History of anthropometry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of
 In 1716
In 1716 
 Intelligence testing was compared with anthropometrics.
Intelligence testing was compared with anthropometrics.
 In 1883, Frenchman Alphonse Bertillon introduced a system of identification that was named after him. The "Bertillonage" system was based on the finding that several measures of physical features, such as the dimensions of bony structures in the body, remain fairly constant throughout adult life. Bertillon concluded that when these measurements were made and recorded systematically, every individual would be distinguishable. This cites as authorities:
* Lombroso, ''Antropometria di 400 delinquenti'' (1872)
* Roberts, ''Manual of Anthropometry'' (1878)
* Ferri, ''Studi comparati di antropometria'' (2 vols., 1881–1882)
* Lombroso, ''Rughe anomale speciali ai criminali'' (1890)
* Bertillon, ''Instructions signalétiques pour l'identification anthropométrique'' (1893)
* Livi, ''Anthropometria'' (Milan, 1900)
* Fürst, ''Indextabellen zum anthropometrischen Gebrauch'' (Jena, 1902)
* ''Report of Home Office Committee on the Best Means of Identifying Habitual Criminals'' (1893–1894) Bertillon's goal was a way of identifying recidivists ("repeat offenders"). Previously police could only record general descriptions. Photography of criminals had become commonplace, but there was no easy way to sort the many thousands of photographs except by name. Bertillon's hope was that, through the use of measurements, a set of identifying numbers could be entered into a filing system installed in a single cabinet.
In 1883, Frenchman Alphonse Bertillon introduced a system of identification that was named after him. The "Bertillonage" system was based on the finding that several measures of physical features, such as the dimensions of bony structures in the body, remain fairly constant throughout adult life. Bertillon concluded that when these measurements were made and recorded systematically, every individual would be distinguishable. This cites as authorities:
* Lombroso, ''Antropometria di 400 delinquenti'' (1872)
* Roberts, ''Manual of Anthropometry'' (1878)
* Ferri, ''Studi comparati di antropometria'' (2 vols., 1881–1882)
* Lombroso, ''Rughe anomale speciali ai criminali'' (1890)
* Bertillon, ''Instructions signalétiques pour l'identification anthropométrique'' (1893)
* Livi, ''Anthropometria'' (Milan, 1900)
* Fürst, ''Indextabellen zum anthropometrischen Gebrauch'' (Jena, 1902)
* ''Report of Home Office Committee on the Best Means of Identifying Habitual Criminals'' (1893–1894) Bertillon's goal was a way of identifying recidivists ("repeat offenders"). Previously police could only record general descriptions. Photography of criminals had become commonplace, but there was no easy way to sort the many thousands of photographs except by name. Bertillon's hope was that, through the use of measurements, a set of identifying numbers could be entered into a filing system installed in a single cabinet.
 The system involved 10 measurements; ''height'', ''stretch'' (distance from left
The system involved 10 measurements; ''height'', ''stretch'' (distance from left  The system was soon adapted to police methods: it prevented impersonation and could demonstrate wrongdoing.
Bertillonage was before long represented in Paris by a collection of some 100,000 cards and became popular in several other countries' justice systems. England followed suit when in 1894, a committee sent to Paris to investigate the methods and its results reported favorably on the use of measurements for primary classification and recommended also the partial adoption of the system of
The system was soon adapted to police methods: it prevented impersonation and could demonstrate wrongdoing.
Bertillonage was before long represented in Paris by a collection of some 100,000 cards and became popular in several other countries' justice systems. England followed suit when in 1894, a committee sent to Paris to investigate the methods and its results reported favorably on the use of measurements for primary classification and recommended also the partial adoption of the system of
 Phylogeography is the science of identifying and tracking major human migrations, especially in prehistoric times. Linguistics can follow the movement of languages and archaeology can follow the movement of artefact styles but neither can tell whether a culture's spread was due to a source population's physically migrating or to a destination population's simply copying the technology and learning the language. Anthropometry was used extensively by anthropologists studying human and racial origins: some attempted racial differentiation and classification, often seeking ways in which certain races were inferior to others. Nott translated
Phylogeography is the science of identifying and tracking major human migrations, especially in prehistoric times. Linguistics can follow the movement of languages and archaeology can follow the movement of artefact styles but neither can tell whether a culture's spread was due to a source population's physically migrating or to a destination population's simply copying the technology and learning the language. Anthropometry was used extensively by anthropologists studying human and racial origins: some attempted racial differentiation and classification, often seeking ways in which certain races were inferior to others. Nott translated
ArchaeologyInfo-003
. This school of physical anthropology generally went into decline during the 1940s.
