History of Poland (1918–1939) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of interwar Poland comprises the period from the revival of the independent Polish state in 1918, until the
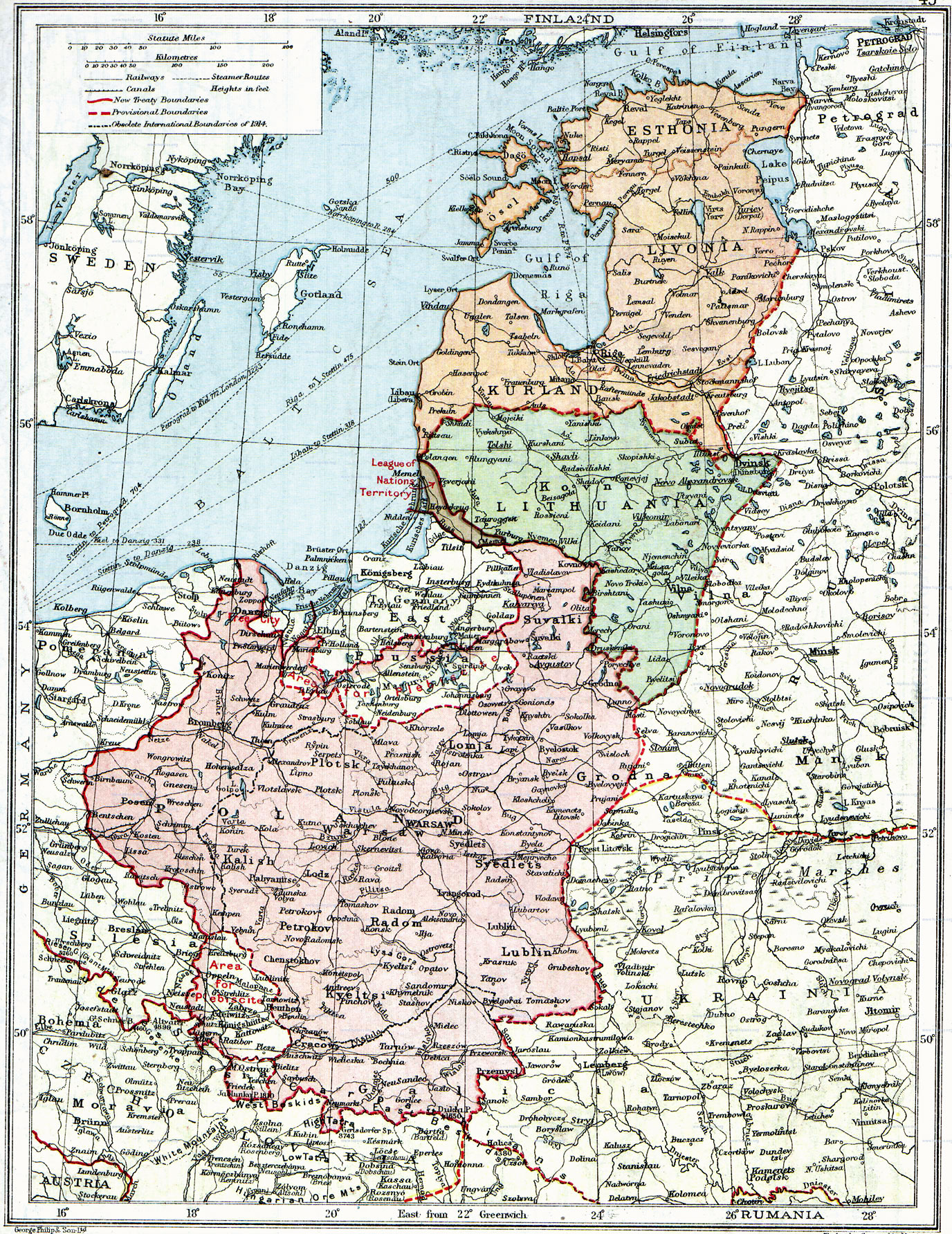 To the southwest, Poland and Czechoslovakia contested boundary disputes (see: Zaolzie). More ominously, an embittered Germany begrudged any territorial loss to its new eastern neighbor. The December 27, 1918 Great Poland Uprising liberated
To the southwest, Poland and Czechoslovakia contested boundary disputes (see: Zaolzie). More ominously, an embittered Germany begrudged any territorial loss to its new eastern neighbor. The December 27, 1918 Great Poland Uprising liberated
 Reborn Poland faced a host of daunting challenges: extensive war damage, a ravaged economy, a population one-third composed of wary
Reborn Poland faced a host of daunting challenges: extensive war damage, a ravaged economy, a population one-third composed of wary  The new, inexperienced government faced serious problems; already there was rampant corruption among government officials; a dizzying turnover of cabinets caused confusion and distrust. At a deeper level there was profound disagreement about inclusiveness in the new state.
The new, inexperienced government faced serious problems; already there was rampant corruption among government officials; a dizzying turnover of cabinets caused confusion and distrust. At a deeper level there was profound disagreement about inclusiveness in the new state.

