History of South America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
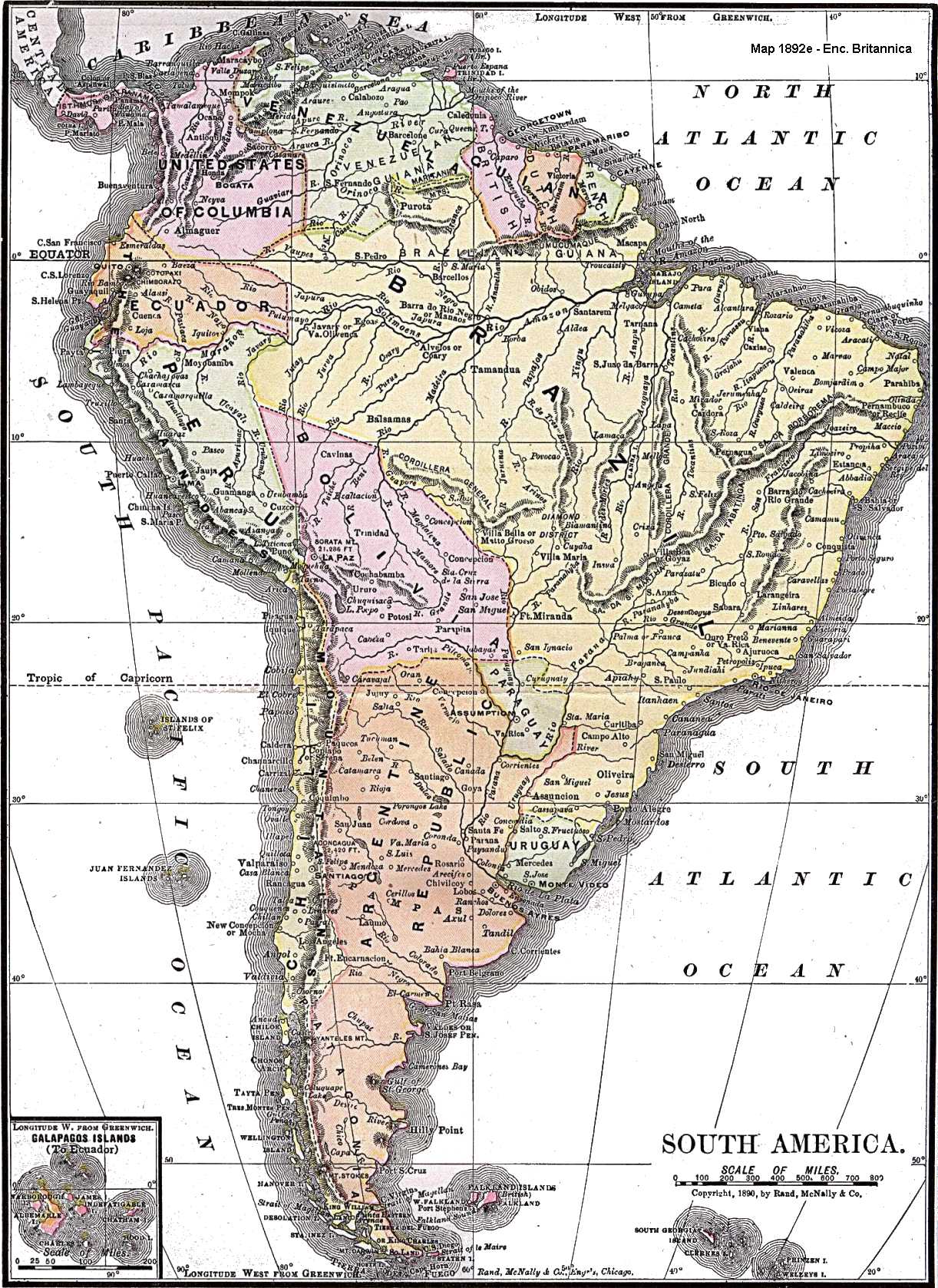

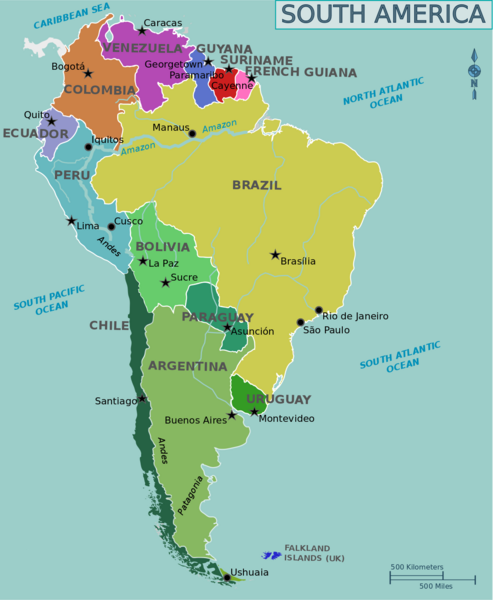 The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of
The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of

 In the
In the
 The earliest archaeological evidence from human settlement comes from Monte Verde (possibly as early as 16,500 BCE). Based on
The earliest archaeological evidence from human settlement comes from Monte Verde (possibly as early as 16,500 BCE). Based on  For a long time it was thought that the Amazon rainforest was only ever sparsely populated, as it was impossible to sustain a large population through
For a long time it was thought that the Amazon rainforest was only ever sparsely populated, as it was impossible to sustain a large population through


 The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of
The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. The continent continues to be home to indigenous peoples, some of whom built high civilizations prior to the arrival of Europeans in the late 1400s and early 1500s. South America has a history that has a wide range of human cultures and forms of civilization. The Norte Chico civilization in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
is the oldest civilization in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
and one of the first six independent civilizations in the world; it was contemporaneous with the Egyptian pyramids. It predated the Mesoamerican Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
by nearly two millennia.
Millennia of independent indigenous existence was disrupted by European colonization from Spain and Portugal, and by demographic collapse. However, the resulting culture both in continent's ''mestizos'', and in indigenous cultures remained quite distinct from those of their colonizers. Through the trans-Atlantic slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, South America (especially Brazil) became the home of millions of people of the African diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from native Africans or people from Africa, predominantly in the Americas. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the West and Central Africans who were ...
. The mixing of ethnic groups led to new social structures.
The tensions between Europeans, indigenous peoples, and African slaves and their descendants shaped South America, starting in sixteenth century. Most of Spanish America achieved its independence in the early nineteenth century through hard fought wars, while Portuguese Brazil first became the seat of the Portuguese empire and then an empire independent of Portugal. With the revolution for independence from the Spanish crown achieved during the 19th century, South America underwent yet more social and political changes. These have included nation building projects, absorbing waves of immigration from Europe in the late 19th and 20th centuries, dealing with increased international trade, colonization of hinterlands, and wars about territory ownership and power balance. During this period there has also been the reorganization of Indigenous rights and duties, subjugation of Indigenous peoples living in the states' frontiers, that lasted until the early 1900s; liberal-conservative conflicts among the ruling classes, and major demographic and environmental changes accompanying the development of sensitive habitats.
Prehistory

 In the
In the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
and Early Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
eras, South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
were connected in a landmass called Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
, as part of the supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leav ...
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. In the Albian
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous Epoch/ Series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0 ...
, around 110 mya, South America and Africa began to diverge along the southern Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North A ...
, giving rise to a landmass of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
and South America. During the late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', ...
, around 35 mya, Antarctica and South America separated and South America became a massive, biologically rich island-continent. During approximately 30 million years, the biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
of South America was isolated from the rest of the world, leading to the evolution of species within the continent.
The event that caused the mass-extinction of dinosaurs 66 Mya gave rise to neotropical
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In bioge ...
rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s like the Amazonia
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
, replacing species composition and structure of local forests. During ~6 million years of recovery to former levels of plant diversity, they evolved from widely spaced gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
-dominated forests to the forests with thick canopies which block sunlight, prevalent flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants t ...
s and high vertical layering as known today.
Geological evidence suggests that approximately 3 million years ago, South America became connected to North America when the Bolivar Trough marine barrier disappeared and the Panamanian land bridge formed. The joining of these two land masses led to the Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which lan ...
, in which biota from both continents expanded their ranges. The first species known to have made the northward migration was '' Pliometanastes'', a fossil ground sloth
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. The term is used to refer to all extinct sloths because of the large size of the earliest forms discovered, compared to existing tree sloths. The Caribb ...
roughly the size of a modern black bear. Migrations to the Southern Hemisphere were undertaken by several North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
n mammalian carnivores. Fewer species migrated in the opposite direction from south to north. The result of the expansion of a North American fauna was a mass extinction in which hundreds of species disappeared in a relatively short time. About 60% of present-day South American mammals have evolved from North American species. Some South American species were able to adapt and spread into North America. Apart from ''Pliometanastes'', during the Irvingtonian
The Irvingtonian North American Land Mammal Age on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology (NALMA), spanning from 1.9 million – 250,000 years BP.
stage of the mammal land stages, around 1.9 mya, species as '' Pampatherium'', a giant armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, alo ...
, ground sloth '' Megatherium'', giant anteater
Anteater is a common name for the four extant mammal species of the suborder Vermilingua (meaning "worm tongue") commonly known for eating ants and termites. The individual species have other names in English and other languages. Together wit ...
''Myrmecophaga
The giant anteater (''Myrmecophaga tridactyla'') is an insectivorous mammal native to Central and South America. It is one of four living species of anteaters, of which it is the largest member. The only extant member of the genus ''Myrmecophag ...
'', a Neogene capybara
The capybaraAlso called capivara (in Brazil), capiguara (in Bolivia), chigüire, chigüiro, or fercho (in Colombia and Venezuela), carpincho (in Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay) and ronsoco (in Peru). or greater capybara (''Hydrochoerus hydro ...
