
The recorded history of the Dominican Republic began in 1492 when the
Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
-born navigator
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
, working for the
Crown of Castile, happened upon a large island in the region of the western Atlantic Ocean that later came to be known as the
Caribbean. It was inhabited by the
Taíno
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
, an
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Great ...
an people, who called the eastern part of the island Quisqueya (Kiskeya), meaning "mother of all lands." Columbus promptly claimed the island for the
Spanish Crown, naming it La Isla Española ("the Spanish Island"), later Latinized to
Hispaniola. The Taínos were nearly wiped out due to European infectious diseases. Other causes were abuse, suicide, the breakup of family,
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompani ...
, the
encomienda system, which resembled a
feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
in Medieval Europe, war with the
Castilians, changes in lifestyle, and mixing with other peoples. Laws passed for the Indians' protection (beginning with the
Laws of Burgos, 1512–13) were never truly enforced.
What would become the
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
was the Spanish
Captaincy General of Santo Domingo until 1821, except for a time as a French colony from 1795 to 1809. It was then part of a unified Hispaniola with Haiti from 1822 until 1844. In 1844, Dominican independence was proclaimed and the republic, which was often known as Santo Domingo until the early 20th century, maintained its independence except for a short Spanish occupation from 1861 to 1865 and occupation by the United States from 1916 to 1924. During the 19th century, Dominicans were often at war, fighting the French, Haitians, Spanish, or amongst themselves, resulting in a society heavily influenced by ''
caudillo
A ''caudillo'' ( , ; osp, cabdillo, from Latin , diminutive of ''caput'' "head") is a type of personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise definition of ''caudillo'', which is often used interchangeably with " ...
s'', who ruled the country as if it were their personal kingdom. Between 1844 and 1914, the Dominican Republic had 53 presidents (of whom only 3 had completed their terms) and 19 constitutions. Most came to power through the barrel of a gun and left the same way.
Around 1930, the Dominican Republic found itself under the control of the dictator
Rafael Trujillo, who ruled the country until his assassination in 1961. Juan Bosch was elected president in 1962 but was deposed in a military coup in 1963. In 1965, the United States led an intervention in the midst of a bloody
civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
sparked by an uprising to restore Bosch. In 1966, the ''caudillo'' Joaquín Balaguer defeated Bosch in the presidential election. Balaguer maintained a tight grip on power for most of the next 30 years when U.S. reaction to flawed elections forced him to curtail his term in 1996. Since then, regular competitive elections have been held in which opposition candidates have won the presidency.
Pre-European history
The
Taíno people
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
called the island ''Quisqueya'' (mother of all lands) and ''Ayiti'' (land of high mountains). At the time of Columbus' arrival in 1492, the island's territory consisted of five chiefdoms: Marién, Maguá, Maguana,
Jaragua, and Higüey. These were ruled respectively by ''
caciques'' Guacanagarix, Guarionex, Caonabo, Bohechío, and Cayacoa.

Spanish colony: 1492–1795
Arrival of the Spanish
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
reached the island of Hispañola on his
first voyage, in December 1492.
Guacanagarí, the chief who hosted Columbus and his men, treated them kindly and provided them with everything they desired. However, the Taínos' egalitarian social system clashed with the Europeans' feudalist system, which had more rigid class structures. The Europeans believed the Taínos to be either weak or misleading, and they began to treat the tribes with violence. Columbus successfully tempered this trend, and he and his men departed from Ayiti, the Taínos' name for the island, on good terms.
After the sinking of the ''
Santa María'', Columbus established a small fort to support his claim to the island. The fort was called
La Navidad
La Navidad ("The Nativity", i.e. Christmas) was a settlement that Christopher Columbus and his men established on the northeast coast of Haiti (near what is now Caracol, Nord-Est Department, Haiti) in 1492 from the remains of the Spanish ship th ...
because the shipwrecking and the founding of the fort occurred on Christmas Day. While Columbus was away, the garrison manning the fort was wracked by divisions that evolved into conflict. The more rapacious men began to terrorize the Taíno, the
Ciguayo
At the time of first contact between Europe and the Americas, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean included the Taíno of the northern Lesser Antilles, most of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles, the Cigua ...
, and the
Macorix peoples, which included attempts to take their women. Guacanagarix tried to reach an accommodation with the Spaniards; however, the Spaniards and some of his own people viewed him as weak. The Spaniards treated him with contempt, including the kidnapping of some of his wives. Fed up, the powerful
Cacique Caonabo of the
Maguana Chiefdom attacked the Europeans and destroyed La Navidad. Guacanagarix was dismayed by these events but did not try hard to aid the Europeans, probably hoping that the troublesome outsiders would never return.
In 1493, Columbus came back to the island on his second voyage and founded the first Spanish colony in the New World, the city of
La Isabela
La Isabela in Puerto Plata Province, Dominican Republic was the first Spanish town in the Americas. The site is 42 km west of the city of Puerto Plata, adjacent to the village of El Castillo. The area now forms a National Historic Park.
...
. Isabela nearly failed because of hunger and disease. In 1496,
Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
was built and became the new capital, and remains the oldest continuously inhabited European city in the Americas.

An estimated 400,000 Tainos living on the island were soon enslaved to work in gold mines. By 1508, their numbers had decreased to around 60,000 because of forced labor, hunger, disease, and mass killings. By 1535, only a few dozen were still alive.

During this period, the colony's Spanish leadership changed several times. When Columbus departed on another exploration,
Francisco de Bobadilla
Francisco Fernández de Bobadilla (c. 1448 – 1 July 1502) was an official under the Crown of Castile and a knight of the Order of Calatrava. He was also the brother of Beatriz de Bobadilla, marchioness (''marquesa'') of Moya and of Peñalosa, ...
became governor. Settlers' allegations of mismanagement by Columbus helped create a tumultuous political situation. In 1502,
Nicolás de Ovando replaced de Bobadilla as governor, with an ambitious plan to expand Spanish influence in the region. It was he who dealt most brutally with the Taíno people. The Taino population declined by up to 95% in the century after the Spanish arrival,
[David Moshman (2007) Us and Them: Identity and Genocide, Identity: An International Journal of Theory and Research, 7:2, page 125, DOI: 10.1080/15283480701326034, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15283480701326034] from a pre contact population of tens of thousands
to 8,000,000.
Many authors have described the treatment of the Taino in
Hispaniola under the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
as genocide.
The conquistador-turned-priest
Bartolomé de las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP ( ; ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a 16th-century Spanish landowner, friar, priest, and bishop, famed as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman then became a Dominican friar ...
wrote an eyewitness history of the Spanish incursion into the island of Hispaniola that reported the conquistadors' almost feral misconduct:
One rebel, however, successfully fought back.
Enriquillo led a group who fled to the mountains and attacked the Spanish repeatedly for fourteen years. The Spanish ultimately offered him a peace treaty and gave Enriquillo and his followers their own town in 1534. The town lasted only a few years. Rebellious slaves burned it to the ground and killed all who stayed behind.
Sixteenth century
In 1501, the Spanish monarchs,
Ferdinand I and
Isabella, first granted permission to the colonists of the Caribbean to import African slaves, who began arriving to the island in 1503. In 1510, the first sizable shipment, consisting of 250
Black Ladinos, arrived in Hispaniola from Spain. Eight years later African-born slaves arrived in the
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
. The Colony of Santo Domingo was organized as the
Royal Audiencia of Santo Domingo in 1511.
Sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
was introduced to Hispaniola from the
Canary Islands, and the first sugar mill in the New World was established in 1516, on Hispaniola. The need for a labor force to meet the growing demands of sugar cane cultivation led to an exponential increase in the importation of slaves over the following two decades. The sugar mill owners soon formed a new colonial elite and convinced the Spanish king to allow them to elect the members of the
Real Audiencia from their ranks. Poorer colonists subsisted by hunting the herds of wild cattle that roamed throughout the island and selling their hides.
The first major slave revolt in the Americas occurred in
Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
on December 25, 1521, when enslaved
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
of the
Wolof nation led an uprising in the sugar plantation of admiral Don
Diego Colon, son of
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
. Many of these insurgents managed to escape to the mountains where they formed independent
maroon communities, but the Admiral had a lot of the captured rebels hanged.
While sugar cane dramatically increased Spain's earnings on the island, large numbers of the newly imported slaves fled into the nearly impassable mountain ranges in the island's interior, joining the growing communities of ''cimarrónes''—literally, 'wild animals'. By the 1530s, ''
cimarrón'' bands had become so numerous that in rural areas the Spaniards could only safely travel outside their plantations in large armed groups. When Archdeacon Alonso de Castro toured Hispaniola in 1542, he estimated the maroon population at 2,000–3,000 persons, living mainly on the Cape of San Nicolas, in the Ciguayos, on the Samana peninsular, and on the Cape of Iguey. Latter that decade, there were also rebellions of enslaved people, led by Diego de Guzman, Diego de Campo, and Captain Lemba.


Beginning in the 1520s, the
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
was raided by increasingly numerous French pirates. In 1541, Spain authorized the construction of Santo Domingo's fortified wall, and in 1560 decided to restrict sea travel to enormous, well-armed convoys. In another move, which would destroy
Hispaniola's sugar industry, in 1561
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. , more strategically located in relation to the
Gulf Stream, was selected as the designated stopping point for the merchant ''
flotas,'' which had a royal monopoly on commerce with the Americas. In 1564, the island's main inland cities
Santiago de los Caballeros
Santiago de los Caballeros (; '' en, Saint James of the Knights''), often shortened to Santiago, is the second-largest city in the Dominican Republic and the fourth-largest city in the Caribbean by population. It is the capital of Santiago Prov ...
and
Concepción de la Vega were destroyed by an earthquake. In the 1560s, English privateers joined the French in regularly raiding Spanish shipping in the Americas.
With the conquest of the American mainland, Hispaniola quickly declined. Most Spanish colonists left for the silver-mines of
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
and
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, while new immigrants from Spain bypassed the island. Agriculture dwindled, new imports of slaves ceased, and white colonists, free blacks, and slaves alike lived in poverty, weakening the racial hierarchy and aiding ''intermixing,'' resulting in a population of predominantly mixed Spaniard, African, and Taíno descent. Except for the city of Santo Domingo, which managed to maintain some legal exports, Dominican ports were forced to rely on
contraband trade, which, along with livestock, became the sole source of livelihood for the island dwellers.
In 1586, the privateer
Francis Drake of England captured the city of Santo Domingo, collecting a ransom for its return to Spanish rule. In 1592,
Christopher Newport of England attacked the town of Azua on the bay of Ocoa, which was taken and plundered.
In 1595, the Spanish, frustrated by the twenty-year
rebellion of their Dutch subjects, closed their home ports to rebel shipping from the Netherlands cutting them off from the critical salt supplies necessary for their herring industry. The Dutch responded by sourcing new salt supplies from Spanish America where colonists were more than happy to trade. So large numbers of Dutch traders and buccaneers joined their English and French counterparts on the
Spanish Main.
Seventeenth century

In 1605, Spain was infuriated that Spanish settlements on the northern and western coasts of the island were carrying out large scale and illegal trade with the Dutch, who were at that time fighting a war of independence against Spain in Europe, and the English, a very recent enemy state, and so decided to forcibly resettle the colony's inhabitants closer to the city of Santo Domingo. This action, known as the ''
Devastaciones de Osorio'', proved disastrous; more than half of the resettled colonists died of starvation or disease, over 100,000 cattle were abandoned, and many slaves escaped. Five of the existing thirteen settlements on the island were brutally razed by Spanish troops – many of the inhabitants fought, escaped to the jungle, or fled to the safety of passing Dutch ships. The settlements of La Yaguana, and Bayaja, on the west and north coasts respectively of modern-day Haiti were burned, as were the settlements of Monte Cristi and Puerto Plata on the north coast and San Juan de la Maguana in the southwestern area of the modern-day Dominican Republic.
French and English
buccaneer
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from the Restoration in 1660 until about 168 ...
s took advantage of Spain's retreat into a corner of Hispaniola to settle the island of
Tortuga, off the northwest coast of Hispaniola, in 1629. France established direct control in 1640, reorganizing it into an official colony and expanding to the north coast of Hispaniola itself, whose western end Spain ceded to France in 1697 under the
Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Gran ...
.
In 1655,
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
of England dispatched a fleet, commanded by Admiral
Sir William Penn
Sir William Penn (23 April 1621 – 16 September 1670) was an English admiral and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1660 to 1670. He was the father of William Penn, founder of the Province of Pennsylvania (today, Commonwealth of Pe ...
, to capture Santo Domingo. After meeting heavy resistance, the English retreated. Despite the fact that the English were defeated in their
attempt to capture the island, they nevertheless captured the nearby Spanish colony of
Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, and other foreign strongholds subsequently began to be established throughout the West Indies. Madrid sought to contest such encroachments on its own imperial control by using Santo Domingo as a
forward military base, but Spanish power was by now too depleted to recapture lost colonies. The city itself was furthermore subjected to a
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
epidemic, cacao blight, and hurricane in 1666; another storm two years later; a second epidemic in 1669; a third hurricane in September 1672; plus an earthquake in May 1673 that killed twenty-four residents.
