History of Hungary before the Hungarians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of Hungary before the
 The oldest
The oldest
 In 375 AD, the nomadic
In 375 AD, the nomadic

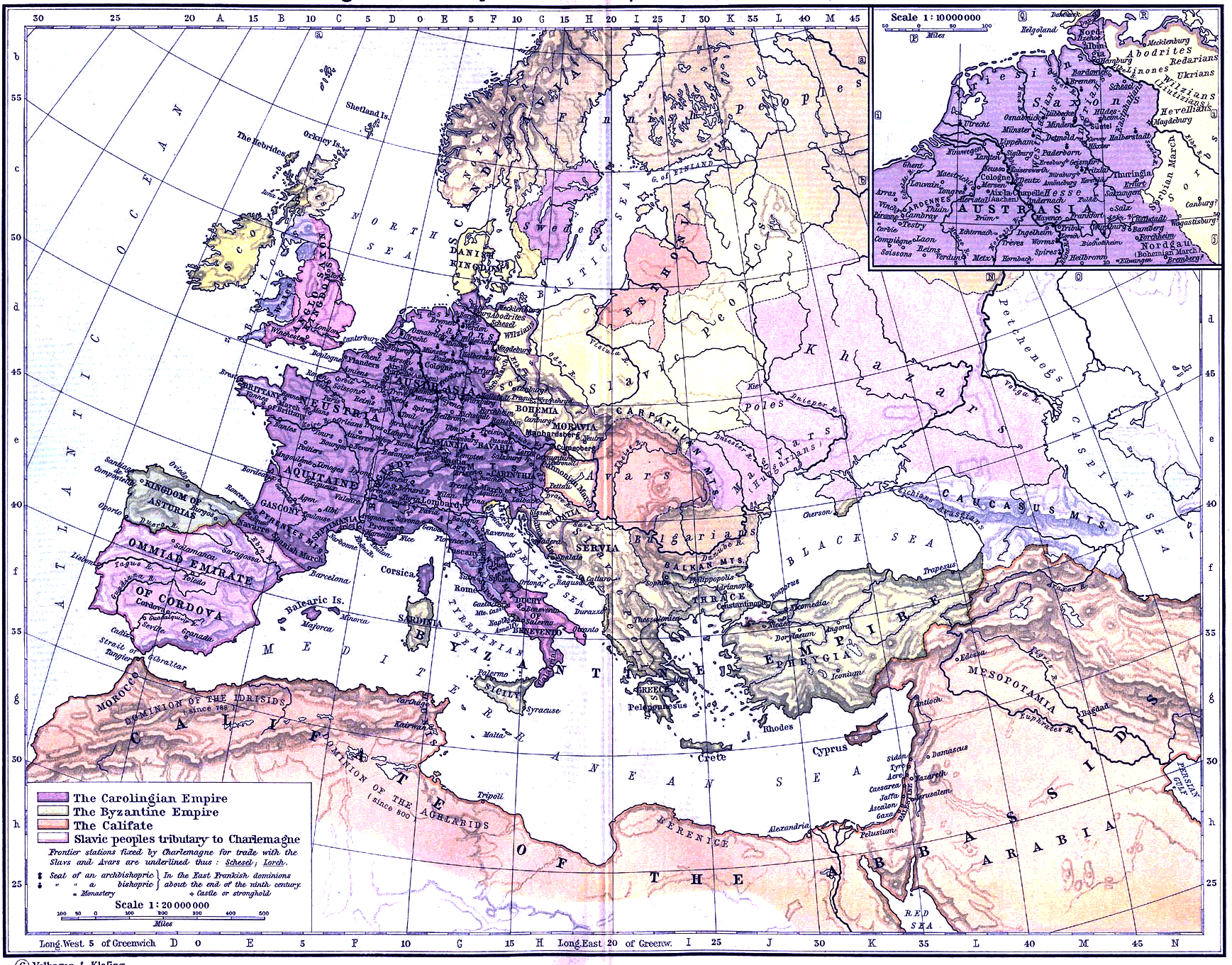 Roman influence in Pannonia had begun to decline as early as the arrival of the Huns in the 4th century. The remaining romanized Pannonians created at the end of the 5th century the Keszthely culture, around
Roman influence in Pannonia had begun to decline as early as the arrival of the Huns in the 4th century. The remaining romanized Pannonians created at the end of the 5th century the Keszthely culture, around
A History of Hungary- By the Hungarian Ministry of TourismHungary Before the Hungarians
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pannonian Basin Before The Hungarians Hungarian prehistory
Hungarian conquest Hungarian may refer to:
* Hungary, a country in Central Europe
* Kingdom of Hungary, state of Hungary, existing between 1000 and 1946
* Hungarians, ethnic groups in Hungary
* Hungarian algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm for solving the assignm ...
spans the time period before the Hungarian conquest in the 9th century of the territories that would become the Principality of Hungary
The (Grand) Principality of HungaryS. Wise BauerThe history of the medieval world: from the conversion of Constantine to the First Crusade W. W. Norton & Company, 2010, p. 586George H. HodosThe East-Central European region: an historical outline ...
and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
.
