh or net or perforated sheet material. ...
or milling the organic materials to fine dusts is often necessary.
* biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology an ...
degradation and conversion processes of organic materials can make mineral ingredients available to plants.
* some organic materials (i.e. particularly manures
Manure is organic matter that is used as organic fertilizer in agriculture. Most manure consists of animal feces; other sources include compost and green manure. Manures contribute to the fertility of soil by adding organic matter and nutrie ...
and offal
Offal (), also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the organs of a butchered animal. The word does not refer to a particular list of edible organs, which varies by culture and region, but usually excludes muscle. Offal may also refe ...
) can further degrade
Degradation may refer to:
Science
* Degradation (geology), lowering of a fluvial surface by erosion
* Degradation (telecommunications), of an electronic signal
* Biodegradation of organic substances by living organisms
* Environmental degradatio ...
to emit foul odors under anaerobic conditions.
* many organic molecules (i.e. sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
s) demand additional oxygen during aerobic degradation, which is essential for cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
in the plant roots.
* organic compounds (i.e. sugars, vitamin
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism. Essential nutrie ...
s, a.o.) are not necessary for normal plant nutrition.
Nevertheless, if precautions are taken, organic fertilizers can be used successfully in hydroponics.
Organically sourced macronutrients
Examples of suitable materials, with their average nutritional contents tabulated in terms of percent dried mass, are listed in the following table.Organically sourced micronutrients
Micronutrients can be sourced from organic fertilizers as well. For example,compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by decomposing plant, food waste, recycling organic materials and manure. The resulting ...
ed pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
bark is high in manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of ...
and is sometimes used to fulfill that mineral requirement in hydroponic solutions. To satisfy requirements for National Organic Program
The National Organic Program (NOP) is the federal regulatory framework in the United States of America governing organic food. It is also the name of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) program ...
s, pulverized, unrefined mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s (e.g. Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywa ...
, Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratc ...
, and glauconite
Glauconite is an iron potassium phyllosilicate ( mica group) mineral of characteristic green color which is very friable and has very low weathering resistance.
It crystallizes with a monoclinic geometry. Its name is derived from the Gre ...
) can also be added to satisfy a plant's nutritional needs.
Additives
Compounds can be added in both organic and conventional hydroponic systems to improve nutrition acquisition and uptake by the plant''.'' Chelating agents and humic acid have been shown to increase nutrient uptake. Additionally, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), which are regularly utilized in field and greenhouse agriculture, have been shown to benefit hydroponic plant growth development and nutrient acquisition. Some PGPR are known to increase nitrogen fixation. While nitrogen is generally abundant in hydroponic systems with properly maintained fertilizer regimens, ''Azospirillum'' and ''Azotobacter'' genera can help maintain mobilized forms of nitrogen in systems with higher microbial growth in the rhizosphere. Traditional fertilizer methods often lead to high accumulated concentrations of nitrate within plant tissue at harvest. ''Rhodopseudo-monas palustris'' has been shown to increase nitrogen use efficiency, increase yield, and decrease nitrate concentration by 88% at harvest compared to traditional hydroponic fertilizer methods in leafy greens. Many ''Bacillus'' spp., ''Pseudomonas'' spp. and ''Streptomyces'' spp. convert forms of phosphorus in the soil that are unavailable to the plant into soluble anions by decreasing soil pH, releasing phosphorus bound in chelated form that is available in a wider pH range, and mineralizing organic phosphorus. Some studies have found that ''Bacillus'' inoculants allow hydroponic leaf lettuce to overcome high salt stress that would otherwise reduce growth. This can be especially beneficial in regions with high electrical conductivity or salt content in their water source. This could potentially avoid costly reverse osmosis filtration systems while maintaining high crop yield.Tools
Common equipment
Managing nutrient concentrations, oxygen saturation, and pH values within acceptable ranges is essential for successful hydroponichorticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
. Common tools used to manage hydroponic solutions include:
* Electrical conductivity meter
An electrical conductivity meter (EC meter) measures the electrical conductivity in a solution. It has multiple applications in research and engineering, with common usage in hydroponics, aquaculture, aquaponics, and freshwater systems to moni ...
s, a tool which estimates nutrient ppm by measuring how well a solution transmits an electric current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The movi ...
.
* pH meter
A pH meter is a scientific instrument that measures the hydrogen-ion activity in water-based solutions, indicating its acidity or alkalinity expressed as pH. The pH meter measures the difference in electrical potential between a pH elect ...
, a tool that uses an electric current to determine the concentration of hydrogen ion
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particle ...
s in solution.
* Oxygen electrode, an electrochemical sensor for determining the oxygen concentration in solution.
* Litmus paper
Litmus is a water-soluble mixture of different dyes extracted from lichens. It is often absorbed onto filter paper to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator, used to test materials for acidity. It is a purple dye that is extracted ...
, disposable pH indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a solution so the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by changes in absorption and/or emission properties. Hence, ...
strips that determine hydrogen ion concentrations by color changing chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking ...
.
* Graduated cylinder
A graduated cylinder, also known as a measuring cylinder or mixing cylinder, is a common piece of laboratory equipment used to measure the volume of a liquid. It has a narrow cylindrical shape. Each marked line on the graduated cylinder represent ...
s or measuring spoons to measure out premixed, commercial hydroponic solutions.
