Hudson Valley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the
 The Hudson River was a key river during the Revolutionary War. The Hudson's connection to the Mohawk River allowed travelers to get to the Great Lakes and the
The Hudson River was a key river during the Revolutionary War. The Hudson's connection to the Mohawk River allowed travelers to get to the Great Lakes and the
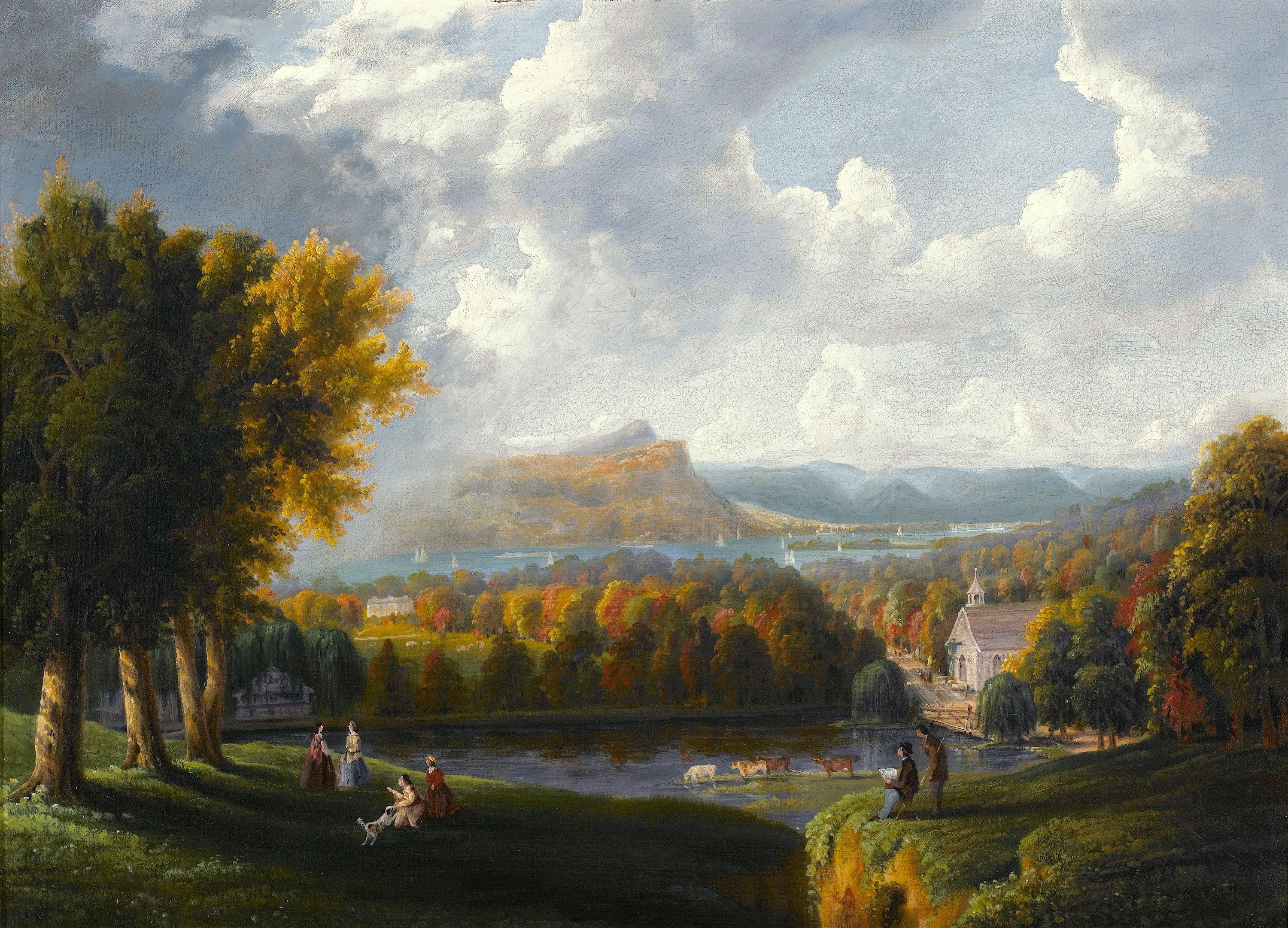 In the early 19th century, popularized by the stories of Washington Irving, the Hudson Valley gained a reputation as a somewhat gothic region characterized by remnants of the early days of the Dutch colonization of New York (see " The Legend of Sleepy Hollow"). The area is also associated with the
In the early 19th century, popularized by the stories of Washington Irving, the Hudson Valley gained a reputation as a somewhat gothic region characterized by remnants of the early days of the Dutch colonization of New York (see " The Legend of Sleepy Hollow"). The area is also associated with the
 The Hudson Valley has a long agricultural history, as it was settled with agriculture being its main industry. Around the 1700s,
The Hudson Valley has a long agricultural history, as it was settled with agriculture being its main industry. Around the 1700s,

 The Hudson Valley is divided into three regions: Upper, Middle, and Lower. The following is a list of the counties within the Hudson Valley sorted by region. The Lower Hudson Valley is typically considered part of the
The Hudson Valley is divided into three regions: Upper, Middle, and Lower. The following is a list of the counties within the Hudson Valley sorted by region. The Lower Hudson Valley is typically considered part of the
Capital District * Albany * Columbia *
 Major interstates in the Hudson Valley include Interstate 87 (part of the New York State Thruway), a small section of Interstate 95 in Southeastern Westchester County,
Major interstates in the Hudson Valley include Interstate 87 (part of the New York State Thruway), a small section of Interstate 95 in Southeastern Westchester County,

Hudson Valley Directory
at hudsonvalleydirectory.com
Hudson River Valley Greenway
at hudsongreenway.ny.gov
Hudson River Valley Heritage
digital collection of historical materials, at hrvh.org
Hudson River Valley National Heritage Area
at hudsonrivervalley.com {{Authority control Physiographic sections Upstate New York Regions of New York (state) River valleys of the United States Valleys of New York (state) Landforms of Westchester County, New York Landforms of Rockland County, New York Landforms of Putnam County, New York Landforms of Dutchess County, New York Landforms of Orange County, New York Landforms of Ulster County, New York Landforms of Sullivan County, New York Landforms of Columbia County, New York Landforms of Greene County, New York Landforms of Rensselaer County, New York Landforms of Albany County, New York
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to Yonkers
Yonkers () is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States. Developed along the Hudson River, it is the third most populous city in the state of New York (state), New York, after New York City and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo. The popul ...
in Westchester County, bordering New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
.
History
Pre-Columbian era
The Hudson Valley was inhabited by indigenous peoples ages before Europeans arrived. The Lenape, Wappinger, and Mahican branches of theAlgonquins
The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely related to the Odawa, Potawatomi ...
