History of archery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The oldest depictions of
The oldest depictions of


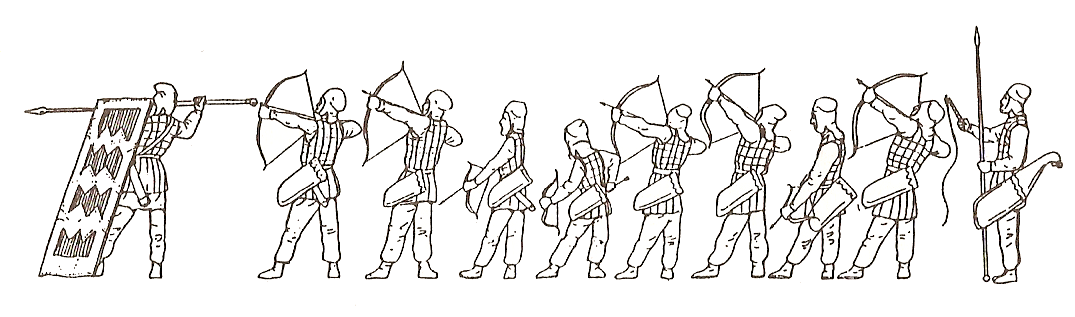 The
The
 The people of Crete practiced archery and Cretan mercenary archers were in great demand. Crete was known for its unbroken tradition of archery.
During the Alexander the Great#Invasion of India, invasion of India by Alexander the Great, archers are listed among the troops Alexander personally commanded.
The early Romans had very few archers, if any. As their empire grew, they recruited auxiliary archers from other nations. Julius Caesar's armies in Gaul included Cretan archers, and Vercingetorix his enemy ordered "all the archers, of whom there was a very great number in Gaul, to be collected". By the 4th century, archers with powerful composite bows were a regular part of Roman armies throughout the empire. After the fall of the western empire, the Romans came under severe pressure from the highly skilled mounted archery, mounted archers belonging to the Hun invaders, and later Eastern Roman armies relied heavily on mounted archery.
The people of Crete practiced archery and Cretan mercenary archers were in great demand. Crete was known for its unbroken tradition of archery.
During the Alexander the Great#Invasion of India, invasion of India by Alexander the Great, archers are listed among the troops Alexander personally commanded.
The early Romans had very few archers, if any. As their empire grew, they recruited auxiliary archers from other nations. Julius Caesar's armies in Gaul included Cretan archers, and Vercingetorix his enemy ordered "all the archers, of whom there was a very great number in Gaul, to be collected". By the 4th century, archers with powerful composite bows were a regular part of Roman armies throughout the empire. After the fall of the western empire, the Romans came under severe pressure from the highly skilled mounted archery, mounted archers belonging to the Hun invaders, and later Eastern Roman armies relied heavily on mounted archery.

 The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian general Bahram Chobin has been credited with writing a manual of archery in the tenth century in Ibn al-Nadim's catalogue ''Kitab al-Fihrist''.
A complete arrow of 75 cm (along with other fragments and arrow heads) dated back to 1283 AD, was discovered inside a cave situated in the Qadisha Valley, Lebanon.
A treatise on Arab archery by Muḥammad ibn Abī Bakr, called Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya (1292AD-1350AD) comes from the 14th century.
A treatise on Saracen archery was written in 1368. This was a didactic poem on archery dedicated to a Mameluke sultan by Ṭaibughā al-Ashrafī.
A 14th-century treatise on Arab archery, ''Kitāb fī maʿrifat ʿilm ramy al-sihām'', was written by Hussain bin Abd al-Rahman.
A treatise, ''A book on the excellence of the bow & arrow'' of c. 1500 details the practices and techniques of archery among the Arabs of that time.
An anonymous book written in Picardy, France in the late 15th century details how archery in medieval Europe was practiced. The book was titled ''Le Fachon de tirer l'arc a main''. It describes the means of how a yew bow could be made, the kinds of wood that could be used, how to shoot it, string it and different kind of arrows. According to the writer, its purpose is for posterity, possibly due to the rise of the gun.
In Mali Empire, Mali, the infantry, footmen were dominated by archers. Three archers to one spearman was the general ratio of Malian formations in the 16th century. The archers generally opened battle, softening up the enemy for cavalry charges or the advance of the spearmen.
The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian general Bahram Chobin has been credited with writing a manual of archery in the tenth century in Ibn al-Nadim's catalogue ''Kitab al-Fihrist''.
A complete arrow of 75 cm (along with other fragments and arrow heads) dated back to 1283 AD, was discovered inside a cave situated in the Qadisha Valley, Lebanon.
A treatise on Arab archery by Muḥammad ibn Abī Bakr, called Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya (1292AD-1350AD) comes from the 14th century.
A treatise on Saracen archery was written in 1368. This was a didactic poem on archery dedicated to a Mameluke sultan by Ṭaibughā al-Ashrafī.
A 14th-century treatise on Arab archery, ''Kitāb fī maʿrifat ʿilm ramy al-sihām'', was written by Hussain bin Abd al-Rahman.
A treatise, ''A book on the excellence of the bow & arrow'' of c. 1500 details the practices and techniques of archery among the Arabs of that time.
An anonymous book written in Picardy, France in the late 15th century details how archery in medieval Europe was practiced. The book was titled ''Le Fachon de tirer l'arc a main''. It describes the means of how a yew bow could be made, the kinds of wood that could be used, how to shoot it, string it and different kind of arrows. According to the writer, its purpose is for posterity, possibly due to the rise of the gun.
In Mali Empire, Mali, the infantry, footmen were dominated by archers. Three archers to one spearman was the general ratio of Malian formations in the 16th century. The archers generally opened battle, softening up the enemy for cavalry charges or the advance of the spearmen.
 The advent of Gunpowder warfare, firearms eventually rendered bows obsolete in warfare. Despite the high social status, ongoing utility, and widespread pleasure of archery, almost every culture that gained access to even early firearms used them widely, to the relative neglect of archery.
In Ireland, Geoffrey Keating (c. 1569 – c. 1644) mentions archery as having been practiced "down to a recent period within our own memory."
