Human cannibalism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Human cannibalism is the act or practice of humans eating the flesh or internal organs of other human beings. A person who practices
''
 In some societies, cannibalism is a
In some societies, cannibalism is a

 Cannibalism features in the folklore and legends of many cultures and is most often attributed to evil characters or as extreme retribution for some wrongdoing. Examples include the witch in "
Cannibalism features in the folklore and legends of many cultures and is most often attributed to evil characters or as extreme retribution for some wrongdoing. Examples include the witch in "
 In
In
 For a brief time in Europe, an unusual form of cannibalism occurred when thousands of
For a brief time in Europe, an unusual form of cannibalism occurred when thousands of
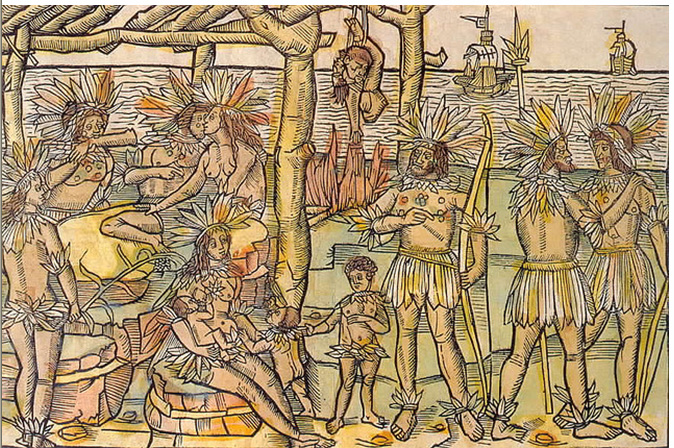 European explorers and colonizers brought home many stories of cannibalism practiced by the native peoples they encountered. In Spain's overseas expansion to the New World, the practice of cannibalism was reported by
European explorers and colonizers brought home many stories of cannibalism practiced by the native peoples they encountered. In Spain's overseas expansion to the New World, the practice of cannibalism was reported by  In early Brazil, there is reportage of cannibalism among the Tupinamba. It is recorded about the natives of the captaincy of
In early Brazil, there is reportage of cannibalism among the Tupinamba. It is recorded about the natives of the captaincy of  The very first encounter between Europeans and Māori may have involved cannibalism of a Dutch sailor. In June 1772, the French explorer
The very first encounter between Europeans and Māori may have involved cannibalism of a Dutch sailor. In June 1772, the French explorer  This period of time was also rife with instances of explorers and seafarers resorting to cannibalism for survival.
* There is archeological and written evidence for English settlers' cannibalism in 1609 in the
This period of time was also rife with instances of explorers and seafarers resorting to cannibalism for survival.
* There is archeological and written evidence for English settlers' cannibalism in 1609 in the

 Further instances include cannibalism as ritual practice; cannibalism in times of drought, famine and other destitution; as well as cannibalism as criminal acts and war crimes throughout the 20th and 21st centuries.
Further instances include cannibalism as ritual practice; cannibalism in times of drought, famine and other destitution; as well as cannibalism as criminal acts and war crimes throughout the 20th and 21st centuries.
July 4, 2018). ''ChannelNewsAsia.com''. Retrieved November 18, 2018. and the civil wars in
July 31, 2007. ''The Washington Post''. This may be done in desperation, as during peacetime cannibalism is much less frequent; at other times, it is consciously directed at certain groups believed to be relatively helpless, such as Congo
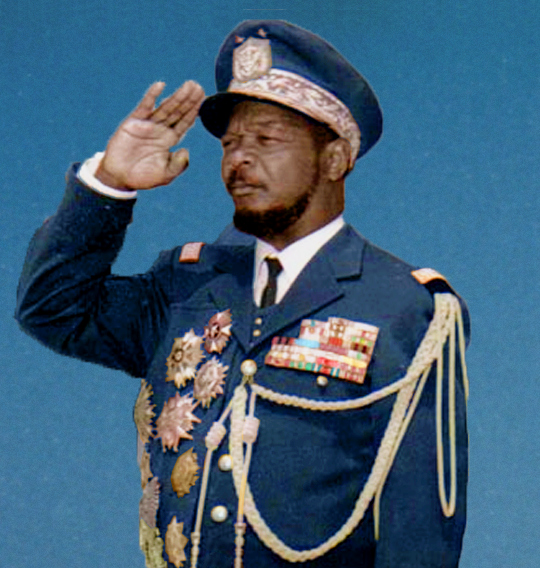 The self-declared emperor of the
The self-declared emperor of the
; Ahmed Kamara, January 8, 2010,
'', Newstime Africa.
 In his book, ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Soviet writer Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn described cases of cannibalism in 20th-century Soviet Union.A. Solzhenitsyn (1973), ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Part I, Chapter 9. Of the Russian famine of 1921, famine in Povolzhie (1921–1922) he wrote: "That horrible famine was up to cannibalism, up to consuming children by their own parents – the famine, which Russia had never known even in the Time of Troubles [in 1601–1603]".
Cannibalism was widespread during the Holodomor (famine of Ukraine) in 1932 and 1933. During the 1930s, multiple acts of cannibalism were reported from Ukraine, Volga region, Russia's Volga, South Siberian, and Kuban regions during the Soviet famine of 1932–1933.
In his book, ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Soviet writer Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn described cases of cannibalism in 20th-century Soviet Union.A. Solzhenitsyn (1973), ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Part I, Chapter 9. Of the Russian famine of 1921, famine in Povolzhie (1921–1922) he wrote: "That horrible famine was up to cannibalism, up to consuming children by their own parents – the famine, which Russia had never known even in the Time of Troubles [in 1601–1603]".
Cannibalism was widespread during the Holodomor (famine of Ukraine) in 1932 and 1933. During the 1930s, multiple acts of cannibalism were reported from Ukraine, Volga region, Russia's Volga, South Siberian, and Kuban regions during the Soviet famine of 1932–1933.
Sleeping with Cannibals
. ''Smithsonian Magazine''. A local cannibal cult killed and ate victims as late as 2012. As in some other Papuan societies, the Urapmin people engaged in cannibalism in war. Notably, the Urapmin also had a system of food taboos wherein dogs could not be eaten and they had to be kept from breathing on food, unlike humans who could be eaten and with whom food could be shared.
 Before 1931, ''The New York Times'' reporter William Buehler Seabrook, in the interests of research, obtained from a hospital intern at the Sorbonne (building), Sorbonne a chunk of human meat from the body of a healthy human killed in an accident, then cooked and ate it. He reported, "It was like good, fully developed veal, not young, but not yet beef. It was very definitely like that, and it was not like any other meat I had ever tasted. It was so nearly like good, fully developed veal that I think no person with a palate of ordinary, normal sensitiveness could distinguish it from veal. It was mild, good meat with no other sharply defined or highly characteristic taste such as for instance, goat, high game, and pork have. The steak was slightly tougher than prime veal, a little stringy, but not too tough or stringy to be agreeably edible. The roast, from which I cut and ate a central slice, was tender, and in color, texture, smell as well as taste, strengthened my certainty that of all the meats we habitually know, veal is the one meat to which this meat is accurately comparable."
When
Before 1931, ''The New York Times'' reporter William Buehler Seabrook, in the interests of research, obtained from a hospital intern at the Sorbonne (building), Sorbonne a chunk of human meat from the body of a healthy human killed in an accident, then cooked and ate it. He reported, "It was like good, fully developed veal, not young, but not yet beef. It was very definitely like that, and it was not like any other meat I had ever tasted. It was so nearly like good, fully developed veal that I think no person with a palate of ordinary, normal sensitiveness could distinguish it from veal. It was mild, good meat with no other sharply defined or highly characteristic taste such as for instance, goat, high game, and pork have. The steak was slightly tougher than prime veal, a little stringy, but not too tough or stringy to be agreeably edible. The roast, from which I cut and ate a central slice, was tender, and in color, texture, smell as well as taste, strengthened my certainty that of all the meats we habitually know, veal is the one meat to which this meat is accurately comparable."
When
Is there a relation between cannibalism and amyloidosis?
All about Cannibalism: The Ancient Taboo in Modern Times (Cannibalism Psychology)
at CrimeLibrary.com
''Cannibalism'', Víctor Montoya
Notes arguing that routine cannibalism is myth
(from
Harry J. Brown, 'Hans Staden among the Tupinambas.'
{{Authority control Cannibalism,
cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
is called a cannibal. The meaning of "cannibalism" has been extended into zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
to describe an individual of a species consuming all or part of another individual of the same species as food, including sexual cannibalism
Sexual cannibalism is when an animal, usually the female, cannibalizes its mate prior to, during, or after copulation.Polis, G.A. & Farley, R.D. Behavior and Ecology of Mating in the journal of Arachnology 33-46 (1979). It is a trait observed in m ...
.
The Island Carib
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated languag ...
people of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
, from whom the word "cannibalism" is derived, acquired a long-standing reputation as cannibals after their legends were recorded in the 17th century. Some controversy exists over the accuracy of these legends and the prevalence of actual cannibalism in the culture. Cannibalism was practiced in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
and in parts of the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capita ...
, and flesh markets existed in some parts of Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
. Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
was once known as the "Cannibal Isles". Cannibalism has been well documented in much of the world, including Fiji, the Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivi ...
, the Congo, and the Māori people
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several ce ...
of New Zealand.
Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
s are believed to have practiced cannibalism, and Neanderthals may have been eaten by anatomically modern human
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
s. Cannibalism was also practiced in ancient Egypt, Roman Egypt
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt
, common_name = Egypt
, subdivision = Province
, nation = the Roman Empire
, era = Late antiquity
, capital = Alexandria
, title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis
, image_map = Roman E ...
and during famines in Egypt such as the great famine of 1199–1202.
