History of Sindh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of Sindh refers to the history of the modern-day
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
i province of Sindh, as well as neighboring regions that periodically came under its sway.
Sindh was the site of one of the Cradle of civilizations, the bronze age Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
that flourished from about 3000 B.C. and declined rapidly 1,000 years later, following the Indo-Aryan migrations
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lank ...
that overran the region in waves between 1500 and 500 B.C. The migrating Indo-Aryan tribes gave rise to the Iron age vedic civilization, which lasted till 500 BC. During this era, the Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute th ...
were composed. In 518 BC, the Achaemenid empire conquered Indus valley and established Hindush
Hindush (Old Persian cuneiform: 𐏃𐎡𐎯𐎢𐏁, , transcribed as since the nasal "n" before consonants was omitted in the Old Persian script, and simplified as ) was a province of the Achaemenid Empire in lower Indus Valley established a ...
satrapy in Sindh. Following Alexander the Great's invasion, Sindh became part of the Mauryan Empire. After its decline, Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
, Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
and Indo-Parthians
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the India ...
ruled in Sindh.
Sindh is sometimes referred to as the ''Bab-ul Islam'' (), as it was one of the first regions of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
to fall under Islamic rule. Parts of the modern-day province were intermittently subject to raids by the Rashidun army
The Rashidun army () was the core of the Rashidun Caliphate's armed forces during the early Muslim conquests in the 7th century. The army is reported to have maintained a high level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization, granti ...
during the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, but the region did not fall under Muslim rule until the Arab invasion of Sind occurred under the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
, headed by Muhammad ibn Qasim
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqāfī ( ar, محمد بن القاسم الثقفي; –) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (part of modern Pakistan), inaugurating the Umayy ...
in 712 CE. Afterwards, Sindh was ruled by a series of dynasties including Habbaris, Soomras, Sammas, Arghuns and Tarkhans. The Mughal empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
conquered Sindh in 1591 and organized it as ''Subah of Thatta'', the first-level imperial division. Sindh again became independent under Kalhora dynasty
The Kalhora dynasty ( sd, ڪلهوڙا راڄ, translit=Kalhora Raj) was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Sindhi Kalhora origin based in the region of Sindh in what is now Pakistan. They claimed an Arab origin. The dynasty ruled Sindh and parts of the P ...
. The British conquered Sindh in 1843 AD after Battle of Hyderabad
The Battle of Hyderabad (), sometimes called as the Battle of Dubbo was one of the major campaigns of the British against then Sindh led by the Talpurs which was fought on 24 March 1843 between the forces of the British East India Company and the ...
from the Talpur dynasty
The Talpur dynasty ( sd, ٽالپردور) were rulers based in Sindh. Four branches of the dynasty were established following the defeat of the Kalhora dynasty at the Battle of Halani in 1783: one ruled lower Sindh from the city of Hyderabad, ...
. Sindh became separate province in 1936, and after independence became part of Pakistan.
Sindh is home to two UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
-designated World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
: the Makli Necropolis
Makli Necropolis ( ur, ; sd, مڪلي جو مقام) is one of the largest funerary sites in the world, spread over an area of 10 kilometres near the city of Thatta, in the Pakistani province of Sindh. The site houses approximately 500,000 ...
and Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro (; sd, موئن جو دڙو'', ''meaning 'Mound of the Dead Men';Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
who conquered Sindh in 325 BC under the command of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
referred to the Indus River as '' Indós'', hence the modern ''Indus''. The ancient Iranians referred to everything east of the river Indus as ''hind''. The word ''Sindh'' is a Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
derivative of the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
term ''Sindhu,'' meaning "river" - a reference to Indus River. Southworth suggests that the name ''Sindhu'' is in turn derived from ''Cintu'', a Dravidian word for date palm, a tree commonly found in Sindh.
The previous spelling "Sind" (from the Perso-Arabic ) was discontinued in 1988 by an amendment passed in Sindh Assembly
The Provincial Assembly of Sindh ( ur, ) is a unicameral legislature of elected representatives of the Pakistani provinces, Pakistani province of Sindh, and is located in Karachi, the provincial capital. It was established under Article 106 of ...
, and is now spelt "Sindh."
Bronze age
Indus Valley Civilization (3300–1300 BC)
Sindh and surrounding areas contain the ruins of the Indus Valley Civilization. There are remnants of thousand-year-old cities and structures, with a notable example in Sindh being that of Mohenjo Daro. Built around 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus civilisation or Harappan culture, with features such as standardized bricks, street grids, and covered sewerage systems. It was one of the world's earliest majorcities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, contemporaneous with the civilizations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, Minoan Crete
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
, and Caral-Supe. Mohenjo-daro was abandoned in the 19th century BCE as the Indus Valley Civilization declined, and the site was not rediscovered until the 1920s. Significant excavation has since been conducted at the site of the city, which was designated a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1980. The site is currently threatened by erosion and improper restoration.
The cities of the ancient Indus were noted for their urban planning
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, ...
, baked brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured con ...
houses, elaborate drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess of water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic condition ...
systems, water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
systems, clusters of large non-residential buildings, and techniques of handicraft and metallurgy. Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro (; sd, موئن جو دڙو'', ''meaning 'Mound of the Dead Men';Harappa very likely grew to contain between 30,000 and 60,000 individuals, and the civilisation may have contained between one and five million individuals during its florescence. A gradual drying of the region during the 3rd millennium BCE may have been the initial stimulus for its urbanisation. Eventually it also reduced the water supply enough to cause the civilisation's demise and to disperse its population to the east.

 Alexander conquered parts of Sindh after Punjab for few years and appointed his general
Alexander conquered parts of Sindh after Punjab for few years and appointed his general
D'Anville, ''Orbis Veteribus Notus''
/ref>Alexander Burnes, ''Travels into Bokhara: Containing the Narrative of a Voyage on the Indus,'' London, Murray, 1839, Vol.I, p.27. William Robertson, ''An Historical Disquisition concerning Ancient India,'' Basel, Tourneisen, 1792, pp.20: “Patala (the modern Tatta)”; p.40: “Pattala (now Tatta).” William Vincent, ''The Commerce and Navigation of the Ancients in the Indian Ocean,'' London, Cadell and Davies, 1807, p.138. “Tatta, the Páttala of the ancients.” Cf. M. Nisard, ''Pomponius Méla, oeuvres complètes,'' Paris, Dubochet et Le Chevalier, 1850, p.656: "Cette région atalène qui tirait son nom de Patala, sa principale ville, est comprise aujourd'hui dans ce qu'on appelle le Sindh y, qui avait autrefois pour capitale Tatta, ville de douze à quinze mille âmes, qui occupe l'emplacement de l'antique Patala". But the identity of Patala is much debated among scholars.