lived along the river, mostly in peace with the other groups. The lower Hudson River was inhabited by the Lenape, The Lenape people waited for the explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano onshore, traded with Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
, and sold the island of Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
. Further north, the Wappingers lived from Manhattan Island up to Poughkeepsie
Poughkeepsie ( ), officially the City of Poughkeepsie, separate from the Town of Poughkeepsie around it) is a city in the U.S. state of New York. It is the county seat of Dutchess County, with a 2020 census population of 31,577. Poughkeepsie ...
. They lived a similar lifestyle to the Lenape, residing in various villages along the river. They traded with both the Lenape to the south and the Mahicans to the north. The Mahicans lived in the northern valley from present-day Kingston to Lake Champlain, with their capital located near present-day Albany. The Algonquins in the region lived mainly in small clans and villages throughout the area. One major fortress was called Navish, which was located at Croton Point, overlooking the Hudson River. Other fortresses were located in various locations throughout the Hudson Highlands
The Hudson Highlands are mountains on both sides of the Hudson River in New York state lying primarily in Putnam County on its east bank and Orange County on its west. They continue somewhat to the south in Westchester County and Rockland Count ...
.
Hudson River exploration
In 1497, John Cabot traveled along the coast and claimed the entire country for England; he is credited with the Old World's discovery of continental North America. Between then and about 1609, exploration took place around New York Bay, but not into the Hudson Valley. In 1609, theDutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
financed English navigator Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
in his attempt to search for the Northwest Passage. During this attempt, Henry Hudson decided to sail his ship up the river that would later be named after him. As he continued up the river, its width expanded, into Haverstraw Bay, leading him to believe he had successfully reached the Northwest Passage. He also proceeded upstream as far as present-day Troy before concluding that no such strait existed there.
Colonization
After Henry Hudson realized that the Hudson River was not the Northwest Passage, theDutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
began to examine the region for potential trading opportunities. Dutch explorer and merchant Adriaen Block
Adriaen (Arjan) Block (c. 1567 – buried April 27, 1627) was a Dutch private trader, privateer, and ship's captain who is best known for exploring the coastal and river valley areas between present-day New Jersey and Massachusetts during four v ...
led voyages there between 1611 and 1614, which led the Dutch to determine that fur trade would be profitable in the region. As such, the Dutch established the colony of New Netherland. The Dutch settled three major fur-trading outposts in the colony, along the river, south to north: New Amsterdam, Wiltwyck, and Fort Orange
Fort Orange ( nl, Fort Oranje) was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city of Albany, New York developed at this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearb ...
. New Amsterdam later became known as New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, Wiltwyck became Kingston, and Fort Orange became Albany. In 1664, the British invaded New Netherland via the port of New Amsterdam. New Amsterdam and New Netherland as a whole was surrendered to the British, and renamed New York.