The relatively warm and fertile Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large Sedimentary basin, basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The Geomorphology, geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewh ...
has been settled since around 500,000 years ago. The first known traces belong to the Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' i ...
, with scarce or nonexistent evidence of human presence until the Neanderthals around 100,000 years ago. Anatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish '' Homo sapiens'' (the only extant Hominina species) that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from exti ...
arrived at the Carpathian Basin before and belonged to the Aurignacian group. The rest of the Stone Age is marked by minimal or not-yet-processed archeological evidence, with the exception of the Linear Pottery culture—the "garden type civilization" that introduced agriculture to the Carpathian Basin.
During the Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
s, three significant groups were the Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
, the Makó and the Ottomány (to not be confused with Ottoman Turks) cultures. The major improvement was obviously metalworking, but the Baden culture also brought about cremation and even long-distance trade with remote areas such as the Baltic or Iran. Turbulent changes during the late Bronze Age gave an end to the native, relatively advanced civilization, and the beginning of the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
saw mass immigration of Indo-European nomads believed to be of ancient Iranian
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
ancestry. However, as the time went on, the Carpathian Basin attracted immigration from all directions: the Hallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of Hallstätter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut ...
Celts from the west were the first and most influential at around 750 BC, the mysterious Sigynnae
The Sigynnae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an obscure nomadic people of antiquity who were part of the Scythian cultures.
Location
The Sigynnae were a nomadic people of uncertain, but possibly Iranian or pre-Iranian origin, who lived north of t ...
around 500 BC, the Pannonians
This is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria ( grc-gre, Ἰλλυρία; la, Illyria). The name ''Illyrians'' seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greeks ...
—an Illyrian tribe gave the future Roman province its name, while the very east became occupied by other Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
, Iranian and later Celtic tribes. Before 100 BC, most of the area was occupied by various Celtic or celticized people, such as the successor
Successor may refer to:
* An entity that comes after another (see Succession (disambiguation))
Film and TV
* ''The Successor'' (film), a 1996 film including Laura Girling
* ''The Successor'' (TV program), a 2007 Israeli television program Musi ...
of the Halstatt culture, the Taurisci, the Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul ( Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom ...
and the Pannonians.
The Roman era began with several attacks between 156 and 70 BC, but their gradual conquest was interrupted by the Dacian king Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
, whose kingdom stretched as far as today's Slovakia at its greatest extent. However, the period of Dacian dominance did not last long, and by 9 BC the Romans had subjugated the entire area and made it into the Pannonia subprovince of province Illyricum and eventually Pannonia province. Under Roman rule, many contemporary cities such as Buda, Győr
Győr ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Győr-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia region, and – halfway between Budapest and Vienna – situated on one of ...
and Sopron
Sopron (; german: Ödenburg, ; sl, Šopron) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő.
History
Ancient times-13th century
When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a ...
were founded and the population romanized, and culture as a whole flourished. Roman emperors sometimes tolerated other tribes settling in the territory, such as the Iazyges
The Iazyges (), singular Ἰάζυξ. were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between th ...
or Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
. Christianity spread during the fourth century AD, when it became the state religion.
In the first years of the Age of Migration, the Carpathian Basin was settled by the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
who by 430 had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe centered in the basin. Numerous Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
lived alongside them such as the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Or ...
, Quadi or Gepidi, the last of which stayed the longest and whose peoples incorporated into the Hunnic Empire. The next wave of migration during the sixth century saw other Germanic tribes, the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
and Heruli
The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Roman authors as one of several " Scythian" groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking ...
overpower the Gepidi, only to be ousted by another major nomadic tribe, the Avars. Like the Huns, the Avars established an empire there and posed a significant threat to their neighbours but were eventually defeated by both neighbouring states and internal strife (around 800). However, Avar population remained quite steady until the Hungarian conquest. The territory became divided between East Francia and First Bulgarian Empire with the northeastern part under Moravian Slavic Principality of Nitra
The Principality of Nitra ( sk, Nitrianske kniežatstvo, Nitriansko, Nitrava, lit=Duchy of Nitra, Nitravia, Nitrava; hu, Nyitrai Fejedelemség), also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements th ...
