History of the administrative divisions of China before 1912 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of the administrative divisions of China before 1912 is quite complex. Across history, what is called 'China' has taken many shapes, and many political organizations. For various reasons, both the borders and names of political divisions have changed—sometimes to follow topography, sometimes to weaken former states by dividing them, and sometimes to realize a philosophical or historical ideal. For recent times, the number of recorded tiny changes is quite large; by contrast, the lack of clear, trustworthy data for ancient times forces historians and geographers to draw approximate borders for respective divisions. But thanks to imperial records and geographic descriptions, political divisions may often be redrawn with some precision. Natural changes, such as changes in a river's course (known for the


 The
The * One of the original provinces established during the
 Throughout the
Throughout the  Eastern Jin launched several expeditions in its last years and regained many territories. When the
Eastern Jin launched several expeditions in its last years and regained many territories. When the 
 To defend the invasion of
To defend the invasion of 

 Emperor Taizong (r. 626−649) set up 10 " circuits" (道, ''dào'') in 627 as inspection areas for imperial commissioners monitoring the operation of prefectures, rather than a new primary level of administration. In 639, there were 10 circuits, 43 commanderies (都督府, ''dūdū fǔ''), and 358 prefectures (州 and later 府, ''fǔ''). In 733, Emperor Xuanzong expanded the number of circuits to 15 by establishing separate circuits for the areas around Chang'an and Luoyang, and by splitting the large Shannan and Jiangnan circuits into 2 and 3 new circuits respectively. He also established a system of permanent inspecting commissioners, though without executive powers.
The Tang dynasty also created military districts (藩鎮/藩镇, ''fānzhèn'') controlled by military commissioners (節度使/节度使, ''jiédushǐ'') charged with protecting frontier areas susceptible to foreign attack (similar to the Western
Emperor Taizong (r. 626−649) set up 10 " circuits" (道, ''dào'') in 627 as inspection areas for imperial commissioners monitoring the operation of prefectures, rather than a new primary level of administration. In 639, there were 10 circuits, 43 commanderies (都督府, ''dūdū fǔ''), and 358 prefectures (州 and later 府, ''fǔ''). In 733, Emperor Xuanzong expanded the number of circuits to 15 by establishing separate circuits for the areas around Chang'an and Luoyang, and by splitting the large Shannan and Jiangnan circuits into 2 and 3 new circuits respectively. He also established a system of permanent inspecting commissioners, though without executive powers.
The Tang dynasty also created military districts (藩鎮/藩镇, ''fānzhèn'') controlled by military commissioners (節度使/节度使, ''jiédushǐ'') charged with protecting frontier areas susceptible to foreign attack (similar to the Western * Circuits established under Xuanzong, as opposed to Taizong's original ten circuits.
** Circuits established under Xuanzong by dividing Taizong's Jiangnan and Shannan circuits.
Other Tang-era circuits include the West Lingnan,
 The
The  The
The 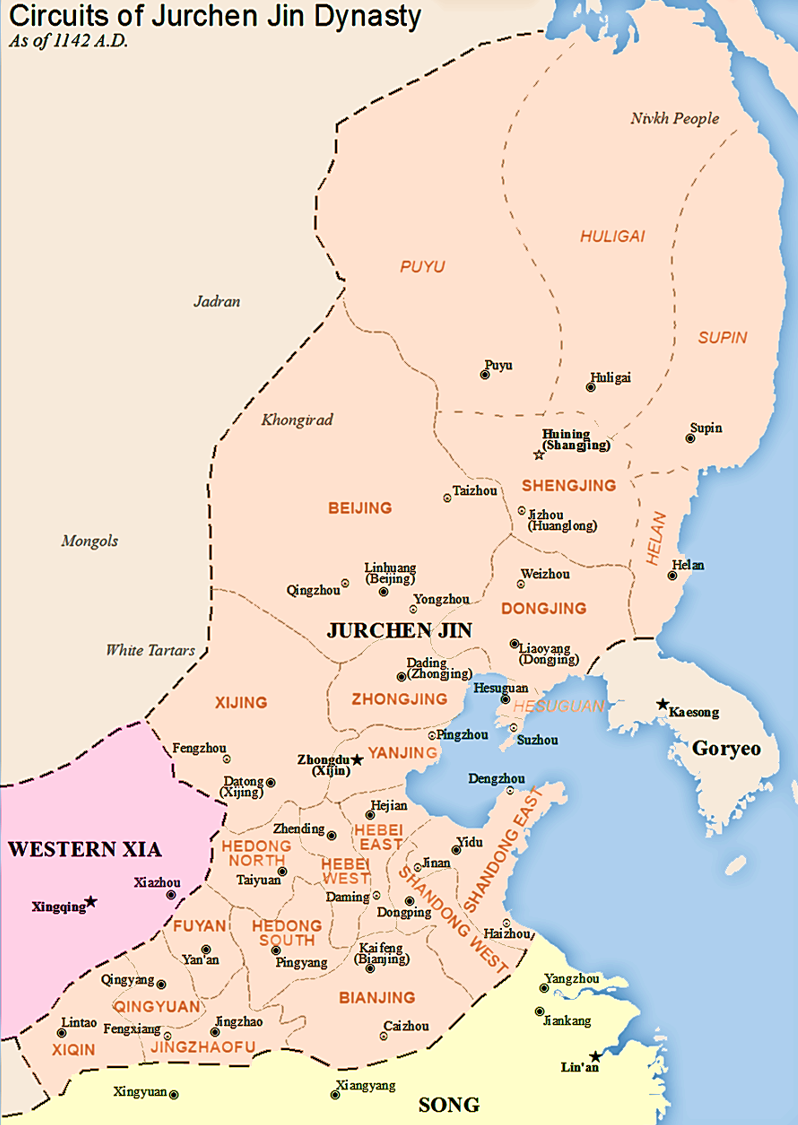 The
The
 The
The
 The
The

 The
The
Summary of terms
– maps of various ''sheng'', ''dao'', ''fu'', ''ting'', and ''xian'' of the late Qing era.