Eighteenth century

The
House of Bourbon replaced the
House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
in Spain in 1700 and introduced economic reforms that gradually began to revive trade in Santo Domingo. The crown progressively relaxed the rigid controls and restrictions on commerce between Spain and the colonies and among the colonies. The last ''flotas'' sailed in 1737; the monopoly port system was abolished shortly thereafter. By the middle of the century, the population was bolstered by emigration from the
Canary Islands, resettling the northern part of the colony and planting tobacco in the
Cibao Valley, and importation of slaves was renewed. The population of Santo Domingo grew from about 6,000 in 1737 to approximately 125,000 in 1790. Of this number, about 40,000 were white landowners, about 25,000 were mulatto freedmen, and some 60,000 were slaves. However, it remained poor and neglected, particularly in contrast with its western, French neighbor
Saint-Domingue, which became the wealthiest colony in the New World and had half a million inhabitants.
When the
War of Jenkins' Ear
The War of Jenkins' Ear, or , was a conflict lasting from 1739 to 1748 between Britain and the Spanish Empire. The majority of the fighting took place in New Granada and the Caribbean Sea, with major operations largely ended by 1742. It is con ...
broke out in 1739, Spanish
privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s, including those from Santo Domingo, began to patrol the Caribbean Sea, a development that lasted until the end of the eighteenth century. During this period, Spanish privateers from Santo Domingo sailed into enemy ports looking for ships to plunder, thus disrupting commerce between Spain's enemies in the
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
. As a result of these developments, Spanish privateers frequently sailed back into Santo Domingo with their holds filled with captured plunder which were sold in Hispaniola's ports, with profits accruing to individual sea raiders. The revenue acquired in these acts of piracy was invested in the economic expansion of the colony and led to repopulation from Europe.
Dominican privateers captured British, Dutch, French and Danish ships throughout the eighteenth century. Dominicans constituted one of the many diverse units which fought alongside Spanish forces under Bernardo de Gálvez during the conquest of
British West Florida
British West Florida was a colony of the Kingdom of Great Britain from 1763 until 1783, when it was ceded to Spain as part of the Peace of Paris.
British West Florida comprised parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Alab ...
(1779–1781).
As restrictions on colonial trade were relaxed, the colonial elites of St. Domingue offered the principal market for Santo Domingo's exports of beef, hides, mahogany, and tobacco. With the outbreak of the
Haitian Revolution in 1791, the rich urban families linked to the colonial bureaucracy fled the island, while most of the rural ''hateros'' (cattle ranchers) remained, even though they lost their principal market. Spain saw in the unrest an opportunity to seize all, or part, of the western third of the island in an alliance of convenience with the rebellious slaves. But after the slaves and French reconciled, the Spanish suffered a setback, and in 1795, France gained control of the whole island under the
Treaty of Basel.
French occupation
In 1801,
Toussaint Louverture
François-Dominique Toussaint Louverture (; also known as Toussaint L'Ouverture or Toussaint Bréda; 20 May 1743 – 7 April 1803) was a Haitian general and the most prominent leader of the Haitian Revolution. During his life, Louverture ...
arrived in Santo Domingo, proclaiming the abolition of slavery on behalf of the French Republic. Shortly afterwards, Napoleon dispatched an army which subdued the whole island and ruled it for a few months. Mulattoes and blacks again rose up against these French in October 1802 and finally defeated them in November 1803. On 1 January 1804, the victors declared Saint-Domingue to be the independent republic of Haiti, the Taíno name for the entire island. Even after their defeat by the Haitians, a small French garrison remained in Santo Domingo. Slavery was reestablished and many of the émigré Spanish colonists returned. In 1805, after crowning himself Emperor, Jean-Jacques Dessalines invaded, reaching Santo Domingo before retreating in the face of a French naval squadron. In their retreat through the
Cibao
The Cibao, usually referred as "El Cibao", is a region of the Dominican Republic located at the northern part of the country. As of 2009 the Cibao has a population of 5,622,378 making it the most populous region in the country.
The region constit ...
, the Haitians sacked the towns of Santiago and
Moca, slaughtering most of their residents.
The French held on to the eastern part of the island until dealt a serious blow by the Dominican General Juan Sánchez Ramírez at the
Battle of Palo Hincado on November 7, 1808. With help from the
British Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
, Ramírez laid siege to the city of Santo Domingo. The French in the besieged city finally capitulated on July 9, 1809, initiating a twelve-year period of Spanish rule, known in Dominican history as "
the Foolish Spain."
Spanish colony: 1809–1821
The population of the new Spanish colony stood at approximately 104,000. Of this number, about 30,000 were slaves, working predominantly on cattle ranches, and the rest a mixture of Spanish,
taino and black. The European Spaniards were few, and consisted principally of
Catalans
Catalans (Catalan, French and Occitan: ''catalans''; es, catalanes, Italian: ''catalani'', sc, cadelanos) are a Romance ethnic group native to Catalonia, who speak Catalan. The current official category of "Catalans" is that of the citize ...
and
Canary Islanders.
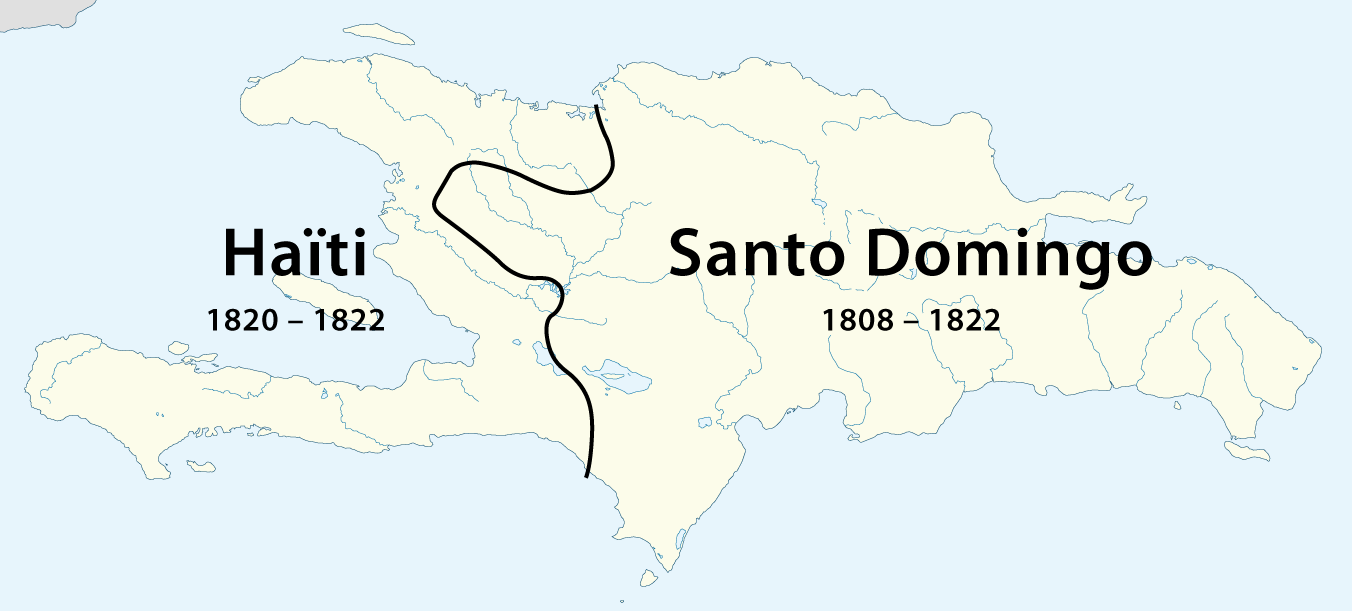
During this period in time, the Spanish crown wielded little to no influence in the colony of Santo Domingo. Some wealthy cattle ranchers had become leaders, and sought to bring control and order in the southeast of the colony where the "law of machete" ruled the land. On December 1, 1821, the former Captain general in charge of the colony,
José Núñez de Cáceres, influenced by all the
Revolutions
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
that were going on around him, finally decided to overthrow the Spanish government and proclaimed the independence of "
Spanish Haiti
The Independent Republic of Spanish Haiti ( es, República del Haití Español), also called the Independent State of Spanish Haiti () was the independent state that resulted from the defeat of Spanish colonialists from Santo Domingo on November ...
".
The white and mulatto slave owners on the eastern part of the island—recognizing their vulnerability both to Spanish and to Haitian attack and also seeking to maintain their slaves as property—attempted to annex themselves to
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central Ameri ...
. While this request was in transit,
Jean-Pierre Boyer
Jean-Pierre Boyer (15 February 1776 – 9 July 1850) was one of the leaders of the Haitian Revolution, and President of Haiti from 1818 to 1843. He reunited the north and south of the country into the Republic of Haiti in 1820 and also annexed ...
, the ruler of Haiti, invaded Santo Domingo on February 9, 1822, with a 10,000-strong army. Having no capacity to resist, Núñez de Cáceres surrendered the capital.
Haitian occupation 1822–1844
The twenty-two-year Haitian occupation that followed is recalled by Dominicans as a period of brutal military rule, though the reality is more complex. It led to large-scale land expropriations and failed efforts to force production of export crops, impose military services, restrict the use of the Spanish language, and eliminate traditional customs such as
cockfighting
A cockfight is a blood sport, held in a ring called a cockpit. The history of raising fowl for fighting goes back 6,000 years. The first documented use of the ''word'' gamecock, denoting use of the cock as to a "game", a sport, pastime or ente ...
. It reinforced Dominicans' perceptions of themselves as different from Haitians in "language, race, religion and domestic customs". Yet, this was also a period that definitively ended slavery as an institution in the eastern part of the island.
Haiti's constitution forbade whites from owning land, and the major landowning families were forcibly deprived of their properties. Most emigrated to the Spanish colonies of Cuba and Puerto Rico, or to independent Gran Colombia, usually with the encouragement of Haitian officials, who acquired their lands. The Haitians, who associated the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
with the French slave-masters who had exploited them before independence, confiscated all church property, deported all foreign clergy, and severed the ties of the remaining clergy to the
Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
.
Santo Domingo's university, the oldest in the Western Hemisphere, lacking students, teachers, and resources, closed down. In order to receive diplomatic recognition from
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and end the threat of a French invasion, Haiti was forced to pay an indemnity of 150 million francs to the former French colonists, which was subsequently lowered to 60 million francs, and Haiti imposed heavy taxes on the eastern part of the island. Since Haiti was unable to adequately provision its army, the occupying forces largely survived by commandeering or confiscating food and supplies at gunpoint.
Attempts to redistribute land conflicted with the system of communal land tenure (''terrenos comuneros''), which had arisen with the ranching economy, and newly emancipated slaves resented being forced to grow cash crops under Boyer's ''Code Rural''. In rural areas, the Haitian administration was usually too inefficient to enforce its own laws. It was in the city of Santo Domingo that the effects of the occupation were most acutely felt, and it was there that the movement for independence originated.
Independence: First Republic 1844–1861
On July 16, 1838,
Juan Pablo Duarte
Juan Pablo Duarte y Díez (January 26, 1813 – July 15, 1876) was a Dominican military leader, writer, activist, and nationalist politician who was the foremost of the founding fathers of the Dominican Republic and bears the title of Father of ...
together with Pedro Alejandrino Pina, Juan Isidro Pérez, Felipe Alfau, Benito González, Félix María Ruiz, Juan Nepumoceno Ravelo and Jacinto de la Concha founded a secret society called ''
La Trinitaria'' to win independence from Haiti. A short time later, they were joined by
Ramón Matías Mella, and
Francisco del Rosario Sánchez
Francisco del Rosario Sánchez (March 9, 1817 – July 4, 1861) was a Dominican revolutionary, politician, and former president of the Dominican Republic. He is considered by Dominicans as the second leader of the 1844 Dominican War of Independe ...
. In 1843, they allied with a Haitian movement in overthrowing Boyer. Because they had revealed themselves as revolutionaries working for Dominican independence, the new Haitian president,
Charles Rivière-Hérard, exiled or imprisoned the leading ''Trinitarios'' (Trinitarians). At the same time,
Buenaventura Báez
Ramón Buenaventura Báez Méndez (July 14, 1812March 14, 1884), was a Dominican politician and military figure. He was president of the Dominican Republic for five nonconsecutive terms. His rule was characterized by being very corrupt and govern ...