 The Indo Scythians ruled Sindh with its capital at
The Indo Scythians ruled Sindh with its capital at
 Sindh came under the
Sindh came under the
Victoria & Albert Museum, UK Early estimates placed the site in the 4th to 5th-century. The stupa is now dated between the 5th to early 6th-century, because its artwork is more complex and resembles those found in the dated sites such as the Ajanta and Bhitargaon in India. The
 The
The
 The
The
 After the death of the Islamic prophet
After the death of the Islamic prophet
p. 456
/ref> 60,000 slaves, including 30 young royal women, were sent to al-Hajjaj. During the capture of one of the forts of Sindh, the women committed the
 The third dynasty,
The third dynasty,
/ref> Jam Unar was the founder of Samma dynasty mentioned by Ibn Battuta.Directions in the History and Archaeology of Sindh by M. H. Panhwar
/ref> The Samma civilization contributed significantly to the evolution of the Indo-Islamic architectural style. Thatta is famous for its necropolis, which covers 10 square km on the
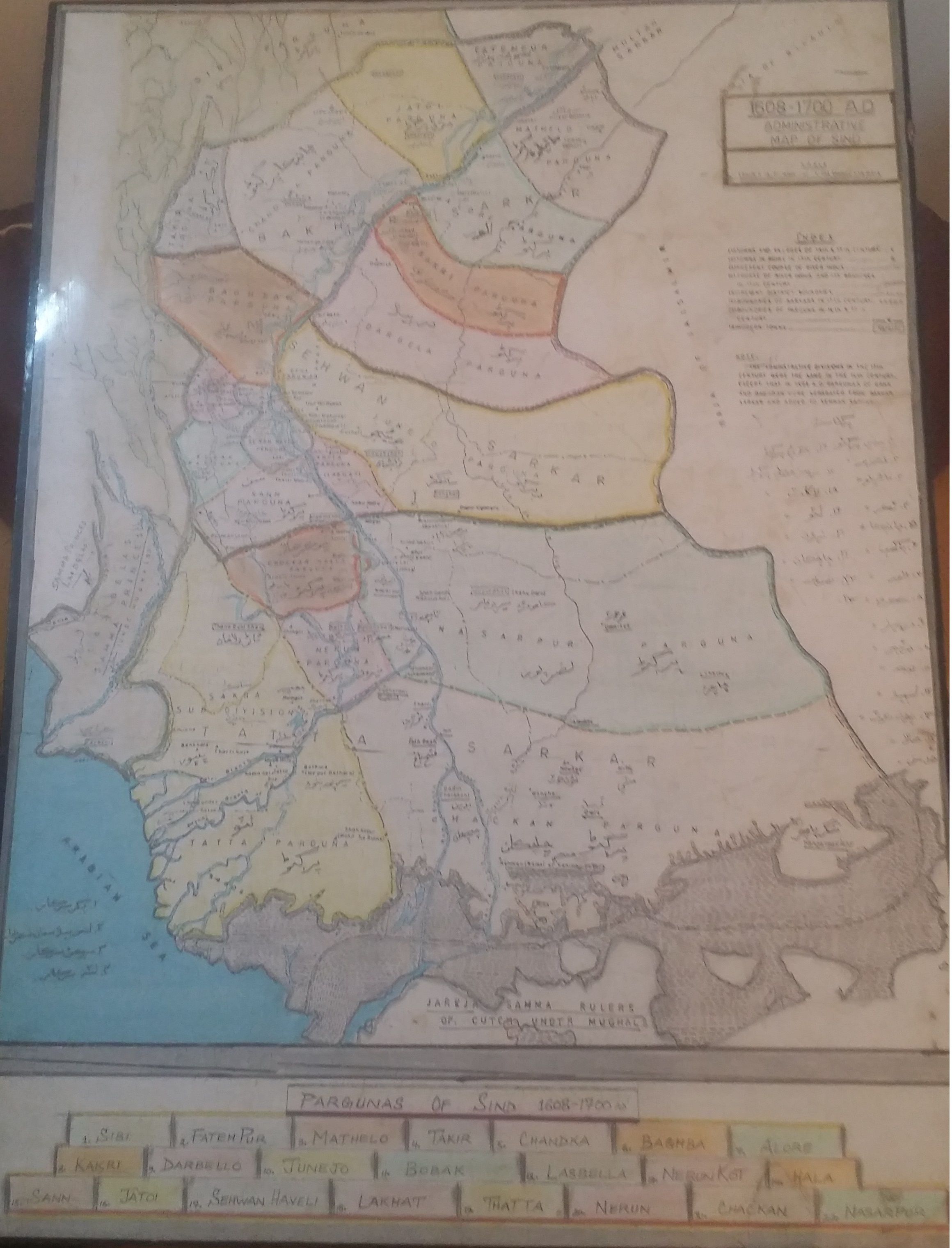 Dynasties came and went for several hundred years until the late 16th century, when Sindh was brought into the
Dynasties came and went for several hundred years until the late 16th century, when Sindh was brought into the
 The Talpurs were ethnically Baloch. They ruled from 1783, until 1843, when they were in turn defeated by the British at the
The Talpurs were ethnically Baloch. They ruled from 1783, until 1843, when they were in turn defeated by the British at the

Iron age (c. 1300 – c. 516 BC)
Sindhu-Sauvera kingdoms

Sindhu-Sauvīra
Sindhu-Sauvīra (Sanskrit: ; Pāli: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan kingdom in the western region of the subcontinent whose existence is attested during the Iron Age in India. The inhabitants of Sindhu were called the Saindhavas, and the inhabita ...
(Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
: ; Pāli
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or '' Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravāda'' Buddhi ...
: ) was an ancient Indo-Aryan kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
of western South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
whose existence is attested during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
. The inhabitants of Sindu were called the Saindhavas, and the inhabitants of Sauvīra were called Sauvīrakas.
The territory of Sindhu-Sauvīra covered the lower Indus Valley, with its southern border being the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
and its northern border being the Pañjāb around Multān.
Sindhu was the name of the inland area between the Indus River and the Sulaiman Mountains
The Sulaiman Mountains, also known as Kōh-e Sulaymān ( Balochi/Urdu/ fa, ; "Mountains of Solomon") or Da Kasē Ghrūna ( ps, د كسې غرونه; "Mountains of Kasi"), are a north–south extension of the southern Hindu Kush mountain system i ...