 France was an ally of both Poland and Czechoslovakia and tried repeatedly to get them to resolve their border disputes and become allies, and also collaborate with the Soviet Union. There was no success, not just because of the border issues but also because Prague's willingness to work with Moscow clashed with the firm resolve of Warsaw to keep its distance from Moscow. Czechoslovakian President
France was an ally of both Poland and Czechoslovakia and tried repeatedly to get them to resolve their border disputes and become allies, and also collaborate with the Soviet Union. There was no success, not just because of the border issues but also because Prague's willingness to work with Moscow clashed with the firm resolve of Warsaw to keep its distance from Moscow. Czechoslovakian President


 Poland did have PZL, the state aviation company that made good planes. In 1931 it developed the PZL P.11, the most advanced fighter in the world of the early 1930s. In the mid-1930s its successor the P-24 was even better armed and faster, but Poland exported it to earn currency, forcing the use of semi-obsolete PZL P.11 and a couple of dozen old PZL P.7 fighters. They were no match against the German Messerschmitt 109 which could fly higher, was better armed, and flew 100 km/h faster. In spite of the shortcomings, at least 110 victories were credited to the P.11 for the loss of about 30 of their own. The
Poland did have PZL, the state aviation company that made good planes. In 1931 it developed the PZL P.11, the most advanced fighter in the world of the early 1930s. In the mid-1930s its successor the P-24 was even better armed and faster, but Poland exported it to earn currency, forcing the use of semi-obsolete PZL P.11 and a couple of dozen old PZL P.7 fighters. They were no match against the German Messerschmitt 109 which could fly higher, was better armed, and flew 100 km/h faster. In spite of the shortcomings, at least 110 victories were credited to the P.11 for the loss of about 30 of their own. The
Poland
online edition
*''The Cambridge History of Poland'', (2 vols., Cambridge University Press, 1941) covers 1697–1935 *
online edition
*Lerski, George J. ''Historical Dictionary of Poland, 966–1945.'' Greenwood, 1996. 750 pp
online edition
*Leslie, R. F. et al. ''The History of Poland since 1863.'' Cambridge U. Press, 1980. 494 pp. *Lukowski, Jerzy and Zawadzki, Hubert. ''A Concise History of Poland.'' Cambridge U. Press, 2nd ed 2006. 408pp. *Pogonowski, Iwo Cyprian. ''Poland: A Historical Atlas.'' Hippocrene, 1987. 321 pp. new designed maps *Sanford, George. ''Historical Dictionary of Poland.'' Scarecrow Press, 2003. 291 pp. * Stachura, Peter D. ''Poland, 1918-1945: An Interpretive and Documentary History of the Second Republic'' (2004
online
* Stachura, Peter D. ed. ''Poland Between the Wars, 1918-1939'' (1998) essays by scholars *Watt, Richard M. ''Bitter Glory: Poland and Its Fate, 1918-1939'' (1998), comprehensive survey
online
* Davies, Norman. ''White Eagle, Red Star: The Polish-Soviet War 1919-1920 and The Miracle on the Vistula'' (2003) *Drzewieniecki, Walter M. "The Polish Army on the Eve of World War II," ''Polish Review'' (1981) 26#3 pp 54-64
in JSTOR
* Garlicki, Andrzej. ''Józef Piłsudski, 1867-1935'' (New York: Scolar Press 1995), scholarly biography; one-vol version of 4 vol Polish edition * Hetherington, Peter. ''Unvanquished: Joseph Pilsudski, Resurrected Poland, and the Struggle for Eastern Europe'' (2012) 752pp * Jędrzejewicz, W. ''Piłsudski. A Life for Poland'' (1982), scholarly biography * Karski, Jan. ''The great powers and Poland: From Versailles to Yalta'' (2014) * Kochanski, Halik. ''The Eagle Unbowed: Poland and the Poles in the Second World War'' (2012) * Korbel, Josef. ''Poland Between East and West: Soviet and German Diplomacy toward Poland, 1919–1933'' (Princeton University Press, 1963
online
* Polonsky, A. ''Politics in Independent Poland, 1921-1939: The Crisis of Constitutional Government'' (1972) * Remak, Joachim
''The Nazi Years: A Documentary History''
Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 1990. Originally published Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1969. . * Riekhoff, H. von. '' German-Polish Relations, 1918-1933'' (Johns Hopkins University Press 1971) * Rothschild, J. ''Piłsudski's Coup d'État'' (New York: Columbia University Press 1966) * Seidner, Stanley S. "The Camp of National Unity: An Experiment in Domestic Consolidation," ''The Polish Review'' 20 (2-3): 231-236 * Shirer, William L.br>''The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich: A History of Nazi Germany''
New York: Simon and Schuster, 2011. Originally published New York: Simon and Schuster, 1950. . * Wandycz, P. S. ''Polish Diplomacy 1914-1945: Aims and Achievements'' (1988) * Wandycz, P. S. ''Soviet-Polish Relations, 1917-1921'' (Harvard University Press 1969) * Wandycz, P. S. ''The United States and Poland'' (1980) * Williamson, David G. ''Poland Betrayed: The Nazi-soviet Invasions of 1939'' (2011), pp 1-62 *Zamoyski, Adam. ''Warsaw 1920: Lenin's Failed Conquest of Europe'' (2008)
* Wynot, E. D. ''Warsaw Between the Wars. Profile of the Capital City in a Developing Land, 1918-1939'' (1983) * Żółtowski, A. ''Border of Europe. A Study of the Polish Eastern Provinces'' (London: Hollis & Carter 1950)
Eva Plach, "Dogs and dog breeding in interwar Poland,"
Canadian Slavonic Papers 60, no 3-4
in JSTOR
*Polonsky, Antony. "The History of Inter-War Poland Today," ''Survey'' (1970) pp143–159.
1932 ''Statistical Yearbook,'' (''Mały rocznik statystyczny 1932'')
complete text (in Polish)
Commonwealth of Diverse Cultures: Poland's Heritage
Old maps of Poland from Hipkiss' Scanned Old Maps
Poland Catholic Church and Rome
Polish Cinema's Golden Age: The Glamour & Progress Of Poland's Inter-War Films
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Poland (1918-1939) .
Invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
from the West by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
in 1939 at the onset of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, followed by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
from the East two weeks later. The two decades of Poland's sovereignty between the world wars are known as the Interbellum
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
.
Poland re-emerged in November 1918 after more than a century of partitions
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of ...
by Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
s.Norman Davies. ''Heart of Europe: The Past in Poland's Present''. Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print book ...
. 2001. pp. 100-101. Its independence was confirmed by the victorious powers through the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
of June 1919, and most of the territory won in a series of border wars fought from 1918 to 1921. Poland's frontiers were settled in 1922 and internationally recognized in 1923.
The Polish political scene was democratic but chaotic until Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
(1867–1935) seized power in May 1926 and democracy ended. The policy of agrarianism
Agrarianism is a political and social philosophy that has promoted subsistence agriculture, smallholdings, and egalitarianism, with agrarian political parties normally supporting the rights and sustainability of small farmers and poor peasants ag ...
led to the redistribution of lands to peasants and the country achieved significant economic growth between 1921 and 1939. A third of the population consisted of minorities—Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, Jews, Belarusians, Lithuanians and Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
.
Formative years (1918-1921)
The independence of Poland had been successfully promoted to the Allies in Paris byRoman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
and Ignacy Paderewski. U.S. President Woodrow Wilson made the independence of Poland a war goal in his Fourteen Points, and this goal was endorsed by the Allies in spring 1918. As part of the Armistice terms imposed on Germany, all German forces had to stand down in Poland and other occupied areas. So as the war ended, the Germans sent Piłsudski, then under arrest, back to Warsaw. On November 11, 1918, he took control of the puppet government the Germans had set up. Ignacy Daszyński
Ignacy Ewaryst Daszyński (; 26 October 1866 – 31 October 1936) was a Polish socialist politician, journalist, and very briefly Prime Minister of the Second Polish Republic's first government, formed in Lublin in 1918.
In October 1892 he co ...
headed a short-lived Polish government in Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
from November 6 but Piłsudski had overwhelming prestige at this point. Daszyński and the other Polish leaders acknowledged him as head of the army and in effect head of what became the Republic of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
. Germany, now defeated, followed the terms of the Armistice and withdrew its forces. Jędrzej Moraczewski became the first prime minister (in November 1918) and Dmowski headed the largest party.''A Concise History of Poland'', by Jerzy Lukowski and Hubert Zawadzki, p. 217-222.
