History of Southeast Asia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of Southeast Asia covers the people of
The history of Southeast Asia covers the people of  The wide topographical diversity of Southeast Asia has greatly influenced its history. For instance, Mainland Southeast Asia with its continuous but rugged and difficult terrain provided the basis for the early Cham, Khmer, and
The wide topographical diversity of Southeast Asia has greatly influenced its history. For instance, Mainland Southeast Asia with its continuous but rugged and difficult terrain provided the basis for the early Cham, Khmer, and 
 Though there are numerous ancient historic Asian designations for Southeast Asia, none are geographically consistent with each other. Names referring to Southeast Asia include '' Suvarnabhumi'' or ''Sovannah Phoum'' (''Golden Land'') and '' Suvarnadvipa'' (''Golden Islands'') in Indian tradition, the ''Lands below the Winds'' in
Though there are numerous ancient historic Asian designations for Southeast Asia, none are geographically consistent with each other. Names referring to Southeast Asia include '' Suvarnabhumi'' or ''Sovannah Phoum'' (''Golden Land'') and '' Suvarnadvipa'' (''Golden Islands'') in Indian tradition, the ''Lands below the Winds'' in
 The region was already inhabited by ''
The region was already inhabited by '' Ocean drops of up to below the present level during
Ocean drops of up to below the present level during
 The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the
The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the
 Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of
Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of
 The first true maritime trade network in the
The first true maritime trade network in the
 By around 500 BCE, Asia's expanding land and maritime trade led to socio-economic and cultural stimulation and diffusion of mainly
By around 500 BCE, Asia's expanding land and maritime trade led to socio-economic and cultural stimulation and diffusion of mainly
 The earliest attested trading contacts in Southeast Asia were with the Chinese
The earliest attested trading contacts in Southeast Asia were with the Chinese
 Local rulers benefited from the introduction of
Local rulers benefited from the introduction of  Between the 5th and the 13th century CE, Buddhism flourished in Southeast Asia. By the 8th century, the Buddhist
Between the 5th and the 13th century CE, Buddhism flourished in Southeast Asia. By the 8th century, the Buddhist
 In
In  In the
In the
 By the 8th century CE, less than 200 years after the History of Islam, establishment of Islam in
By the 8th century CE, less than 200 years after the History of Islam, establishment of Islam in  Unlike in other Islamic regions, Islam developed in Southeast Asia in a distinctly Syncretism, syncretic manner that allowed the continuation and inclusion of elements and ritual practices of
Unlike in other Islamic regions, Islam developed in Southeast Asia in a distinctly Syncretism, syncretic manner that allowed the continuation and inclusion of elements and ritual practices of  Islam and its notion of exclusivity and finality is seemingly incompatible with other religions, including the Chinese concept of Mandate of Heaven, heavenly harmony and the Son of Heaven as its enforcer. The integration of the traditional East Asian tributary system with China at the centre Muslim Malays and Indonesians exacted a pragmatic approach of cultural Islam in diplomatic relations with China.
Islam and its notion of exclusivity and finality is seemingly incompatible with other religions, including the Chinese concept of Mandate of Heaven, heavenly harmony and the Son of Heaven as its enforcer. The integration of the traditional East Asian tributary system with China at the centre Muslim Malays and Indonesians exacted a pragmatic approach of cultural Islam in diplomatic relations with China.
 By the end of the 14th century, Ming dynasty, Ming China had conquered
By the end of the 14th century, Ming dynasty, Ming China had conquered
 The earliest European ethnic groups, Europeans to have visited Southeast Asia were Marco Polo during the 13th century in the service of Kublai Khan and Niccolò de' Conti during the early 15th century. Regular and momentous voyages only began in the 16th century after the arrival of the Portuguese, who actively sought direct and competitive trade. They were usually accompanied by missionaries, who hoped to promote Christianity.
Portugal was the first European power to establish a bridgehead on the lucrative
The earliest European ethnic groups, Europeans to have visited Southeast Asia were Marco Polo during the 13th century in the service of Kublai Khan and Niccolò de' Conti during the early 15th century. Regular and momentous voyages only began in the 16th century after the arrival of the Portuguese, who actively sought direct and competitive trade. They were usually accompanied by missionaries, who hoped to promote Christianity.
Portugal was the first European power to establish a bridgehead on the lucrative  The British, in the guise of the Honourable East India Company, East India Company led by Josiah Child#Career with the East India Company, Josiah Child, had little interest or impact in the region, and were effectively expelled following the Anglo-Siamese War. British empire#Britain's imperial century (1815–1914), Britain later turned their attention to the Bay of Bengal following the Peace of Paris (1783)#Peace with France and Spain, Peace with France and Spain (1783). During the conflicts, Britain had struggled for naval superiority with the French, and the need of good harbours became evident. Penang Island#History, Penang Island had been brought to the attention of the Company rule in India, Government of India by Francis Light. In 1786, the settlement of George Town, Penang, George Town was founded at the northeastern tip of Penang Island by Captain Francis Light, under the administration of Sir John Macpherson, 1st Baronet, Sir John Macpherson; this marked the beginning of British expansion into the
The British, in the guise of the Honourable East India Company, East India Company led by Josiah Child#Career with the East India Company, Josiah Child, had little interest or impact in the region, and were effectively expelled following the Anglo-Siamese War. British empire#Britain's imperial century (1815–1914), Britain later turned their attention to the Bay of Bengal following the Peace of Paris (1783)#Peace with France and Spain, Peace with France and Spain (1783). During the conflicts, Britain had struggled for naval superiority with the French, and the need of good harbours became evident. Penang Island#History, Penang Island had been brought to the attention of the Company rule in India, Government of India by Francis Light. In 1786, the settlement of George Town, Penang, George Town was founded at the northeastern tip of Penang Island by Captain Francis Light, under the administration of Sir John Macpherson, 1st Baronet, Sir John Macpherson; this marked the beginning of British expansion into the  The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 obligated the Dutch to ensure the safety of shipping and overland trade in and around Aceh, who accordingly sent the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army on the Dutch expedition on the west coast of Sumatra, punitive expedition of 1831. President Andrew Jackson also ordered America's first Sumatran expedition, first Sumatran punitive expedition of 1832, which was followed by a second Sumatran expedition, punitive expedition in 1838. The ''Friendship'' incident thus afforded the Dutch a reason to take over Ache; and Jackson, to dispatch Edmund Roberts (diplomat), diplomatist Edmund Roberts, who in 1833 secured the Siamese-American Treaty of Amity and Commerce, Roberts Treaty with Siam. In 1856 negotiations for amendment of this treaty, Townsend Harris#Harris Treaty of 1856 with Siam, Townsend Harris stated the position of the United States:
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 obligated the Dutch to ensure the safety of shipping and overland trade in and around Aceh, who accordingly sent the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army on the Dutch expedition on the west coast of Sumatra, punitive expedition of 1831. President Andrew Jackson also ordered America's first Sumatran expedition, first Sumatran punitive expedition of 1832, which was followed by a second Sumatran expedition, punitive expedition in 1838. The ''Friendship'' incident thus afforded the Dutch a reason to take over Ache; and Jackson, to dispatch Edmund Roberts (diplomat), diplomatist Edmund Roberts, who in 1833 secured the Siamese-American Treaty of Amity and Commerce, Roberts Treaty with Siam. In 1856 negotiations for amendment of this treaty, Townsend Harris#Harris Treaty of 1856 with Siam, Townsend Harris stated the position of the United States: Only History of Thailand, Thailand was spared the experience of foreign rule, though Thailand, too, was greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. The Monthon reforms of the late 19th Century continuing up till around 1910, imposed a Westernised form of government on the country's partially independent cities called Mueang, such that the country could be said to have successfully colonised itself. Western powers did, however, continue to interfere in both internal and external affairs.
Only History of Thailand, Thailand was spared the experience of foreign rule, though Thailand, too, was greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. The Monthon reforms of the late 19th Century continuing up till around 1910, imposed a Westernised form of government on the country's partially independent cities called Mueang, such that the country could be said to have successfully colonised itself. Western powers did, however, continue to interfere in both internal and external affairs.
 By 1913, the British had occupied
By 1913, the British had occupied
 In September 1940, following the Fall of France and pursuant to the Pacific war goals of Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan, the Japanese Imperial Army invaded Japanese invasion of French Indochina, Vichy French Indochina, which ended in the abortive Japanese coup de main in French Indochina of 9 March 1945. On 5 January 1941, Thailand launched the Franco-Thai War, ended on 9 May 1941 by a Japanese-imposed treaty signed in Tokyo. On 7/8 December, Japan's entry into
In September 1940, following the Fall of France and pursuant to the Pacific war goals of Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan, the Japanese Imperial Army invaded Japanese invasion of French Indochina, Vichy French Indochina, which ended in the abortive Japanese coup de main in French Indochina of 9 March 1945. On 5 January 1941, Thailand launched the Franco-Thai War, ended on 9 May 1941 by a Japanese-imposed treaty signed in Tokyo. On 7/8 December, Japan's entry into
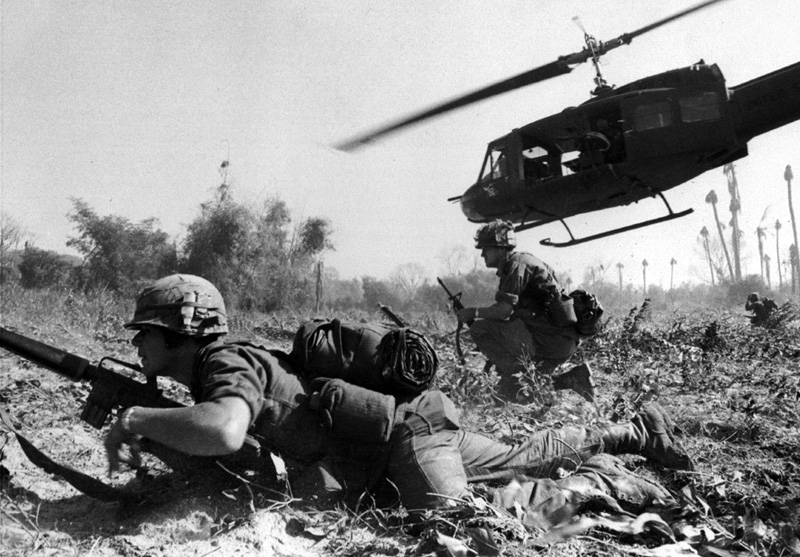 With the rejuvenated nationalist movements in wait, the Europeans returned to a very different Southeast Asia after
With the rejuvenated nationalist movements in wait, the Europeans returned to a very different Southeast Asia after
 Modern Southeast Asia has been characterised by high economic growth by most countries and closer regional integration.