, an
Azua mahogany exporter and deputy in the
Haitian National Assembly, was negotiating with the French Consul-General for the establishment of a French protectorate. In an uprising timed to preempt Báez, on February 27, 1844, the Trinitarios declared independence from Haiti, expelling all Haitians and confiscating their property. The Trinitarios were backed by
Pedro Santana, a wealthy cattle-rancher from
El Seibo
El Seibo (), alternatively spelt El Seybo, is a Provinces of the Dominican Republic, province of the Dominican Republic. Before 1992 it included what is now Hato Mayor Province, Hato Mayor province.
Municipalities and municipal districts
The pro ...
who commanded a private army of
peons who worked on his estates.
In March 1844, Rivière-Hérard sent three columns totaling 30,000 troops to reestablish his authority. In the south, Santana defeated Rivière-Hérard at the
Battle of Azua on March 19. The outnumbered Dominican forces suffered only five casualties in the battle, while the Haitians sustained over 1,000 killed. In the north, the Haitian column led by Jean-Louis Pierrot was repelled in an attack on Santiago by Dominican forces entrenched in a fort. The Haitians again suffered disproportionate casualties.
Meanwhile, at sea, the Dominicans defeated the Haitians at the
Battle of Tortuguero off the coast of Azua on April 15, temporarily expelling Haitian forces.
First Republic

In July 1844, Pedro Santana seized power from the liberal president Francisco del Rosario Sánchez in a military coup after Rosario Sánchez ousted the conservative
Tomás Bobadilla from power. Santana inaugurated a military dictatorship with Bobadilla as a member of his junta.
The Dominican Republic's first
constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
was adopted on November 6, 1844. The state was commonly known as Santo Domingo in English until the early 20th century. It featured a presidential form of government with many liberal tendencies, but it was marred by Article 210, imposed by Santana on the constitutional assembly by force, giving him the privileges of a dictatorship until the
war of independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List o ...
was over. These privileges not only served him to win the war but also allowed him to persecute, execute and drive into exile his political opponents, among which Duarte was the most important. Santana imprisoned and ultimately exiled Duarte to Germany. Santana made the first martyr of the republic when he had
María Trinidad Sánchez executed for refusing to name "conspirators" against him.
During the first decade of independence, Haiti and the Dominican Republic were periodically at war, each invading the other in response to previous invasions. Santana used the ever-present threat of Haitian invasion as a justification for consolidating dictatorial powers. For the Dominican elite—mostly landowners, merchants and priests—the threat of re-annexation by more populous Haiti was sufficient to seek protection from a
foreign power. Offering the deepwater harbor of
Samaná bay as bait, over the next two decades, negotiations were made with Britain, France, the United States and Spain to declare a protectorate over the country.
The population of the Dominican Republic in 1845 was approximately 230,000 people (100,000 whites; 40,000 blacks; and 90,000 mulattoes).
Without adequate roads, the regions of the Dominican Republic developed in isolation from one another. In the south, the economy was dominated by cattle-ranching (particularly in the southeastern savannah) and cutting mahogany and other hardwoods for export. This region retained a semi-feudal character, with little commercial agriculture, the ''
hacienda'' as the dominant social unit, and the majority of the population living at a subsistence level.
In the
Cibao Valley, the nation's richest farmland, peasants supplemented their subsistence crops by growing
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
for export, mainly to Germany. Tobacco required less land than cattle ranching and was mainly grown by smallholders, who relied on itinerant traders to transport their crops to
Puerto Plata and
Monte Cristi. Santana antagonized the Cibao farmers, enriching himself and his supporters at their expense by resorting to multiple peso printings that allowed him to buy their crops for a fraction of their value.
In 1848, Santana was forced to resign and was succeeded by his vice-president,
Manuel Jimenes
Manuel José Jimenes González (January 14, 1808December 22, 1854) was a military figure and politician in the Dominican Republic. He served as the second President of the Dominican Republic from September 8, 1848, until May 29, 1849. Prior to ...
. After returning to lead Dominican forces against a new Haitian invasion in 1849, Santana marched on Santo Domingo, deposing Jimenes. At his behest, Congress elected
Buenaventura Báez
Ramón Buenaventura Báez Méndez (July 14, 1812March 14, 1884), was a Dominican politician and military figure. He was president of the Dominican Republic for five nonconsecutive terms. His rule was characterized by being very corrupt and govern ...
as president.
Báez immediately began an offensive campaign against Haiti; whole villages on the Haitian coast were plundered and burned, and the crews of captured ships were butchered without regard to age or gender.
In 1853, Santana was elected president for his second term, forcing Báez into exile. After repulsing the last Haitian invasion, Santana negotiated a treaty leasing a portion of Samaná Peninsula to a U.S. company; popular opposition forced him to abdicate, enabling Báez to return and seize power.
With the treasury depleted, Báez printed eighteen million uninsured pesos, purchasing the 1857 tobacco crop with this currency and exporting it for hard cash at immense profit to himself and his followers. The Cibanian tobacco planters, who were ruined when inflation ensued, revolted, recalling Santana from exile to lead their rebellion. After a year of civil war, Santana seized Santo Domingo and installed himself as president.
Spanish colony: 1861–1865
Pedro Santana inherited a bankrupt government on the brink of collapse. Having failed in his initial bids to secure annexation by the U.S. or France, Santana initiated negotiations with Queen
Isabella II of Spain
Isabella II ( es, Isabel II; 10 October 1830 – 9 April 1904), was Queen of Spain from 29 September 1833 until 30 September 1868.
Shortly before her birth, the King Ferdinand VII of Spain issued a Pragmatic Sanction to ensure the successi ...
and the Captain-General of Cuba to have the island reconverted into a Spanish colony.
The
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
rendered the United States incapable of enforcing the
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile act ...
. In Spain, Prime Minister
Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
Leopoldo O'Donnell
Leopoldo O'Donnell y Jorris, 1st Duke of Tetuán, GE (12 January 1809 – 5 November 1867), was a Spanish general and Grandee who was Prime Minister of Spain on several occasions.
Early life
He was born at Santa Cruz de Tenerife in the Canar ...
advocated renewed colonial expansion,
waging a campaign in northern
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
that conquered the city of
Tétouan
Tétouan ( ar, تطوان, tiṭwān, ber, ⵜⵉⵟⵟⴰⵡⴰⵏ, tiṭṭawan; es, Tetuán) is a city in northern Morocco. It lies along the Martil Valley and is one of the two major ports of Morocco on the Mediterranean Sea, a few miles so ...
. In March 1861, Santana officially restored the Dominican Republic to Spain.
This move was widely rejected and there were several failed uprisings against Spanish rule. On July 4, 1861, former President Francisco del Rosario Sánchez was captured and executed by Santana after leading a failed invasion of Santo Domingo from Haiti.
War of Restoration
On August 16, 1863, a
national war of restoration began in
Monte Cristi Province, where the rebels defeated Spanish detachments. On September 4, Spanish reinforcements marched from Puerto Plata to relieve the besieged garrison of Santiago, defeating the rebels under the command of Gaspar Polanco and Gregorio Luperon. The rebels later burned the town and besieged the forts again. On September 14, the Spaniards abandoned Santiago and made their way to Puerto Plata harassed by guerrilla attacks that inflicted 1,300 casualties. In December 1863, a Spanish expedition sent west along the southern seacoast was successful in expelling rebel bands (already demoralized by dissensions) from San Cristobal, Bani, Azua, Barohona, Neiba, and San Juan, and driving them into Haiti.
Santana, who had been given the title of
Marquess of Las Carreras by Queen Isabella II, initially was named Capitan-General of the new Spanish province, but it soon became obvious that Spanish authorities planned to deprive him of his power, leading him to resign in 1862. Condemned to death by the provisional government, Santana died of
rheumatic fever in 1864.
Restrictions on trade, discrimination against the mulatto majority, Rumors to reimpose slavery, and an unpopular campaign by the new Spanish Archbishop against extramarital unions, which were widespread after decades of abandonment by the Catholic Church, all fed resentment of Spanish rule.
Confined to the major towns, Spain's largely
mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any ...
army was unable to defeat the
guerillas
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tacti ...
or contain the insurrection, and suffered heavy losses due to
yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
. In the south, Dominican forces under
José María Cabral defeated the Spanish in an open field at the Battle of La Canela on December 4, 1864.
Spanish colonial authorities encouraged Queen Isabella II to abandon the island, seeing the occupation as a nonsensical waste of troops and money. However, the rebels were in a state of political disarray and proved unable to present a cohesive set of demands. The first president of the provisional government,
Pepillo Salcedo (allied with Báez) was deposed by General
Gaspar Polanco in September 1864, who, in turn, was deposed by General Antonio Pimentel three months later. The rebels formalized their provisional rule by holding a national convention in February 1865, which enacted a new constitution, but the new government exerted little authority over the various regional guerrilla ''
caudillo
A ''caudillo'' ( , ; osp, cabdillo, from Latin , diminutive of ''caput'' "head") is a type of personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise definition of ''caudillo'', which is often used interchangeably with " ...
s'', who were largely independent of one another.
Unable to extract concessions from the disorganized rebels, when the American Civil War ended, in March 1865, Queen Isabella annulled the annexation and independence was restored, with the last Spanish troops departing by July.
Restoration: Second Republic 1865–1916
Second Republic
By the time the Spanish departed, most of the main towns lay in ruins and the island was divided among several dozen ''caudillos''.
José María Cabral controlled most of
Barahona and the southwest with the support of Báez's mahogany-exporting partners, while cattle rancher
Cesáreo Guillermo assembled a coalition of former ''Santanista'' generals in the southeast, and
Gregorio Luperón controlled the north coast.
From the Spanish withdrawal to 1879, there were twenty-one changes of government and at least fifty military uprisings. In the course of these conflicts, two parties emerged. The
Partido Rojo (Literally "Red Party") represented the southern cattle ranching
latifundia
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious" and ''fundus'', "farm, estate") is a very extensive parcel of privately owned land. The latifundia of Roman history were great landed estates specializing in agriculture destined for export: grain, o ...
and mahogany-exporting interests, as well as the artisans and laborers of Santo Domingo, and was dominated by Báez, who continued to seek annexation by a foreign power. The
Partido Azul (literally "Blue Party"), led by Luperón, represented the tobacco farmers and merchants of the Cibao and Puerto Plata and was nationalist and liberal in orientation.
During these wars, the small and corrupt national army was far outnumbered by militias organized and maintained by local ''caudillos'' who set themselves up as provincial governors. These militias were filled out by poor farmers or landless plantation workers impressed into service who usually took up banditry when not fighting in revolution.

Within a month of the nationalist victory, Cabral, whose troops were the first to enter Santo Domingo, ousted Pimentel, but a few weeks later General Guillermo led a rebellion in support of Báez, forcing Cabral to resign and allowing Báez to retake the presidency in October.
Báez was overthrown by the Cibao farmers under Luperón, leader of the Partido Azul, the following spring, but Luperón's allies turned on each other and Cabral reinstalled himself as president in a coup in 1867. After bringing several ''Azules'' ("Blues") into his cabinet the ''Rojos'' ("Reds") revolted, returning Báez to power.
In 1869, U.S. President
Ulysses S. Grant ordered U.S. Marines to the island for the first time. Dominican pirates operating from Haiti had been raiding U.S. merchant shipping in the Caribbean,
and Grant directed the Marines to stop them at their source.
[
Following the virtual takeover of the island, Báez negotiated a treaty of annexation with the United States. Supported by ]U.S. Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
William Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
, who hoped to establish a Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
base at Samaná, in 1871 the treaty was defeated in the United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and pow ...
through the efforts of abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
Senator Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner (January 6, 1811March 11, 1874) was an American statesman and United States Senator from Massachusetts. As an academic lawyer and a powerful orator, Sumner was the leader of the anti-slavery forces in the state and a leader of th ...
.
In 1874, the ''Rojo'' governor of Puerto Plata, Ignacio Maria González Santín, staged a coup in support of an ''Azul'' rebellion but was deposed by the ''Azules'' two years later. In February 1876, Ulises Espaillat, backed by Luperón, was named president, but ten months later troops loyal to Báez returned him to power. One year later, a new rebellion allowed González to seize power, only to be deposed by Cesáreo Guillermo in September 1878, who was in turn deposed by Luperón in December 1879.
Ruling the country from his hometown of Puerto Plata, enjoying an economic boom due to increased tobacco exports to Germany, Luperón enacted a new constitution setting a two-year presidential term limit and providing for direct elections, suspended the semi-formal system of bribes and initiated construction on the nation's first railroad, linking the town of La Vega with the port of Sánchez on Samaná Bay.
The Ten Years' War
The Ten Years' War ( es, Guerra de los Diez Años; 1868–1878), also known as the Great War () and the War of '68, was part of Cuba's fight for independence from Spain. The uprising was led by Cuban-born planters and other wealthy natives. O ...
in Cuba brought Cuban sugar planters to the country in search of new lands and security from the insurrection that freed their slaves and destroyed their property. Most settled in the southeastern coastal plain, and, with assistance from Luperón's government, built the nation's first mechanized sugar mills. They were later joined by Italians, Germans, Puerto Ricans and Americans in forming the nucleus of the Dominican sugar bourgeoisie, marrying into prominent families to solidify their social position.