Cannibalism has recently been both practiced and fiercely condemned in several wars, especially in Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
. It was still practiced in Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
as of 2012, for cultural reasons and in ritual as well as in war in various Melanesian tribes. Cannibalism has been said to test the bounds of cultural relativism
Cultural relativism is the idea that a person's beliefs and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture. Proponents of cultural relativism also tend to argue that the norms and values of one culture should not be evaluated ...
because it challenges anthropologists "to define what is or is not beyond the pale of acceptable human behavior". Some scholars argue that no firm evidence exists that cannibalism has ever been a socially acceptable practice anywhere in the world, at any time in history, although this has been consistently debated against.
A form of cannibalism popular in early modern Europe was the consumption of body parts or blood for medical purposes. This practice was at its height during the 17th century, although as late as the second half of the 19th century some peasants attending an execution are recorded to have "rushed forward and scraped the ground with their hands that they might collect some of the bloody earth, which they subsequently crammed in their mouth, in hope that they might thus get rid of their disease."
Cannibalism has occasionally been practiced as a last resort by people suffering from famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
, even in modern times. Famous examples include the ill-fated Donner Party
The Donner Party, sometimes called the Donner–Reed Party, was a group of American pioneers who migrated to California in a wagon train from the Midwest. Delayed by a multitude of mishaps, they spent the winter of 1846–1847 snowbound in th ...
(1846–47) and, more recently, the crash of Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571
The Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571 was a chartered flight from Montevideo, Uruguay, bound for Santiago, Chile, that crashed in the Andes mountains on October 13, 1972. The accident and subsequent survival became known as the Andes flight disast ...
(1972), after which some survivors ate the bodies of the dead. Additionally, there are cases of people suffering from mental illness engaging in cannibalism for sexual pleasure, such as Jeffrey Dahmer
Jeffrey Lionel Dahmer (; May 21, 1960 – November 28, 1994), also known as the Milwaukee Cannibal or the Milwaukee Monster, was an American serial killer and sex offender who killed and dismemberment, dismembered seventeen men and boys ...
, Issei Sagawa
also known as Pang or The Kobe Cannibal, was a Japanese murderer, cannibal, and necrophiliac known for the killing of Renée Hartevelt in Paris in 1981.
Sagawa murdered Hartevelt then mutilated, cannibalized, and performed necrophilia on her ...
, and Albert Fish
Hamilton Howard "Albert" Fish (May 19, 1870 – January 16, 1936) was an American serial killer, Rape, rapist, child molestation, child molester, and cannibalism, cannibal who committed at least three child murders from July 1924 to June 1 ...
. There is resistance to formally labeling cannibalism a mental disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
.Eat or be eaten: Is cannibalism a pathology as listed in the DSM-IV?''
The Straight Dope
"The Straight Dope" was a question-and-answer newspaper column written under the pseudonym Cecil Adams. Contributions were made by multiple authors, and it was illustrated (also pseudonymously) by Slug Signorino. It was first published in 1973 in ...
'' by Cecil Adams. Retrieved March 16, 2010.
Etymology
The word "cannibalism" is derived from ''Caníbales'', the Spanish name for theCaribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
, a West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
tribe that may have practiced cannibalism, from Spanish ''canibal'' or ''caribal'', "a savage". The term ''anthropophagy'', meaning "eating humans", is also used for human cannibalism.
Reasons
 In some societies, cannibalism is a
In some societies, cannibalism is a cultural norm
Social norms are shared standards of acceptable behavior by groups. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into rules and laws. Social normative influences or soci ...
. Consumption of a person from within the same community is called endocannibalism
Endocannibalism is a practice of cannibalism in one's own locality or community. Endocannibalism has also been used to describe the consumption of relics in a mortuary context.
As a cultural practice
Herodotus (3.38) mentions funerary cannibal ...
; ritual cannibalism of the recently deceased can be part of the grieving process or be seen as a way of guiding the souls of the dead into the bodies of living descendants.
Exocannibalism
Exocannibalism (from Greek ''exo-'', "from outside" and cannibalism, "to eat humans"), as opposed to endocannibalism, is the consumption of flesh outside one's close social group—for example, eating one's enemy. When done ritually, it has been a ...
is the consumption of a person from outside the community, usually as a celebration of victory against a rival tribe. Both types of cannibalism can also be fueled by the belief that eating a person's flesh or internal organs will endow the cannibal with some of the characteristics of the deceased.
In '' Guns, Germs and Steel'', Jared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond (born September 10, 1937) is an American geographer, historian, ornithologist, and author best known for his popular science books ''The Third Chimpanzee'' (1991); ''Guns, Germs, and Steel'' (1997, awarded a Pulitzer Prize); ...
suggests that protein deficiency was the ultimate reason why cannibalism was formerly common in the New Guinea highlands.
In most parts of the world, cannibalism is not a societal norm, but is sometimes resorted to in situations of extreme necessity. The survivors of the shipwrecks of the ''Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G ...
'' and '' Méduse'' in the 19th century are said to have engaged in cannibalism, as did the members of Franklin's lost expedition
Franklin's lost expedition was a failed British voyage of Arctic exploration led by Captain Sir John Franklin that departed England in 1845 aboard two ships, and , and was assigned to traverse the last unnavigated sections of the Northwest ...
and the Donner Party
The Donner Party, sometimes called the Donner–Reed Party, was a group of American pioneers who migrated to California in a wagon train from the Midwest. Delayed by a multitude of mishaps, they spent the winter of 1846–1847 snowbound in th ...
. Such cases generally involve necro-cannibalism (eating the corpse of someone who is already dead) as opposed to homicidal cannibalism (killing someone for food). In English law, the latter is always considered a crime, even in the most trying circumstances. The case of ''R v Dudley and Stephens
''R v Dudley and Stephens'' (188414 QBD 273, DCis a leading English criminal case which established a precedent throughout the common law world that necessity is not a defence to a charge of murder. The case concerned survival cannibalism foll ...
'', in which two men were found guilty of murder for killing and eating a cabin boy while adrift at sea in a lifeboat, set the precedent that necessity
Necessary or necessity may refer to:
* Need
** An action somebody may feel they must do
** An important task or essential thing to do at a particular time or by a particular moment
* Necessary and sufficient condition, in logic, something that i ...
is no defence to a charge of murder.
In pre-modern medicine, the explanation given by the now-discredited theory of humorism
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
for cannibalism was that it came about within a black acrimonious humor, which, being lodged in the linings of the ventricle, produced the voracity for human flesh.
Medical aspects
A well-known case of mortuary cannibalism is that of the Fore tribe inNew Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
, which resulted in the spread of the prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It ...
disease kuru
Kuru may refer to:
Anthropology and history
* Kuru (disease), a type of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy associated with the cannibalistic funeral practices of the Fore people
* Kuru (mythology), part of Meithei mythology
* Kuru Kingdom, ...
. Although the Fore's mortuary cannibalism was well-documented, the practice had ceased before the cause of the disease was recognized. However, some scholars argue that although post-mortem dismemberment was the practice during funeral rites, cannibalism was not. Marvin Harris
Marvin Harris (August 18, 1927 – October 25, 2001) was an American anthropologist. He was born in Brooklyn, New York City. A prolific writer, he was highly influential in the development of cultural materialism and environmental determinism. ...
theorizes that it happened during a famine period coincident with the arrival of Europeans and was rationalized as a religious rite.
In 2003, a publication in ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
'' received a large amount of press attention when it suggested that early humans may have practiced extensive cannibalism. According to this research, genetic markers commonly found in modern humans worldwide suggest that today many people carry a gene that evolved as protection against the brain diseases
Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). T ...
that can be spread by consuming human brain tissue. A 2006 reanalysis of the data questioned this hypothesis, because it claimed to have found a data collection bias, which led to an erroneous conclusion. This claimed bias came from incidents of cannibalism used in the analysis not being due to local cultures, but having been carried out by explorers, stranded seafarers or escaped convicts. The original authors published a subsequent paper in 2008 defending their conclusions.
Myths, legends and folklore

 Cannibalism features in the folklore and legends of many cultures and is most often attributed to evil characters or as extreme retribution for some wrongdoing. Examples include the witch in "
Cannibalism features in the folklore and legends of many cultures and is most often attributed to evil characters or as extreme retribution for some wrongdoing. Examples include the witch in "Hansel and Gretel
"Hansel and Gretel" (; german: Hänsel und Gretel ) is a German fairy tale collected by the German Brothers Grimm and published in 1812 in ''Grimm's Fairy Tales'' (KHM 15). It is also known as Little Step Brother and Little Step Sister.
Hansel ...
", Lamia
LaMia Corporation S.R.L., operating as LaMia (short for ''Línea Aérea Mérida Internacional de Aviación''), was a Bolivian charter airline headquartered in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, as an EcoJet subsidiary. It had its origins from the failed ...
of Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
and Baba Yaga
In Slavic folklore, Baba Yaga, also spelled Baba Jaga (from Polish), is a supernatural being (or one of a trio of sisters of the same name) who appears as a deformed and/or ferocious-looking woman. In fairy tales Baba Yaga flies around in a ...
of Slavic folklore
Slavic folklore encompasses the folklore of the Slavic peoples from their earliest records until today. Folklorists have published a variety of works focused specifically on the topic over the years.See, for example, Kononenko 2007.
See also
* ...
.
A number of stories in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
involve cannibalism, in particular cannibalism of close family members, e.g., the stories of Thyestes
In Greek mythology, Thyestes (pronounced , gr, Θυέστης, ) was a king of Olympia. Thyestes and his brother, Atreus, were exiled by their father for having murdered their half-brother, Chrysippus, in their desire for the throne of Olym ...