Modern Southeast Asia has been characterised by high economic growth by most countries and closer regional integration.
online version of 1955 edition, 810pp
* * Lokesh, Chandra, & International Academy of Indian Culture. (2000). ''Society and culture of Southeast Asia: Continuities and changes. New Delhi: International Academy of Indian Culture and Aditya Prakashan.'' * * * * Embree, Ainslie T., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Asian history'' (1988)
vol. 1 onlinevol 2 onlinevol 3 onlinevol 4 online
* * * * * * * * Heidhues, Mary Somer. "'Southeast Asia: A Concise History" * * * * * Osborne, Milton. ''Southeast Asia. An introductory history''. * * * Scott, James C., The Art of Not Being Governed: An Anarchist History of Upland Southeast Asia (Yale Agrarian Studies Series), 464 pages, Yale University Press (30 September 2009), , * Tarling, Nicholas (ed). ''The Cambridge history of Southeast Asia'' Vol I-IV. * R. C. Majumdar, Study of Sanskrit in South-East Asia * R. C. Majumdar, ''India and South-East Asia'', I.S.P.Q.S. History and Archaeology Series Vol. 6, 1979, . * * * * * * Yule, Paul. ''The Bronze Age Metalwork of India''. Prähistorische Bronzefunde XX,8, Munich, 1985, . * * * * * *
A Short History of China and Southeast Asia.pdf
Ancient Southeast Asia Throbbing Blood Tube
* :v:Topic:Southeast Asian history, Wikiversity – Department of Southeast Asian History
雲南・東南アジアに関する漢籍史料
Citizenship and Democratization in Southeast Asia
Democracy and Citizen Politics in East Asia
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of Southeast Asia History of Southeast Asia,
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
from prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The us ...
to the present in two distinct sub-regions: Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
(or Indochina) and Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
(or Insular Southeast Asia). Mainland Southeast Asia comprises Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
, Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
(or Burma), Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
whereas Maritime Southeast Asia comprises Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by th ...
, Cocos (Keeling) Islands
)
, anthem = "''Advance Australia Fair''"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = Australia on the globe (Cocos (Keeling) Islands special) (Southeast Asia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
, map_caption = ...
, Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian external territory comprising the island of the same name. It is located in the Indian Ocean, around south of Java and Sumatra and around north-west of the ...
, East Malaysia
East Malaysia (), or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. Near the coast of Sabah is a small archipelago called Labuan. East Malaysia li ...
, East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-w ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
.
The earliest ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
'' presence in Mainland Southeast Asia can be traced back to 70,000 years ago and to at least 50,000 years ago in Maritime Southeast Asia. Since 25,000 years ago, East Asian-related (Basal East Asian) groups expanded southwards into Maritime Southeast Asia from Mainland Southeast Asia. As early as 10,000 years ago, Hoabinhian
Hoabinhian is a lithic techno-complex of archaeological sites associated with assemblages in Southeast Asia from late Pleistocene to Holocene, dated to c.10,000–2000 BCE. It is attributed to hunter-gatherer societies of the region and their ...
settlers from Mainland Southeast Asia had developed a tradition and culture of distinct artefact and tool production. During the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
, Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
peoples populated Indochina via land routes, and sea-borne Austronesian immigrants preferably settled in Maritime Southeast Asia. The earliest agricultural societies that cultivated millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets a ...
and wet-rice
A paddy field is a flooded field of arable land used for growing semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in southern China, associated with pre-Aust ...
emerged around 1700 BCE in the lowlands and river floodplains of Indochina.
The Phung Nguyen culture Phung may refer to:
* Phùng, a Vietnamese surname
* Phùng (township), Đan Phượng District, Hà Nội, Vietnam
* Phung River (disambiguation), several rivers in Thailand
See also
* Feng (disambiguation)
{{disambig ...
(modern northern Vietnam) and the Ban Chiang site (modern Thailand) account for the earliest use of copper by around 2,000 BCE, followed by the Dong Son culture, which by around 500 BCE had developed a highly sophisticated industry of bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids suc ...
production and processing. Around the same time, the first Agrarian Kingdoms emerged where territory was abundant and favourable, such as Funan
Funan (; km, ហ៊្វូណន, ; vi, Phù Nam, Chữ Hán: ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''(Mandala)''—located in mainla ...
at the lower Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth longest river and the third longest in Asia. Its estimated length is , and it drains an area of , discharging of water annual ...
and Van Lang
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
in the Red River delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
. Smaller and insular principalities increasingly engaged in and contributed to the rapidly expanding sea trade.
 The wide topographical diversity of Southeast Asia has greatly influenced its history. For instance, Mainland Southeast Asia with its continuous but rugged and difficult terrain provided the basis for the early Cham, Khmer, and
The wide topographical diversity of Southeast Asia has greatly influenced its history. For instance, Mainland Southeast Asia with its continuous but rugged and difficult terrain provided the basis for the early Cham, Khmer, and Mon
Mon, MON or Mon. may refer to:
Places
* Mon State, a subdivision of Myanmar
* Mon, India, a town in Nagaland
* Mon district, Nagaland
* Mon, Raebareli, a village in Uttar Pradesh, India
* Mon, Switzerland, a village in the Canton of Grisons
* A ...
civilizations. The sub-region's extensive coastline and major river systems of the Irrawaddy, Salween, Chao Phraya, Mekong and Red River have directed socio-cultural and economic activities towards the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
and South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
.
In Maritime Southeast Asia, apart from exceptions such as Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, the patchwork of recurring land-sea patterns on widely dispersed islands and archipelagos admitted moderately sized thalassocratic states indifferent to territorial ambitions, where growth and prosperity were associated with sea trade. Since around 100 BCE, Maritime Southeast Asia has occupied a central position at the crossroads of the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
and the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
trading routes, immensely stimulating its economy and influencing its culture and society. Most local trading polities selectively adopted India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
elements of statecraft, religion, culture and administration during the early centuries of the common era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
, which marked the beginning of recorded history in the area and the continuation of a characteristic cultural development. Chinese culture diffused into the region more indirectly and sporadically, as trade was mostly based on land routes like the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
. Long periods of Chinese isolationism and political relations that were confined to ritualistic tribute procedures prevented deep acculturation
Acculturation is a process of social, psychological, and cultural change that stems from the balancing of two cultures while adapting to the prevailing culture of the society. Acculturation is a process in which an individual adopts, acquires and ...
.
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, particularly in Indochina, began to affect political structures beginning in the 8th to 9th centuries CE. Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ma ...
ideas arrived in insular Southeast Asia as early as the 8th century, and the first Muslim societies in the area emerged by the 13th century. The era of European colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
, early Modernity and the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
era revealed the reality of limited political significance for the various Southeast Asian polities. Post-World War II
The aftermath of World War II was the beginning of a new era started in late 1945 (when World War II ended) for all countries involved, defined by the decline of all colonial empires and simultaneous rise of two superpowers; the Soviet Union (US ...
national survival and progress required a modern state and a strong national identity. Most modern Southeast Asian countries enjoy a historically unprecedented degree of political freedom and self-determination and have embraced the practical concept of intergovernmental co-operation within the Association of Southeast Asian Nations
ASEAN ( , ), officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, mi ...
(ASEAN).
Name
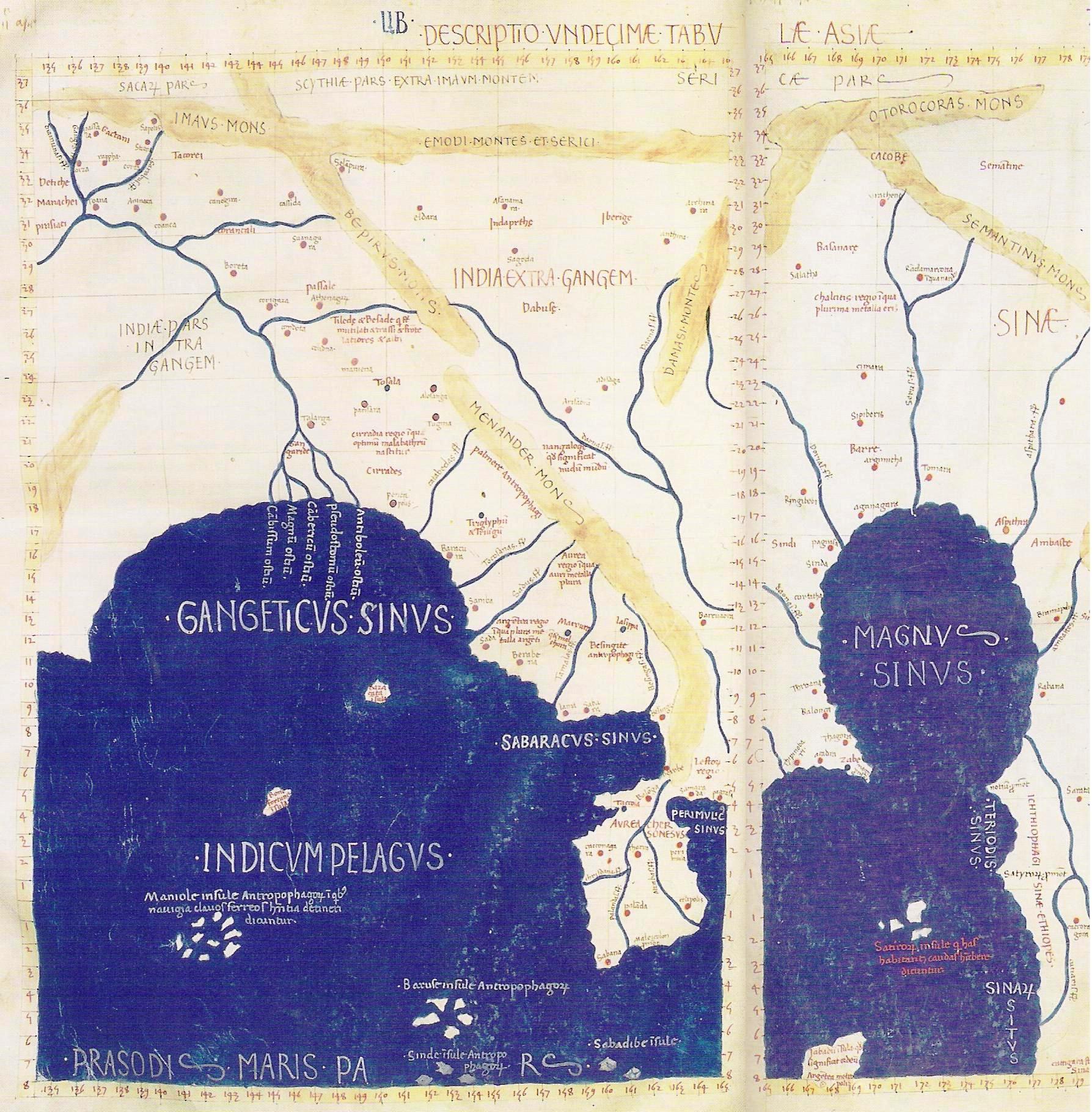
 Though there are numerous ancient historic Asian designations for Southeast Asia, none are geographically consistent with each other. Names referring to Southeast Asia include '' Suvarnabhumi'' or ''Sovannah Phoum'' (''Golden Land'') and '' Suvarnadvipa'' (''Golden Islands'') in Indian tradition, the ''Lands below the Winds'' in
Though there are numerous ancient historic Asian designations for Southeast Asia, none are geographically consistent with each other. Names referring to Southeast Asia include '' Suvarnabhumi'' or ''Sovannah Phoum'' (''Golden Land'') and '' Suvarnadvipa'' (''Golden Islands'') in Indian tradition, the ''Lands below the Winds'' in Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Pl ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, ''Nanyang
Nanyang is the romanization of two common Chinese place names. It may refer to:
Written as 南洋 (Southern Ocean)
* Nanyang (region), a Chinese term denoting the Southeast Asian lands surrounding the South China Sea
;China
* Nanyang Fleet, Qing ...
