Howdah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A howdah, or houdah (
A howdah, or houdah (
File:Hathi Howdah, Mehrangarh Fort Museum.jpg, ''Hathi Howdah'',
File:Bactrian phalera (front) with military elephants, 2nd century BCE, Hermitage Museum, Saint Peterburg.jpg, Bactrian phalera with military elephant carrying a howdah fortress manned by a soldier wearing a
 A derived symbol used in Europe is the "elephant and castle": an elephant carrying a
A derived symbol used in Europe is the "elephant and castle": an elephant carrying a 
 Alternatively, modern uses may derive from later contacts with howdahs. Fanciful images of war elephants with elaborate castles on their back date to 12th century Spain, as at right.
Notably, 13th century English use may come from the elephant given by
Alternatively, modern uses may derive from later contacts with howdahs. Fanciful images of war elephants with elaborate castles on their back date to 12th century Spain, as at right.
Notably, 13th century English use may come from the elephant given by 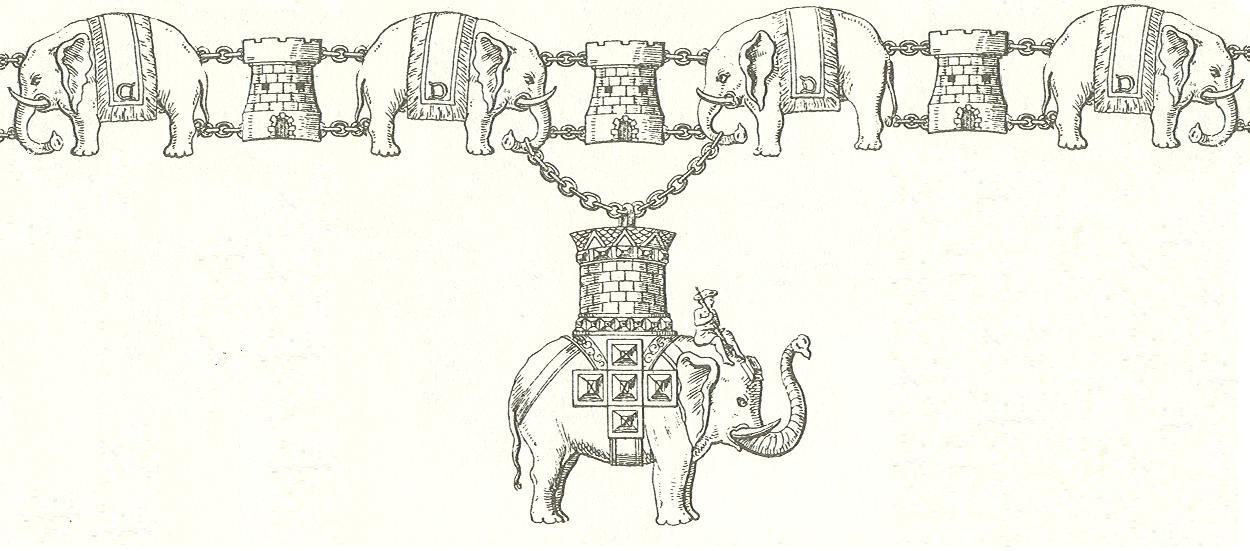 The symbol of an elephant and castle has also been used in the
The symbol of an elephant and castle has also been used in the
 *In
*In
Travels in the Mogul Empire, AD 1656-1668
Oxford University Press. . p. 53.

 A howdah, or houdah (
A howdah, or houdah (Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
: हौदा ''haudā''), derived from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
(hawdaj), which means "bed carried by a camel", also known as ''hathi howdah'' (''hāthī haudā'', हाथी हौदा), is a carriage
A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping ...
which is positioned on the back of an elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
, or occasionally some other animal such as a camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. ...
, used most often in the past to carry wealthy people during progresses or processions, hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
or in war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
fare. It was also a symbol of wealth for the owner and as a result might be elaborately decorated, even with expensive gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, ...
s.
Notable howdahs are the Golden Howdah, on display at the Napier Museum at Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
, which was used by the Maharaja of Travancore and that used traditionally during the Elephant Procession of the famous Mysore Dasara
Mysore Dasara is the ''Nadahabba'' (state festival) of the state of Karnataka in India. It is a 10-day festival, starting with nine nights called Navaratri and the last day being Vijayadashami. The festival is observed on the tenth day in th ...
. The Mehrangarh Fort Museum in Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
, has a gallery of royal howdahs.