Under British colonial rule, the Hudson Valley became an agricultural hub, with manors being developed on the east side of the river. At these manors, landlords rented out land to their tenants, letting them take a share of the crops grown while keeping and selling the rest of the crops. Tenants were often kept at a subsistence level so that the landlord could minimize his costs. Landlords held immense political power in the colony due to driving such a large proportion of the agricultural output. Meanwhile, land west of Hudson River contained smaller landholdings with many small farmers living off the land. A large crop grown in the region was grain, which was largely shipped downriver to New York City, the colony's main seaport, for export back to Great Britain. In order to export the grain, colonial merchants were given monopolies to grind the grain into flour and export it. Grain production was also at high levels in the Mohawk River Valley.
Revolutionary War
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
eventually. In addition, the river's close proximity to Lake George and Lake Champlain would allow the British navy to control the water route from Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
to New York City. In doing so, the British, under General John Burgoyne
General John Burgoyne (24 February 1722 – 4 August 1792) was a British general, dramatist and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1761 to 1792. He first saw action during the Seven Years' War when he participated in several bat ...
's strategy, would be able to cut off the patriot
A patriot is a person with the quality of patriotism.
Patriot may also refer to:
Political and military groups United States
* Patriot (American Revolution), those who supported the cause of independence in the American Revolution
* Patriot m ...
hub of New England (which is on the eastern side of the Hudson River) and focus on rallying the support of loyalists in the South and Mid-Atlantic regions. The British knew that total occupation of the colonies would be unfeasible, which is why this strategy was chosen. As a result of the strategy, numerous battles were fought along the river, including several in the Hudson Valley.
Industrial Revolution
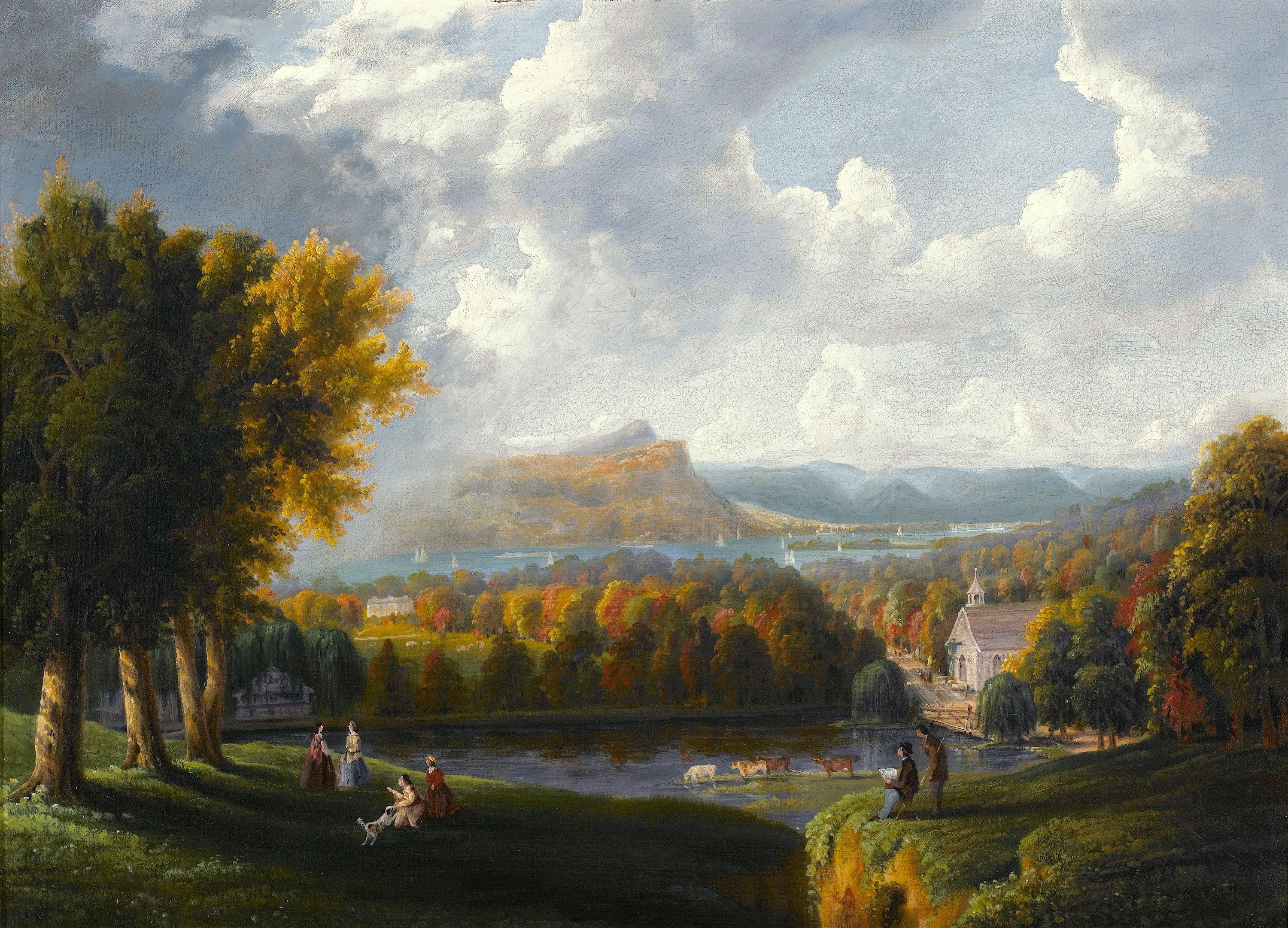 In the early 19th century, popularized by the stories of Washington Irving, the Hudson Valley gained a reputation as a somewhat gothic region characterized by remnants of the early days of the Dutch colonization of New York (see " The Legend of Sleepy Hollow"). The area is also associated with the
In the early 19th century, popularized by the stories of Washington Irving, the Hudson Valley gained a reputation as a somewhat gothic region characterized by remnants of the early days of the Dutch colonization of New York (see " The Legend of Sleepy Hollow"). The area is also associated with the Hudson River School
The Hudson River School was a mid-19th century American art movement embodied by a group of landscape painters whose aesthetic vision was influenced by Romanticism. The paintings typically depict the Hudson River Valley and the surrounding area ...