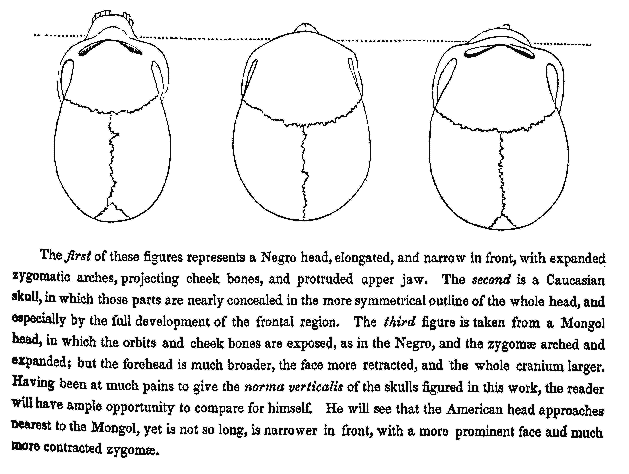 In ''Crania Americana'' Morton claimed that Caucasians had the biggest brains, averaging 87 cubic inches, Indians were in the middle with an average of 82 cubic inches and Negroes had the smallest brains with an average of 78 cubic inches. In 1873
In ''Crania Americana'' Morton claimed that Caucasians had the biggest brains, averaging 87 cubic inches, Indians were in the middle with an average of 82 cubic inches and Negroes had the smallest brains with an average of 78 cubic inches. In 1873
Ariani, indogermani, stirpi mediterranee: aspetti del dibattito sulle razze europee (1870-1914)
, '' Cromohs'', 1998 Virchow later rejected measure of skulls as legitimate means of
/ref> He also compared equatorial Africans from the poorest and least educated areas of Africa with Asians from the wealthiest, most educated areas and colder climates. According to Z. Z. Cernovsky Rushton's own study shows that the average cranial capacity of North American blacks is similar to that of Caucasians from comparable climatic zones, though a previous work by Rushton showed appreciable differences in cranial capacity between North Americans of different race. This is consistent with the findings of Z. Z. Cernovsky that people from different climates tend to have minor differences in brain size.
 Observable craniofacial differences included: head shape (mesocephalic, brachycephalic, dolichocephalic) breadth of nasal aperture, nasal root height, sagittal crest appearance, jaw thickness, brow ridge size and forehead slope. Using this skull-based categorization, German philosopher Christoph Meiners in his The Outline of History of Mankind (1785) identified three racial groups:
*
Observable craniofacial differences included: head shape (mesocephalic, brachycephalic, dolichocephalic) breadth of nasal aperture, nasal root height, sagittal crest appearance, jaw thickness, brow ridge size and forehead slope. Using this skull-based categorization, German philosopher Christoph Meiners in his The Outline of History of Mankind (1785) identified three racial groups:
*
Forensic Misclassification of Ancient Nubian Crania: Implications for Assumptions about Human Variation, Frank L'Engle Williams, Robert L. Belcher, and George J. Armelagos
(pdf)
Anthropometric Survey of Army Personnel: Methods and Summary Statistics 1988
* ISO 7250: Basic human body measurements for technological design,
Anthropometry Procedures Manual
'. CDC: Atlanta, USA; 2007. * *Folia Anthropologica: tudományos és módszertani folyóirat. 9: 5–17. ISSN 1786-5654 * (A classic review of human body sizes.) * Stewart A. "Kinanthropometry and body composition: A natural home for three dimensional photonic scanning". ''Journal of Sports Sciences'', March 2010; 28(5): 455–457. {{Historical definitions of race *
anthropometry
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various at ...
includes its use as an early tool of anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
, use for identification, use for the purposes of understanding human physical variation in paleoanthropology and in various attempts to correlate physical with racial and psychological traits. At various points in history, certain anthropometrics have been cited by advocates of discrimination and eugenics often as part of novel or based upon pseudoscience.
Craniometry and paleoanthropology
 In 1716
In 1716 Louis-Jean-Marie Daubenton
Louis Jean-Marie Daubenton (29 May 1716 – 1 January 1800) was a French naturalist and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie ou Dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers''.
Biography
Daubenton was born at Montbard, Côte-d' ...
, who wrote many essays on comparative anatomy for the Académie française, published his ''Memoir on the Different Positions of the Occipital Foramen in Man and Animals'' (''Mémoire sur les différences de la situation du grand trou occipital dans l'homme et dans les animaux''). Six years later Pieter Camper
Petrus Camper FRS (11 May 1722 – 7 April 1789), was a Dutch physician, anatomist, physiologist, midwife, zoologist, anthropologist, palaeontologist and a naturalist in the Age of Enlightenment. He was one of the first to take an interest i ...
(1722–1789), distinguished both as an artist and as an anatomist, published some lectures that laid the foundation of much work. Camper invented the " facial angle," a measure meant to determine intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
among various species. According to this technique, a "facial angle" was formed by drawing two lines: one horizontally from the nostril
A nostril (or naris , plural ''nares'' ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbi ...
to the ear
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of ...
; and the other perpendicularly from the advancing part of the upper jawbone to the most prominent part of the forehead. Camper's measurements of facial angle were first made to compare the skulls of men with those of other animals. Camper claimed that antique statues presented an angle of 90°, Europeans of 80°, Central Africans of 70° and the orangutan of 58°.
Swedish professor of anatomy Anders Retzius
Anders Adolph Retzius (13 October 1796 – 18 April 1860), was a Swedish professor of anatomy and a supervisor at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
Biography
Retzius was born in Lund, Sweden, in 1796. He enrolled at Lund University in 1 ...
(1796–1860) first used the cephalic index in physical anthropology to classify ancient human remains found in Europe. He classed skulls in three main categories; "dolichocephalic" (from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
''kephalê'' "head", and ''dolikhos'' "long and thin"), "brachycephalic" (short and broad) and "mesocephalic" (intermediate length and width). Scientific research was continued by Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (15 April 177219 June 1844) was a French naturalist who established the principle of "unity of composition". He was a colleague of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and expanded and defended Lamarck's evolutionary theories ...
(1772–1844) and Paul Broca
Pierre Paul Broca (, also , , ; 28 June 1824 – 9 July 1880) was a French physician, anatomist and anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that is named after him. Broca's area is involve ...