The province in history
by John Fitzgerald {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Administrative Divisions Of China Before 1912 Provinces of China Administrative divisions of China Former administrative divisions of China
Huang He
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan H ...
, but also occurring for others), or loss of data, still make this issue difficult for ancient times.
Summary
Pre-Qin era
Before the establishment of theQin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
, China was ruled by a network of kings, nobles, and tribes. There was no unified system of administrative divisions. According to ancient texts, China in the Xia and Zhou dynasties consisted of nine ''zhou'', but various texts differ as to the names and even functions of these .
During the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
, the nation was nominally controlled by the "Son of Heaven
Son of Heaven, or ''Tianzi'' (), was the sacred monarchical title of the Chinese sovereign. It originated with the Zhou dynasty and was founded on the political and spiritual doctrine of the Mandate of Heaven. Since the Qin dynasty, the secu ...
". In reality, however, the country was divided into competing states, each with a hereditary head, variously styled "prince", "duke", or "king". The rivalry of these groups culminated in the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
, which ended with the victory of Qin.
Jun under the Qin dynasty
After the Kingdom of Qin managed to subdue the rest of China in 221 BC, theFirst Emperor
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor ( ...
divided his realm into relatively small commanderies, which were divided into still smaller counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
. Repudiating the fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
s of the Zhou, both levels were centrally and tightly controlled as part of a meritocratic system. There was also a separately-administered capital district known as the Neishi. Control over some of these, particularly modern Fujian (Minzhong Commandery), was particularly loose.
There were also four other commanderies , and and 23 unaffiliated counties.
Zhou under the Han dynasty
 The
The Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
initially added a top level of "kingdoms" or "principalities" (王国, ''wángguó''), each headed by a local king or a prince of the imperial family. From the establishment of the dynasty, however, the tendency was to slowly absorb this quasi-federal structure into the imperial bureaucracy. After the Rebellion of the Seven States
The Rebellion of the Seven States or Revolt of the Seven Kingdoms () took place in 154 BC against the Han dynasty of China by its regional semi-autonomous kings, to resist the emperor's attempt to centralize the government further.
Background ...
, the system was standardized, replacing the kingdoms and principalities with thirteen province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
s (州, ''zhōu'').
* Provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
* Commanderies
* Counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
Eastern Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
Ping was formed out of You; Qin out of Liang (涼/凉); Liang (梁) and Ning out of Yi; and Guang out of Jiao. Jiao had been established from a territory called Jiaozhi
Jiaozhi (standard Chinese, pinyin: ''Jiāozhǐ''), or Giao Chỉ (Vietnamese), was a historical region ruled by various Chinese dynasties, corresponding to present-day northern Vietnam. The kingdom of Nanyue (204–111 BC) set up the Jiaozhi Co ...
(交趾); Si too was a new creation, its territory formerly administered by a metropolitan commandant (司隷校尉, ''Sīlì xiàowèi'') with capacities similar to the provincial governors'. Shuofang
Shuofang () was an ancient Chinese commandery, situated in the Hetao region in modern-day Inner Mongolia near Baotou. First founded by Emperor Wu of Han in the wake of the successful reconquest of the area from Xiongnu tribes, it was dissolved du ...
(朔方, ''Shuòfāng''), a similar territory in northern Shaanxi, was merged into Bing rather than becoming a full province in its own right.
Provinces during the Jin dynasty and the Southern and Northern dynasties
 Throughout the
Throughout the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
, the Three Kingdoms period
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the We ...
, and the early period of Jin dynasty, the administrative division system remained intact. This changed, however, with the invasion of nomadic tribes from the north in 310s, who disrupted the unity of China and set up a variety of governments.