Early firearms were inferior in rate of fire (a Tudor English author expects eight shots from the English longbow in the time needed for a "ready shooter" to give five from the musket), and François Bernier reports that well-trained mounted archers at the Battle of Samugarh in 1658 were "shooting six times before a musketeer can fire twice". Firearms were also very susceptible to wet weather. However, they had a longer effective range (up to 200 yards for the longbow, up to 600 yards for the musket), greater penetration, were extremely powerful compared to any previous man-portable missile weapon (16th century arquebuses and muskets had 1,300 to 3,000 joules per shot depending on size and powder load, as compared to 80-100 joules for a typical longbow arrow or 150-200 joules for a crossbow bolt), and were tactically superior in the common situation of soldiers shooting at each other from behind obstructions. They also penetrated steel armour without any need to develop special musculature. Armies equipped with guns could thus provide superior firepower, and highly trained archers became obsolete on the battlefield. The Battle of Cerignola in 1503 was won by Spain mainly by the use of matchlock firearms, marking the first time a major battle in Europe was won through the use of firearms.
The last regular unit armed with bows was the Archers' Company of the Honourable Artillery Company, ironically a part of the oldest regular unit in England to be armed with gunpowder weapons. The last recorded use of bows in battle in England seems to have been a skirmish at Bridgnorth; in October 1642, during the English Civil War, an impromptu militia, armed with bows, was effective against un-armoured musketmen. The last use of the bow in battle in Britain is said to have occurred at the Battle of Tippermuir in Scotland on 1 September 1644, when James Graham, 1st Marquess of Montrose's Royalist highlanders defeated an army of Scottish Covenanters. Among Montrose's army were bowmen.
Archery continued in some areas that were subject to limitations on the ownership of arms, such as the Scottish Highlands during the repression that followed the decline of the Jacobitism, Jacobite cause, and the Cherokees after the Trail of Tears. The Tokugawa shogunate severely limited the import and manufacture of guns, and encouraged traditional martial skills among the samurai; towards the end of the Satsuma Rebellion in 1877, some rebels fell back on the use of bows and arrows. Archery remained an important part of the military examinations until 1894 in Korean bow, Korea and 1904 in China.
Within the steppe of Eurasia, archery continued to play an important part in warfare, although now restricted to mounted archery. The Ottoman Empire still fielded auxiliary cavalry which was noted for its use of bows from horseback. This practice was continued by the Ottoman subject nations, despite the Empire itself being a proponent of early firearms. The practice declined after the Crimean Khanate was absorbed by Russia; however mounted archers remained in the Ottoman order of battle until the post-1826 reforms to the Ottoman Army. The art of traditional archery remained in minority use for sport and for hunting in Turkey up until the 1920s, but the knowledge of constructing composite bows fell out of use with the death of the last bowyer in the 1930s. The rest of the Middle East also lost the continuity of its archery tradition at this time.
An exception to this trend was the Comanche culture of North America, where
The advent of Gunpowder warfare, firearms eventually rendered bows obsolete in warfare. Despite the high social status, ongoing utility, and widespread pleasure of archery, almost every culture that gained access to even early firearms used them widely, to the relative neglect of archery.
In Ireland, Geoffrey Keating (c. 1569 – c. 1644) mentions archery as having been practiced "down to a recent period within our own memory."
Early firearms were inferior in rate of fire (a Tudor English author expects eight shots from the English longbow in the time needed for a "ready shooter" to give five from the musket), and François Bernier reports that well-trained mounted archers at the Battle of Samugarh in 1658 were "shooting six times before a musketeer can fire twice". Firearms were also very susceptible to wet weather. However, they had a longer effective range (up to 200 yards for the longbow, up to 600 yards for the musket), greater penetration, were extremely powerful compared to any previous man-portable missile weapon (16th century arquebuses and muskets had 1,300 to 3,000 joules per shot depending on size and powder load, as compared to 80-100 joules for a typical longbow arrow or 150-200 joules for a crossbow bolt), and were tactically superior in the common situation of soldiers shooting at each other from behind obstructions. They also penetrated steel armour without any need to develop special musculature. Armies equipped with guns could thus provide superior firepower, and highly trained archers became obsolete on the battlefield. The Battle of Cerignola in 1503 was won by Spain mainly by the use of matchlock firearms, marking the first time a major battle in Europe was won through the use of firearms.
The last regular unit armed with bows was the Archers' Company of the Honourable Artillery Company, ironically a part of the oldest regular unit in England to be armed with gunpowder weapons. The last recorded use of bows in battle in England seems to have been a skirmish at Bridgnorth; in October 1642, during the English Civil War, an impromptu militia, armed with bows, was effective against un-armoured musketmen. The last use of the bow in battle in Britain is said to have occurred at the Battle of Tippermuir in Scotland on 1 September 1644, when James Graham, 1st Marquess of Montrose's Royalist highlanders defeated an army of Scottish Covenanters. Among Montrose's army were bowmen.
Archery continued in some areas that were subject to limitations on the ownership of arms, such as the Scottish Highlands during the repression that followed the decline of the Jacobitism, Jacobite cause, and the Cherokees after the Trail of Tears. The Tokugawa shogunate severely limited the import and manufacture of guns, and encouraged traditional martial skills among the samurai; towards the end of the Satsuma Rebellion in 1877, some rebels fell back on the use of bows and arrows. Archery remained an important part of the military examinations until 1894 in Korean bow, Korea and 1904 in China.
Within the steppe of Eurasia, archery continued to play an important part in warfare, although now restricted to mounted archery. The Ottoman Empire still fielded auxiliary cavalry which was noted for its use of bows from horseback. This practice was continued by the Ottoman subject nations, despite the Empire itself being a proponent of early firearms. The practice declined after the Crimean Khanate was absorbed by Russia; however mounted archers remained in the Ottoman order of battle until the post-1826 reforms to the Ottoman Army. The art of traditional archery remained in minority use for sport and for hunting in Turkey up until the 1920s, but the knowledge of constructing composite bows fell out of use with the death of the last bowyer in the 1930s. The rest of the Middle East also lost the continuity of its archery tradition at this time.
An exception to this trend was the Comanche culture of North America, where

Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In ...