'' ( Chinese: 南洋; ) in China and '' Nan’yō'' (南洋) in Japan. A 2nd-century world map created by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
names the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
as ''Chersonesus Aurea'' ().
The term "Southeast Asia" was first used in 1839 by American pastor Howard Malcolm in his book ''Travels in South-Eastern Asia''. Malcolm only included the Mainland section and excluded the Maritime section in his definition of Southeast Asia. The term was officially used to designate the area of operation (the South East Asia Command, SEAC) for Anglo-American forces in the Pacific Theater of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
from 1941 to 1945.
Prehistory
Paleolithic
 The region was already inhabited by ''
The region was already inhabited by ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
'' from approximately 1,500,000 years ago during the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. Th ...
age. Data analysis of stone tool assemblages and fossil discoveries from Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, Southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
and more recently Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
and Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
has established ''Homo erectus'' migration routes and episodes of presence as early as 120,000 years ago, with even older isolated finds dating back to 1.8 million years ago. Java Man
Java Man (''Homo erectus erectus'', formerly also ''Anthropopithecus erectus'', ''Pithecanthropus erectus'') is an early human fossil discovered in 1891 and 1892 on the island of Java (Dutch East Indies, now part of Indonesia). Estimated to be b ...
(''Homo erectus erectus'') and '' Homo floresiensis'' attest to a sustained regional presence and isolation, long enough for notable diversification of the species' specifics. Rock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also m ...
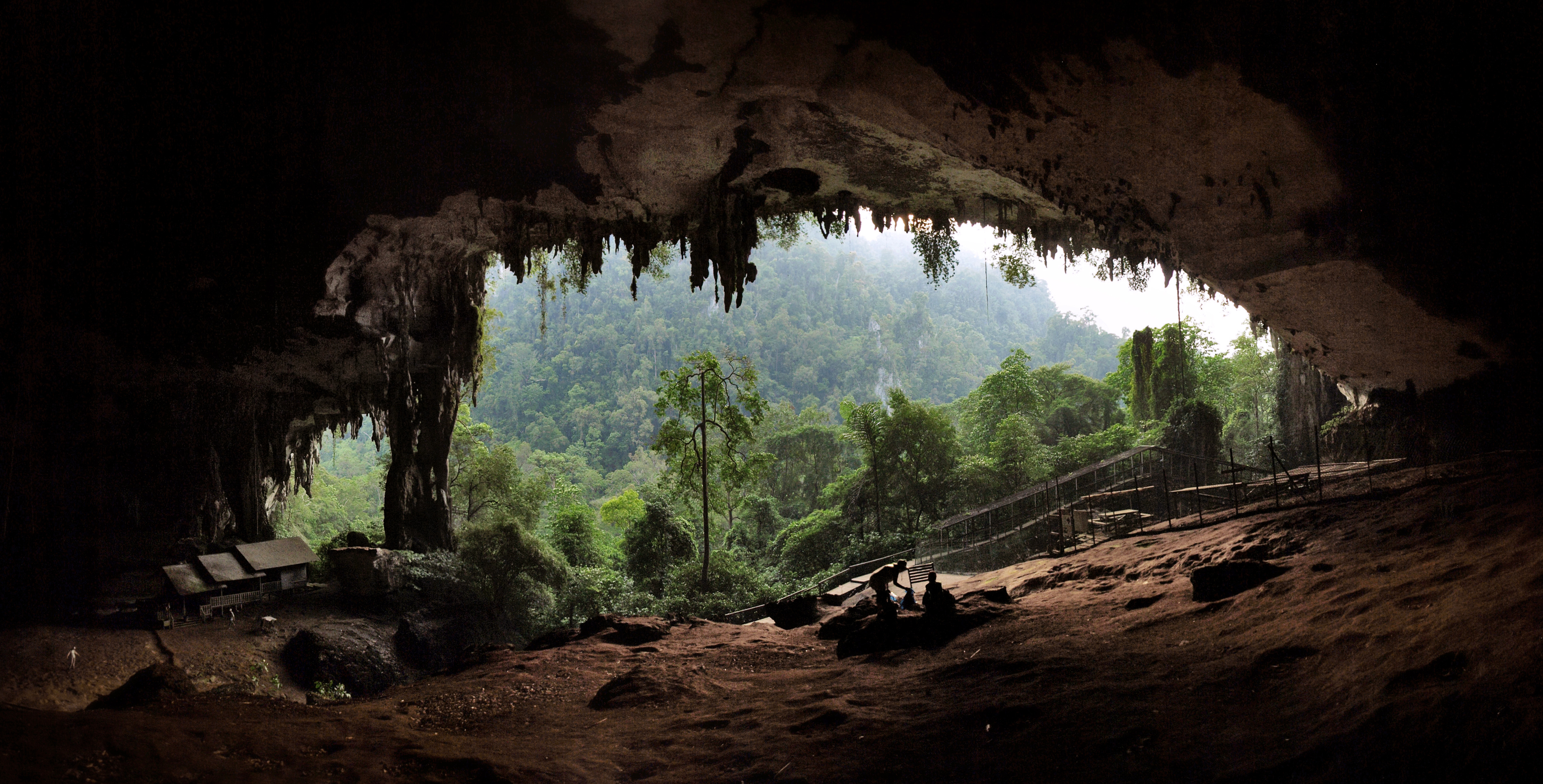
(parietal art) dating from 40,000 years ago (which is currently the world's oldest) has been discovered in the caves of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
. '' Homo floresiensis'' also lived in the area up until at least 50,000 years ago, after which they became extinct. Distinct ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
'' groups, ancestral to East-Eurasian (East Asian-related) populations, and South-Eurasian (Papuan-related) populations, reached the region by 50,000BCE to 70,000BCE, with some arguing earlier. These immigrants might have, to some extent, merged and reproduced with members of the archaic population of ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
'', as the fossil discoveries in the Tam Pa Ling Cave
Tam Pa Ling (''Cave of the Monkeys'') is a cave in the Annamite Mountains in north-eastern Laos. It is situated at the top of Pa Hang Mountain, above sea level.
Three hominin fossils have been discovered in the cave: ''TPL1'', a skull belongin ...
suggest. During much of this time the present-day islands of western Indonesia were joined into a single landmass known as Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
due to lower sea levels.
Ancient remains of hunter-gatherers in Maritime Southeast Asia, such as one Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
hunter-gatherer from South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi ( id, Sulawesi Selatan) is a province in the southern peninsula of Sulawesi. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital is Makassar. The province is bordered by Central Sul ...
, had ancestry from both the South-Eurasian lineage (represented by Papuans
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
and Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait ...
), and the East-Eurasian lineage (represented by East Asians). The hunter-gatherer individual had approximately 50% "Basal-East Asian" ancestry and was positioned in between modern East Asians and Papuans of Oceania. The authors writing about the individual concluded that East Asian-related ancestry expanded from Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
into Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
much earlier than previously suggested, as early as 25,000BCE, long before the expansion of Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
and Austronesian groups.
Distinctive Basal-East Asian (East-Eurasian) ancestry was recently found to have originated in Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
at ~50,000BCE, and expanded through multiple migration waves southwards and northwards respectively. Geneflow of East-Eurasian ancestry into Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
is estimated to ~25,000BCE (possibly as early as 50,000BCE). The pre-Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
South-Eurasian populations of Maritime Southeast Asia were largely replaced by the expansion of various East-Eurasian populations, beginning about 25,000BCE from Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
. Southeast Asia was dominated by East Asian-related ancestry already in 15,000BCE, predating the expansion of Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
and Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
.
 Ocean drops of up to below the present level during
Ocean drops of up to below the present level during Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
glacial periods revealed the vast lowlands known as Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
, enabling hunter-gatherer populations to freely access insular Southeast Asia via extensive terrestrial corridors. Modern human presence in the Niah cave on East Malaysia
East Malaysia (), or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. Near the coast of Sabah is a small archipelago called Labuan. East Malaysia li ...
dates back to 40,000 years BP, although archaeological documentation of the early settlement period suggests only brief occupation phases. However, author Charles Higham argues that despite glacial periods, modern humans were able to cross the sea barrier beyond Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
and Timor
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, ...