, Tereus
In Greek mythology, Tereus (; Ancient Greek: Τηρεύς) was a Thracian king,Thucydides: ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' 2:29 the son of Ares and the naiad Bistonis. He was the brother of Dryas. Tereus was the husband of the Athenian p ...
and especially Cronus
In Ancient Greek religion and mythology, Cronus, Cronos, or Kronos ( or , from el, Κρόνος, ''Krónos'') was the leader and youngest of the first generation of Titans, the divine descendants of the primordial Gaia (Mother Earth) and ...
, who was Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
in the Roman pantheon. The story of Tantalus
Tantalus ( grc, Τάνταλος ) was a Greek mythological figure, most famous for his punishment in Tartarus: he was made to stand in a pool of water beneath a fruit tree with low branches, with the fruit ever eluding his grasp, and the wate ...
also parallels this.
The wendigo
Wendigo () is a mythological creature or evil spirit originating from the folklore of Plains and Great Lakes Natives as well as some First Nations. It is based in and around the East Coast forests of Canada, the Great Plains region of the U ...
is a creature appearing in the legends
A legend is a historical narrative, a symbolic representation of folk belief.
Legend(s) or The Legend(s) may also refer to:
Narrative
* Urban legend, a widely repeated story of dubious truth
* A fictitious identity used in espionage
Books, co ...
of the Algonquian people. It is thought of variously as a malevolent cannibalistic spirit that could possess humans or a monster that humans could physically transform into. Those who indulged in cannibalism were at particular risk, and the legend appears to have reinforced this practice as taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
. The Zuni people
The Zuni ( zun, A:shiwi; formerly spelled ''Zuñi'') are Native American Pueblo peoples native to the Zuni River valley. The Zuni are a Federally recognized tribe and most live in the Pueblo of Zuni on the Zuni River, a tributary of the Lit ...
tell the story of the Átahsaia
Átahsaia (alternatively spelled A'tahsaia or Atasaya) is a giant cannibalistic demon in the religion and mythos of the Zuni people of the Southwestern United States.
Depiction
Átahsaia is a demon, and thus a spiritual creature. But Átahsaia ...
– a giant who cannibalizes his fellow demons and seeks out human flesh.
The wechuge
The wechuge is a man-eating creature or evil spirit appearing in the legends of the Athabaskan people. In Beaver (Dane-zaa) mythology, it is said to be a person who has been possessed or overwhelmed by the power of one of the ancient giant spiri ...
is a demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in media such as comics, video games, movies, ani ...
ic cannibalistic creature that seeks out human flesh appearing in the Native American mythology
The indigenous peoples of the Americas comprise numerous different cultures. Each has its own mythologies. Some are quite distinct, but certain themes are shared across the cultural boundaries.
Northern America
There is no single mythology o ...
of the Athabaskan people. It is said to be half monster and half human-like; however, it has many shapes and forms.
Scepticism
William Arens, author of '' The Man-Eating Myth: Anthropology and Anthropophagy'', questions the credibility of reports of cannibalism and argues that the description by one group of people of another people as cannibals is a consistent and demonstrable ideological and rhetorical device to establish perceived cultural superiority. Arens bases his thesis on a detailed analysis of numerous "classic" cases of cultural cannibalism cited by explorers, missionaries, and anthropologists. He asserts that many were steeped in racism, unsubstantiated, or based on second-hand or hearsay evidence. Accusations of cannibalism helped characterize indigenous peoples as "uncivilized", "primitive", or even "inhuman." These assertions promoted the use of military force as a means of "civilizing" and "pacifying" the "savages". During theSpanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the eve ...
and its earlier conquests in the Caribbean there were widespread reports of cannibalism, justifying the conquest. Cannibals were exempt from Queen Isabella's prohibition on enslaving the indigenous. Another example of the sensationalism of cannibalism and its connection to imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
occurred during Japan's 1874 expedition to Taiwan. As Eskildsen describes, there was an exaggeration of cannibalism by Taiwanese indigenous peoples
Taiwanese indigenous peoples (formerly Taiwanese aborigines), also known as Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 5 ...
in Japan's popular media such as newspapers and illustrations at the time.
''This Horrid Practice
''This Horrid Practice: The Myth and Reality of Traditional Maori Cannibalism'' is a 2008 non-fiction book by New Zealand historian Paul Moon. The book is a comprehensive survey of the history of human cannibalism among the Māori people, Māori ...
: The Myth and Reality of Traditional Maori Cannibalism'' (2008) by New Zealand historian Paul Moon
Evan Paul Moon (born 18 October 1968) is a New Zealand historian and a professor at the Auckland University of Technology. He is a writer of New Zealand history and biography, specialising in Māori people, Māori history, the Treaty of Waita ...
received a hostile reception by many Maori, who felt the book tarnished their whole people.
The title of the book is drawn from the 16 January 1770 journal entry of Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
, who, in describing acts of Māori cannibalism, stated "though stronger evidence of this horrid practice prevailing among the inhabitants of this coast will scarcely be required, we have still stronger to give."
History
Among modern humans, cannibalism has been practiced by various groups. It was practiced by humans inPrehistoric Europe
Prehistoric Europe is Europe with human presence but before the start of recorded history, beginning in the Lower Paleolithic. As history progresses, considerable regional irregularities of cultural development emerge and increase. The region o ...
, Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
, South America, among Iroquoian peoples in North America, Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
in New Zealand, the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capita ...
, parts of West Africa and Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
, some of the islands of Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
, Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, and Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
. Evidence of cannibalism has been found in ruins associated with the Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, a ...
of the Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Ne ...
as well (at Cowboy Wash
Cowboy Wash is a group of nine archaeological sites used by Ancestral Puebloans (previously known as Anasazi) in Montezuma County, southwestern Colorado, United States. Each site includes one to three pit houses, and was discovered in 1993 duri ...
in Colorado).
Pre-history
There is evidence, both archaeological and genetic, that cannibalism has been practiced for hundreds of thousands of years by early ''Homo sapiens'' and archaic hominins. Human bones that have been "de-fleshed" by other humans go back 600,000 years. The oldest ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' bones (from Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
) show signs of this as well. Some anthropologists, such as Tim D. White
Tim D. White (born August 24, 1950) is an American paleoanthropologist and Professor of Integrative Biology at the University of California, Berkeley. He is best known for leading the team which discovered Ardi, the type specimen of ''Ardipithe ...
, suggest that ritual cannibalism was common in human societies prior to the beginning of the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
period. This theory is based on the large amount of "butchered human" bones found in Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
and other Lower/Middle Paleolithic sites. Cannibalism in the Lower and Middle Paleolithic may have occurred because of food shortages. It has been also suggested that removing dead bodies through ritual cannibalism might have been a means of predator control, aiming to eliminate predators' and scavengers' access to hominid (and early human) bodies. Jim Corbett
Edward James Corbett (25 July 1875 – 19 April 1955) was a British hunter, tracker, naturalist, and author who hunted a number of man-eating tigers and leopards in the Indian subcontinent.
He held the rank of colonel in the British Indian ...
proposed that after major epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics ...
s, when human corpses are easily accessible to predators, there are more cases of man-eating leopards, so removing dead bodies through ritual cannibalism (before the cultural traditions of burying and burning bodies appeared in human history) might have had practical reasons for hominids and early humans to control predation.
 In
In Gough's Cave
Gough's Cave ( ) is located in Cheddar Gorge on the Mendip Hills, in Cheddar, Somerset, England. The cave is deep and is long,
and contains a variety of large chambers and rock formations. It contains the Cheddar Yeo, the largest underground ...
, England, remains of human bones and skulls, around 14,700 years old, suggest that cannibalism took place amongst the people living in or visiting the cave, and that they may have used human skulls as drinking vessels.
The archaeological site of Herxheim was a ritual center and a mass grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of execution, although an exact ...
formed by people of the Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
in Neolithic Europe
The European Neolithic is the period when Neolithic (New Stone Age) technology was present in Europe, roughly between 7000 BCE (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) and c.2000–1700 BCE (the beginning of the Bronze Age ...
. Herxheim contained the scattered remains of at least 450 individuals. Whether for religious purpose or war, it is apparent from the 2009 study that the humans at the site of Herxheim were butchered and eaten.
Researchers have found physical evidence of cannibalism in ancient times. In 2001, archaeologists at the University of Bristol found evidence of Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
cannibalism in Gloucestershire. Cannibalism was practiced as recently as 2000 years ago in Prehistoric Britain
Several species of humans have intermittently occupied Great Britain for almost a million years. The earliest evidence of human occupation around 900,000 years ago is at Happisburgh on the Norfolk coast, with stone tools and footprints prob ...
.
Early history
Cannibalism is mentioned many times in early history and literature.Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
in "'' The Histories''" (450s to the 420s BCE) claimed, that after eleven days' voyage up the Borysthenes
Borysthenes (; grc, Βορυσθένης) is a geographical name from classical antiquity. The term usually refers to the Dnieper River and its eponymous river god, but also seems to have been an alternative name for Pontic Olbia, a town situate ...
(Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
in Europe) a desolated land extended for a long way, and later the country of the man-eaters (other than Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
Hi ...
ns) was located, and beyond it again a desolated area extended where no men lived.
The tomb of ancient Egyptian king Unas
Unas or Wenis, also spelled Unis ( egy, wnjs, hellenized form Oenas or Onnos), was a pharaoh, the ninth and last ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Unas reigned for 15 to 30 years in the mid- 24th century BC (circa ...
contained a hymn in praise to the king portraying him as a cannibal.
The Stoic
Stoic may refer to:
* An adherent of Stoicism; one whose moral quality is associated with that school of philosophy
* STOIC, a programming language
* ''Stoic'' (film), a 2009 film by Uwe Boll
* ''Stoic'' (mixtape), a 2012 mixtape by rapper T-Pain
* ...
philosopher Chrysippus
Chrysippus of Soli (; grc-gre, Χρύσιππος ὁ Σολεύς, ; ) was a Greek Stoic philosopher. He was a native of Soli, Cilicia, but moved to Athens as a young man, where he became a pupil of the Stoic philosopher Cleanthes. When Clean ...
wrote in his treatise ''On Justice'' that cannibalism was ethically acceptable.