(1824–1880), founder of the Anthropological Society in France in 1859. Paleoanthropologists still rely upon craniofacial anthropometry to identify species in the study of fossilized hominid bones. Specimens of ''Homo erectus'' and athletic specimens of ''Homo sapiens'', for example, are virtually identical from the neck down but their skulls can easily be told apart.

Samuel George Morton
Samuel George Morton (January 26, 1799 – May 15, 1851) was an American physician, natural scientist, and writer who argued against the single creation story of the Bible, monogenism, instead supporting a theory of multiple racial creations, p ...
(1799–1851), whose two major monographs were the ''Crania Americana'' (1839), ''An Inquiry into the Distinctive Characteristics of the Aboriginal Race of America'' and ''Crania Aegyptiaca'' (1844) concluded that the ancient Egyptians were not Negroid but Caucasoid and that Caucasians and Negroes were already distinct three thousand years ago. Since ''The Bible'' indicated that Noah's Ark
Noah's Ark ( he, תיבת נח; Biblical Hebrew: ''Tevat Noaḥ'')The word "ark" in modern English comes from Old English ''aerca'', meaning a chest or box. (See Cresswell 2010, p.22) The Hebrew word for the vessel, ''teva'', occurs twice in ...
had washed up on Mount Ararat
Mount Ararat or , ''Ararat''; or is a snow-capped and dormant compound volcano in the extreme east of Turkey. It consists of two major volcanic cones: Greater Ararat and Little Ararat. Greater Ararat is the highest peak in Turkey and th ...
only a thousand years before this Noah's sons could not account for every race on earth. According to Morton's theory of polygenism
Polygenism is a theory of human origins which posits the view that the human races are of different origins (''polygenesis''). This view is opposite to the idea of monogenism, which posits a single origin of humanity. Modern scientific views no ...
the races had been separate from the start.David Hurst Thomas
David Hurst Thomas (born 1945) is the curator of North American Archaeology in the Division of Anthropology at the American Museum of Natural History and a professor at Richard Gilder Graduate School. He was previously a chairman of the American Mu ...
, ''Skull Wars: Kennewick Man, Archaeology, and the Battle for Native American Identity'', 2001, pp. 38–41 Josiah C. Nott and George Gliddon
George Robbins Gliddon (1809 – November 16, 1857) was an English-born American Egyptologist.
Biography
He was born in Devonshire, England. His father, a merchant, was United States consul at Alexandria where Gliddon was taken at an early age. ...
carried Morton's ideas further. Charles Darwin, who thought the single-origin hypothesis
In paleoanthropology, the recent African origin of modern humans, also called the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA), recent single-origin hypothesis (RSOH), replacement hypothesis, or recent African origin model (RAO), is the dominant model of the ...
essential to evolutionary theory
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, opposed Nott and Gliddon in his 1871 ''The Descent of Man
''The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex'' is a book by English naturalist Charles Darwin, first published in 1871, which applies evolutionary theory to human evolution, and details his theory of sexual selection, a form of biol ...
'', arguing for monogenism
Monogenism or sometimes monogenesis is the theory of human origins which posits a common descent for all human races. The negation of monogenism is polygenism. This issue was hotly debated in the Western world in the nineteenth century, as the ...
.
In 1856, workers found in a limestone quarry the skull of a Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
hominid male, thinking it to be the remains of a bear. They gave the material to amateur naturalist Johann Karl Fuhlrott who turned the fossils over to anatomist Hermann Schaaffhausen. The discovery was jointly announced in 1857, giving rise to the discipline of paleoanthropology. By comparing skeletons of apes to man, T. H. Huxley (1825–1895) backed up Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
's theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variatio ...
, first expressed in ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'' (1859). He also developed the " Pithecometra principle," which stated that man and ape were descended from a common ancestor.
Eugène Dubois
Marie Eugène François Thomas Dubois (; 28 January 1858 – 16 December 1940) was a Dutch paleoanthropologist and geologist. He earned worldwide fame for his discovery of ''Pithecanthropus erectus'' (later redesignated ''Homo erectus''), or "Java ...
' (1858–1940) discovery in 1891 in Indonesia of the "Java Man
Java Man (''Homo erectus erectus'', formerly also ''Anthropopithecus erectus'', ''Pithecanthropus erectus'') is an early human fossil discovered in 1891 and 1892 on the island of Java (Dutch East Indies, now part of Indonesia). Estimated to be b ...
", the first specimen of Homo erectus to be discovered, demonstrated mankind's deep ancestry outside Europe. Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919) became famous for his "recapitulation theory
The theory of recapitulation, also called the biogenetic law or embryological parallelism—often expressed using Ernst Haeckel's phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"—is a historical hypothesis that the development of the embryo of an a ...
", according to which each individual mirrors the evolution of the whole species during his life.
Typology and personality
 Intelligence testing was compared with anthropometrics.
Intelligence testing was compared with anthropometrics. Samuel George Morton
Samuel George Morton (January 26, 1799 – May 15, 1851) was an American physician, natural scientist, and writer who argued against the single creation story of the Bible, monogenism, instead supporting a theory of multiple racial creations, p ...
(1799–1851) collected hundreds of human skulls from all over the world and started trying to find a way to classify them according to some logical criterion. Morton claimed that he could judge intellectual capacity by cranial capacity
The size of the brain is a frequent topic of study within the fields of anatomy, biological anthropology, animal science and evolution. Brain size is sometimes measured by weight and sometimes by volume (via MRI scans or by skull volume). Neur ...