, a group of American Romantic painters who worked from about 1830 to 1870.
Following the building of the Erie Canal, the area became an important industrial center. The canal opened the Hudson Valley and New York City to commerce with the Midwest and Great Lakes regions. However, in the mid 20th century, many of the industrial towns went into decline.
The first railroad in New York, the Mohawk and Hudson Railroad, opened in 1831 between Albany and Schenectady on the Mohawk River, enabling passengers to bypass the slowest part of the Erie Canal. The Hudson Valley proved attractive for railroads, once technology progressed to the point where it was feasible to construct the required bridges over tributaries. The Troy and Greenbush Railroad was chartered in 1845 and opened that same year, running a short distance on the east side between Troy and Greenbush, now known as East Greenbush (east of Albany). The Hudson River Railroad was chartered the next year as a continuation of the Troy and Greenbush south to New York City, and was completed in 1851. In 1866 the Hudson River Bridge opened over the river between Greenbush and Albany, enabling through traffic between the Hudson River Railroad and the New York Central Railroad west to Buffalo. When the Poughkeepsie Bridge opened in 1889, it became the longest single-span bridge in the world.
The New York, West Shore and Buffalo Railway began at Weehawken Terminal
Weehawken Terminal was the waterfront intermodal terminal on the North River (Hudson River) in Weehawken, New Jersey for the New York Central Railroad's West Shore Railroad division, whose route traveled along the west shore of the Hudson River ...
and ran up the west shore of the Hudson as a competitor to the merged New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Construction was slow, and was finally completed in 1884; the New York Central purchased the line the next year.
During the Industrial Revolution, the Hudson River Valley became a major location for production. The river allowed for fast and easy transport of goods from the interior of the Northeast to the coast. Hundreds of factories were built around the Hudson, in towns including Poughkeepsie, Newburgh, Kingston, and Hudson. The North Tarrytown Assembly (later owned by General Motors), on the river in Sleepy Hollow, was a large and notable example. The river links to the Erie Canal and Great Lakes, which allowed manufacturers in the Midwest, including automobile factories in Detroit, to use the river for transport. With industrialization came new technologies, such as streamboats, for faster transport. In 1807, the ''North River Steamboat
The ''North River Steamboat'' or ''North River'', colloquially known as the ''Clermont'', is widely regarded as the world's first vessel to demonstrate the viability of using steam propulsion for commercial water transportation. Built in 1807, t ...
'' (later known as Clermont), became the first commercially successful steamboat. It carried passengers between New York City and Albany along the Hudson River. At the end of the 19th century, the Hudson River region of New York State would become the world's largest brick manufacturing region, with 130 brickyards lining the shores of the Hudson River from Mechanicsville to Haverstraw and employing 8,000 people. At its peak, about 1 billion bricks were produced a year, with many being sent to New York City for use in its construction industry.
Tourism became a major industry as early as 1810. With convenient steamboat connections in New York City, and numerous attractive hotels in romantic settings, tourism became an important industry. Early guidebooks provided suggestions for travel itineraries. Middle-class people who read James Fenimore Cooper's novels, or saw the paintings of the Hudson River School, were especially attracted to the region.
Geology and physiography
The Hudson River valley runs primarily north to south down the eastern edge of New York State, cutting through a series of rock types includingTriassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
sandstones and redbeds in the south and much more ancient Precambrian gneiss in the north (and east). In the Hudson Highlands, the river enters a fjord cut during previous ice ages. To the west lie the extensive Appalachian highlands. In the Tappan Zee region, the west side of the river has high cliffs produced by an erosion-resistant diabase; the cliffs range from in height.
The Hudson Valley is one physiographic section of the larger Ridge-and-Valley province, which in turn is part of the larger Appalachian physiographic division. The northern portions of the Hudson Valley fall within the Eastern Great Lakes and Hudson Lowlands Ecoregion
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
.