('' Hydrochoerus''), '' Meizonyx'', opossum '' Didelphis'', and ''Mixotoxodon
''Mixotoxodon'' ("mixture ''Toxodon''") is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene epoch, from 1,800,000—12,000 years a ...
'' followed the route north. The terror bird
Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct clade of large carnivorous flightless birds that were one of the largest species of apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era; their conventionally accepted temporal ...
'' Titanis'', the only large carnivore in South American, dispersed into North America.
Pre-Columbian era
Agriculture and domestication of animals
The Americas are thought to have been first inhabited by people from eastern Asia who crossed theBering Land Bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
to present-day Alaska; the land separated and the continents are divided by the Bering Strait. Over the course of millennia, three waves of migrants spread to all parts of the Americas. Genetic and linguistic evidence has shown that the last wave of migrant peoples settled across the northern tier, and did not reach South America.
The first evidence for the existence of agricultural practices in South America dates back to circa 6500 BCE, when potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es, chilies and bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes th ...
s began to be cultivated for food in the Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Boli ...
. Pottery evidence suggests that manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, which remains a staple foodstuff today, was being cultivated as early as 2000 BCE.O'Brien, Patrick. (General Editor). ''Oxford Atlas of World History''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2005. p. 25
South American cultures began domesticating llamas and alpacas in the highlands of the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
circa 3500 BCE. These animals were used for both transportation and meat; their fur was shorn or collected to use to make clothing. Guinea pigs were also domesticated as a food source at this time.
By 2000 BCE, many agrarian village communities had developed throughout the Andes and the surrounding regions. Fishing became a widespread practice along the coast, with fish being the primary source of food for those communities. Irrigation systems were also developed at this time, which aided in the rise of agrarian societies. The food crops were quinoa
Quinoa (''Chenopodium quinoa''; , from Quechua ' or ') is a flowering plant in the amaranth family. It is a herbaceous annual plant grown as a crop primarily for its edible seeds; the seeds are rich in protein, dietary fiber, B vitamins, ...
, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, lima beans, common bean
''Phaseolus vulgaris'', the common bean, is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its botanical classification, alo ...
s, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small an ...
s, manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato ('' Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the bindweed or morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable. The young ...
es, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es, oca
OCA or Oca may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions
* The ancient town and bishopric Oca in Asia Minor (present Asia Turkey), now a Latin Catholic titular see
* The former Spanish Oca, modern Villafranca Montes de Oca, also see of a medieval bis ...
and squashes
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
. Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
was also grown and was particularly important as the only major fiber crop.
Among the earliest permanent settlements, dated to 4700 BC is the Huaca Prieta
Huaca Prieta is the site of a prehistoric settlement beside the Pacific Ocean in the Chicama Valley, just north of Trujillo, La Libertad Province, Peru. It is a part of the El Brujo Archaeological Complex, which also includes Moche (culture) si ...
site on the coast of Peru, and at 3500 BC the Valdivia culture in Ecuador. Other groups also formed permanent settlements. Among those groups were the Muisca or "Muysca," and the Tairona, located in present-day Colombia. The Cañari
The Cañari (in Kichwa: Kañari) are an indigenous ethnic group traditionally inhabiting the territory of the modern provinces of Azuay and Cañar in Ecuador. They are descended from the independent pre-Columbian tribal confederation of the ...
of Ecuador, Quechua of Peru, and Aymara of Bolivia were the three most important Native peoples who developed societies of sedentary agriculture in South America.
In the last two thousand years, there may have been contact with the Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
ns who sailed to and from the continent across the South Pacific Ocean. The sweet potato, which originated in South America, spread through some areas of the Pacific. There is no genetic legacy of human contact.
Human activity
 The earliest archaeological evidence from human settlement comes from Monte Verde (possibly as early as 16,500 BCE). Based on
The earliest archaeological evidence from human settlement comes from Monte Verde (possibly as early as 16,500 BCE). Based on archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence from an excavation at Caverna da Pedra Pintada
Caverna da Pedra Pintada (Painted Rock Cave ), is an archaeological site in northern Brazil, with evidence of human presence dating ca. 11,200 years ago.Saraceni, Jessica E. and Adriana Franco da Sá"People of South America."''Archaeology.'' Vol. ...
, human inhabitants first settled in the Amazon region at least 11,200 years ago.
 For a long time it was thought that the Amazon rainforest was only ever sparsely populated, as it was impossible to sustain a large population through
For a long time it was thought that the Amazon rainforest was only ever sparsely populated, as it was impossible to sustain a large population through agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
given the poor soil. Archaeologist Betty Meggers
Betty Jane Meggers (December 5, 1921 – July 2, 2012) was an American archaeologist best known for her work in South America. She was considered influential at the Smithsonian Institution, where she was long associated in research,geoglyphs have been discovered on deforested land dating between 01250CE, leading to claims about
 On the north-central coast of present-day
On the north-central coast of present-day
 The
The
 The Chibcha-speaking communities were the most numerous, the most extended by territory, and the most socio-economically developed of the Pre-Hispanic Colombian cultures. They were divided into two linguistic subgroups; the Arwako-Chimila languages, with the Tairona, Kankuamo,
The Chibcha-speaking communities were the most numerous, the most extended by territory, and the most socio-economically developed of the Pre-Hispanic Colombian cultures. They were divided into two linguistic subgroups; the Arwako-Chimila languages, with the Tairona, Kankuamo,
 Of these indigenous groups, the Muisca were the most advanced and formed one of the four grand civilisations in the Americas. With the