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
records that Hannibal Monomachus once suggested to the Carthaginian general Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
that he teach his army to adopt cannibalism in order to be properly supplied in his travel to Italy, although Barca and his officers could not bring themselves to practice it. In the same war, Gaius Terentius Varro
Gaius Terentius Varro ( 218–200 BC) was a Roman politician and general active during the Second Punic War. A plebeian son of a butcher, he was a populist politician who was elected consul for the year 216 BC. While holding that office, he was de ...
once claimed to the citizens of Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrusc ...
that Barca's Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and Spanish mercenaries fed on human flesh, though this claim seemed to be acknowledged as false.
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
recorded cannibalism practiced by the ''bucoli'', Egyptian tribes led by Isidorus
Isidorus (born c. 139) was a native ancient Egyptian priest in the 2nd century during the Roman rule in Egypt. He led the native Egyptian revolt against Roman rule during the reign of emperor Marcus Aurelius.Dio CassiusEpitome 72/ref> The likely ...
against Rome. They sacrificed and devoured two Roman officers in ritualistic fashion, swearing an oath over their entrails.
According to Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Hadr ...
, during the Roman Siege of Numantia
The Celtiberian oppidum of Numantia was attacked more than once by Roman forces, but the Siege of Numantia refers to the culminating and pacifying action of the long-running Numantine War between the forces of the Roman Republic and those of th ...
in the 2nd century BCE, the population of Numantia
Numantia ( es, Numancia) is an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the current municipality of Garray ( Soria), Spain.
Numantia is famous for its role in the Celtiberian Wars. In ...
was reduced to cannibalism and suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
.
Cannibalism was reported by Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly d ...
during the siege of Jerusalem by Rome in 70 CE.
Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, th ...
, in his letter '' Against Jovinianus'', discusses how people come to their present condition as a result of their heritage, and he then lists several examples of peoples and their customs. In the list, he mentions that he has heard that Attacotti
The Attacotti (variously spelled ''Atticoti'', ''Attacoti'', ''Atecotti'', ''Atticotti'', ''Atecutti'', etc.) were a people who despoiled Roman Britain between 364 and 368, along with the Scoti, Picts, Saxons, Roman military deserters and the i ...
eat human flesh and that Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translati ...
and ''Derbices'' (a people on the borders of India) kill and eat old people.
Reports of cannibalism were recorded during the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
, as Crusaders were alleged to have fed on the bodies of their dead opponents following the Siege of Ma'arra
The Siege of Ma'arra occurred in late 1098 in the city of Ma'arrat al-Numan, in what is modern-day Syria, during the First Crusade. It is infamous for the claims of widespread cannibalism displayed by the Crusaders.
Prologue
After the Crusader ...
. Amin Maalouf
Amin Maalouf (; ar, أمين معلوف; born 25 February 1949) is a Lebanese-born French"Amin ...
also alleges further cannibalism incidents on the march to Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, and to the efforts made to delete mention of these from Western history. Even though this account does not appear in any contemporary Muslim chronicle. The famine and cannibalism are recognised as described by Fulcher of Chartres, but the torture and the killing of Muslim captives for cannibalism by Radulph of Caen are very unlikely since no Arab or Muslim records of the events exist. Had they occurred, they would have probably been recorded. That has been noted by BBC Timewatch series, the episode ''The Crusades: A Timewatch Guide'', which included experts Thomas Asbridge
Thomas Scott Asbridge (born 1969) is a historian at Queen Mary University of London, a position he has held since 1999. He is the author of ''The First Crusade: A New History'' (2004), a book which describes the background, events, and consequences ...
and Muslim Arabic historian Fozia Bora
Fozia Bora is a lecturer in Middle Eastern history and Islamic history at the School of Languages, Cultures and Societies at the University of Leeds. Her research and teaching is concerned primarily with Arabic history and historiography, in parti ...
, who state that Radulph of Caen's description does not appear in any contemporary Muslim chronicle. During Europe's Great Famine of 1315–17
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
, there were many reports of cannibalism among the starving populations. In North Africa, as in Europe, there are references to cannibalism as a last resort in times of famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
.
The Moroccan Muslim explorer ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
reported that one African king advised him that nearby people were cannibals (although this may have been a prank played on ibn Battuta by the king to fluster his guest). Ibn Batutta reported that Arabs and Christians were safe, as their flesh was "unripe" and would cause the eater to fall ill.
Egyptian mummies
The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. These rituals included mummifying the body, casting magic spells, and burials with specific grave goods ...
preserved in bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
were ground up and sold as medicine. The practice developed into a wide-scale business which flourished until the late 16th century. This "fad" ended because the mummies were revealed actually to be recently killed slaves. Two centuries ago, mummies were still believed to have medicinal properties against bleeding, and were sold as pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
s in powdered form (see human mummy confection and mummia).Quotes from John Sanderson
Lieutenant General John Murray Sanderson, (born 4 November 1940) is a retired senior Australian Army officer and vice-regal representative. He served as Force Commander of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia from 1992 to 1993 ...
's ''Travels'' (1586) in
In China during the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
, cannibalism was supposedly resorted to by rebel forces early in the period (who were said to raid neighboring areas for victims to eat), as well as both soldiers and civilians besieged during the rebellion of An Lushan
An Lushan (; 20th day of the 1st month 19 February 703 – 29 January 757) was a general in the Tang dynasty and is primarily known for instigating the An Lushan Rebellion.
An Lushan was of Sogdian and Göktürk origin,Yang, Zhijiu, "An Lushan ...
. Eating an enemy's heart and liver was also claimed to be a feature of both official punishments and private vengeance. References to cannibalizing the enemy have also been seen in poetry written in the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
(for example, in '' Man Jiang Hong''), although the cannibalizing is perhaps poetic symbolism, expressing hatred towards the enemy.
Charges of cannibalism were levied against the Qizilbash
Qizilbash or Kizilbash ( az, Qızılbaş; ota, قزيل باش; fa, قزلباش, Qezelbāš; tr, Kızılbaş, lit=Red head ) were a diverse array of mainly Turkoman Shia militant groups that flourished in Iranian Azerbaijan, Anatolia, the ...
of the Safavid Ismail.
There is universal agreement that some Mesoamerican
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Withi ...
people practiced human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherein ...
, but there is a lack of scholarly consensus as to whether cannibalism in pre-Columbian America was widespread. At one extreme, anthropologist Marvin Harris, author of '' Cannibals and Kings'', has suggested that the flesh of the victims was a part of an aristocratic diet as a reward, since the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
diet was lacking in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s. While most historians of the pre-Columbian era believe that there was ritual cannibalism related to human sacrifices, they do not support Harris's thesis that human flesh was ever a significant portion of the Aztec diet. Others have hypothesized that cannibalism was part of a blood revenge in war.
Early modern and colonial era
 European explorers and colonizers brought home many stories of cannibalism practiced by the native peoples they encountered. In Spain's overseas expansion to the New World, the practice of cannibalism was reported by
European explorers and colonizers brought home many stories of cannibalism practiced by the native peoples they encountered. In Spain's overseas expansion to the New World, the practice of cannibalism was reported by Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
in the Caribbean islands, and the Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
were greatly feared because of their supposed practice of it. Queen Isabel of Castile had forbidden the Spaniards to enslave the indigenous, unless they were "guilty" of cannibalism. The accusation of cannibalism became a pretext for attacks on indigenous groups and justification for the Spanish conquest. In Yucatán, shipwrecked Spaniard Jerónimo de Aguilar, who later became a translator for Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
, reported to have witnessed fellow Spaniards sacrificed and eaten, but escaped from captivity where he was being fattened for sacrifice himself. In the Florentine Codex
The ''Florentine Codex'' is a 16th-century ethnographic research study in Mesoamerica by the Spanish Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún. Sahagún originally titled it: ''La Historia General de las Cosas de Nueva España'' (in English: ''Th ...
(1576) compiled by Franciscan Bernardino de Sahagún
Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he ...
from information provided by indigenous eyewitnesses has questionable evidence of Mexica (Aztec) cannibalism. Franciscan friar Diego de Landa
Diego de Landa Calderón, O.F.M. (12 November 1524 – 29 April 1579) was a Spanish Franciscan bishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Yucatán. Many historians criticize his campaign against idolatry. In particular, he burned almost a ...
reported on Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the political divisions of Mexico, federal entities of Mexico. I ...
instances. In early Brazil, there is reportage of cannibalism among the Tupinamba. It is recorded about the natives of the captaincy of
In early Brazil, there is reportage of cannibalism among the Tupinamba. It is recorded about the natives of the captaincy of Sergipe
Sergipe (), officially State of Sergipe, is a state of Brazil. Located in the Northeast Region along the Atlantic coast of the country, Sergipe is the smallest state in Brazil by geographical area at , larger only than the Federal District. Serg ...
in Brazil: "They eat human flesh when they can get it, and if a woman miscarries devour the abortive immediately. If she goes her time out, she herself cuts the navel-string with a shell, which she boils along with the secondine .e._placenta.html" ;"title="placenta.html" ;"title=".e. placenta">.e. placenta">placenta.html" ;"title=".e. placenta">.e. placenta and eats them both." (see human placentophagy). In modern Brazil, a black comedy film, ''How Tasty Was My Little Frenchman'', mostly in the Tupi language, portrays a Frenchman captured by the indigenous and his demise.
The 1913 ''Handbook of Indians of Canada'' (reprinting 1907 material from the Bureau of American Ethnology
The Bureau of American Ethnology (or BAE, originally, Bureau of Ethnology) was established in 1879 by an act of Congress for the purpose of transferring archives, records and materials relating to the Indians of North America from the Interior D ...
), claims that North American natives practicing cannibalism included "... the Montagnais, and some of the tribes of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
; the Algonkin, Armouchiquois, Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
, and Micmac; farther west the Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakoda ...
, Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
, Foxes
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
, Chippewa, Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a East Coast of the United States, coastal metropolis and the County seat, county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade C ...
, Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, Kickapoo, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
, Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin (; Dakota language, Dakota: Help:IPA, /otʃʰeːtʰi ʃakoːwĩ/) are groups of Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes and First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in North America. The ...
, and Winnebago; in the south the people who built the mounds in Florida, and the Tonkawa
The Tonkawa are a Native American tribe indigenous to present-day Oklahoma. Their Tonkawa language, now extinct, is a linguistic isolate.
Today, Tonkawa people are enrolled in the federally recognized Tonkawa Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma.
...
, Attacapa, Karankawa
The Karankawa were an Indigenous people concentrated in southern Texas along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico, largely in the lower Colorado River and Brazos River valleys."Karankawa." In ''Cassell's Peoples, Nations and Cultures,'' edited by John ...
, Caddo
The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.
The Caddo Confederacy was a network of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, wh ...
, and Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
; in the northwest and west, portions of the continent, the Thlingchadinneh and other Athapascan
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific ...
tribes, the Tlingit
The Tlingit ( or ; also spelled Tlinkit) are indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their language is the Tlingit language (natively , pronounced ),
, Heiltsuk
The Heiltsuk or Haíɫzaqv , sometimes historically referred to as ''Bella Bella'', are an Indigenous people of the Central Coast region in British Columbia, centred on the island community of Bella Bella. The government of the Heiltsuk people ...
, Kwakiutl, Tsimshian
The Tsimshian (; tsi, Ts’msyan or Tsm'syen) are an Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Their communities are mostly in coastal British Columbia in Terrace, British Columbia, Terr ...
, Nootka, Siksika
The Siksika Nation ( bla, Siksiká) is a First Nations in Canada, First Nation in southern Alberta, Canada. The name ''Siksiká'' comes from the Blackfoot language, Blackfoot words ''sik'' (black) and ''iká'' (foot), with a connector ''s'' bet ...
, some of the Californian tribes, and the Ute
Ute or UTE may refer to:
* Ute (band), an Australian jazz group
* Ute (given name)
* ''Ute'' (sponge), a sponge genus
* Ute (vehicle), an Australian and New Zealand term for certain utility vehicles
* Ute, Iowa, a city in Monona County along ...
. There is also a tradition of the practice among the Hopi, and mentions of the custom among other tribes of New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
and Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
. The Mohawk Mohawk may refer to:
Related to Native Americans
* Mohawk people, an indigenous people of North America (Canada and New York)
*Mohawk language, the language spoken by the Mohawk people
* Mohawk hairstyle, from a hairstyle once thought to have been ...
, and the Attacapa, Tonkawa
The Tonkawa are a Native American tribe indigenous to present-day Oklahoma. Their Tonkawa language, now extinct, is a linguistic isolate.
Today, Tonkawa people are enrolled in the federally recognized Tonkawa Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma.
...
, and other Texas tribes were known to their neighbours as 'man-eaters.'" The forms of cannibalism described included both resorting to human flesh during famines and ritual cannibalism, the latter usually consisting of eating a small portion of an enemy warrior. From another source, according to Hans Egede
Hans Poulsen Egede (31 January 1686 – 5 November 1758) was a Dano-Norwegian Lutheran missionary who launched mission efforts to Greenland, which led him to be styled the Apostle of Greenland. He established a successful mission among the Inui ...
, when the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
killed a woman accused of witchcraft, they ate a portion of her heart.
As with most lurid tales of native cannibalism, these stories are treated with a great deal of scrutiny, as accusations of cannibalism were often used as justifications for the subjugation or destruction of "savages". The very first encounter between Europeans and Māori may have involved cannibalism of a Dutch sailor. In June 1772, the French explorer
The very first encounter between Europeans and Māori may have involved cannibalism of a Dutch sailor. In June 1772, the French explorer Marion du Fresne
Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne (22 May 1724 – 12 June 1772) was a French privateer, East India captain and explorer. The expedition he led to find the hypothetical ''Terra Australis'' in 1771 made important geographic discoveries in the sout ...
and 26 members of his crew were killed and eaten in the Bay of Islands
The Bay of Islands is an area on the east coast of the Far North District of the North Island of New Zealand. It is one of the most popular fishing, sailing and tourist destinations in the country, and has been renowned internationally for its ...
. In an 1809 incident known as the Boyd massacre
The ''Boyd'' massacre occurred in December 1809 when Māori of Whangaroa Harbour in northern New Zealand killed between 66 and 70 European crew of the ''Boyd''. Cannibalism was described or alluded to in contemporary reports. This is reputedly ...
, about 66 passengers and crew of the ''Boyd'' were killed and eaten by Māori on the Whangaroa peninsula, Northland. Cannibalism was already a regular practice in Māori wars. In another instance, on July 11, 1821, warriors from the Ngapuhi tribe killed 2,000 enemies and remained on the battlefield "eating the vanquished until they were driven off by the smell of decaying bodies". Māori warriors fighting the New Zealand government in Titokowaru's War in New Zealand's North Island in 1868–69 revived ancient rites of cannibalism as part of the radical Hauhau movement of the Pai Marire Pai or PAI may refer to:
People
* Pai (surname), Indian surname from coastal Karnataka and Goa plus people with the name
* Pai (Chinese surname), includes Chinese name origin, plus people with the name
Fictional characters
* Pai (Manga charact ...
religion.
In parts of Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
, cannibalism was still practiced in the early 20th century, for a variety of reasons—including retaliation, to insult an enemy people, or to absorb the dead person's qualities. One tribal chief, Ratu Udre Udre
Ratu Udre Udre (pronounced , ; died 1840) was a Fijian chief. He is listed by ''Guinness World Records'' as "most prolific cannibal
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a commo ...
in Rakiraki, Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, is said to have consumed 872 people and to have made a pile of stones to record his achievement. Fiji was nicknamed the "Cannibal Isles" by European sailors, who avoided disembarking there. The dense population of the Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' ( North Marquesan) and ' ( South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in th ...
, in what is now French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of Frenc ...
, was concentrated in narrow valleys, and consisted of warring tribes, who sometimes practiced cannibalism on their enemies. Human flesh was called "long pig". W. D. Rubinstein wrote:
 This period of time was also rife with instances of explorers and seafarers resorting to cannibalism for survival.
* There is archeological and written evidence for English settlers' cannibalism in 1609 in the
This period of time was also rife with instances of explorers and seafarers resorting to cannibalism for survival.
* There is archeological and written evidence for English settlers' cannibalism in 1609 in the Jamestown Colony
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement
''English Settlement'' is the fifth studio album and first double album by the English rock band XTC, released 12 February 1982 on Virgin Reco ...
under famine conditions.
* The survivors of the sinking of the French ship '' Méduse'' in 1816 resorted to cannibalism after four days adrift on a raft, and their plight was made famous by Théodore Géricault
Jean-Louis André Théodore Géricault (; 26 September 1791 – 26 January 1824) was a French painter and lithographer, whose best-known painting is ''The Raft of the Medusa''. Although he died young, he was one of the pioneers of the Romantic ...
's painting ''Raft of the Medusa
''The Raft of the Medusa'' (french: Le Radeau de la Méduse ) – originally titled ''Scène de Naufrage'' (''Shipwreck Scene'') – is an oil painting of 1818–19 by the French Romantic painter and lithographer Théodore Géricault (1791� ...
''.
* After a whale sank the ''Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G ...
'' of Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachuse ...
on 20 November 1820 (an important source event for Herman Melville
Herman Melville (Name change, born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American people, American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance (literature), American Renaissance period. Among his bes ...
's ''Moby-Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is the sailor Ishmael (Moby-Dick), Ishmael's narrative of the obsessive quest of Captain Ahab, Ahab, captain of the whaler, whaling ship ''Pequod (Moby- ...
''), the survivors, in three small boats, resorted, by common consent, to cannibalism in order for some to survive.
* Sir John Franklin
Sir John Franklin (16 April 1786 – 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. After serving in wars against Napoleonic France and the United States, he led two expeditions into the Canadian Arctic and through ...
's lost polar expedition is another example of cannibalism out of desperation.
* On land, the Donner Party
The Donner Party, sometimes called the Donner–Reed Party, was a group of American pioneers who migrated to California in a wagon train from the Midwest. Delayed by a multitude of mishaps, they spent the winter of 1846–1847 snowbound in th ...
found itself stranded by snow in the Donner Pass
Donner Pass is a mountain pass in the northern Sierra Nevada, above Donner Lake and Donner Memorial State Park about west of Truckee, California. Like the Sierra Nevada themselves, the pass has a steep approach from the east and a gradual appro ...
, a high mountain pass in California, without adequate supplies during the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, leading to several instances of cannibalism.Johnson, Kristin (ed.) (1996). ''Unfortunate Emigrants: Narratives of the Donner Party'', Utah State University Press.
* One notorious cannibal was mountain man Boone Helm
Levi Boone Helm (January 28, 1828 – January 14, 1864) was an American mountain man, Old West gunfighter and serial killer known as the Kentucky Cannibal. Helm gained his nickname for his opportunistic and unrepentant proclivity for consuming ...
, who was known as "The Kentucky Cannibal" for eating several of his fellow travelers, from 1850 until his eventual hanging in 1864.
* The case of ''R v. Dudley and Stephens
''R v Dudley and Stephens'' (188414 QBD 273, DCis a leading English criminal case which established a precedent throughout the common law world that necessity is not a defence to a charge of murder. The case concerned survival cannibalism fo ...
'' (1884) 14 QBD 273 (QB) is an English case which dealt with four crew members of an English yacht, the ''Mignonette'', who were cast away in a storm some from the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is t ...