, or the use of bow and arrow
The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles (arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was common ...
s, was probably developed in Africa by the later Middle Stone Age
The Middle Stone Age (or MSA) was a period of African prehistory between the Early Stone Age and the Late Stone Age. It is generally considered to have begun around 280,000 years ago and ended around 50–25,000 years ago. The beginnings of ...
(approx. 70,000 years ago). It is documented as part of warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regu ...
and hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
from the classical period (where it figures in the mythologies of many cultures) until the late medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
period when it was made obsolete by the increased use of firearms
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
.
Archers were a widespread if supplemental part of the military in the classical period, and bowmen fought on foot, in chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
s or mounted on horses. Archery rose to prominence in Europe in the later medieval period, where victories such as the Battle of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt ( ; french: Azincourt ) was an English victory in the Hundred Years' War. It took place on 25 October 1415 ( Saint Crispin's Day) near Azincourt, in northern France. The unexpected English victory against the numeric ...
cemented the longbow in military lore.
Archery in both hunting and warfare was eventually replaced by firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s in Europe in the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
and early modern period. Firearms eventually diffused throughout Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
via the Gunpowder empires, gradually reducing the importance of archery in warfare throughout the world.
Archery is still practiced today, for hunting and as a target sport.
Prehistory
Paleolithic and Epipaleolithic
The oldest known evidence of arrows comes from South African sites such asSibudu Cave
Sibudu Cave is a rock shelter in a sandstone cliff in northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It is an important Middle Stone Age site occupied, with some gaps, from years ago to years ago.
Evidence of some of the earliest examples of modern h ...
, where likely arrowheads have been found, dating from approximately 72,000–60,000 years ago, on some of which poisons may have been used.
The earliest probable arrowheads found outside of Africa have been discovered in 2020 in Fa Hien Cave, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
. It has been dated to 48,000 years ago. "Bow-and-arrow hunting at the Sri Lankan site likely focused on monkeys and smaller animals, such as squirrels... Remains of these creatures were found in the same sediment as the bone points."
At the site of Nataruk
Nataruk in Turkana County, Kenya, is the site of an archaeological investigation which uncovered the 10,000-year-old remains of 27 people. The remains have garnered wide media attention for possible bioarchaeological evidence of interpersonal vio ...
in Turkana County
Turkana County is a county in the former Rift Valley Province of Kenya. It is Kenya's largest county by land area (followed by Marsabit County), and also its northwesternmost. It is bordered by the countries of Uganda to the west; South Sudan ...
, Kenya, obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.
Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements such as silicon ...
bladelets found embedded in a human skull and within the thoracic cavity of another human skeleton, suggest the use of stone-tipped arrows as weapons about 10,000 years ago.
In the Sahara, Mesolithic
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
rock art of the Tassili plateau depicts people carrying bows from 5,000 BP or earlier.
Based on indirect evidence, the bow seems also to have appeared or reappeared later in Eurasia around the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
.
In the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, artifacts which may be arrow-shaft straighteners are known from the Natufian culture
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduct ...
, (ca. 12,800–10,300 BP) onwards. The Khiamian and PPN A shouldered Khiam-points may well be arrowheads.
Possible fragments of a bow found at Mannheim-Vogelstang have been dated to the Early Magdelenian age (c. 17,500 to 18,000 years ago) and at Stellmoor dated 11,000 years ago. Azilian
The Azilian is a Mesolithic industry of the Franco-Cantabrian region of northern Spain and Southern France. It dates approximately 10,000–12,500 years ago. Diagnostic artifacts from the culture include projectile points (microliths with ro ...
points found in Grotte du Bichon
Grotte du Bichon is a karstic cave in the Swiss Jura, overlooking the river Doubs at an altitude of 846 m, some 5 km north of La Chaux-de-Fonds. It is the site of the discovery of the skeleton a hunter-gatherer of the Azilian (late U ...
, Switzerland, alongside the remains of both a bear and a hunter, with flint fragments found in the bear's third vertebra, suggest the use of arrows at 13,500 years ago.
Other early indications of archery in Europe come from Stellmoor in the Ahrensburg valley north of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, Germany. They were associated with artifacts of the late Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
(11,000–9,000 BP). The arrows were made of pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
and consisted of a mainshaft and a 15–20 centimetre (6–8 inches) long foreshaft with a flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start ...
point. They had shallow grooves on the base, indicating that they were shot from a bow.
The oldest definite bows known so far come from the Holmegård swamp in Denmark. In the 1940s, two bows were found there, dated to about 8,000 BP. The Holmegaard bow The Holmegaard bows are a series of self bows found in the bogs of Northern Europe dating from the Mesolithic period.Comstock, P (1992). ''Ancient European Bows'', pp. 87-88. The Traditional Bowyers Bible Volume 2. The Lyons Press, 1992. They a ...
s are made of elm and have flat arms and a D-shaped midsection. The center section is biconvex. The complete bow is (5 ft) long. Bows of Holmegaard-type were in use until the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
; the convexity of the midsection has decreased with time.
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
pointed shafts have been found in England, Germany, Denmark, and Sweden. They were often rather long, up to (4 ft) and made of European hazel (''Corylus avellana
''Corylus avellana'', the common hazel, is a species of flowering plant in the birch family Betulaceae. It is native to Europe and western Asia. It is an important component of the hedgerows that were the traditional field boundaries in lowland E ...
''), wayfaring tree (''Viburnum lantana
''Viburnum lantana'', the wayfarer or wayfaring tree, is a species of '' Viburnum'', native to central, southern and western Europe (north to Yorkshire in England), northwest Africa, and southwestern Asia.Blamey, M. & Grey-Wilson, C. (1989). ' ...
'') and other small woody shoots. Some still have flint arrow-heads preserved; others have blunt wooden ends for hunting birds and small game. The ends show traces of fletching, which was fastened on with birch-tar
Birch tar or birch pitch is a substance (liquid when heated) derived from the dry distillation of the bark of the birch tree.
Compounds
It is composed of phenols such as guaiacol, cresol, xylenol, and creosol.
Ancient and modern uses
Birc ...
.
 The oldest depictions of
The oldest depictions of combat
Combat (French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
, found in Iberian cave art of the Mesolithic, show battles between archers.
