History of Sweden (1772–1809) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
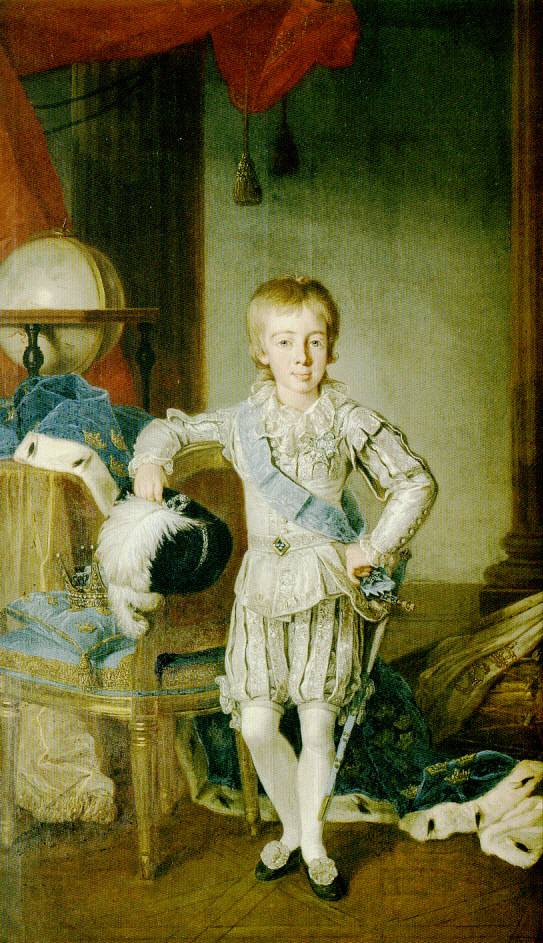

 The immediate consequence of the Russian invasion was the deposition of Gustav IV Adolf by the
The immediate consequence of the Russian invasion was the deposition of Gustav IV Adolf by the
History of Sweden
The history of Sweden can be traced back to the melting of the Northern Polar Ice Caps. From as early as 12000 BC, humans have inhabited this area. Throughout the Stone Age, between 8000 BC and 6000 BC, early inhabitants used st ...
from 1772 through 1809 is better known as the Gustavian era of Kings Gustav III
Gustav III (29 March 1792), also called ''Gustavus III'', was King of Sweden from 1771 until his assassination in 1792. He was the eldest son of Adolf Frederick of Sweden and Queen Louisa Ulrika of Prussia.
Gustav was a vocal opponent of what ...
and Gustav IV, as well as the reign of King Charles XIII of Sweden
Charles XIII, or Carl XIII ( sv, Karl XIII, 7 October 1748 – 5 February 1818), was King of Sweden from 1809 and King of Norway from 1814 to his death. He was the second son (and younger brother to King Gustav III) of King Adolf Frederick of S ...
.
Gustav III
Adolf Frederick of Sweden
Adolf Frederick, or Adolph Frederick ( sv, Adolf Fredrik, german: Adolf Friedrich; 14 May 171012 February 1771) was King of Sweden from 1751 until his death. He was the son of Christian August of Holstein-Gottorp, Prince of Eutin, and Albertina ...
died on 12 February 1771. The elections afterward resulted in a partial victory for the Caps party, especially among the lower orders; but in the estate of the peasantry the Caps majority was merely nominal, while the mass of the nobility was dead against them. Nothing could be done, however, till the return of the new king, Gustav III, from Paris.
Coronation oath
The new coronation oath contained three revolutionary clauses: #The first aimed at making abdications in the future impossible by binding the king to reign uninterruptedly. #The second obliged him to abide, not by the decision of all the estates together, as heretofore, but by that of the majority only, with the view of enabling the actually dominant lower estates (in which there was a large Cap majority) to rule without the nobility. #The third clause required him, in all cases of preferment, to be guided not "principally" as heretofore, but "solely" by merit. All through 1771 the estates wrangled over the clauses. An attempt of the king to mediate foundered on the suspicions of the estate of burgesses, and on 24 February 1772. the nobility yielded.Constitution
The non-noble Cap majority now proceeded to attack the Privy Council. the ''Riksrådet'', the last stronghold of the Hats, and, on 25 April of that year, it succeeded in ousting them. It was now, for the first time, that Gustav began to consider the possibility of a revolution. The newconstitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
of 20 August 1772 which Gustav III imposed upon the Riksdag of the Estates
Riksdag of the Estates ( sv, Riksens ständer; informally sv, Ståndsriksdagen) was the name used for the Estates of Sweden when they were assembled. Until its dissolution in 1866, the institution was the highest authority in Sweden next to t ...