Of these indigenous groups, the Muisca were the most advanced and formed one of the four grand civilisations in the Americas. With the
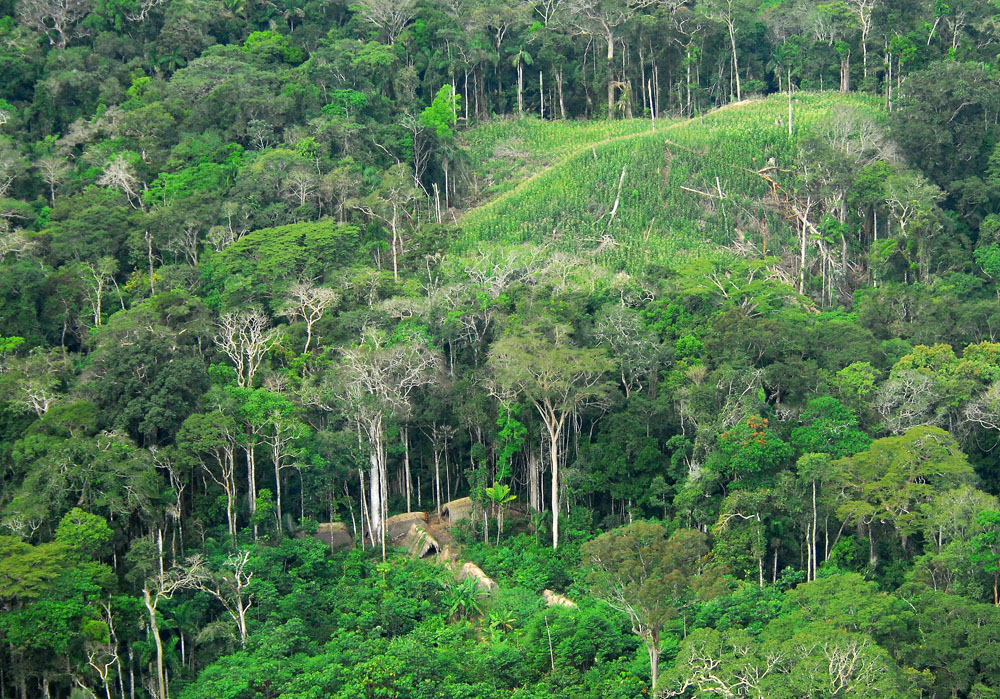
 For a long time, scholars believed that Amazon forests were occupied by small numbers of hunter-gatherer tribes. Archeologist Betty J. Meggers was a prominent proponent of this idea, as described in her book ''Amazonia: Man and Culture in a Counterfeit Paradise''. However, recent archeological findings have suggested that the region was densely populated. From the 1970s, numerous geoglyphs have been discovered on deforested land dating between 0–1250 AD. Additional finds have led to conclusions that there were highly developed and populous cultures in the forests, organized as
For a long time, scholars believed that Amazon forests were occupied by small numbers of hunter-gatherer tribes. Archeologist Betty J. Meggers was a prominent proponent of this idea, as described in her book ''Amazonia: Man and Culture in a Counterfeit Paradise''. However, recent archeological findings have suggested that the region was densely populated. From the 1970s, numerous geoglyphs have been discovered on deforested land dating between 0–1250 AD. Additional finds have led to conclusions that there were highly developed and populous cultures in the forests, organized as
 The Moche thrived on the north coast of Peru between the first and ninth century CE. The heritage of the Moche comes down to us through their elaborate burials, excavated by former UCLA professor
The Moche thrived on the north coast of Peru between the first and ninth century CE. The heritage of the Moche comes down to us through their elaborate burials, excavated by former UCLA professor
Oil Wealth and the Fate of the Forest: A Comparative Study of Eight Tropical Countries
',
Pope Benedict Argues Catholic Church 'Purified' Indigenous Peoples
'' posted on '' AlterNet'' June 18, 2007 In 1494, Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign
Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign
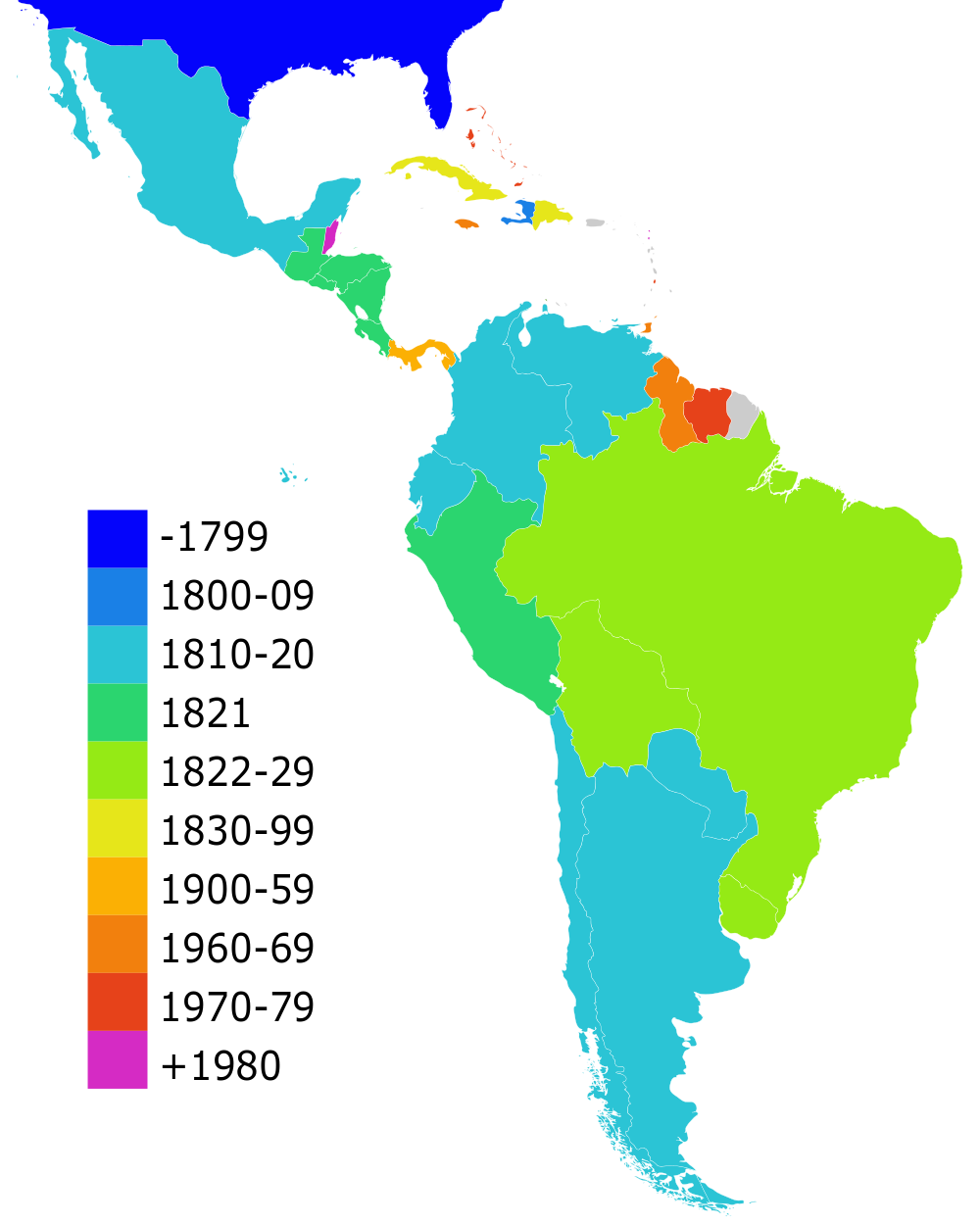 The Spanish colonies won their independence in the first quarter of the 19th century, in the
The Spanish colonies won their independence in the first quarter of the 19th century, in the  A struggle for power emerged among the new nations, and several further wars were soon fought thereafter.
The first few wars were fought for supremacy in the northern and southern parts of the continent. The Gran Colombia – Peru War of the north and the
A struggle for power emerged among the new nations, and several further wars were soon fought thereafter.
The first few wars were fought for supremacy in the northern and southern parts of the continent. The Gran Colombia – Peru War of the north and the

 Intellectuals and government leaders in South America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialization. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the ups and downs of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration (1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a good neighbor policy and allowed the nationalization of some American companies in South America. The
Intellectuals and government leaders in South America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialization. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the ups and downs of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration (1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a good neighbor policy and allowed the nationalization of some American companies in South America. The
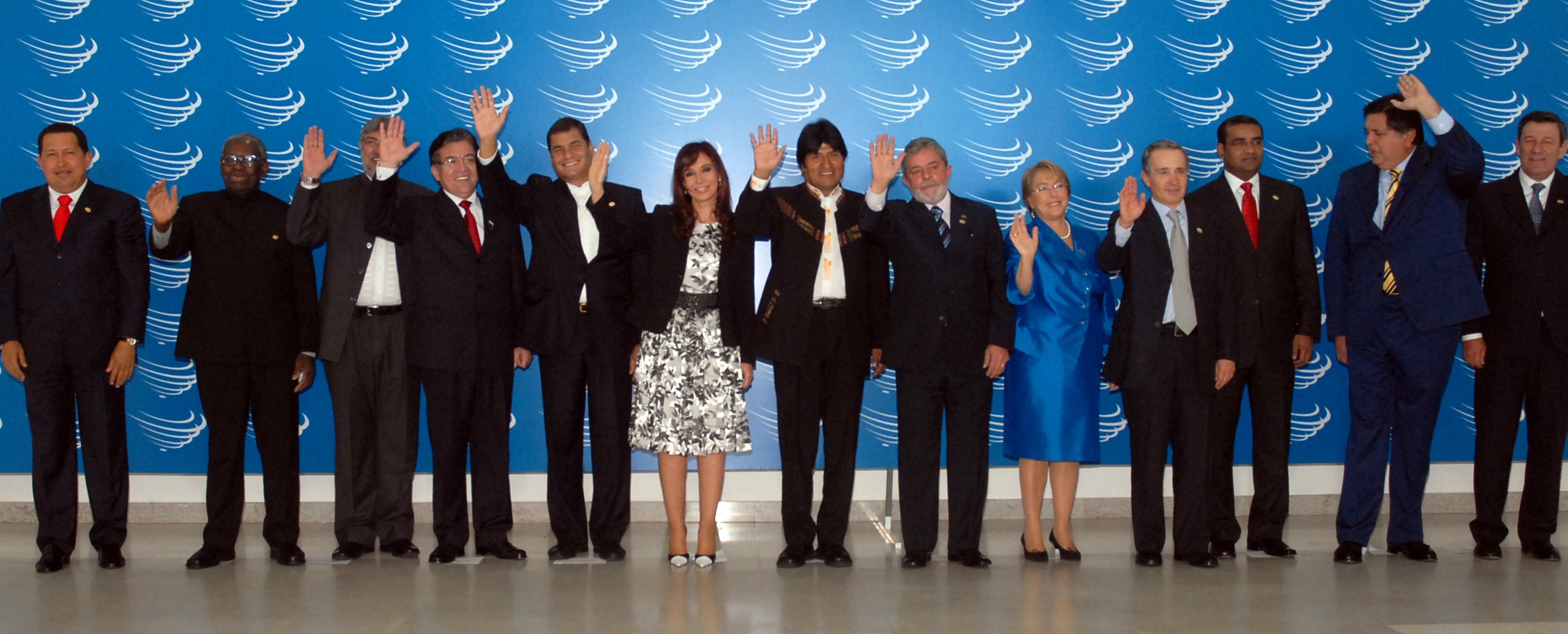 By the 1970s, leftists had acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of each individual country's upper class to support coups d'état to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarisation. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorships that were supported by the United States of America.
Also around the 1970s, the regimes of the
By the 1970s, leftists had acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of each individual country's upper class to support coups d'état to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarisation. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorships that were supported by the United States of America.
Also around the 1970s, the regimes of the 
 Revolutionary movements and right-wing military dictatorships became common after
Revolutionary movements and right-wing military dictatorships became common after
 The set of specific economic policy prescriptions that were considered the "standard" reform package were promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, DC-based institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and the US Treasury Department during the 1980s and '90s.
The set of specific economic policy prescriptions that were considered the "standard" reform package were promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, DC-based institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and the US Treasury Department during the 1980s and '90s.
 The term 'pink tide' ( es, link=no, marea rosa, pt, onda rosa) or 'turn to the Left' (Sp.: ''vuelta hacia la izquierda'', Pt.: ''Guinada à Esquerda'') are phrases which are used in contemporary 21st century Political science, political analysis in the media and elsewhere to describe the perception that leftism, leftist ideology in general, and left-wing politics in particular, were increasingly becoming influential in Latin America.
Since the 2000s or 1990s in some countries, left-wing political parties have risen to power. Hugo Chávez in Venezuela, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff in Brazil, Fernando Lugo in Paraguay, Néstor Kirchner, Néstor and Cristina Fernández de Kirchner in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez and José Mujica in Uruguay, the Ricardo Lagos, Lagos and Michelle Bachelet, Bachelet governments in Chile, Evo Morales in Bolivia, and Rafael Correa of Ecuador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who also often declare themselves socialists, Latin Americanists or Anti-imperialism, anti-imperialists.
The term 'pink tide' ( es, link=no, marea rosa, pt, onda rosa) or 'turn to the Left' (Sp.: ''vuelta hacia la izquierda'', Pt.: ''Guinada à Esquerda'') are phrases which are used in contemporary 21st century Political science, political analysis in the media and elsewhere to describe the perception that leftism, leftist ideology in general, and left-wing politics in particular, were increasingly becoming influential in Latin America.
Since the 2000s or 1990s in some countries, left-wing political parties have risen to power. Hugo Chávez in Venezuela, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff in Brazil, Fernando Lugo in Paraguay, Néstor Kirchner, Néstor and Cristina Fernández de Kirchner in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez and José Mujica in Uruguay, the Ricardo Lagos, Lagos and Michelle Bachelet, Bachelet governments in Chile, Evo Morales in Bolivia, and Rafael Correa of Ecuador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who also often declare themselves socialists, Latin Americanists or Anti-imperialism, anti-imperialists.