From its inception, the Republic fought a series of wars to secure its boundaries. The nation was rural and poor; the richest areas were in the former German areas in the west. Industrialization came very slowly, and was promoted in the mid-1930s with the development of the Central Industrial District.
Boundaries
Most Polish leaders of that period wanted to create a larger Polish state; one optimal plan, dating back to the Paris Peace Conference, included the incorporation of East Prussia and the German city of Königsberg being placed in a customs union with Poland. At the same time, the exact boundaries of the formerPolish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
were not desired, though mentioned as an opening gambit by Roman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
. Much of this land had been controlled by the Russian Empire since the Partitions of Poland and its inhabitants were struggling to create their own states (such as Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, and the Baltics: Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia). The Polish leadership did not aim to restore the nation to its 17th-century boundaries.Sandra Halperin, ''In the Mirror of the Third World: Capitalist Development in Modern Europe'', (1996) pp. 40, 41. Opinions varied among Polish politicians as to how much of the territory a new, Polish-led state should contain and what form it should take. Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
advocated a democratic, Polish-led federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-gover ...
of independent states — while Roman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
leader of the '' Endecja'' movement represented by the National Democratic Party, set his mind on a more compact Poland composed of ethnic Polish or ' polonizable' territories.
 To the southwest, Poland and Czechoslovakia contested boundary disputes (see: Zaolzie). More ominously, an embittered Germany begrudged any territorial loss to its new eastern neighbor. The December 27, 1918 Great Poland Uprising liberated
To the southwest, Poland and Czechoslovakia contested boundary disputes (see: Zaolzie). More ominously, an embittered Germany begrudged any territorial loss to its new eastern neighbor. The December 27, 1918 Great Poland Uprising liberated Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest cit ...
. The 1919 Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
settled the German-Polish borders in the Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
. The port city of Danzig ( pl, Gdańsk), with a majority German population and Polish minority was declared a free city independent of Germany, and became a bone of contention for decades. Allied arbitration divided the ethnically mixed and highly coveted industrial and mining district of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
between Germany and Poland, with Poland receiving the smaller in size, but a more industrialized eastern section in 1922, after series of three Silesian Uprisings.
War with Soviet Russia
The military conflict with the Soviets proved the determinant of Poland's frontiers in the east, a theater rendered chaotic by the repercussions of the Russian revolutions andcivil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
. Piłsudski envisioned creating a federation with the rest of Ukraine (led by the Polish-friendly government in Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
he was to help to install) and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, thus forming a Central and East European federation called " Intermarium" (Polish: "Międzymorze", literally "area between seas"). Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
, leader of the new communist government of Russia, saw Poland as the bridge over which communism would pass into the labor class of a disorganized postwar Germany. And the issue was further complicated as some of the disputed regions had assumed various economic and political identities since the partition in the late 18th century while some did not have an ethnically Polish majority in the first place they were still viewed by Poles as their historic regions since they envisioned Poland as a multiethnic state. In the end, the negotiations broke down, sinking Piłsudski's idea of Międzymorze
Intermarium ( pl, Międzymorze, ) was a post- World War I geopolitical plan conceived by Józef Piłsudski to unite former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth lands within a single polity. The plan went through several iterations, some of which anti ...
federation; instead, wars like the Polish-Lithuanian War or the Polish-Ukrainian War decided the borders of the region for the next two decades.
The Polish-Soviet war, began in 1919, was the most important of the regional wars. Piłsudski first carried out a major military thrust into Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
in 1920 and in May Polish-Ukrainian forces reached Kiev. Just a few weeks later, however, the Polish offensive was met with a Soviet counter-offensive, and Polish forces were forced into a retreat by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
. Poland was driven out of Ukraine and back into the Polish heartland. Most observers at the time marked Poland for extinction and Bolshevization, However at the Battle of Warsaw Piłsudski organized a stunning counterattack that won a famous victory. This "Miracle on the Vistula" became an iconic victory in Polish memory. Piłsudski resumed the offensive, pushing the Red forces east. Eventually, both sides, exhausted, signed a compromise peace treaty at Riga in early 1921 that divided the disputed territories of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Ukraine between the two combatants. These acquisitions were recognized by the international agreement with the Entente. The treaty gave Poland an eastern border well beyond what the peacemakers in Paris had envisioned and added 4,000,000 Ukrainians, 2,000,000 Jews, and 1,000,000 Belarusians to Poland's minority population.
In Soviet historiography
Soviet historiography is the methodology of history studies by historians in the Soviet Union (USSR). In the USSR, the study of history was marked by restrictions imposed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). Soviet historiography i ...
, the Polish-Soviet War was also referred to as "the war against White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
Poles", with epithet "White Poles" (''belopoliaki'') alleging the "counter-revolutionary" character of Poland at the time, in an analogy with Russian White Movement.
In 1922, in the aftermath of the Polish-Soviet War and Polish-Lithuanian War, Poland also officially annexed Central Lithuania following a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
, which was never recognized by Lithuania.
The Riga arrangement influenced the fate of the entire region for the years to come. Ukrainians and Belarusians found themselves without a country or province of their own, and some Polish speakers also found themselves within the borders of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. The latter experienced forced collectivistion, state terror, suppression of religion, purges, labor camps and famine. The newly formed Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World ...
, one-third of whose citizens were non-ethnic Poles, engaged in promoting Polish identity, culture and language at the expense of the country's ethnic minorities who felt alienated by the process.
From democracy to authoritarian government
national minorities
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
, an economy largely under the control of German industrial interests, and a need to reintegrate the three zones that had been forcibly kept apart during the era of partition. Poland's formal political life began in 1921 with the adoption of a constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these pr ...
that designed Poland as a republic modeled after the French Third Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940 ...
, vesting most authority in the legislature, the Sejm. This was mainly to prevent Piłsudski from establishing himself as a dictator. A multitude of political parties emerged, of which there were four major and dozens of minor ones. All had very different ideologies and voter bases, and could scarcely agree on any major issue. There had been no serious consideration of re-establishing a monarchy, and although the great Polish noble families continued to have their names mentioned in newspapers, it was mostly in the society pages. The chief parties were the left-wing Polish Peasant Party (PSL) and on the right National Democracy National Democracy may refer to:
* National Democracy (Czech Republic)
* National Democracy (Italy)
* National Democracy (Philippines)
* National Democracy (Poland)
* National Democracy (Spain)
See also
* Civic nationalism, a general concept
* ...
party (ND) led by Dmowski.
 The new, inexperienced government faced serious problems; already there was rampant corruption among government officials; a dizzying turnover of cabinets caused confusion and distrust. At a deeper level there was profound disagreement about inclusiveness in the new state.