During the last ice age, the valley was filled by a large glacier that pushed south as far as Long Island. Near the end of the last ice age, the Great Lakes drained south down the Hudson River, from a large glacial lake called Lake Iroquois. Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border ...
is the remnant of that Lake. Large sand deposits remain from where Lake Iroquois drained into the Hudson; these are now part of the Rome Sand Plains
Rome Sand Plains is a pine barrens about west of the city center of Rome in Oneida County in central New York. It consists of a mosaic of sand dunes rising about above low peat bogs that lie between the dunes. The barrens are covered with mix ...
.
Due to its resemblance, the Hudson River often has been described as "America's Rhine." In 1939, the magazine ''Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
'' described the river as such, comparing it to the stretch of the Rhine in Central and Western Europe.
Major industries
Agriculture
 The Hudson Valley has a long agricultural history, as it was settled with agriculture being its main industry. Around the 1700s,
The Hudson Valley has a long agricultural history, as it was settled with agriculture being its main industry. Around the 1700s, tenant farming
A tenant farmer is a person (farmer or farmworker) who resides on land owned by a landlord. Tenant farming is an agricultural production system in which landowners contribute their land and often a measure of operating capital and management, ...
was highly practiced. The farms' main products were grains (predominantly wheat), though hops, maple syrup, vegetables, dairy products, honey, wool, livestock, and tobacco were produced there. The region became the breadbasket
The breadbasket of a country or of a region is an area which, because of the richness of the soil and/or advantageous climate, produces large quantities of wheat or other grain. Rice bowl is a similar term used to refer to Southeast Asia; and C ...
of colonial America, given that the surrounding New England and Catskills areas were more mountainous and had rockier soils. In the late 1800s, most farms transitioned from tenant farming to being family-owned, with more incentive to improve the land. Grain production moved west to the Genesee Valley, and so Hudson Valley farms specialized, especially in viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for '' vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of '' Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ...
, berries, and orchard cultivation. Agriculture began to decline in the 19th century, and rapidly declined in the 20th century.
By the 1970s, the United States' culinary revolution began, and the Hudson Valley began to lead the farm-to-table movement, the local food movement, and sustainable agricultural practices. The fertile Black Dirt Region of the Wallkill and Schoharie valleys also began to be farmed. Dairy farms are predominant, though fruit, vegetable, poultry, meat, and maple syrup production is also common. Orchard cultivation is common in Orange, Ulster, Dutchess, and Columbia counties.
Winemaking
The Hudson Valley is one of the oldest winemaking and grape-growing regions in the United States, with its first vineyards planted in 1677 in current-dayNew Paltz
New Paltz () is an incorporated U.S. town in Ulster County, New York. The population was 14,003 at the 2010 U.S. Census. The town is located in the southeastern part of the county and is south of Kingston. New Paltz contains a village, also wit ...
. The region has experienced a resurgence in winemaking in the 21st century. Many wineries are located in the Hudson Valley, offering wine-tasting and other tours. Numerous wine festival
Annual wine festivals celebrate viticulture and usually occur after the harvest of the grapes which, in the northern hemisphere, generally falls at the end of September and runs until well into October or later. They are common in most wine regio ...
s are held in the Hudson Valley, with themes often varying by season. Rhinebeck is home to the Hudson Valley Wine & Food Fest, hosted at the Dutchess County Fairgrounds.
The region has sunlight, moisture, chalky soil, and drainage conducive to grape growing, especially grapes used in Champagne.
Tech Valley

Tech Valley
Tech Valley began as a marketing name for the eastern part of the U.S. state of New York, encompassing the Capital District and the Hudson Valley. Originating in 1998 to promote the greater Albany area as a high-tech competitor to regions such as ...
is a marketing name for the eastern part of New York State, including the Hudson Valley and the Capital District. Originated in 1998 to promote the greater Albany area as a high-tech competitor to regions such as Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo Coun ...
and Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, it has since grown to represent the counties in New York between IBM's Westchester County plants in the south and the Canada–US border to the north. The area's high technology ecosystem is supported by technologically focused academic institutions
Academic institution is an educational institution dedicated to education and research, which grants academic degrees. See also academy and university.
Types
* Primary schools – (from French ''école primaire'') institutions where children r ...
including Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and the State University of New York Polytechnic Institute. Tech Valley encompasses 19 counties straddling both sides of the Adirondack Northway
Interstate 87 (I-87) is a north–south Interstate Highway located entirely within the US state of New York. It is most of the main highway between New York City and Montreal. The highway begins at exit 47 off I-278 in the New York ...
and the New York Thruway
{{Infobox road
, state = NY
, type = NYST
, alternate_name = Governor Thomas E. Dewey Thruway
, maint = NYSTA
, map = {{maplink, frame=yes, plain=yes, frame-align=center, frame-width=290, type=line, stroke-width=2, type2=line, from2=New Yor ...