, who around 45,000 years ago left traces in the Ivane Valley
Ivane is a Georgia (country), Georgian masculine given name. It is a cognate of the name John (given name), John. Notable people with the name include:
*Ivane Abazasdze (Georgian: იოანე აბაზასძე), 11th-century Georgian fe ...
in eastern New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
"at an altitude of exploiting yams and pandanus
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with some 750 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. The greatest number of species are found in Madagascar and Malaysia. Common name ...
, hunting and making stone tools between 43,000 and 49,000 years ago."
The oldest habitation discovered in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
is located at the Tabon Caves and dates back to approximately 50,000 years BP. Items found there such as burial jars, earthenware, jade ornaments and other jewellery, stone tools, animal bones and human fossils date back to 47,000 years BP. Unearthed human remains are approximately 24,000 years old.
Signs of an early tradition are discernible in the Hoabinhian
Hoabinhian is a lithic techno-complex of archaeological sites associated with assemblages in Southeast Asia from late Pleistocene to Holocene, dated to c.10,000–2000 BCE. It is attributed to hunter-gatherer societies of the region and their ...
, the name given to an industry and cultural continuity of stone tools and flaked cobble artefacts that appear around 10,000 BP in caves and rock shelters first described in Hòa Bình, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
, and later documented in Terengganu
Terengganu (; Terengganu Malay: ''Tranung'', Jawi: ), formerly spelled Trengganu or Tringganu, is a sultanate and constitutive state of federal Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, ''Dāru l- Īmān'' ("Abode of Faith") ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
, Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
and Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
, southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. Research emphasises considerable variations in quality and nature of the artefacts, influenced by region-specific environmental conditions and proximity and access to local resources. The Hoabinhian culture accounts for the first verified ritual burials in Southeast Asia.
Neolithic migrations
TheNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
was characterized by several migrations into Mainland and Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
from southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
by Austronesian, Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
, Kra-Dai and Hmong-Mien-speakers.
The most widespread migration event was the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
, which began around 5,500 BP (3,500 BCE) from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
and coastal southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. Due to their early invention of ocean-going outrigger boats and voyaging catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran
Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-sta ...
s, Austronesians rapidly colonized Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
, before spreading further into Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, ...
, Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, V ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
and the Comoros
The Comoros,, ' officially the Union of the Comoros,; ar, الاتحاد القمري ' is an independent country made up of three islands in southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. It ...
. They dominated the lowlands and coasts of Island Southeast Asia, intermarrying with the indigenous Negrito
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the On ...
and Papuan peoples to varying degrees, giving rise to modern Islander Southeast Asians
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
, Micronesians
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Ethn ...
, Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
, Melanesians
Melanesians are the predominant and indigenous inhabitants of Melanesia, in a wide area from Indonesia's New Guinea to as far East as the islands of Vanuatu and Fiji. Most speak either one of the many languages of the Austronesian language fam ...
and Malagasy.
The Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are th ...
migration wave involved the Mon
Mon, MON or Mon. may refer to:
Places
* Mon State, a subdivision of Myanmar
* Mon, India, a town in Nagaland
* Mon district, Nagaland
* Mon, Raebareli, a village in Uttar Pradesh, India
* Mon, Switzerland, a village in the Canton of Grisons
* A ...
and Khmer peoples, who originated in north-eastern India around 5,000 BP and migrated to the broad riverine floodplains of Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
, Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
.
Early agricultural societies
Territorial principalities in both Insular and Mainland Southeast Asia, characterised as ''Agrarian kingdoms,'' developed an economy by around 500 BCE based on surplus crop cultivation and moderate coastal trade of domestic natural products. Several states of the Malayan-Indonesian " thalassian" zone shared these characteristics with Indochinese polities like thePyu city-states
, conventional_long_name = Pyu city-states
, common_name = Pyu City States
, era = Classical antiquity
, status = City
, event_start = Earliest Pyu presence in Upper Burma
, year_start = c. 2nd century BCE
, date_start =
, event_en ...
in the Irrawaddy River
The Irrawaddy River ( Ayeyarwady River; , , from Indic ''revatī'', meaning "abounding in riches") is a river that flows from north to south through Myanmar (Burma). It is the country's largest river and most important commercial waterway. Orig ...
valley, the Văn Lang kingdom in the Red River delta
The Red River Delta or Hong River Delta ( vi, Châu thổ sông Hồng) is the flat low-lying plain formed by the Red River and its distributaries merging with the Thái Bình River in northern Vietnam. ''Hồng'' (紅) is a Sino-Vietnamese word ...
and Funan
Funan (; km, ហ៊្វូណន, ; vi, Phù Nam, Chữ Hán: ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''(Mandala)''—located in mainla ...
around the lower Mekong
The Mekong or Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth longest river and the third longest in Asia. Its estimated length is , and it drains an area of , discharging of water annual ...
. Văn Lang, founded in the 7th century BCE, endured until 258 BCE under the Hồng Bàng dynasty
The Hồng Bàng period (Vietnamese: ''thời kỳ Hồng Bàng''), also called the Hồng Bàng dynasty,Pelley, p. 151 was a legendary, semi-mythical period in Vietnamese historiography, spanning from the beginning of the rule of Kinh Dươn ...
, as part of the Đông Sơn culture that sustained a dense and organised population that produced an elaborate Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
industry.
Intensive wet-rice cultivation in an ideal climate enabled the farming communities to produce a regular crop surplus that was used by the ruling elite to raise, command and pay work forces for public construction and maintenance projects such as canals and fortifications.
Though millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets a ...
and rice cultivation was introduced around 2000 BCE, hunting and gathering remained an important aspect of food provision, in particular in forested and mountainous inland areas. Many tribal communities of the aboriginal Australo-Melanesian settlers continued a lifestyle of mixed sustenance until the modern era. Many areas in Southeast Asia participated in the Maritime Jade Road, a diverse sea-based trade network which functioned for 3,000 years, mostly in Southeast Asia, between 2000 BCE to 1000 CE.
Bronze Age Southeast Asia
 The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the
The earliest known evidence of copper and bronze production in Southeast Asia was found at Ban Chiang in north-east Thailand and among the Phùng Nguyên culture
The Phùng Nguyên culture of Vietnam (c. 2,000 – 1,500 BC) is a name given to a culture of the Bronze Age in Vietnam which takes its name from an archeological site in Phùng Nguyên, east of Việt Trì discovered in 1958. It was during this p ...
of northern Vietnam around 2000 BCE.
The Đông Sơn culture established a tradition of bronze production and the manufacture of evermore refined bronze and iron objects, such as plows, axes and sickles with shaft holes, socketed arrows and spearheads and small ornamented items. By about 500 BCE, large and delicately decorated bronze drums of remarkable quality, weighing more than , were produced in the laborious lost-wax casting
Lost-wax casting (also called "investment casting", "precision casting", or ''cire perdue'' which has been adopted into English from the French, ) is the process by which a duplicate metal sculpture (often silver, gold, brass, or bronze) is ...
process. This industry of highly sophisticated metal processing was developed independent of Chinese or Indian influence. Historians relate these achievements to the presence of well-organised, centralised and hierarchical communities and a large population.
Pottery culture
 Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of
Between 1000 BCE and 100 CE, the Sa Huỳnh culture flourished along the south-central coast of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
. Ceramic jar burial sites that included grave goods have been discovered at various sites along the entire territory. Among large, thin-walled terracotta jars, ornamented and colourised cooking pots, glass items, jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
earrings and metal objects were deposited near the rivers and along the coast.
The Buni culture is the name given to another early independent centre of refined pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
production that has been well documented on the basis of excavated burial gifts, deposited between 400 BCE and 100 CE in coastal north-western Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
. The objects and artefacts of the Buni tradition are known for their originality and remarkable quality of incised and geometric decors. Its resemblance to the Sa Huỳnh culture and the fact that it represents the earliest ''Indian Rouletted Ware'' recorded in Southeast Asia are subjects of ongoing research.
Early historical era
Austronesian maritime trade network
 The first true maritime trade network in the
The first true maritime trade network in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
was the Austronesian maritime trade network
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sin ...
initiated by the Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
of Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
. They established trade routes with Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
as early as 1500 BCE, exchanging material culture
Material culture is the aspect of social reality grounded in the objects and architecture that surround people. It includes the usage, consumption, creation, and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms, and rituals that the objects crea ...
(like catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran
Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-sta ...
s, outrigger boats, sewn-plank boats and paan) and cultigens (like coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the f ...
s, sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus '' Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for ...
, banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", disting ...
s and sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
). The trade network also connected the material cultures of India and China, as well as constituting the majority of the Indian Ocean component of the spice trade. Indonesians
Indonesians ( Indonesian: ''orang Indonesia'') are citizens or people originally from Indonesia, regardless of their ethnic or religious background. There are more than 1,300 ethnicities in Indonesia, making it a multicultural archipelagic co ...
in particular were trading in spices (mainly cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus '' Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakf ...
and cassia) with East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
using catamarans and outrigger boats and sailing with the help of the Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and tren ...
in the Indian Ocean. This trade network expanded to reach as far as Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, resulting in the Austronesian colonization of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
by 500 CE. It continued through historic times, later becoming the Maritime Silk Road
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the Maritime history, maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, China, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian peninsula, Somalia, Egypt and Europe. It began by the 2n ...
. This trade network also included smaller trade routes within Island Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
, including the lingling-o
''Lingling-o'' or ''ling-ling-o'', is a type of penannular or double-headed pendant or amulet that has been associated with various late Neolithic to late Iron Age Austronesian cultures. Most ''lingling-o'' were made in jade workshops in the Ph ...
jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
and trepanging networks.
In eastern Austronesia
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
, various traditional maritime trade networks also existed. Among them were the ancient Lapita trade network of Island Melanesia
Island Melanesia is a subregion of Melanesia in Oceania.
It is located east of New Guinea island, from the Bismarck Archipelago to New Caledonia.Steadman, 2006. ''Extinction & biogeography of tropical Pacific birds''
See also Archaeology an ...
; the Hiri trade cycle, Sepik Coast exchange Sepik Coast exchange is the method of social networking and alliance in the Sepik Coast area of Papua New Guinea.
Families living along the Sepik Coast in northern Papua New Guinea form alliances with families in other communities. Depending on th ...
and Kula ring
Kula, also known as the Kula exchange or Kula ring, is a ceremonial exchange system conducted in the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. The Kula ring was made famous by the father of modern anthropology, Bronisław Malinowski, who used this ...
of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
; the ancient trading voyages in Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, ...
between the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
and the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the ce ...