After the Yongjia Disaster, Jin dynasty lost a significant amount of territories in the north. Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by ...
were established by barbarians in the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
plain, while the court of Jin dynasty shifted to Jiankang
Jiankang (), or Jianye (), as it was originally called, was capital city of the Eastern Wu (229–265 and 266–280 CE), the Jin dynasty (317–420 CE) and the Southern Dynasties (420–552), including the Chen dynasty (557–589 CE). Its wal ...
and survived in the south as Eastern Jin. Among previous provinces of Jin dynasty, only a few remained. They include:
*Yangzhou
*Jiangzhou
*Jingzhou
*Ningzhou
*Jiaozhou
*Guangzhou
*Yuzhou (only the southern part)
*Xuzhou (only the southern part)
With the loss of traditional lands in the north to nomadic tribes, many ethnic Han moved south as refugees with the Jin court. The Jin government established "immigrant provinces" (qiaozhou) based on the homelands of immigrants. For example, while Yan-, Qing- and Youzhou were lost, Southern Yan-, Southern Qing- and Southern You- were established in the south.
 Eastern Jin launched several expeditions in its last years and regained many territories. When the
Eastern Jin launched several expeditions in its last years and regained many territories. When the Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. ...
replaced Eastern Jin as the first Southern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as ...
, it re-constructed the administrative divisions. For example, Yanzhou, Yongzhou and Jizhou were restored. During the reign of Emperor Xiaowu, Liu Song had 22 provinces (, Zhou), 238 commanderies (, Jun) and 1179 counties (Xian, ):
*Yangzhou
*Xuzhou
*Southern Xuzhou
*Yanzhou
*Southern Yanzhou
*Yuzhou
*Southern Yuzhou
*Jiangzhou
*Qingzhou
*Jizhou
*Sizhou
*Jingzhou
*Yingzhou
*Xiangzhou
*Yongzhou
*Liangzhou
*Qinzhou
*Yizhou
*Ningzhou
*Guangzhou
*Jiaozhou
*Yuezhou
Later, due to the conflict with Northern Wei and the change of territories, Liu Song's provincial divisions changed several times. Liu Song's successors, Southern Qi
Qi, known in historiography as the Southern Qi ( or ) or Xiao Qi (), was a Chinese imperial dynasty and the second of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties era. It followed the Liu Song dynasty and was succe ...
and Liang dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was preceded by the South ...
, kept the bulk part of Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. ...
's administrative divisions except for the Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
peninsula which was lost again to the north. Liang dynasty also set first counties on the Hainan Island
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slight ...
. The last of Southern Dynasties, the Chen dynasty, however, lost every division to the north of the Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
river.

Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by ...
of the northern China were unified by Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during t ...
, the empire established by Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
people. Although emperors of Northern Wei tried to be Sinicized, there were serious internal struggles between Xianbei and Han styles in Northern Wei. As a result, the administrative divisions of Northern Wei were pretty complicated and unstable. The southern part of the empire used the Han-style administrative system, while the northern part of the empire was relatively poorly organized. Due to the rivalry and wars between the north and south, the area between Huai River and Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
suffered significant population loss. After Northern Wei took that area from Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. ...
and Southern Qi
Qi, known in historiography as the Southern Qi ( or ) or Xiao Qi (), was a Chinese imperial dynasty and the second of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties era. It followed the Liu Song dynasty and was succe ...
, many towns and villages there were vacant. Therefore, the administrative divisions in those areas were poorly designed. Provinces of Northern Wei include:
*Daizhou
*Youzhou
*Yingzhou
*Pingzhou
*Dingzhou
*Jizhou ()
*Jizhou ()
*Yanzhou
*Yuzhou
*Jingzhou ()
*Luozhou (Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
)
*Yongzhou (Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
)
*Huazhou
*Qinzhou
*Weizhou
*Jingzhou ()
*Sizhou
*Bingzhou
*Eastern Qinzhou
*Eastern Yongzhou
 To defend the invasion of
To defend the invasion of Rouran
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizat ...
, Northern Wei set many (initially six) military towns in the north, and turned the northern part into military districts. After shifting the capital city from Pingcheng
Datong is a prefecture-level city in northern Shanxi Province in the People's Republic of China. It is located in the Datong Basin at an elevation of and borders Inner Mongolia to the north and west and Hebei to the east. As of the 2020 cen ...
to Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
, Northern Wei gradually lost many territories to Rouran and northwestern states. Then, those military towns rebelled and weakened the Xianbei empire. At last, the internal struggle split Northern Wei into Eastern Wei and Western Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Western Wei (), was an imperial dynasty of China that followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei. One of the Northern dynasties during the era of the Northern and Southern dynasties, it ruled the weste ...
, which would be replaced by Northern Qi
Qi, known as the Northern Qi (), Later Qi (後齊) or Gao Qi (高齊) in historiography, was a Chinese imperial dynasty and one of the Northern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties era. It ruled the eastern part of northern China ...
and Northern Zhou
Zhou (), known in historiography as the Northern Zhou (), was a Xianbei-led dynasty of China that lasted from 557 to 581. One of the Northern dynasties of China's Northern and Southern dynasties period, it succeeded the Western Wei dynasty a ...