. After several days, one of the crew, a seventeen-year-old cabin boy, fell unconscious due to a combination of the famine and drinking seawater. The others (one possibly objecting) decided then to kill him and eat him. They were picked up four days later. Two of the three survivors were found guilty of murder. A significant outcome of this case was that necessity in English criminal law
In English law, the defence of necessity recognizes that there may be situations of such overwhelming urgency that a person must be allowed to respond by breaking the law. There have been very few cases in which the defence of necessity has succ ...
was determined to be no defence against a charge of murder.
Further examples

Roger Casement
Roger David Casement ( ga, Ruairí Dáithí Mac Easmainn; 1 September 1864 – 3 August 1916), known as Sir Roger Casement, CMG, between 1911 and 1916, was a diplomat and Irish nationalist executed by the United Kingdom for treason during Worl ...
, writing to a consular colleague in Lisbon on August 3, 1903, from Lake Mantumba in the Congo Free State, said:
During the 1892–1894 war between the Congo Free State and the Swahili–Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
city-states of Nyangwe
Nyangwe is a town in Kasongo, Maniema on the right bank of the Lualaba River, Lualaba in the Democratic Republic of Congo (territory of Kasongo). It was an important hub for the Arabs for trade goods like ivory, gold, iron & slaves: it was one of ...
and Kasongo
Kasongo, also known as Piani Kasongo, is a town and a Territory, located in the Maniema Province of the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Geography
Kasongo lies east of the Lualaba River, northwest of its confluence with the Luama River ...
in Eastern Congo, there were reports of widespread cannibalization of the bodies of defeated Arab combatants by the Batetela
The Tetela people (or Batetela in the plural) are an ethnic group of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, most of whom speak the Tetela language.
Description
The Batetela live in the region between Lusambo and the Upper Congo River, in the prov ...
allies of Belgian commander Francis Dhanis. The Batetela, "like most of their neighbors were inveterate cannibals."Pakenham, 439 According to Dhanis's medical officer, Captain Hinde, their town of Ngandu had "at least 2,000 polished human skulls" as a "solid white pavement in front" of its gates, with human skulls crowning every post of the stockade.
In April 1892, 10,000 of the Batetela, under the command of Gongo Lutete, joined forces with Dhanis in a campaign against the Swahili–Arab leaders Sefu and Mohara. After one early skirmish in the campaign, Hinde "noticed that the bodies of both the killed and wounded had vanished." When fighting broke out again, Hinde saw his Batetela allies drop human arms, legs and heads on the road. One young Belgian officer wrote home: "Happily Gongo's men ate them up n a few hours It's horrible but exceedingly useful and hygienic ... I should have been horrified at the idea in Europe! But it seems quite natural to me here. Don't show this letter to anyone indiscreet." After the massacre at Nyangwe, Lutete "hid himself in his quarters, appalled by the sight of thousands of men smoking human hands and human chops on their camp fires, enough to feed his army for many days."
In West Africa, the Leopard Society
The Leopard Society (not to be confused with Ekpe), was a secret society that originated in Sierra Leone. Beatty, p.3 It was believed that members of the society could transform into leopards through the use of witchcraft. The earliest referenc ...
was a cannibalistic secret society that existed until the mid-1900s. Centered in Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
, the ''Leopard men'' would dress in leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
skins, and waylay travelers with sharp claw-like weapons in the form of leopards' claws and teeth. The victims' flesh would be cut from their bodies and distributed to members of the society.
Modern era
 Further instances include cannibalism as ritual practice; cannibalism in times of drought, famine and other destitution; as well as cannibalism as criminal acts and war crimes throughout the 20th and 21st centuries.
Further instances include cannibalism as ritual practice; cannibalism in times of drought, famine and other destitution; as well as cannibalism as criminal acts and war crimes throughout the 20th and 21st centuries.
World War II
Many instances of cannibalism by necessity were recorded during World War II. For example, during the 872-daySiege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
, reports of cannibalism began to appear in the winter of 1941–1942, after all birds, rats, and pets were eaten by survivors. Leningrad police even formed a special division to combat cannibalism.
Some 2.8 million Soviet POWs died in Nazi custody in less than eight months during 1941–42. According to the USHMM
The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM) is the United States' official memorial to the Holocaust. Adjacent to the National Mall in Washington, D.C., the USHMM provides for the documentation, study, and interpretation of Holocaust hist ...
, by the winter of 1941, "starvation and disease resulted in mass death of unimaginable proportions". This deliberate starvation led to many incidents of cannibalism.
Following the Soviet victory at Stalingrad
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stal ...
it was found that some German soldiers in the besieged city, cut off from supplies, resorted to cannibalism. Later, following the German surrender in January 1943, roughly 100,000 German soldiers were taken prisoner of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of wa ...
(POW). Almost all of them were sent to POW camps in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
or Central Asia where, due to being chronically underfed by their Soviet captors, many resorted to cannibalism. Fewer than 5,000 of the prisoners taken at Stalingrad survived captivity.
Cannibalism took place in the concentration and death camps in the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
(NDH), a Nazi German
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its o ...
which was governed by the fascist Ustasha organization, who committed the Genocide of Serbs and the Holocaust in NDH. Some survivors testified that some of the Ustashas drank the blood from the slashed throats of the victims.
Japanese
The Australian War Crimes Section of theTokyo tribunal
The International Military Tribunal for the Far East (IMTFE), also known as the Tokyo Trial or the Tokyo War Crimes Tribunal, was a military trial convened on April 29, 1946 to try leaders of the Empire of Japan for crimes against peace, conve ...
, led by prosecutor William Webb (the future Judge-in-Chief), collected numerous written reports and testimonies that documented Japanese soldiers' acts of cannibalism among their own troops, on enemy dead, as well as on Allied prisoners of war in many parts of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
The , also known as the GEACPS, was a concept that was developed in the Empire of Japan and propagated to Asian populations which were occupied by it from 1931 to 1945, and which officially aimed at creating a self-sufficient bloc of Asian peo ...
. In September 1942, Japanese daily rations on New Guinea consisted of 800 grams of rice and tinned meat. However, by December, this had fallen to 50 grams. According to historian Yuki Tanaka, "cannibalism was often a systematic activity conducted by whole squads and under the command of officers".
In some cases, flesh was cut from living people. A prisoner of war from the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
, Lance Naik Hatam Ali, testified that in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
: "the Japanese started selecting prisoners and every day one prisoner was taken out and killed and eaten by the soldiers. I personally saw this happen and about 100 prisoners were eaten at this place by the Japanese. The remainder of us were taken to another spot away where 10 prisoners died of sickness. At this place, the Japanese again started selecting prisoners to eat. Those selected were taken to a hut where their flesh was cut from their bodies while they were alive and they were thrown into a ditch where they later died."
Another well-documented case occurred in Chichi-jima
, native_name_link =
, image_caption = Map of Chichijima, Anijima and Otoutojima
, image_size =
, pushpin_map = Japan complete
, pushpin_label = Chichijima
, pushpin_label_position =
, pushpin_map_alt =
, ...
in February 1945, when Japanese soldiers killed and consumed five American airmen. This case was investigated in 1947 in a war crimes trial, and of 30 Japanese soldiers prosecuted, five (Maj. Matoba, Gen. Tachibana, Adm. Mori, Capt. Yoshii, and Dr. Teraki) were found guilty and hanged. In his book '' Flyboys: A True Story of Courage'', James Bradley
James Bradley (1692–1762) was an English astronomer and priest who served as the third Astronomer Royal from 1742. He is best known for two fundamental discoveries in astronomy, the aberration of light (1725–1728), and the nutation of th ...
details several instances of cannibalism of World War II Allied prisoners by their Japanese captors.
The author claims that this included not only ritual cannibalization of the livers of freshly killed prisoners, but also the cannibalization-for-sustenance of living prisoners over the course of several days, amputating limbs only as needed to keep the meat fresh.
There are more than 100 documented cases in Australia's government archives of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese soldiers practicing cannibalism on enemy soldiers and civilians in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
during the war. For instance, from an archived case, an Australian lieutenant describes how he discovered a scene with cannibalized bodies, including one "consisting only of a head which had been scalped and a spinal column" and that " all cases, the condition of the remains were such that there can be no doubt that the bodies had been dismembered and portions of the flesh cooked". In another archived case, a Pakistani corporal (who was captured in Singapore and transported to New Guinea by the Japanese) testified that Japanese soldiers cannibalized a prisoner (some were still alive) per day for about 100 days. There was also an archived memo, in which a Japanese general stated that eating anyone except enemy soldiers was punishable by death. Toshiyuki Tanaka, a Japanese scholar in Australia, mentions that it was done "to consolidate the group feeling of the troops" rather than due to food shortage in many of the cases. Tanaka also states that the Japanese committed the cannibalism under supervision of their senior officers and to serve as a power projection tool.
Jemadar Abdul Latif ( VCO of the 4/9 Jat Regiment of the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
and POW
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war ...
rescued by the Australians at Sepik
The Sepik () is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun (formerly West Se ...
Bay in 1945) stated that the Japanese soldiers ate both Indian POWs and local New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
n people. At the camp for Indian POWs in Wewak
Wewak is the capital of the East Sepik province of Papua New Guinea. It is on the northern coast of the island of New Guinea. It is the largest town between Madang and Jayapura. It is the see city (seat) of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Wewak. ...
, where many died and 19 POWs were eaten, the Japanese doctor and lieutenant Tumisa would send an Indian out of the camp after which a Japanese party would kill and eat flesh from the body as well as cut off and cook certain body parts (liver, buttock muscles, thighs, legs, and arms), according to Captain R. U. Pirzai in a ''The Courier-Mail'' report of 25 August 1945.