. This state lasted until the arrival of the Magyar tribes in the late 9th century.
Prehistory
Stone Age
archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology a ...
which yielded evidence of human presence—human bones, pebble tools and kitchen refuse—in the Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large Sedimentary basin, basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The Geomorphology, geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewh ...
was excavated at Vértesszőlős in Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( hu, Dunántúl; german: Transdanubien, hr, Prekodunavlje or ', sk, Zadunajsko :sk:Zadunajsko) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Trad ...
in the 1960s. The Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. Th ...
site was situated in calcareous tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
basins with a diameter of that the nearby warm springs had formed. The site at Vértesszőlős was occupied five times between about 500,000 and 250,000 years ago.The occipital bone of an adult male ''Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' i ...
'', who is now known as " Samu", and a child's milk tooth were found. Tools of quartzite and silex
Silex is any of various forms of ground stone. In modern contexts the word refers to a finely ground, nearly pure form of silica or silicate.
In the late 16th century, it meant powdered or ground up "flints" (i.e. stones, generally meaning the c ...
pebbles collected at the nearby river were also found, as well as a fireplace with hearths made from crushed animal bones, with remains of wild horses, aurochs, bisons, red deer, deer, wolves, bears, and saber-toothed cats.
There is a gap in the archaeological record, with no evidence of human presence between about 250,000 to 100,000 years ago. The earliest Middle Palaeolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Pale ...
sites are dated to the transitory period between the Riss
The Riss (german: Riß) is a small river in Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, right tributary of the Danube. Its source is in Upper Swabia, between Bad Waldsee and Bad Schussenried. It flows north, through the town of Biberach an der Ri ...
and Würm
The Würm is a river in Bavaria, Germany, right tributary of the Amper. The length of the river is , or including the ''Steinbach'', the main feed of Lake Starnberg. It drains the overflow from Lake Starnberg and flows swiftly through the villag ...
glacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
s around 100,000 years ago. Remains of skulls show that Neanderthals inhabited northeastern Transdanubia and the Bükk Mountains
The Bükk Mountains () are a section of the North Hungarian Mountains of the Inner Western Carpathians. Much of the area is included in the Bükk National Park.
Geography
Although Kékes, the highest point in Hungary, is not here but in the n ...
during this period. The Neanderthals who lived in the region of Érd
Érd (; german: Hanselbeck; hr, Andzabeg) is a town in Pest County, Budapest metropolitan area, Hungary. It is a city with county rights.
History
The area has been inhabited since ancient times. Archaeological findings indicate that prehistoric ...
between around 100,000 and 40,000 BC used quartzite pebbles. They led hunting expeditions as far as the Gerecse Hills for cave bear
The cave bear (''Ursus spelaeus'') is a prehistoric species of bear that lived in Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene and became extinct about 24,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum.
Both the word "cave" and the scientific name ' ...
s, wild horses, woolly rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a me ...
and other animals. A Neanderthal community settled near the hot-water springs at Tata around 50,000 BC. They hunted mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks an ...
calves, brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear species found across Eurasia and North America. In North America, the populations of brown bears are called grizzly bears, while the subspecies that inhabits the Kodiak Islands of Alaska is ...
, wild horses and reed deer. A flat oval object made from mammoth tooth lamella
Lamella (plural lamellae) means a small plate or flake in Latin, and in English may refer to:
Biology
* Lamella (mycology), a papery rib beneath a mushroom cap
* Lamella (botany)
* Lamella (surface anatomy), a plate-like structure in an animal
...
, similar to the Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
' ritual ''tjurunga
A Tjurunga, also spelt Churinga and Tjuringa, is an object considered to be of religious significance by Central Australian Aboriginal people of the Arrernte (Aranda, Arunta) groups. Tjurunga often had a wide and indeterminate native significa ...
'', was found at the site. A third group of Neanderthals settled in the caves of the Pilis
Pilis () is a town in Pest County, Hungary.
History
The town was inhabited in prehistoric times, but was abandoned at the end of the Roman rule. Pilis was then first mentioned in 1326. It was destroyed during the Ottoman rule in the 16th cen ...
, Vértes and Gerecse Hills. They regularly visited the Bükk Mountains and the White Carpathians
The White Carpathians ( cs, Bílé Karpaty; sk, Biele Karpaty; german: Weiße Karpaten; hu, Fehér-Kárpátok) are a mountain range on the border of the Czech Republic and Slovakia, part of the Carpathians.