Disruptions in global production caused by the Ten Years' War, the American Civil War and the Franco-Prussian War allowed the Dominican Republic to become a major sugar exporter. Over the following two decades, sugar surpassed tobacco as the leading export, with the former fishing hamlets of San Pedro de Macorís
San Pedro de Macorís is a city and municipality (''municipio'') in the Dominican Republic and the capital of the San Pedro de Macorís province in the east region of the country; it is among the 10 largest cities of the Dominican Republic. The ...
and La Romana transformed into thriving ports. To meet their need for better transportation, over 300 miles of private rail-lines were built by and serving the sugar plantations by 1897.
An 1884 slump in prices led to a wage freeze, and a subsequent labor shortage was filled by migrant workers from the Leeward Islands—the Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands ( es, Islas Vírgenes) are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rico Trench and St. Cro ...
, St. Kitts and Nevis, Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The terr ...
, and Antigua (referred to by Dominicans as '' cocolo''s). These English-speaking blacks were often victims of racism, but many remained in the country, finding work as stevedore
A stevedore (), also called a longshoreman, a docker or a dockworker, is a waterfront manual laborer who is involved in loading and unloading ships, trucks, trains or airplanes.
After the shipping container revolution of the 1960s, the number ...
s and in railroad construction and sugar refineries.
Ulises Heureaux and U.S. protectorate
 Allying with the emerging sugar interests, the dictatorship of General
Allying with the emerging sugar interests, the dictatorship of General Ulises Heureaux
Ulises Hilarión Heureaux Leibert (; October 21, 1845 – July 26, 1899) nicknamed Lilís, was president of the Dominican Republic from September 1, 1882 to September 1, 1884, from January 6, 1887 to February 27, 1889 and again from April 30, 18 ...
, who was popularly known as Lilís, brought unprecedented stability to the island through an iron-fisted rule that lasted almost two decades. The son of a Haitian father and a mother from St. Thomas, Virgin Islands, Lilís was distinguished by his blackness from most Dominican political leaders, with the exception of Luperón. He served as President 1882–1883, 1887, and 1889–1899, wielding power through a series of puppet presidents when not occupying the office. Incorporating both '' Rojos'' and '' Azules'' into his government, he developed an extensive network of spies and informants to crush potential opposition. His government undertook a number of major infrastructure projects, including the electrification of Santo Domingo, the beginning of telephone and telegraph service, the construction of a bridge over the Ozama River, and the completion of a single-track railroad linking Santiago and Puerto Plata, financed by the Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
-based Westendorp Co.
Lilís's dictatorship was dependent upon heavy borrowing from European and American banks to enrich himself, stabilize the existing debt, strengthen the bribe system, pay for the army, finance infrastructural development and help set up sugar mills. However, sugar prices underwent a steep decline in the last two decades of the 19th century. When the Westendorp Co. went bankrupt in 1893, he was forced to mortgage the nation's customs fees, the main source of government revenues, to a New York financial firm called the San Domingo Improvement Co. (SDIC), which took over its railroad contracts and the claims of its European bondholders in exchange for two loans, one of $1.2 million and the other of £2 million.
As the growing public debt made it impossible to maintain his political machine, Heureaux relied on secret loans from the SDIC, sugar planters and local merchants. In 1897, with his government virtually bankrupt, Lilís printed five million uninsured pesos, known as ''papeletas de Lilís'', ruining most Dominican merchants and inspiring a conspiracy that ended in his death. In 1899, when Lilís was assassinated by the Cibao tobacco merchants whom he had been begging for a loan, the national debt was over $35 million, fifteen times the annual budget.
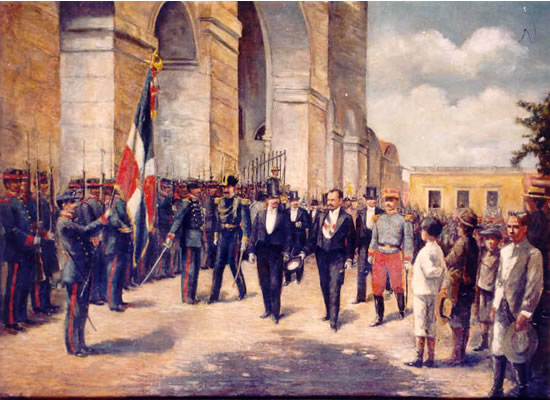 The six years after Lilís's death witnessed four revolutions and five different presidents. The Cibao politicians who had conspired against Heureaux— Juan Isidro Jimenes, the nation's wealthiest tobacco planter, and General
The six years after Lilís's death witnessed four revolutions and five different presidents. The Cibao politicians who had conspired against Heureaux— Juan Isidro Jimenes, the nation's wealthiest tobacco planter, and General Horacio Vásquez
Felipe Horacio Vásquez Lajara (October 22, 1860 – March 25, 1936) was a Dominican general and political figure. He served as the president of the Provisional Government Junta of the Dominican Republic in 1899, and again between 1902 and 1903. ...
—after being named president and Vice-President, quickly fell out over the division of spoils among their supporters, the ''Jimenistas'' and ''Horacistas''.
Troops loyal to Vásquez overthrew Jimenes in 1903, but Vásquez was deposed by Jimenista General Alejandro Woss y Gil, who seized power for himself. The Jimenistas toppled his government, but their leader, Carlos Morales, refused to return power to Jimenes, allying with the Horacistas, and he soon faced a new revolt by his betrayed Jimenista allies. During the revolt, American warships bombarded insurgents in Santo Domingo for insulting the United States flag and damaging an American steamer.
With the nation on the brink of defaulting, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
sent warships to Santo Domingo to press the claims of their nationals. In order to preempt military intervention, United States president Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
introduced the Roosevelt Corollary
In the history of United States foreign policy, the Roosevelt Corollary was an addition to the Monroe Doctrine articulated by President Theodore Roosevelt in his State of the Union address in 1904 after the Venezuelan crisis of 1902–1903. ...
to the Monroe Doctrine, declaring that the United States would assume responsibility for ensuring that the nations of Latin America met their financial obligations.
In January 1905, under this corollary, the United States assumed administration of the Dominican Republic's customs. Under the terms of this agreement, a Receiver-General, appointed by the U.S. president, kept 55% of total revenues to pay off foreign claimants, while remitting 45% to the Dominican government. After two years, the nation's external debt was reduced from $40 million to $17 million. In 1907, this agreement was converted into a treaty, transferring control over customs receivership to the U.S. Bureau of Insular Affairs
The Bureau of Insular Affairs was a division of the United States Department of War that oversaw civil aspects of the administration of several territories from 1898 until 1939.
History
The bureau was created 13 December 1898 as the Division of ...
and providing a loan of $20 million from a New York bank as payment for outstanding claims, making the United States the Dominican Republic's only foreign creditor. In 1905, the Dominican Peso was replaced by the U.S. Dollar.
 In 1906, Morales resigned, and Horacista vice-president Ramón Cáceres became president. After suppressing a rebellion in the northwest by Jimenista General Desiderio Arias, his government brought political stability and renewed economic growth, aided by new American investment in the sugar industry.
However, his assassination in 1911, for which Morales and Arias were at least indirectly responsible, once again plunged the republic into chaos. For two months, executive power was held by a civilian junta dominated by the chief of the army, General Alfredo Victoria. The surplus of more than 4 million pesos left by Cáceres was quickly spent to suppress a series of insurrections. He forced Congress to elect his uncle, Eladio Victoria, as president, but the latter was soon replaced by the neutral Archbishop Adolfo Nouel. After four months, Nouel resigned and was succeeded by Horacista Congressman José Bordas Valdez, who aligned with Arias and the Jimenistas to maintain power.
In 1906, Morales resigned, and Horacista vice-president Ramón Cáceres became president. After suppressing a rebellion in the northwest by Jimenista General Desiderio Arias, his government brought political stability and renewed economic growth, aided by new American investment in the sugar industry.
However, his assassination in 1911, for which Morales and Arias were at least indirectly responsible, once again plunged the republic into chaos. For two months, executive power was held by a civilian junta dominated by the chief of the army, General Alfredo Victoria. The surplus of more than 4 million pesos left by Cáceres was quickly spent to suppress a series of insurrections. He forced Congress to elect his uncle, Eladio Victoria, as president, but the latter was soon replaced by the neutral Archbishop Adolfo Nouel. After four months, Nouel resigned and was succeeded by Horacista Congressman José Bordas Valdez, who aligned with Arias and the Jimenistas to maintain power.
 In 1913, Vásquez returned from exile in Puerto Rico to lead a new rebellion. In June 1914, U.S. President
In 1913, Vásquez returned from exile in Puerto Rico to lead a new rebellion. In June 1914, U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
issued an ultimatum for the two sides to end hostilities and agree on a new president, or have the United States impose one. After the provisional presidency of Ramón Báez, Jimenes was elected in October, and soon faced new demands, including the appointment of an American director of public works and financial advisor and the creation of a new military force commanded by U.S. officers. The Dominican Congress rejected these demands and began impeachment proceedings against Jimenes.
The United States occupied Haiti in July 1915, with the implicit threat that the Dominican Republic might be next. Jimenes's Minister of War Desiderio Arias staged a coup d'état in April 1916, providing a pretext for the United States to occupy the Dominican Republic.
United States occupation: 1916–1924
Conventional campaign
United States Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through com ...
landed in Santo Domingo on May 15, 1916. Prior to their landing, Jimenes resigned, refusing to exercise an office "regained with foreign bullets". On June 1, Marines occupied Monte Cristi and Puerto Plata.
On June 26, a column of Marines under Colonel Joseph H. Pendleton marched toward Arias's stronghold of Santiago. Along the way, Dominicans tore up the railroad tracks, forcing Marines to walk; they also burned bridges, delaying the march. Twenty-four miles into the march, the Marines encountered Las Trencheras, two fortified ridges the Dominicans had long thought invulnerable: the Spanish had been defeated there in 1864. At 08:00 hours on June 27, Pendleton ordered his artillery to pound the ridgeline. Machine guns offered covering fire. A bayonet attack cleared the first ridge. Rifle fire removed the rebels who were threatening from atop the second.
A week later, the Marines encountered another entrenched rebel force at Guayacanas. The rebels kept up single-shot
Single-shot firearms are firearms that hold only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot. The history of firearms began with single-shot designs, then multi-barreled designs appeared, and eventually many cent ...
fire against the automatic weapons of the Marines before the Marines drove them off. With his supporters defeated, Arias surrendered on July 5 in exchange for being pardoned.
Occupation
 The Dominican Congress elected Dr. Francisco Henríquez y Carvajal as president, but in November, after he refused to meet the U.S. demands, Wilson announced the imposition of a U.S. military government, with Rear Admiral
The Dominican Congress elected Dr. Francisco Henríquez y Carvajal as president, but in November, after he refused to meet the U.S. demands, Wilson announced the imposition of a U.S. military government, with Rear Admiral Harry Shepard Knapp
Harry Shepard Knapp (June 27, 1856 – April 6, 1923) was a Vice Admiral of the United States Navy, Military Governor of Santo Domingo, and Military Representative of the United States in Haiti.
Biography
Born in New Britain, Connecticut, Knapp gr ...
as Military Governor.
At San Francisco de Macorís
San Francisco de Macorís is a city in the Dominican Republic located in the northeast portion of the island, in the Cibao region. It is the capital of the Duarte Province, and the sixth most populated city in the country. The name ''San Fran ...
, Governor Juan Pérez, a supporter of Arias, refused to recognize the U.S. military government. Using some 300 released prisoners, he was preparing to defend the old Spanish colonial structure, the '' Fortazela''. On November 29, U.S. Marine Lt. Ernest C. Williams, whose detachment was billeted in San Francisco, charged the closing gates of the fort at nightfall with twelve Marines. Eight were shot down; the others, including Williams, forced their way in and seized the old structure. Another Marine detachment seized the police station. Reinforcements from nearby detachments soon suppressed the uprising.
The American military government implemented many of the institutional reforms carried out in the United States during the Progressive Era
The Progressive Era (late 1890s – late 1910s) was a period of widespread social activism and political reform across the United States focused on defeating corruption, monopoly, waste and inefficiency. The main themes ended during Am ...
, including reorganization of the tax system, accounting and administration, expansion of primary education, the creation of a nationwide police force to unify the country, and the construction of a national system of roads, including a highway linking Santiago to Santo Domingo.