Argentina
Following the crash ofUruguayan Air Force Flight 571
The Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571 was a chartered flight from Montevideo, Uruguay, bound for Santiago, Chile, that crashed in the Andes mountains on October 13, 1972. The accident and subsequent survival became known as the Andes flight disast ...
on a glacier in Argentina at altitude, multiple survivors resorted to eating their dead fellow passengers. In an account of the accident and aftermath, survivor Roberto Canessa
Roberto Jorge Canessa Urta, M.D., (born 17 January 1953) is one of the 16 survivors of the Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571, which crashed in the Andes mountains on 13 October 1972, and a Uruguayan political figure. He was portrayed by Josh Hamilt ...
described the decision to eat the pilots and their dead friends and family members:
Africa
Cannibalism has been reported in several recent African conflicts, including the Second Congo War,"Mass Rape, Cannibalism, Dismemberment – UN Team Finds Atrocities in Congo War"July 4, 2018). ''ChannelNewsAsia.com''. Retrieved November 18, 2018. and the civil wars in
Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
.
Democratic Republic of Congo
A UN human rights expert reported in July 2007 that sexual atrocities against Congolese women go "far beyond rape" and includesexual slavery
Sexual slavery and sexual exploitation is an attachment of any ownership rights, right over one or more people with the intent of Coercion, coercing or otherwise forcing them to engage in Human sexual activity, sexual activities. This include ...
, forced incest
Incest ( ) is human sexual activity between family members or close relatives. This typically includes sexual activity between people in consanguinity (blood relations), and sometimes those related by affinity (marriage or stepfamily), adoption ...
, fistula
A fistula (plural: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") in anatomy is an abnormal connection between two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow or ...
mutilation of genitals with sharp objects, and cannibalism.Congo's Sexual Violence Goes 'Far Beyond Rape'July 31, 2007. ''The Washington Post''. This may be done in desperation, as during peacetime cannibalism is much less frequent; at other times, it is consciously directed at certain groups believed to be relatively helpless, such as Congo
Pygmies
In anthropology, pygmy peoples are ethnic groups whose average height is unusually short. The term pygmyism is used to describe the phenotype of endemic short stature (as opposed to disproportionate dwarfism occurring in isolated cases in a pop ...
, even considered subhuman by some other Congolese.
Central African Republic
 The self-declared emperor of the
The self-declared emperor of the Central African Empire
From 4 December 1976 to 21 September 1979, the Central African Republic was officially known as the Central African Empire (french: Empire centrafricain), after military dictator (and president at the time) Marshal Jean-Bédel Bokassa declared ...
, Jean-Bédel Bokassa
Jean-Bédel Bokassa (; 22 February 1921 – 3 November 1996), also known as Bokassa I, was a Central African political and military leader who served as the second president of the Central African Republic (CAR) and as the emperor of its s ...
, was tried on October 24, 1986, for several cases of cannibalism although he was never convicted. Between April 17 and April 19, 1979, a number of elementary school students were arrested after they had protested against wearing the expensive, government-required school uniforms. Around 100 were killed. Bokassa is said to have participated in the massacre, beating some of the children to death with his cane and allegedly ate some of his victims. In June 1987, he was cleared of charges of cannibalism, but found guilty of the murder of schoolchildren and other crimes.
Further reports of cannibalism were reported against the Seleka Muslim minority during the ongoing Central African Republic conflict (2012–present), Central African Republic conflict.
South Sudan
During South Sudanese Civil War cannibalism and forced cannibalism have been reported.Uganda
In the 1970s the Ugandan dictator Idi Amin was reputed to practice cannibalism. More recently, the Lord's Resistance Army has been accused of routinely engaging in ritual or magical cannibalism. It is also reported by some that witch doctors in the country sometimes use the body parts of children in their medicine.Child Sacrifices on the Rise in Uganda as Witch Doctors Expand Their Practices; Ahmed Kamara, January 8, 2010,
'', Newstime Africa.
West Africa
In the 1980s, Médecins Sans Frontières, the international medical charity, supplied photographic and other documentary evidence of ritualized cannibal feasts among the participants inLiberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
's internecine strife to representatives of Amnesty International who were on a fact-finding mission to the neighboring state of Guinea. However, Amnesty International declined to publicize this material; the Secretary-General of the organization, Pierre Sane, said at the time in an internal communication that "what they do with the bodies after human rights violations are committed is not part of our mandate or concern". The existence of cannibalism on a wide scale in Liberia was subsequently verified.
Eurasia
China
Cannibalism is documented to have occurred in China during the Great Leap Forward, when rural China was hit hard by drought andfamine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
.
During Mao Zedong's Cultural Revolution, local governments' documents revealed hundreds of incidents of cannibalism for ideological reasons (e.g., the large-scale cannibalism during the Guangxi Massacre). Public events for cannibalism were organised by local Communist Party officials, and people took part in them together in order to prove their revolutionary passion. The writer Zheng Yi documented incidents of cannibalism in Guangxi in 1968 in his 1993 book, ''Scarlet Memorial: Tales of Cannibalism in Modern China''.Eastern Europe and Russia
 In his book, ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Soviet writer Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn described cases of cannibalism in 20th-century Soviet Union.A. Solzhenitsyn (1973), ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Part I, Chapter 9. Of the Russian famine of 1921, famine in Povolzhie (1921–1922) he wrote: "That horrible famine was up to cannibalism, up to consuming children by their own parents – the famine, which Russia had never known even in the Time of Troubles [in 1601–1603]".
Cannibalism was widespread during the Holodomor (famine of Ukraine) in 1932 and 1933. During the 1930s, multiple acts of cannibalism were reported from Ukraine, Volga region, Russia's Volga, South Siberian, and Kuban regions during the Soviet famine of 1932–1933.
In his book, ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Soviet writer Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn described cases of cannibalism in 20th-century Soviet Union.A. Solzhenitsyn (1973), ''The Gulag Archipelago'', Part I, Chapter 9. Of the Russian famine of 1921, famine in Povolzhie (1921–1922) he wrote: "That horrible famine was up to cannibalism, up to consuming children by their own parents – the famine, which Russia had never known even in the Time of Troubles [in 1601–1603]".
Cannibalism was widespread during the Holodomor (famine of Ukraine) in 1932 and 1933. During the 1930s, multiple acts of cannibalism were reported from Ukraine, Volga region, Russia's Volga, South Siberian, and Kuban regions during the Soviet famine of 1932–1933.
Survival was a moral as well as a physical struggle. A woman doctor wrote to a friend in June 1933 that she had not yet become a cannibal, but was "not sure that I shall not be one by the time my letter reaches you". The good people died first. Those who refused to steal or to prostitute themselves died. Those who gave food to others died. Those who refused to eat corpses died. Those who refused to kill their fellow man died. ... At least 2,505 people were sentenced for cannibalism in the years 1932 and 1933 in Ukraine, though the actual number of cases was certainly much higher.Solzhenitsyn said of the
Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
(1941–1944): "Those who consumed human flesh, or dealt with the human liver trading from dissecting rooms ... were accounted as the political criminals". And of the building of Northern Railway Labor Camp ("Sevzheldorlag") Solzhenitsyn reports, "An ordinary hard working political prisoner almost could not survive at that penal camp. In the camp Sevzheldorlag (chief: colonel Klyuchkin) in 1946–47 there were many cases of cannibalism: they cut human bodies, cooked and ate."
The Soviet journalist Yevgenia Ginzburg was a long-term political prisoner who spent time in the Soviet prisons, Gulag camps and settlements from 1938 to 1955. She described in her memoir, ''Harsh Route'' (or ''Steep Route''), of a case which she was directly involved in during the late 1940s, after she had been moved to the prisoners' hospital.
The chief warder shows me the black smoked pot, filled with some food: "I need your medical expertise regarding this meat." I look into the pot, and hardly hold vomiting. The fibres of that meat are very small, and don't resemble me anything I have seen before. The skin on some pieces bristles with black hair ... A former smith from Poltava, Kulesh worked together with Centurashvili. At this time, Centurashvili was only one month away from being discharged from the camp ... And suddenly he surprisingly disappeared. The wardens looked around the hills, stated Kulesh's evidence, that last time Kulesh had seen his workmate near the fireplace, Kulesh went out to work and Centurashvili left to warm himself more; but when Kulesh returned to the fireplace, Centurashvili had vanished; who knows, maybe he got frozen somewhere in snow, he was a weak guy ... The wardens searched for two more days, and then assumed that it was an escape case, though they wondered why, since his imprisonment period was almost over ... The crime was there. Approaching the fireplace, Kulesh killed Centurashvili with an axe, burned his clothes, then dismembered him and hid the pieces in snow, in different places, putting specific marks on each burial place. ... Just yesterday, one body part was found under two crossed logs.