They are part of the Slovak-Moravian ...
to collect raw material for their tools. Ibex
An ibex (plural ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa ...
was the main prey of the Neanderthals of the Middle Palaeolothic sites in the Bükk Mountains. In addition to local stone, they used raw material from the White Carpathians and the region of the river Prut
The Prut (also spelled in English as Pruth; , uk, Прут) is a long river in Eastern Europe. It is a left tributary of the Danube. In part of its course it forms Romania's border with Moldova and Ukraine.
Characteristics
The Prut originates ...
. Archaeological research suggest that the Neanderthals disappeared from the northern regions of the Carpathian Basin around 40,000 years ago.
Latest research shows that the first communities of anatomically modern humans
Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish '' Homo sapiens'' (the only extant Hominina species) that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from exti ...
came to the Carpathian Basin between . Consequently, the cohabitation of the Neanderthals and modern humans in the territory, which was assumed by earlier scholarship, cannot be proved. The Aurignacian group of modern humans who settled in the Istállóskő Cave primarily used tools made of bones and used the cave as a seasonal camping site during their hunts for chamois, red deer, reindeer and other local animals. Their tools made of stone suggest that they came to the Bükk Mountains from the northern Carpathians and the region of the Prut. According to a scholarly view, a local archaeological culture—the " Szeleta culture"—can be distinguished, which represents a transition between the Middle and Upper Palaeolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
and was featured by leaf-shaped spearheads from around . However, the existence of a distinct archaeological culture is not unanimously accepted by specialists, because most prehistoric tools from the eponymous Szeleta Cave (in the eastern side of the Bükk) are similar to those found in the Upper Palaeolithic sites of Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
.
Attracted by the rich fauna of the lowlands in the centre of the Carpathian Basin, groups of "Gravettian
The Gravettian was an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by ...
" hunters penetrated into the territory from the west about 27,000 years ago. The central grasslands were not covered by ice even at the maximum of the last glaciation (around 20,000 years ago). The new arrivals settled on hilltops along the rivers Hornád
Hornád ( Slovak, ) or Hernád ( Hungarian, ) is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary.
It is a tributary to the river Slaná (Sajo). The source of the Hornád is the eastern slopes of Kráľova hoľa hill, south of Šuňava.
...
and Bodrog
The Bodrog is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary. It is a tributary to the river Tisza. The Bodrog is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ondava and Latorica near Zemplín in eastern Slovakia. It crosses the Slovak–H ...
. They primarily hunted mammoth and elk and used stone blades to work skin, bone, antler and wood. Artistic finds are rare; for instance, a disc with serrated edges, which was made of polished limestone, was found at Bodrogkeresztúr. A second wave of "Gravettians" arrived during the warmer period that began about 20,000 years ago. They primarily made their tools from pebbles, similar to Lower Palaeolithic communities, but no continuity between the two groups can be detected. The remains of semi-sunken huts were excavated at a site on a hilltop near Sárvár
Sárvár (german: Kotenburg or ; la, Bassiana; sl, Mala Sela) is a town in Vas County, Hungary.
Sárvár lies on the banks of the River Rába at Kemeneshát. The population is nearly 16,000. The town has become a tourist centre of internatio ...
where reindeer bones were also found. The site also yielded a perforated (but not decorated) reindeer antler. In addition to permanent settlements, the Gravettian hunters' temporary camps were unearthed in the plains of the Jászság
Jászság ("Jaszygia", la, Jazigia) is a historical, ethnographical and geographical region in Hungary. Its territory is situated in the north-western part of the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. The main town in the region is Jászberény. Já ...
and around Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also other alternative names) is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat of Csongrád-Csanád county. The University of Szeged is one of the m ...
. About 15,000 years ago, new hunters came to the territory; their best-known settlements were situated in northeastern Transdanubia. A pendant made of wolf tooth, a pair of red deer teeth and similar finds suggest that these hunters wore ornaments.
Mesolithic sites are rare but start to appear after systematic surveys, especially in the Jászság area.
Neolithic
Neolithic settlement begins with the CrişKörös culture
The Körös () or Criș () ( German: ''Kreisch'') is a river in eastern Hungary and western Romania. Its length is from the confluence of its two source rivers Fehér-Körös ('' Crișul Alb'') and Fekete-Körös ('' Crișul Negru'') to its out ...