A group of three archers encircled by a group of four is found in Cueva del Roure, Morella la Vella, Castellón, Valencia. A depiction of a larger battle (which may, however, date to the early Neolithic), in which eleven archers are attacked by seventeen running archers, is found in Les Dogue, Ares del Maestrat
Ares del Maestrat, also known as ''Ares del Maestre'' in Spanish or simply Ares, is a municipality in the province of Castelló in the Valencian Country. It is situated near the top of the Mola d'Ares mountain, at an elevation of 1,148 m.
As a r ...
, Castellón, Valencia.
At Val del Charco del Agua Amarga, Alcañiz
Alcañiz () is a town and municipality of Teruel province in the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. The town is located on the banks of the river Guadalope. Alcañiz is the unofficial capital of the Lower Aragon historical region. It lies ...
, Aragon, seven archers with plumes on their heads are fleeing a group of eight archers running in pursuit.
Archery seems to have arrived in the Americas via Alaska, as early as 6000 BC, with the Arctic small tool tradition, about 2,500 BC, spreading south into the temperate zones as early as 2,000 BC, and was widely known among the indigenous peoples of North America
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Am ...
from about 500 AD.
Neolithic
The oldest Neolithic bow known from Europe was found in anaerobic layers dating between 7,400 and 7,200 BP, the earliest layer of settlement at the lake settlement at La Draga,Banyoles
Banyoles () is a city of 20,168 inhabitants (2021) located in the province of Girona in northeastern Catalonia, Spain.
The town is the capital of the Catalan ''comarca'' " Pla de l'Estany". Although an established industrial centre many of th ...
, Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The city had an official population of 103,369 in 2020. Girona is the capit ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. The intact specimen is short at 1.08m, has a D-shaped cross-section, and is made of yew wood. Stone wrist-guards, interpreted as display versions of bracer
A bracer (or arm-guard) is a strap or sheath, commonly made of leather, stone or plastic, that covers the ventral (inside) surface of an archer's bow-holding arm. It protects the archer's forearm against injury by accidental whipping from th ...
s, form a defining part of the Beaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from a ...
and arrowheads are also commonly found in Beaker graves. European Neolithic fortifications, arrow-heads, injuries, and representations indicate that, in Neolithic and Early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
Europe, archery was a major form of interpersonal violence. For example, the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
settlement at Carn Brea was occupied between around 3700 and 3400 BC; excavations found that every timber structure on the site had been burnt, and there was a concentration of arrow heads around a probable entrance to the enclosure; these arrows may have been used by a large group of archers in an organized assault.
Bronze Age
Chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
-borne archers became a defining feature of Middle Bronze Age warfare, from Europe to Eastern Asia and India. However, in the Middle Bronze Age, with the development of massed infantry tactics, and with the use of chariots for shock tactics or as prestigious command vehicles, archery seems to have lessened in importance in European warfare. In approximately the same period, with the Seima-Turbino Phenomenon
The Seima-Turbino phenomenon is a pattern of burial sites with similar bronze artifacts dated to ca. 2300-1700 BC (2017 dated from 2100 BC to 1900 BC, 2007 dated to 1650 BC onwards) found across northern Eurasia, particularly Siberia and Cent ...
and the spread of the Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
, mounted archery
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, f ...
became a defining feature of Eurasian nomad
The Eurasian nomads were a large group of nomadic peoples from the Eurasian Steppe, who often appear in history as invaders of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, and South Asia.
A nomad is a member of people having no permanent a ...
cultures and a foundation of their military success, until the massed use of guns.
Ancient history

Ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
civilizations, notably the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
, Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
ns, Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
, Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
ns, Indians, Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply r ...
, Chinese, and Japanese fielded large numbers of archers in their armies. Arrows were destructive against massed formations, and the use of archers often proved decisive. The Sanskrit term for archery, dhanurveda, came to refer to martial arts in general.

North Africa
The ancient Egyptian people took to archery as early as 5,000 years ago. It was widespread by the time of the earliestpharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
s and was practiced both for hunting and use in warfare. Legendary figures from the tombs of Thebes are depicted giving "lessons in archery". Some Egyptian deities are also connected to archery.
The " Nine bows" were a conventional representation of Egypt's external enemies. One of the oldest representations of the Nine bows is on the seated statue of Pharaoh Djoser
Djoser (also read as Djeser and Zoser) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 3rd Dynasty during the Old Kingdom, and was the founder of that epoch. He is also known by his Hellenized names Tosorthros (from Manetho) and Sesorthos (from Eusebiu ...
(3rd Dynasty, 27th century BC).
Many of the archers in service to Egypt were of Nubian
Nubian may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Nubia, a region along the Nile river in Southern Egypt and northern Sudan.
*Nubian people
*Nubian languages
*Anglo-Nubian goat, a breed of goat
* Nubian ibex
* , several ships of the Britis ...
extraction commonly referred to as Medjay
Medjay (also ''Medjai'', ''Mazoi'', ''Madjai'', ''Mejay'', Egyptian ''mḏꜣ.j'', a nisba of ''mḏꜣ'',) was a demonym used in various ways throughout ancient Egyptian history to refer initially to a nomadic group from Nubia and later as a ge ...
, who go from a mercenary force during their initial service to Egypt in the Middle Kingdom to an elite paramilitary unit by the New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
. So effective were the Nubians as archers that Nubia as whole would be referred to Ta-Seti or land of the bow by the Ancient Egyptians.
Mesopotamia
TheAssyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
ns and Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
ians extensively used the bow and arrow for hunting and warfare. The empires in ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
formed the first standing armies used exclusively for warfare. This included soldiers trained and employed as archers. The archers served as an integral division of the military and was used on foot and on chariots.
 The
The Chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
warriors of the Kassites
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylo ...
relied heavily on the bow. The Nuzi texts The Nuzi texts are ancient documents found during an excavation of Nuzi, an ancient Mesopotamian city southwest of Kirkuk in modern Kirkuk Governorate of Iraq, located near the Tigris river. The site consists of one medium-sized multiperiod tell a ...
detail the bows and the number of arrows assigned to the chariot crew. Archery was essential to the role of the light horse-drawn chariot as a vehicle of warfare.
The Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
has multiple references to archery as a skill identified with the ancient Hebrews
The terms ''Hebrews'' (Hebrew: / , Modern: ' / ', Tiberian: ' / '; ISO 259-3: ' / ') and ''Hebrew people'' are mostly considered synonymous with the Semitic-speaking Israelites, especially in the pre-monarchic period when they were still ...
. Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
describes long bow
A longbow (known as warbow in its time, in contrast to a hunting bow) is a type of tall bow that makes a fairly long draw possible. A longbow is not significantly recurved. Its limbs are relatively narrow and are circular or D-shaped in cross ...
s used to great effect in Corduene.
Three-bladed (trilobate) arrowheads have been found in the United Arab Emirates, dated to 100BC-150AD.
Eurasian Steppes
The composite bow was first produced in the Eurasian Steppes during the Bronze Age, and from there it diffused throughout the Old World. The nomads from the Eurasian steppes are believed to play an integral part in introducing the composite bow to other civilizations, including Mesopotamia, Iran, India, East Asia, and Europe. There are arrowheads from the earliest chariot burials at Krivoye Lake, part of the Sintashta culture about 2100–1700 BC. These people are also believed to have invented spoke-wheeled chariots, and chariot archery became an integral component of the militaries of early Indo-Europeans. Domestication of horses and mounted horseback archery are also believed to have originated in the Eurasian steppes. This revolutionized warfare as well as the practice of archery.India
The use of bow and arrow was recorded extensively throughout the history of the Indian subcontinent. The paleolithic paintings of Bhimbetka rock shelters depict archery. Vedas, Vedic hymns in the Rigveda, Yajurveda, and Atharvaveda lay emphasis on the use of the bow and arrow. The second Veda, the Yajurveda contains Dhanurveda (dhanus "bow" and veda "knowledge"), which was an ancient treatise on the science of archery and its use in warfare. The existence of Dhanurveda or "Science of Archery" in antiquity is evident from references made in several works of ancient literature. The Viṣṇu Purāṇa refers it as one of the eighteen branches of knowledge taught, while the Mahābhārata mentions it as having sutras like other vedas. Shukra-Niti, Śukranīti describes it as that 'upaveda of yajurveda' which has five arts or practical aspects. The Dhanurveda enumerates the rules of archery, and describes the uses of weapons and the training the army. Besides providing the account of the training of the archers, Vasiṣṭha's Dhanurveda describes the different types of bows and arrows, as well as the process of making them. Detailed accounts of training methodologies in early India considered to be an essential martial skill in early India. The composite bow in India was being used by 2nd millennium BCE. The bow was used extensively on foot as well on chariots. It was incorporated into the standing armies of the Mahajanapadas, and used in mounted warfare on horses, camels, and elephants with a howdah. The importance of archery continued through antiquity during the Maurya Empire. The Arthashastra, a military treaties written by Chanakya during the Maurya Era, goes in depth on the importance and implementation of archery. It also mentions an archery school at Taxila which enrolled 103 princes from different kingdoms across the empire. During the era of the Gupta Empire mounted archery was largely supplanted by foot archers. This was in contrast to the nomadic armies on horseback from Central Asia such as the Iranian, Scythians, Parthians, Kushans, and Hunas. Later Indian kingdoms entities would maintain and field large numbers of mounted archers. The use of bows and arrows continued to be used as the mainstay of most Indian armies until the advent offirearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s, introduced by Mongol gunpowder empires.
Greco-Roman antiquity
 The people of Crete practiced archery and Cretan mercenary archers were in great demand. Crete was known for its unbroken tradition of archery.
During the Alexander the Great#Invasion of India, invasion of India by Alexander the Great, archers are listed among the troops Alexander personally commanded.
The early Romans had very few archers, if any. As their empire grew, they recruited auxiliary archers from other nations. Julius Caesar's armies in Gaul included Cretan archers, and Vercingetorix his enemy ordered "all the archers, of whom there was a very great number in Gaul, to be collected". By the 4th century, archers with powerful composite bows were a regular part of Roman armies throughout the empire. After the fall of the western empire, the Romans came under severe pressure from the highly skilled mounted archery, mounted archers belonging to the Hun invaders, and later Eastern Roman armies relied heavily on mounted archery.
The people of Crete practiced archery and Cretan mercenary archers were in great demand. Crete was known for its unbroken tradition of archery.
During the Alexander the Great#Invasion of India, invasion of India by Alexander the Great, archers are listed among the troops Alexander personally commanded.
The early Romans had very few archers, if any. As their empire grew, they recruited auxiliary archers from other nations. Julius Caesar's armies in Gaul included Cretan archers, and Vercingetorix his enemy ordered "all the archers, of whom there was a very great number in Gaul, to be collected". By the 4th century, archers with powerful composite bows were a regular part of Roman armies throughout the empire. After the fall of the western empire, the Romans came under severe pressure from the highly skilled mounted archery, mounted archers belonging to the Hun invaders, and later Eastern Roman armies relied heavily on mounted archery.