 ;The list of leftist South American presidents is, by date of election, the following:
* 1998: Hugo Chávez, Venezuela
* 1999: Ricardo Lagos, Chile
* 2002: Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, Luís Inácio Lula da Silva, Brazil
* 2002: Lucio Gutiérrez, Ecuador
* 2003: Néstor Kirchner, Argentina
* 2004: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay
* 2005: Evo Morales, Bolivia
* 2006: Michelle Bachelet, Chile
* 2006: Rafael Correa, Ecuador
;The list of leftist South American presidents is, by date of election, the following:
* 1998: Hugo Chávez, Venezuela
* 1999: Ricardo Lagos, Chile
* 2002: Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, Luís Inácio Lula da Silva, Brazil
* 2002: Lucio Gutiérrez, Ecuador
* 2003: Néstor Kirchner, Argentina
* 2004: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay
* 2005: Evo Morales, Bolivia
* 2006: Michelle Bachelet, Chile
* 2006: Rafael Correa, Ecuador
"Avenger against oligarchy" wins in Ecuador
' The Real News, 27 April 2009. * 2007: Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, Argentina * 2008: Fernando Lugo, Paraguay * 2010: José Mujica, Uruguay * 2010: Dilma Rousseff, BrazilEFE
"Dilma, 1ª mulher presidente e única economista em 121 anos de República"
BOL. 31 October 2010.Bennett, Alle
"Dilma Rousseff biography"
, Agência Brasil, 9 August 2010 * 2011: Ollanta Humala, Peru''The Guardian'', April 11, 2011
Peru elections: Fujimori and Humala set for runoff vote
/ref>''Hoy (Peruvian newspaper), Diario Hoy'', October 31, 2000
PERU, CORONELAZO NO CUAJA
/ref> BBC, January 4, 2005
Perú: insurgentes se rinden
/ref> * 2013: Nicolás Maduro, Venezuela"Nicolas Maduro sworn in as new Venezuelan president"
BBC News. 19 April 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2013 * 2014: Michelle Bachelet, Chile * 2015: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay * 2017: Lenín Moreno, Ecuador * 2019: Alberto Fernández, Argentina * 2020: Luis Arce, Bolivia * 2021: Pedro Castillo, Peru * 2022: Gabriel Boric, Gabriel Boric Font, Chile * 2022: Gustavo Petro, Colombia
online
* * * * * Uribe, Victor M. "The Enigma of Latin American Independence: Analyses of the Last Ten Years," ''Latin American Research Review'' (1997) 32#1 pp. 236–25
in JSTOR
* Wade, Lizzie. (2015).
Drones and satellites spot lost civilizations in unlikely places
" ''American Association for the Advancement of Science, Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science),'' *
Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
civilisations.
Norte Chico
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, the Norte Chico civilization emerged as one of six civilizations to develop independently in the world. It was roughly contemporaneous with the Egyptian pyramids. It preceded the civilization of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Wit ...
by two millennia. It is believed to have been the only civilization dependent on fishing rather than agriculture to support its population.
The Caral Supe complex is one of the larger Norte Chico sites and has been dated to 27th century BCE. It is noteworthy for having absolutely no signs of warfare. It was contemporary with urbanism's rise in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
.
Cañari
 The
The Cañari
The Cañari (in Kichwa: Kañari) are an indigenous ethnic group traditionally inhabiting the territory of the modern provinces of Azuay and Cañar in Ecuador. They are descended from the independent pre-Columbian tribal confederation of the ...
were the indigenous natives of today's Ecuadorian provinces of Cañar and Azuay at the time of European contact. They were an elaborate civilization with advanced architecture and religious belief. Most of their remains were either burned or destroyed from attacks by the Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, ( Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The adm ...
and later the Spaniards. Their old city "Guapondelig", was replaced twice, first by the Incan city of Tomipamba, and later by the colonial city of Cuenca. The city was believed by the Spanish to be the site of El Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king ...
, the city of gold from the mythology of Colombia.
The Cañari were most notable in having repulsed the Incan invasion with fierce resistance for many years until they fell to Tupac Yupanqui. It is said that the Inca strategically married the Cañari princess Paccha to conquer the people. Many of their descendants still reside in Cañar.
Chibchan Nations
 The Chibcha-speaking communities were the most numerous, the most extended by territory, and the most socio-economically developed of the Pre-Hispanic Colombian cultures. They were divided into two linguistic subgroups; the Arwako-Chimila languages, with the Tairona, Kankuamo,
The Chibcha-speaking communities were the most numerous, the most extended by territory, and the most socio-economically developed of the Pre-Hispanic Colombian cultures. They were divided into two linguistic subgroups; the Arwako-Chimila languages, with the Tairona, Kankuamo, Kogi
Kogi State is a state in the North Central region of Nigeria, bordered to the west by the states of Ekiti and Kwara, to the north by the Federal Capital Territory, to the northeast by Nasarawa State, to the northwest by Niger State, to th ...
, Arhuaco
The Arhuaco are an indigenous people of Colombia. They are Chibchan-speaking people and descendants of the Tairona culture, concentrated in northern Colombia in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta.
Name
The Arhuaco are also known as the Aruaco, ...
, Chimila and Chitarero people
The Chitarero were an indigenous Chibcha-speaking people in the Andes of north-eastern Colombia and north-western Venezuela. They were responsible for the death of the German ''conquistador'' Ambrosius Ehinger in 1533 by means of poisoned arrows ...
and the Kuna-Colombian languages with Kuna
Kuna may refer to:
Places
* Kuna, Idaho, a town in the United States
** Kuna Caves, a lava tube in Idaho
* Kuna Peak, a mountain in California
* , a village in the Orebić municipality, Croatia
* , a village in the Konavle municipality, Croatia ...
, Nutabe, Motilon, U'wa, Lache
The Lache ( ; sometimes simply Lache) is a housing estate in the city of Chester, in Cheshire, United Kingdom, with a population of around 10,000. It is located approximately southwest of the ancient city, with good local transport links en r ...
, Guane, Sutagao and Muisca.
Muisca
 Of these indigenous groups, the Muisca were the most advanced and formed one of the four grand civilisations in the Americas. With the
Of these indigenous groups, the Muisca were the most advanced and formed one of the four grand civilisations in the Americas. With the Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, ( Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The adm ...
in Peru, they constituted the two developed and specialised societies of South America. The Muisca, meaning "people" or "person" in their version of the Chibcha language; ''Muysccubun'', inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboyacense
The Altiplano Cundiboyacense () is a high plateau located in the Eastern Cordillera of the Colombian Andes covering parts of the departments of Cundinamarca and Boyacá. The altiplano corresponds to the ancient territory of the Muisca. The Alt ...
, the high plateau in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
and surrounding valleys, such as the Tenza Valley. Commonly set at 800 AD, their history succeeded the Herrera Period
The Herrera Period is a phase in the history of Colombia. It is part of the Andean preceramic and ceramic, time equivalent of the North American pre-Columbian formative and classic stages and age dated by various archaeologists. The Herrera P ...
. The people were organised in a loose confederation of rulers, later called the Muisca Confederation
The Muisca Confederation was a loose confederation of different Muisca rulers (''zaques'', ''zipas'', ''iraca'', and ''tundama'') in the central Andean highlands of present-day Colombia before the Spanish conquest of northern South America. T ...
.Gamboa Mendoza, 2016 At the time of the Spanish conquest, their reign spread across the modern departments Cundinamarca and Boyacá with small parts of southern Santander with a surface area of approximately and a total population of between 300,000 and two million individuals.Although sources state "47,000", this cannot be correct as that would be whole Boyacá and Cundinamarca and include Panche, Lache and Muzo
The Muisca were known as "The Salt People", thanks to their extraction of and trade in halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
from brines in various salt mines of which those in Zipaquirá
Zipaquirá () is a municipality and city of Colombia in the department of Cundinamarca. Its neighboring municipalities are Cogua and Nemocón to the north; Tocancipá to the east; Tabio, Cajicá and Sopó to the south; and Subachoque and ...
and Nemocón are still the most important. This extraction process was the work of the Muisca women exclusively and formed the backbone of their highly regarded trading with other Chibcha-, Arawak- and Cariban-speaking neighboring indigenous groups.Daza, 2013, p. 23 Trading was performed using salt, small cotton cloths and larger mantles and ceramics as barter trade
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists dist ...
.Francis, 1993, p. 44 Their economy was agricultural in nature, profiting from the fertile soils of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
Lake Humboldt
Lake Humboldt or Humboldt Lake is an endorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as riv ...
that existed on the Bogotá savanna until around 30,000 years BP. Their crops were cultivated using irrigation and drainage on elevated terraces and mounds. To the Spanish conquistadors they were best known for their advanced gold-working, as represented in the '' tunjos'' (votive offer pieces), spread in museum collections
A museum is distinguished by a collection of often unique objects that forms the core of its activities for exhibitions, education, research, etc. This differentiates it from an archive or library, where the contents may be more paper-based, repla ...
all around the world. The famous Muisca raft
The Muisca raft (''Balsa Muisca'' in Spanish), sometimes referred to as the Golden Raft of El Dorado, is a pre-Columbian votive piece created by the Muisca, an indigenous people of Colombia in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The pi ...
, centerpiece in the collection of the Museo del Oro in the Colombian capital Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the larges ...
, shows the skilled goldworking of the inhabitants of the Altiplano. The Muisca were the only pre-Columbian civilization known in South America to have used coins (''tejuelos'').
The gold and '' tumbaga'' (a gold-silver-copper alloy elaborated by the Muisca) created the legend of ''El Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king ...