, carbon-dated to around 6200 BC. In the Middle Neolithic, the Western Linear Pottery culture in Transdanubia and the Satu-Mare (Szatmar) and Eastern Linear pottery (called "Alföld Linear Pottery" in Hungary) in the east, developed into Želiezovce
Želiezovce ( hu, Zselíz, (formerly) Zseliz (till 1895), Zeliz, Zeléz, german: Zelis (rare)) is a town in Slovakia in the Nitra Region in the Levice District, near the Hron river.
Districts
* Jarok ( hu, Nyitra-Ivánka)
* Karolína
* Mi ...
(Slovakia) and Szakálhát and Bükk, respectively. The Late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Tisza culture
The Tisza culture is a Neolithic archaeological culture of the Alföld plain in modern-day Hungary, Western Romania, Eastern Slovakia, and Ukrainian Zakarpattia Oblast in Central Europe. The culture is dated to between 4900 BCE and 4500/4400 BCE. ...
is followed by the Eneolithic
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often v ...
Tiszapolgár and Bodrogkeresztúr cultures.
Copper & Bronze Ages
TheBaden culture
The Baden culture was a Chalcolithic culture from 3520–2690 BC.
It was found in Central and Southeast Europe, and is in particular known from Moravia (Czech Republic), Hungary, southern Poland, Slovakia, northern Croatia and eastern Austria. I ...
( circa 3600 – 2800 BCE) was a Copper Age (Chalcolithic) material culture found in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
. In Hungarian and Slovakian sites, cremated
Cremation is a method of final disposition of a dead body through burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an open-air pyre i ...
human remains were often placed in anthropomorphic urns, whereas in Nitriansky Hrádok Nitriansky Hrádok is a district of a town of Šurany, Slovakia. This settlement was annexed to Šurany in 1976.Official website of Šuran ...
, a mass grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of execution, although an exact ...
has been found. The only known cemetery with individual graves was found in an early Baden ("Boleráz phase") site is Pilismarót, in Komárom-Esztergom County, which also contained a few examples of goods possibly exported from the Stroke-ornamented ware culture
The Stroke-ornamented ware (culture) or (German) Stichbandkeramik (abbr. STK or STbK), Stroked Pottery culture, Danubian Ib culture of V. Gordon Childe, or Middle Danubian culture is the successor of the Linear Pottery culture, a major archae ...
(centred in what is now Poland). The Baden culture is claimed by some scholars to have been an early example of an Indo-European culture
Proto-Indo-European society is the reconstructed culture of Proto-Indo-Europeans, the ancient speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language, ancestor of all modern Indo-European languages.
Scientific approaches
Many of the modern ideas in this ...
in Central Europe.
Makó (a town in modern Csongrád County
Csongrád ( ro, Ciongrad; tr, Conğrad sr, Чонград, Čongrad, archaically also ''Црноград/Crnograd'') is a town in Csongrád County in southern Hungary.
History
At the time of the Hungarian Conquest (the end of 9th century) th ...
) lends its name to a 3rd millennium BCE material culture (also known as the Makó-Caka or Kosihy-Caka culture) and other archaeological finds from the Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
/Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
s. There are more than 180 registered archaeological sites around Makó, the most important of which are at Kiszombor. The Makó culture is often regarded as a subset or offshoot of the broader Vučedol culture, centred on Vukovar
Vukovar () ( sr-Cyrl, Вуковар, hu, Vukovár, german: Wukowar) is a city in Croatia, in the eastern region of Slavonia. It contains Croatia's largest river port, located at the confluence of the Vuka and the Danube. Vukovar is the seat of ...
). While there is no consensus on the cultural affiliations of the Makó sites, kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central As ...
s, buckles, jewelry and equestrian equipment found near Makó may suggest links to nomads migrating from the Eurasian steppe. In later phases, these sites contain very large numbers of objects associated with the Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
s.
The Ottomány culture (also known as the Otomani-Füzesabony
Füzesabony is a town in Heves County, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to t ...
culture) was a Bronze Age culture (circa 2100–1400 BC) stretching from eastern Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
and western Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
to southeast Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and western Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In ...
exported on prehistoric trade routes from the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
is often found at Ottomány sites and the people of this culture appear to have held a central part of the so-called "Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade.
...
", which connected the powerful and rising ancient Mediterranean
The history of the Mediterranean region and of the cultures and people of the Mediterranean Basin is important for understanding the origin and development of the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Canaanite, Phoenician, Hebrew, Carthaginian, Minoan, Gre ...
states to the south-eastern Baltic region. The Ottomány culture was succeeded by the Tumulus culture
__NOTOC__
The Tumulus culture (German::de:Mittlere Bronzezeit, ''Hügelgräberkultur'') dominated Central Europe during the European Bronze Age, Middle Bronze Age ( 1600 to 1300 BC).