, and with heavy state taxpayer subsidy, has experienced significant growth in the computer hardware industry, with great strides in the nanotechnology sector, digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usual ...
design, and water- and electricity-dependent integrated microchip circuit manufacturing, involving companies including IBM in Armonk and its Thomas J. Watson Research Center
The Thomas J. Watson Research Center is the headquarters for IBM Research. The center comprises three sites, with its main laboratory in Yorktown Heights, New York, U.S., 38 miles (61 km) north of New York City, Albany, New York and wit ...
in Yorktown, GlobalFoundries
GlobalFoundries Inc. (GF or GloFo) is a multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company incorporated in the Cayman Islands and headquartered in Malta, New York. Created by the divestiture of the manufacturing arm of AMD, ...
in Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, and others. Westchester County has developed a burgeoning biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
sector in the 21st century, with over US$1 billion in planned private investment as of 2016, earning the county the nickname ''Biochester''.
Regions
Downstate New York
Downstate New York is a region that generally consists of the southeastern and more densely populated portion of the U.S. state of New York, in contrast to Upstate New York, which comprises a larger geographic area with much sparser population di ...
region due to its geographical and cultural proximity to New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
.
Lower Hudson
* Putnam
* Rockland
* Westchester
Mid-Hudson
* Dutchess
*Orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
*Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kin ...
Upper Hudson/Capital District * Albany * Columbia *
Greene
Greene may refer to:
Places United States
*Greene, Indiana, an unincorporated community
*Greene, Iowa, a city
*Greene, Maine, a town
** Greene (CDP), Maine, in the town of Greene
*Greene (town), New York
** Greene (village), New York, in the town ...
* Rensselaer
Infrastructure
Interstate 287
Interstate 287 (I-287) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway in the US states of New Jersey and New York. It is a partial beltway around New York City, serving the northern half of New Jersey and the counties of Rockland and Westchester in ...
serving Westchester and Rockland Counties, Interstate 84 serving Putnam, Dutchess, and Orange Counties, and Interstate 684
Interstate 684 (I-684) is a north–south auxiliary Interstate Highway in the state of New York in the United States. There is also a short portion in Connecticut with no junctions. The highway connects I-84 with I-287 and the Hutchinson ...
serving Westchester and Putnam Counties. parkways in the region include the Bronx River Parkway, the Cross County Parkway
The Cross County Parkway (CCP) is a parkway in lower Westchester County, New York, in the United States. The parkway is a critical east–west connection throughout Westchester, having full interchanges with every major north–south high ...
, the Hutchinson River Parkway
The Hutchinson River Parkway (known colloquially as The Hutch) is a north–south parkway in southern New York in the United States. It extends for from the massive Bruckner Interchange in the Throggs Neck section of the Bronx to the New York ...
, the Sprain Brook Parkway
The Sprain Brook Parkway (also known as The Sprain) is a long north–south parkway in Westchester County, New York, United States. It begins at an interchange with the Bronx River Parkway in the city of Yonkers, and ends at the former site ...
, and the Saw Mill River Parkway
The Saw Mill River Parkway (also known as the Saw Mill Parkway or the Saw Mill) is a north–south parkway that extends for through Westchester County, New York, in the United States. It begins at the border between Westchester County and the Bro ...
serving solely Westchester County, the Taconic State Parkway
The Taconic State Parkway (often called the Taconic or the TSP and known administratively as New York State Route 987G or NY 987G) is a parkway between Kensico Dam and Chatham, the longest in the U.S. state of New York. It follows ...
serving Westchester, Putnam, Dutchess, and Columbia Counties, and the Palisades Interstate Parkway
The Palisades Interstate Parkway (PIP) is a limited-access highway in the U.S. states of New Jersey and New York. The parkway is a major commuter route into New York City from Rockland and Orange counties in New York and Bergen County in New ...
serving Rockland and a very small portion of southwestern Orange County. New York State Route 17 operates as a freeway in much of Orange County and will be designated Interstate 86 in the future.
Hudson River crossings in the Hudson Valley region from south to north include the Tappan Zee Bridge between South Nyack in Rockland County and Tarrytown
Tarrytown is a village in the town of Greenburgh in Westchester County, New York. It is located on the eastern bank of the Hudson River, approximately north of Midtown Manhattan in New York City, and is served by a stop on the Metro-North Hu ...
in Westchester County, the Bear Mountain Bridge
The Bear Mountain Bridge, ceremonially named the Purple Heart Veterans Memorial Bridge, is a toll suspension bridge in New York State. It carries US 6 and US 202 across the Hudson River between Bear Mountain State Park in Orange Co ...
between Peekskill
Peekskill is a city in northwestern Westchester County, New York, United States, from New York City. Established as a village in 1816, it was incorporated as a city in 1940. It lies on a bay along the east side of the Hudson River, across fr ...
in Westchester County and Fort Montgomery in Orange County, the Newburgh-Beacon Bridge between Newburgh in Orange County and Beacon
A beacon is an intentionally conspicuous device designed to attract attention to a specific location. A common example is the lighthouse, which draws attention to a fixed point that can be used to navigate around obstacles or into port. More mode ...
in Dutchess County, the Mid-Hudson Bridge
The Franklin Delano Roosevelt Mid-Hudson Bridge is a toll suspension bridge which carries US 44 and NY 55 across the Hudson River between Poughkeepsie and Highland in the state of New York.