, converted a weak and disunited republic into a strong but limited monarchy. The estates could assemble only when summoned by him; he could dismiss them whenever he thought fit; and their deliberations were to be confined exclusively to the propositions which he laid before them. But these extensive powers were subjected to important checks. Thus, without the previous consent of the estates, no new law could be imposed, no old law abolished, no offensive war undertaken, no extraordinary war subsidy levied. The estates alone could tax themselves; they had the absolute control of the Riksbank – the Bank of Sweden, and the right of controlling the national expenditure.
In Sweden the change was most popular. But Gustav's first Riksdag, that of 1778, opened the eyes of the deputies to the fact that their political supremacy had departed. The king was now their sovereign lord; and, for all his courtesy and gentleness, the jealousy with which he guarded and the vigour with which he enforced the prerogative plainly showed that he meant to remain so. But it was not till after eight years more had elapsed that actual trouble began. The Riksdag of 1778 had been obsequious; the Riksdag of 1786 was mutinous. It rejected nearly all the royal measures outright, or so modified them that Gustav himself withdrew them. When he dismissed the estates, the speech from the throne held out no prospect of their speedy revocation.
Nevertheless, within three years, the king was obliged to summon another Riksdag, which met at Stockholm on 26 January 1789. His attempt in the interval to rule without a parliament had been disastrous. It was only by a breach of his own constitution that he had been able to declare war against Russia in April 1788; the Conspiracy of Anjala (July) had paralysed all military operations at the very opening of the campaign; and the sudden invasion of his western provinces by the Danes, almost simultaneously (September), seemed to bring him to the verge of ruin. But the contrast, at this crisis, between his self-sacrificing patriotism and the treachery of the Russophil aristocracy was so striking that, when the Riksdag assembled, Gustav found that the three lower estates were ultra-royalist, and with their aid he succeeded, not without running great risks in crushing the opposition of the nobility by a second coup d'état on 16 February 1789 and passing the famous Act of Union and Security which gave the king an absolutely free hand as regards foreign affairs and the command of the army, and made further treason impossible. The nobility never forgave him.
Foreign affairs
Abroad the Swedish revolution made a great sensation. Catherine II of Russia concluded a secret alliance withDenmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, in which the Swedish revolution was described as "an act of violence" justifying both powers in seizing the first favourable opportunity for intervention to restore the Swedish constitution of 1720.
Unknown to party leaders, Gustav had renewed the Swedish alliance with France and had received solemn assurances of assistance from Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached ...
if Gustav were to reestablish monarchical rule in Sweden. Moreover, France agreed to pay its outstanding subsidies to Sweden, amounting to 1.5 million livres annually, beginning from January 1772. What's more, Charles Gravier, comte de Vergennes, was to be sent to Stockholm to circumvent the designs of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
just as he had previously done in the Sublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
History
The name ...
at Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
.
Gustav IV
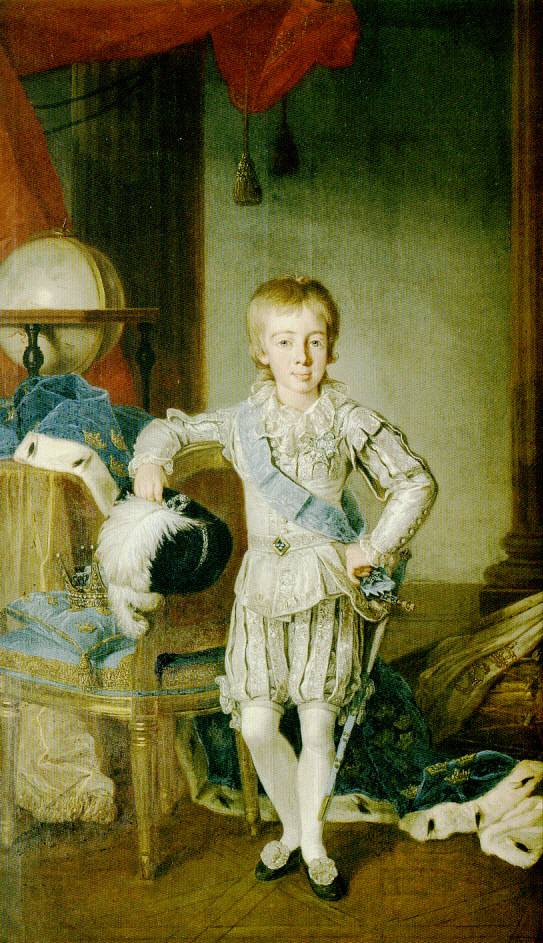

Reuterholm
The new king, Gustav IV, still a minor, was brought up amongJacobins
, logo = JacobinVignette03.jpg
, logo_size = 180px
, logo_caption = Seal of the Jacobin Club (1792–1794)
, motto = "Live free or die"(french: Vivre libre ou mourir)
, successor = P ...