Today, howdahs are used mainly for tourist or commercial purposes in South East Asia and are the subject of controversy as animal rights groups
This list of animal rights groups consists of groups in the animal rights movement. Such animal rights groups work towards their ideals, which include the viewpoint that animals should have equivalent rights to humans, such as not being "used" in ...
and organizations, such as Millennium Elephant Foundation
Millennium Elephant Foundation (MEF) is an organization and charity set up to rescue and care for captive Asian elephants in Sri Lanka. The foundation is situated on a 15-acre estate by the name of Samaragiri, which is located northwest of Kega ...
, openly criticize their use, citing evidence that howdahs can cause permanent damage to an elephant's spine, lungs, and other organs and can significantly shorten the animal's life.
History
A passage from Roman historian Curtius describes the lifestyles ofancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by ...
n kings during the "Second urbanisation" (c. 600 – c. 200 BCE) who rode on chariot mounted on elephants or howdahs when going on distant expeditions.
Howdah Gallery, Mehrangarh Fort Museum
TheMehrangarh Fort
Mehrangarh Fort covers an area of 1,200 acres (486 hectares) in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. The complex is located on a hilltop around 122 metres above the surrounding plain, and was constructed by Rajput ruler Rao Jodha, though most of the exi ...
Museum, Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the ...
, has a gallery dedicated to an array of Hathi Howdah, used by the Maharaja of Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and ...
, mostly for ceremonial occasions.
Mehrangarh Fort
Mehrangarh Fort covers an area of 1,200 acres (486 hectares) in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. The complex is located on a hilltop around 122 metres above the surrounding plain, and was constructed by Rajput ruler Rao Jodha, though most of the exi ...
Museum.
File:Silver Hathi Howdah, Mehrangarh Fort Museum.jpg, Silver ''Hathi Howdah'', Mehrangarh Fort Museum.
File:Hathi Howdah or Elephant seat in the Mehrangarh Fort Museum.jpg, Hathi Howdah or Elephant seat in the Mehrangarh Fort Museum.Howdah for armies
Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
helmet. 2nd century BCE, Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the larges ...
.
File:Howdah of the Golconda Sultanate, Qutb Shahi dynasty.png, Howdah of the Qutb Shahi dynasty
The Qutb Shahi dynasty also called as Golconda Sultanate (Persian: ''Qutb Shāhiyān'' or ''Sultanat-e Golkonde'') was a Persianate Shia Islam dynasty of Turkoman origin that ruled the sultanate of Golkonda in southern India. After the co ...
.
File:Death of the Nabob of the Carnatic by Paul Philippoteaux.jpg, Howdah were used extensively during the Carnatic Wars
The Carnatic Wars were a series of military conflicts in the middle of the 18th century in India's coastal Carnatic region, a dependency of Hyderabad State, India. Three Carnatic Wars were fought between 1744 and 1763.
The conflicts involved n ...
.
File:Hannibal traverse le Rhône Henri Motte 1878.jpg, Howdahs with battlement
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at interv ...
s inspired "elephant and castle" imagery
References in literature
The American authorHerman Melville
Herman Melville ( born Melvill; August 1, 1819 – September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance period. Among his best-known works are '' Moby-Dick'' (1851); '' Typee'' (1846), a ...
in Chapter 42 ("The Whiteness of the Whale") of ''Moby Dick
''Moby-Dick; or, The Whale'' is an 1851 novel by American writer Herman Melville. The book is the sailor Ishmael's narrative of the obsessive quest of Ahab, captain of the whaling ship ''Pequod'', for revenge against Moby Dick, the giant whi ...
'' (1851), writes "To the native Indian of Peru, the continual site of the snow-howdahed Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
conveys naught of dread, except, perhaps, in the more fancy of the eternal frosted desolateness reigning at such vast altitudes, and the natural conceit of what a fearfulness it would be to lose oneself in such inhuman solitudes." It also appears in Chapter 11 of Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the '' Voyages extra ...
s' classic adventure novel ''Around the World in Eighty Days
''Around the World in Eighty Days'' (french: link=no, Le tour du monde en quatre-vingts jours) is an adventure novel by the French writer Jules Verne, first published in French in 1872. In the story, Phileas Fogg of London and his newly employe ...
'' (1873), in which we are told "The Parsee, who was an accomplished elephant driver, covered his back with a sort of saddle-cloth, and attached to each of his flanks some curiously uncomfortable howdahs.” It is mentioned in the first chapter of Ben-Hur: “Exactly at noon the dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius'' or ;), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel, or one-humped camel, is a large even-toed ungulate, of the genus '' Camelus'', with one hump on its back.