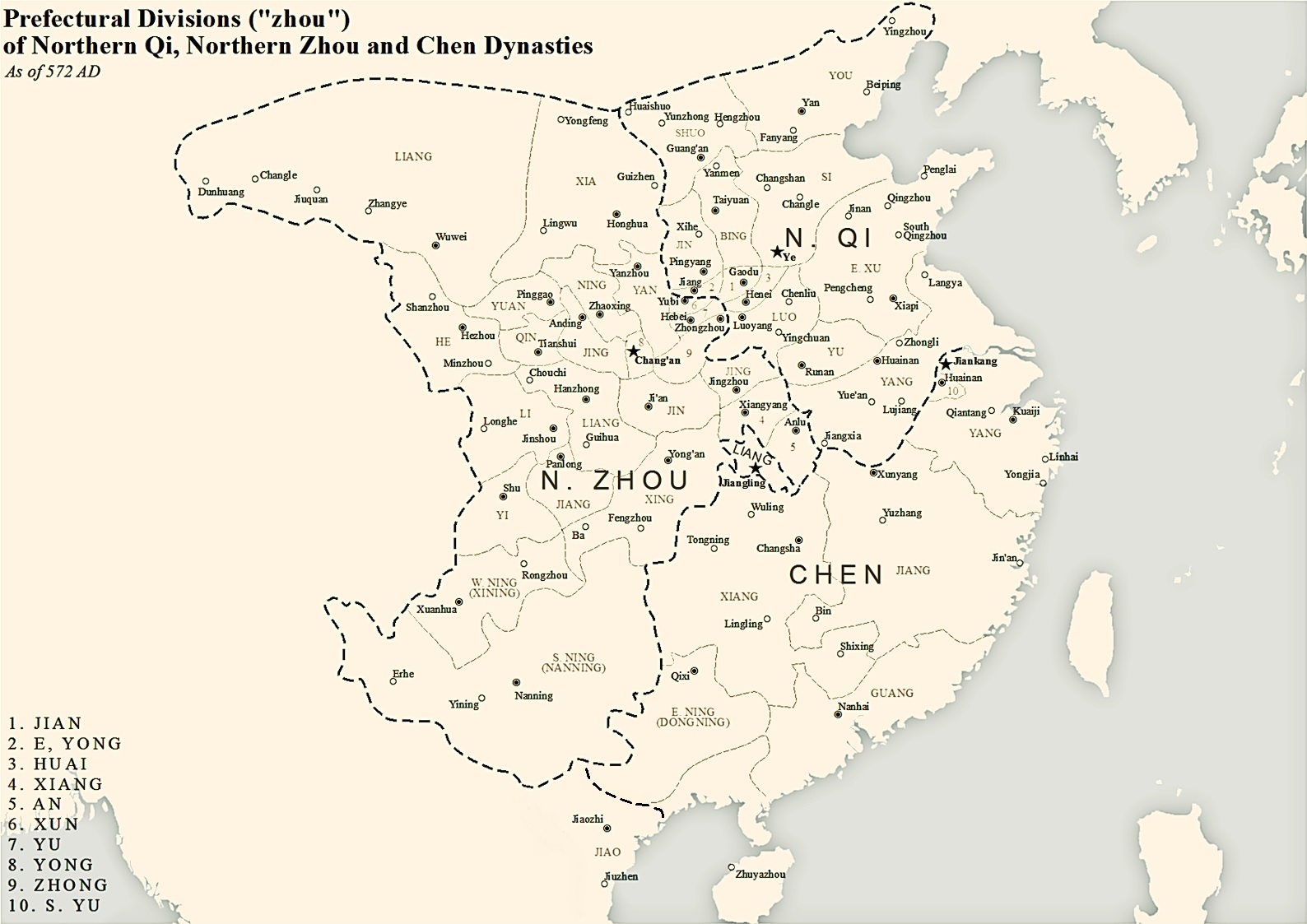
, respectively. Northern Qi and Northern Zhou invaded the Southern Dynasties and occupied many areas of the Chen dynasty.
In their early years, both Northern Qi and Northern Zhou redesigned the administrative divisions. Many provinces of the former Northern Wei dynasty were abolished and merged with each other. Some new provinces were established. Provinces of Northern Qi include:
*Youzhou
*Shuozhou
*Sizhou
*Eastern Xuzhou
*Yuzhou
*Yangzhou
*Luozhou
*Bingzhou
*Jinzhou ()
*Huaizhou
*Eastern Yongzhou
*Jianzhou
Provinces of Northern Zhou include:
*Yongzhou
*Jingzhou
*Xiangzhou
*Anzhou
*Xingzhou
*Jinzhou ()
*Liangzhou ()
*Lizhou
*Yizhou
*Jiangzhou ()
*Yuanzhou
*Qinzhou
*Xunzhou
*Yuzhou
*Zhongzhou
*Hezhou
*Liangzhou ()
*Xiazhou
*Ningzhou
*Western Ningzhou (Xiningzhou)
*Southern Ningzhou (Nanningzhou)
At the same time, the Chen dynasty in the south had similar provinces with its forerunners (Liu Song
Song, known as Liu Song (), Former Song (前宋) or Song of (the) Southern Dynasty (南朝宋) in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. ...