The new, inexperienced government faced serious problems; already there was rampant corruption among government officials; a dizzying turnover of cabinets caused confusion and distrust. At a deeper level there was profound disagreement about inclusiveness in the new state. Roman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
envisioned an ethnically-homogeneous Polish nation, and a pro-Western, anti-German path to modernization; he also espoused strong anti-Semitic attitudes, and emphasized that Poland should be a Catholic and hierarchical state. Piłsudski, however, rooted his ideal in notions about the multi-ethnic Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
. In practice that meant ignoring the minority vote at home and seeking agreements with nearby countries. Universal suffrage gave the minorities a voice, especially when they formed a coalition, the Bloc of National Minorities (BMN) led by the Jews and including the others who together comprised a third of the population and 20% of the vote. However, the districts were gerrymandered
In representative democracies, gerrymandering (, originally ) is the political manipulation of electoral district boundaries with the intent to create undue advantage for a party, group, or socioeconomic class within the constituency. The m ...
to minimize minority representation. The BMN helped elect Gabriel Narutowicz as president on the PSL ticket in 1922, but he came under nasty attacks from the right and was assassinated after five days in office. The BMN coalition declined in significance and shut down in 1930 as the different groups cut their own deals with the government on isolated issues.
Coup of 1926
After the constitution was adopted, Piłsudski resigned from office, unhappy with the limited role of the executive branch. But he continued to keep a close eye on political developments. The ineffectiveness of the Sejm led some of his inner circle to suggest that he launch a military coup and regain power; he said no. By 1926 he was persuaded and launched the coup of May 1926, which succeeded with little violence. For the next decade, Piłsudski dominated Polish affairs as strongman of a generally popularcentrist
Centrism is a political outlook or position involving acceptance or support of a balance of social equality and a degree of social hierarchy while opposing political changes that would result in a significant shift of society strongly to the ...
regime, although he never held a formal title except for minister of defense. He retained the 1921 constitution, and the noisy, ineffective Sejm continued to operate, but it nearly always gave him what he wanted. Critics of the regime were occasionally arrested, but most were sued for libel. The marshal portrayed himself as a national saviour who was above partisan politics and gained more popular support by distancing himself from the Polish Socialist Party
The Polish Socialist Party ( pl, Polska Partia Socjalistyczna, PPS) is a socialist political party in Poland.
It was one of the most important parties in Poland from its inception in 1892 until its merger with the communist Polish Workers' ...
. In 1935 a new Polish Constitution was adopted, but Piłsudski soon died and his protégé successors drifted toward open authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voti ...
. Opposition voices were increasingly harassed or jailed, a situation that was not surprising in view of the regime's growing fears over national security.
In many respects, the Second Republic fell short of the high expectations of 1918. As happened elsewhere in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, with the exception of Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, the attempt to implant democracy did not succeed. Governments polarized between right- and left-wing factions, neither of which was prepared to honor the actions taken by the other.
Economic and social problems
Serious difficulties arose in dealing with foreign assets and internal minorities. The government nationalized foreign-owned assets and operated them because there was insufficient domestic capital to buy them and because it was easier than determining who should get what. Overall, Poland had a higher degree of state involvement in the economy and less foreign investment than any other nation in eastern Europe. This emphasis on economic centralization hampered Poland's development. The economy was largely rural, and the worldwideGreat Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
that began in 1929 saw hardship in every sector. Worst hit were the peasants whose incomes plunged 50% or more. The government had few solutions except to reduce its own spending as tax revenues fell.
Minorities
About a third of the total population were members of minorities, including five or six millionUkrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, over three million Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, one and a half million Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
, and some 800,000 Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
. These minorities were increasingly alienated, complaining that they were marginalized in politics and denied rights Poland had agreed to in treaties. Historian Peter D. Stachura
Peter D. Stachura is a British historian, writer, lecturer and essayist. He was Professor of Modern European History at the University of Stirling and Director of its Centre for Research in Polish History. He has published extensively on the subj ...
has examined the ethnic issue in interwar Poland and summarizes the consensus of historians, he writes:
:"It is undeniable that the Second Republic did not face any greater challenge than that of devising a policy towards the minorities that would bring harmony and peaceful coexistence rather than bitterness, confrontation and strife. The historiographical verdict is that Poland signally failed to address this question in a satisfactory manner. Indeed, the vast majority of historians have adopted a highly censorious attitude towards the multitude of policies and attitudes which were pursued towards the minorities by the state. Often influenced by Communist, Marxist, Soviet or liberal political and ideological perspectives, they refer unequivocally to 'oppression', 'persecution', 'terror', 'discrimination', even 'murder', as the salient characteristics of an intrinsically chauvinistic Polish approach that was designed to relegate the minorities to the status of second-class citizens. Such a situation, it is argued, meant that Poland failed repeatedly to respect the formal statutory guarantees which were introduced after 1918, notably through the Minorities' Treaty of 1919, the Treaty of Riga (Article VII) in 1921, and the Polish constitutions of 1921 and 1935."
Stachura himself thinks that historians have been too harsh in their negative judgment. He notes that Poland had to contend with "an obstreperous and fundamentally disloyal German minority" that was incited by "fanatical" German nationalists next door. Poles talked of forced assimilation and seizure of industrial assets, but the governments before 1926 were too weak to carry them out. After 1926 Piłsudski had no interest in so doing. The Germans in Poland had above-average incomes, had a full panoply of civic organizations and German-language schools, and were represented in the Sejm. A stalemate resulted. Their status became a major threat after Hitler came to power in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
in 1933, because "the overwhelming majority of these Germans became ardent Nazis in the 1930s and a 'fifth column' when Poland was attacked in September 1939."
Relations with the much larger Ukrainian minority, who formed 15% or so of the national population and were in the majority in several eastern provinces, were even more strained. The Ukrainians were poor peasants who resented their Polish landlords and the government's policy of polonizing them. The schools after 1924 were bilingual (students had to learn Polish), and government offices were not allowed to use Ukrainian. Some Ukrainians tried to sabotage, and the government cracked down with mass arrests; it tolerated the Polish arson of Ukrainian community centers. Orthodox churches were closed, especially in Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
province. Some men went underground and tried to assassinate Ukrainians who collaborated with the government, as well as top Polish officials. A compromise was reached in 1935 that somewhat quieted the situation, but the Polish Army saw a war with the USSR looming and refused to support the policy.
As the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
worsened in the 1930s, antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
began to rise even though Poland was home to over three million Jews (10 percent of Poland's population), the largest Jewish population in Europe at the time. The impoverished Jewish families relied on their own local charities, which by 1929 had reached unprecedented proportions, providing services such as religion, education, health and other services to the value of 200 million zlotys a year, thanks in part to Jewish '' per capita'' income among the working Jews more than 40% higher than that of Polish non-Jews.
From the 1920s the Polish government excluded Jews from receiving government bank credits, public sector employment, and obtaining business licenses. From the 1930s limits were placed on Jewish enrollment in university education, Jewish shops, Jewish export firms, Shechita
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''.
Sources
states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtere ...