Despite the reforms, virtually all Dominicans resented the loss of their sovereignty to foreigners, few of whom spoke Spanish or displayed much real concern for the nation's welfare, and the military government, unable to win the backing of any prominent Dominican political leaders, imposed strict censorship laws and imprisoned critics of the occupation. In 1920, U.S. authorities enacted a Land Registration Act, which broke up the ''terrenos comuneros'' and dispossessed thousands of peasants who lacked formal titles to the lands they occupied, while legalizing false titles held by the sugar companies. In the southeast, dispossessed peasants formed armed bands, called ''gavilleros'', waging a guerrilla war that lasted six years, with most of the fighting in Hato Mayor and El Seibo
El Seibo (), alternatively spelt El Seybo, is a Provinces of the Dominican Republic, province of the Dominican Republic. Before 1992 it included what is now Hato Mayor Province, Hato Mayor province.
Municipalities and municipal districts
The pro ...
. At any given time, the Marines faced eight to twelve such bands each composed of several hundred followers. The guerrillas benefited from a superior knowledge of the terrain and the support of the local population, and the Marines relied on superior firepower. However, rivalries between various gavilleros often led them to fight against one another, and even cooperate with occupation authorities. In addition, cultural schisms between the ''campesinos'' (i.e. rural people, or peasants) and city dwellers prevented the guerrillas from cooperating with the urban middle-class nationalist movement.
U.S. Marines and Dominican bandits led by Vicente Evangelista clashed in eastern Dominican Republic beginning on January 10, 1917. In March 1917, Evangelista executed two American civilians, engineers from an American-owned plantation, who were lashed to trees, hacked with machetes, then left dangling for ravenous wild boars. Evangelista and 200 bandits surrendered to U.S. Marines in El Seibo on July 4, 1917. U.S. Marines shot and killed Evangelista as he was "attempting to escape" on July 6, 1917. The unrest in the eastern provinces lasted until 1922 when the guerrillas finally agreed to surrender in return for amnesty. The Marines' anti-bandit campaigns in the Dominican Republic were hot, often godlessly uncomfortable, and largely devoid of heroism and glory. Some 1,000 individuals, including 144 U.S. Marines, were killed during the conflict. (Forty U.S. sailors died separately when a hurricane wrecked their ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
on Santo Domingo's rocky shore.)
 In what was referred to as ''la danza de los millones'', with the destruction of European sugar-beet farms during World War I, sugar prices rose to their highest level in history, from $5.50 in 1914 to $22.50 per pound in 1920. Dominican sugar exports increased from 122,642 tons in 1916 to 158,803 tons in 1920, earning a record $45.3 million. However, European beet sugar production quickly recovered, which, coupled with the growth of global sugar cane production, glutted the world market, causing prices to plummet to only $2.00 by the end of 1921. This crisis drove many of the local sugar planters into bankruptcy, allowing large U.S. conglomerates to dominate the sugar industry. By 1926, only twenty-one major estates remained, occupying an estimated . Of these, twelve U.S.-owned companies owned more than 81% of this total area. While the foreign planters who had built the sugar industry integrated into Dominican society, these corporations expatriated their profits to the United States. As prices declined, sugar estates increasingly relied on Haitian laborers. This was facilitated by the military government's introduction of regulated contract labor, the growth of sugar production in the southwest, near the Haitian border, and a series of strikes by '' cocolo'' cane cutters organized by the
In what was referred to as ''la danza de los millones'', with the destruction of European sugar-beet farms during World War I, sugar prices rose to their highest level in history, from $5.50 in 1914 to $22.50 per pound in 1920. Dominican sugar exports increased from 122,642 tons in 1916 to 158,803 tons in 1920, earning a record $45.3 million. However, European beet sugar production quickly recovered, which, coupled with the growth of global sugar cane production, glutted the world market, causing prices to plummet to only $2.00 by the end of 1921. This crisis drove many of the local sugar planters into bankruptcy, allowing large U.S. conglomerates to dominate the sugar industry. By 1926, only twenty-one major estates remained, occupying an estimated . Of these, twelve U.S.-owned companies owned more than 81% of this total area. While the foreign planters who had built the sugar industry integrated into Dominican society, these corporations expatriated their profits to the United States. As prices declined, sugar estates increasingly relied on Haitian laborers. This was facilitated by the military government's introduction of regulated contract labor, the growth of sugar production in the southwest, near the Haitian border, and a series of strikes by '' cocolo'' cane cutters organized by the Universal Negro Improvement Association
The Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League (UNIA-ACL) is a black nationalist fraternal organization founded by Marcus Garvey, a Jamaican immigrant to the United States, and Amy Ashwood Garvey. The Pan-Africa ...
.
Withdrawal
 In the 1920 United States presidential election
In the 1920 United States presidential election Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
candidate Warren Harding
Warren Gamaliel Harding (November 2, 1865 – August 2, 1923) was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party, he was one of the most popular sitting U.S. presidents. A ...
criticized the occupation and promised eventual U.S. withdrawal. While Jimenes and Vásquez sought concessions from the United States, the collapse of sugar prices discredited the military government and gave rise to a new nationalist political organization, the Dominican National Union, led by Dr. Henríquez from exile in Santiago de Cuba
Santiago de Cuba is the second-largest city in Cuba and the capital city of Santiago de Cuba Province. It lies in the southeastern area of the island, some southeast of the Cuban capital of Havana.
The municipality extends over , and contains ...
, Cuba, which demanded unconditional withdrawal. They formed alliances with frustrated nationalists in Puerto Rico and Cuba, as well as critics of the occupation in the United States itself, most notably ''The Nation
''The Nation'' is an American liberal biweekly magazine that covers political and cultural news, opinion, and analysis. It was founded on July 6, 1865, as a successor to William Lloyd Garrison's '' The Liberator'', an abolitionist newspaper t ...
'' and the Haiti-San Domingo Independence Society. In May 1922, a Dominican lawyer, Francisco Peynado, went to Washington, D.C. and negotiated what became known as the Hughes–Peynado Plan. It stipulated the immediate establishment of a provisional government pending elections, approval of all laws enacted by the U.S. military government, and the continuation of the 1907 treaty until all the Dominican Republic's foreign debts had been settled. On October 1, Juan Bautista Vicini, the son of a wealthy Italian immigrant sugar planter, was named provisional president, and the process of U.S. withdrawal began. The principal legacy of the occupation was the creation of a National Police Force, used by the Marines to help fight against the various guerrillas, and later the main vehicle for the rise of Rafael Trujillo.
The rise and fall of Trujillo: Third Republic 1924–1965
Horacio Vásquez 1924–1930
 The occupation ended in 1924, with a democratically elected government under president Vásquez. The Vásquez administration brought great social and economic prosperity to the country and respected political and civil rights. Rising export commodity prices and government borrowing allowed the funding of public works projects and the expansion and modernization of Santo Domingo.
The occupation ended in 1924, with a democratically elected government under president Vásquez. The Vásquez administration brought great social and economic prosperity to the country and respected political and civil rights. Rising export commodity prices and government borrowing allowed the funding of public works projects and the expansion and modernization of Santo Domingo. Though considered to be a relatively principled man, Vásquez had risen amid many years of political infighting. In a move directed against his chief opponent Federico Velasquez, in 1927 Vásquez agreed to have his term extended from four to six years. The change was approved by the Dominican Congress, but was of debatable legality; "its enactment effectively invalidated the constitution of 1924 that Vásquez had previously sworn to uphold."
Though considered to be a relatively principled man, Vásquez had risen amid many years of political infighting. In a move directed against his chief opponent Federico Velasquez, in 1927 Vásquez agreed to have his term extended from four to six years. The change was approved by the Dominican Congress, but was of debatable legality; "its enactment effectively invalidated the constitution of 1924 that Vásquez had previously sworn to uphold."[ Vásquez also removed the prohibition against presidential reelection and postulated himself for another term in elections to be held in May 1930. However, his actions had by then led to doubts that the contest could be fair.][ Furthermore, these elections took place amid economic problems, as the Great Depression had dropped sugar prices to less than one dollar per pound.
In February, a revolution was proclaimed in Santiago by a lawyer named Rafael Estrella Ureña. When the commander of the ''Guardia Nacional Dominicana'' (the new designation of the armed force created under the Occupation), Rafael Leonidas Trujillo Molina, ordered his troops to remain in their barracks, the sick and aging Vásquez was forced into exile and Estrella proclaimed provisional president. In May, Trujillo was elected with 95% of the vote, having used the army to harass and intimidate electoral personnel and potential opponents. After his inauguration in August, at his request, the Dominican Congress proclaimed the beginning of the 'Era of Trujillo'.][
]
The era of Trujillo 1931–1961
 Trujillo established absolute political control while promoting economic development—from which mainly he and his supporters benefitted—and severe repression of domestic human rights. Trujillo treated his political party, ''El Partido Dominicano'' (The Dominican Party), as a rubber-stamp for his decisions. The true source of his power was the ''Guardia Nacional''—larger, better armed, and more centrally controlled than any military force in the nation's history. By disbanding the regional militias, the Marines eliminated the main source of potential opposition, giving the Guard "a virtual monopoly on power". By 1940, Dominican military spending was 21% of the national budget. At the same time, he developed an elaborate system of espionage agencies. By the late 1950s, there were at least seven categories of intelligence agencies, spying on each other as well as the public. All citizens were required to carry identification cards and good-conduct passes from the secret police.
Obsessed with adulation, Trujillo promoted an extravagant cult of personality. When a hurricane struck Santo Domingo in 1930, killing over 3,000 people, he rebuilt the city and renamed it ''Ciudad Trujillo'': "Trujillo City"; he also renamed the country's and the Caribbean's highest mountain,
Trujillo established absolute political control while promoting economic development—from which mainly he and his supporters benefitted—and severe repression of domestic human rights. Trujillo treated his political party, ''El Partido Dominicano'' (The Dominican Party), as a rubber-stamp for his decisions. The true source of his power was the ''Guardia Nacional''—larger, better armed, and more centrally controlled than any military force in the nation's history. By disbanding the regional militias, the Marines eliminated the main source of potential opposition, giving the Guard "a virtual monopoly on power". By 1940, Dominican military spending was 21% of the national budget. At the same time, he developed an elaborate system of espionage agencies. By the late 1950s, there were at least seven categories of intelligence agencies, spying on each other as well as the public. All citizens were required to carry identification cards and good-conduct passes from the secret police.
Obsessed with adulation, Trujillo promoted an extravagant cult of personality. When a hurricane struck Santo Domingo in 1930, killing over 3,000 people, he rebuilt the city and renamed it ''Ciudad Trujillo'': "Trujillo City"; he also renamed the country's and the Caribbean's highest mountain, Pico Duarte
Pico Duarte is the highest peak in the Dominican Republic, on the island of Hispaniola and in all the Caribbean. At above sea level, it gives the Dominican Republic the 16th-highest maximum elevation of any island in the world. Additionally, it ...
(Duarte Peak), ''Pico Trujillo''. Over 1,800 statues of Trujillo were built, and all public works projects were required to have a plaque with the inscription "Era of Trujillo, Benefactor of the Fatherland".
As sugar estates turned to Haiti for seasonal migrant labor, increasing numbers settled in the Dominican Republic permanently. The census of 1920, conducted by the U.S. occupation government, gave a total of 28,258 Haitians living in the country; by 1935 there were 52,657.
In September 1937, Trujillo welcomed a Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
delegation and publicly accepted the gift of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's Mein Kampf. The following month, Trujillo ordered the massacre of up to 67,000 Haitian men, women, and children living in the Cibao region, the alleged justification being Haiti's support for Dominican exiles plotting to overthrow his regime. Over the course of five days, Dominican troops, who came mostly from other areas of the country, killed Haitians with guns, machetes, clubs, and knives. Haitian women were stabbed and mutilated, babies bayoneted, and men tied up and thrown into the sea, where shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s finished what Trujillo had begun. This event later became known as the Parsley Massacre
The Parsley massacre (Spanish: ''el corte'' "the cutting"; Creole: ''kout kouto-a'' "the stabbing") (french: Massacre du Persil; es, Masacre del Perejil; ht, Masak nan Pèsil) was a mass killing of Haitians living in the Dominican Republic's nor ...
because of the story that Dominican soldiers identified Haitians by their inability to pronounce the Spanish word ''perejil''. A shocked American missionary, Father Barnes, wrote about the massacre in a letter to his sister. Trujillo's spies intercepted the letter. Father Barnes was found on the floor of his home, murdered brutally.Generalissimo
''Generalissimo'' ( ) is a military rank of the highest degree, superior to field marshal and other five-star ranks in the states where they are used.
Usage
The word (), an Italian term, is the absolute superlative of ('general') thus me ...
Francisco Franco, he welcomed Spanish Republican refugees following the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
. During the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
in the Second World War, the Dominican Republic took in many Jews fleeing Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
who had been refused entry by other countries. The Jews settled in Sosua. These decisions arose from a policy of ''blanquismo'', closely connected with anti-Haitian xenophobia, which sought to add more light-skinned individuals to the Dominican population by promoting immigration from Europe. As part of the Good Neighbor policy
The Good Neighbor policy ( ) was the foreign policy of the administration of United States President Franklin Roosevelt towards Latin America. Although the policy was implemented by the Roosevelt administration, President Woodrow Wilson had prev ...