It was the descendant of the Unetice culture. Its heartl ...
and Urnfield culture
The Urnfield culture ( 1300 BC – 750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and p ...
.
Iron Age
In the Carpathian Basin, theIron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
commenced around 800 BC, when a new population moved into the territory and took possession of the former population's centers fortified by earthworks. The new population may have consisted of ancient Iranian tribes that had seceded from the federation of the tribes living under the suzerainty of the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
. They were equestrian nomads
The Eurasian nomads were a large group of nomadic peoples from the Eurasian Steppe, who often appear in history as invaders of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, and South Asia.
A nomad is a member of people having no permanent ...
and formed the people of the Mezőcsát culture who used tools and weapons made of iron. They extended their rule over what are now the Great Hungarian Plain
The Great Hungarian Plain (also known as Alföld or Great Alföld, hu, Alföld or ) is a plain occupying the majority of the modern territory of Hungary. It is the largest part of the wider Pannonian Plain. (However, the Great Hungarian plain ...
and the eastern parts of Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( hu, Dunántúl; german: Transdanubien, hr, Prekodunavlje or ', sk, Zadunajsko :sk:Zadunajsko) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Trad ...
.
Around 750 BC, people of the Hallstatt culture gradually occupied the western parts of Transdanubia, but the earlier population of the territory also survived and thus the two archaeological cultures existed together for centuries. The people of the Hallstatt culture took over the former population's fortifications (''e.g.'', in Velem, Celldömölk, Tihany
Tihany /ˈtihɒɲ/ is a village on the northern shore of Lake Balaton on the Tihany Peninsula (Hungary, Veszprém County). The whole peninsula is a historical district.
The center of the district is the Benedictine Tihany Abbey, which was foun ...
) but they also built new ones enclosed with earthworks (''e.g.'', in Sopron
Sopron (; german: Ödenburg, ; sl, Šopron) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő.
History
Ancient times-13th century
When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a ...
). The nobility were buried in chamber tomb
A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interred than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could ...
s covered by earth. Some of their settlements situated along the Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade.
...
developed into commercial centers.
Between 550 and 500 BC, new people settled along the river Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
and in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. Their immigration may have been connected either to the military campaigns of king Darius I of Persia (522 BC - 486 BC) on the Balkan Peninsula or to the struggles between the Cimmerians and the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
. Those people, who settled down in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
and in the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
, may be identified with the Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
(probably an ancient Thracian tribe whose presence on the territory was recorded by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
); while those who lived in what is now the Great Hungarian Plain may be identified with the Sigynnae
The Sigynnae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an obscure nomadic people of antiquity who were part of the Scythian cultures.
Location
The Sigynnae were a nomadic people of uncertain, but possibly Iranian or pre-Iranian origin, who lived north of t ...
. The new population introduced the use of the potter's wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in the shaping (known as throwing) of clay into round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during the process of trimming excess clay from leather-hard dried ware that is stiff but malleable, a ...
in the Carpathian Basin and they maintained close commercial contacts with the neighboring peoples.
The Pannonians
This is a list of ancient tribes in the ancient territory of Illyria ( grc-gre, Ἰλλυρία; la, Illyria). The name ''Illyrians'' seems to be the name of a single Illyrian tribe that was the first to come into contact with the ancient Greeks ...
(an Illyrian tribe) may have moved to the southern territories of Transdanubia in the course of the 5th century BC.
In the 4th century BC, Celtic tribes immigrated to the territories around the river Rába
The Rába (german: Raab; hu, Rába; sl, Raba ) is a river in southeastern Austria and western Hungary and a right tributary of the Danube.
Geography
Its source is in Austria, some kilometres east of Bruck an der Mur below Heubodenhöhe Hill. ...
and defeated the Illyrian people who had been living there, but the Illyrians managed to assimilate the Celts, who adopted their language. In the 290s and 280s BC, the Celtic people who were migrating towards the Balkan Peninsula passed through Transdanubia but some of the tribes settled on the territory. Following 279 BC, the Scordisci
The Scordisci ( el, Σκορδίσκοι) were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically n ...
(a Celtic tribe), who had been defeated at Delphi, settled at the confluence of the rivers Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
and they extended their rule over the southern parts of Transdanubia. Around that time, the northern parts of Transdanubia were ruled by the Taurisci
The Taurisci were a federation of Celtic tribes who dwelt in today's Carinthia and northern Slovenia (Carniola) before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC). According to Pliny the Elder, they are the same as the people known as the Norici.