, Jewish admission to the medical and legal professions, Jews in business associations, etc. While in 1921-22 25% of students were Jews, by 1938-9 the proportion went down to 8%. The far-right National Democracy National Democracy may refer to:
* National Democracy (Czech Republic)
* National Democracy (Italy)
* National Democracy (Philippines)
* National Democracy (Poland)
* National Democracy (Spain)
See also
* Civic nationalism, a general concept
* ...
(Endeks) organized anti-Jewish boycotts. Following the death of Poland's ruler Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
in 1935, the Endeks intensified their efforts. In 1937 the Endeks passed resolutions that "its main aim and duty must be to remove the Jews from all spheres of social, economic, and cultural life in Poland". The government in response organized the Camp of National Unity (OZON); OZON advocated mass emigration of Jews from Poland, boycott of Jews, numerus clausus (see also Ghetto benches), and other limitation on Jewish rights. At the same time the Polish government supported the Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
Irgun
Irgun • Etzel
, image = Irgun.svg , image_size = 200px
, caption = Irgun emblem. The map shows both Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan, which the Irgun claimed in its entirety for a future Jewish state. The acronym "Etzel" i ...
, training its members in Tatra Mountains and in 1937 the Polish authorities began to deliver large amounts of weapons to the Jewish underground in Palestine, capable of arming up to 10,000 men. On international arena Poland supported the creation of Jewish state in Palestine hoping gradual emigration over next 30 years will lower Jewish population in Poland to 500,0000 and cooperated with the leader of Revisionist Zionism
Revisionist Zionism is an ideology developed by Ze'ev Jabotinsky, who advocated a "revision" of the "practical Zionism" of David Ben-Gurion and Chaim Weizmann which was focused on the settling of ''Eretz Yisrael'' (Land of Israel) by independent ...
, Ze'ev Jabotinsky
Ze'ev Jabotinsky ( he, זְאֵב זַ׳בּוֹטִינְסְקִי, ''Ze'ev Zhabotinski'';, ''Wolf Zhabotinski'' 17 October 1880 – 3 August 1940), born Vladimir Yevgenyevich Zhabotinsky, was a Russian Jewish Revisionist Zionist leade ...
who hoped Poland would inherit mandate of Palestine from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
; his "Evacuation Plan" called for the settlement of 1.5 million Jews within 10 years in Palestine, including 750,000 Polish Jews This idea was warmly received by Polish government which pursued a policy of mass emigration towards its Jewish population and was looking for locations for them to resettle; Jabotinsky on his part viewed antisemitism in Poland as a result of the shortage of jobs and economic situation, rather than rabid racism as was in Nazi Germany
Agrarianism
Seven out of ten of the people worked on farms as peasants. Polish agriculture suffered from the usual handicaps of Eastern European nations: technological backwardness, low productivity, and lack of capital and access to markets. The former German areas in the west had better rainfall and soil quality and were the most productive, while the former Russian and Austrian areas were below-average. The Polish peasantry believed that it would be so much better if they owned their land and did not pay rents to a landowner. They endorsedagrarianism
Agrarianism is a political and social philosophy that has promoted subsistence agriculture, smallholdings, and egalitarianism, with agrarian political parties normally supporting the rights and sustainability of small farmers and poor peasants ag ...
and called for land redistribution away from large estates to peasants. This was done and also many very small farms were consolidated into viable units. Land reforms were undertaken along ethnic lines. In the west, Germans who had been made foreigners in 1919 quickly lost their land. In the east, by contrast, Ukrainian and Belarusian peasants tilled for Polish landowners and no serious moves toward land redistribution were taken. No alternative industrial jobs were developed and underemployment was high in rural areas.
The socialist politician Bolesław Limanowski
Bolesław Limanowski (; 18 October 1835 – 15 February 1935) was a Polish socialist politician, as well as historian and journalist and advocate of Agrarianism. He was one of the first people to promote socialist ideas in Poland.
Political act ...
thought deeply about Agrarianism and worked out an eclectic program that fit Polish conditions. His practical experience as a farm manager combined with socialist, "single-tax," and Slavic communal ideas shaped his worldview. He proposed a form of agrarian socialism with large state farms to counteract the inefficiency of very smallholdings. In independent Poland, he advocated expropriation of gentry estates. His observation of peasant individualism convinced him that Poland should combine voluntary collectivism and individual possession of the leased land. His pragmatism left the room even for private peasant ownership, despite his Marxism.
International relations
Foreign minister Józef Beck was in full charge of foreign policy by 1935 but he had a weak hand. Poland with 35 million people had a large population but a thin industrial base; its war plans focused on the Soviet Union instead of Germany. Poland had long borders with two more powerful dictatorships, Hitler's Germany and Stalin's USSR. Poland was increasingly isolated. Overy says that of all the new states in Europe: :"Poland was almost certainly the most disliked and her Foreign Minister the most distrusted. Poland's pursuit of an independent line left her bereft of any close friends by the end of 1938.... The Western powers saw Poland as a greedy revisionist power, illiberal, anti-Semitic, pro-German; Beck was a 'menace,' 'arrogant and treacherous.'" In February 1921, Poland signed a secret military agreement with France, which obliged each party to mutual aid in the event of German aggression. In March 1921, the Poles signed a treaty of mutual assistance with Romania, directed against the threat from the Soviet Union. Poland sought to be the leader of an independent bloc of nations between the Soviet Union and Germany that would unite to fend off those powers. However, Poland ran into so many disputes with its smaller neighbors that it was never able to build a bloc. At first, France favored Poland, because France wanted an ally against Germany; if Germany faced a two-front war, it would be less likely to attack France. France was especially helpful at the 1919 Paris conference and in the 1920s when it resisted British efforts to weaken Poland. After 1935, however, France distrusted Beck and lost interest in Eastern Europe and Poland stood increasingly alone. In 1925, Berlin formally recognized its post-1918 boundaries in the west with France, but not in the east with Poland.Kochanski (2012), ''The Eagle Unbowed'', p. 36 The same year, Germany slashed coal imports from Poland by half, which triggered the German–Polish trade war. Relations with the Soviet Union remained hostile, but Piłsudski was willing to negotiate, and in 1932 the two countries signed a non-aggression pact. Shortly afterward, Hitler came to power. Rumors circulated to the effect that Piłsudski proposed to France that Poland and France launch a preemptive military strike to overthrow Hitler in 1933. Most historians do not believe this happened, pointing out that Piłsudski's war plans were focused on Russia and he made no preparations for any sort of war with Germany. Furthermore, no one in France reported any such inquiry from Poland. Piłsudski made demands regarding Danzig that Hitler immediately approved; relations between Poland and Nazi Germany became friendly and they signed the German–Polish Non-Aggression Pact in January 1934. At the same time, Czechoslovakia, Romania, and Yugoslavia were allied in theLittle Entente
The Little Entente was an alliance formed in 1920 and 1921 by Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (since 1929 Yugoslavia) with the purpose of common defense against Hungarian revanchism and the prospect of a ...
with French support. Polish membership there could have provided additional security; however, relations with Prague were unfriendly due to border disputes, so they never reached an agreement.