, while Sauvīra was the name for the coastal part of the kingdom as well as the inland area to the east of the Indus river as far north as the area of modern-day Multan.
The capital of Sindhu-Sauvīra was named Roruka and Vītabhaya or Vītībhaya, and corresponds to the mediaeval Arohṛ and the modern-day Rohṛī.
Ancient history
Achaemenid Era (516–326 BC)
Achaemenid empire may have controlled parts of present-day Sindh as part of the province ofHindush
Hindush (Old Persian cuneiform: 𐏃𐎡𐎯𐎢𐏁, , transcribed as since the nasal "n" before consonants was omitted in the Old Persian script, and simplified as ) was a province of the Achaemenid Empire in lower Indus Valley established a ...
. The territory may have corresponded to the area covering the lower and central Indus basin (present day Sindh and the southern Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
regions of Pakistan). To the north of Hindush was Gandāra
Gandāra, or Gadāra in Achaemenid inscriptions (Old Persian cuneiform: 𐎥𐎭𐎠𐎼, , also transliterated as since the nasal "n" before consonants was omitted in the Old Persian script, and simplified as or sometimes )Some sounds are o ...
(spelt as ''Gandāra'' by the Achaememids). These areas remained under Persian control until the invasion by Alexander.
Alternatively, some authors consider that ''Hindush'' may have been located in the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
area.
Hellenistic era (326–317 BC)
 Alexander conquered parts of Sindh after Punjab for few years and appointed his general
Alexander conquered parts of Sindh after Punjab for few years and appointed his general Peithon
Peithon or Pithon (Greek: ''Πείθων'' or ''Πίθων'', 355 – 314 BC) was the son of Crateuas, a nobleman from Eordaia in western Macedonia. He was famous for being one of the bodyguards of Alexander the Great, becoming the later ...
as governor. The ancient city of Patala was located at the mouth of the Indus River. The Indus parted into two branches at the city of Patala before reaching the sea, and the island thus formed was called Patalene, the district of Patala. Alexander constructed a harbour at Patala.
Some scholars identify Patala with Thatta
Thatta ( sd, ٺٽو; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh. Thatta was the medieval capital of Sindh, and served as the seat of power for three successive dynasties. Thatta's historic significance has yielded several monuments in and ...
, a one-time capital of Sindh.Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville, ''A Geographical Illustration of the Map of India,'' Translated by William Herbert, London, 1759, p.19; "Tatta est non seulement un ville, mais encore une province de l'Inde, selon les voyageurs modernes. La ville ainsi nommée a pris la place de l'ancienne Patala ou Pattala, qui donnoit autrefois le nom à terrain renfermé entre les bouches de l’Indus." Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville, ''Eclaircissements géographiques sur la carte de l'Inde,'' Paris, Imprimerie Royale, 1753, p.39D'Anville, ''Orbis Veteribus Notus''
/ref>Alexander Burnes, ''Travels into Bokhara: Containing the Narrative of a Voyage on the Indus,'' London, Murray, 1839, Vol.I, p.27. William Robertson, ''An Historical Disquisition concerning Ancient India,'' Basel, Tourneisen, 1792, pp.20: “Patala (the modern Tatta)”; p.40: “Pattala (now Tatta).” William Vincent, ''The Commerce and Navigation of the Ancients in the Indian Ocean,'' London, Cadell and Davies, 1807, p.138. “Tatta, the Páttala of the ancients.” Cf. M. Nisard, ''Pomponius Méla, oeuvres complètes,'' Paris, Dubochet et Le Chevalier, 1850, p.656: "Cette région atalène qui tirait son nom de Patala, sa principale ville, est comprise aujourd'hui dans ce qu'on appelle le Sindh y, qui avait autrefois pour capitale Tatta, ville de douze à quinze mille âmes, qui occupe l'emplacement de l'antique Patala". But the identity of Patala is much debated among scholars.
Siltation
Siltation, is water pollution caused by particulate Terrestrial ecoregion, terrestrial Clastic rock, clastic material, with a particle size dominated by silt or clay. It refers both to the increased concentration of suspended sediments and to the ...
has caused the Indus to change its course many times since the days of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, and the site of ancient Patala has been subject to much conjecture.
Mauryan Era (316–180 BC)
Chandragupta Maurya had established his empire around 320 BC. The early life of Chandragupta Maurya is not clear. Janapadas of Punjab and Sindh, he had gone on to conquer much of the North West. He then defeated the Nanda rulers in Pataliputra to capture the throne. Chandragupta Maurya fought Alexander's successor in the east,Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
, when the latter invaded. In a peace treaty, Seleucus ceded all territories west of the Indus River and offered a marriage, including a portion of Bactria, while Chandragupta granted Seleucus 500 elephants.
Indo-Greek era (180–90 BC)
Following a century of Mauryan rule which ended by 180 BC, the region came under the Greco-Bactrians based in what is todayAfghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and these rulers would also convert to and proliferate Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
in the region. The Buddhist city of Siraj-ji-Takri is located along the western limestone terraces of the Rohri Hills in the Sukkur
Sukkur (; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh along the western bank of the Indus River, directly across from the historic city of Rohri. Sukkur is the third largest city in Sindh after Karachi and Hyderabad, and 14th largest city ...
district of Upper Sindh, along the road that leads to Sorah. Its ruins are still visible on the top of three different mesas, in the form of stone and mud-brick walls and small mounds, whilst other architectural remains were observed along the slopes of the hills in the 1980s.
Indo Scythians (90–20 BC)
 The Indo Scythians ruled Sindh with its capital at
The Indo Scythians ruled Sindh with its capital at Minnagara
Minnagara ( grc, Μινναγάρ and Μιννάγαρα) was a city of the Indo-Scythian kingdom, located on the Indus river in modern Pakistan, north of the coastal city of Barbaricum, or along the Narmada river, upstream of Barygaza. There wer ...
. It was located on the Indus river, north of the coastal city of Barbaricum, or along the Narmada river, upstream of Barygaza. There were two cities named Minnagara, one on Indus River delta near Karachi and the other at Narmada River delta near modern Bharuch. The Ptolemy world map
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
, as well as the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and ...
mention prominently, the country of Scythia on the Indus Valley, as well as Roman Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
. The Periplus states that Minnagara
Minnagara ( grc, Μινναγάρ and Μιννάγαρα) was a city of the Indo-Scythian kingdom, located on the Indus river in modern Pakistan, north of the coastal city of Barbaricum, or along the Narmada river, upstream of Barygaza. There wer ...
was the capital of Scythia, and that Parthian Princes from within it were fighting for its control during the 1st century CE.