, Southern Qi
Qi, known in historiography as the Southern Qi ( or ) or Xiao Qi (), was a Chinese imperial dynasty and the second of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties era. It followed the Liu Song dynasty and was succe ...
and Liang dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was preceded by the South ...
), but some provinces in the north and west were ceded to northern dynasties. Chen redesigned administrative divisions. It set 42 provinces, but gave provinces different ranks. Tier-1 provinces of Chen dynasty include:
*Yangzhou
*Southern Yuzhou
*Jiangzhou
*Guangzhou
*Xiangzhou
*Jiaozhou ()
*Eastern Ningzhou (Dongningzhou)
In their later years, however, Northern Qi and Northern Zhou set up many new provinces to represent areas not under their control. For example, Northern Qi set up Guangzhou which were controlled by Chen dynasty and Yizhou which were controlled by Northern Zhou. In the area between Yangtze and Huai rivers, people who ran away to escape from wars in earlier periods started to move back to their hometowns. However, many of their original hometowns were destroyed completely. As a result, people from the same town gathered and established new towns and named those towns with original names. This led to the situation that many towns with the same name were established. For example, within Luozhou and Yuzhou, there were multiple counties named Chenliu.
Chen dynasty also set up a series of new immigrant provinces along the Yangtze River, such as the Southern Xuzhou and Northern Jiangzhou, etc. The administrative division began to mess up. Northern and Southern dynasties were eventually reunified by Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
in 589. At that time, there were hundreds of provinces all over China.
Zhou under Sui dynasty
By the time unity was finally reestablished by theSui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
, the provinces had been divided and redivided so many times by different governments that they were almost the same size as commanderies, rendering the two-tier system superfluous. As such, the Sui merged the two together. In English, this merged level is translated as "prefectures". In Chinese, the name changed between ''zhou'' and ''jun'' several times before being finally settled on ''zhou''. Based on the apocryphal Nine Province system, the Sui restored nine ''zhou''.Book of Sui
The ''Book of Sui'' (''Suí Shū'') is the official history of the Sui dynasty. It ranks among the official Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written by Yan Shigu, Kong Yingda, and Zhangsun Wuji, with Wei Zheng as the lead author. ...
, Treatises, Vol 24-26, Geography
The Sui had 9 provinces, 190 prefectures, 1,225 counties, and about 9 million registered households or approximately 50 million people.

Circuits under the Tang dynasty
marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a national "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diff ...
and marcher lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in ...
s). This system was eventually generalized to other parts of the country as well and essentially merged into the circuits. Just as in the West, the greater autonomy and strength of the commissioners permitted insubordination and rebellion, which in China led to the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen conc ...
.
* Circuits and Military Districts
* Commanderies and Prefectures
* Counties
Wu'an
Wu'an is a county-level city in the southwest of Hebei Province, China, bordering Shanxi Province to the west. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Handan.
History
People's Republic
In August 1949, Wu'an was one of thr ...
, and Qinhua circuits.
Circuits under the Liao, Song and Jurchen-led Jin dynasties
 The
The Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
was further divided into five "circuits", each with a capital city. The general idea for this system was taken from the Balhae, although no captured Balhae cities were made into circuit capitals. The five capital cities were Shangjing (), meaning Supreme Capital, which is located in modern-day Inner Mongolia; Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
(), meaning Southern Capital, which is located near modern-day Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
; Dongjing (), meaning Eastern Capital, which is located near modern-day Liaoning; Zhongjing (), meaning Central Capital, which is located in modern-day Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
province near the Laoha river; and Xijing (), meaning Western Capital, which is located near modern-day Datong. Each circuit was headed by a powerful viceroy who had the autonomy to tailor policies to meet the needs of the population within his circuit. Circuits were further subdivided into administrations called fu (), which were metropolitan areas surrounding capital cities, and outside of metropolitan areas were divided into prefectures called zhou (), which themselves were divided into counties called xian (). The
The Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
abolished the commissioners and renamed their circuits 路 (''lù'', which however is still usually translated into English as "circuits"). They also added a number of army/military prefectures (州级军 ''zhouji jun'', or simply 軍/军, ''jūn'').