. A large skull meant a large brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
and high intellectual capacity, a small skull indicated a small brain and decreased intellectual capacity. Modern science has since confirmed that there is a correlation between cranium size (measured in various ways) and intelligence as measured by IQ tests, although it is a weak correlation at about 0.2. Today, brain volume as measured with MRI scanners also find a correlation between brain size and intelligence at about 0.4.
Craniometry
Craniometry is measurement of the cranium (the main part of the skull), usually the human cranium. It is a subset of cephalometry, measurement of the head, which in humans is a subset of anthropometry, measurement of the human body. It is dis ...
was also used in phrenology, which purported to determine character, personality traits, and criminality on the basis of the shape of the head. At the turn of the 19th century, Franz Joseph Gall
Franz Josef Gall (; 9 March 175822 August 1828) was a German neuroanatomist, physiologist, and pioneer in the study of the localization of mental functions in the brain.
Claimed as the founder of the pseudoscience of phrenology, Gall was an ea ...
(1758–1822) developed "cranioscopy" (Ancient Greek ''kranion'' "skull", ''scopos'' "vision"), a method to determine the personality and development of mental and moral faculties on the basis of the external shape of the skull. Cranioscopy was later renamed phrenology (''phrenos'': mind, ''logos'': study) by his student Johann Spurzheim
Johann Gaspar Spurzheim (31 December 1776 – 10 November 1832) was a German physician who became one of the chief proponents of phrenology, which was developed c. 1800 by Franz Joseph Gall (1758–1828).
Biography
Spurzheim was born near Tr ...
(1776–1832), who wrote extensively on "Drs. Gall and Spurzheim's physiognomical
Physiognomy (from the Greek , , meaning "nature", and , meaning "judge" or "interpreter") is the practice of assessing a person's character or personality from their outer appearance—especially the face. The term can also refer to the general ...
System." These all claimed the ability to predict traits or intelligence and were intensively practised in the 19th and the first part of the 20th century.
During the 1940s anthropometry was used by William Sheldon when evaluating his somatotype
Somatotype is a highly disputed taxonomy developed in the 1940s by American psychologist William Herbert Sheldon to categorize the human physique according to the relative contribution of three fundamental elements which he termed ''somatotypes'' ...
s, according to which characteristics of the body can be translated into characteristics of the mind. Inspired by Cesare Lombroso's criminal anthropology, he also believed that criminality
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definitions of", in Ca ...
could be predicted according to the body type. A basically anthropometric division of body types into the categories endomorphic, ectomorphic
Somatotype is a highly disputed taxonomy developed in the 1940s by American psychologist William Herbert Sheldon to categorize the human physique according to the relative contribution of three fundamental elements which he termed ''somatotypes'' ...
and mesomorphic derived from Sheldon's somatotype
Somatotype is a highly disputed taxonomy developed in the 1940s by American psychologist William Herbert Sheldon to categorize the human physique according to the relative contribution of three fundamental elements which he termed ''somatotypes'' ...
theories is today popular among people doing weight training
Weight training is a common type of strength training for developing the strength, size of skeletal muscles and maintenance of strength.Keogh, Justin W, and Paul W Winwood. “Report for: The Epidemiology of Injuries Across the Weight-Trai ...
.
Forensic anthropometry
Bertillon, Galton and criminology
 In 1883, Frenchman Alphonse Bertillon introduced a system of identification that was named after him. The "Bertillonage" system was based on the finding that several measures of physical features, such as the dimensions of bony structures in the body, remain fairly constant throughout adult life. Bertillon concluded that when these measurements were made and recorded systematically, every individual would be distinguishable. This cites as authorities:
* Lombroso, ''Antropometria di 400 delinquenti'' (1872)
* Roberts, ''Manual of Anthropometry'' (1878)
* Ferri, ''Studi comparati di antropometria'' (2 vols., 1881–1882)
* Lombroso, ''Rughe anomale speciali ai criminali'' (1890)
* Bertillon, ''Instructions signalétiques pour l'identification anthropométrique'' (1893)
* Livi, ''Anthropometria'' (Milan, 1900)
* Fürst, ''Indextabellen zum anthropometrischen Gebrauch'' (Jena, 1902)
* ''Report of Home Office Committee on the Best Means of Identifying Habitual Criminals'' (1893–1894) Bertillon's goal was a way of identifying recidivists ("repeat offenders"). Previously police could only record general descriptions. Photography of criminals had become commonplace, but there was no easy way to sort the many thousands of photographs except by name. Bertillon's hope was that, through the use of measurements, a set of identifying numbers could be entered into a filing system installed in a single cabinet.
In 1883, Frenchman Alphonse Bertillon introduced a system of identification that was named after him. The "Bertillonage" system was based on the finding that several measures of physical features, such as the dimensions of bony structures in the body, remain fairly constant throughout adult life. Bertillon concluded that when these measurements were made and recorded systematically, every individual would be distinguishable. This cites as authorities:
* Lombroso, ''Antropometria di 400 delinquenti'' (1872)
* Roberts, ''Manual of Anthropometry'' (1878)
* Ferri, ''Studi comparati di antropometria'' (2 vols., 1881–1882)
* Lombroso, ''Rughe anomale speciali ai criminali'' (1890)
* Bertillon, ''Instructions signalétiques pour l'identification anthropométrique'' (1893)
* Livi, ''Anthropometria'' (Milan, 1900)
* Fürst, ''Indextabellen zum anthropometrischen Gebrauch'' (Jena, 1902)
* ''Report of Home Office Committee on the Best Means of Identifying Habitual Criminals'' (1893–1894) Bertillon's goal was a way of identifying recidivists ("repeat offenders"). Previously police could only record general descriptions. Photography of criminals had become commonplace, but there was no easy way to sort the many thousands of photographs except by name. Bertillon's hope was that, through the use of measurements, a set of identifying numbers could be entered into a filing system installed in a single cabinet.