, in 1940, the U.S. State Department signed a treaty with Trujillo relinquishing control over the nation's customs. When the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor Trujillo followed the United States in declaring war on the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
, although the Dominican Republic did not have any participation in the war. During the Cold War, he maintained close ties to the United States, declaring himself the world's "Number One Anticommunist" and becoming the first Latin American President to sign a Mutual Defense Assistance Agreement with the United States.
Ramfis
Rafael Leónidas Trujillo Martínez (5 June 1929 – 27 December 1969), better known as Ramfis Trujillo Martínez, was the adopted son of Rafael Leónidas Trujillo, dictator of the Dominican Republic, after whose 1961 assassination he briefly ...
(the dictator's son) and Porfirio Rubirosa
Porfirio Rubirosa Ariza (January 22, 1909 – July 5, 1965) was a Dominican diplomat, race car driver, soldier and polo player. He was a supporter of dictator Rafael Trujillo, and was also a political assassin under his regime. Rubirosa made ...
became a major part of the Rafael Trujillo regime's image in the foreign press, as a result of their lavish lifestyle and relationships with Hollywood actresses.
Trujillo and his family established a near-monopoly over the national economy. By the time of his death, he had accumulated a fortune of around $800 million; he and his family owned 50–60% of the arable land, some , and Trujillo-owned businesses accounted for 80% of the commercial activity in the capital. He exploited nationalist sentiment to purchase most of the nation's sugar plantations and refineries from U.S. corporations; operated monopolies on salt, rice, milk, cement, tobacco, coffee, and insurance; owned two large banks, several hotels, port facilities, an airline and shipping line; deducted 10% of all public employees' salaries (ostensibly for his party); and received a portion of prostitution revenues.
World War II brought increased demand for Dominican exports, and the 1940s and early 1950s witnessed economic growth and considerable expansion of the national infrastructure. During this period, the capital city was transformed from merely an administrative center to the national center of shipping and industry, although "it was hardly coincidental that new roads often led to Trujillo's plantations and factories, and new harbors benefited Trujillo's shipping and export enterprises." Mismanagement and corruption resulted in major economic problems. By the end of the 1950s, the economy was deteriorating because of a combination of overspending on a festival to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the regime, overspending to purchase privately owned sugar mills and electricity plants, and a decision to make a major investment in state sugar production that proved economically unsuccessful.
In 1956, Trujillo's agents in New York murdered Jesús María de Galíndez, a Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
exile who had worked for Trujillo but who later denounced the Trujillo regime and caused public opinion in the United States to turn against Trujillo.
In 1957, Trujillo created the Military Intelligence Service
The Military Intelligence Service ( ja, アメリカ陸軍情報部, ''America Rikugun Jōhōbu'') was a World War II U.S. military unit consisting of two branches, the Japanese American unit (described here) and the German-Austrian unit based ...
, secret police, headed by Johnny Abbes García, who briefly operated in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, Guatemala, New York, Costa Rica, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
.
On June 14, 1959, leftist Dominican exiles launched an invasion of the Dominican Republic from Cuba with the hope of overthrowing the Trujillo regime. Trujillo's forces quickly routed the invaders at Constanza. A week later, another group of invaders in two yachts were intercepted on the north coast and blasted by mortar fire and bazookas from the shore. Trujillo's planes, operating from San Isidro, zoomed low over the yachts and shot rockets, killing most of the invaders. A few survivors managed to swim to the shore and escape into the forest; the military used napalm
Napalm is an incendiary mixture of a gelling agent and a volatile petrochemical (usually gasoline (petrol) or diesel fuel). The name is a portmanteau of two of the constituents of the original thickening and gelling agents: coprecipitated alu ...
to get them out.Rómulo Betancourt
Rómulo Ernesto Betancourt Bello (22 February 1908 – 28 September 1981; ), known as "The Father of Venezuelan Democracy", was the president of Venezuela, serving from 1945 to 1948 and again from 1959 to 1964, as well as leader of Acción De ...
with a car bomb. Betancourt had been involved in the 1959 Cuba-based invasion of the Dominican Republic.
The United States broke diplomatic relations with the Dominican Republic on August 26, 1960, and in January 1961 suspended the export of trucks, parts, crude oil, gasoline and other petroleum products. U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
also took advantage of OAS sanctions to cut drastically purchases of Dominican sugar. This action ultimately cost the Dominican Republic almost $22,000,000 in lost revenues at a time when its economy was in a rapid decline. Trujillo threatened to align with the Communist world in response to U.S. and Latin American rejection of his regime. La Voz Dominicana and Radio Caribe began attacking the U.S. in Marxian terms, and the Dominican Communist Party
The Dominican Communist Party ( es, Partido Comunista Dominicano) was a political party in the Dominican Republic. The party was founded in 1944 under the name Dominican Revolutionary Democratic Party. The party worked under the name Dominican Pop ...
was legalized. The United States government turned to the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
to devise a plan to kill Trujillo.
The post-Trujillo instability 1961–1965
At the insistence of the United States, Balaguer was forced to share power with a seven-member Council of State, established on January 1, 1962, and including moderate members of the opposition. OAS sanctions were lifted January 4, and, after an attempted coup, Balaguer resigned and went into exile on January 16. The reorganized Council of State, under President Rafael Filiberto Bonnelly
Rafael Filiberto Bonnelly Fondeur (August 22, 1904 – December 28, 1979) was a lawyer, scholar, diplomat, and, from 1962 until 1963, the
President of the Dominican Republic. Before he became president, he was vice president of the country fro ...
headed the Dominican government until elections could be held. These elections, in December 1962, were won by Juan Bosch, a scholar and poet who had founded the opposition ''Partido Revolucionario Dominicano'' (Dominican Revolutionary Party
The Dominican Revolutionary Party ( es, link=no, Partido Revolucionario Dominicano, PRD) is a political party in the Dominican Republic. Traditionally a left-of-centre party and social democratic in nature, the party has shifted since the 2000 ...
, or PRD) in exile, during the Trujillo years. His leftist policies, including land redistribution, nationalization of certain foreign holdings, and attempts to bring the military under civilian control, antagonized the military officer corps, the Catholic hierarchy, and the upper-class, who feared "another Cuba".
In September 1963, Bosch was overthrown by a right-wing military coup led by Colonel Elías Wessin and was replaced by a three-man military junta
A military junta () is a government led by a committee of military leaders. The term ''junta'' means "meeting" or "committee" and originated in the national and local junta organized by the Spanish resistance to Napoleon's invasion of Spain in ...
. Bosch went into exile to Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
. Afterwards, a supposedly civilian triumvirate established a de facto dictatorship.
Dominican Civil War and second United States occupation 1965–66
On April 16, 1965, growing dissatisfaction generated another military rebellion on April 24, 1965 that demanded Bosch's restoration. The insurgents, reformist officers and civilian combatants loyal to Bosch commanded by Colonel Francisco Caamaño, and who called themselves the Constitutionalists, staged a coup, seizing the national palace. Immediately, conservative military forces, led by Wessin and calling themselves Loyalists, struck back with tank assaults and aerial bombings against Santo Domingo.
Strafing
Strafing is the military practice of attacking ground targets from low-flying aircraft using aircraft-mounted automatic weapons.
Less commonly, the term is used by extension to describe high-speed firing runs by any land or naval craft such ...
by the airplanes on the Duarte Bridge killed 200 civilians, and bombing shattered many of the buildings and structures to the west. Outwardly the damage west of the bridge seemed impressive with body parts scattered on the streets.[ On April 27, a sizeable Loyalist force of tanks, armored cars, artillery, and infantry began to rumble across Duarte Bridge under covering fire from 12.7 mm machine guns on the eastern bank. The Constitutionalists left two large truck trailers blocking the path, but as the Loyalist armor pushed its way through these obstacles, one of the two pre–]World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
75 mm cannon on the Constitutionalist side got off one shot and destroyed the first tank. Soon a hail of machine gun fire silenced the 75 mm cannons and the rest of the tanks proceeded into the city. When the armored column passed José Martí Street one block from Duarte Avenue, armed civilians attacked the Loyalist infantry and unleashed a hail of fire from machine guns and mortars; most of the troops either fled or were killed. Without infantry support, the unescorted tanks, already in the narrow streets of the neighborhood, were easy targets for the Molotov cocktails soon being tossed from the surrounding buildings. The Loyalists were routed and several tanks were abandoned and put into use by the rebels.[
On April 28, the anti-Bosch army elements requested U.S. military intervention and U.S. forces landed, ostensibly to protect U.S. citizens and to evacuate U.S. and other foreign nationals. A rebel sniper killed a Marine near the U.S. embassy, and in the ensuing crossfire a hand grenade fatally wounded a Dominican girl. The evacuation was completed without further loss of life. U.S. President ]Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
, convinced of the defeat of the Loyalist forces and fearing the creation of "a second Cuba" on America's doorstep, ordered U.S. forces to restore order. In what was initially known as Operation Power Pack
The Dominican Civil War (), also known as the April Revolution (), took place between April 24, 1965, and September 3, 1965, in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. It started when civilian and military supporters of the overthrown democratica ...
, 27,677 U.S. troops were ultimately ordered to the Dominican Republic.
Denied a military victory, the Constitutionalist rebels quickly had a Constitutionalist congress elect Caamaño president of the country. U.S. officials countered by backing General Antonio Imbert
Major General Antonio Cosme Imbert Barrera (December 3, 1920 – May 31, 2016) was a two-star army general advitam of the Dominican Army and was President of the Dominican Republic from May to August 1965.
Imbert, who plotted to assassinate di ...
. On May 7, Imbert was sworn in as president of the Government of National Reconstruction. The next step in the stabilization process, as envisioned by Washington and the OAS, was to arrange an agreement between President Caamaño and President Imbert to form a provisional government committed to early elections. However, Caamaño refused to meet with Imbert until several of the Loyalist officers, including Wessin y Wessin, were made to leave the country.
On May 13, Imbert launched an eight-day offensive to eliminate rebel resistance in the northern sector. Meanwhile, U.S. troops advanced towards the El Timbeque neighborhood, in order to take over a power plant, but were repulsed by the Constitutionalists. Imbert's forces took the northern part of the capital, destroying many buildings and killing many civilians. A cease-fire was negotiated by May 21, marking the beginning of neutrality for U.S. forces. At this time, 20 Americans had been killed in action and 102 wounded.
 By May 14, the Americans had established a "safety corridor" connecting the San Isidro Air Base and the "Duarte" Bridge to the Embajador Hotel and United States Embassy in the center of Santo Domingo, essentially sealing off the Constitutionalist area of Santo Domingo. Roadblocks were established and patrols ran continuously. Some 6,500 people from many nations were evacuated to safety. In addition, the US forces airlifted in relief supplies for Dominican nationals.
By mid-May, a majority of the OAS voted for Operation "Push Ahead", the reduction of United States forces and their replacement by an Inter-American Peace Force (IAPF). The Inter-American Peace Force was formally established on May 23. The following troops were sent by each country: Brazil – 1,130, Honduras – 250,
By May 14, the Americans had established a "safety corridor" connecting the San Isidro Air Base and the "Duarte" Bridge to the Embajador Hotel and United States Embassy in the center of Santo Domingo, essentially sealing off the Constitutionalist area of Santo Domingo. Roadblocks were established and patrols ran continuously. Some 6,500 people from many nations were evacuated to safety. In addition, the US forces airlifted in relief supplies for Dominican nationals.
By mid-May, a majority of the OAS voted for Operation "Push Ahead", the reduction of United States forces and their replacement by an Inter-American Peace Force (IAPF). The Inter-American Peace Force was formally established on May 23. The following troops were sent by each country: Brazil – 1,130, Honduras – 250, Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
– 184, Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
– 160, Costa Rica – 21 military police, and El Salvador – 3 staff officers. The first contingent to arrive was a rifle company from Honduras which was soon backed by detachments from Costa Rica, El Salvador, and Nicaragua. Brazil provided the largest unit, a reinforced infantry battalion. Brazilian General Hugo Panasco Alvim assumed command of the OAS ground forces, and on May 26 the U.S. forces began to withdraw.
On June 15, Camaaño hurled all his best remaining units and weapons against the American lines, and soon mortar rounds were hitting the 82nd Airborne Division. Although their heaviest weapons were recoilless cannons, the 82nd Airborne soundly defeated the rebels.G.I.
G.I. are initials used to describe the soldiers of the United States Army and airmen of the United States Air Force and general items of their equipment. The term G.I. has been used as an initialism of "Government Issue", "General Issue", or " ...
died instantly; the other died at a hospital.
A total of 44 American soldiers died, 27 in action; 172 were wounded in action, as were six Brazilians and five Paraguayans. An estimated 1,425 Dominican soldiers and police died.