(and possibly also New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
); and the vast inter-island trade networks of Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
.
Indianised kingdoms
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
beliefs into the regional cosmology of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
. Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
trade expansion also caused regional geostrategic
Geostrategy, a subfield of geopolitics, is a type of foreign policy guided principally by geographical factors as they inform, constrain, or affect political and military planning. As with all strategies, geostrategy is concerned with matching m ...
remodelling. Southeast Asia was now situated at the convergence of the Indian and the East Asian maritime trade routes, a basis for economic and cultural growth. The concept of " Indianised kingdoms", a term coined by French scholar George Cœdès
George Cœdès (; 10 August 1886 – 2 October 1969) was a 20th-century French scholar of southeast Asian archaeology and history.
Biography
Cœdès was born in Paris to a family of supposed Hungarian-Jewish émigrés. In fact, the family was ...
, describes how Southeast Asian principalities incorporated central aspects of Indian institutions, religion, statecraft, administration, culture, epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the w ...
, writing and architecture.
The earliest Hindu kingdoms emerged in Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, followed by mainland polities such as Funan
Funan (; km, ហ៊្វូណន, ; vi, Phù Nam, Chữ Hán: ) was the name given by Chinese cartographers, geographers and writers to an ancient Indianized state—or, rather a loose network of states ''(Mandala)''—located in mainla ...
and Champa
Champa ( Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd ...
. Selective adoption of Indian sociocultural elements stimulated the emergence of centralised states and development of highly organised societies. Local leaders began to adopt Hindu worship into state religion, using the Hindu concept of devarāja to reinforce divine rule (as opposed to the Chinese concept of Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, '' Tian'') – which embodies the nat ...
).
The exact nature, process and extent of Indian influence upon the civilizations of the region is still fiercely debated by contemporary scholars. One such debate is over the extent to which Indian merchants, Brahmins
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests ( purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
, nobles or Southeast Asian mariner-merchants played central roles in bringing Indian conceptions to Southeast Asia. Additionally, the depth of the influence of Indian traditions is still contested. Whereas early 20th-century scholars emphasized the thorough Indianisation of Southeast Asia, more recent authors have argued that Indian influence was much more limited, affecting only a small section of the elite.
Maritime trade from China to India passed Champa and Funan at the Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta ( vi, Đồng bằng Sông Cửu Long, lit=Nine Dragon River Delta or simply vi, Đồng Bằng Sông Mê Kông, lit=Mekong River Delta, label=none), also known as the Western Region ( vi, Miền Tây, links=no) or South-weste ...
, proceeded along the coast to the Isthmus of Kra, portaged across the narrow and transhipped for distribution in India. This trading link boosted the development of Funan, its successor Chenla
Chenla or Zhenla (; km, ចេនឡា, ; vi, Chân Lạp) is the Chinese designation for the successor polity of the kingdom of Funan preceding the Khmer Empire that existed from around the late sixth to the early ninth century in Indoc ...
and the Malayan states of Langkasuka
Langkasuka was an ancient Hindu-Buddhist kingdom located in the Malay Peninsula. The name is Sanskrit in origin; it is thought to be a combination of ''langkha'' for "resplendent land" -'' sukkha'' for "bliss". The kingdom, along with Old K ...
on the eastern coast and Kedah
Kedah (), also known by its honorific Darul Aman and historically as Queda, is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and it consists of the mainland ...
on the western.
Numerous coastal communities in maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
adopted Hindu and Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
cultural and religious elements from India and developed complex polities ruled by native dynasties. Early Hindu kingdoms in Indonesia include the 4th-century Kutai that rose in East Kalimantan
East Kalimantan ( Indonesian: ) is a province of Indonesia. Its territory comprises the eastern portion of Borneo. It had a population of about 3.03 million at the 2010 census (within the current boundary), 3.42 million at the 2015 census, and 3 ...
, Tarumanagara in West Java
West Java ( id, Jawa Barat, su, ᮏᮝ ᮊᮥᮜᮧᮔ᮪, romanized ''Jawa Kulon'') is a province of Indonesia on the western part of the island of Java, with its provincial capital in Bandung. West Java is bordered by the province of Banten ...
and Kalingga in Central Java
Central Java ( id, Jawa Tengah) is a province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogyakart ...
.
Early relations with China
 The earliest attested trading contacts in Southeast Asia were with the Chinese
The earliest attested trading contacts in Southeast Asia were with the Chinese Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty a ...
(), when cowry shells served as currency. During the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
(1050771 BCE), various natural products, such as ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals i ...
, rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct specie ...
horn, tortoise
Tortoises () are reptiles of the family Testudinidae of the order Testudines (Latin: ''tortoise''). Like other turtles, tortoises have a shell to protect from predation and other threats. The shell in tortoises is generally hard, and like oth ...
shells, pearls and birds' feathers found their way to Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
, the Zhou capital. Although current knowledge about port localities and shipping lanes is very limited, it is assumed that most of this exchange took place on land routes, and only a small percentage was shipped "on coastal vessels crewed by Malay and Yue traders".
Military conquests during the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(202 BCE220 CE) brought a number of foreign peoples within the Chinese empire when the Imperial Chinese tributary system
The tributary system of China (), or Cefeng system () was a network of loose international relations focused on China which facilitated trade and foreign relations by acknowledging China's predominant role in East Asia. It involved multiple relati ...
began to evolve under Han rule. This tributary system was based on the Chinese worldview that had developed under the Shang dynasty, in which China was deemed the center and apogee of culture and civilization, the "Middle kingdom" ( Mandarin: 中国, Zhōngguó), surrounded by several layers of increasingly barbarous peoples. Contact with Southeast Asia steadily increased by the end of the Han period.
Between the 2nd-century BCE and 15th-century CE, the Maritime Silk Road
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the Maritime history, maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, China, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian peninsula, Somalia, Egypt and Europe. It began by the 2n ...
flourished, connecting China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, the Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
and all the way to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. Despite its association with China in recent centuries, the Maritime Silk Road was primarily established and operated by Austronesian sailors in Southeast Asia and by Persian and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
traders in the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channe ...
.
The Maritime Silk Road developed from the earlier Austronesian spice trade networks of Islander Southeast Asians
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrone ...
with Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
and Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
(established 1000600 BCE), as well as the jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
industry trade in ''lingling-o
''Lingling-o'' or ''ling-ling-o'', is a type of penannular or double-headed pendant or amulet that has been associated with various late Neolithic to late Iron Age Austronesian cultures. Most ''lingling-o'' were made in jade workshops in the Ph ...
'' artifacts from the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
in the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
(). For most of its history, Austronesian thalassocracies controlled the flow of the Maritime Silk Road, especially the polities around the Strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean chan ...
of Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has bee ...
and Bangka, the Malay peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
and the Mekong delta
The Mekong Delta ( vi, Đồng bằng Sông Cửu Long, lit=Nine Dragon River Delta or simply vi, Đồng Bằng Sông Mê Kông, lit=Mekong River Delta, label=none), also known as the Western Region ( vi, Miền Tây, links=no) or South-weste ...
(although Chinese records misidentified these kingdoms as being "Indian" due to the Indianization of these regions). Prior to the 10th century, the route was primarily used by Southeast Asian traders, although Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
** Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, na ...
and Persian traders also sailed them. The route was influential in the early spread of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
to the East.
China later built its own fleets starting from the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
in the 10th century, participating directly in the trade route up until the end of the Colonial Era and the collapse of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
.
Spread of Buddhism
 Local rulers benefited from the introduction of
Local rulers benefited from the introduction of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
during the early common era, using it to greatly enhance the legitimacy of their reign as devarāja. Historians increasingly argue that the process of Hindu religious diffusion in the region must be attributed to the initiative of the local chieftains. Buddhist teachings, which almost simultaneously arrived in Southeast Asia, developed during the subsequent centuries, gaining more appeal among the general population. In the 3rd century BCE, the Buddhist Indian Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
initiated missionary efforts to send trained monks and missionaries abroad to proselytise Buddhism, including its sizeable body of literature, oral traditions, iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
and art. To missionaries used Buddhist teachings to offer guidance in central existential questions, placing an emphasis on individual effort and conduct.
 Between the 5th and the 13th century CE, Buddhism flourished in Southeast Asia. By the 8th century, the Buddhist
Between the 5th and the 13th century CE, Buddhism flourished in Southeast Asia. By the 8th century, the Buddhist Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th ...
kingdom based in Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
emerged as a major trading power in central Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
. Around the same period, the Shailendra dynasty
The Shailendra dynasty (, derived from Sanskrit combined words ''Śaila'' and ''Indra'', meaning "King of the Mountain", also spelled Sailendra, Syailendra or Selendra) was the name of a notable Indianised dynasty that emerged in 8th-century ...
of Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
extensively promoted Buddhist art that found its strongest expression in the vast Borobudur
Borobudur, also transcribed Barabudur ( id, Candi Borobudur, jv, ꦕꦤ꧀ꦝꦶꦧꦫꦧꦸꦝꦸꦂ, Candhi Barabudhur) is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Magelang Regency, not far from the town of Muntilan, in Central Java, Indone ...
temple. Following the establishment of the Khmer Empire in Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
, the first Buddhist kings of Mainland Southeast Asia emerged during the 11th century. Mahayana Buddhism
''Mahāyāna'' (; "Great Vehicle") is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mahāyāna Buddhism developed in India (c. 1st century BCE onwards) and is considered one of the three main existing br ...
took hold first in Southeast Asia, as the original Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
had fallen out of favor India centuries before reaching the region. However, a pure form of Theravada Buddhist teachings had been preserved in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
since the 3rd century. Pilgrims and wandering monks from Sri Lanka introduced Theravada Buddhism in the Pagan Empire
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-da ...
of Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
, the Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom ( th, สุโขทัย, , IAST: , ) was a post-classical Thai kingdom ( mandala) in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. The kingdom was ...
in northern Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
, the Lower Mekong Basin during Cambodia's dark ages and further into Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
and Maritime Southeast Asia.