 The system involved 10 measurements; ''height'', ''stretch'' (distance from left
The system involved 10 measurements; ''height'', ''stretch'' (distance from left shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder mak ...
to middle finger
The middle finger, long finger, second finger, third finger, toll finger or tall man is the third digit of the human hand, located between the index finger and the ring finger. It is typically the longest digit. In anatomy, it is also calle ...
of raised right arm), ''bust'' (torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a huma ...
from head to seat when seated), ''head length'' (crown to forehead) and ''head width'' temple to temple) ''width'' of cheeks
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the insi ...
, and "lengths" of the ''right ear
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of ...
'', the ''left foot, middle finger
The middle finger, long finger, second finger, third finger, toll finger or tall man is the third digit of the human hand, located between the index finger and the ring finger. It is typically the longest digit. In anatomy, it is also calle ...
'', and ''cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding ...
'' (elbow to tip of middle finger). It was possible, by exhaustion, to sort the cards on which these details were recorded (together with a photograph) until a small number produced the measurements of the individual sought, independently of name.
 The system was soon adapted to police methods: it prevented impersonation and could demonstrate wrongdoing.
Bertillonage was before long represented in Paris by a collection of some 100,000 cards and became popular in several other countries' justice systems. England followed suit when in 1894, a committee sent to Paris to investigate the methods and its results reported favorably on the use of measurements for primary classification and recommended also the partial adoption of the system of
The system was soon adapted to police methods: it prevented impersonation and could demonstrate wrongdoing.
Bertillonage was before long represented in Paris by a collection of some 100,000 cards and became popular in several other countries' justice systems. England followed suit when in 1894, a committee sent to Paris to investigate the methods and its results reported favorably on the use of measurements for primary classification and recommended also the partial adoption of the system of finger print
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
s suggested by Francis Galton, then in use in Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
, where measurements were abandoned in 1897 after the fingerprint system was adopted throughout British India. Three years later England followed suit, and, as the result of a fresh inquiry ordered by the Home Office, relied upon fingerprints alone.
Bertillonage exhibited certain defects and was gradually supplanted by the system of fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfac ...
s and, latterly, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
. Bertillon originally measured variables he thought were independent – such as forearm length and leg length – but Galton had realized that both were the result of a single causal variable (in this case, stature) and developed the statistical concept of correlation.
Other complications were: it was difficult to tell whether or not individuals arrested were first-time offenders; instruments employed were costly and liable to break down; skilled measurers were needed; errors were frequent and all but irremediable; and it was necessary to repeat measurements three times to arrive at a mean result.
Physiognomy
Physiognomy claimed a correlation between physical features (especially facial features) and character traits. It was made famous by Cesare Lombroso (1835–1909), the founder ofanthropological criminology
Anthropological criminology (sometimes referred to as criminal anthropology, literally a combination of the study of the human species and the study of criminals) is a field of offender profiling, based on perceived links between the nature of ...
, who claimed to be able to scientifically identify links between the nature of a crime and the personality or physical appearance of the offender. The originator of the concept of a " born criminal" and arguing in favor of biological determinism
Biological determinism, also known as genetic determinism, is the belief that human behaviour is directly controlled by an individual's genes or some component of their physiology, generally at the expense of the role of the environment, whether i ...
, Lombroso tried to recognize criminals by measurements of their bodies. He concluded that skull and facial features were clues to genetic criminality and that these features could be measured with craniometers and calipers with the results developed into quantitative research. A few of the 14 identified traits of a criminal included large jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serv ...
s, forward projection of jaw, low sloping forehead; high cheekbones, flattened or upturned nose; handle-shaped ear
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of ...
s; hawk-like nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes ...
s or fleshy lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be ...
s; hard shifty eyes; scanty beard or baldness; insensitivity to pain; long arms, and so on.
Phylogeography, race and human origins
 Phylogeography is the science of identifying and tracking major human migrations, especially in prehistoric times. Linguistics can follow the movement of languages and archaeology can follow the movement of artefact styles but neither can tell whether a culture's spread was due to a source population's physically migrating or to a destination population's simply copying the technology and learning the language. Anthropometry was used extensively by anthropologists studying human and racial origins: some attempted racial differentiation and classification, often seeking ways in which certain races were inferior to others. Nott translated
Phylogeography is the science of identifying and tracking major human migrations, especially in prehistoric times. Linguistics can follow the movement of languages and archaeology can follow the movement of artefact styles but neither can tell whether a culture's spread was due to a source population's physically migrating or to a destination population's simply copying the technology and learning the language. Anthropometry was used extensively by anthropologists studying human and racial origins: some attempted racial differentiation and classification, often seeking ways in which certain races were inferior to others. Nott translated Arthur de Gobineau
Joseph Arthur de Gobineau (; 14 July 1816 – 13 October 1882) was a French aristocrat who is best known for helping to legitimise racism by the use of scientific racist theory and "racial demography", and for developing the theory of the Ary ...