Fourth Republic 1966–present
Balaguer's second Presidency 1966–1978
In June 1966, Joaquín Balaguer, leader of the Reformist Party (which later became the Social Christian Reformist Party
The Social Christian Reformist Party ( es, Partido Reformista Social Cristiano, PRSC) is a Christian democratic right-wing political party in the Dominican Republic. It was established on July 24, 1984, by the union of Joaquín Balaguer's ' ...
(PRSC)), was elected and then re-elected to office in May 1970 and May 1974, both times after the major opposition parties withdrew late in the campaign because of the high degree of violence by pro-government groups. On November 28, 1966 a constitution was created, signed, and put into effect. The constitution stated that the president was elected to a four-year term. If there was a close election there would be a second round of voting to decide the winner. The voting age was eighteen, but married people under eighteen could also vote.
 On one hand, Balaguer was considered to be a ''
On one hand, Balaguer was considered to be a ''caudillo
A ''caudillo'' ( , ; osp, cabdillo, from Latin , diminutive of ''caput'' "head") is a type of personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise definition of ''caudillo'', which is often used interchangeably with " ...
'' who led a regime of terror where 11,000 victims were either torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. definitions of tortur ...
d or forcibly disappeared and killed. However, Balaguer was also considered to be a major reformer who was instrumental in the liberalization of the Dominican government.GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
growth rate of 9.4% between 1970 and 1975), to the extent that people talked about the "Dominican miracle". Foreign, mostly U.S. investment, as well as foreign aid, flowed into the country. Sugar, then the country's main export product, enjoyed good prices in the international market, and tourism grew tremendously. As part of Balaguer's land reform policies, land was dished out to peasants among the country's rural population.Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 76th governor of Georgia from 1 ...
refused to recognize Balaguer's claim, and, faced with the loss of foreign aid, Balaguer stepped down.
Guzmán / Blanco interregnum 1978–1986
Guzmán's inauguration on August 16 marked the country's first peaceful transfer of power from one freely elected president to another.
Hurricane David hit the Dominican Republic in August 1979, which caused over $1 billion in damage.
By the late 1970s, economic expansion slowed considerably as sugar prices declined and oil prices rose. Rising inflation and unemployment diminished support for the government and helped trigger a wave of mass emigration from the Dominican Republic to New York, coming on the heels of the similar migration of Puerto Ricans in the preceding decades.
Elections were again held in 1982. Salvador Jorge Blanco of the Dominican Revolutionary Party defeated Bosch and a resurgent Balaguer.
Balaguer's third Presidency 1986–1996
Balaguer completed his return to power in 1986 when he won the Presidency again and remained in office for the next ten years. Elections in 1990 were marked by violence and suspected electoral fraud. The 1994 election too saw widespread pre-election violence, often aimed at intimidating members of the opposition. Balaguer won in 1994 but most observers felt the election had been stolen. Under pressure from the United States, Balaguer agreed to hold new elections in 1996. He himself would not run.
Since 1996
Fernández: First administration 1996–2000
In 1996, U.S.-raised Leonel Fernández Reyna of Bosch's '' Partido de la Liberación Dominicana'' (Dominican Liberation Party) secured more than 51% of the vote, through an alliance with Balaguer. The first item on the president's agenda was the partial sale of some state-owned enterprises. Fernández was praised for ending decades of isolationism and improving ties with other Caribbean countries, but he was criticized for not fighting corruption or alleviating the poverty that affected 60% of the population.
Mejía's administration 2000–2004
In May 2000 the center-left Hipólito Mejía of the PRD was elected president amid popular discontent over power outages in the recently privatized electric industry. His presidency saw major inflation and instability of the peso in 2003 because of the bankruptcy of three major commercial banks in the country due to the bad policies of the principal managers. During his remaining time as president, he took action to save most savers of the closed banks, avoiding a major crisis. The relatively stable currency fell from about 16 Dominican pesos to 1 United States dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the officia ...
to about 60 DOP to US$1 and was in the 40s to the dollar when he left office in August 2004. In the May 2004 presidential elections, he was defeated by former president Leonel Fernández
Leonel Antonio Fernández Reyna () (born 26 December 1953) is a Dominican lawyer, academic, and was the 50th and 52nd President of the Dominican Republic from 1996 to 2000 and from 2004 to 2012. From 2016 until 2020, he was the President of th ...
.
Fernández: Second administration 2004–2012
Fernández instituted austerity measures to deflate the peso and rescue the country from its economic crisis, and in the first half of 2006, the economy grew 11.7%. The peso is currently (2019) at the exchange rate of c. 52 DOP to US$1.
Over the last three decades, remittances (''remesas'') from Dominicans living abroad, mainly in the United States, have become increasingly important to the economy. From 1990 to 2000, the Dominican population of the U.S. doubled in size, from 520,121 in 1990 to 1,041,910, two-thirds of whom were born in the Dominican Republic itself. More than half of all Dominican Americans
Dominican Americans ( es, domínico-americanos, ) are Americans who trace their ancestry to the Dominican Republic. The word may refer to someone born in the United States of Dominican descent or to someone who has migrated to the United Stat ...
live in New York City, with the largest concentration in the neighborhood of Washington Heights in northern Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
. Over the past decade, the Dominican Republic has become the largest source of immigration to New York City, and today the metropolitan area of New York has a larger Dominican population than any city except Santo Domingo. Dominican communities have also developed in New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
(particularly Paterson), Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
, Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
, Providence, Rhode Island
Providence is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. One of the oldest cities in New England, it was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, a Reformed Baptist theologian and religious exile from the Massachusetts ...
, and Lawrence, Massachusetts. In addition, tens of thousands of Dominicans and their descendants live in Puerto Rico. Many Dominicans arrive in Puerto Rico illegally by sea across the Mona Passage
The Mona Passage ( es, Canal de la Mona) is a strait that separates the islands of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico. The Mona Passage connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Sea and is an important shipping route between the Atlantic and the Panama ...
, some staying and some moving on to the mainland U.S. (See Dominican immigration to Puerto Rico
Dominican immigration to Puerto Rico dates back to the beginning of European colonization of the Americas. Immigrants have moved from the territory of the Dominican Republic to its eastern neighbor, Puerto Rico, for centuries. Dominican immigrant ...
.) Dominicans living abroad sent an estimated $3 billion in remittances to relatives at home, in 2006. In 1997, a new law took effect, allowing Dominicans living abroad to retain their citizenship and vote in presidential elections. President Fernández, who grew up in New York, was the principal beneficiary of this law.
The Dominican Republic was involved in the Iraq War, US-led coalition in Iraq, as part of the Spain-led Latin-American Plus Ultra Brigade. But in 2004, the nation pulled its 300 or so troops out of Iraq.[Dominican troops were under constant mortar attacks but suffered no casualties.]
Danilo Medina's administration 2012–2020
Danilo Medina began his tenure with a series of controversial tax reforms so as to deal with the government's troublesome fiscal situation encountered by the new administration. In 2012, he had won presidency as the candidate of ruling Dominican Liberation Party (PLD).
In 2016, President Medina won 2016 Dominican Republic general election, re-election, defeating the main opposition candidate businessman Luis Abinader, with a wide margin.
Luis Abinader 2020-present
In 2020 Luis Abinader, the presidential candidate for the opposition Modern Revolutionary Party (PRM) won the election and he became the new president, ending the 16-year rule of PLD since 2004.
See also
*History of Haiti
*History of Latin America
*History of North America
*History of the Americas
*History of the Caribbean
*List of presidents of the Dominican Republic
*Politics of the Dominican Republic
*Spanish colonization of the Americas
*Timeline of Santo Domingo (city)
Notes
References
Further reading
* Betances, Emelio. ''State and society in the Dominican Republic'' (Routledge, 2018).
* Derby, Robin. ''The Dictator's Seduction: Politics and the Popular Imagination in the Era of Trujillo''. Durham: Duke University Press 2008.
* Pons, Frank Moya. ''The Dominican Republic: a national history'' (Markus Wiener Publishers, 2010).
* Tillman, Ellen D. ''Dollar Diplomacy by Force: Nation-Building and Resistance in the Dominican Republic'' (UNC Press Books, 2016).
* Turits, Richard Lee. ''Foundations of Despotism: Peasants, the Trujillo Regime, and Modernity in Dominican History''. Stanford: Stanford University Press 2003.
* Wiarda, Howard J., and Michael J. Kryzanek. ''The Dominican Republic: A Caribbean Crucible.'' (Routledge, 2019).
* "The Dominican Republic," ''History Today'' (Nov 1965) 15#11 pp 770–779, diplomatic history 1482–1965.
External links
Map of the Dominican Republic
from 1910
*Betances, Emelio.
The Dominican Grassroots Movement and the Organized Left, 1978–1986
. Science & Society 79.3 (July 2015), 388–413.
The Political Force of Images
, ''Vistas: Visual Culture in Spanish America'', 1520–1820.
{{Authority control
History of the Dominican Republic,
History of the Caribbean
History of Latin America
History of Hispanic America
Spanish colonization of Latin America
Spanish West Indies
 The recorded history of the Dominican Republic began in 1492 when the
The recorded history of the Dominican Republic began in 1492 when the 
 An estimated 400,000 Tainos living on the island were soon enslaved to work in gold mines. By 1508, their numbers had decreased to around 60,000 because of forced labor, hunger, disease, and mass killings. By 1535, only a few dozen were still alive.
An estimated 400,000 Tainos living on the island were soon enslaved to work in gold mines. By 1508, their numbers had decreased to around 60,000 because of forced labor, hunger, disease, and mass killings. By 1535, only a few dozen were still alive.
 During this period, the colony's Spanish leadership changed several times. When Columbus departed on another exploration,
During this period, the colony's Spanish leadership changed several times. When Columbus departed on another exploration, 
 Beginning in the 1520s, the
Beginning in the 1520s, the  In 1605, Spain was infuriated that Spanish settlements on the northern and western coasts of the island were carrying out large scale and illegal trade with the Dutch, who were at that time fighting a war of independence against Spain in Europe, and the English, a very recent enemy state, and so decided to forcibly resettle the colony's inhabitants closer to the city of Santo Domingo. This action, known as the '' Devastaciones de Osorio'', proved disastrous; more than half of the resettled colonists died of starvation or disease, over 100,000 cattle were abandoned, and many slaves escaped. Five of the existing thirteen settlements on the island were brutally razed by Spanish troops – many of the inhabitants fought, escaped to the jungle, or fled to the safety of passing Dutch ships. The settlements of La Yaguana, and Bayaja, on the west and north coasts respectively of modern-day Haiti were burned, as were the settlements of Monte Cristi and Puerto Plata on the north coast and San Juan de la Maguana in the southwestern area of the modern-day Dominican Republic.
French and English
In 1605, Spain was infuriated that Spanish settlements on the northern and western coasts of the island were carrying out large scale and illegal trade with the Dutch, who were at that time fighting a war of independence against Spain in Europe, and the English, a very recent enemy state, and so decided to forcibly resettle the colony's inhabitants closer to the city of Santo Domingo. This action, known as the '' Devastaciones de Osorio'', proved disastrous; more than half of the resettled colonists died of starvation or disease, over 100,000 cattle were abandoned, and many slaves escaped. Five of the existing thirteen settlements on the island were brutally razed by Spanish troops – many of the inhabitants fought, escaped to the jungle, or fled to the safety of passing Dutch ships. The settlements of La Yaguana, and Bayaja, on the west and north coasts respectively of modern-day Haiti were burned, as were the settlements of Monte Cristi and Puerto Plata on the north coast and San Juan de la Maguana in the southwestern area of the modern-day Dominican Republic.
French and English  The House of Bourbon replaced the
The House of Bourbon replaced the  During this period in time, the Spanish crown wielded little to no influence in the colony of Santo Domingo. Some wealthy cattle ranchers had become leaders, and sought to bring control and order in the southeast of the colony where the "law of machete" ruled the land. On December 1, 1821, the former Captain general in charge of the colony, José Núñez de Cáceres, influenced by all the
During this period in time, the Spanish crown wielded little to no influence in the colony of Santo Domingo. Some wealthy cattle ranchers had become leaders, and sought to bring control and order in the southeast of the colony where the "law of machete" ruled the land. On December 1, 1821, the former Captain general in charge of the colony, José Núñez de Cáceres, influenced by all the  In July 1844, Pedro Santana seized power from the liberal president Francisco del Rosario Sánchez in a military coup after Rosario Sánchez ousted the conservative Tomás Bobadilla from power. Santana inaugurated a military dictatorship with Bobadilla as a member of his junta.
The Dominican Republic's first
In July 1844, Pedro Santana seized power from the liberal president Francisco del Rosario Sánchez in a military coup after Rosario Sánchez ousted the conservative Tomás Bobadilla from power. Santana inaugurated a military dictatorship with Bobadilla as a member of his junta.
The Dominican Republic's first  Within a month of the nationalist victory, Cabral, whose troops were the first to enter Santo Domingo, ousted Pimentel, but a few weeks later General Guillermo led a rebellion in support of Báez, forcing Cabral to resign and allowing Báez to retake the presidency in October.