. During the king's minority, Gustaf Reuterholm virtually ruled Sweden. After the execution of Louis XVI of France
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
on 21 January 1793, Sweden recognized the new French republic, and secret negotiations for contracting an alliance were begun in May of the same year until the protests of Catherine of Russia, supported by all the other European powers, finally induced Sweden to suspend them.
The negotiations with the French Jacobins exacerbated the hatred which Gustav's supporters felt for the Jacobin counselors of Charles, the duke-regent, later Charles XIII of Sweden
Charles XIII, or Carl XIII ( sv, Karl XIII, 7 October 1748 – 5 February 1818), was King of Sweden from 1809 and King of Norway from 1814 to his death. He was the second son (and younger brother to King Gustav III) of King Adolf Frederick of S ...
. They formed a conspiracy to overthrow the government, led by Gustaf Mauritz Armfelt
Count Gustaf Mauritz Armfelt (russian: Граф Густав-Маврикий Максимович Армфельт, tr, ; 31 March 1757 – 19 August 1814) was a Finnish- Swedish- Russian courtier and diplomat. In Finland, he is considered one ...
, which was to have been supported by a Russian fleet and a rising of the Dalecarlia
Dalarna () is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in central Sweden. English exonyms for it are Dalecarlia () and the Dales.
Dalarna adjoins Härjedalen, Hälsingland, Gästrikland, Västmanland and Värmland. It is also bordered by Norway ...
ns. The conspiracy was discovered and vigorously suppressed.
Rapprochement
A rapprochement took place between theScandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
n kingdoms during the revolutionary wars. Thus, on 27 March 1794, a neutrality compact was formed between with Denmark and Sweden; and their united squadrons patrolled the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
to protect their merchantmen from the British cruisers. The French republic was officially recognized by the Swedish government on 23 April 1795. In return, Sweden received a subsidy and a treaty between the two powers was signed on 14 September 1795. But an attempt to regain the friendship of Russia, which had broken off diplomatic relations with Sweden, was frustrated by the refusal of the king to accept as his bride the Russian grand duchess Alexandra, whom Reuterholm had provided. This was Reuterholm's last official act. On 1 November 1796, Gustav IV at age 18 took the government into his own hands.
Gustavian government
The government ofGustav IV of Sweden
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland.
The occupation of Finland in 1808–09 ...
was almost a pure autocracy. At his very first Riksdag, held at Norrköping in March 1800, the nobility were compelled to ratify Gustav III's Act of Union and Security.
A notable change took place in Sweden's foreign policy in December 1800 when Denmark, Sweden and Russia acceded to a second League of Armed Neutrality
The Second League of Armed Neutrality or the League of the North was an alliance of the north European naval powers Denmark–Norway, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia. It existed between 1800 and 1801 during the War of the Second Coalition and was ...
, directed against Great Britain. Hitherto Sweden had kept aloof from continental complications, but the arrest and execution of the Duc d'Enghien
Duke of Enghien (french: Duc d'Enghien, pronounced with a silent ''i'') was a noble title pertaining to the House of Condé. It was only associated with the town of Enghien for a short time.
Dukes of Enghien – first creation (1566–1569)
The ...
in 1804 inspired Gustav IV with such a hatred of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
that when a general coalition was formed against the French emperor he was one of the first to join it (3 December 1804), pledging himself to send an army corps to cooperate with the English and Russians in driving the enemy out of the Netherlands and Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
. But his quarrel with Frederick William III of Prussia detained him in Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, and when at last in December 1805 he led his 6,000 men towards the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
district, the third coalition had already been dissipated by the victories of Ulm
Ulm () is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Danube on the border with Bavaria. The city, which has an estimated population of more than 126,000 (2018), forms an urban district of its own (german: link=no, ...
and Austerlitz Austerlitz may refer to:
History
* Battle of Austerlitz, an 1805 victory by the French Grand Army of Napoleon Bonaparte
Places
* Austerlitz, German name for Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic, which gave its name to the Battle of Austerlitz a ...