Gupta Empire
 Sindh came under the
Sindh came under the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
, which reached its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, covering much of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
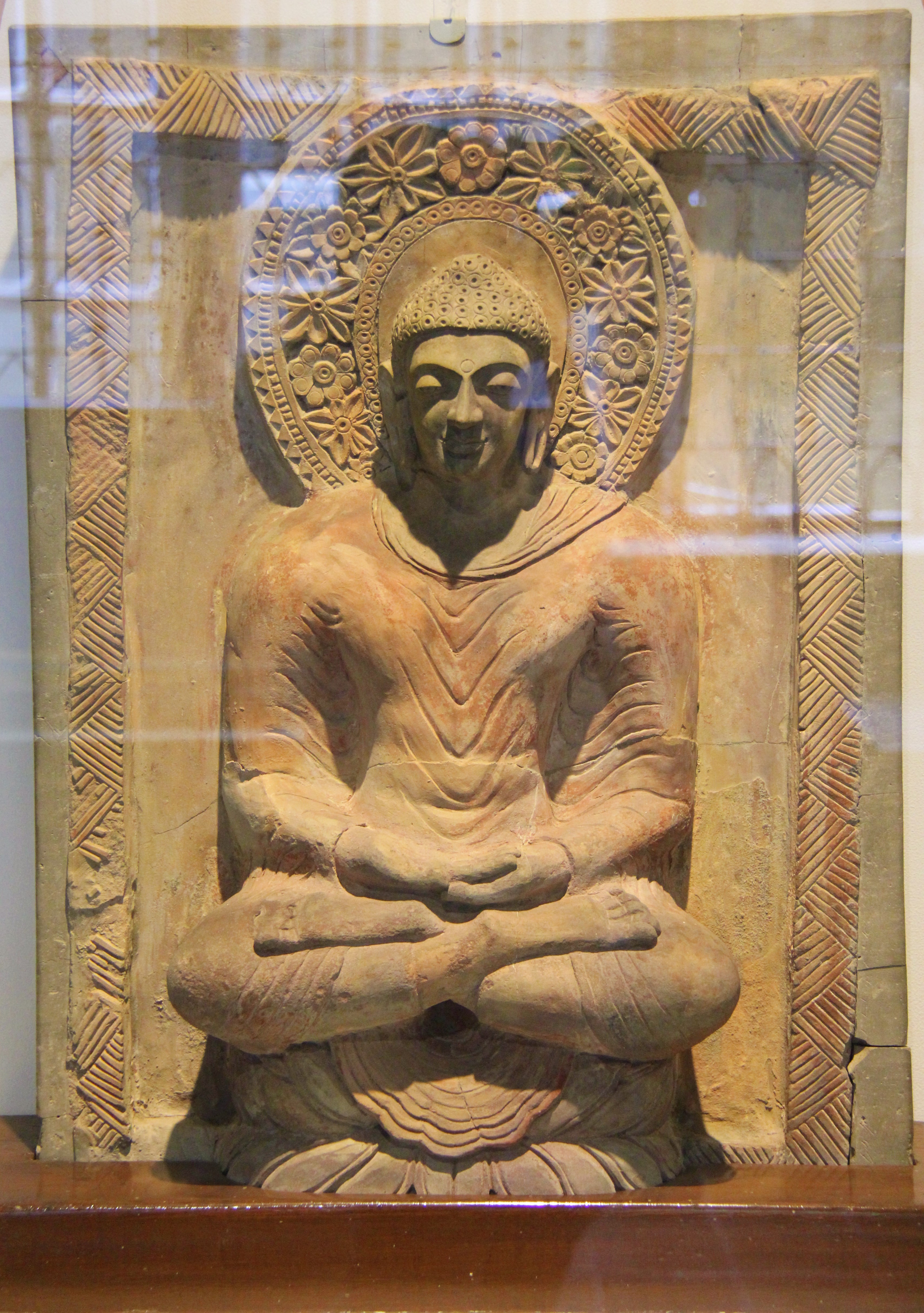
. The Kahu-Jo-Darro stupa is an ancient Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
stupa found at the Mirpurkhas
Mirpur Khas (Sindhi and ; ''meaning "Town of the most-high Mirs"'') is the capital city of the Mirpur Khas District and Mirpur Khas Division in the Sindh province, Pakistan. Mirpur Khas is the 16th largest city in Sindh province and the 80th ...
archaeological site.Relief Panel: 5th century - 6th Century from Mirpur Khas PakistanVictoria & Albert Museum, UK Early estimates placed the site in the 4th to 5th-century. The stupa is now dated between the 5th to early 6th-century, because its artwork is more complex and resembles those found in the dated sites such as the Ajanta and Bhitargaon in India. The
Prince of Wales Museum
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya, (CSMVS) originally named Prince of Wales Museum of Western India, is a museum in Mumbai (Bombay) which documents the history of India from prehistoric to modern times.
It was founded during Briti ...
describes the style of Mirpur Khas stupa as a conflation of the Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara, and Gupta art
Gupta art is the art of the Gupta Empire, which ruled most of northern India, with its peak between about 300 and 480 CE, surviving in much reduced form until c. 550. The Gupta period is generally regarded as a classic peak and golden age of North ...
:
Sassanian Empire (325–480 AD)
Sasanian rulers from the reign ofShapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩, Šābuhr ) was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardas ...
claimed control of the Sindh area in their inscriptions. Shapur I installed his son Narseh
Narseh (also spelled Narses or Narseus; pal, 𐭭𐭥𐭮𐭧𐭩, New Persian: , ''Narsē'') was the seventh Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 293 to 303.
The youngest son of Shapur I (), Narseh served as the governor of Sakastan, Hind and ...
as "King of the Sakas" in the areas of Eastern Iran as far as Sindh. Two inscriptions during the reign of Shapur II mention his control of the regions of Sindh, Sakastan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan ( ...
and Turan
Turan ( ae, Tūiriiānəm, pal, Tūrān; fa, توران, Turân, , "The Land of Tur") is a historical region in Central Asia. The term is of Iranian origin and may refer to a particular prehistoric human settlement, a historic geographical re ...
. Still, the exact term used by the Sasanian rulers in their inscription is ''Hndy'', similar to ''Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used by ...
'', which cannot be said for sure to mean "Sindh". Al-Tabari mentioned that Shapur II built cities in Sind and Sijistan.
Rai Dynasty (c. 489 – 632 AD)
 The
The Rai dynasty
The Rai dynasty (c. 489–632 CE) was a polity of ancient Sindh.