East Asia
Archery featured prominently in ancient Chinese culture and philosophy Confucius himself was an archery teacher; and Lie Yukou, Lie Zi (a Daoism, Daoist philosopher) was an avid archer. In China, crossbows were developed, and Han Dynasty writers attributed Chinese success in Han–Xiongnu War, battles against nomad invaders to the massed use of crossbows, first definitely attested at the Battle of Maling, Battle of Ma-Ling in 341 BC. Because the cultures associated with Chinese society spanned a wide geography and time range, the techniques and equipment associated with Chinese archery are diverse.Medieval history
Europe
At the start of the medieval period, shortbows were used for both hunting and warfare. Medieval shortbows were structurally similar to ancient bows, but new construction materials significantly increased their usefulness. With a range of about 100yds a shortbow had the ability to kill or injure an unarmoured man at close range, but were often ineffective against armour. Vikings made extensive use of shortbows both on land and at sea, but other early medieval armies less so, with some notable exceptions. Both sides used archers at the Battle of Hastings, and the Norman archers struck a decisive blow by firing their arrows into the air and (avoiding shields and armour which they could not penetrate) and wounding Saxon Harold Godwinson, King Harold. The shortbow remained the primary ranged weapon throughout early medieval Europe. Archers were usually unarmoured, and were typically peasants or townsmen rather than nobles or men-at-arms. Around the tenth century the crossbow was introduced in Europe. Crossbows generally had a longer range, greater accuracy and more penetration than the shortbow, but suffered from a much slower rate of fire. Unlike the longbow they did not require special skill or strength to use effectively. They were also controversial, attracting stigma to those who used them, and were outlawed by the Lateran Council of 1139. Despite this, crossbows were used in the early Crusades, with models having a range of 300yds and being able to penetrate armour or kill a horse. They fired short metal bolts rather than arrows. The French army relied substantially on the crossbow in late medieval times. The longbow first appeared in Europe in the 13th century, although similar weapons were described in antiquity. It did not appear with any frequency until the 14th. Like their shortbow predecessors longbow archers were more likely to be peasants or yeomen than men-at-arms. The longbow had a similar range and penetration as the crossbow, but a much higher rate of fire. It also required more skill and strength to use effectively than a crossbow. Its lack of accuracy at long ranges made it a mass weapon rather than an individual one. During the late medieval period the English army famously relied on massed archers armed with the longbow. In Highland Scotland, the use of archers in battle continued until 1689 at Killiekrankie with a documented fatal shot from the Hanoverian Government army but in numbers at the last clan battle between the MacDonalds and the Mackintoshes in 1688ad. Highlanders are most regularly recorded or depicted using the short recurve or "McNaughton Bow" in this period. Significant victories attributable to the longbow, such as the Battle of Crecy andBattle of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt ( ; french: Azincourt ) was an English victory in the Hundred Years' War. It took place on 25 October 1415 ( Saint Crispin's Day) near Azincourt, in northern France. The unexpected English victory against the numeric ...
resulted in the English longbow becoming part of military lore. In both England and Scotland legislation was passed to ensure a supply of trained longbowmen, such as the Unlawful Games Act 1541 which prohibited "Several new devised Games" that might detract from archery training.
The Middle East
In the Middle East the composite bow was the preferred bow in the later Medieval period. More powerful than the shortbow, they had the advantage over the longer longbow that they could be fired from horseback. However they also required skilled craftsmen to manufacture, and, like the longbow, extensive training to use well. The Byzantine Empire was already using mounted archers extensively by the 5th Century, and the Emperor Mavrikios laid down principles for their use in his seminal military work the Strategikon of Maurice. The core of the Byzantine army was the Cataphract, an armoured horse archer. The Byzantines also recruited mercenary light mounted archers from the Steppes. Turkish tribes, of which the Seljuk Turks are representative, used mounted archers against the European First Crusade, especially at the Battle of Dorylaeum (1097). Their archers were more lightly armoured than the Cataphracts, and consequently more mobile. Their tactic was to fire at the enemy infantry, and use their superior mobility to prevent the enemy from closing with them.Asia
The Mongol armies of Ghenghis Khan and his successors relied almost exclusively on mounted warriors, who used the Mongol bow (a form of recurve composite bow) as their principal weapon. Mongol bows of that period were constructed from leather, horn, and wood with animal sinew outside, held together with fish glue and covered with tree bark to protect against water. 13th century bows were said to be able to shoot 700-800 meters accurately. Warriors would carry two bows, a long one for shooting at range and a short one for close fighting. They also carried different types of arrows for different uses, some of which could pierce thick armour. The bow was also used for hunting, and warriors were trained from an early age, and competed in tournaments. In Korea Joseon adopted a military-service examination system from China that included a focus on archery skills and that contributed to the development of Korean archery as a practical martial art. In Asia archery was one of the Six Noble Arts of the Zhou dynasty of China (1146–256 BC); archery skill was a virtue for Chinese emperors. The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian general Bahram Chobin has been credited with writing a manual of archery in the tenth century in Ibn al-Nadim's catalogue ''Kitab al-Fihrist''.
A complete arrow of 75 cm (along with other fragments and arrow heads) dated back to 1283 AD, was discovered inside a cave situated in the Qadisha Valley, Lebanon.
A treatise on Arab archery by Muḥammad ibn Abī Bakr, called Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya (1292AD-1350AD) comes from the 14th century.
A treatise on Saracen archery was written in 1368. This was a didactic poem on archery dedicated to a Mameluke sultan by Ṭaibughā al-Ashrafī.
A 14th-century treatise on Arab archery, ''Kitāb fī maʿrifat ʿilm ramy al-sihām'', was written by Hussain bin Abd al-Rahman.
A treatise, ''A book on the excellence of the bow & arrow'' of c. 1500 details the practices and techniques of archery among the Arabs of that time.
An anonymous book written in Picardy, France in the late 15th century details how archery in medieval Europe was practiced. The book was titled ''Le Fachon de tirer l'arc a main''. It describes the means of how a yew bow could be made, the kinds of wood that could be used, how to shoot it, string it and different kind of arrows. According to the writer, its purpose is for posterity, possibly due to the rise of the gun.
In Mali Empire, Mali, the infantry, footmen were dominated by archers. Three archers to one spearman was the general ratio of Malian formations in the 16th century. The archers generally opened battle, softening up the enemy for cavalry charges or the advance of the spearmen.
The Sasanian Empire, Sasanian general Bahram Chobin has been credited with writing a manual of archery in the tenth century in Ibn al-Nadim's catalogue ''Kitab al-Fihrist''.
A complete arrow of 75 cm (along with other fragments and arrow heads) dated back to 1283 AD, was discovered inside a cave situated in the Qadisha Valley, Lebanon.
A treatise on Arab archery by Muḥammad ibn Abī Bakr, called Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya (1292AD-1350AD) comes from the 14th century.
A treatise on Saracen archery was written in 1368. This was a didactic poem on archery dedicated to a Mameluke sultan by Ṭaibughā al-Ashrafī.
A 14th-century treatise on Arab archery, ''Kitāb fī maʿrifat ʿilm ramy al-sihām'', was written by Hussain bin Abd al-Rahman.
A treatise, ''A book on the excellence of the bow & arrow'' of c. 1500 details the practices and techniques of archery among the Arabs of that time.
An anonymous book written in Picardy, France in the late 15th century details how archery in medieval Europe was practiced. The book was titled ''Le Fachon de tirer l'arc a main''. It describes the means of how a yew bow could be made, the kinds of wood that could be used, how to shoot it, string it and different kind of arrows. According to the writer, its purpose is for posterity, possibly due to the rise of the gun.