 France was an ally of both Poland and Czechoslovakia and tried repeatedly to get them to resolve their border disputes and become allies, and also collaborate with the Soviet Union. There was no success, not just because of the border issues but also because Prague's willingness to work with Moscow clashed with the firm resolve of Warsaw to keep its distance from Moscow. Czechoslovakian President
France was an ally of both Poland and Czechoslovakia and tried repeatedly to get them to resolve their border disputes and become allies, and also collaborate with the Soviet Union. There was no success, not just because of the border issues but also because Prague's willingness to work with Moscow clashed with the firm resolve of Warsaw to keep its distance from Moscow. Czechoslovakian President Edvard Beneš
Edvard Beneš (; 28 May 1884 – 3 September 1948) was a Czech politician and statesman who served as the president of Czechoslovakia from 1935 to 1938, and again from 1945 to 1948. He also led the Czechoslovak government-in-exile 1939 to 194 ...
warned that military or even strong political ties with Poland could prove dangerous for Czechoslovakia and rejected Beck's proposal to establish anti-German cooperation.
The failure to establish any alliances in Eastern Europe meant the only ally was France; Piłsudski increasingly doubted the value of that alliance. The Locarno Pact, signed in 1925 by the major West European powers with the aim of guaranteeing peace in the region, contained no guarantee of Poland's western border.
In May 1934, the Polish-Soviet non-aggression pact was extended until 31 December 1945. During the period 1934–1939, Polish-Soviet relations were correct but cool, while Polish-German relations were normal and occasionally friendly.
Military capabilities
The budget for the year 1934-35 allocated 762 million zlotych for the army, about 32% of the total. It provided for an effective strength of 7,905 officers, 37,000 professional soldiers, and 211,110 militia soldiers. Apart from the army, the budget provided 105 million zlotych for police troops consisting of 774 officers and 28,592 men. By 1939 Poland had a large army, with 283,000 on active duty, in 37 infantry divisions, 11 cavalry brigades, and two armored brigades, plus artillery units. Another 700,000 men served in the reserves. A major problem was lack of funds. The limited defense budget allowed minimal mechanization; most weapons were produced in Poland, but the production rate was low (7TP
The 7TP (''siedmiotonowy polski'' - 7-tonne Polish) was a Polish light tank of the Second World War. It was developed from the British Vickers 6-ton. A standard tank of the Polish Army during the 1939 Invasion of Poland, its production did not e ...
tank is a prime example), and foreign exchange was scarce.
The fact that Poland was halfway through the rearming process that was to end in 1942 did not help. Ten divisions were never mobilized. The cancellation of the mobilization, under the pressure from France and Great Britain, and restarting the mobilization less than a week later created confusion. Moreover, not only did the German military and civilian volunteers commit war crimes against the ethnic Poles and Polish Jews, they spread rumors of massive ethnic cleansing which led thousands of people to flee the German advance and made military maneuver difficult.


 Poland did have PZL, the state aviation company that made good planes. In 1931 it developed the PZL P.11, the most advanced fighter in the world of the early 1930s. In the mid-1930s its successor the P-24 was even better armed and faster, but Poland exported it to earn currency, forcing the use of semi-obsolete PZL P.11 and a couple of dozen old PZL P.7 fighters. They were no match against the German Messerschmitt 109 which could fly higher, was better armed, and flew 100 km/h faster. In spite of the shortcomings, at least 110 victories were credited to the P.11 for the loss of about 30 of their own. The
Poland did have PZL, the state aviation company that made good planes. In 1931 it developed the PZL P.11, the most advanced fighter in the world of the early 1930s. In the mid-1930s its successor the P-24 was even better armed and faster, but Poland exported it to earn currency, forcing the use of semi-obsolete PZL P.11 and a couple of dozen old PZL P.7 fighters. They were no match against the German Messerschmitt 109 which could fly higher, was better armed, and flew 100 km/h faster. In spite of the shortcomings, at least 110 victories were credited to the P.11 for the loss of about 30 of their own. The PZL.37 Łoś
The PZL.37 ''Łoś'' (''moose'') was a Polish twin-engined medium bomber designed and manufactured by national aircraft company PZL. It is also known as "PZL P-37" or "PZL P.37", but the letter "P" was generally reserved for fighters of Zygmunt Pu� ...
was an excellent twin-engine medium bomber; Poland had 36 ready-to-fight when the war started. In 1939 Poland had 390 combat planes that were mostly obsolescent. Germany had 2800 new fighter planes plus bombers and transports.
The Poles, in spite of their desperate situation, managed to win two battles against the invading Soviets, including one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
where the Soviet infantry was charging the Polish positions marching shoulder to shoulder, making them into an extremely easy target to the machine guns, and some of the Soviet POW's switched sides to the Polish.
Poles broke the early diplomatic version of Enigma cipher and transferred the results to France and the United Kingdom.
In spite of its shortcomings, the Polish military can easily be ranked in the top 10 strongest national militaries as of 1939; not because the Polish military was so great, but because other national military forces were so weak and backward. Zaloga and Madej point out, in "The Polish Campaign 1939" that Poland had one of the largest tank forces on Earth, as of 1939 bigger than the tank force of the US.
The relative strength of the Polish armed forces and the fear of the Polish military might be shown by Lithuania ( 1938 Polish ultimatum to Lithuania) made the Polish government's propaganda believable to the public. The Polish government had no choice, but to claim that an attack either by the Germans or by the Soviets would have been successfully repelled. The Polish government could not afford a capitulation of the Polish public because of the industrialization projects such as Central Industrial Region (Poland), nearly finished by early 1939, and the projects that were to follow it.
Foreign policy 1935–39
After the death of Piłsudski in May 1935, policies in Poland were set by five senior officials, including PresidentIgnacy Mościcki
Ignacy Mościcki (; 1 December 18672 October 1946) was a Polish chemist and politician who was the country's president from 1926 to 1939. He was the longest serving president in Polish history. Mościcki was the President of Poland when Germany ...
; Vice-President Eugeniusz Kwiatkowski; the Premier, Felicjan Sławoj Składkowski; and Marshal Edward Smigly-Rydz, the Commander-in-Chief of the army. Foreign policy was the exclusive domain of the Foreign Minister, Colonel Józef Beck. Elections were held but there was no democracy and the Sejm was merely a rubber stamp. Watt notes that these men had emerged victorious from their struggles for independence and had never known conquest. "Courage, flair, heroism, devouring ambition, all these they had in abundance; realism and worst-case analysis, let alone defeatism or appeasement, were alien to them entirely."