Etym ...
(also a Celtic tribe) and by 230 BC, Celtic people (the people of the La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
) had occupied gradually the whole territory of the Great Hungarian Plain. Between 150 and 100 BC, a new Celtic tribe, the Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul ( Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom ...
moved to the Carpathian Basin and they occupied the northern and northeastern parts of the territory (mainly the territory of present Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
).
Roman era
TheRomans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
commenced their military raids in the Carpathian Basin in 156 BC when they attacked the Scordisci living in the Transdanubian region. In 119 BC, they marched against Siscia (today Sisak in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
) and strengthened their rule over the future Illyricum province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
south of the Carpathian Basin. In 88 BC, the Romans defeated the Scordisci whose rule was driven back to the eastern parts of Syrmia, while the Pannonians moved to the northern parts of Transdanubia. When King Mithridates VI of Pontus made plans to attack the Romans by way of the Balkan Peninsula, he referred to the Pannonic tribes, and not to the Scordisci, as masters of the region on his path; it appears, therefore, that around 70–60 BC, the Pannonic tribes were no longer subjugated.
Around 50 BC, the mainly Celtic tribes living on the territory were confronted by Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
, king of the Dacians (82-44 BC), who began suddenly to expand his domain centered in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. The sources do not indicate clearly whether Burebista was the original unifier of the Dacian tribes, or whether his efforts at unification built upon the work of his predecessors. Burebista subjugated the Taurisci and the Anarti; in the process, he confronted the Celtic tribal alliance led by the Boii. Burebista's victory over the Celts led not only to the breakup of their tribal alliance, but also to the establishment of Dacian settlements in the southern parts of today's Slovakia. Burebista, however, fell victim to his political enemies, and his domain was divided into four parts.
The period between 15 BC and 9 AD was characterized by the continuous uprisings of the Pannonians against the emerging power of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. The Romans, however, could strengthen their supremacy over the rebellious tribes and they organised the occupied territory into a new province.
Pannonia province
The Roman Empire subdued the Pannonians, Dacians, Celts and other peoples in this territory. The territory west of the Danube was conquered by the Roman Empire between 35 and 9 BC, and became a province of the Roman Empire under the name of Pannonia. The easternmost parts of present-day Hungary were later (106 AD) organized as the Roman province ofDacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
(lasting until 271). The territory between the Danube and the Tisza was inhabited by the Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
Iazyges
The Iazyges (), singular Ἰάζυξ. were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between th ...
between the 1st and 4th centuries AD, or even earlier (earliest remains have been dated to 80 BC). Roman Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
officially allowed the Iazyges to settle there as confederates. The remaining territory was in Thracian (Dacian) hands. In addition, the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
settled on the upper Tisza in the 2nd half of the 2nd century AD.
The four centuries of Roman rule created an advanced and flourishing civilization. Many of the important cities of today's Hungary were founded during this period, such as Aquincum (Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
), Sopianae (Pécs
Pécs ( , ; hr, Pečuh; german: Fünfkirchen, ; also known by other #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the countr ...
), Arrabona (Győr
Győr ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Győr-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia region, and – halfway between Budapest and Vienna – situated on one of ...
), Solva
Solva ( cy, Solfach) is a village, community and electoral ward in Pembrokeshire, Wales. The village comprises principally Lower Solva and Upper Solva. The community also includes Middle Mill and Whitchurch.
Location
Solva lies on the north ...
(Esztergom
Esztergom ( ; german: Gran; la, Solva or ; sk, Ostrihom, known by alternative names) is a city with county rights in northern Hungary, northwest of the capital Budapest. It lies in Komárom-Esztergom County, on the right bank of the river Dan ...
), Savaria (Szombathely
Szombathely (; german: Steinamanger, ; see also other alternative names) is the 10th largest city in Hungary. It is the administrative centre of Vas county in the west of the country, located near the border with Austria. Szombathely lies by t ...
) and Scarbantia (Sopron
Sopron (; german: Ödenburg, ; sl, Šopron) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő.
History
Ancient times-13th century
When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a ...
). Christianity spread in Pannonia in the 4th century, when it became the empire's official religion.
Migration period
 In 375 AD, the nomadic
In 375 AD, the nomadic Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
began invading Europe from the eastern steppes, instigating the Great Age of Migrations
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
. In 380, the Huns penetrated into present-day Hungary, and remained an important factor in the region well into the 5th century.