In Mali Empire, Mali, the infantry, footmen were dominated by archers. Three archers to one spearman was the general ratio of Malian formations in the 16th century. The archers generally opened battle, softening up the enemy for cavalry charges or the advance of the spearmen.
Decline of archery
 The advent of Gunpowder warfare, firearms eventually rendered bows obsolete in warfare. Despite the high social status, ongoing utility, and widespread pleasure of archery, almost every culture that gained access to even early firearms used them widely, to the relative neglect of archery.
In Ireland, Geoffrey Keating (c. 1569 – c. 1644) mentions archery as having been practiced "down to a recent period within our own memory."
Early firearms were inferior in rate of fire (a Tudor English author expects eight shots from the English longbow in the time needed for a "ready shooter" to give five from the musket), and François Bernier reports that well-trained mounted archers at the Battle of Samugarh in 1658 were "shooting six times before a musketeer can fire twice". Firearms were also very susceptible to wet weather. However, they had a longer effective range (up to 200 yards for the longbow, up to 600 yards for the musket), greater penetration, were extremely powerful compared to any previous man-portable missile weapon (16th century arquebuses and muskets had 1,300 to 3,000 joules per shot depending on size and powder load, as compared to 80-100 joules for a typical longbow arrow or 150-200 joules for a crossbow bolt), and were tactically superior in the common situation of soldiers shooting at each other from behind obstructions. They also penetrated steel armour without any need to develop special musculature. Armies equipped with guns could thus provide superior firepower, and highly trained archers became obsolete on the battlefield. The Battle of Cerignola in 1503 was won by Spain mainly by the use of matchlock firearms, marking the first time a major battle in Europe was won through the use of firearms.
The last regular unit armed with bows was the Archers' Company of the Honourable Artillery Company, ironically a part of the oldest regular unit in England to be armed with gunpowder weapons. The last recorded use of bows in battle in England seems to have been a skirmish at Bridgnorth; in October 1642, during the English Civil War, an impromptu militia, armed with bows, was effective against un-armoured musketmen. The last use of the bow in battle in Britain is said to have occurred at the Battle of Tippermuir in Scotland on 1 September 1644, when James Graham, 1st Marquess of Montrose's Royalist highlanders defeated an army of Scottish Covenanters. Among Montrose's army were bowmen.
Archery continued in some areas that were subject to limitations on the ownership of arms, such as the Scottish Highlands during the repression that followed the decline of the Jacobitism, Jacobite cause, and the Cherokees after the Trail of Tears. The Tokugawa shogunate severely limited the import and manufacture of guns, and encouraged traditional martial skills among the samurai; towards the end of the Satsuma Rebellion in 1877, some rebels fell back on the use of bows and arrows. Archery remained an important part of the military examinations until 1894 in Korean bow, Korea and 1904 in China.
Within the steppe of Eurasia, archery continued to play an important part in warfare, although now restricted to mounted archery. The Ottoman Empire still fielded auxiliary cavalry which was noted for its use of bows from horseback. This practice was continued by the Ottoman subject nations, despite the Empire itself being a proponent of early firearms. The practice declined after the Crimean Khanate was absorbed by Russia; however mounted archers remained in the Ottoman order of battle until the post-1826 reforms to the Ottoman Army. The art of traditional archery remained in minority use for sport and for hunting in Turkey up until the 1920s, but the knowledge of constructing composite bows fell out of use with the death of the last bowyer in the 1930s. The rest of the Middle East also lost the continuity of its archery tradition at this time.
An exception to this trend was the Comanche culture of North America, where
The advent of Gunpowder warfare, firearms eventually rendered bows obsolete in warfare. Despite the high social status, ongoing utility, and widespread pleasure of archery, almost every culture that gained access to even early firearms used them widely, to the relative neglect of archery.
In Ireland, Geoffrey Keating (c. 1569 – c. 1644) mentions archery as having been practiced "down to a recent period within our own memory."
Early firearms were inferior in rate of fire (a Tudor English author expects eight shots from the English longbow in the time needed for a "ready shooter" to give five from the musket), and François Bernier reports that well-trained mounted archers at the Battle of Samugarh in 1658 were "shooting six times before a musketeer can fire twice". Firearms were also very susceptible to wet weather. However, they had a longer effective range (up to 200 yards for the longbow, up to 600 yards for the musket), greater penetration, were extremely powerful compared to any previous man-portable missile weapon (16th century arquebuses and muskets had 1,300 to 3,000 joules per shot depending on size and powder load, as compared to 80-100 joules for a typical longbow arrow or 150-200 joules for a crossbow bolt), and were tactically superior in the common situation of soldiers shooting at each other from behind obstructions. They also penetrated steel armour without any need to develop special musculature. Armies equipped with guns could thus provide superior firepower, and highly trained archers became obsolete on the battlefield. The Battle of Cerignola in 1503 was won by Spain mainly by the use of matchlock firearms, marking the first time a major battle in Europe was won through the use of firearms.
The last regular unit armed with bows was the Archers' Company of the Honourable Artillery Company, ironically a part of the oldest regular unit in England to be armed with gunpowder weapons. The last recorded use of bows in battle in England seems to have been a skirmish at Bridgnorth; in October 1642, during the English Civil War, an impromptu militia, armed with bows, was effective against un-armoured musketmen. The last use of the bow in battle in Britain is said to have occurred at the Battle of Tippermuir in Scotland on 1 September 1644, when James Graham, 1st Marquess of Montrose's Royalist highlanders defeated an army of Scottish Covenanters. Among Montrose's army were bowmen.
Archery continued in some areas that were subject to limitations on the ownership of arms, such as the Scottish Highlands during the repression that followed the decline of the Jacobitism, Jacobite cause, and the Cherokees after the Trail of Tears. The Tokugawa shogunate severely limited the import and manufacture of guns, and encouraged traditional martial skills among the samurai; towards the end of the Satsuma Rebellion in 1877, some rebels fell back on the use of bows and arrows. Archery remained an important part of the military examinations until 1894 in Korean bow, Korea and 1904 in China.