''; the "land, city or man of gold". The Spanish conquistadors who landed in the Caribbean city of Santa Marta
Santa Marta (), officially Distrito Turístico, Cultural e Histórico de Santa Marta ("Touristic, Cultural and Historic District of Santa Marta"), is a city on the coast of the Caribbean Sea in northern Colombia. It is the capital of Magdalena ...
were informed of the rich gold culture and led by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada
Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada y Rivera, also spelled as Ximénez and De Quezada, (;1496 16 February 1579) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador in northern South America, territories currently known as Colombia. He explored the territory named ...
and his brother Hernán Pérez, organised the most strenuous of the Spanish conquests into the heart of the Andes in April 1536. After an expedition of a year, where 80% of the soldiers died due to the harsh climate, carnivores such as caimans and jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
s and the frequent attacks of the indigenous peoples found along the route, Tisquesusa
Tisquesusa, also spelled Thisquesuza, Thysquesuca or Thisquesusha (referred to in the earliest sources as Bogotá, the Elder) (died Facatativá, 1537) was the fourth and last independent ruler ('' psihipqua'') of Muyquytá, main settlement of t ...
, the ''zipa
When the Spanish arrived in the central Colombian highlands, the region was organized into the Muisca Confederation, which had two rulers; the ''zipa'' was the ruler of the southern part and based in Muyquytá. The ''hoa'' was the ruler of the ...
'' of Bacatá, on the Bogotá savanna
The Bogotá savanna is a montane savanna, located in the southwestern part of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in the center of Colombia. The Bogotá savanna has an extent of and an average altitude of . The savanna is situated in the Eastern Ran ...
, was beaten by the Spanish on April 20, 1537, and died "bathing in his own blood", as prophesied by the mohan Popón.
Amazon
 For a long time, scholars believed that Amazon forests were occupied by small numbers of hunter-gatherer tribes. Archeologist Betty J. Meggers was a prominent proponent of this idea, as described in her book ''Amazonia: Man and Culture in a Counterfeit Paradise''. However, recent archeological findings have suggested that the region was densely populated. From the 1970s, numerous geoglyphs have been discovered on deforested land dating between 0–1250 AD. Additional finds have led to conclusions that there were highly developed and populous cultures in the forests, organized as
For a long time, scholars believed that Amazon forests were occupied by small numbers of hunter-gatherer tribes. Archeologist Betty J. Meggers was a prominent proponent of this idea, as described in her book ''Amazonia: Man and Culture in a Counterfeit Paradise''. However, recent archeological findings have suggested that the region was densely populated. From the 1970s, numerous geoglyphs have been discovered on deforested land dating between 0–1250 AD. Additional finds have led to conclusions that there were highly developed and populous cultures in the forests, organized as Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
civilizations. The BBC's '' Unnatural Histories'' claimed that the Amazon rainforest, rather than being a pristine wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
, has been shaped by man for at least 11,000 years through practices such as forest gardening
Forest gardening is a low-maintenance, sustainable, plant-based food production and agroforestry system based on woodland ecosystems, incorporating fruit and nut trees, shrubs, herbs, vines and perennial vegetables which have yields directly u ...
.
The first European to travel the length of the Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
was Francisco de Orellana in 1542. The BBC documentary ''Unnatural Histories'' presents evidence that Francisco de Orellana, rather than exaggerating his claims as previously thought, was correct in his observations that an advanced civilization was flourishing along the Amazon in the 1540s. It is believed that the civilization was later devastated by the spread of infectious diseases from Europe, such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
, to which the natives had no immunity. Some 5 million people may have lived in the Amazon region in 1500, divided between dense coastal settlements, such as that at Marajó
Marajó () is a large coastal island in the state of Pará, Brazil. It is the main and largest of the islands in the Marajó Archipelago. Marajó Island is separated from the mainland by Marajó Bay, Pará River, smaller rivers (especially M ...
, and inland dwellers. By 1900 the population had fallen to 1 million, and by the early 1980s, it was less than 200,000.
Researchers have found that the fertile ''terra preta
''Terra preta'' (, locally , literally "black soil" in Portuguese) is a type of very dark, fertile anthropogenic soil (anthrosol) found in the Amazon Basin. It is also known as "Amazonian dark earth" or "Indian black earth". In Portuguese its ful ...
'' (black earth) is distributed over large areas in the Amazon forest. It is now widely accepted that these soils are a product of indigenous soil management
Soil management is the application of operations, practices, and treatments to protect soil and enhance its performance (such as soil fertility or soil mechanics). It includes soil conservation, soil amendment, and optimal soil health. In agricu ...
. The development of this soil enabled agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
and silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, and quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and wo ...
to be conducted in the previously hostile environment. Large portions of the Amazon rainforest are therefore probably the result of centuries of human management, rather than naturally occurring as has previously been supposed. In the region of the Xinguanos tribe, remains of some of these large, mid-forest Amazon settlements were found in 2003 by Michael Heckenberger and colleagues of the University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
. Among those remains were evidence of constructed roads, bridges and large plazas.
Andean civilizations
Chavín
The Chavín, a South American preliterate civilization, established a trade network and developed agriculture by 900 BCE, according to some estimates and archeological finds. Artifacts were found at a site called Chavín de Huantar in modernPeru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
at an elevation of 3,177 meters. Chavín civilization spanned 900 to 200 BCE.
Moche
 The Moche thrived on the north coast of Peru between the first and ninth century CE. The heritage of the Moche comes down to us through their elaborate burials, excavated by former UCLA professor
The Moche thrived on the north coast of Peru between the first and ninth century CE. The heritage of the Moche comes down to us through their elaborate burials, excavated by former UCLA professor Christopher B. Donnan Christopher B. Donnan is an archaeologist. He has researched the Moche civilization of ancient Peru for more than fifty years, conducting numerous excavations of Peruvian archaeological sites. Donnan has traveled the world photographing Moche artw ...
in association with the National Geographic Society
The National Geographic Society (NGS), headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest non-profit scientific and educational organizations in the world.
Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, ...
.
Skilled artisans, the Moche were a technologically advanced people who traded with faraway peoples, like the Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
. Knowledge about the Moche has been derived mostly from their ceramic pottery, which is carved with representations of their daily lives. They practiced human sacrifice, had blood-drinking rituals, and their religion incorporated non-procreative sexual practices (such as fellatio).
Inca
Holding their capital at the great puma-shaped city of Cuzco, theInca civilization
The Incas were most notable for establishing the Inca Empire in Pre-Columbian America, which was centered in modern day South America in Peru and Chile. It was about 2,500 miles from the northern to southern tip. The civilization lasted from 1 ...
dominated the Andes region from 1438 to 1533. Known as ''Tawantin suyu'', or "the land of the four regions," in Quechua, the Inca civilization was highly distinct and developed. Inca rule extended to nearly a hundred linguistic or ethnic communities, some 9 to 14 million people connected by a 25,000-kilometre road system. Cities were built with precise, unmatched stonework, constructed over many levels of mountain terrain. Terrace farming
In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore ...
was a useful form of agriculture. There is evidence of excellent metalwork and successful skull surgery in Inca civilization. The Inca had no written language, but used quipu
''Quipu'' (also spelled ''khipu'') are recording devices fashioned from strings historically used by a number of cultures in the region of Andean South America.
A ''quipu'' usually consisted of cotton or camelid fiber strings. The Inca peop ...
, a system of knotted strings, to record information.
Arawak and Carib civilizations
TheArawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greate ...
lived along the eastern coast of South America, from present-day Guayana to as far south as what is now Brazil. Explorer Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
described them at first encounter as a peaceful people, although the Arawak had already dominated other local groups such as the Ciboney. The Arawak had, however, come under increasing military pressure from the Carib, who are believed to have left the Orinoco
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers , with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the wor ...
river area to settle on islands and the coast of the Caribbean Sea. Over the century leading up to Columbus' arrival in the Caribbean archipelago in 1492, the Carib are believed to have displaced many of the Arawak who previously settled the island chains. The Carib also encroached on Arawak territory in what is modern Guyana.
The Carib were skilled boatbuilders and sailors who owed their dominance in the Caribbean basin to their military skills. The Carib war rituals included cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
; they had a practice of taking home the limbs of victims as trophies.
It is not known how many indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
lived in Venezuela and Colombia before the Spanish Conquest; it may have been approximately one million, including groups such as the Auaké, Caquetio, Mariche
Mariche is the name of a former native Venezuelan tribe.
Not much information from them as a tribe has survived to the present day. It is known that their descendants lived in what is now called Filas de Mariches, distrito Sucre, Estado Miranda an ...
, and Timoto-cuicas. The number of people fell dramatically after the Conquest, mainly due to high mortality rates in epidemics of infectious Eurasian diseases introduced by the explorers, who carried them as an endemic disease.Wunder, Sven (2003), Oil Wealth and the Fate of the Forest: A Comparative Study of Eight Tropical Countries
',
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law ...
. p. 130, . There were two main north–south axes of pre-Columbian population; producing maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
in the west and manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
in the east. Large parts of the llanos
The Llanos ( Spanish ''Los Llanos'', "The Plains"; ) is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grassla ...
plains were cultivated through a combination of slash and burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed veget ...
and permanent settled agriculture.
European colonization
Before the arrival of Europeans 20–30 million people lived in South America. Between 1452 and 1493, a series of papal bulls ( Dum Diversas,Romanus Pontifex
(from Latin: "The Roman Pontiff") are papal bulls issued in 1436 by Pope Eugenius IV and in 1455 by Pope Nicholas V praising catholic King Afonso V of Portugal for his battles against the Muslims, endorsing his military expeditions into Weste ...