Medieval period
 In
In Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
, the Srivijaya kingdom on Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
developed into the dominant power by the 5th century CE. Its capital Palembang
Palembang () is the capital city of the Indonesian province of South Sumatra. The city proper covers on both banks of the Musi River on the eastern lowland of southern Sumatra. It had a population of 1,668,848 at the 2020 Census. Palembang ...
became a major seaport and functioned as an '' entrepôt'' on the Spice Route between India and China. Srivijaya was also a notable center of Vajrayāna
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
Buddhist learning and influence. Around the 6th century CE, Malay merchants began sailing to Srivijaya, where goods were transported directly in Sumatran ports. The winds of the Northeast Monsoon during October to December prevented sailing ships from proceeding directly from the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
to the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
, as did the Southwest Monsoon during July to September, forcing trade routes to pass through Srivijaya. However, the kingdom's wealth and influence began to fade when advancements in nautical technology in the 10th century enabled Chinese and Indian merchants to ship cargo directly between their countries. These advancements also aided the Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
dynasty of Tamilakam
Tamiḻakam (Tamil: தமிழகம்; Malayalam: തമിഴകം), refers to the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covering the southernmost region of the Indian subcontinent. Tamilakam covered today's Tamil Nad ...
, Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
, in carrying out a series of destructive attacks on Srivijaya, effectively ending Palembang's ''entrepôt'' position in the Indo-Chinese trade route. As the influence of the Srivijaya kingdom faded by about the 13th century, Sumatra came to be ruled by a kaleidoscope of Buddhist kingdoms for the next two centuries, including the Malayu, Pannai, and Dharmasraya
Dharmasraya, is the capital of the 11th century Buddhist polity known as Melayu Kingdom, based on the Batanghari river system in modern-day West Sumatra and Jambi, on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia.J.L.A. Brandes, 1902, ''Nāgarakrětāga ...
kingdoms.
To the southeast of Sumatra, West Java
West Java ( id, Jawa Barat, su, ᮏᮝ ᮊᮥᮜᮧᮔ᮪, romanized ''Jawa Kulon'') is a province of Indonesia on the western part of the island of Java, with its provincial capital in Bandung. West Java is bordered by the province of Banten ...
was ruled by the Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
Sunda Kingdom () after the fall of the Tarumanagara, while Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and East Java
East Java ( id, Jawa Timur) is a province of Indonesia located in the easternmost hemisphere of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern and ...
were dominated by a myriad of competing agrarian kingdoms including the Shailendra dynasty
The Shailendra dynasty (, derived from Sanskrit combined words ''Śaila'' and ''Indra'', meaning "King of the Mountain", also spelled Sailendra, Syailendra or Selendra) was the name of a notable Indianised dynasty that emerged in 8th-century ...
(), Mataram Kingdom
The Mataram Kingdom (, jv, ꦩꦠꦫꦩ꧀, ) was a Javanese Hindu–Buddhist kingdom that flourished between the 8th and 11th centuries. It was based in Central Java, and later in East Java. Established by King Sanjaya, the kingdom was rule ...
(), Kediri Kingdom (), Singhasari
Singhasari ( jv, ꦏꦫꦠꦺꦴꦤ꧀ꦱꦶꦔ꧀ꦲꦱꦫꦶ, translit=Karaton Singhasari or , id, Kerajaan Singasari) was a Javanese Hindu kingdom located in east Java between 1222 and 1292. The kingdom succeeded the Kingdom of Kediri as ...
(12221292), and Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese Hindu-Buddhist thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was based on the island of Java (in modern-day Indonesia ...
(). In the 8th and 9th centuries, the Sailendra dynasty that ruled the Mataram kingdom built a number of massive monuments in Central Java, including the Sewu and Borobudur
Borobudur, also transcribed Barabudur ( id, Candi Borobudur, jv, ꦕꦤ꧀ꦝꦶꦧꦫꦧꦸꦝꦸꦂ, Candhi Barabudhur) is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Magelang Regency, not far from the town of Muntilan, in Central Java, Indone ...
Buddhist temples. According to the '' Nagarakṛtāgama'', an Old Javanese
Old Javanese or Kawi is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the island ...
poem from around the 13th century, vassal states of the Majapahit Empire spread throughout much of today's Indonesia, making it possibly the largest empire ever to exist in Southeast Asia. The empire declined in the 15th century after the rise of Islamic state, Islamic states in coastal Java, the Peninsular Malaysia, Malay peninsula, and Sumatra.
 In the
In the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, the Laguna Copperplate Inscription dating from 900 CE is the earliest known calendar-dated document from the islands. It relates a debt granted from a ''maginoo'' (royalty) who lived in the Tagalog people, Tagalog city-state of Tondo (historical polity), Tondo which is now part of History of Manila, Manila area. The document mentions several contemporary states in the area, including Mataram Kingdom
The Mataram Kingdom (, jv, ꦩꦠꦫꦩ꧀, ) was a Javanese Hindu–Buddhist kingdom that flourished between the 8th and 11th centuries. It was based in Central Java, and later in East Java. Established by King Sanjaya, the kingdom was rule ...
in Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
.
The Khmer Empire covered much of mainland Southeast Asia from the early 9th until the 15th century, during which time a Khmer architecture, sophisticated architecture was developed, exemplified in the structures of the capital city Angkor. Situated in modern-day Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
, the kingdoms of Đại Việt and Champa
Champa ( Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd ...
were rivals to the Khmer Empire in the region. The Mon
Mon, MON or Mon. may refer to:
Places
* Mon State, a subdivision of Myanmar
* Mon, India, a town in Nagaland
* Mon district, Nagaland
* Mon, Raebareli, a village in Uttar Pradesh, India
* Mon, Switzerland, a village in the Canton of Grisons
* A ...
kingdom of Dvaravati was another major regional presence, first appearing in records around the 6th century CE. By the 10th century, however, Dvaravati had come under the influence of the Khmer. Nearby, Thai people, Thai tribes conquered the Chao Phraya River valley of modern-day central Thailand around the 12th century and established the Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom ( th, สุโขทัย, , IAST: , ) was a post-classical Thai kingdom ( mandala) in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. The kingdom was ...
in the 13th century and the Ayutthaya Kingdom in the 14th century.
By the mid-16th century, the Burma, Burmese First Toungoo Empire was one of the largest, strongest and richest empires in Southeast Asia. At its peak, it was the dominant power in mainland Southeast Asia, exercising "suzerainty from Manipur to the Cambodia, Cambodian March (territory), marches and from the borders of Kingdom of Mrauk U, Arakan to Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
".Lieberman 2003: 151–152 The empire included Mon kingdoms, Mon and Shan states and annexed territories in the Lan Na, Kingdom of Lan Na, Lan Xang, Kingdom of Laos, and the Ayutthaya kingdom. Early European accounts describe the lower part of the Toungoo Empire as having possessed 34 excellent ports that facilitated considerable trade in a variety of goods. The empire supplied the port of Malacca with rice and other foodstuffs, along with luxury goods such as Ruby, rubies, Sapphire, sapphires, deer musk, musk, lac, Benzoin (resin), benzoin, and gold to trade. In return, the lower part of the empire imported Chinese manufactures and Indonesian spices through its ports. Additionally, merchants from West Asia and India exchanged large quantities of Textile industry in India, Indian textiles for Burmese luxury products and eastern goods. The arrival of the Portuguese in the 16th century further strengthened the empire's position, both commercially and militarily.
Spread of Islam
 By the 8th century CE, less than 200 years after the History of Islam, establishment of Islam in
By the 8th century CE, less than 200 years after the History of Islam, establishment of Islam in Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Pl ...
, the first Islamic traders and merchants who adhered to Mohammad's prophecies began to appear in maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
. However, Islam did not play a notable role anywhere in mainland Southeast Asia until the 13th century. Instead, widespread and gradual replacement of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
by Theravada Buddhism, Theravāda Buddhism reflected a shift to a more personal, introverted spirituality acquired through individual ritual activities and effort.
In addressing the issue of how Islam was introduced into Southeast Asia, historians have elaborated various routes from Arabia to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and then from India to Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
. Of these, two seem to take prominence: either Arabian traders and scholars who did not live or settle in India spread Islam directly to maritime Southeast Asia, or Arab traders that had been settling in coastal India and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
for generations did. Muslim traders from India (Gujarat) and converts of South Asian descent are variously considered to play a major role.
A number of sources propose the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
as another route of Islamic introduction to Southeast Asia. Arguments for this hypothesis include the following:
* Extensive trade between Arabia and China before the 10th century is well documented and has been corroborated by archaeological evidence (see, for example, Belitung shipwreck).
* During the Mongol conquest of China, Mongol conquest and the subsequent rule of the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), hundreds of thousands of Muslims entered China. In Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
, Islam was propagated and commonly embraced.
* Kufic grave stones in Champa
Champa ( Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ; km, ចាម្ប៉ា; vi, Chiêm Thành or ) were a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is contemporary central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd ...
, modern-day Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
, are indices of an early and permanent Islamic community in mainland Southeast Asia.
* The founder of the Demak Sultanate in Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
was of Sino-Javanese origin.
* Hui people, Hui mariner Zheng He proposed ancient Chinese architecture as the stylistic basis for the oldest Javanese mosques during his 15th-century visit to Demak, Demak, Demak, Banten, and the Red Mosque of Panjunan in Cirebon, West Java
West Java ( id, Jawa Barat, su, ᮏᮝ ᮊᮥᮜᮧᮔ᮪, romanized ''Jawa Kulon'') is a province of Indonesia on the western part of the island of Java, with its provincial capital in Bandung. West Java is bordered by the province of Banten ...
.
In 2013, the European Union published the ''European Commission Forum'', which maintains an inclusive attitude on the matter:
 Unlike in other Islamic regions, Islam developed in Southeast Asia in a distinctly Syncretism, syncretic manner that allowed the continuation and inclusion of elements and ritual practices of
Unlike in other Islamic regions, Islam developed in Southeast Asia in a distinctly Syncretism, syncretic manner that allowed the continuation and inclusion of elements and ritual practices of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and ancient Pan-East Asian animism. Most principalities developed highly distinctive cultures as a result of centuries of active participation in cultural exchange situated at the cross-roads of the Maritime Silk Road
The Maritime Silk Road or Maritime Silk Route is the Maritime history, maritime section of the historic Silk Road that connected Southeast Asia, China, the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian peninsula, Somalia, Egypt and Europe. It began by the 2n ...
coming from across the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
in the West and the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
in the East. Cultural and institutional adoption was a creative and selective process, in which foreign elements were incorporated into a local synthesis. Unlike some other "Islamised" regions like Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, North Africa, Umayyad conquest of Hispania, Iberia, the Arab–Byzantine wars, Middle East and later northern Muslim conquests of the Indian subcontinent, India, Islamic faith in Southeast Asia was not enforced in the wake of Early Muslim conquests, territorial conquests, but because of trade routes. In this way, the Islamisation of Southeast Asia is more akin to that of Islam in Central Asia, Turkic Central Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, South India, southern India and Islam in China, northwest China.