's ''An Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races
''Essai sur l'inégalité des races humaines'' (Essay on the Inequality of the Human Races, 1853–1855) is a racist and pseudoscientific work of French writer Joseph Arthur, Comte de Gobineau, which argues that there are intellectual differen ...
'' (1853–1855), a founding work of racial segregationism that made three main divisions between races, based not on colour but on climatic conditions and geographic location, and privileged the "Aryan" race. Science has tested many theories aligning race and personality, which have been current since Boulainvilliers (1658–1722) contrasted the '' Français'' (French people), alleged descendants of the Nordic Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, and members of the aristocracy, to the Third Estate
The estates of the realm, or three estates, were the broad orders of social hierarchy used in Christendom (Christian Europe) from the Middle Ages to early modern Europe. Different systems for dividing society members into estates developed and ...
, considered to be indigenous Gallo-Roman
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context ...
people subordinated by right of conquest
The right of conquest is a right of ownership to land after immediate possession via force of arms. It was recognized as a principle of international law that gradually deteriorated in significance until its proscription in the aftermath of Worl ...
.
François Bernier
François Bernier (25 September 162022 September 1688) was a French physician and traveller. He was born in Joué-Etiau in Anjou. He stayed (14 October 165820 February 1670) for around 12 years in India.
His 1684 publication "Nouvel ...
, Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his Nobility#Ennoblement, ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalise ...
and Blumenbach had examined multiple observable human characteristics in search of a typology. Bernier based his racial classification on physical type which included hair shape, nose shape and skin color. Linnaeus based a similar racial classification scheme. As anthropologists gained access to methods of skull measure they developed racial classification based on skull shape.
Theories of scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
became popular, one prominent figure being Georges Vacher de Lapouge
Count Georges Vacher de Lapouge (; 12 December 1854 – 20 February 1936) was a French anthropologist and a theoretician of eugenics and racialism. He is known as the founder of anthroposociology, the anthropological and sociological study of race ...
(1854–1936), who in ''L'Aryen et son rôle social'' ("The Aryan and his social role", 1899) divided humanity into various, hierarchized, different " races", spanning from the " Aryan white race, dolichocephalic" to the "brachycephalic" (short and broad-headed) race. Between these Vacher de Lapouge identified the "'' Homo europaeus'' (Teutonic, Protestant, etc.), the "'' Homo alpinus''" (Auvergnat
or (endonym: ) is a northern dialect of Occitan spoken in central and southern France, in particular in the former administrative region of Auvergne.
Currently, research shows that there is not really a true Auvergnat dialect but rather a va ...
, Turkish, etc.) and the "'' Homo mediterraneus''" (Napolitano Napolitano (Italian language#Modern era, Modern Italian ''"Napoletano (disambiguation), Napoletano"'', Neapolitan: ''Nnapulitano'') is translated in English as Neapolitan (disambiguation), Neapolitan. The word can refer to people from Naples, Napoli ...
, Andalus, etc.). "Homo africanus" (Congo, Florida) was excluded from discussion. His racial classification ("Teutonic", "Alpine" and "Mediterranean") was also used by William Z. Ripley (1867–1941) who, in '' The Races of Europe'' (1899), made a map of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
according to the cephalic index of its inhabitants.
Vacher de Lapouge became one of the leading inspirations of Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
anti-semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
and Nazi ideology
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
relied on anthropometric measurements to distinguish Aryans from Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
s and many forms of anthropometry were used for the advocacy of eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior o ...
. During the 1920s and 1930s, though, members of the school of cultural anthropology of Franz Boas began to use anthropometric approaches to discredit the concept of fixed biological race. Boas used the cephalic index to show the influence of environmental factors. Researches on skulls and skeletons eventually helped liberate 19th century European science from its ethnocentric
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead o ...
bias."Cultural Biases Reflected in the Hominid Fossil Record" (history), by Joshua Barbach and Craig Byron, 2005, ''ArchaeologyInfo.com'' webpageArchaeologyInfo-003
. This school of physical anthropology generally went into decline during the 1940s.
Race and brain size
Several studies have demonstrated correlations between race and brain size, with varying results. In some studies, Caucasians were reported to have larger brains than other racial groups, whereas in recent studies and reanalysis of previous studies, East Asians were reported as having larger brains and skulls. More common among the studies was the report that Africans had smaller skulls than either Caucasians or East Asians. Criticisms have been raised against a number of these studies regarding questionable methods. In ''Crania Americana'' Morton claimed that Caucasians had the biggest brains, averaging 87 cubic inches, Indians were in the middle with an average of 82 cubic inches and Negroes had the smallest brains with an average of 78 cubic inches. In 1873
In ''Crania Americana'' Morton claimed that Caucasians had the biggest brains, averaging 87 cubic inches, Indians were in the middle with an average of 82 cubic inches and Negroes had the smallest brains with an average of 78 cubic inches. In 1873 Paul Broca
Pierre Paul Broca (, also , , ; 28 June 1824 – 9 July 1880) was a French physician, anatomist and anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that is named after him. Broca's area is involve ...
(1824–1880) found the same pattern described by Samuel Morton's ''Crania Americana'' by weighing brains at autopsy. Other historical studies alleging a Black–White difference in brain size include Bean (1906), Mall, (1909), Pearl, (1934) and Vint (1934). But in Germany Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder ...