Scholarship
Pre-Islamic Sindh has been the subject of voluminous scholarship concerning the eve of Arab conquests; otherwise, the paucity of source materials remains a severe hi ...
of Sindh was the first dynasty of Sindh and at its height of power ruled much of the Northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent. The dynasty reigned for a period of 144 years c. 489 - 632 A.D, concurrent with the Huna invasions of North India. The names of rulers might have been corruptions of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
names — Devaditya, Harsha, and SInhasena. The origins of the dynasty, caste status, and how they rose to power remains unknown. They apparently had familial ties with other rulers of South Asia including Kashmir, Kabul, Rajasthan, Gujarat etc. — Aror
Aror ( Sindhi: اروهڙ) or Alor or Arorkot (Sindhi: اروهڙ ڪوٽ) is the medieval name of the city of Rohri (in Sindh, modern Pakistan). Aror once served as the capital of Sindh.
History
As Roruka, capital of the Sauvira Kingdom, i ...
is noted to be the capital of both Hind and Sindh. Alexander Cunningham had proposed an alternate chronology (? - >641 A.D.) — primarily on the basis of numismatic and literary evidence — identifying the first two Rais as Hunas and the later three as rulers of Zabulistan
Zabulistan ( fa, زابلستان ''Zābulistān''/''Zābolistān''/''Zāwulistān'' or simply ''Zābul'', ps, زابل ''Zābəl''), was a historical region in southern Afghanistan roughly corresponding to the modern provinces of Zabul and ...
and Khorasan. However, there exists little historical evidence to favor the proposition of Hunas ever making to Sindh and the individual bases of his hypothesis stands discredited in modern scholarship. Chintaman Vinayak Vaidya supported Cunningham's chronology (? - >641 A.D.) but held the Rais to be descendants of Mauryas
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
and Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
, by caste.
Harsha Empire
Harshacharitta, a biography written by Banabhatta mentions King Harsha badly defeated the ruler of Sindh and took possession of his fortunes.Brahmin dynasty (c. 632 – c. 724 AD)
 The
The Brahmin dynasty of Sindh
The Brahmin dynasty of Sindh (), also known as the Chacha dynasty, were the Brahmin Hindu ruling family of the Chacha Empire. The Brahmin dynasty were successors of the Rai dynasty. The dynasty ruled on the Indian subcontinent which originate ...
(), also known as the Chacha dynasty, were the Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (gur ...
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
ruling family of the Chacha Empire. The Brahmin dynasty were successors of the Rai dynasty
The Rai dynasty (c. 489–632 CE) was a polity of ancient Sindh.
Scholarship
Pre-Islamic Sindh has been the subject of voluminous scholarship concerning the eve of Arab conquests; otherwise, the paucity of source materials remains a severe hi ...
. The dynasty ruled on the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
which originated in the region of Sindh, present-day Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
. Most of the information about its existence comes from the ''Chach Nama
''Chach Nama'' ( sd, چچ نامو; ur, چچ نامہ; "Story of the Chach"), also known as the ''Fateh nama Sindh'' ( sd, فتح نامه سنڌ; "Story of the conquest of Sindh"), and as ''Tareekh al-Hind wa a's-Sind'' ( ar, تاريخ اله� ...
'', a historical account of the Chach-Brahmin dynasty.
After the Chacha Empire's fall in 712, though the empire had ended, its dynasty's members administered parts of Sindh under the Umayyad Caliphate's Caliphal province of Sind
Sind () was an administrative division of the Umayyad Caliphate and later of the Abbasid Caliphate in post-classical India, from around 711 CE with the conquest of Sind by the Arab military commander Muhammad ibn Qasim, to around 854 CE with ...
. These rulers include Hullishāh and Shishah.
Medieval era
Arab Sindh (711–854 AD)
 After the death of the Islamic prophet
After the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
, the Arab expansion towards the east reached the Sindh region beyond Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. An initial expedition in the region launched because of the Sindhi pirate attacks on Arabs in 711–12, failed.
The first clash with the Hindu kings of Sindh took place in 636 (15 A.H.) under Caliph Umar ibn al-Khattab
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
with the governor of Bahrain, Uthman ibn Abu-al-Aas, dispatching naval expeditions against Thane
Thane (; also known as Thana, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city in Maharashtra, India. It is situated in the north-eastern portion of the Salsette Island. Thane city is entirely within Thane taluka, one of the seven taluk ...
and Bharuch under the command of his brother, Hakam. Another brother of his, al-Mughira, was given the command of the expedition against Debal
Debal (Urdu, Arabic, sd, ) was an ancient port located near modern Karachi, Pakistan. It is adjacent to the nearby Manora Island and was administered by Mansura, and later Thatta.
Etymology
In Arabic history books, most notably in the early ...
. Al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī ( ar, أحمد بن يحيى بن جابر البلاذري) was a 9th-century Muslim historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and e ...
states they were victorious at Debal but doesn't mention the results of other two raids. However, the ''Chach Nama
''Chach Nama'' ( sd, چچ نامو; ur, چچ نامہ; "Story of the Chach"), also known as the ''Fateh nama Sindh'' ( sd, فتح نامه سنڌ; "Story of the conquest of Sindh"), and as ''Tareekh al-Hind wa a's-Sind'' ( ar, تاريخ اله� ...
'' states that the raid of Debal was defeated and its governor killed the leader of the raids.
These raids were thought to be triggered by a later pirate attack on Umayyad ships. Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prop ...
was warned by Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
against it who said "O brother of Thaqif, you have put the worm on the wood. I swear, by Allah that if they had been smitten, I would have taken the equivalent (in men) from your families." Baladhuri adds that this stopped any more incursions until the reign of Uthman.