* Circuits (路, ''lù'')
* Prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
s (larger: 府, ''fǔ''; smaller: 州, ''zhōu''; military: 軍/军, ''jūn'')
* Counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
 The
The Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They lived in the northeast of China, later known as Manch ...
invaded China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
in Jin–Song wars
The Jin–Song Wars were a series of conflicts between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty (1115–1234) and the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279). In 1115, Jurchen tribes rebelled against their overlords, the Khitan-led Liao dynasty (916–1125), ...
of the 12th century. In 1142, peace was formalized between the Jurchen Jin dynasty Jurchen may refer to:
* Jurchen people, Tungusic people who inhabited the region of Manchuria until the 17th century
** Haixi Jurchens, a grouping of the Jurchens as identified by the Chinese of the Ming Dynasty
** Jianzhou Jurchens, a grouping of ...
and the Southern Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
, which was forced to cede all of North China
North China, or Huabei () is a geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north of the Qinling–Hu ...
to the Jurchens.
By the beginning of the 13th century, the Jurchens had moved their capital to Zhongdu
Zhongdu (, lit. "Central Capital") was the capital of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in medieval China. It was located in the southwestern part of Beijing's Xicheng District. It had a population of nearly one million by the late 12th century, and ...
(modern Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
) and had adopted Chinese administrative structures. The Song dynasty also maintained the same structure over the southern half of China that they continued to govern.
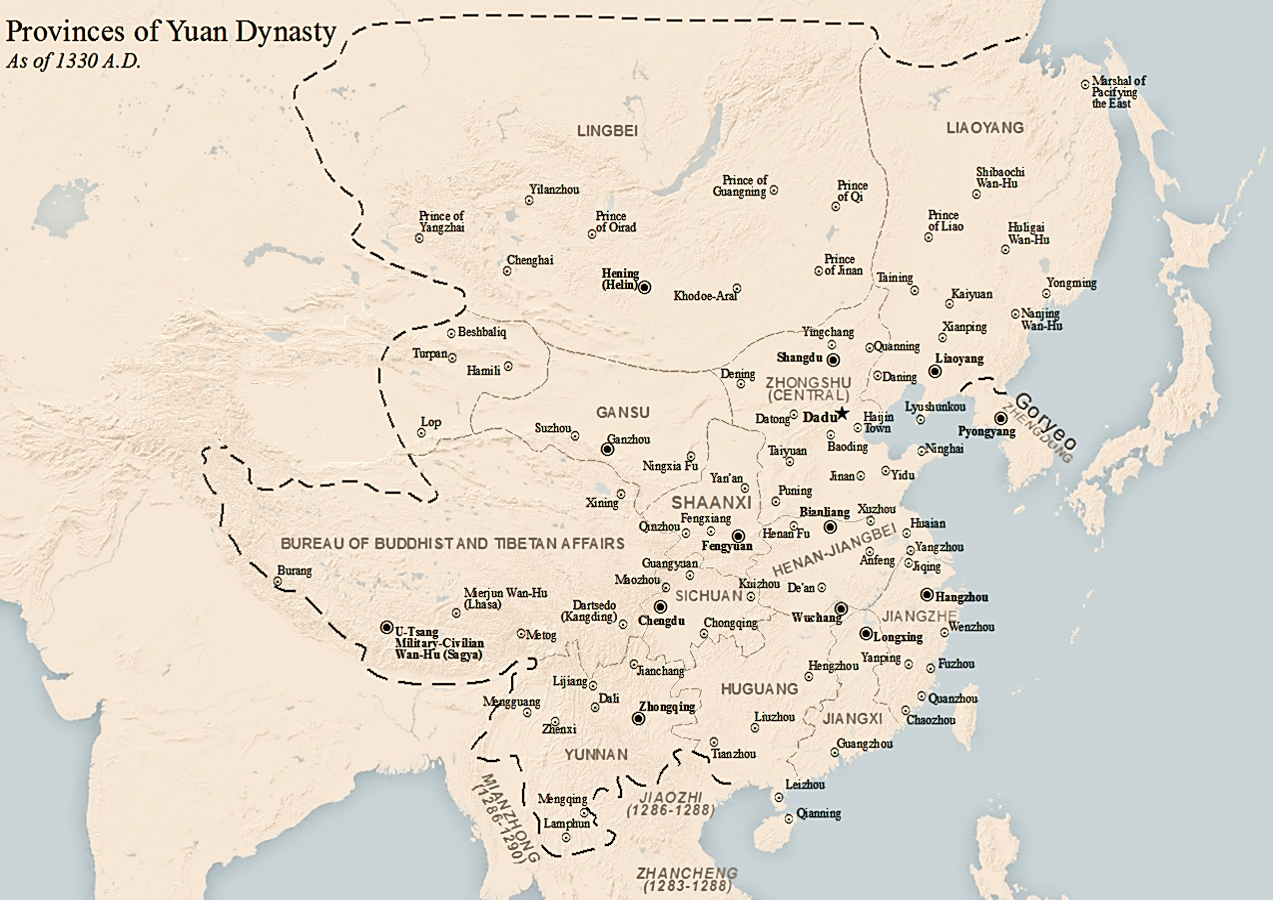
Provinces under the Yuan dynasty
 The
The Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
-led Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
, founded in 1271 and unified all of China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
in 1279, introduced the precursors to the modern provinces as a new primary administrative level:
* Province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
s (行中書省/行中书省, ''xíngzhōngshūshěng'')
* Circuits (路, ''lù'')
* Prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
s (larger: 府, ''fǔ''; smaller: 州, ''zhōu'')
* Counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
The area around the capital, corresponding to modern Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
, Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
, Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
, central Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
, and Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
, was called the Central Region (腹裏/腹里) and not put into any province, but was directly controlled by the Central Secretariat (Zhongshu Sheng). The Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
was controlled by the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs __NOTOC__
The Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan () was a government agency of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China to handle Buddhist affairs across the empire in addition to managing the territory of Tibet. It was origi ...