, and Inter caetera) paved the way for the European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense be ...
and Catholic missions
Missionary work of the Catholic Church has often been undertaken outside the geographically defined parishes and dioceses by religious orders who have people and material resources to spare, and some of which specialized in missions. Eventually, ...
in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
. These authorized the European Christian nations to "take possession" of non-Christian lands and encouraged subduing and converting the non-Christian people of Africa and the Americas.David A. Love, Pope Benedict Argues Catholic Church 'Purified' Indigenous Peoples
'' posted on '' AlterNet'' June 18, 2007 In 1494,
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, the two great maritime powers of that time, signed the Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
in the expectation of new lands being discovered in the west. Through the treaty, they agreed that all the land outside Europe should be an exclusive duopoly
A duopoly (from Greek δύο, ''duo'' "two" and πωλεῖν, ''polein'' "to sell") is a type of oligopoly where two firms have dominant or exclusive control over a market. It is the most commonly studied form of oligopoly due to its simplicit ...
between the two countries. The treaty established an imaginary line along a north–south meridian 370 leagues west of Cape Verde Islands, roughly 46° 37' W. In terms of the treaty, all land to the west of the line (which is now known to include most of the South American soil), would belong to Spain, and all land to the east, to Portugal. Because accurate measurements of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek let ...
were not possible at that time, the line was not strictly enforced, resulting in a Portuguese expansion of Brazil across the meridian.
In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
sailed near the Orinoco Delta and then landed in the Gulf of Paria
The Gulf of Paria ( ; es, Golfo de Paria) is a shallow (180 m at its deepest) semi-enclosed inland sea located between the island of Trinidad (Republic of Trinidad and Tobago) and the east coast of Venezuela. It separates the two countries ...
(Actual Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
). Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in his moving letter to Isabella I and Ferdinand II that he must have reached heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
 Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign
Beginning in 1499, the people and natural resources of South America were repeatedly exploited by foreign conquistadors
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, ...
, first from Spain and later from Portugal. These competing colonial nations claimed the land and resources as their own and divided it into colonies.
European diseases (smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
, measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
and typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. ...
) to which the native populations had no resistance were the overwhelming cause of the depopulation of the Native American population. Cruel systems of forced labor (such as encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
s and mining industry's mita) under Spanish control also contributed to depopulation. Lower bound estimates speak of a decline in the population of around 20–50 percent, whereas high estimates arrive at 90 percent. Following this, enslaved Africans, who had developed immunity to these diseases, were quickly brought in to replace them.
The Spaniards were committed to converting their American subjects to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
and were quick to purge any native cultural practices that hindered this end. However, most initial attempts at this were only partially successful; American groups simply blended Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
with their traditional beliefs. The Spaniards did not impose their language to the degree they did their religion. In fact, the missionary work of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
in Quechua, Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
, and Guarani actually contributed to the expansion of these American languages, equipping them with writing systems.
Eventually, the natives and the Spaniards interbred, forming a Mestizo
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
class. Mestizos and the Native Americans were often forced to pay unfair taxes to the Spanish government (although all subjects paid taxes) and were punished harshly for disobeying their laws. Many native artworks were considered pagan idols and destroyed by Spanish explorers. This included a great number of gold and silver sculptures, which were melted down before transport to Europe.
17th and 18th centuries
In 1616, the Dutch, attracted by the legend ofEl Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king ...
, founded a fort in Guayana and established three colonies:
In 1624 France attempted to settle in the area of modern-day French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label= French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas ...
, but was forced to abandon it in the face of hostility from the Portuguese, who viewed it as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
. However French settlers returned in 1630 and in 1643 managed to establish a settlement at Cayenne
Cayenne (; ; gcr, Kayenn) is the capital city of French Guiana, an overseas region and department of France located in South America. The city stands on a former island at the mouth of the Cayenne River on the Atlantic coast. The city's m ...
along with some small-scale plantations.
Since the sixteenth century, there were some movements of discontent to the Spanish and Portuguese colonial system. Among these movements, the most famous being that of the Maroons
Maroons are descendants of Africans in the Americas who escaped from slavery and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with indigenous peoples, eventually evolving into separate creole cultures such as the Garifuna and the Mascogos. ...
, slaves who escaped their masters and in the shelter of the forest communities organized free communities. Attempts to subject them by the royal army were unsuccessful because the Maroons had learned to master the South American jungles. In a royal decree of 1713, the king gave legality to the first free population of the continent: Palenque de San Basilio in Colombia today, led by Benkos Bioho. Brazil saw the formation of a genuine African kingdom on their soil, with the Quilombo of Palmares.
Between 1721 and 1735, the Revolt of the Comuneros of Paraguay arose, because of clashes between the Paraguayan settlers and the Jesuits, who ran the large and prosperous Jesuit Reductions and controlled a large number of Christianized Natives.
Between 1742 and 1756, was the insurrection of Juan Santos Atahualpa in the central jungle of Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
. In 1780, the Viceroyalty of Peru
The Viceroyalty of Peru ( es, Virreinato del Perú, links=no) was a Spanish imperial provincial administrative district, created in 1542, that originally contained modern-day Peru and most of the Spanish Empire in South America, governed fro ...
was met with the insurrection of curaca Joseph Gabriel Condorcanqui or Tupac Amaru II
Tupac Amaru Shakur ( ; born Lesane Parish Crooks, June 16, 1971 – September 13, 1996), also known as 2Pac and Makaveli, was an American rapper. He is widely considered one of the most influential rappers of all time. Shakur is among the b ...
, which would be continued by Tupac Katari in Upper Peru
Upper Peru (; ) is a name for the land that was governed by the Real Audiencia of Charcas. The name originated in Buenos Aires towards the end of the 18th century after the Audiencia of Charcas was transferred from the Viceroyalty of Peru to t ...
.
In 1763, the African Coffy led a revolt in Guyana which was bloodily suppressed by the Dutch.
In 1781, the Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada)
The Revolt of the Comuneros was a popular uprising in the Viceroyalty of New Granada (now Colombia and parts of Venezuela) against the Spanish authorities from March through October 1781. The revolt was in reaction to the increase in taxation to ...
, an insurrection of the villagers in the Viceroyalty of New Granada
The Viceroyalty of New Granada ( es, Virreinato de Nueva Granada, links=no ) also called Viceroyalty of the New Kingdom of Granada or Viceroyalty of Santafé was the name given on 27 May 1717, to the jurisdiction of the Spanish Empire in norther ...
, was a popular revolution that united indigenous people and mestizos. The villagers tried to be the colonial power and despite the capitulation were signed, the Viceroy Manuel Antonio Flórez did not comply, and instead ran to the main leaders José Antonio Galán.
In 1796, the Dutch colony of Essequibo Essequibo is the largest traditional region of Guyana but not an administrative region of Guyana today. It may also refer to:
* Essequibo River, the largest river in Guyana
* Essequibo (colony), a former Dutch colony in what is now Guyana;
* Esseq ...
was captured by the British during the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Pruss ...
.
During the eighteenth century, the figure of the priest, mathematician and botanist José Celestino Mutis
José Celestino Bruno Mutis y Bosio (6 April 1732 – 11 September 1808) was a Spanish priest, botanist and mathematician. He was a significant figure in the Spanish American Enlightenment, whom Alexander von Humboldt met with on his expedit ...
(1732–1808), was delegated by the Viceroy Antonio Caballero y Gongora to conduct an inventory of the nature of the Nueva Granada, which became known as the Botanical Expedition, which classified plants, wildlife and founded the first astronomical observatory in the city of Santa Fé de Bogotá.
On August 15, 1801, the Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister ...
reached Fontibón where Mutis had begun his expedition to New Granada New Granada may refer to various former national denominations for the present-day country of Colombia.
* New Kingdom of Granada, from 1538 to 1717
*Viceroyalty of New Granada, from 1717 to 1810, re-established from 1816 to 1819
*United Provinces of ...
, Quito. The meeting between the two scholars is considered the brightest spot of the botanical expedition.
Humboldt also visited Venezuela, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Chile, and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
.
Through his observations of temperature differences between the Pacific Ocean between Chile and Peru in different periods of the year, he discovered cold currents moving from south to north up the coast of Peru, which was named the Humboldt Current in his honor.
Between 1806 and 1807, British military forces tried to invade the area of the Rio de la Plata, at the command of Home Riggs Popham and William Carr Beresford
General William Carr Beresford, 1st Viscount Beresford, 1st Marquis of Campo Maior, (; 2 October 1768 – 8 January 1854) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and politician. A general in the British Army and a Marshal in the Portuguese Army, he fought ...
, and John Whitelocke
John Whitelocke (1757 – 23 October 1833) was a British Army officer.
Military career
Educated at Marlborough Grammar School and at Lewis Lochée's military academy in Chelsea, Whitelocke entered the army in 1778 and served in Jamaica and in Sa ...
. The invasions were repelled, but powerfully affected the Spanish authority.
Independence and 19th century
Spanish American wars of independence
The Spanish American wars of independence (25 September 1808 – 29 September 1833; es, Guerras de independencia hispanoamericanas) were numerous wars in Spanish America with the aim of political independence from Spanish rule during the early ...
. Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and B ...
(Greater Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1 ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
), José de San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras (25 February 177817 August 1850), known simply as José de San Martín () or '' the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru'', was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and centr ...
( United Provinces of the River Plate, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
, and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
), and Bernardo O'Higgins
Bernardo O'Higgins Riquelme (; August 20, 1778 – October 24, 1842) was a Chilean independence leader who freed Chile from Spanish rule in the Chilean War of Independence. He was a wealthy landowner of Basque-Spanish and Irish ancestry. Alth ...
(Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
) led their independence struggle. Although Bolivar attempted to keep the Spanish-speaking parts of the continent politically unified, they rapidly became independent of one another.
Unlike the Spanish colonies, the Brazilian independence came as an indirect consequence of the Napoleonic Invasions to Portugal – French invasion under General Junot led to the capture of Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
on 8 December 1807. In order not to lose its sovereignty, the Portuguese Court moved the capital from Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
to Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, which was the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
's capital between 1808 and 1821 and rose the relevance of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
within the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
's framework. Following the Portuguese Liberal Revolution of 1820, and after several battles and skirmishes were fought in Pará and in Bahia, the heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
Pedro, son of King John VI of Portugal
, house = Braganza
, father = Peter III of Portugal
, mother = Maria I of Portugal
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Queluz Palace, Queluz, Portugal
, death_date =
, death_place = Bemposta Palace, Lisbon, Portuga ...