In 712, when Mohammed Bin Qasim invaded Sindh with 8000 cavalry while also receiving reinforcements, Al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf instructed him not to spare anyone in Debal. The historian al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī ( ar, أحمد بن يحيى بن جابر البلاذري) was a 9th-century Muslim historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and e ...
stated that after conquest of Debal, Qasim kept slaughtering its inhabitants for three days. The custodians of the Buddhist stupa were killed and the temple was destroyed. Qasim gave a quarter of the city to Muslims and built a mosque there. According to the ''Chach Nama'', after the Arabs scaled Debal's walls, the besieged denizens opened the gates and pleaded for mercy but Qasim stated he had no orders to spare anyone. No mercy was shown and the inhabitants were accordingly thus slaughtered for three days, with its temple desecrated and 700 women taking shelter there enslaved. At Ror, 6000 fighting men were massacred with their families enslaved. The massacre at Brahamanabad has various accounts of 6,000 to 26,000 inhabitants slaughtered.''The Classical age'', by R. C. Majumdarp. 456
/ref> 60,000 slaves, including 30 young royal women, were sent to al-Hajjaj. During the capture of one of the forts of Sindh, the women committed the
jauhar
Jauhar, sometimes spelled Jowhar or Juhar, was a Hindu practice of mass self-immolation by women, in the Indian subcontinent, to avoid capture, enslavement and rape by an invading army, when facing certain defeat during a war. Some reports of ...
and burnt themselves to death according to the ''Chach Nama''. S.A.A. Rizvi citing the ''Chach Nama'', considers that conversion to Islam by political pressure began with Qasim's conquests. The ''Chach Nama'' has one instance of conversion, that of a slave from Debal converted at Qasim's hands. After executing Sindh's ruler, Raja Dahir
Raja Dahiraud (; ''Raja Dahiraud ''; 663 – 712 CE) was the last Hindu ruler of Sindh in present-day Pakistan. In 711 CE his kingdom was invaded by the Umayyad Caliphate led by Muhammad bin Qasim where Dahiraud died while defending his ki ...
, his two daughters were sent to the caliph and they accused Qasim of raping them. The caliph ordered Qasim to be sewn up in hide of a cow and died of suffocation.Habbari Arab dynasty (854–1024)
 The third dynasty,
The third dynasty, Habbari dynasty
The Habbari (, Sindhi: حباري خاندان) were an Arab dynasty that ruled much of Greater Sindh, as a semi-independent ''emirate'' from 854 to 1024. Beginning with the rule of 'Umar bin Abdul Aziz al-Habbari in 854 CE, the region became sem ...
ruled much of Greater Sindh, as a semi-independent ''emirate'' from 854 to 1024. Beginning with the rule of 'Umar bin Abdul Aziz al-Habbari in 854 CE, the region became semi-independent from the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
in 861, while continuing to nominally pledge allegiance to the Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
.P. M. ( Nagendra Kumar Singh), ''Muslim Kingship in India'', Anmol Publications, 1999, , pg 43-45.P. M. ( Derryl N. Maclean), ''Religion and society in Arab Sindh'', Published by Brill, 1989, , pg 140-143. The Habbari ascension marked the end of a period of direct rule of Sindh by the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
and Abbasid Caliphates, which had begun in 711 CE. The Habbaris were based in the city of Mansura, and ruled central and southern Sindh south of Aror
Aror ( Sindhi: اروهڙ) or Alor or Arorkot (Sindhi: اروهڙ ڪوٽ) is the medieval name of the city of Rohri (in Sindh, modern Pakistan). Aror once served as the capital of Sindh.
History
As Roruka, capital of the Sauvira Kingdom, i ...
, near the modern-day metropolis of Sukkur
Sukkur (; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh along the western bank of the Indus River, directly across from the historic city of Rohri. Sukkur is the third largest city in Sindh after Karachi and Hyderabad, and 14th largest city ...
. The Habbaris ruled Sindh until they were defeated by Sultan Mahmud Ghaznavi
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
in 1026, who then went on to destroy the old Habbari capital of Mansura, and annex the region to the Ghaznavid Empire, thereby ending Arab rule of Sindh.
Ghaznavids
Some of the territory in Sindh found itself under raids from the Turkic ruler,Mahmud Ghaznavi
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
in 1025, who ended Arab rule of Sindh. During his raids of northern Sindh, the Arab capital of Sindh, Mansura, was largely destroyed.
Soomra dynasty (1011–1333)
TheSoomra dynasty
The Soomra (or Soomro) dynasty (, '' lit.'' the family/dynasty of the Soomras) was a late medieval dynasty of Sindh, and at times adjacent regions, located in what is now Pakistan.
Sources
The only contemporary literary source remains the ' ...
was a local Sindhi muslim dynasty that ruled between early 11th century and the 14th century.
Later chroniclers like Ali ibn al-Athir
Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ash-Shaybānī, better known as ʿAlī ʿIzz ad-Dīn Ibn al-Athīr al-Jazarī ( ar, علي عز الدین بن الاثیر الجزري) lived 1160–1233) was an Arab or Kurdish historian a ...
(c. late 12th c.) and Ibn Khaldun (c. late 14th c.) attributed the fall of Habbarids to Mahmud of Ghazni, lending credence to the argument of Hafif being the last Habbarid. The Soomras appear to have established themselves as a regional power in this power vacuum.
The Ghurids
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غوریان, translit=Dudmân-e Ğurīyân; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty and a clan of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the ...
and Ghaznavids continued to rule parts of Sindh, across the eleventh and early twelfth century, alongside Soomrus. The precise delineations are not yet known but Sommrus were probably centered in lower Sindh.
Some of them were adherents of Isma'ilism
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-S ...
. One of their kings Shimuddin Chamisar had submitted to Iltutmish
Shams ud-Din Iltutmish ( fa, شمس الدین ایلتتمش; died 30 April 1236, ) was the third of the Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk kings who ruled the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in northern India. He was the first Muslim sove ...
, the Sultan of Delhi
The following list of Indian monarchs is one of several lists of incumbents. It includes those said to have ruled a portion of the Indian subcontinent, including Sri Lanka.
The earliest Indian rulers are known from epigraphical sources fou ...
, and was allowed to continue on as a vassal.
Samma dynasty (1333–1520)
TheSamma dynasty
The Samma dynasty ( sd, سمن جو راڄ, ) was a medieval Sindhi dynasty in the Indian subcontinent, that ruled Sindh, as well as parts of Kutch, Punjab and Balochistan from 1351 to 1524 CE, with their capital at Thatta known as Sa ...
was a Sindhi dynasty that ruled in Sindh, and parts of Kutch, Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
and Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
from 1351 to 1524 CE, with their capital at Thatta
Thatta ( sd, ٺٽو; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh. Thatta was the medieval capital of Sindh, and served as the seat of power for three successive dynasties. Thatta's historic significance has yielded several monuments in and ...
.
The Sammas overthrew the Soomras soon after 1335 and the last Soomra ruler took shelter with the governor of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, under the protection of Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (1290 – 20 March 1351) was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from February 1325 until his death in 1351. The sultan was the eldest son of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, founder of the Tughlaq dynasty. In 1321, the youn ...
, the sultan of Delhi
The following list of Indian monarchs is one of several lists of incumbents. It includes those said to have ruled a portion of the Indian subcontinent, including Sri Lanka.
The earliest Indian rulers are known from epigraphical sources fou ...