There are various records of lay Muslim missionaries, scholars and mystics, particularly Sufism, Sufis, who were active in peacefully proselytizing in Southeast Asia. Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, for example, received Islam by nine men, referred to as the "Wali Sanga" or "Nine Saints," although the historical identity of such people is almost impossible to determine. The foundation of the first Islamic kingdom in Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, the Samudera Pasai Sultanate, took place during the 13th century.
The conversion of the remnants of the Buddhist Srivijaya, Srivijaya empire that once controlled trade in much of Southeast Asia, in particular the Strait of Malacca, marked a religious turning point with the conversion of the strait into an Islamic water. With the fall of Srivijaya, the way was open for effective and widespread proselytization and the establishment of Muslim trading centers. Many modern Malays view the Sultanate of Malacca, which existed from the 15th to the early 16th century, as the first political entity of contemporary Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
.
The idea of equality before God for the ''Ummah'' (the people of God) and a personal religious effort through regular prayer in Islam could have been more appealing than a perceived fatalism in Hinduism at the time. However, Islam also taught obedience and submission, which could have helped guarantee that the social structure of a converted people or political entity saw less fundamental changes.
 Islam and its notion of exclusivity and finality is seemingly incompatible with other religions, including the Chinese concept of Mandate of Heaven, heavenly harmony and the Son of Heaven as its enforcer. The integration of the traditional East Asian tributary system with China at the centre Muslim Malays and Indonesians exacted a pragmatic approach of cultural Islam in diplomatic relations with China.
Islam and its notion of exclusivity and finality is seemingly incompatible with other religions, including the Chinese concept of Mandate of Heaven, heavenly harmony and the Son of Heaven as its enforcer. The integration of the traditional East Asian tributary system with China at the centre Muslim Malays and Indonesians exacted a pragmatic approach of cultural Islam in diplomatic relations with China.
Chinese treasure voyages
 By the end of the 14th century, Ming dynasty, Ming China had conquered
By the end of the 14th century, Ming dynasty, Ming China had conquered Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
in the South, yet it had lost control of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
after the fall of the Mongol Yuan dynasty. The ruling Yongle Emperor resolved to focus on the Indian Ocean sea routes, seeking to consolidate the ancient Imperial Chinese Tributary System, Imperial Tributary System, establish greater diplomatic and military presence, and widen the Chinese sphere of influence. He ordered the construction of a huge Treasure voyages, trade and representation fleet that, between 1405 and 1433, undertook several voyages into Southeast Asia, India, the Persian Gulf, and as far as East Africa. Under the leadership of Zheng He, hundreds of naval vessels of then unparalleled size, grandeur, and technological advancement and manned by sizeable military contingents, ambassadors, merchants, artists and scholars repeatedly visited major Southeast Asian principalities. The individual fleets engaged in a number of clashes with pirates and occasionally supported various royal contenders. However, pro-expansionist voices at the court in Beijing lost influence after the 1450s, and the voyages were discontinued. The protraction of the ritualistic ceremonies and scanty travels of emissaries in the Tributary System alone was not sufficient to develop firm and lasting Chinese commercial and political influence in the region, especially during the impending onset of highly competitive global trade. During the Chenghua Emperor, Chenghua period of the Ming Dynasty, Liu Daxia, who later became the Shangshu of the Ministry of War, hid or burned the archives of Ming treasure voyages.
Early modern era
European colonisation
 The earliest European ethnic groups, Europeans to have visited Southeast Asia were Marco Polo during the 13th century in the service of Kublai Khan and Niccolò de' Conti during the early 15th century. Regular and momentous voyages only began in the 16th century after the arrival of the Portuguese, who actively sought direct and competitive trade. They were usually accompanied by missionaries, who hoped to promote Christianity.
Portugal was the first European power to establish a bridgehead on the lucrative
The earliest European ethnic groups, Europeans to have visited Southeast Asia were Marco Polo during the 13th century in the service of Kublai Khan and Niccolò de' Conti during the early 15th century. Regular and momentous voyages only began in the 16th century after the arrival of the Portuguese, who actively sought direct and competitive trade. They were usually accompanied by missionaries, who hoped to promote Christianity.
Portugal was the first European power to establish a bridgehead on the lucrative maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
#Maritime trade, trade route, with the conquest of the Sultanate of Malacca in 1511. The Netherlands and Spain followed and soon superseded Portugal as the main European powers in the region. In 1599, Spain began to colonise the History of the Philippines (1521–1898), Philippines via the Mexico-governed Viceroyalty of New Spain, which the Philippines was territory of. In 1619, acting through the Batavia, Dutch East Indies#Dutch East India Company (17th – 18th century), Dutch East India Company, the Dutch took the city of Sunda Kelapa, renamed it Batavia (now Jakarta) as a base for trading and expansion into the other parts of Java (island), Java and the surrounding territory. In 1641, the Dutch took Malacca from the Portuguese.''For fifty or sixty years, the Portuguese enjoyed the exclusive trade to China and Japan. In 1717, and again in 1732, the Chinese government offered to make Macao the emporium for all foreign trade, and to receive all duties on imports; but, by a strange infatuation, the Portuguese government refused, and its decline is dated from that period.'' (Roberts, 2007 PDF image 173 p. 166) Economic opportunities attracted Overseas Chinese to the region in great numbers. In 1775, the Lanfang Republic, possibly the first republic in the region, was established in West Kalimantan, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, as a tributary state of the Qing Empire; the republic lasted until 1884, when it fell under Dutch occupation as Qing influence waned.Other experiments in republicanism in adjacent regions were the Japanese Republic of Ezo (1869) and the Republic of Taiwan (1895).
 The British, in the guise of the Honourable East India Company, East India Company led by Josiah Child#Career with the East India Company, Josiah Child, had little interest or impact in the region, and were effectively expelled following the Anglo-Siamese War. British empire#Britain's imperial century (1815–1914), Britain later turned their attention to the Bay of Bengal following the Peace of Paris (1783)#Peace with France and Spain, Peace with France and Spain (1783). During the conflicts, Britain had struggled for naval superiority with the French, and the need of good harbours became evident. Penang Island#History, Penang Island had been brought to the attention of the Company rule in India, Government of India by Francis Light. In 1786, the settlement of George Town, Penang, George Town was founded at the northeastern tip of Penang Island by Captain Francis Light, under the administration of Sir John Macpherson, 1st Baronet, Sir John Macpherson; this marked the beginning of British expansion into the
The British, in the guise of the Honourable East India Company, East India Company led by Josiah Child#Career with the East India Company, Josiah Child, had little interest or impact in the region, and were effectively expelled following the Anglo-Siamese War. British empire#Britain's imperial century (1815–1914), Britain later turned their attention to the Bay of Bengal following the Peace of Paris (1783)#Peace with France and Spain, Peace with France and Spain (1783). During the conflicts, Britain had struggled for naval superiority with the French, and the need of good harbours became evident. Penang Island#History, Penang Island had been brought to the attention of the Company rule in India, Government of India by Francis Light. In 1786, the settlement of George Town, Penang, George Town was founded at the northeastern tip of Penang Island by Captain Francis Light, under the administration of Sir John Macpherson, 1st Baronet, Sir John Macpherson; this marked the beginning of British expansion into the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
.Company agent John_Crawfurd used the census taken in 1824 for a statistical analysis of the relative economic prowess of the peoples there, giving special attention to the Chinese: ''The Chinese amount to 8595, and are landowners, field-labourers, mechanics of almost every description, shopkeepers, and general merchants. They are all from the two provinces of Canton and Fo-kien, and three-fourths of them from the latter. About five-sixths of the whole number are unmarried men, in the prime of life : so that, in fact, the Chinese population, in point of effective labour, may be estimated as equivalent to an ordinary population of above 37,000, and, as will afterwards be shown, to a numerical Malay population of more than 80,000!'' (Crawfurd image 48. p.30)
The British also temporarily possessed French and British interregnum in the Dutch East Indies, Dutch territories during the Napoleonic Wars; and British occupation of Manila, Spanish areas in the Seven Years' War. In 1819, Stamford Raffles established Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
as a key trading post for Britain in their rivalry with the Dutch. However, their rivalry cooled in 1824 when an Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, Anglo-Dutch treaty demarcated their respective interests in Southeast Asia. British rule in Burma began with the first Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826).
Early United States entry into what was then called the East Indies (usually in reference to the Malay Archipelago) was low key. In 1795, a secret voyage for black pepper, pepper set sail from Salem, Massachusetts#Trade with China and the East Indies, Salem, Massachusetts on an 18-month voyage that returned with a bulk cargo of pepper, the first to be so imported into the country, which sold at the extraordinary profit of seven hundred per cent. In 1831, the merchantman Friendship of Salem#Friendship (1830s), ''Friendship'' of Salem returned to report the ship had been plundered, and the first officer and two crewmen murdered in Sumatra.
 The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 obligated the Dutch to ensure the safety of shipping and overland trade in and around Aceh, who accordingly sent the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army on the Dutch expedition on the west coast of Sumatra, punitive expedition of 1831. President Andrew Jackson also ordered America's first Sumatran expedition, first Sumatran punitive expedition of 1832, which was followed by a second Sumatran expedition, punitive expedition in 1838. The ''Friendship'' incident thus afforded the Dutch a reason to take over Ache; and Jackson, to dispatch Edmund Roberts (diplomat), diplomatist Edmund Roberts, who in 1833 secured the Siamese-American Treaty of Amity and Commerce, Roberts Treaty with Siam. In 1856 negotiations for amendment of this treaty, Townsend Harris#Harris Treaty of 1856 with Siam, Townsend Harris stated the position of the United States:
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 obligated the Dutch to ensure the safety of shipping and overland trade in and around Aceh, who accordingly sent the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army on the Dutch expedition on the west coast of Sumatra, punitive expedition of 1831. President Andrew Jackson also ordered America's first Sumatran expedition, first Sumatran punitive expedition of 1832, which was followed by a second Sumatran expedition, punitive expedition in 1838. The ''Friendship'' incident thus afforded the Dutch a reason to take over Ache; and Jackson, to dispatch Edmund Roberts (diplomat), diplomatist Edmund Roberts, who in 1833 secured the Siamese-American Treaty of Amity and Commerce, Roberts Treaty with Siam. In 1856 negotiations for amendment of this treaty, Townsend Harris#Harris Treaty of 1856 with Siam, Townsend Harris stated the position of the United States:The United States does not hold any possessions in the East, nor does it desire any. The form of government forbids the holding of colonies. The United States therefore cannot be an object of jealousy to any Eastern Power. Peaceful commercial relations, which give as well as receive benefits, is what the President wishes to establish with Siam, and such is the object of my mission.From the end of the 1850s onwards, while the attention of the United States shifted to maintaining their union, the pace of European colonisation shifted to a significantly higher gear. This phenomenon, denoted New Imperialism, saw the conquest of nearly all Southeast Asian territories by the colonial powers. The Dutch East India Company and British East India Company were dissolved by their respective governments, who took over the direct administration of the colonies.