(Xuanzheng Yuan).
Provinces under the Ming dynasty
 The
The Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
continued with this system and had provinces that were almost exactly the same as those in modern China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
. The differences were Huguang had not yet been split into Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The p ...
and Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangx ...
; Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
and Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1 ...
were still part of Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
; Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze Riv ...
and Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with it ...
were together as South Zhili; portions of what are today the provinces of Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
, Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
, and Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
were part of the province of North Zhili
Zhili, alternately romanized as Chihli, was a northern administrative region of China since the 14th-century that lasted through the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty until 1911, when the region was dissolved, converted to a province, and rena ...
; and Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the ...
, and Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Co ...
were still parts of their original provinces at this time. This makes for a total of 15 provinces. Jiaozhi Province
Jiaozhi Province was a province of the Chinese Ming dynasty that existed during its brief rule of northern Vietnam from 1407 to 1427, known in historiography as the Fourth Era of Northern Domination. The province's name, Jiaozhi, was an earli ...
, formerly known as Jiaozhi, Jiaozhou, Lingnan and Rinan, was also re-established in 1407 when the area encompassing northern and central Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
was reconquered for the fourth time. However, the province eventually emerged as its own state in 1428 under the Later Lê dynasty
Later may refer to:
* Future, the time after the present
Television
* ''Later'' (talk show), a 1988–2001 American talk show
* '' Later... with Jools Holland'', a British music programme since 1992
* ''The Life and Times of Eddie Roberts'', or ...
of Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), often known as Annam ( vi, An Nam, Chữ Hán: 安南), was a monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day H ...
.
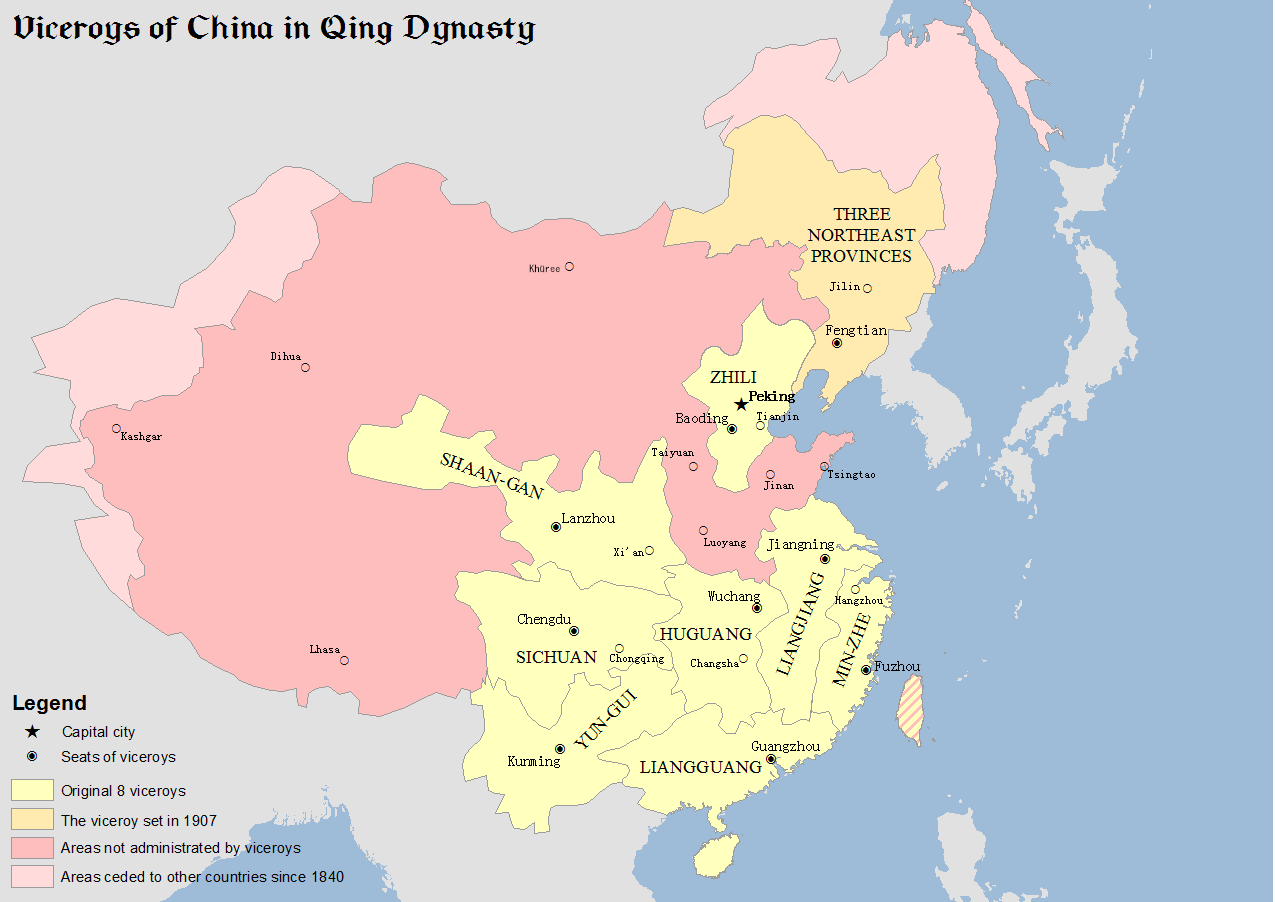
Provinces and Feudatory Regions under the Qing dynasty

 The
The Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) an ...