, proclaimed the country's independence in 1822 and became Brazil's first emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( ...
(He later also reigned as Pedro IV of Portugal). This was one of the most peaceful colonial independences ever seen in human history.
 A struggle for power emerged among the new nations, and several further wars were soon fought thereafter.
The first few wars were fought for supremacy in the northern and southern parts of the continent. The Gran Colombia – Peru War of the north and the
A struggle for power emerged among the new nations, and several further wars were soon fought thereafter.
The first few wars were fought for supremacy in the northern and southern parts of the continent. The Gran Colombia – Peru War of the north and the Cisplatine War
The Cisplatine War (), also known as the Argentine-Brazilian War () or, in Argentine and Uruguayan historiography, as the Brazil War (''Guerra del Brasil''), the War against the Empire of Brazil (''Guerra contra el Imperio del Brasil'') or t ...
(between the Empire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom ...
and the United Provinces of the River Plate) ended in stalemate, although the latter resulted in the independence of Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
(1828). A few years later, after the break-up of Gran Colombia in 1831, the balance of power shifted in favor of the newly formed Peru-Bolivian Confederation (1836–1839). Nonetheless, this power structure proved temporary and shifted once more as a result of the Northern Peruvian State's victory over the Southern Peruvian State-Bolivia War of the Confederation (1836–1839), and the Argentine Confederation
The Argentine Confederation (Spanish: ''Confederación Argentina'') was the last predecessor state of modern Argentina; its name is still one of the official names of the country according to the Argentine Constitution, Article 35. It was the name ...
's defeat in the Guerra Grande (1839–1852).
Later conflicts between the South American nations continued to define their borders and power status. In the Pacific coast, Chile and Peru continued to exhibit their increasing domination, defeating Spain in the Chincha Islands War
The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War ( es, Guerra hispano-sudamericana), was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The ...
. Finally, after precariously defeating Peru during the War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific ( es, link=no, Guerra del Pacífico), also known as the Saltpeter War ( es, link=no, Guerra del salitre) and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought ...
(1879–1883), Chile emerged as the dominant power of the Pacific Coast of South America. In the Atlantic side, Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
attempted to gain a more dominant status in the region, but an alliance of Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay (in the resulting 1864–1870 War of the Triple Alliance
The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadlies ...
) ended Paraguayan ambitions. Thereupon, the Southern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
nations of Argentina, Brazil, and Chile entered the 20th century as the major continental powers.
A few countries did not gain independence until the 20th century:
* Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
, from Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
, in 1903
* Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
, from the United Kingdom, in 1962
* Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
, from the United Kingdom, in 1966
* Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the nor ...
, from the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, in 1975
French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label= French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas ...
remains an overseas department of France.
20th century

1900–1920
By the start of the century, the United States continued its interventionist attitude, which aimed to directly defend its interests in the region. This was officially articulated inTheodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
's Big Stick Doctrine, which modified the old Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile act ...
, which had simply aimed to deter European intervention in the hemisphere.
1930–1960
TheGreat Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
posed a challenge to the region. The collapse of the world economy meant that the demand for raw materials drastically declined, undermining many of the economies of South America. Intellectuals and government leaders in South America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialization. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the ups and downs of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration (1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a good neighbor policy and allowed the nationalization of some American companies in South America. The
Intellectuals and government leaders in South America turned their backs on the older economic policies and turned toward import substitution industrialization. The goal was to create self-sufficient economies, which would have their own industrial sectors and large middle classes and which would be immune to the ups and downs of the global economy. Despite the potential threats to United States commercial interests, the Roosevelt administration (1933–1945) understood that the United States could not wholly oppose import substitution. Roosevelt implemented a good neighbor policy and allowed the nationalization of some American companies in South America. The Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
also brought the United States and most Latin American nations together.
The history of South America during World War II is important because of the significant economic, political, and military changes that occurred throughout much of the region as a result of the war. In order to better protect the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
, combat Axis influence, and optimize the production of goods for the war effort, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
through Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (), was a policy under which the United States supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and other Allied nations with food, oil, ...
and similar programs greatly expanded its interests in Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
, resulting in large-scale modernization and a major economic boost for the countries that participated.
Strategically, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
was of great importance because of its having the closest point in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
to Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
where the Allies were actively engaged in fighting the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
. For the Axis, the Southern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
nations of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
were where they found most of their South American support, and they utilised it to the fullest by interfering with internal affairs, conducting espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tang ...
, and distributing propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
.
Brazil was the only country to send an Expeditionary force to the European theatre; however, several countries had skirmishes with German U-Boats and cruisers in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
and South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
. Mexico sent a fighter squadron of 300 volunteers to the Pacific, the ''Escuadrón 201'' were known as the Aztec Eagles (''Aguilas Aztecas'').
The Brazilian active participation on the battle field in Europe was divined after the Casablanca Conference
The Casablanca Conference (codenamed SYMBOL) or Anfa Conference was held at the Anfa Hotel in Casablanca, French Morocco, from January 14 to 24, 1943, to plan the Allied European strategy for the next phase of World War II. In attendance were ...
. The President of the U.S., Franklin D. Roosevelt on his way back from Morocco met the President of Brazil, Getulio Vargas, in Natal, Rio Grande do Norte
Natal ( ) is the capital and largest city of the state of Rio Grande do Norte, located in northeastern Brazil. According to IBGE's 2021 estimate, the city had a total population o896,708 making it the 19th largest city in the country. Natal is ...
, this meeting is known as the Potenji River Conference, and defined the creation of the Brazilian Expeditionary Force
The Brazilian Expeditionary Force ( pt, Força Expedicionária Brasileira, FEB), nicknamed Cobras Fumantes (literally "the Smoking Snakes"), was a military division of the Brazilian Army and Air Force that fought with Allied forces in the ...
.
Economics
According to author Thomas M. Leonard,World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
had a major impact on Latin American economies. Following the December 7, 1941 Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
, most of Latin America either severed relations with the Axis powers or declared war on them. As a result, many nations (including all of Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
) suddenly found that they were now dependent on the United States for trade. The United States' high demand for particular products and commodities during the war further distorted trade. For example, the United States wanted all of the platinum produced in Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
, all the silver of Chile, and all of cotton, gold and copper of Peru. The parties agreed upon set prices, often with a high premium, but the various nations lost their ability to bargain and trade in the open market.
Cold War
Wars became less frequent in the 20th century, with Bolivia-Paraguay and Peru-Ecuador fighting the last inter-state wars. Early in the 20th century, the three wealthiest South American countries engaged in a vastly expensive naval arms race which was catalyzed by the introduction of a new warship type, the "dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
". At one point, the Argentine government was spending a fifth of its entire yearly budget for just two dreadnoughts, a price that did not include later in-service costs, which for the Brazilian dreadnoughts was sixty percent of the initial purchase.
The continent became a battlefield of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
in the late 20th century. Some democratically elected governments of Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Uruguay, and Paraguay were overthrown or displaced by military dictatorships in the 1960s and 1970s. To curtail opposition, their governments detained tens of thousands of political prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although nu ...
s, many of whom were tortured and/or killed on inter-state collaboration. Economically, they began a transition to neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent f ...
economic policies. They placed their own actions within the US Cold War doctrine of "National Security" against internal subversion. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Peru suffered from an internal conflict. South America, like many other continents, became a battlefield for the superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position characterized by its extensive ability to exert influence or project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political and cultural ...
s during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
in the late 20th century. In the postwar period, the expansion of communism became the greatest political issue for both the United States and governments in the region. The start of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
forced governments to choose between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Late 20th century military regimes and revolutions
 By the 1970s, leftists had acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of each individual country's upper class to support coups d'état to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarisation. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorships that were supported by the United States of America.
Also around the 1970s, the regimes of the
By the 1970s, leftists had acquired a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of each individual country's upper class to support coups d'état to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarisation. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorships that were supported by the United States of America.
Also around the 1970s, the regimes of the Southern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
collaborated in Operation Condor killing many leftist dissidents, including some urban guerrillas.
However, by the early 1990s all countries had restored their democracies.
Colombia has had an ongoing, though diminished internal conflict, which started in 1964 with the creation of Marxism, Marxist guerrilla warfare, guerrillas (Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, FARC-EP) and then involved several illegal armed groups of leftist-leaning ideology as well as the private armies of powerful drug lords. Many of these are now defunct, and only a small portion of the ELN remains, along with the stronger, though also greatly reduced FARC. These leftist groups smuggle narcotics out of Colombia to fund their operations, while also using kidnapping, bombings, land mines and assassinations as weapons against both elected and non-elected citizens.

World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, but since the 1980s, a wave of democratisation came through the continent, and democratic rule is widespread now. Nonetheless, allegations of corruption are still very common, and several countries have developed crises which have forced the resignation of their governments, although, in most occasions, regular civilian succession has continued.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the governments of Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Uruguay were overthrown or displaced by U.S.-aligned military dictatorships. These detained tens of thousands of political prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although nu ...
s, many of whom were tortured and/or killed (on inter-state collaboration, see Operation Condor). Economically, they began a transition to neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent f ...
economic policies. They placed their own actions within the U.S. Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
doctrine of
"National Security" against internal subversion. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
suffered from an Internal conflict in Peru, internal conflict (see Túpac Amaru Revolutionary Movement and Shining Path). Revolutionary movements and right-wing military dictatorships have been common, but starting in the 1980s a wave of democratization came through the continent, and democratic rule is now widespread. Allegations of corruption remain common, and several nations have seen crises which have forced the resignation of their presidents, although normal civilian succession has continued. Debt of developing countries, International indebtedness became a recurrent problem, with examples like the Latin American debt crisis, 1980s debt crisis, the mid-1990s Mexican peso crisis and Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
's 1998–2002 Argentine great depression, 2001 default.