Equipment
Chemical equipment can also be used to perform accurate chemical analyses of nutrient solutions. Examples include: * Balances for accurately measuring materials. *Laboratory glassware
Laboratory glassware refers to a variety of equipment used in scientific work, and traditionally made of glass. Glass can be blown, bent, cut, molded, and formed into many sizes and shapes, and is therefore common in chemistry, biology, and anal ...
, such as burette
A burette is a graduated glass tube with a tap at one end, for delivering known volumes of a liquid, especially in titrations. It is a long, graduated glass tube, with a stopcock at its lower end and a tapered capillary tube at the stopcock's outl ...
s and pipette
A pipette (sometimes spelled as pipett) is a laboratory tool commonly used in chemistry, biology and medicine to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with diff ...
s, for performing titration
Titration (also known as titrimetry and volumetric analysis) is a common laboratory method of quantitative chemical analysis to determine the concentration of an identified analyte (a substance to be analyzed). A reagent, termed the ''titrant'' ...
s.
* Colorimeters for solution tests which apply the Beer–Lambert law
The Beer–Lambert law, also known as Beer's law, the Lambert–Beer law, or the Beer–Lambert–Bouguer law relates the attenuation of light to the properties of the material through which the light is travelling. The law is commonly applied t ...
.
* Spectrophotometer to measure the concentrations of the key parameter nitrate and other nutrients, such as phosphate, sulfate or iron.
Using chemical equipment for hydroponic solutions can be beneficial to growers of any background because nutrient solutions are often reusable. Because nutrient solutions are virtually never completely depleted, and should never be due to the unacceptably low osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure ...
that would result, re-fortification of old solutions with new nutrients can save growers money and can control point source pollution, a common source for the eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phyt ...
of nearby lakes and streams.
Software
Although pre-mixed concentrated nutrient solutions are generally purchased from commercial nutrient manufacturers by hydroponic hobbyists and small commercial growers, several tools exist to help anyone prepare their own solutions without extensive knowledge about chemistry. The free and open source tools HydroBuddy and HydroCal have been created by professional chemists to help any hydroponics grower prepare their own nutrient solutions. The first program is available for Windows, Mac and Linux while the second one can be used through a simple JavaScript interface. Both programs allow for basic nutrient solution preparation although HydroBuddy provides added functionality to use and save custom substances, save formulations and predict electrical conductivity values.Mixing solutions
Often mixing hydroponic solutions using individual salts is impractical for hobbyists or small-scale commercial growers because commercial products are available at reasonable prices. However, even when buying commercial products, multi-component fertilizers are popular. Often these products are bought as three part formulas which emphasize certain nutritional roles. For example, solutions for vegetative growth (i.e. high in nitrogen), flowering (i.e. high in potassium and phosphorus), and micronutrient solutions (i.e. with trace minerals) are popular. The timing and application of these multi-part fertilizers should coincide with a plant's growth stage. For example, at the end of anannual plant
An annual plant is a plant that completes its life cycle, from germination to the production of seeds, within one growing season, and then dies. The length of growing seasons and period in which they take place vary according to geographical ...
's life cycle, a plant should be restricted from high nitrogen fertilizers. In most plants, nitrogen restriction inhibits vegetative growth and helps induce flowering.
Additional improvements

Growrooms
With pest problems reduced and nutrients constantly fed to the roots, productivity in hydroponics is high; however, growers can further increase yield by manipulating a plant's environment by constructing sophisticated growrooms.CO2 enrichment
To increase yield further, some sealed greenhouses inject CO2 into their environment to help improve growth and plant fertility.See also
*Aeroponics
Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in the air or mist environment without soil or an aggregate medium. The word "aeroponic" is derived from the Greek meanings of ''aer'' ("air") and ''ponos'' ("labour"). It is a subset of hydroponic ...
* Anthroponics
* Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a food production system that couples aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as fish, crayfish, snails or prawns in tanks) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) whereby the nutrient-rich aquaculture water is fed to hydr ...
* Fogponics
Fogponics, or atmoponics (from Ancient Greek ἀτμός (atmós), meaning ''"vapour"'' or ''"steam"''), is a subset of aeroponics. Fogponics uses a suspension of nutrient enriched water to deliver nutrients and oxygen to plant roots.
This is i ...
* Folkewall
The Folkewall is a construction with the dual functions of growing plants and purifying greywater. It was designed by Folke Günther in Sweden.
Inspired by the "Sanitas wall" at Dr Gösta Nilsson's Sanitas farm project in Botswana, this techniqu ...
* Grow box
A grow box is a partially or completely enclosed system for raising plants indoors or in small areas. Grow boxes are used for a number of reasons, including lack of available outdoor space or the desire to grow vegetables, herbs or flowers during c ...
* Growroom
* Organoponics
* Passive hydroponics
* Plant factory
* Plant nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element i ...
* Plant pathology
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, ...
* Root rot
Root rot is a condition in which anoxic conditions in the soil or potting media around the roots of a plant cause them to rot. This occurs due to excessive standing water around the roots. It is found in both indoor and outdoor plants, although ...
* Vertical farming
* Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping is the process of Garden design, landscaping, or gardening, that reduces or eliminates the need for irrigation. It is promoted in regions that do not have accessible, plentiful, or reliable supplies of fresh water and has gained accep ...
References
{{Authority control Hydroculture Aeroponics de:Hydrokultur