It is the tallest of the three species o ...
, of its own will, stopped, and uttered the cry or moan, peculiarly piteous, by which its kind always protest against an overload, and sometimes crave attention and rest. The master thereupon bestirred himself, waking, as it were, from sleep. He threw the curtains of the houdah up, looked at the sun, surveyed the country on every side long and carefully, as if to identify an appointed place.”
Tolkien wrote in ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'' of the Mûmakil (Elephants) of Harad with howdahs on their backs.
Elephant and castle symbol
 A derived symbol used in Europe is the "elephant and castle": an elephant carrying a
A derived symbol used in Europe is the "elephant and castle": an elephant carrying a castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
on its back, being used especially to symbolize strength. The symbol was used in Europe in classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
and more recently has been used in England since the 13th century, and in Denmark since at least the 17th century.
In antiquity, the Romans made use of war elephants, and turreted elephants feature on the coinage of Juba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
of Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
, in the 1st century BC. Elephants were used in the Roman campaigns against the Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hi ...
, against the Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They sp ...
, and against the Britons, the ancient historian Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; grc-gre, Πoλύαινoς, Polyainos, "much-praised") was a 2nd-century CE Greek author, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' ( grc-gre, Στρατηγήματα, Strategemata), which has been pr ...
writing, "Caesar had one large elephant, which was equipped with armor and carried archers and slingers in its tower. When this unknown creature entered the river, the Britons and their horses fled and the Roman army crossed over." However, he may have confused this incident with the use of a similar war elephant in Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor ...
' final conquest of Britain.

 Alternatively, modern uses may derive from later contacts with howdahs. Fanciful images of war elephants with elaborate castles on their back date to 12th century Spain, as at right.
Notably, 13th century English use may come from the elephant given by
Alternatively, modern uses may derive from later contacts with howdahs. Fanciful images of war elephants with elaborate castles on their back date to 12th century Spain, as at right.
Notably, 13th century English use may come from the elephant given by Louis IX of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the d ...
to Henry III of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of King John and Isabella of Angoulême, Henry ...
, for his menagerie in the Tower of London in 1225, this being the first elephant in England since Claudius.
Today the symbol is most known in the United Kingdom from the Elephant and Castle
The Elephant and Castle is an area around a major road junction in London, England, in the London Borough of Southwark. The name also informally refers to much of Walworth and Newington, due to the proximity of the London Underground stati ...
intersection in south London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, which derives its name from a pub, using the old site of a cutler's, who had used the symbol of the Worshipful Company of Cutlers. The Cutlers, in turn, used the symbol due to the use of ivory in sword and cutlery handles.
The elephant and castle symbol has been used since the 13th century in the coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
of the city of Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a city in the West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed b ...
, and forms the heraldic crest of the Corbet family, feudal barons of Caus, of Caus Castle
Caus Castle is a ruin of a hill fort and medieval castle in the civil parish of Westbury in the English county of Shropshire. It is situated up on the eastern foothills of the Long Mountain guarding the route from Shrewsbury, Shropshire to Mo ...
in Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to ...
, powerful marcher lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in ...
s. It was used in the 17th century by the Royal African Company
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English mercantile ( trading) company set up in 1660 by the royal Stuart family and City of London merchants to trade along the west coast of Africa. It was led by the Duke of York, who was the brother ...
, which led to its use on the guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
gold coin.
 The symbol of an elephant and castle has also been used in the
The symbol of an elephant and castle has also been used in the Order of the Elephant
The Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) is a Danish order of chivalry and is Denmark's highest-ranked honour. It has origins in the 15th century, but has officially existed since 1693, and since the establishment of constitutional ...
, the highest order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
in Denmark, since 1693.
Camel howdah
 *In
*In Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, a camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. ...
howdah used to be a common means of transport. Bernier, Francois. (1891)Travels in the Mogul Empire, AD 1656-1668
Oxford University Press. . p. 53.

See also
* Mahout, the driver of an elephant *Howdah pistol
The howdah pistol was a large-calibre handgun, often with two or four barrels, used in Africa and India from the beginning of the nineteenth century and into the early twentieth century during the British Empire era. It was intended for defence ...
s, large handguns used to defend howdahs from predators
* Persian war elephants
References
External links
* {{Elephants ElephantsAnimal-powered vehicles
{{Cat main, Horse-drawn vehicle
This category is to list all animal-powered vehicles.
Animal-powered transport
Vehicles by fuel ...
Animal equipment
Elephants in India
Camels
Indian culture
Hindi words and phrases
Livestock
de:Sänfte#Spezielle Sänften