Poland's dream of leading a bloc of neutral nations in Eastern Europe collapsed after 1933 with the advent of Hitler's openly expansionist Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
regime in Germany and the obvious warning of France's desire to resist Germany's expansion. Piłsudski retained the French connection but had progressively less faith in its usefulness. Hitler's long-term goals included annexing Polish territories and subordinating the remaining parts of Poland, an idea that he revealed to his closest circle already in 1933 Poland's solution was a policy of normal relations with both Germany and the Soviet Union but alliance with neither (also described as 'the policy of equal distance' or 'equilibrium'). Accordingly, the Polish leadership rejected German proposals of cooperation against Russia. At the same time, Beck's goal was 'to avoid isolated confrontation with Germany as long as this was possible'. The policy rested on two pillars: the non-aggression pacts signed by Poland with Germany and the USSR.
Following a border incident in March 1938, Poland presented an ultimatum to Lithuania, demanding the re-establishment of diplomatic relations between Poland and Lithuania and the previously closed border with Poland to be reopened. Faced with the threat of war, the Lithuanian government accepted the Polish demands. In October 1938, the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
, with British and French approval, allowed Germany to take over areas of Czechoslovakia with a significant German minority, the so-called Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the ...
. Poland had long been hostile to Czechoslovakia and now sided with Germany. Poland demanded that Czechoslovakia give up the Teschen, where Poles made about 70% of inhabitants, or otherwise Poland threatened to take it by force. Faced with an ultimatum from both Poland and Germany, Czechoslovakia gave up the area, which was annexed by Poland on October 2, 1938.
In early 1939, Germany invaded the rest of Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, which, in March 1939, then ceased to exist. Germany had demanded that Poland join the Anti-Comintern Pact as a satellite state of Germany. Germany demanded an extraterritorial highway connecting Germany proper with Danzig and then East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, which would cut off Poland from the sea and its main trade route to which Poland refused. Germany also pressed for the incorporation of Danzig, a Nazi ruled city-state with a 90% German population that had been separated from Germany in 1920 and functioning as a Free City Free city may refer to: Historical places
* Free city (antiquity) a self-governed city during the Hellenistic and Roman Imperial eras
* Free imperial city, self-governed city in the Holy Roman Empire subordinate only to the emperor
** Free City of ...
in a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
with Poland ever since.
After it rejected German territorial demands regarding Danzig and Gdańsk Pomerania
Gdańsk Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze Gdańskie), csb, Gduńsczim Pòmòrzã, german: Danziger Pommern) is a geographical region within Pomerelia in northern and northwestern Poland, covering the bulk of Pomeranian Voivodeship.
It forms a part and ...
, Poland's position was steadily weakening as other nations such as Hungary and Romania gravitated toward Germany's orbit. Poland was at the time allied with Romania and France.
Two critical developments caught Poland by surprise. At the end of March 1939, Britain and France announced that if Germany invaded Poland they would declare war. In terms of helping Poland in an actual war, everyone realized they could do very little. The hope was that the threat of a two-front war would deter Germany, especially since it had to worry about the role of the Soviet Union. Hitler thought Britain and France were bluffing, but he handled the Soviet problem in late August, by a stunning agreement with Stalin in what amounted to a friendly alliance, which included secret provisions to partition Poland—and indeed divide up much of eastern Europe The British and French offer was not a bluff—they declared war on Germany when it invaded Poland, but neither was in a position to provide serious help. Poland itself had a million-man army (and another million in the reserves) but fell far short in terms of training, airpower, artillery, tanks, machine guns, radios, and trucks. The Polish military budget was about 2% of Germany's; its commanding general Marshal Smigly-Rydz was not well prepared for the challenge.
Polish Corridor and Danzig
The Germans wanted restoration of the pre-Versailles Treaty borders and so they launched new demands on Poland. They insisted on a plebiscite to determine the ownership of the " Polish corridor". Only those living in the corridor prior to 1918 would be allowed to vote. The proposal called for a subsequent population exchange that would move all Germans, then in Poland, out of the final region declared to be "Poland". The same would occur for all Poles living in what was declared, after the vote, to be "Germany". Danzig was to become part of Germany regardless of the vote, but if Germany lost, it was still guaranteed access to East Prussia through an autobahn system that it would administer, stretching from Germany proper to Danzig to East Prussia. If Poland lost the vote, the corridor would go to Germany and the seaport ofGdynia
Gdynia ( ; ; german: Gdingen (currently), (1939–1945); csb, Gdiniô, , , ) is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With a population of 243,918, it is the 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in th ...
would become a Polish exclave with a route connecting Poland with Gdynia. After the British-French guarantee of support for Poland was announced on April 3, negotiations over Danzig ended. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The issue of Danzig was not the cause of the German invasion; Hitler told his generals in May 1939: “It is not Danzig that is at stake. For us, it is a matter of expanding our living space in the east and making food supplies secure.” The total destruction of the Polish state, Polish culture, and indeed the Polish population had become Hitler's main objective. He wanted the agricultural land to resettle German farmers.Anita J. Prazmowska, “Poland” in The Origins of World War Two: The Debate Continues ed. by Robert Boyce and Joseph A. Maiolo (2003), p. 155-164.
See also
*1934 flood in Poland
1934 flood in Poland ( pl, Powódź w Polsce, 1934) was the biggest flood in the Second Polish Republic. It began with heavy rains in the Dunajec river basin, which took place between 13 and 17 July 1934. In the following days, the flood spread t ...
* Independent Operational Group Silesia
* Prometheism
Prometheism or Prometheanism ( Polish: ''Prometeizm'') was a political project initiated by Józef Piłsudski, a principal statesman of the Second Polish Republic from 1918 to 1935. Its aim was to weaken the Russian Empire and its successor stat ...
* Provisional Polish Revolutionary Committee
Notes
References
*Poland
Further reading
Surveys
* Berend, Iván T. ''Decades of Crisis: Central and Eastern Europe before World War II'' (1998), comparisons with other countries *Biskupski, M. B. ''The History of Poland.'' Greenwood, 2000. 264 pponline edition
*''The Cambridge History of Poland'', (2 vols., Cambridge University Press, 1941) covers 1697–1935 *
Davies, Norman
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a Welsh-Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Professo ...
. '' God's Playground. A History of Poland. Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present''. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1981.
*Davies, Norman. ''Heart of Europe: A Short History of Poland.'' Oxford University Press, 1984. 511 pp.