. Mohammad bin Tughlaq made an expedition against Sindh in 1351 and died at Sondha, possibly in an attempt to restore the Soomras. With this, the Sammas became independent. The next sultan, Firuz Shah Tughlaq attacked Sindh in 1365 and 1367, unsuccessfully, but with reinforcements from Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
he later obtained Banbhiniyo's surrender. For a period the Sammas were therefore subject to Delhi again. Later, as the Sultanate of Delhi collapsed they became fully independent.Directions in the History and Archaeology of Sindh by M. H. Panhwar/ref> Jam Unar was the founder of Samma dynasty mentioned by Ibn Battuta.Directions in the History and Archaeology of Sindh by M. H. Panhwar
/ref> The Samma civilization contributed significantly to the evolution of the Indo-Islamic architectural style. Thatta is famous for its necropolis, which covers 10 square km on the
Makli Hill
Makli Necropolis ( ur, ; sd, مڪلي جو مقام) is one of the largest funerary sites in the world, spread over an area of 10 kilometres near the city of Thatta, in the Pakistani province of Sindh. The site houses approximately 500,000 to ...
. It has left its mark in Sindh with magnificent structures including the Makli Necropolis
Makli Necropolis ( ur, ; sd, مڪلي جو مقام) is one of the largest funerary sites in the world, spread over an area of 10 kilometres near the city of Thatta, in the Pakistani province of Sindh. The site houses approximately 500,000 ...
of its royals in Thatta.
Arghun dynasty (1520–1591)
The Arghun dynasty were a dynasty of eitherMongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
,Davies, p. 627 Turkic or Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventuall ...
ethnicity,Bosworth, "New Islamic Dynasties," p. 329 who ruled over the area between southern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, and Sindh from the late 15th century to the early 16th century as the Sindh's sixth dynasty. They claimed their descent and name from Ilkhanid-Mongol Arghun Khan
Arghun Khan (Mongolian Cyrillic: ''Аргун хан''; Traditional Mongolian: ; c. 1258 – 10 March 1291) was the fourth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate, from 1284 to 1291. He was the son of Abaqa Khan, and like his father, was a de ...
.
Arghun rule was divided into two branches: the Arghun branch of Dhu'l-Nun Beg Arghun that ruled until 1554, and the Tarkhan branch of Muhammad 'Isa Tarkhan
Tarkhan ( otk, 𐱃𐰺𐰴𐰣, Tarqan, mn, or ; fa, ترخان; ; ar , طرخان; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján'') is an ancient Central Asia ...
that ruled until 1591 as the seventh dynasty of Sindh.
Early modern era
Mughal Era (1591–1701)
 Dynasties came and went for several hundred years until the late 16th century, when Sindh was brought into the
Dynasties came and went for several hundred years until the late 16th century, when Sindh was brought into the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
by Akbar, himself born in the Hindu Rajput kingdom of Umerkot
Umerkot (formerly known as Amarkot) is a city in the Sindh province of Pakistan.
The local language is Dhatki, which is one of the Rajasthani languages of the Indo-Aryan language family. It is most closely related to Marwari. Sindhi, Urdu an ...
in Sindh. Mughal rule from their provincial capital of Thatta
Thatta ( sd, ٺٽو; ) is a city in the Pakistani province of Sindh. Thatta was the medieval capital of Sindh, and served as the seat of power for three successive dynasties. Thatta's historic significance has yielded several monuments in and ...
was to last in lower Sindh until the early 18th century. Upper Sindh was a different picture, however, with the indigenous Kalhora dynasty
The Kalhora dynasty ( sd, ڪلهوڙا راڄ, translit=Kalhora Raj) was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Sindhi Kalhora origin based in the region of Sindh in what is now Pakistan. They claimed an Arab origin. The dynasty ruled Sindh and parts of the P ...
holding power, consolidating their rule until the mid-18th century, when the Persian sacking of the Mughal throne in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders ...
allowed them to grab the rest of Sindh. Akbar, unlike his predecessors, was renowned for his religious freedom.
Early in his reign in 1563, the emperor abolished taxes on Hindu pilgrims and allowed Hindu temples to be built and repaired. In 1564 he abolished the jizya, the tax paid by all non-Muslims.
Kalhora dynasty (1701–1783)
TheKalhora dynasty
The Kalhora dynasty ( sd, ڪلهوڙا راڄ, translit=Kalhora Raj) was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Sindhi Kalhora origin based in the region of Sindh in what is now Pakistan. They claimed an Arab origin. The dynasty ruled Sindh and parts of the P ...
was a Sunni dynasty based in Sindh. This dynasty as the eighth dynasty of Sindh ruled Sindh and parts of the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
between 1701 and 1783 from their capital of Khudabad, before shifting to Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India ...
from 1768 onwards.
Kalhora rule of Sindh began in 1701 when Mian Yar Muhammad Kalhoro was invested with title of ''Khuda Yar Khan'' and was made governor of Upper Sindh sarkar by royal decree of the Mughals. Later, he was made governor of Siwi through imperial decree. He founded a new city Khudabad after he obtained from Aurangzeb a grant of the track between the Indus and the Nara and made it the capital of his kingdom. Thenceforth, Mian Yar Muhammad became one of the imperial agents or governors. Later he extended his rule to Sehwan and Bukkur
Bukkur Fort (Urdu, Sindhi: بکر) is an island located in Rohri, Sukkur District of Sindh province in Pakistan.
Named Bukkur (Dawn) by Sayyid Muhammad Al-Makki in the seventh century of Hijri, this island is a limestone rock, oval in shape, long ...
and became sole ruler of Northern and central Sindh except Thatto which was still under the administrative control of Mughal Empire.
During the rule of Kalhora dynasty Sindh progressed and developed very fast,a few of their landmark achievements are listed below 1- Got digged the network of new canals to irrigate barren land of Sindh,2-they built new city Hyderabad and also made two forts to protect the city from outsider invaders,3-they defined geographical boundaries of Sindh,4-built the mesouleum of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai, 5-improved the literature and worked on ordering Sindhi alphabetical latters,6-built many mosques and schools.
Talpur dynasty (1783–1843)
TheTalpur dynasty
The Talpur dynasty ( sd, ٽالپردور) were rulers based in Sindh. Four branches of the dynasty were established following the defeat of the Kalhora dynasty at the Battle of Halani in 1783: one ruled lower Sindh from the city of Hyderabad, ...
(Sindhi: ٽالپردور; Urdu: سلسله تالپور) were rulers based in Sindh, in what is now the modern-day Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
. It was the ninth and last of the dynasties of Sindh. Four branches of the dynasty were established following the defeat of the Kalhora dynasty at the Battle of Halani in 1743. one ruled lower Sindh from the city of Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India ...