History
Proposals for the Mid-Hudson span were made ...
between Poughkeepsie
Poughkeepsie ( ), officially the City of Poughkeepsie, separate from the Town of Poughkeepsie around it) is a city in the U.S. state of New York. It is the county seat of Dutchess County, with a 2020 census population of 31,577. Poughkeepsie ...
in Dutchess County and Highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
in Ulster County, the Kingston-Rhinecliff Bridge between Rhinecliff in Dutchess County and Kingston in Ulster County, and the Rip Van Winkle Bridge
The Rip Van Winkle Bridge is a cantilever bridge
spanning the Hudson River between Hudson, New York and Catskill, New York. Affording of clearance over the water, the structure carries NY 23 across the river, connecting US 9W and NY 385 on t ...
between Hudson in Columbia County and Catskill in Greene County. The Walkway Over the Hudson is a pedestrian bridge which parallels the Mid-Hudson Bridge and was formerly a railroad bridge.
NY Waterway
NY Waterway (or New York Waterway) is a private transportation company running ferry and bus service in the Port of New York and New Jersey and in the Hudson Valley. The company utilizes public-private partnership with agencies such as the Port ...
operates the Haverstraw-Ossining Ferry between Haverstraw
Haverstraw is a town in Rockland County, New York, United States, located north of the Town of Clarkstown and the Town of Ramapo; east of Orange County; south of the Town of Stony Point; and west of the Hudson River. The town runs from the w ...
in Rockland County and Ossining in Westchester County, as well as ferry service between Newburgh in Orange County and Beacon
A beacon is an intentionally conspicuous device designed to attract attention to a specific location. A common example is the lighthouse, which draws attention to a fixed point that can be used to navigate around obstacles or into port. More mode ...
in Dutchess County. Intercity and commuter bus transit are provided by Rockland Coaches
Rockland Coaches Inc., also known as The Red and Tan Lines, is a commuter coach company owned by Coach USA based in Westwood, New Jersey, United States, that operates commuter bus service between New York City and points in Bergen County, New Je ...
in Rockland County, Short Line in Orange and Rockland Counties, and Leprechaun Lines in Orange and Dutchess Counties. There are also several local bus providers, including the Bee-Line Bus System in Westchester County and Transport of Rockland in Rockland County.
The Hudson Valley is served by two airports with commercial airline service: Westchester County Airport
Westchester County Airport is a county-owned airport in Westchester County, New York, three miles (6 km) northeast of downtown White Plains, with territory in the towns of North Castle and Harrison, New York, and village of Rye Brook, N ...
(HPN) near White Plains and Stewart International Airport
Stewart International Airport, officially New York Stewart International Airport , is a public/military airport in Orange County, New York, United States. It is in the southern Hudson Valley, west of Newburgh, south of Kingston, and southwest ...
(SWF) near Newburgh.
Rail service

Commuter rail
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting Commuting, commuters to a Downtown, central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter r ...
service in the region is provided by Metro-North Railroad (operated by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority
The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is a public benefit corporation responsible for public transportation in the New York City metropolitan area of the U.S. state of New York. The MTA is the largest public transit authority in th ...
). Metro-North operates three rail lines east of the Hudson River to Grand Central Terminal in Manhattan, from east to west they are the New Haven Line
The Metro-North Railroad New Haven Line is a commuter rail line running from New Haven, Connecticut to New York City. It joins the Harlem Line at Mount Vernon, New York and continues south to Grand Central Terminal in Manhattan. The New Haven ...
(serving southeast Westchester County), the Harlem Line
The Metro-North Railroad Harlem Line, originally chartered as the New York and Harlem Railroad, is an commuter rail line running north from New York City to Wassaic, in eastern Dutchess County. The lower from Grand Central Terminal to Sou ...
(serving Central and Eastern Westchester, Putnam, and Dutchess Counties), and the Hudson Line (serving western Westchester, Putnam, and Dutchess Counties). West of the Hudson, New Jersey Transit
New Jersey Transit Corporation, branded as NJ Transit, and often shortened to NJT, is a state-owned public transportation system that serves the U.S. state of New Jersey, along with portions of New York State and Pennsylvania. It operates bu ...
operates two lines rail service under contract with Metro-North Railroad to Hoboken Terminal
Hoboken Terminal is a commuter-oriented intermodal passenger station in Hoboken, Hudson County, New Jersey. One of the New York metropolitan area's major transportation hubs, it is served by nine NJ Transit (NJT) commuter rail lines, one Metr ...