Báez was overthrown by the Cibao farmers under Luperón, leader of the Partido Azul, the following spring, but Luperón's allies turned on each other and Cabral reinstalled himself as president in a coup in 1867. After bringing several ''Azules'' ("Blues") into his cabinet the ''Rojos'' ("Reds") revolted, returning Báez to power.
In 1869, U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant ordered U.S. Marines to the island for the first time. Dominican pirates operating from Haiti had been raiding U.S. merchant shipping in the Caribbean, and Grant directed the Marines to stop them at their source.
Following the virtual takeover of the island, Báez negotiated a treaty of annexation with the United States. Supported by
Within a month of the nationalist victory, Cabral, whose troops were the first to enter Santo Domingo, ousted Pimentel, but a few weeks later General Guillermo led a rebellion in support of Báez, forcing Cabral to resign and allowing Báez to retake the presidency in October.
Báez was overthrown by the Cibao farmers under Luperón, leader of the Partido Azul, the following spring, but Luperón's allies turned on each other and Cabral reinstalled himself as president in a coup in 1867. After bringing several ''Azules'' ("Blues") into his cabinet the ''Rojos'' ("Reds") revolted, returning Báez to power.
In 1869, U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant ordered U.S. Marines to the island for the first time. Dominican pirates operating from Haiti had been raiding U.S. merchant shipping in the Caribbean, and Grant directed the Marines to stop them at their source.
Following the virtual takeover of the island, Báez negotiated a treaty of annexation with the United States. Supported by  Allying with the emerging sugar interests, the dictatorship of General
Allying with the emerging sugar interests, the dictatorship of General  The six years after Lilís's death witnessed four revolutions and five different presidents. The Cibao politicians who had conspired against Heureaux— Juan Isidro Jimenes, the nation's wealthiest tobacco planter, and General
The six years after Lilís's death witnessed four revolutions and five different presidents. The Cibao politicians who had conspired against Heureaux— Juan Isidro Jimenes, the nation's wealthiest tobacco planter, and General  In 1906, Morales resigned, and Horacista vice-president Ramón Cáceres became president. After suppressing a rebellion in the northwest by Jimenista General Desiderio Arias, his government brought political stability and renewed economic growth, aided by new American investment in the sugar industry.
However, his assassination in 1911, for which Morales and Arias were at least indirectly responsible, once again plunged the republic into chaos. For two months, executive power was held by a civilian junta dominated by the chief of the army, General Alfredo Victoria. The surplus of more than 4 million pesos left by Cáceres was quickly spent to suppress a series of insurrections. He forced Congress to elect his uncle, Eladio Victoria, as president, but the latter was soon replaced by the neutral Archbishop Adolfo Nouel. After four months, Nouel resigned and was succeeded by Horacista Congressman José Bordas Valdez, who aligned with Arias and the Jimenistas to maintain power.
In 1906, Morales resigned, and Horacista vice-president Ramón Cáceres became president. After suppressing a rebellion in the northwest by Jimenista General Desiderio Arias, his government brought political stability and renewed economic growth, aided by new American investment in the sugar industry.
However, his assassination in 1911, for which Morales and Arias were at least indirectly responsible, once again plunged the republic into chaos. For two months, executive power was held by a civilian junta dominated by the chief of the army, General Alfredo Victoria. The surplus of more than 4 million pesos left by Cáceres was quickly spent to suppress a series of insurrections. He forced Congress to elect his uncle, Eladio Victoria, as president, but the latter was soon replaced by the neutral Archbishop Adolfo Nouel. After four months, Nouel resigned and was succeeded by Horacista Congressman José Bordas Valdez, who aligned with Arias and the Jimenistas to maintain power.
 In 1913, Vásquez returned from exile in Puerto Rico to lead a new rebellion. In June 1914, U.S. President
In 1913, Vásquez returned from exile in Puerto Rico to lead a new rebellion. In June 1914, U.S. President  The Dominican Congress elected Dr. Francisco Henríquez y Carvajal as president, but in November, after he refused to meet the U.S. demands, Wilson announced the imposition of a U.S. military government, with Rear Admiral
The Dominican Congress elected Dr. Francisco Henríquez y Carvajal as president, but in November, after he refused to meet the U.S. demands, Wilson announced the imposition of a U.S. military government, with Rear Admiral  In what was referred to as ''la danza de los millones'', with the destruction of European sugar-beet farms during World War I, sugar prices rose to their highest level in history, from $5.50 in 1914 to $22.50 per pound in 1920. Dominican sugar exports increased from 122,642 tons in 1916 to 158,803 tons in 1920, earning a record $45.3 million. However, European beet sugar production quickly recovered, which, coupled with the growth of global sugar cane production, glutted the world market, causing prices to plummet to only $2.00 by the end of 1921. This crisis drove many of the local sugar planters into bankruptcy, allowing large U.S. conglomerates to dominate the sugar industry. By 1926, only twenty-one major estates remained, occupying an estimated . Of these, twelve U.S.-owned companies owned more than 81% of this total area. While the foreign planters who had built the sugar industry integrated into Dominican society, these corporations expatriated their profits to the United States. As prices declined, sugar estates increasingly relied on Haitian laborers. This was facilitated by the military government's introduction of regulated contract labor, the growth of sugar production in the southwest, near the Haitian border, and a series of strikes by '' cocolo'' cane cutters organized by the
In what was referred to as ''la danza de los millones'', with the destruction of European sugar-beet farms during World War I, sugar prices rose to their highest level in history, from $5.50 in 1914 to $22.50 per pound in 1920. Dominican sugar exports increased from 122,642 tons in 1916 to 158,803 tons in 1920, earning a record $45.3 million. However, European beet sugar production quickly recovered, which, coupled with the growth of global sugar cane production, glutted the world market, causing prices to plummet to only $2.00 by the end of 1921. This crisis drove many of the local sugar planters into bankruptcy, allowing large U.S. conglomerates to dominate the sugar industry. By 1926, only twenty-one major estates remained, occupying an estimated . Of these, twelve U.S.-owned companies owned more than 81% of this total area. While the foreign planters who had built the sugar industry integrated into Dominican society, these corporations expatriated their profits to the United States. As prices declined, sugar estates increasingly relied on Haitian laborers. This was facilitated by the military government's introduction of regulated contract labor, the growth of sugar production in the southwest, near the Haitian border, and a series of strikes by '' cocolo'' cane cutters organized by the  In the 1920 United States presidential election
In the 1920 United States presidential election  The occupation ended in 1924, with a democratically elected government under president Vásquez. The Vásquez administration brought great social and economic prosperity to the country and respected political and civil rights. Rising export commodity prices and government borrowing allowed the funding of public works projects and the expansion and modernization of Santo Domingo.
The occupation ended in 1924, with a democratically elected government under president Vásquez. The Vásquez administration brought great social and economic prosperity to the country and respected political and civil rights. Rising export commodity prices and government borrowing allowed the funding of public works projects and the expansion and modernization of Santo Domingo.
 Though considered to be a relatively principled man, Vásquez had risen amid many years of political infighting. In a move directed against his chief opponent Federico Velasquez, in 1927 Vásquez agreed to have his term extended from four to six years. The change was approved by the Dominican Congress, but was of debatable legality; "its enactment effectively invalidated the constitution of 1924 that Vásquez had previously sworn to uphold." Vásquez also removed the prohibition against presidential reelection and postulated himself for another term in elections to be held in May 1930. However, his actions had by then led to doubts that the contest could be fair. Furthermore, these elections took place amid economic problems, as the Great Depression had dropped sugar prices to less than one dollar per pound.
In February, a revolution was proclaimed in Santiago by a lawyer named Rafael Estrella Ureña. When the commander of the ''Guardia Nacional Dominicana'' (the new designation of the armed force created under the Occupation), Rafael Leonidas Trujillo Molina, ordered his troops to remain in their barracks, the sick and aging Vásquez was forced into exile and Estrella proclaimed provisional president. In May, Trujillo was elected with 95% of the vote, having used the army to harass and intimidate electoral personnel and potential opponents. After his inauguration in August, at his request, the Dominican Congress proclaimed the beginning of the 'Era of Trujillo'.
Though considered to be a relatively principled man, Vásquez had risen amid many years of political infighting. In a move directed against his chief opponent Federico Velasquez, in 1927 Vásquez agreed to have his term extended from four to six years. The change was approved by the Dominican Congress, but was of debatable legality; "its enactment effectively invalidated the constitution of 1924 that Vásquez had previously sworn to uphold." Vásquez also removed the prohibition against presidential reelection and postulated himself for another term in elections to be held in May 1930. However, his actions had by then led to doubts that the contest could be fair. Furthermore, these elections took place amid economic problems, as the Great Depression had dropped sugar prices to less than one dollar per pound.
In February, a revolution was proclaimed in Santiago by a lawyer named Rafael Estrella Ureña. When the commander of the ''Guardia Nacional Dominicana'' (the new designation of the armed force created under the Occupation), Rafael Leonidas Trujillo Molina, ordered his troops to remain in their barracks, the sick and aging Vásquez was forced into exile and Estrella proclaimed provisional president. In May, Trujillo was elected with 95% of the vote, having used the army to harass and intimidate electoral personnel and potential opponents. After his inauguration in August, at his request, the Dominican Congress proclaimed the beginning of the 'Era of Trujillo'.
 Trujillo established absolute political control while promoting economic development—from which mainly he and his supporters benefitted—and severe repression of domestic human rights. Trujillo treated his political party, ''El Partido Dominicano'' (The Dominican Party), as a rubber-stamp for his decisions. The true source of his power was the ''Guardia Nacional''—larger, better armed, and more centrally controlled than any military force in the nation's history. By disbanding the regional militias, the Marines eliminated the main source of potential opposition, giving the Guard "a virtual monopoly on power". By 1940, Dominican military spending was 21% of the national budget. At the same time, he developed an elaborate system of espionage agencies. By the late 1950s, there were at least seven categories of intelligence agencies, spying on each other as well as the public. All citizens were required to carry identification cards and good-conduct passes from the secret police.
Obsessed with adulation, Trujillo promoted an extravagant cult of personality. When a hurricane struck Santo Domingo in 1930, killing over 3,000 people, he rebuilt the city and renamed it ''Ciudad Trujillo'': "Trujillo City"; he also renamed the country's and the Caribbean's highest mountain,
Trujillo established absolute political control while promoting economic development—from which mainly he and his supporters benefitted—and severe repression of domestic human rights. Trujillo treated his political party, ''El Partido Dominicano'' (The Dominican Party), as a rubber-stamp for his decisions. The true source of his power was the ''Guardia Nacional''—larger, better armed, and more centrally controlled than any military force in the nation's history. By disbanding the regional militias, the Marines eliminated the main source of potential opposition, giving the Guard "a virtual monopoly on power". By 1940, Dominican military spending was 21% of the national budget. At the same time, he developed an elaborate system of espionage agencies. By the late 1950s, there were at least seven categories of intelligence agencies, spying on each other as well as the public. All citizens were required to carry identification cards and good-conduct passes from the secret police.
Obsessed with adulation, Trujillo promoted an extravagant cult of personality. When a hurricane struck Santo Domingo in 1930, killing over 3,000 people, he rebuilt the city and renamed it ''Ciudad Trujillo'': "Trujillo City"; he also renamed the country's and the Caribbean's highest mountain,  By May 14, the Americans had established a "safety corridor" connecting the San Isidro Air Base and the "Duarte" Bridge to the Embajador Hotel and United States Embassy in the center of Santo Domingo, essentially sealing off the Constitutionalist area of Santo Domingo. Roadblocks were established and patrols ran continuously. Some 6,500 people from many nations were evacuated to safety. In addition, the US forces airlifted in relief supplies for Dominican nationals.
By mid-May, a majority of the OAS voted for Operation "Push Ahead", the reduction of United States forces and their replacement by an Inter-American Peace Force (IAPF). The Inter-American Peace Force was formally established on May 23. The following troops were sent by each country: Brazil – 1,130, Honduras – 250,
By May 14, the Americans had established a "safety corridor" connecting the San Isidro Air Base and the "Duarte" Bridge to the Embajador Hotel and United States Embassy in the center of Santo Domingo, essentially sealing off the Constitutionalist area of Santo Domingo. Roadblocks were established and patrols ran continuously. Some 6,500 people from many nations were evacuated to safety. In addition, the US forces airlifted in relief supplies for Dominican nationals.
By mid-May, a majority of the OAS voted for Operation "Push Ahead", the reduction of United States forces and their replacement by an Inter-American Peace Force (IAPF). The Inter-American Peace Force was formally established on May 23. The following troops were sent by each country: Brazil – 1,130, Honduras – 250,  On one hand, Balaguer was considered to be a ''
On one hand, Balaguer was considered to be a ''