Around the same time (379-395), the Roman Empire allowed the groups of Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
, Huns, Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Or ...
and Quadi to settle Pannonia, which still was a Roman territory. The Visigoths, Alans, Vandals and most of the Quadi and Marcomanni, however, left this territory around 400, and moved on to western and southern Europe.
The Huns, taking advantage of the departure of the Goths, Quadi, ''et al.'', created a significant empire in 423 based in Hungary. In 453 they reached the height of their expansion under the well-known conqueror, Attila the Hun. The empire collapsed in 455, when the Huns were defeated by the neighbouring Germanic tribes (such as the Quadi, Gepidi and Sciri).
The Gepidi (having lived to the east of the upper Tisza river since 260 AD) then moved into the eastern Carpathian Basin in 455. They ceased to exist in 567 when they were defeated by the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
and Avars (see below).
The Germanic Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
inhabited Pannonia, with Rome's consent, between 456 and 471.
After the Romans

 Roman influence in Pannonia had begun to decline as early as the arrival of the Huns in the 4th century. The remaining romanized Pannonians created at the end of the 5th century the Keszthely culture, around
Roman influence in Pannonia had begun to decline as early as the arrival of the Huns in the 4th century. The remaining romanized Pannonians created at the end of the 5th century the Keszthely culture, around Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the largest inflow of water to the lake, and ...
.
The first Slavs came to the region, almost certainly from the north, soon after the departure of the Ostrogoths (471 AD), together with the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
and Heruli
The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Roman authors as one of several " Scythian" groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking ...
s. Around 530, the Germanic Lombards settled in Pannonia. They had to fight against the Gepidi and the Slavs. In 568, pushed out by the Avars, they moved into northern Italy.
The nomadic Avars arrived from Asia in the 560s, utterly destroyed the Gepidi in the east, drove away the Lombards in the west, and subjugated the Slavs, partly assimilating them. The Avars established a large empire, just as the Huns had decades prior. This empire was destroyed around 800 by Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
and Bulgar
Bulgar may refer to:
*Bulgars, extinct people of Central Asia
*Bulgar language, the extinct language of the Bulgars
* Oghur languages
Bulgar may also refer to:
*Bolghar, the capital city of Volga Bulgaria
*Bulgur, a wheat product
* Bulgar, an Ash ...
attacks, and above all by internal feuds, however Avar population remained in numbers until the arrival of Árpád's Magyars. From 800, the whole area of Pannonian Basin was under control between two powers ( East Francia and First Bulgarian Empire). Around 800, northeastern Hungary became part of the Slavic Principality of Nitra
The Principality of Nitra ( sk, Nitrianske kniežatstvo, Nitriansko, Nitrava, lit=Duchy of Nitra, Nitravia, Nitrava; hu, Nyitrai Fejedelemség), also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements th ...
, which then became part of Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
in 833.
Also, after 800, southeastern Hungary was conquered by Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
. Western Hungary (Pannonia) was a tributary to the Franks. In 839 the Slavic Balaton Principality
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spo ...
was founded in southwestern Hungary (under Frank suzerainty). During the reign of Svatopluk I
Svatopluk I or Svätopluk I, also known as Svatopluk the Great (Latin: ''Zuentepulc'', ''Zuentibald'', ''Sventopulch'', ''Zvataplug''; Old Church Slavic: Свѧтопълкъ and transliterated ''Svętopъłkъ''; Polish: ''Świętopełk''; Greek ...
northwestern Hungary was conquered by Great Moravia. Pannonia remained under Frankish control until the Hungarian Conquest.Kristó, Gyula (1996). Hungarian History in the Ninth Century. Szeged: Szegedi Középkorász Műhely. p. 229. .
See also
*History of Hungary
Hungary in its modern (post-1946) borders roughly corresponds to the Great Hungarian Plain (the Pannonian Basin). During the Iron Age, it was located at the crossroads between the cultural spheres of the Celtic tribes (such as the Scordisci, Boii ...
*Hungarian prehistory
Hungarian prehistory ( hu, magyar őstörténet) spans the period of history of the Hungarian people, or Magyars, which started with the separation of the Hungarian language from other Finno-Ugric or Ugric languages around , and ended with the ...
*Seuso Treasure
The Seuso Treasure or Sevso Treasure ( hu, Seuso-kincsek; hr, Seusovo blago), is a hoard of silver objects (14 items) from the late Roman Empire. The first pieces appeared on the market in London in 1980, and the treasure was acquired by a co ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * *External links
A History of Hungary- By the Hungarian Ministry of Tourism
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pannonian Basin Before The Hungarians Hungarian prehistory