.
In 1806 a rupture between Sweden and Prussia was prevented only by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's assault upon the latter power. After Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
Napoleon attempted to win over Sweden, but Gustav rejected every overture. The result was the total loss of Swedish Pomerania, and the Swedish army was saved from destruction only by the ingenuity of Johan Christopher Toll
Count Johan Christopher Toll (1 February 1743 – 21 May 1817), Swedish statesman and soldier, was born at Mölleröd in Scania (now part of Hässleholm Municipality, Skåne County). Toll came of an ancient family, of Dutch origin, which can b ...
. At Tilsit
Sovetsk (russian: Сове́тск; german: Tilsit; Old Prussian: ''Tilzi''; lt, Tilžė; pl, Tylża) is a town in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the south bank of the Neman River which forms the border with Lithuania.
Geography
So ...
the emperor Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I (; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first King of Congress Poland from 1815, and the Grand Duke of Finland from 1809 to his death. He was the eldest son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg.
The son o ...
had undertaken to compel "Russia's geographical enemy," as Napoleon designated Sweden, to accede to the newly established "Continental Russian System". Gustav IV rejected all the proposals of Alexander to close the Baltic against the English, but he took no measures to defend Finland against Russia. On 21 February 1808, a Russian army crossed the Finnish border. On 2 April the king ordered a general levy of 30,000 men.
Charles XIII
 The immediate consequence of the Russian invasion was the deposition of Gustav IV Adolf by the
The immediate consequence of the Russian invasion was the deposition of Gustav IV Adolf by the Coup of 1809
The Coup of 1809 ( sv, Statskuppen 1809) also referred to as the Revolution of 1809 (Swedish: ''Revolutionen 1809'') was a Swedish coup d'état by a group of noblemen led by Georg Adlersparre. The coup resulted in the deposition of King Gustav I ...
on 13 March 1809, and the exclusion of his whole family from the succession. On 5 June 1809 the duke regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
was proclaimed king, under the title of Charles XIII, after accepting the new liberal constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
, which was ratified by the Riksdag of the Estates
Riksdag of the Estates ( sv, Riksens ständer; informally sv, Ståndsriksdagen) was the name used for the Estates of Sweden when they were assembled. Until its dissolution in 1866, the institution was the highest authority in Sweden next to t ...
the same day. Peace negotiations had been opened at Fredrikshamn, but the war carried on. Defeats of at the Battle of Sävar and Battle of Ratan
The Battle of Ratan was the last battle fought on Swedish soil during the Russian-Swedish War of 1808 - 1809. It took place a day apart from the Battle of Sävar, on 20 August 1809. Having conquered Finland from Sweden, the Russians had a small ...
on 19 and 20 August 1809, broke the spirit of the Swedish Army; and peace was obtained by the surrender of all Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, the Åland
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an autonomous and demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1,580 km2, and a populat ...
islands, "the fore-posts of Stockholm," as Napoleon described them, and Västerbotten
Västerbotten (), known in English as West Bothnia or Westrobothnia, is a province (''landskap'') in the north of Sweden, bordering Ångermanland, Lapland, North Bothnia, and the Gulf of Bothnia. It is known for the cheese named after the p ...
and Lappland as far as the rivers of Torneå and Muonio
Muonio (previously called ''Muonionniska'', se, Muoná) is a municipality of Finland. The town is located in far northern Finland above the Arctic Circle on the country's western border, within the area of the former Lappi (Lapland) province. ...
at the Treaty of Fredrikshamn
The Treaty of Fredrikshamn ( sv, Freden i Fredrikshamn; russian: Фридрихсгамский мирный договор), or the Treaty of Hamina ( fi, Haminan rauha), was a peace treaty concluded between Sweden and Imperial Russia on 17 ...
, on 17 September 1809.
See also
* * * * Gustavian styleReferences
Sources
* {{Sweden topics 01 Early Modern history of Sweden 18th century in Sweden 19th century in Sweden 18th century in Finland 19th century in Finland 1772 establishments in Sweden 1809 disestablishments in Sweden History of Sweden by period