's study led him to denounce " Nordic mysticism" in the 1885 Anthropology Congress in Karlsruhe
Karlsruhe ( , , ; South Franconian: ''Kallsruh'') is the third-largest city of the German state (''Land'') of Baden-Württemberg after its capital of Stuttgart and Mannheim, and the 22nd-largest city in the nation, with 308,436 inhabitants. ...
. Josef Kollmann, a collaborator of Virchow, stated in the same congress that the people of Europe, be them German, Italian, English or French, belonged to a "mixture of various races," furthermore declaring that the "results of craniology" led to "struggle against any theory concerning the superiority of this or that European race".Andrea Orsucci,Ariani, indogermani, stirpi mediterranee: aspetti del dibattito sulle razze europee (1870-1914)
, '' Cromohs'', 1998 Virchow later rejected measure of skulls as legitimate means of
taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
. Paul Kretschmer Paul Kretschmer (2 May 1866 – 9 March 1956) was a German linguist who studied the earliest history and interrelations of the Indo-European languages and showed how they were influenced by non-Indo-European languages, such as Etruscan.
Biograph ...
quoted an 1892 discussion with him concerning these criticisms, also citing Aurel von Törok's 1895 work, who basically proclaimed the failure of craniometry.
Stephen Jay Gould (1941–2002) claimed Samuel Morton had fudged data and "overpacked" the skulls. A subsequent study by John Michael concluded that " ntrary to Gould's interpretation... Morton's research was conducted with integrity." In 2011 physical anthropologists at the university of, which owns Morton's collection, published a study that concluded that "Morton did not manipulate his data to support his preconceptions, contra Gould." They identified and remeasured half of the skulls used in Morton's reports, finding that in only 2% of cases did Morton's measurements differ significantly from their own and that these errors either were random or gave a larger than accurate volume to African skulls, the reverse of the bias that Dr. Gould imputed to Morton. Difference in brain size, however, does not necessarily imply differences in intelligence: women tend to have smaller brains than men yet have more neural complexity and loading in certain areas of the brain. This claim has been criticized by, among others, John S. Michael, who reported in 1988 that Morton's analysis was "conducted with integrity" while Gould's criticism was "mistaken".
Similar claims were previously made by Ho et al. (1980), who measured 1,261 brains at autopsy, and Beals et al. (1984), who measured approximately 20,000 skulls, finding the same East Asian → Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
an → Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n pattern but warning against using the findings as indicative of racial traits, "If one merely lists such means by geographical region or race, causes of similarity by genogroup and ecotype are hopelessly confounded". Rushton's findings have been criticized for confusing African-Americans with equatorial Africans, who generally have smaller craniums as people from hot climates often have slightly smaller crania.Cernovsky, Z. Z. (1997) A critical look at intelligence research, In Fox, D. & Prilleltensky, I. (Eds.) Critical Psychology, London: Sage, ps 121-133./ref> He also compared equatorial Africans from the poorest and least educated areas of Africa with Asians from the wealthiest, most educated areas and colder climates. According to Z. Z. Cernovsky Rushton's own study shows that the average cranial capacity of North American blacks is similar to that of Caucasians from comparable climatic zones, though a previous work by Rushton showed appreciable differences in cranial capacity between North Americans of different race. This is consistent with the findings of Z. Z. Cernovsky that people from different climates tend to have minor differences in brain size.
Race, identity and cranio-facial description
 Observable craniofacial differences included: head shape (mesocephalic, brachycephalic, dolichocephalic) breadth of nasal aperture, nasal root height, sagittal crest appearance, jaw thickness, brow ridge size and forehead slope. Using this skull-based categorization, German philosopher Christoph Meiners in his The Outline of History of Mankind (1785) identified three racial groups:
*
Observable craniofacial differences included: head shape (mesocephalic, brachycephalic, dolichocephalic) breadth of nasal aperture, nasal root height, sagittal crest appearance, jaw thickness, brow ridge size and forehead slope. Using this skull-based categorization, German philosopher Christoph Meiners in his The Outline of History of Mankind (1785) identified three racial groups:
*Caucasoid
The Caucasian race (also Caucasoid or Europid, Europoid) is an obsolete racial classification of human beings based on a now-disproven theory of biological race. The ''Caucasian race'' was historically regarded as a biological taxon which, de ...
characterized by a tall dolichocephalic skull, receded zygomas, large brow ridge and projecting-narrow nasal apertures.
*Negroid
Negroid (less commonly called Congoid) is an obsolete racial grouping of various people indigenous to Africa south of the area which stretched from the southern Sahara desert in the west to the African Great Lakes in the southeast, but also to i ...
characterized by a short dolichocephalic skull, receded zygomas and wide nasal apertures.
*Mongoloid
Mongoloid () is an obsolete racial grouping of various peoples indigenous to large parts of Asia, the Americas, and some regions in Europe and Oceania. The term is derived from a now-disproven theory of biological race. In the past, other terms ...
characterized by a medium brachycephalic skull, projecting zygomas, small brow ridge and small nasal apertures.