Washington Consensus
 The set of specific economic policy prescriptions that were considered the "standard" reform package were promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, DC-based institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and the US Treasury Department during the 1980s and '90s.
The set of specific economic policy prescriptions that were considered the "standard" reform package were promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, DC-based institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and the US Treasury Department during the 1980s and '90s.
21st century
A turn to the left
According to the BBC, a "common element of the 'pink tide' is a clean break with what was known at the outset of the 1990s as the 'Washington consensus', the mixture of open markets and privatisation pushed by the United States". According to Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, a pink tide president herself, Hugo Chávez of Venezuela (inaugurated 1999), Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva of Brazil (inaugurated 2003) and Evo Morales of Bolivia (inaugurated 2006) were "the three musketeers" of the left in South America. By 2005, the BBC reported that out of 350 million people in South America, three out of four of them lived in countries ruled by "left-leaning President (government title), presidents" elected during the preceding six years. Despite the presence of a number of Latin American governments which profess to embrace a leftist ideology, it is difficult to categorize Latin American states "according to dominant political tendencies, like a Red states and blue states, red-blue post-electoral map of the United States." Institute for Policy Studies: Latin America's Pink Tide? According to the Institute for Policy Studies, a Liberalism, liberal non-profit organization, non-profit think-tank based in Washington, D.C.: "a deeper analysis of elections in Ecuador, Venezuela, Nicaragua, and Mexico indicates that the "pink tide" interpretation—that a diluted trend leftward is sweeping the continent—may be insufficient to understand the complexity of what's really taking place in each country and the region as a whole". While this political shift is difficult to quantify, its effects are widely noticed. According to the Institute for Policy Studies, 2006 meetings of the South American Summit of Nations and the Social Forum for the Integration of Peoples demonstrated that certain discussions that "used to take place on the margins of the dominant discourse of neoliberalism, (have) now moved to the centre of Public sphere, public debate."Pink tide
 The term 'pink tide' ( es, link=no, marea rosa, pt, onda rosa) or 'turn to the Left' (Sp.: ''vuelta hacia la izquierda'', Pt.: ''Guinada à Esquerda'') are phrases which are used in contemporary 21st century Political science, political analysis in the media and elsewhere to describe the perception that leftism, leftist ideology in general, and left-wing politics in particular, were increasingly becoming influential in Latin America.
Since the 2000s or 1990s in some countries, left-wing political parties have risen to power. Hugo Chávez in Venezuela, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff in Brazil, Fernando Lugo in Paraguay, Néstor Kirchner, Néstor and Cristina Fernández de Kirchner in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez and José Mujica in Uruguay, the Ricardo Lagos, Lagos and Michelle Bachelet, Bachelet governments in Chile, Evo Morales in Bolivia, and Rafael Correa of Ecuador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who also often declare themselves socialists, Latin Americanists or Anti-imperialism, anti-imperialists.
The term 'pink tide' ( es, link=no, marea rosa, pt, onda rosa) or 'turn to the Left' (Sp.: ''vuelta hacia la izquierda'', Pt.: ''Guinada à Esquerda'') are phrases which are used in contemporary 21st century Political science, political analysis in the media and elsewhere to describe the perception that leftism, leftist ideology in general, and left-wing politics in particular, were increasingly becoming influential in Latin America.
Since the 2000s or 1990s in some countries, left-wing political parties have risen to power. Hugo Chávez in Venezuela, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff in Brazil, Fernando Lugo in Paraguay, Néstor Kirchner, Néstor and Cristina Fernández de Kirchner in Argentina, Tabaré Vázquez and José Mujica in Uruguay, the Ricardo Lagos, Lagos and Michelle Bachelet, Bachelet governments in Chile, Evo Morales in Bolivia, and Rafael Correa of Ecuador are all part of this wave of left-wing politicians who also often declare themselves socialists, Latin Americanists or Anti-imperialism, anti-imperialists.
 ;The list of leftist South American presidents is, by date of election, the following:
* 1998: Hugo Chávez, Venezuela
* 1999: Ricardo Lagos, Chile
* 2002: Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, Luís Inácio Lula da Silva, Brazil
* 2002: Lucio Gutiérrez, Ecuador
* 2003: Néstor Kirchner, Argentina
* 2004: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay
* 2005: Evo Morales, Bolivia
* 2006: Michelle Bachelet, Chile
* 2006: Rafael Correa, Ecuador
;The list of leftist South American presidents is, by date of election, the following:
* 1998: Hugo Chávez, Venezuela
* 1999: Ricardo Lagos, Chile
* 2002: Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, Luís Inácio Lula da Silva, Brazil
* 2002: Lucio Gutiérrez, Ecuador
* 2003: Néstor Kirchner, Argentina
* 2004: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay
* 2005: Evo Morales, Bolivia
* 2006: Michelle Bachelet, Chile
* 2006: Rafael Correa, Ecuador"Avenger against oligarchy" wins in Ecuador
' The Real News, 27 April 2009. * 2007: Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, Argentina * 2008: Fernando Lugo, Paraguay * 2010: José Mujica, Uruguay * 2010: Dilma Rousseff, BrazilEFE
"Dilma, 1ª mulher presidente e única economista em 121 anos de República"
BOL. 31 October 2010.Bennett, Alle
"Dilma Rousseff biography"
, Agência Brasil, 9 August 2010 * 2011: Ollanta Humala, Peru''The Guardian'', April 11, 2011
Peru elections: Fujimori and Humala set for runoff vote
/ref>''Hoy (Peruvian newspaper), Diario Hoy'', October 31, 2000
PERU, CORONELAZO NO CUAJA
/ref> BBC, January 4, 2005
Perú: insurgentes se rinden
/ref> * 2013: Nicolás Maduro, Venezuela"Nicolas Maduro sworn in as new Venezuelan president"
BBC News. 19 April 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2013 * 2014: Michelle Bachelet, Chile * 2015: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay * 2017: Lenín Moreno, Ecuador * 2019: Alberto Fernández, Argentina * 2020: Luis Arce, Bolivia * 2021: Pedro Castillo, Peru * 2022: Gabriel Boric, Gabriel Boric Font, Chile * 2022: Gustavo Petro, Colombia
Politics
During the first decade of the 21st century, South American governments move to the political left, with leftist leaders being elected in Chile, Uruguay, Brazil, Argentina, Ecuador, Bolivia, Paraguay, Peru, and Venezuela. Most South American countries are making an increasing use of protectionist policies, undermining a greater global integration but helping local development. In 2008, the Union of South American Nations (USAN) was founded, which aimed to merge the two existing customs unions, Mercosur and the Andean Community, thus forming the third-largest trade bloc in the world. The organization is planning for political integration in the European Union style, seeking to establish free movement of people, economic development, a common defense policy and the elimination of tariffs. According to Noam Chomsky, USAN represents that "for the first time since the European conquest, Latin America began to move towards integration".Most recent heads of state in South America
* 2010: Dilma Rousseff, Brazil * 2010: José Mujica, Uruguay * 2010: Sebastián Piñera, Chile * 2010: Juan Manuel Santos * 2011: Ollanta Humala, Peru * 2013: Nicolás Maduro, Venezuela * 2013: Horacio Cartes, Horacio Cartés, Paraguay * 2014: Michelle Bachelet, Chile * 2015: Mauricio Macri, Argentina * 2015: Tabaré Vázquez, Uruguay * 2015: David A. Granger, David Granger, Guyana * 2016: Michel Temer, Brazil * 2016: Pedro Pablo Kuczynski, Pedro Pablo Kuczynski Godard, Peru * 2017: Lenín Moreno, Ecuador * 2018: Sebastián Piñera, Chile * 2018: Iván Duque Márquez, Colombia * 2018: Martín Vizcarra, Peru * 2018: Mario Abdo Benítez, Mario Abdo, Paraguay * 2019: Jair Bolsonaro, Brazil * 2019: Alberto Fernández, Argentina * 2020: Luis Lacalle Pou, Luis Lacalle, Uruguay * 2020: Luis Arce, Bolivia * 2020: Manuel Merino, Manuel Merino de Lama, Peru * 2020: Chan Santokhi, Chandrikapersad "Chan" Santokhi, Suriname * 2020: Irfaan Ali, Guyana * 2020: Francisco Sagasti, Peru * 2021: Guillermo Lasso, Ecuador * 2021: Pedro Castillo, Peru * 2022: Gabriel Boric, Gabriel Boric Font, Chile * 2022: Gustavo Petro, Colombia * 2022: Dina Boluarte, PeruSee also
* Inca Empire * Gran Colombia * History of Latin America * Military history of South America * Peru–Bolivian Confederation *Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and B ...
* José de San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras (25 February 177817 August 1850), known simply as José de San Martín () or '' the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru'', was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and centr ...
* Francisco Pizarro
Notes
References
Historiography
* ''Deforestation.'' ''World Geography.'' Columbus, Ohio: McGraw-Hill/Glencoe, 2000. 202–204 * * * Hensel, Silke. "Was There an Age of Revolution in Latin America?: New Literature on Latin American Independence." ''Latin American Research Review'' (2003) 38#3 pp. 237–249online
* * * * * Uribe, Victor M. "The Enigma of Latin American Independence: Analyses of the Last Ten Years," ''Latin American Research Review'' (1997) 32#1 pp. 236–25
in JSTOR
* Wade, Lizzie. (2015).
Drones and satellites spot lost civilizations in unlikely places
" ''American Association for the Advancement of Science, Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science),'' *
Bibliography
Prehistory
*Muisca
* * * * * * *Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of South America History of South America,