Germany
Karl Denke, Carl Großmann, Fritz Haarmann, Joachim Kroll, Peter Stumpp are some of the many known German cannibals. Armin Meiwes is a former computer repair technician who achieved international notoriety for killing and eating a Consensual homicide, voluntary victim in 2001, whom he had found via the Internet. After Meiwes and the victim jointly attempted to eat the victim's severed Human penis, penis, Meiwes killed his victim and proceeded to eat a large amount of his flesh. He was arrested in December 2002. In January 2004, Meiwes was convicted of manslaughter and sentenced to eight years and six months in prison. In a retrial May 2006, he was convicted of murder and sentenced to Life imprisonment in Germany, life imprisonment. He reported that there are over 800 active cannibals in Germany.India
The Aghoris are Indian Asceticism, ascetics who believe that eating human flesh confers spiritual and physical benefits, such as prevention of aging. They claim to only eat those who have voluntarily willed their body to the sect upon their death, although an Indian TV crew witnessed one Aghori feasting on a corpse discovered floating in the Ganges, and a member of the Doms, Dom caste reports that Aghoris often take bodies from the cremation ''ghat'' (or funeral pyre).Indonesia
In Joshua Oppenheimer's film ''The Look of Silence'', several of the anti-Communist militias active in the Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66 claim that drinking blood from their victims is what prevented them going mad.North Korea
Reports of widespread cannibalism began to emerge from North Korea during the North Korean famine, famine of the 1990s and subsequent ongoing starvation. Kim Jong-il was reported to have ordered a crackdown on cannibalism in 1996, but Chinese travelers reported in 1998 that cannibalism had occurred. Three people in North Korea were reported to have been executed for selling or eating human flesh in 2006. Further reports of cannibalism emerged in early 2013, including reports of a man executed for killing his two children for food. There are competing claims about how widespread cannibalism was in North Korea. While refugees reported that it was widespread, Barbara Demick wrote in her book, ''Nothing to Envy: Ordinary Lives in North Korea'' (2010), that it did not seem to be.Tibet
Flesh pills were used by Tibetan Buddhists. It was believed that mystical powers were bestowed upon people when they consumed Brahmin flesh.United Kingdom
In 2008, a British model called Anthony Morley was imprisoned for the killing, dismemberment and partial cannibalisation of his lover, magazine executive Damian Oldfield. In 1996, Morley was a contestant on the television programme ''God's Gift (TV series), God's Gift''; one of the audience members of that edition was Damian Oldfield. Oldfield was a contestant of another edition of the show in October 1996. On 2 May 2008, it was announced that Morley had been arrested for the murder of Oldfield, who worked for the gay lifestyle magazine ''Bent (magazine), Bent''. After inviting Oldfield into his Leeds flat, police believed that Morley killed him, removed a section of his leg and began cooking it, before he stumbled into a nearby kebab house around 2:30 in the morning, drenched in blood and asking that someone call the police. He was found guilty on 17 October 2008 and sentenced to Life sentence, life imprisonment for the crime.Various cultures
The Korowai people, Korowai tribe of south-eastern Papua (Indonesian province), Papua could be one of the last surviving tribes in the world engaging in cannibalism.Rafaele, Paul (September 2006).Sleeping with Cannibals
. ''Smithsonian Magazine''. A local cannibal cult killed and ate victims as late as 2012. As in some other Papuan societies, the Urapmin people engaged in cannibalism in war. Notably, the Urapmin also had a system of food taboos wherein dogs could not be eaten and they had to be kept from breathing on food, unlike humans who could be eaten and with whom food could be shared.
Individual acts
 Before 1931, ''The New York Times'' reporter William Buehler Seabrook, in the interests of research, obtained from a hospital intern at the Sorbonne (building), Sorbonne a chunk of human meat from the body of a healthy human killed in an accident, then cooked and ate it. He reported, "It was like good, fully developed veal, not young, but not yet beef. It was very definitely like that, and it was not like any other meat I had ever tasted. It was so nearly like good, fully developed veal that I think no person with a palate of ordinary, normal sensitiveness could distinguish it from veal. It was mild, good meat with no other sharply defined or highly characteristic taste such as for instance, goat, high game, and pork have. The steak was slightly tougher than prime veal, a little stringy, but not too tough or stringy to be agreeably edible. The roast, from which I cut and ate a central slice, was tender, and in color, texture, smell as well as taste, strengthened my certainty that of all the meats we habitually know, veal is the one meat to which this meat is accurately comparable."
When
Before 1931, ''The New York Times'' reporter William Buehler Seabrook, in the interests of research, obtained from a hospital intern at the Sorbonne (building), Sorbonne a chunk of human meat from the body of a healthy human killed in an accident, then cooked and ate it. He reported, "It was like good, fully developed veal, not young, but not yet beef. It was very definitely like that, and it was not like any other meat I had ever tasted. It was so nearly like good, fully developed veal that I think no person with a palate of ordinary, normal sensitiveness could distinguish it from veal. It was mild, good meat with no other sharply defined or highly characteristic taste such as for instance, goat, high game, and pork have. The steak was slightly tougher than prime veal, a little stringy, but not too tough or stringy to be agreeably edible. The roast, from which I cut and ate a central slice, was tender, and in color, texture, smell as well as taste, strengthened my certainty that of all the meats we habitually know, veal is the one meat to which this meat is accurately comparable."
When Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571
The Uruguayan Air Force Flight 571 was a chartered flight from Montevideo, Uruguay, bound for Santiago, Chile, that crashed in the Andes mountains on October 13, 1972. The accident and subsequent survival became known as the Andes flight disast ...
crashed into the Andes on October 13, 1972, the survivors resorted to eating the deceased during their 72 days in the mountains. Their story was later recounted in the books ''Alive: The Story of the Andes Survivors'' (1974) and ''Miracle in the Andes: 72 Days on the Mountain and My Long Trek Home'' (2006), as well as the film ''Alive (1993 film), Alive'' (1993), by Frank Marshall (film producer), Frank Marshall, and the documentaries ''Alive: 20 Years Later'' (1993) and ''Stranded: I've Come from a Plane that Crashed in the Mountains'' (2008).
On July 23, 1988, Rick Gibson ate the flesh of another person in public. Because England does not have a specific law against cannibalism, he legally ate a canapé of donated human tonsils in Walthamstow High Street, London. A year later, on April 15, 1989, he publicly ate a slice of human testicle in Lewisham High Street, London. When he tried to eat another slice of human testicle at the Pitt International Galleries in Vancouver on July 14, 1989, the Vancouver police confiscated the testicle hors d'œuvre. However, the charge of publicly exhibiting a disgusting object was dropped, and he finally ate the piece of human testicle on the steps of the Vancouver court house on September 22, 1989.
In 1991, Jeffrey Dahmer
Jeffrey Lionel Dahmer (; May 21, 1960 – November 28, 1994), also known as the Milwaukee Cannibal or the Milwaukee Monster, was an American serial killer and sex offender who killed and dismemberment, dismembered seventeen men and boys ...
of Milwaukee, Wisconsin was arrested after one of his intended victims managed to escape. Found in Dahmer's apartment were two human hearts, an entire torso, a bag full of human organs from his victims, and a portion of arm muscle. He stated that he planned to consume all of the body parts over the next few weeks.
In 2001, Armin Meiwes from Essen, Germany killed and ate the flesh of a willing victim, Bernd Jürgen Brandis, as part of a sexual fantasy between the two. Despite Brandis' consent, which was documented on video, German courts convicted Meiwes of manslaughter, then murder, and sentenced him to life in prison.
See also
* Alexander Pearce, alleged Irish cannibal * Alferd Packer, an American prospector, accused but not convicted of cannibalism * Androphagi, an ancient nation of cannibals * Asmat people, a Papua group with a reputation of cannibalism * Cannibalism in popular culture * Cannibalism in poultry * Chijon family, a Korean gang that killed and ate rich people * Custom of the Sea, the practice of shipwrecked survivors drawing lots to see who would be killed and eaten so that the others might survive * ''Homo antecessor'', an extinct human species, suspected of practicing cannibalism * Human fat has been applied in European pharmacopeia between the 16th and the 19th centuries. *Human placentophagy, the consumption of the placenta (afterbirth) * Idi Amin, Ugandan dictator who is alleged to have consumed humans. *Issei Sagawa
also known as Pang or The Kobe Cannibal, was a Japanese murderer, cannibal, and necrophiliac known for the killing of Renée Hartevelt in Paris in 1981.
Sagawa murdered Hartevelt then mutilated, cannibalized, and performed necrophilia on her ...
, a Japanese celebrity who killed and ate a fellow student
* List of incidents of cannibalism
* Manifesto Antropófago, (Cannibal Manifesto in English), a Brazilian poem
* Noida serial murders, a widely publicized instance of alleged cannibalism in India
* Placentophagy, the act of mammals eating the placenta of their young after childbirth
* Pleistocene human diet
* ''R v Dudley and Stephens
''R v Dudley and Stephens'' (188414 QBD 273, DCis a leading English criminal case which established a precedent throughout the common law world that necessity is not a defence to a charge of murder. The case concerned survival cannibalism foll ...
'', an important trial of two men accused of shipwreck cannibalism
* Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, a progressive condition that affect the brain and nervous system of many animals, including humans
* Vorarephilia, a sexual fetish and paraphilia where arousal occurs from the idea of cannibalism
* Wari’ people, an Amerindian tribe that practiced cannibalism
References
Further reading
* *Berdan, Frances F. ''The Aztecs of Central Mexico: An Imperial Society''. New York 1982. * *Earle, Rebecca. ''The Body of the Conquistador: Food, Race, and the Colonial Experience in Spanish America, 1492–1700''. New York: Cambridge University Press 2012. * * *Jáuregui, Carlos. ''Canibalia: Canibalismo, calibanismo, antropofagía cultural y consumo en América Latina''. Madrid: Vervuert 2008. *Lestringant, Frank. ''Cannibals: The Discovery and Representation of the Cannibal from Columbus to Jules Verne''. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press 1997. * * *Ortiz de Montellano, Bernard R. ''Aztec Medicine, Health, and Nutrition''. New Brunswick 1990. *Read, Kay A. ''Time and Sacrifice in the Aztec Cosmos''. Bloomington 1998. *Sahlins, Marshall. "Cannibalism: An Exchange." ''New York Review of Books 26'', no. 4 (March 22, 1979). *Schutt, Bill. ''Cannibalism: A Perfectly Natural History''. Chapel Hill: Algonquin Books 2017. * *External links
Is there a relation between cannibalism and amyloidosis?
All about Cannibalism: The Ancient Taboo in Modern Times (Cannibalism Psychology)
at CrimeLibrary.com
''Cannibalism'', Víctor Montoya
Notes arguing that routine cannibalism is myth
(from
The Straight Dope
"The Straight Dope" was a question-and-answer newspaper column written under the pseudonym Cecil Adams. Contributions were made by multiple authors, and it was illustrated (also pseudonymously) by Slug Signorino. It was first published in 1973 in ...
)
Harry J. Brown, 'Hans Staden among the Tupinambas.'
{{Authority control Cannibalism,