 Only History of Thailand, Thailand was spared the experience of foreign rule, though Thailand, too, was greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. The Monthon reforms of the late 19th Century continuing up till around 1910, imposed a Westernised form of government on the country's partially independent cities called Mueang, such that the country could be said to have successfully colonised itself. Western powers did, however, continue to interfere in both internal and external affairs.
Only History of Thailand, Thailand was spared the experience of foreign rule, though Thailand, too, was greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. The Monthon reforms of the late 19th Century continuing up till around 1910, imposed a Westernised form of government on the country's partially independent cities called Mueang, such that the country could be said to have successfully colonised itself. Western powers did, however, continue to interfere in both internal and external affairs.
 By 1913, the British had occupied
By 1913, the British had occupied Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
, British Malaya, Malaya and the northern Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
territories, the France, French controlled Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
, the Dutch ruled the Netherlands East Indies while Portugal managed to hold on to Portuguese Timor. In the History of the Philippines (1521–1898), Philippines, the 1872 Cavite Mutiny was a precursor to the Philippine Revolution (1896–1898). When the Spanish–American War began in Cuba in 1898, Filipino revolutionaries Philippine Declaration of Independence, declared Philippine independence and established the First Philippine Republic the following year. In the Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris of 1898 that ended the war with Spain, the United States gained the Philippines and other territories; in refusing to recognise the nascent republic, America effectively reversed her position of 1856. This led directly to the Philippine–American War, in which the First Republic was defeated; wars followed with the Republic of Zamboanga, the Republic of Negros and the Tagalog Republic#Sakay, Republic of Katagalugan, all of which were also defeated.
Colonial rule had had a profound effect on Southeast Asia. While the colonial powers profited much from the region's vast resources and large market, colonial rule did develop the region to a varying extent. Commercial agriculture, mining and an export based economy developed rapidly during this period. The introduction Christianity bought by the colonist also have profound effect in the societal change.
Increased labour demand resulted in mass immigration, especially from British India and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, which brought about massive demographic change. The institutions for a modern nation state like a state bureaucracy, courts of law, print media and to a smaller extent, modern education, sowed the seeds of the fledgling nationalism, nationalist movements in the colonial territories. In the inter-war years, these nationalist movements grew and often clashed with the colonial authorities when they demanded self-determination.
20th-century Southeast Asia
Japanese invasion and occupations
 In September 1940, following the Fall of France and pursuant to the Pacific war goals of Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan, the Japanese Imperial Army invaded Japanese invasion of French Indochina, Vichy French Indochina, which ended in the abortive Japanese coup de main in French Indochina of 9 March 1945. On 5 January 1941, Thailand launched the Franco-Thai War, ended on 9 May 1941 by a Japanese-imposed treaty signed in Tokyo. On 7/8 December, Japan's entry into
In September 1940, following the Fall of France and pursuant to the Pacific war goals of Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan, the Japanese Imperial Army invaded Japanese invasion of French Indochina, Vichy French Indochina, which ended in the abortive Japanese coup de main in French Indochina of 9 March 1945. On 5 January 1941, Thailand launched the Franco-Thai War, ended on 9 May 1941 by a Japanese-imposed treaty signed in Tokyo. On 7/8 December, Japan's entry into World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
began with the Thailand in World War II, invasion of Thailand, the only invaded country to maintain nominal independence, due to her political and military alliance with the Japanese—on 10 May 1942, her northwestern Phayap Army, Payap Army invaded Burma during the Burma Campaign. From 1941 until war's end, Japanese Japanese occupation of Cambodia, occupied Cambodia, Japanese occupation of Malaya, Malaya and the Philippines, which ended in independence movements. Japanese occupation of the Philippines#The occupation, Japanese occupation of the Philippines led to the forming of the Second Philippine Republic, formally dissolved in Tokyo on 17 August 1945. Also on 17 August, a proclamation of Indonesian Independence was read at the conclusion of Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies since March 1942.
Post-war decolonisation
 With the rejuvenated nationalist movements in wait, the Europeans returned to a very different Southeast Asia after
With the rejuvenated nationalist movements in wait, the Europeans returned to a very different Southeast Asia after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 August 1945 and subsequently Indonesian National Revolution, fought a bitter war against the returning Dutch; the Philippines was granted independence by the United States in 1946; Burma secured their independence from Britain in 1948, and the France, French were driven from Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
in 1954 after a bitterly fought war (the Indochina War) against the Vietnamese nationalists. The United Nations provided a forum for nationalism, post-independent self-definition, nation-building and the acquisition of territorial integrity for many newly independent nations.
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, countering the threat of communism was a major theme in the decolonisation process. After suppressing the communist insurrection during the Malayan Emergency from 1948 to 1960, Britain granted independence to Federation of Malaya, Malaya and later, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Sabah and Sarawak in 1957 and 1963 respectively within the framework of the Malaysia, Federation of Malaysia. In one of the most bloody single incidents of violence in Cold War Southeast Asia, General Suharto Overthrow of Sukarno, seized power in Indonesia in 1965 and initiated Indonesian mass killings of 1965–1966, a massacre of approximately 500,000 alleged members of the Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI).
Following the independence of the Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
states with the battle of Dien Bien Phu, North Vietnamese attempts to conquer South Vietnam resulted in the Vietnam War. The conflict spread to Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
and Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
and heavy intervention from the United States. By the war's end in 1975, all these countries were controlled by communist parties. After the communist victory, two wars between communist states—the Cambodian–Vietnamese War of 1975–89 and the Sino-Vietnamese War of 1979—were fought in the region. The victory of the Khmer Rouge in Cambodia resulted in the Cambodian genocide.Olson, James S.; Roberts, Randy (2008). ''Where the Domino Fell: America and Vietnam 1945–1995'' (5th ed.). Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing
In 1975, Portuguese rule ended in East Timor. However, independence was short-lived as Indonesia Indonesian invasion of East Timor, annexed the territory soon after. However, after more than Indonesian occupation of East Timor, 20 years of fighting Indonesia, East Timor won its independence and was recognised by the UN in 2002. Finally, Britain ended its protectorate of the Sultanate of Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by th ...
in 1984, marking the end of European rule in Southeast Asia.
Contemporary Southeast Asia
 Modern Southeast Asia has been characterised by high economic growth by most countries and closer regional integration.
Modern Southeast Asia has been characterised by high economic growth by most countries and closer regional integration. Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
and Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
have traditionally experienced high growth and are commonly recognised as the more developed countries of the region. As of late, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
too had been experiencing an economic boom. However, Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
, Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
and the newly independent East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-w ...
are still lagging economically.
On 8 August 1967, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations
ASEAN ( , ), officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, mi ...
(ASEAN) was founded by Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and the Philippines. Since Cambodian admission into the union in 1999, East Timor is the only Southeast Asian country that is not part of ASEAN, although plans are under way for eventual membership. The association aims to enhance co-operation among Southeast Asian community. ASEAN Free Trade Area has been established to encourage greater trade among ASEAN members. ASEAN has also been a front runner in greater integration of Asia-Pacific region through East Asia Summits.
See also
* Buddhism in Southeast Asia * Hinduism in Southeast Asia * Islam in Southeast Asia * Greater India * Two Layer hypothesis * Spratly Islands * History of Brunei * History of Cambodia * History of East Timor * History of Indonesia * History of Laos * History of Malaysia * History of Myanmar * History of the Philippines * History of Singapore * History of Thailand * History of Vietnam * History of AsiaNotes
References
Bibliography
* * . * * pg.123-125 * * * Sinha, P.C. , ed. ''Encyclopaedia of South East and Far East Asia'' (Anmol, 2006).Further reading
* Reid, Anthony. ''A History of Southeast Asia: Critical Crossroads'' (Blackwell History of the World, 2015) * *online version of 1955 edition, 810pp
* * Lokesh, Chandra, & International Academy of Indian Culture. (2000). ''Society and culture of Southeast Asia: Continuities and changes. New Delhi: International Academy of Indian Culture and Aditya Prakashan.'' * * * * Embree, Ainslie T., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Asian history'' (1988)
vol. 1 online
* * * * * * * * Heidhues, Mary Somer. "'Southeast Asia: A Concise History" * * * * * Osborne, Milton. ''Southeast Asia. An introductory history''. * * * Scott, James C., The Art of Not Being Governed: An Anarchist History of Upland Southeast Asia (Yale Agrarian Studies Series), 464 pages, Yale University Press (30 September 2009), , * Tarling, Nicholas (ed). ''The Cambridge history of Southeast Asia'' Vol I-IV. * R. C. Majumdar, Study of Sanskrit in South-East Asia * R. C. Majumdar, ''India and South-East Asia'', I.S.P.Q.S. History and Archaeology Series Vol. 6, 1979, . * * * * * * Yule, Paul. ''The Bronze Age Metalwork of India''. Prähistorische Bronzefunde XX,8, Munich, 1985, . * * * * * *
External links
A Short History of China and Southeast Asia.pdf
Ancient Southeast Asia Throbbing Blood Tube
* :v:Topic:Southeast Asian history, Wikiversity – Department of Southeast Asian History
雲南・東南アジアに関する漢籍史料
Citizenship and Democratization in Southeast Asia
Democracy and Citizen Politics in East Asia
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of Southeast Asia History of Southeast Asia,