Within the steppe of Eurasia, archery continued to play an important part in warfare, although now restricted to mounted archery. The Ottoman Empire still fielded auxiliary cavalry which was noted for its use of bows from horseback. This practice was continued by the Ottoman subject nations, despite the Empire itself being a proponent of early firearms. The practice declined after the Crimean Khanate was absorbed by Russia; however mounted archers remained in the Ottoman order of battle until the post-1826 reforms to the Ottoman Army. The art of traditional archery remained in minority use for sport and for hunting in Turkey up until the 1920s, but the knowledge of constructing composite bows fell out of use with the death of the last bowyer in the 1930s. The rest of the Middle East also lost the continuity of its archery tradition at this time.
An exception to this trend was the Comanche culture of North America, where mounted archery
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, f ...
remained competitive with muzzle-loading guns. "After... about 1800, most Comanches began to discard muskets and pistols and to rely on their older weapons." Repeating firearms, however, were superior in turn, and the Comanches adopted them when they could. Bows remained effective hunting weapons for skilled horse archers, used to some extent by all Native Americans on the Great Plains to hunt American Bison, buffalo as long as there were buffalo to hunt. The last Comanche hunt was in 1878, and it failed for lack of buffalo, not lack of appropriate weapons.
Ongoing use of bows and arrows was maintained in isolated cultures with little or no contact with the outside world. The use of traditional archery in some African conflicts has been reported in the 21st century, and the Sentinelese people, Sentinelese still use bows as part of a lifestyle scarcely touched by outside contact. A remote group in Brazil, recently photographed from the air, aimed bows at the aeroplane. Bows and arrows saw considerable use in the 2007–2008 Kenyan crisis.
Recreational revival
The British initiated a major revival of archery as an upper-class pursuit from about 1780–1840. Early recreational archery societies included the Finsbury Archers and the Popinjay (sport), Kilwinning Papingo, established in 1688. The latter held competitions in which the archers had to dislodge a wooden parrot from the top of an abbey tower. The Company of Scottish Archers was formed in 1676 and is one of the oldest sporting bodies in the world. It remained a small and scattered pastime, however, until the late 18th century when it experienced a fashionable revival among the aristocracy. Sir Ashton Lever, an antiquarian and collector, formed the Toxophilite Society in London in 1781, with the patronage of George III, George, the Prince of Wales. Archery societies were set up across the country, each with its own strict entry criteria and outlandish costumes. Recreational archery soon became extravagant social and ceremonial events for the nobility, complete with flags, music and 21 gun salutes for the competitors. The clubs were "the drawing rooms of the great country houses placed outside" and thus came to play an important role in the social networks of local elites. As well as its emphasis on display and status, the sport was notable for its popularity with females. Young women could not only compete in the contests but retain and show off their sexuality while doing so. Thus, archery came to act as a forum for introductions, flirtation and romance. It was often consciously styled in the manner of a Medieval tournament with titles and laurel wreaths being presented as a reward to the victor. General meetings were held from 1789, in which local lodges convened together to standardise the rules and ceremonies. Archery was also co-opted as a distinctively British tradition, dating back to the lore of Robin Hood and it served as a patriotic form of entertainment at a time of political tension in Europe. The societies were also elitist, and the new middle class bourgeoisie were excluded from the clubs due to their lack of social status. After the Napoleonic Wars, the sport became increasingly popular among all classes, and it was framed as a nostalgic reimagining of the preindustrial rural Britain. Particularly influential was Sir Walter Scott's 1819 novel, ''Ivanhoe'' that depicted the heroic character Locksley winning an archery tournament.A modern sport
The 1840s saw the first attempts at turning the recreation into a modern sport. The first Grand National Archery Society meeting was held in York in 1844 and over the next decade the extravagant and festive practices of the past were gradually whittled away and the rules were standardised as the 'York Round' – a series of shoots at 60, 80, and 100 yards. Horace A. Ford helped to improve archery standards and pioneered new archery techniques. He won the Grand National 11 times in a row and published a highly influential guide to the sport in 1856. Towards the end of the 19th century, the sport experienced declining participation as alternative sports such as croquet and tennis became more popular among the middle class. By 1889, just 50 archery clubs were left in Britain, but it was still included as a sport at the 1900 Paris Olympics. In the United States, primitive archery was revived in the early 20th century. The last of the Yahi#Yahi, Yahi Indian tribe, a native known as Ishi, came out of hiding in California in 1911. His doctor, Saxton Pope, learned many of Ishi's traditional archery skills, and popularized them. The Pope and Young Club, founded in 1961 and named in honor of Pope and his friend, Arthur Young, became one of North America's leading bowhunting and conservation organizations. Founded as a nonprofit scientific organization, the club was patterned after the prestigious Boone and Crockett Club and advocated responsible bowhunting by promoting quality, fair chase hunting, and sound conservation practices. In Korea, the transformation of archery to a healthy pastime was led by Gojong of the Korean Empire, Emperor Gojong, and is the basis of a popular modern sport. The Japanese continue to make and use their unique yumi, traditional equipment. Among the Cherokees, popular use of their traditional longbows never died out. In China, at the beginning of the 21st century, there has been revival in interest among craftsmen looking to construct bows and arrows, as well as in practicing technique in the traditional Chinese style. In modern times, mounted archery continues to be practiced as a popular competitive sport in modern Hungary and in some Asian countries but it is not recognized as an international competition. Archery is the national sport of the Kingdom of Bhutan. From the 1920s, professional engineers took an interest in archery, previously the exclusive field of traditional craft experts. They led the commercial development of new forms of bow including the modern recurve bow, recurve and compound bow. These modern forms are now dominant in modern Western archery; traditional bows are in a minority. In the 1980s, the skills of traditional archery were revived by American enthusiasts, and combined with the new scientific understanding. Much of this expertise is available in the ''Traditional Bowyer's Bibles'' (see Further reading). Modern game archery owes much of its success to Fred Bear, an American bow hunter and bow manufacturer.See also
*Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In ...
*Arash
*Kyūdō, Japanese archery
*Yabusame, Japanese horseback archery
*Gungdo, Korean archery
*Turkish archery
*Chinese archery
*Archery in India
References
* *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* Online Archery Books with historical content. {{Archery, state=uncollapsed History of archery,