-led Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
was the last dynasty of China. The Qing government applied the following system over China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
:
* Province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
s (省, ''shěng'')
* Circuits (道, ''dào'')
* Prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
s (府, ''fǔ''), Independent Departments (直隸州/直隶州, ''zhílìzhōu''), and Independent Subprefecture
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independe ...
s (直隸廳/厅, ''zhílìtīng'')
* Counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
(縣/县, ''xiàn''), Departments (散州, ''sànzhōu''), Subprefecture
A subprefecture is an administrative division of a country that is below prefecture or province.
Albania
There are twelve Albanian counties or prefectures, each of which is divided into several districts, sometimes translated as subprefectures. ...
s (散廳/散厅, ''sàntīng'')
The Qing split Shaanxi into Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
and Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
, Huguang into Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The p ...
and Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangx ...
, and South Zhili into Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with it ...
and Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze Riv ...
. Hebei was now called Zhili
Zhili, alternately romanized as Chihli, was a northern administrative region of China since the 14th-century that lasted through the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty until 1911, when the region was dissolved, converted to a province, and rena ...
rather than North Zhili. These provinces are now nearly identical to modern ones. Collectively they are called the "Eighteen Provinces", a concept that endured for several centuries as synonymous to China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
.
This system applied only to China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
, with the rest of the empire under differently systems, official name is "Feudatory Regions" (藩部, ''fān bù''). Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
, and Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gain ...
were ruled by military generals assigned by the Lifan Yuan The Lifan Yuan (; ; Mongolian: Гадаад Монголын төрийг засах явдлын яам, ''γadaγadu mongγul un törü-yi jasaqu yabudal-un yamun'') was an agency in the government of the Qing dynasty of China which administered ...
, while Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
was organized into leagues. The Qing court put Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being U-Tsang in the west and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Amdo is also the bi ...
under their direct control and organized it as Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
and also sent imperial commissioners to Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
(Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered ...
and western Kham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
, approximately the area of the present-day Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions ...
) to oversee its affairs.
In the late 19th century, Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
were both set up as provinces. However, Taiwan was ceded to Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
after the First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
in 1895. Near the end of the dynasty, Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
was also reorganized into three more provinces (Fengtian Fengtian (; postal: Fengtien; Manchu: ''Abkai imiyangga fu'') is:
* Shenyang, largest city and provincial capital of Liaoning province, which was formerly administered under Fengtian Fu, which was abolished in 1910
* Liaoning, the province formerl ...
, Jilin
Jilin (; Postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three Provinces of China, provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea (Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, R ...
, Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () Postal romanization, formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a Provinces of China, province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is th ...
), bringing the total number to twenty-two. In 1906, the first romanization system of Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
, postal romanization
Postal romanization was a system of transliterating Chinese place names developed by postal authorities in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. For many cities, the corresponding postal romanization was the most common English-language form ...
, was officially sanctioned by the Imperial Postal Joint-Session Conference, which showed in the following table.
See also
*Administrative divisions of China
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there ...
* Physiographic macroregions of China Physiographic macroregions of China is a term suggested by an American anthropologist G. William Skinner as a subdivision of China Proper into nine areas according to the drainage basins of the major rivers and other travel-constraining geomorpholog ...
References
Sources and further reading
* *External links
Summary of terms
– maps of various ''sheng'', ''dao'', ''fu'', ''ting'', and ''xian'' of the late Qing era.
The province in history
by John Fitzgerald {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Administrative Divisions Of China Before 1912 Provinces of China Administrative divisions of China Former administrative divisions of China