Ripley's ''The Races of Europe'' was rewritten in 1939 by Harvard physical anthropologist Carleton S. Coon. Coon, a 20th-century craniofacial anthropometrist, used the technique for his ''The Origin of Races'' (New York: Knopf, 1962). Because of the inconsistencies in the old three-part system (Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Negroid), Coon adopted a five-part scheme. He defined "Caucasoid" as a pattern of skull measurements and other phenotypical characteristics typical of populations in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, and Northeast Africa (Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, and Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
). He discarded the term "Negroid" as misleading since it implies skin tone, which is found at low latitudes around the globe and is a product of adaptation, and defined skulls typical of sub-Saharan Africa as "Congoid" and those of Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
as "Capoid". Finally, he split "Australoid" from "Mongoloid" along a line roughly similar to the modern distinction between sinodonts in the north and sundadonts in the south. He argued that these races had developed independently of each other over the past half-million years, developing into Homo Sapiens at different periods of time, resulting in different levels of civilization. This raised considerable controversy and led the American Anthropological Association to reject his approach without mentioning him by name.
In '' The Races of Europe'' (1939) Coon classified Caucasoids into racial sub-groups named after regions or archaeological sites such as Brünn, Borreby, Alpine, Ladogan, East Baltic, Neo-Danubian, Lappish, Mediterranean, Atlanto-Mediterranean, Irano-Afghan, Nordic, Hallstatt, Keltic, Tronder, Dinaric, Noric and Armenoid. This typological view of race, however, was starting to be seen as out-of-date at the time of publication. Coon eventually resigned from the American Association of Physical Anthropologists
The American Association of Biological Anthropologists (AABA) is an international professional society of biological anthropologists, based in the United States. The organization publishes the ''American Journal of Physical Anthropology'', a pe ...
, while some of his other works were discounted because he would not agree with the evidence brought forward by Franz Boas, Stephen Jay Gould, Richard Lewontin
Richard Charles Lewontin (March 29, 1929 – July 4, 2021) was an American evolutionary biologist, mathematician, geneticist, and social commentator. A leader in developing the mathematical basis of population genetics and evolutionary theory, ...
, Leonard Lieberman and others.
The concept of biologically distinct races has been rendered obsolete by modern genetics.Templeton, A. (2016). EVOLUTION AND NOTIONS OF HUMAN RACE. In Losos J. & Lenski R. (Eds.), ''How Evolution Shapes Our Lives: Essays on Biology and Society'' (pp. 346-361). Princeton; Oxford: Princeton University Press. , see esp. p. 360: " e answer to the question whether races exist in humans is clear and unambiguous: no." That this view reflects the consensus among American anthropologists is stated in: See also: Different methods of categorizing humans yield different groups, making them non-concordant. John Relethford, The Human Species: An introduction to Biological Anthropology, 5th ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003). Neither will the craniofacial method pin-point geographic origins reliably, due to variation in skulls within a geographic region. About one-third of "white" Americans have detectable African DNA markers, and about five percent of "black" Americans have no detectable "negroid" traits at all, craniofacial or genetic. Given three Americans who self-identify and are socially accepted as white, black and Hispanic, and given that they have precisely the same Afro-European mix of ancestries (one African great-grandparent), there is no objective test that will identify their group membership without an interview."The assignment of skeletal racial origin is based principally upon stereotypical features found most frequently in the most geographically distant populations. While this is useful in some contexts (for example, sorting skeletal material of largely West African ancestry from skeletal material of largely Western European ancestry), it fails to identify populations that originate elsewhere and misrepresents fundamental patterns of human biological diversity"Forensic Misclassification of Ancient Nubian Crania: Implications for Assumptions about Human Variation, Frank L'Engle Williams, Robert L. Belcher, and George J. Armelagos
(pdf)
In popular culture
* The Bertillon system was used by the detectives in Caleb Carr's novel ''The Alienist
''The Alienist'' is a crime novel by Caleb Carr first published in 1994 and is the first book in the Kreizler series. It takes place in New York City in 1896, and includes appearances by many famous figures of New York society in that era, inc ...
''
See also
*Anthropometry
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various at ...
* Anthropometric history
Anthropometric history is the study of the history of human height and weight. The concept was formulated in 1989 although it has historical roots. In the 1830s, Adolphe Quetelet and Louis R. Villermé studied the physical stature of populations. ...
* Historical race concepts
The concept of race as a categorization of anatomically modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') has an extensive history in Europe and the Americas. The contemporary word ''race'' itself is modern; historically it was used in the sense of "nation, eth ...
* Scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism (racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies ...
References
Further reading
Anthropometric Survey of Army Personnel: Methods and Summary Statistics 1988
* ISO 7250: Basic human body measurements for technological design,
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
, 1998.
* ISO 8559: Garment construction and anthropometric surveys — Body dimensions, International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
, 1989.
* ISO 15535: General requirements for establishing anthropometric databases, International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
, 2000.
* ISO 15537: Principles for selecting and using test persons for testing anthropometric aspects of industrial products and designs, International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
, 2003.
* ISO 20685: 3-D scanning methodologies for internationally compatible anthropometric databases, International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
, 2005.
*National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a survey research program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States, and t ...
. Anthropometry Procedures Manual
'. CDC: Atlanta, USA; 2007. * *Folia Anthropologica: tudományos és módszertani folyóirat. 9: 5–17. ISSN 1786-5654 * (A classic review of human body sizes.) * Stewart A. "Kinanthropometry and body composition: A natural home for three dimensional photonic scanning". ''Journal of Sports Sciences'', March 2010; 28(5): 455–457. {{Historical definitions of race *
Anthropometry
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various at ...
Anthropometry
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various at ...
Criminology
Race and intelligence controversy
Biological anthropology
Human height
Human body weight
Scientific racism
History of measurement