: the Pascack Valley Line
The Pascack Valley Line is a commuter rail line operated by the Hoboken Division of New Jersey Transit, in the United States. The line runs north from Hoboken Terminal, through Hudson County and Bergen County in New Jersey, and into Rockland Co ...
(serving central Rockland County) and the Port Jervis Line
The Port Jervis Line is a predominantly single-track commuter rail line running between Suffern and Port Jervis, in the U.S. state of New York. At Suffern, the line continues south into New Jersey as NJ Transit's Main Line. The line is operate ...
(serving western Rockland County and Orange County).
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
serves Yonkers
Yonkers () is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States. Developed along the Hudson River, it is the third most populous city in the state of New York (state), New York, after New York City and Buffalo, New York, Buffalo. The popul ...
, Croton-Harmon, Poughkeepsie
Poughkeepsie ( ), officially the City of Poughkeepsie, separate from the Town of Poughkeepsie around it) is a city in the U.S. state of New York. It is the county seat of Dutchess County, with a 2020 census population of 31,577. Poughkeepsie ...
, Rhinecliff-Kingston, and Hudson along the eastern shores of the Hudson River, as well as New Rochelle
New Rochelle (; older french: La Nouvelle-Rochelle) is a city in Westchester County, New York, United States, in the southeastern portion of the state. In 2020, the city had a population of 79,726, making it the seventh-largest in the state o ...
in southeastern Westchester County.
Sports
TheHudson Valley Renegades
Hudson may refer to:
People
* Hudson (given name)
* Hudson (surname)
* Henry Hudson, English explorer
* Hudson (footballer, born 1986), Hudson Fernando Tobias de Carvalho, Brazilian football right-back
* Hudson (footballer, born 1988), Hudson R ...
is a minor league baseball team affiliated with the New York Yankees
The New York Yankees are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The Yankees compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. They are one of ...
. The team is a member of the Mid-Atlantic League
The Middle Atlantic League (or Mid-Atlantic League) was a lower-level circuit in American minor league baseball that played during the second quarter of the 20th century.
History
The Middle Atlantic League played from 1925 through 1951, with t ...
and plays at Dutchess Stadium
Dutchess Stadium is a baseball park in Wappingers Falls, New York. Opened in 1994, it holds 4,500 people. It is located on New York State Route 9D and is located across Interstate 84 from Fishkill Correctional Facility. Construction of the stadi ...
in Fishkill. The New York Boulders
The New York Boulders are an American independent professional baseball team playing in the Frontier League based in Pomona, Rockland County, New York. The team was founded as a member of the Can-Am League, beginning play in the 2011 season as t ...
of the independent Can-Am League
The Canadian American Association of Professional Baseball, commonly known as the Can-Am League, was a professional, independent baseball league with teams in the Northeast United States and Eastern Canada, founded in 2005 as a reorganization ...
play at Clover Stadium, in Pomona, NY.
Kingston Stockade FC
Kingston Stockade Football Club is an American soccer team based in Kingston, New York. The team was founded in November 2015, and began its first season in May 2016.Vrusho, Spike.Stockade Supermen: Kingston, NY welcomes its own semi-pro soccer t ...
is a soccer team representing the Hudson Valley in the National Premier Soccer League
The National Premier Soccer League (NPSL) is an American men's soccer league. The NPSL is a semi-professional league, comprising some teams that have paid players and some that are entirely amateur. The league is officially affiliated to the Uni ...
(NPSL), a national semi-professional league at the fourth tier of the American Soccer Pyramid. They compete in the North Atlantic conference of the NPSL's Northeast region, and began their first season in May 2016.
References
Informational notes
Citations
Further reading
* * * * Jacobs, Jaap and L.H. Roper (eds.) (2014). ''The Worlds of the Seventeenth-Century Hudson Valley.'' Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. * Levine, David (2020). ''The Hudson Valley: The First 250 Million Years.'' Guilford, Connecticut: Globe Pequot. * * * * Scheltema, Gajus and Westerhuijs, Heleen (eds.),''Exploring Historic Dutch New York''. New York: Museum of the City of New York/Dover Publications, 2011. * * Vernon, Benjamin. ''The History of the Hudson River Valley'' (New York: Overlook, 2016. xiv, 625 pp. * * *External links
Hudson Valley Directory
at hudsonvalleydirectory.com
Hudson River Valley Greenway
at hudsongreenway.ny.gov
Hudson River Valley Heritage
digital collection of historical materials, at hrvh.org
Hudson River Valley National Heritage Area
at hudsonrivervalley.com {{Authority control Physiographic sections Upstate New York Regions of New York (state) River valleys of the United States Valleys of New York (state) Landforms of Westchester County, New York Landforms of Rockland County, New York Landforms of Putnam County, New York Landforms of Dutchess County, New York Landforms of Orange County, New York Landforms of Ulster County, New York Landforms of Sullivan County, New York Landforms of Columbia County, New York Landforms of Greene County, New York Landforms of Rensselaer County, New York Landforms of Albany County, New York