*Frucht, Richard. ''Encyclopedia of Eastern Europe: From the Congress of Vienna to the Fall of Communism'' Garland Pub., 200online edition
*Lerski, George J. ''Historical Dictionary of Poland, 966–1945.'' Greenwood, 1996. 750 pp
online edition
*Leslie, R. F. et al. ''The History of Poland since 1863.'' Cambridge U. Press, 1980. 494 pp. *Lukowski, Jerzy and Zawadzki, Hubert. ''A Concise History of Poland.'' Cambridge U. Press, 2nd ed 2006. 408pp. *Pogonowski, Iwo Cyprian. ''Poland: A Historical Atlas.'' Hippocrene, 1987. 321 pp. new designed maps *Sanford, George. ''Historical Dictionary of Poland.'' Scarecrow Press, 2003. 291 pp. * Stachura, Peter D. ''Poland, 1918-1945: An Interpretive and Documentary History of the Second Republic'' (2004
online
* Stachura, Peter D. ed. ''Poland Between the Wars, 1918-1939'' (1998) essays by scholars *Watt, Richard M. ''Bitter Glory: Poland and Its Fate, 1918-1939'' (1998), comprehensive survey
Politics and diplomacy
* Cienciala, Anna M., and Titus Komarnicki. ''From Versailles to Locarno: keys to Polish foreign policy, 1919–25'' (University Press of Kansas, 1984online
* Davies, Norman. ''White Eagle, Red Star: The Polish-Soviet War 1919-1920 and The Miracle on the Vistula'' (2003) *Drzewieniecki, Walter M. "The Polish Army on the Eve of World War II," ''Polish Review'' (1981) 26#3 pp 54-64
in JSTOR
* Garlicki, Andrzej. ''Józef Piłsudski, 1867-1935'' (New York: Scolar Press 1995), scholarly biography; one-vol version of 4 vol Polish edition * Hetherington, Peter. ''Unvanquished: Joseph Pilsudski, Resurrected Poland, and the Struggle for Eastern Europe'' (2012) 752pp * Jędrzejewicz, W. ''Piłsudski. A Life for Poland'' (1982), scholarly biography * Karski, Jan. ''The great powers and Poland: From Versailles to Yalta'' (2014) * Kochanski, Halik. ''The Eagle Unbowed: Poland and the Poles in the Second World War'' (2012) * Korbel, Josef. ''Poland Between East and West: Soviet and German Diplomacy toward Poland, 1919–1933'' (Princeton University Press, 1963
online
* Polonsky, A. ''Politics in Independent Poland, 1921-1939: The Crisis of Constitutional Government'' (1972) * Remak, Joachim
''The Nazi Years: A Documentary History''
Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 1990. Originally published Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1969. . * Riekhoff, H. von. '' German-Polish Relations, 1918-1933'' (Johns Hopkins University Press 1971) * Rothschild, J. ''Piłsudski's Coup d'État'' (New York: Columbia University Press 1966) * Seidner, Stanley S. "The Camp of National Unity: An Experiment in Domestic Consolidation," ''The Polish Review'' 20 (2-3): 231-236 * Shirer, William L.br>''The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich: A History of Nazi Germany''
New York: Simon and Schuster, 2011. Originally published New York: Simon and Schuster, 1950. . * Wandycz, P. S. ''Polish Diplomacy 1914-1945: Aims and Achievements'' (1988) * Wandycz, P. S. ''Soviet-Polish Relations, 1917-1921'' (Harvard University Press 1969) * Wandycz, P. S. ''The United States and Poland'' (1980) * Williamson, David G. ''Poland Betrayed: The Nazi-soviet Invasions of 1939'' (2011), pp 1-62 *Zamoyski, Adam. ''Warsaw 1920: Lenin's Failed Conquest of Europe'' (2008)
Social and economic topics
* Abramsky, C. et al. eds. ''The Jews in Poland'' (Oxford: Blackwell 1986) * Bartoszewski, W. and Polonsky, A., eds. ''The Jews in Warsaw. A History'' (Oxford: Blackwell 1991) * Blanke, R. ''Orphans of Versailles. The Germans in Western Poland, 1918-1939'' (1993) * Gutman, Y. et al. eds. ''The Jews of Poland Between Two World Wars'' (1989). * Heller, C. S. ''On the Edge of Destruction. Jews of Poland Between the Two World Wars'' (1977) *Hoffman, E. ''Shtetl. The Life and Death of a Small Town and the World of Polish Jews'' (1999). * Landau, Z. and Tomaszewski, J. ''The Polish Economy in the Twentieth Century'' (Routledge, 1985) * Olszewski, A. K. ''An Outline of Polish Art and Architecture, 1890-1980'' (Warsaw: Interpress 1989.) * Roszkowski, Wojciech. ''Landowners in Poland, 1918-1939'' (Cambridge University Press, 1991) * Roszkowski, Wojciech. "Large Estates and Small Farms in the Polish Agrarian Economy between the Wars (1918-1939)," ''Journal of European Economic History'' (1987) 16#1 pp 75-88 * Taylor, J. J. ''The Economic Development of Poland, 1919-1950'' (Cornell University Press 1952) * Thomas, William I., and Florian Znaniecki. ''The Polish Peasant in Europe and America'' (2 vol. 1918); classic sociological study* Wynot, E. D. ''Warsaw Between the Wars. Profile of the Capital City in a Developing Land, 1918-1939'' (1983) * Żółtowski, A. ''Border of Europe. A Study of the Polish Eastern Provinces'' (London: Hollis & Carter 1950)
Eva Plach, "Dogs and dog breeding in interwar Poland,"
Canadian Slavonic Papers 60, no 3-4
Historiography
*Kenney, Padraic. “After the Blank Spots Are Filled: Recent Perspectives on Modern Poland,” ''Journal of Modern History'' (2007) 79#1 pp 134–61in JSTOR
*Polonsky, Antony. "The History of Inter-War Poland Today," ''Survey'' (1970) pp143–159.
Primary sources
1932 ''Statistical Yearbook,'' (''Mały rocznik statystyczny 1932'')
complete text (in Polish)
External links
Commonwealth of Diverse Cultures: Poland's Heritage
Old maps of Poland from Hipkiss' Scanned Old Maps
Poland Catholic Church and Rome
Polish Cinema's Golden Age: The Glamour & Progress Of Poland's Inter-War Films
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Poland (1918-1939) .
1918
This year is noted for the end of the First World War, on the eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month, as well as for the Spanish flu pandemic that killed 50–100 million people worldwide.
Events
Below, the events ...
1918
This year is noted for the end of the First World War, on the eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month, as well as for the Spanish flu pandemic that killed 50–100 million people worldwide.
Events
Below, the events ...
1919
1920
Events January
* January 1
** Polish–Soviet War in 1920: The Russian Red Army increases its troops along the Polish border from 4 divisions to 20.
** Kauniainen, completely surrounded by the city of Espoo, secedes from Espoo as its own ma ...
1930
Events
January
* January 15 – The Moon moves into its nearest point to Earth, called perigee, at the same time as its fullest phase of the Lunar Cycle. This is the closest moon distance at in recent history, and the next one will b ...
.1918
20th century in Poland
he:היסטוריה של פולין: הרפובליקה השנייה