, another ruled over upper Sindh from the city of Khairpur, a third ruled around the eastern city of Mirpur Khas, and a fourth was based in Tando Muhammad Khan.
 The Talpurs were ethnically Baloch. They ruled from 1783, until 1843, when they were in turn defeated by the British at the
The Talpurs were ethnically Baloch. They ruled from 1783, until 1843, when they were in turn defeated by the British at the Battle of Miani
The Battle of Miani (or Battle of Meeanee, ) was a battle between forces of the Bombay Army of the East India Company, under the command of Charles Napier and the Baluch army of Talpur Amirs of Sindh, led by Mir Nasir Khan Talpur. The battle ...
and Battle of Dubbo.
Modern era

British Rule (1843–1947)
TheBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
conquered Sindh in 1843. General Charles Napier is said to have reported victory to the Governor General with a one-word telegram, namely ''"Peccavi"'' – or ''"I have sinned"'' (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
).
The British had two objectives in their rule of Sindh: the consolidation of British rule and the use of Sindh as a market for British products and a source of revenue and raw materials. With the appropriate infrastructure in place, the British hoped to utilise Sindh for its economic potential.
The British incorporated Sindh, some years later after annexing it, into the Bombay Presidency. Distance from the provincial capital, Bombay, led to grievances that Sindh was neglected in contrast to other parts of the Presidency. The merger of Sindh into Punjab province was considered from time to time but was turned down because of British disagreement and Sindhi opposition, both from Muslims and Hindus, to being annexed to Punjab.
The British desired to increase their profitability from Sindh and carried out extensive work on the irrigation system in Sindh, for example, the Jamrao Canal project. However, the local Sindhis were described as both eager and lazy and for this reason, the British authorities encouraged the immigration of Punjabi peasants into Sindh as they were deemed more hard-working. Punjabi migrations to Sindh paralleled the further development of Sindh's irrigation system in the early 20th century. Sindhi apprehension of a ‘Punjabi invasion’ grew.
In his backdrop, desire for a separate administrative status for Sindh grew. At the annual session of the Indian National Congress in 1913, a Sindhi Hindu put forward the demand for Sindh's separation from the Bombay Presidency on the grounds of Sindh's unique cultural character. This reflected the desire of Sindh's predominantly Hindu commercial class to free itself from competing with the more powerful Bombay's business interests. Meanwhile, Sindhi politics was characterised in the 1920s by the growing importance of Karachi and the Khilafat Movement. A number of Sindhi pirs, descendants of Sufi saints who had proselytised in Sindh, joined the Khilafat Movement, which propagated the protection of the Ottoman Caliphate, and those pirs who did not join the movement found a decline in their following. The pirs generated huge support for the Khilafat cause in Sindh. Sindh came to be at the forefront of the Khilafat Movement.
Although Sindh had a cleaner record of communal harmony than other parts of India, the province's Muslim elite and emerging Muslim middle class demanded separation of Sindh from Bombay Presidency as a safeguard for their own interests. In this campaign, local Sindhi Muslims identified ‘Hindu’ with Bombay instead of Sindh. Sindhi Hindus were seen as representing the interests of Bombay instead of the majority of Sindhi Muslims. Sindhi Hindus, for the most part, opposed the separation of Sindh from Bombay.
Sindh's Hindu and Muslim communities lived in close proximity to each other and extensively influenced each other's culture. Scholars have discussed that it was found that Hindu practices in Sindh differed from orthodox Hinduism in the rest of India. Hinduism in Sindh was to a large extent influenced by Islam, Sikhism and Sufism. Sindh's religious syncretism was a result of Sufism. Sufism was a vital component of Sindhi Muslim identity and Sindhi Hindus, more than Hindus in any other part of India, came under the influence of Sufi thought and practices and the majority of them were murids (followers) of Sufi Muslim saints.
However, both the Muslim landed elite, ''waderas'', and the Hindu commercial elements, ''banias'', collaborated in oppressing the predominantly Muslim peasantry of Sindh who were economically exploited. In Sindh's first provincial election after its separation from Bombay in 1936, economic interests were an essential factor of politics informed by religious and cultural issues. Due to British policies, much land in Sindh was transferred from Muslim to Hindu hands over the decades. Religious tensions rose in Sindh over the Sukkur Manzilgah issue where Muslims and Hindus disputed over an abandoned mosque in proximity to an area sacred to Hindus. The Sindh Muslim League exploited the issue and agitated for the return of the mosque to Muslims. Consequentially, a thousand members of the Muslim League were imprisoned. Eventually, due to panic the government restored the mosque to Muslims.
The separation of Sindh from Bombay Presidency triggered Sindhi Muslim nationalists to support the Pakistan Movement. Even while the Punjab and North-West Frontier Province were ruled by parties hostile to the Muslim League, Sindh remained loyal to Jinnah. Although the prominent Sindhi Muslim nationalist G.M. Syed left the All India Muslim League in the mid-1940s and his relationship with Jinnah never improved, the overwhelming majority of Sindhi Muslims supported the creation of Pakistan, seeing in it their deliverance. Sindhi support for the Pakistan Movement arose from the desire of the Sindhi Muslim business class to drive out their Hindu competitors. The Muslim League's rise to becoming the party with the strongest support in Sindh was in large part linked to its winning over of the religious pir families. Although the Muslim League had previously fared poorly in the 1937 elections in Sindh, when local Sindhi Muslim parties won more seats, the Muslim League's cultivation of support from the pirs and saiyids of Sindh in 1946 helped it gain a foothold in the province.
Partition (1947)
In 1947, violence did not constitute a major part of the Sindhi partition experience, unlike in Punjab. There were very few incidents of violence on Sindh, in part due to the Sufi-influenced culture of religious tolerance and in part that Sindh was not divided and was instead made part of Pakistan in its entirety. Sindhi Hindus who left generally did so out of a fear of persecution, rather than persecution itself, because of the arrival of Muslim refugees from India. Sindhi Hindus differentiated between the local Sindhi Muslims and the migrant Muslims from India. A large number of Sindhi Hindus travelled to India by sea, to the ports of Bombay, Porbandar, Veraval and Okha.Priya Kumar & Rita Kothari (2016) Sindh, 1947 and Beyond, ''South Asia: Journal of South Asian Studies'', 39:4, 776-777, DOI: 10.1080/00856401.2016.1244752See Also
* List of Monarchs of SindhReferences
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control